A Review of Reducing Cadmium Pollution in the Rice–Soil System in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
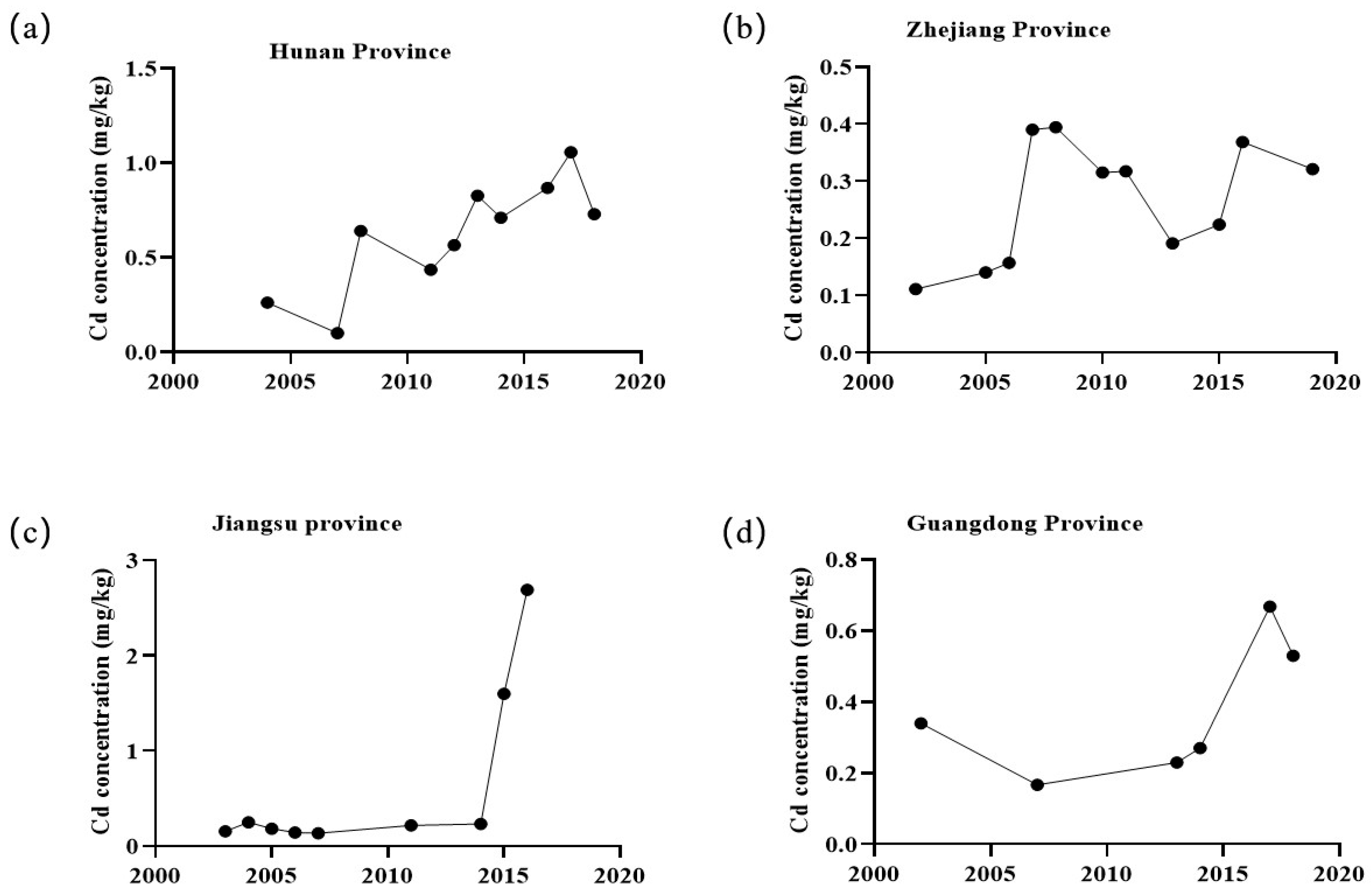
2. Sources and Status of Cadmium Pollution in China
3. Measures for Minimizing Cd Accumulation in Rice Grains
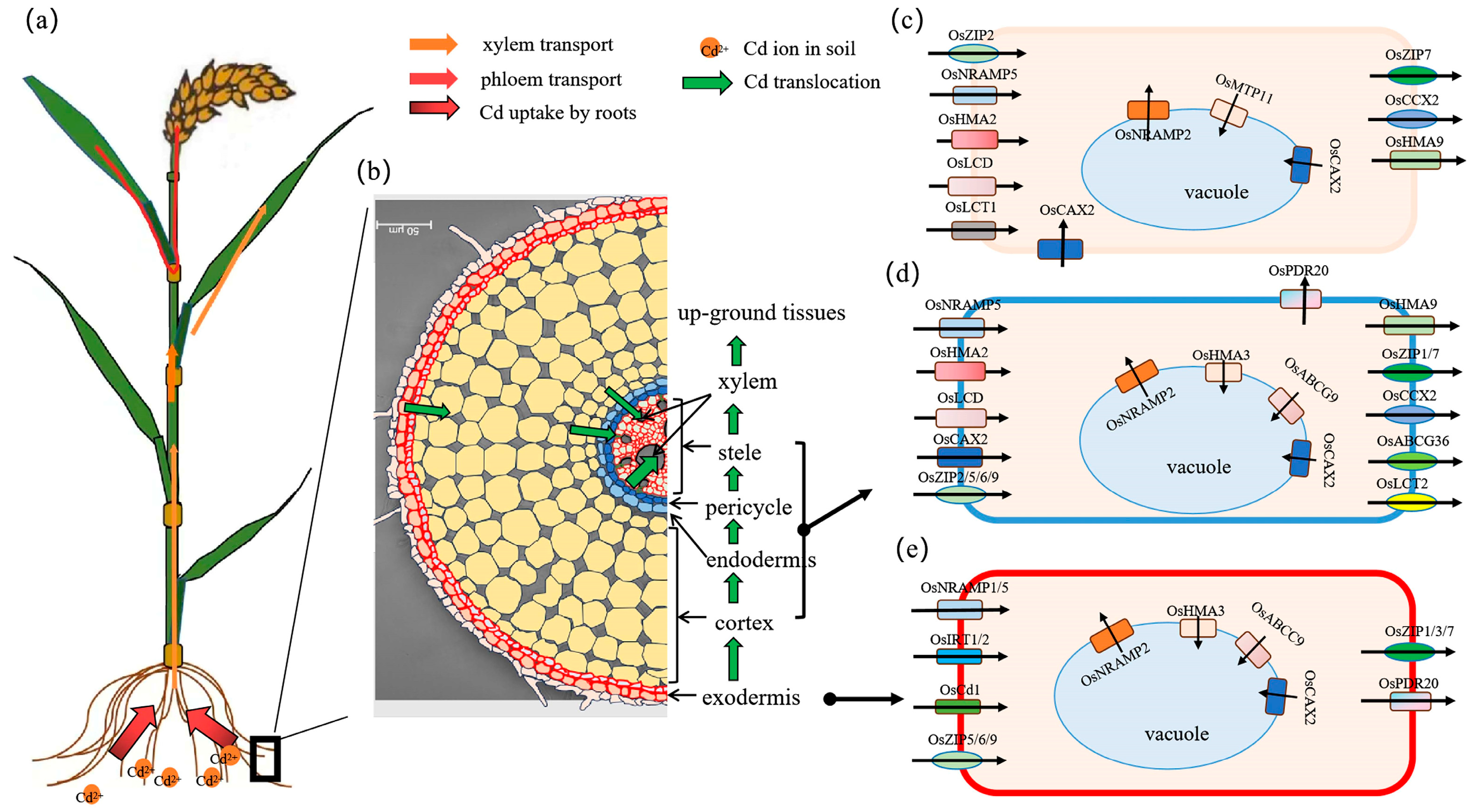
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Cd Absorption and Translocation to Rice Grains
4.1. Transporters Involved in Cd Uptake by Roots
4.2. Transporters Involved in Cd Transfer from Roots to Shoots
4.3. Transporters Involved in Cd Redistribution Through Phloem Transport
5. The Research Progress in Breeding Low-Cd-Accumulation Rice Cultivars
5.1. Screening of Emergency Low-Cd-Accumulation Rice Cultivars Through Conventional Methods
5.2. Construction and Utilization of Low-Cd-Accumulation Rice Cultivars
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loomis, D.; Guha, N.; Hall, A.L.; Straif, K. Identifying occupational carcinogens: An update from the IARC Monographs. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.F.; Shen, R.F.; Shao, J.F. Transport of cadmium from soil to grain in cereal crops: A review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y.-G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.G.; Wu, J.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Song, L. Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Feijoo, R.; Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Arenas-Lago, D. Use of Three Different Nanoparticles to Reduce Cd Availability in Soils: Effects on Germination Early Growth of Sinapis abla L. Plants 2023, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, D.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, M.; Li, X. Assessment of cadmium (Cd) concentration in arable soil in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4932–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.; Ma, J.F. Toxic Heavy Metal and Metalloid Accumulation in Crop Plants and Foods. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil Contamination in China: Current Status and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, W.; Sui, H.; Yong, L.; Yang, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y. Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, P.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Zou, B.; McBride, M.B. Multiple Exposure and Effects Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Population near Mining Area in South China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, S.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H. Environmental and human health risks from cadmium exposure near an active lead-zinc mine and a copper smelter, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Du, P.; Luo, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Xu, G.; Gao, H. Soil contamination with cadmium and potential risk around various mines in China during 2000–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Chang, L.; Wang, Q.; Miao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. Distribution and accumulation of cadmium in soil under wheat-cultivation system and human health risk assessment in coal mining area of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant science: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Guan, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Zheng, X. Spatial and variety distributions, risk assessment, and prediction model for heavy metals in rice grains in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 7298–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Konishi, N.; Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. Local distribution of manganese to leaf sheath is mediated by OsNramp5 in rice. New Phytol. 2024, 241, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Umer, M.J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Abbas, Y.; Ashraf, M.N.; Tahir, N.; Ullah, A.; Gogoi, