Impact of Breed and Slaughter Hygiene on Beef Carcass Quality Traits in Northern Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Animals and Abattoirs
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
2.2.1. Meat pH
2.2.2. Meat Colour
2.2.3. Meat Texture
2.2.4. Meat Chemical Composition and Fatty Acid Profile
2.3. Muscle Histomorphometry
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Effects of Breed (Aberdeen Angus (AA), Holstein (HO), Limousin (LI) Breed, Crossbred (CR) Males) on Carcass Quality Traits
3.1.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.1.2. Effects of Breed on Meat pH, Colour, and Texture Parameters
3.1.3. Effects of Breed on Meat Chemical Composition and Fatty Acid Profile
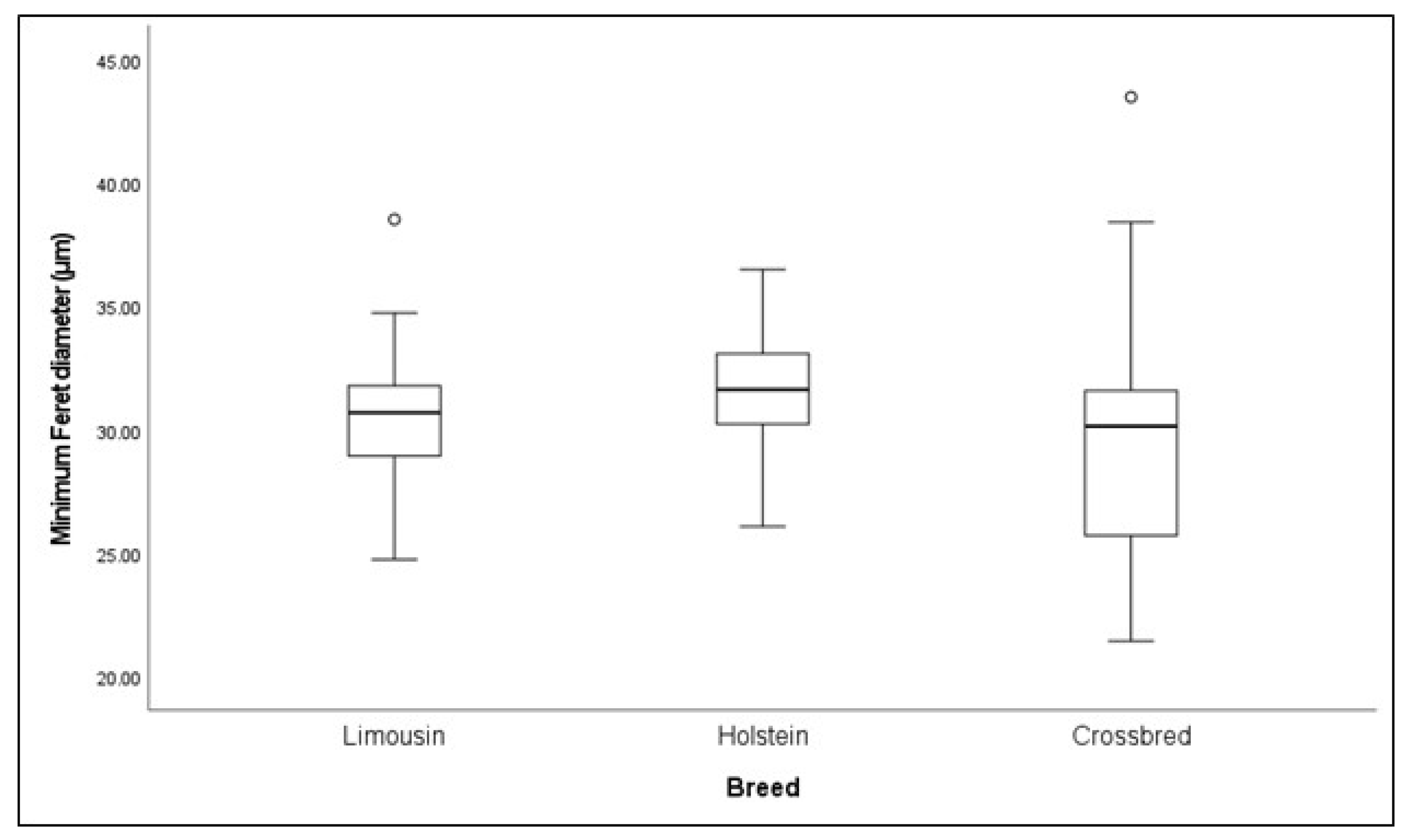
3.1.4. Effect of Breed on Muscle Histomorphometry
3.2. Slaughter Hygiene Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO Food Balances. 2010. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2024–2033; OECD Publishing: Paris, France; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 9789264722590. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.M.d.C.C.; Vicente, A.F.d.R.B. Meat Nutritional Composition and Nutritive Role in the Human Diet. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAfee, A.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Cuskelly, G.J.; Moss, B.W.; Wallace, J.M.W.; Bonham, M.P.; Fearon, A.M. Red Meat Consumption: An Overview of the Risks and Benefits. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission, Eurostat, Agricultural Production-Livestock and Meat, Publication Office of the E.U. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Agricultural_production_-_livestock_and_meat#Veal_and_beef (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- European Commission, Eurostat, Bovine Population-Annual Data, Publication Office of the E.U. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/APRO_MT_LSCATL/default/table?lang=en (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Available online: https://www.statistics.gr (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Gourdouvelis, D.; Dotas, V.; Kaimakamis, I.; Zagorakis, K.; Yiakoulaki, M. Typology and Structural Characterisation of Suckler Cow Farming System in Central Macedonia, Greece. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsos, A.; Economou, V.; Arsenos, G.; Kalitsis, T.; Argyriadou, A.; Theodoridis, A. Greek and European Consumer Behaviour towards Beef, Lamb and Mutton Meat Safety and Quality: A Review. Int. J. Agric. Resour. Gov. Ecol. 2021, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino, V.M.; Borra, D.; Girgenti, V.; Dal Vecchio, A.; Massaglia, S. Beef Meat Preferences of Consumers from Northwest Italy: Analysis of Choice Attributes. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsos, A.; Economou, V.; Chouliara, E.; Ambrosiadis, I.; Arsenos, G. A Comparative Study on Microbiological and Chemical Characteristics of Small Ruminant Carcasses from Abattoirs in Greece. Foods 2022, 11, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Monteiro, M.J.; Voss, H.-P.; Komora, N.; Teixeira, P.; Pintado, M. The Most Important Attributes of Beef Sensory Quality and Production Variables That Can Affect It: A Review. Livest. Sci. 2021, 250, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priolo, A.; Micol, D.; Agabriel, J. Effects of Grass Feeding Systems on Ruminant Meat Colour and Flavour. A Review. Anim. Res. 2001, 50, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conanec, A.; Campo, M.; Richardson, I.; Ertbjerg, P.; Failla, S.; Panea, B.; Chavent, M.; Saracco, J.; Williams, J.L.; Ellies-Oury, M.-P.; et al. Has Breed Any Effect on Beef Sensory Quality? Livest. Sci. 2021, 250, 104548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureš, D.; Bartoň, L. Performance, Carcass Traits and Meat Quality of Aberdeen Angus, Gascon, Holstein and Fleckvieh Finishing Bulls. Livest. Sci. 2018, 214, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertí, P.; Panea, B.; Sañudo, C.; Olleta, J.L.; Ripoll, G.; Ertbjerg, P.; Christensen, M.; Gigli, S.; Failla, S.; Concetti, S.; et al. Live Weight, Body Size and Carcass Characteristics of Young Bulls of Fifteen European Breeds. Livest. Sci. 2008, 114, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambaz, A.; Scheeder, M.R.L.; Kreuzer, M.; Dufey, P.-A. Meat Quality of Angus, Simmental, Charolais and Limousin Steers Compared at the Same Intramuscular Fat Content. Meat Sci. 2003, 63, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuernberg, K.; Dannenberger, D.; Nuernberg, G.; Ender, K.; Voigt, J.; Scollan, N.D.; Wood, J.D.; Nute, G.R.; Richardson, R.I. Effect of a Grass-Based and a Concentrate Feeding System on Meat Quality Characteristics and Fatty Acid Composition of Longissimus Muscle in Different Cattle Breeds. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 94, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying Down Specific Hygiene Rules for on the Hygiene of Foodstuffs. 2004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32004R0853 (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Tsitsos, A.; Economou, V.; Chouliara, E.; Koutouzidou, G.; Arsenos, G.; Ambrosiadis, I. Effect of Chitosan and Alginate-Based Edible Membranes with Oregano Essential Oil and Olive Oil in the Microbiological, Physicochemical and Organoleptic Characteristics of Mutton. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Meat Science Association. AMSA Meat Color Measurement Guidelines; AMSA: Champaign, IL, USA, 2012; ISBN 61820 800-517-2672. [Google Scholar]
- Skaperda, Z.; Argyriadou, A.; Nechalioti, P.M.; Alvanou, M.; Makri, S.; Bouroutzika, E.; Kyriazis, I.D.; Tekos, F.; Veskoukis, A.S.; Kallitsis, T.; et al. Redox Biomarker Baseline Levels in Cattle Tissues and Their Relationships with Meat Quality. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsos, A.; Dokou, S.; Chatzimanou, T.; Giannenas, I.; Economou, V.; Arsenos, G. Improvement of the Meat Quality of Holstein Bulls Fed a Diet Enriched with Oregano Oil. Animals 2024, 14, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriadou, A.; Tsitsos, A.; Stylianaki, I.; Vouraki, S.; Kallitsis, T.; Economou, V.; Arsenos, G. A Comprehensive Study of the Quality of Fat-Tailed Sheep Carcasses in Greece. Animals 2022, 12, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varian, B.J.; Goureshetti, S.; Poutahidis, T.; Lakritz, J.R.; Levkovich, T.; Kwok, C.; Teliousis, K.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Mirabal, S.; Erdman, S.E. Beneficial Bacteria Inhibit Cachexia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11803–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4833-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 21528-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. 2005. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32005R2073 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; Vaughan, D. Dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R Package Version 1.1.4, 2023. Available online: https://dplyr.tidyverse.org (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research. Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois. R Package Version 2.4.12, 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=psych (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Corlett, M.T.; Pethick, D.W.; Kelman, K.R.; Jacob, R.H.; Gardner, G.E. Consumer Perceptions of Meat Redness Were Strongly Influenced by Storage and Display Times. Foods 2021, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, B.W.B.; van de Ven, R.J.; Mao, Y.; Coombs, C.E.O.; Hopkins, D.L. Using Instrumental (CIE and Reflectance) Measures to Predict Consumers’ Acceptance of Beef Colour. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-i-Furnols, M.; Guerrero, L. Consumer Preference, Behavior and Perception about Meat and Meat Products: An Overview. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda-Arteaga, A.; Krell, J.; Gibis, M.; Heinz, V.; Terjung, N.; Tomasevic, I. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors Affecting the Color of Fresh Beef Meat—Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, R.A.; Hunt, M.C. Current Research in Meat Color. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuvelier, C.; Clinquart, A.; Hocquette, J.F.; Cabaraux, J.F.; Dufrasne, I.; Istasse, L.; Hornick, J.L. Comparison of Composition and Quality Traits of Meat from Young Finishing Bulls from Belgian Blue, Limousin and Aberdeen Angus Breeds. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.A.; Shackelford, S.D.; Kuehn, L.A.; Kemp, C.M.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Thallman, R.M.; Wheeler, T.L. Contribution of Genetic Influences to Animal-to-Animal Variation in Myoglobin Content and Beef Lean Color Stability1. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesonen, M.; Honkavaara, M.; Huuskonen, A.K. Effect of Breed on Production, Carcass Traits and Meat Quality of Aberdeen Angus, Limousin and Aberdeen Angus×Limousin Bulls Offered a Grass Silage-Grain-Based Diet. Agric. Food Sci. 2012, 21, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvelier, C.; Cabaraux, J.F.; Dufrasne, I.; Clinquart, A.; Hocquette, J.F.; Istasse, L.; Hornick, J.-L. Performance, Slaughter Characteristics and Meat Quality of Young Bulls from Belgian Blue, Limousin and Aberdeen Angus Breeds Fattened with a Sugar-Beet Pulp or a Cereal-Based Diet. Anim. Sci. 2006, 82, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Huidobro, F.R.; Miguel, E.; Blázquez, B.; Onega, E. A Comparison between Two Methods (Warner–Bratzler and Texture Profile Analysis) for Testing Either Raw Meat or Cooked Meat. Meat Sci. 2005, 69, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masouras, P.K.; Nikolaou, K.; Laliotis, G.P.; Koutsouli, P.; Bizelis, I. Relationship Between Meat Quality Characteristics, Intramuscular Fat and Marbling in Greek Cattle Carcasses. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 10, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfuhl, R.; Bellmann, O.; Kühn, C.; Teuscher, F.; Ender, K.; Wegner, J. Beef versus Dairy Cattle: A Comparison of Feed Conversion, Carcass Composition, and Meat Quality. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2007, 50, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødbotten, R.; Hildrum, K.I.; Berg, J. Effects of Concentrate Level on Carcass Composition, Tenderness and Growth Rate of Angus × NRF and Limousin × NRF Bulls. Acta Agric. Scand. A Anim. Sci. 2002, 52, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N.; Bach, A.; Velarde, A.; Devant, M. Association between Animal, Transportation, Slaughterhouse Practices, and Meat PH in Beef. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, J.K.; Wulf, D.M.; Schwotzer, T.R. A Survey of Beef Muscle Color and PH. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immonen, K.; Ruusunen, M.; Hissa, K.; Puolanne, E. Bovine Muscle Glycogen Concentration in Relation to Finishing Diet, Slaughter and Ultimate PH. Meat Sci. 2000, 55, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.; Patarata, L.; Martins, C. Influence of Ultimate PH on Bovine Meat Tenderness during Ageing. Meat Sci. 1999, 52, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenkel, F.S.; Miller, S.P.; Wilton, J.W. Genetic Parameters and Breed Differences for Feed Efficiency, Growth, and Body Composition Traits of Young Beef Bulls. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 84, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakowski, T.; Grodkowski, G.; Gołebiewski, M.; Slósarz, J.; Kostusiak, P.; Solarczyk, P.; Puppel, K. Genetic and Environmental Determinants of Beef Quality—A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 819605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezagholivand, A.; Nikkhah, A.; Khabbazan, M.H.; Mokhtarzadeh, S.; Dehghan, M.; Mokhtabad, Y.; Sadighi, F.; Safari, F.; Rajaee, A. Feedlot Performance, Carcass Characteristics and Economic Profits in Four Holstein-Beef Crosses Compared with Pure-Bred Holstein Cattle. Livest. Sci. 2021, 244, 104358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, P.P.; Prado, I.N.d.; Prado, R.M.d.; Moletta, J.L.; Silva, R.R.; Perotto, D. Carcass Characteristics and Chemical Composition of the Longissimus Muscle of Nellore, Caracu and Holstein-Friesian Bulls Finished in a Feedlot. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Jurie, C.; Micol, D.; Agabriel, J.; Picard, B.; Garcia-Launay, F. Impact of Animal and Management Factors on Collagen Characteristics in Beef: A Meta-Analysis Approach. Animal 2013, 7, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurie, C.; Martin, J.-F.; Listrat, A.; Jailler, R.; Culioli, J.; Picard, B. Effects of Age and Breed of Beef Bulls on Growth Parameters, Carcass and Muscle Characteristics. Anim. Sci. 2005, 80, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.; Ertbjerg, P.; Failla, S.; Sañudo, C.; Richardson, R.I.; Nute, G.R.; Olleta, J.L.; Panea, B.; Albertí, P.; Juárez, M.; et al. Relationship between Collagen Characteristics, Lipid Content and Raw and Cooked Texture of Meat from Young Bulls of Fifteen European Breeds. Meat Sci. 2011, 87, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, P.T.; Pensel, N.A.; Sancho, A.M.; Latimori, N.J.; Kloster, A.M.; Amigone, M.A.; Casal, J.J. Beef Lipids in Relation to Animal Breed and Nutrition in Argentina. Meat Sci. 2008, 79, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Jiang, H. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Intramuscular Fat Development and Growth in Cattle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogoy, K.M.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Smith, S.B.; Seong, H.A.; Choi, S.H. Oleic Acid in Angus and Hanwoo (Korean Native Cattle) Fat Reduced the Fatty Acid Synthase Activity in Rat Adipose Tissues. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguet, A.; Courdier-Fruh, I.; Foster, M.; Meier, T.; Magyar, J.P. Histological Parameters for the Quantitative Assessment of Muscular Dystrophy in the Mdx-Mouse. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Hou, S. Genome-Wide Association Studies Demonstrate That TASP1 Contributes to Increased Muscle Fiber Diameter. Heredity 2021, 126, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.C.; Cossi, M.V.C.; Silva, W.P.d.; Bersot, L.d.S.; Landgraf, M.; Baranyi, J.; Franco, B.D.G.d.M.; Luís Augusto, N. Microbiological Testing for the Proper Assessment of the Hygiene Status of Beef Carcasses. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSharry, S.; Koolman, L.; Whyte, P.; Bolton, D. The Microbiology of Beef from Carcass Chilling through Primal Storage to Retail Steaks. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaître, N.; Van Damme, I.; De Zutter, L.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Rasschaert, G.; De Reu, K. Occurrence, Distribution and Diversity of Listeria Monocytogenes Contamination on Beef and Pig Carcasses after Slaughter. Meat Sci. 2020, 169, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos-Almeida, M.; Burgos-Mayorga, A.; Gómez, C.A.; Lema-Hurtado, J.L.; Lema, L.; Calvache, I.; Jaramillo, C.; Collaguazo Ruilova, I.; Martínez, E.P.; Estupiñán, P. Association between Animal Welfare Indicators and Microbiological Quality of Beef Carcasses, Including Salmonella Spp., from a Slaughterhouse in Ecuador. Vet. World 2021, 14, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaja, I.F.; Green, E.; Muchenje, V. Aerobic Mesophilic, Coliform, Escherichia Coli, and Staphylococcus Aureus Counts of Raw Meat from the Formal and Informal Meat Sectors in South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Traits | Aberdeen Angus | Limousin | Holstein | Crossbred | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean (±SD) | N | Mean (±SD) | N | Mean (±SD) | N | Mean (±SD) | |
| pH | 34 | 5.5 (0.26) | 39 | 5.6 (0.10) | 42 | 5.6 (0.14) | 38 | 5.6 (0.20) |
| Lightness—L* | 38 | 38.2 (2.09) | 39 | 40.1 (2.87) | 40 | 37.7 (2.29) | 38 | 38.9 (2.09) |
| Redness—a* | 38 | 19.5 (2.17) | 39 | 21.3 (2.09) | 40 | 17.6 (1.78) | 38 | 22.2 (1.70) |
| Yellowness—b* | 38 | 10.2 (1.53) | 39 | 7.0 (1.84) | 40 | 7.8 (2.23) | 38 | 5.4 (1.91) |
| Chroma | 38 | 21.9 (1.89) | 39 | 22.5 (2.05) | 40 | 19.3 (2.02) | 38 | 22.9 (1.99) |
| Hue angle | 38 | 0.5 (0.04) | 39 | 0.3 (0.08) | 40 | 0.4 (0.10) | 38 | 0.2 (0.07) |
| Hardness 1 (g) | 35 | 1019.7 (845.53) | 24 | 1712.2 (835.81) | 36 | 1130.4 (625.75) | 35 | 826.4 (420.18) |
| Hardness 2 (g) | 36 | 862.9 (178.80) | 26 | 1448.2 (692.11) | 37 | 867.1 (470.25) | 35 | 647.3 (340.75) |
| Springiness | 38 | 0.8 (0.08) | 39 | 0.9 (0.13) | 39 | 0.7 (0.08) | 38 | 0.7 (0.08) |
| Cohesiveness | 38 | 0.5 (0.10) | 39 | 0.5 (0.11) | 41 | 0.5 (0.09) | 38 | 0.5 (0.05) |
| Chewiness (g) | 38 | 451.0 (341.51) | 30 | 775.8 (388.33) | 37 | 454.1 (277.82) | 37 | 348.2 (255.07) |
| Protein (%) | 37 | 20.2 (1.22) | 33 | 22.8 (0.97) | 41 | 22.1 (0.98) | N/A | N/A |
| Fat (%) | 36 | 6.6 (2.70) | 33 | 1.7 (0.37) | 40 | 2.7 (0.91) | N/A | N/A |
| Collagen (%) | 35 | 2.2 (0.48) | 33 | 1.3 (0.19) | 40 | 1.4 (0.38) | N/A | N/A |
| Feret’s diameter (μm) | N/A | N/A | 31 | 30.6 (2.54) | 17 | 31.5 (2.75) | 32 | 29.8 (4.93) |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 37 | 3.1 (0.41) | 3 | 3.5 (0.35) | 23 | 3.1 (0.46) | N/A | N/A |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1) | 37 | 0.9 (0.25) | 3 | 0.4 (0.24) | 17 | 0.5 (0.21) | N/A | N/A |
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 36 | 0.4 (0.07) | 3 | 0.5 (0.03) | 15 | 0.4 (0.97) | N/A | N/A |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 37 | 25.4 (2.03) | 3 | 29.7 (1.54) | 23 | 27.6 (1.80) | N/A | N/A |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 37 | 5.0 (0.79) | 3 | 3.7 (0.45) | 23 | 3.7 (0.79) | N/A | N/A |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 37 | 1.1 (0.21) | 3 | 0.9 (0.09) | 23 | 0.9 (0.16) | N/A | N/A |
| Cis-10 Heptadecenoic acid (C17:1) | 32 | 1.0 (0.25) | 3 | 0.4 (0.07) | 17 | 0.5 (0.18) | N/A | N/A |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 37 | 12.2 (2.31) | 3 | 19.3 (1.77) | 23 | 20.1 (3.31) | N/A | N/A |
| Elaidic acid (C18:1n9t) | 37 | 1.3 (1.1) | 3 | 1.8 (0.34) | 19 | 0.9 (0.60) | N/A | N/A |
| Oleic acid (C18:1n9c) | 37 | 47.0 (2.92) | 3 | 36.7 (2.73) | 23 | 39.6 (3.15) | N/A | N/A |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2n6c) | 37 | 1.7 (0.58) | 3 | 0.2 (0.03) | 23 | 2.2 (0.67) | N/A | N/A |
| Saturated fatty acids | 37 | 42.4 (3.98) | 3 | 54.1 (3.34) | 23 | 52.3 (3.99) | N/A | N/A |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 37 | 55.2 (3.58) | 3 | 43.3 (2.28) | 23 | 45.2 (3.80) | N/A | N/A |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 37 | 2.3 (0.67) | 3 | 2.6 (0.13) | 23 | 2.5 (0.70) | N/A | N/A |
| Total mesophilic viable counts (TMVCs, log10 CFU/cm2) | N/A | N/A | 34 | 3.5 (0.72) | 22 | 3.9 (0.70) | 21 | 3.9 (0.94) |
| Total psychrophilic viable counts (TPVCs, log10 CFU/cm2) | N/A | N/A | 34 | 3.7 (1.0) | 22 | 3.1 (0.76) | 21 | 1.9 (1.74) |
| Coliform counts (log10 CFU/cm2) | N/A | N/A | 34 | 1.5 (0.76) | 22 | 0.8 (0.93) | 21 | 0.7 (0.88) |
| Breed | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | AA | LI | HO | CR | |||||
| Mean (±SD) | Mean (±SD) | Mean (±SD) | Mean (±SD) | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p-Value | |
| Lightness—L* | 38.2 b (2.09) | 40.1 a (2.87) | 37.7 c (2.29) | 38.9 abc (2.09) | 126.60 | 3 | 42.20 | 5.86 | <0.001 |
| Redness—a* | 19.5 b (2.17) | 21.3 a (2.09) | 17.6 c (1.78) | 22.2 a (1.70) | 492.30 | 3 | 164.12 | 43.45 | <0.001 |
| Yellowness—b* | 10.2 a (1.53) | 7.0 b (1.84) | 7.8 b (2.23) | 5.4 c (1.91) | 467.50 | 3 | 155.82 | 43.02 | <0.001 |
| Chroma | 21.9 a (1.89) | 22.5 a (2.05) | 19.3 b (2.02) | 22.9 a (1.99) | 309.30 | 3 | 103.09 | 26.06 | <0.001 |
| Breed | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | AA | LI | HO | CR | |||||
| Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | p-Value | |
| Hardness 1 (g) | 683.8 (1061.76) | 63.7 bc | 1611.0 (1217.0) | 111.0 a | 1011.3 (937.52) | 80.5 abc | 730.9 (717.79) | 59.6 bc | <0.001 |
| Hardness 2 (g) | 552.9 (911.52) | 63.6 b | 1424.1 (1081.20) | 113.0 a | 765.3 (692.47) | 78.0 b | 593.5 (581.67) | 61.1 b | <0.001 |
| Springiness | 0.8 (0.13) | 85.1 ab | 0.9 (0.19) | 106.0 a | 0.7 (0.10) | 71.7 bc | 0.7 (0.11) | 53.6 bc | <0.001 |
| Cohesiveness | 0.5 (0.12) | 93.9 a | 0.5 (0.13) | 60.4 b | 0.5 (0.10) | 82.3 ab | 0.5 (0.05) | 79.6 ab | 0.013 |
| Chewiness (g) | 314.2 (583.43) | 64.4 b | 927.2 (782.08) | 111.0 a | 382.9 (328.73) | 80.8 b | 297.6 (251.92) | 58.6 b | <0.001 |
| pH | 5.6 (0.14) | 80.0 a | 5.6 (0.07) | 74.1 a | 5.6 (0.18) | 85.9 a | 5.6 (0.10) | 75.3 a | 0.472 |
| Hue angle | 0.5 (0.04) | 124.0 a | 0.3 (0.07) | 60.70 c | 0.4 (0.16) | 98.10 b | 0.2 (0.12) | 31.2 d | <0.001 |
| Breed | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | AA | LI | HO | ||||
| Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | p-Value | |
| Protein (%) | 20.3 (1.70) | 25.80 b | 22.9 (1.45) | 80.74 a | 22.3 (1.50) | 63.34 a | <0.001 |
| Fat (%) | 6.1 (3.50) | 89.33 a | 1.6 (0.55) | 22.47 c | 2.6 (1.10) | 50.94 b | <0.001 |
| Collagen (%) | 2.1 (0.60) | 88.34 a | 1.4 (0.40) | 35.62 b | 1.4 (0.45) | 40.46 b | <0.001 |
| Breed | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | AA | HO | |||||
| n | Median | IQR | n | Median | IQR | p-Value | |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 37 | 3.1 | 0.64 | 23 | 3.2 | 0.66 | 0.911 |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1) | 37 | 0.9 | 0.34 | 17 | 0.5 | 0.32 | <0.001 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 37 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 15 | 0.3 | 0.10 | 0.108 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 37 | 25.0 | 2.77 | 23 | 27.6 | 1.85 | <0.001 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 37 | 4.8 | 1.15 | 23 | 3.6 | 0.69 | <0.001 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 37 | 1.1 | 0.34 | 23 | 0.9 | 0.17 | 0.003 |
| Cis-10 Heptadecenoic acid (C17:1) | 32 | 1.0 | 0.33 | 17 | 0.4 | 0.25 | <0.001 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 37 | 11.9 | 3.16 | 23 | 20.2 | 4.32 | <0.001 |
| Elaidic acid (C18:1n9t) | 37 | 1.0 | 0.67 | 19 | 0.8 | 0.42 | 0.073 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1n9c) | 37 | 47.6 | 4.04 | 23 | 40.0 | 5.07 | <0.001 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2n6c) | 37 | 1.7 | 0.55 | 23 | 2.2 | 0.80 | <0.001 |
| Saturated fatty acids | 37 | 41.4 | 4.78 | 23 | 51.6 | 5.41 | <0.001 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 37 | 55.9 | 4.22 | 23 | 45.9 | 5.25 | <0.001 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 37 | 2.3 | 0.76 | 23 | 2.6 | 0.91 | 0.088 |
| Abattoir A ** | Abattoir B *** | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median | IQR | n | Median | IQR | p-Value | |
| TMVCs * (log10 CFU/cm2) | 22 | 4.3 | 0.10 | 55 | 3.6 | 1.04 | 0.004 |
| TPVCs * (log10 CFU/cm2) | 22 | 1.7 | 4.20 | 55 | 3.3 | 1.18 | 0.006 |
| Coliform counts (log10 CFU/cm2) | 22 | 0.0 | 1.08 | 55 | 1.3 | 1.57 | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papanikolopoulou, V.; Tsitsos, A.; Dokou, S.; Priskas, S.; Vouraki, S.; Economou, V.; Stylianaki, I.; Argyriadou, A.; Arsenos, G. Impact of Breed and Slaughter Hygiene on Beef Carcass Quality Traits in Northern Greece. Foods 2025, 14, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101776
Papanikolopoulou V, Tsitsos A, Dokou S, Priskas S, Vouraki S, Economou V, Stylianaki I, Argyriadou A, Arsenos G. Impact of Breed and Slaughter Hygiene on Beef Carcass Quality Traits in Northern Greece. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101776
Chicago/Turabian StylePapanikolopoulou, Vasiliki, Anestis Tsitsos, Stella Dokou, Stergios Priskas, Sotiria Vouraki, Vangelis Economou, Ioanna Stylianaki, Angeliki Argyriadou, and Georgios Arsenos. 2025. "Impact of Breed and Slaughter Hygiene on Beef Carcass Quality Traits in Northern Greece" Foods 14, no. 10: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101776
APA StylePapanikolopoulou, V., Tsitsos, A., Dokou, S., Priskas, S., Vouraki, S., Economou, V., Stylianaki, I., Argyriadou, A., & Arsenos, G. (2025). Impact of Breed and Slaughter Hygiene on Beef Carcass Quality Traits in Northern Greece. Foods, 14(10), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101776











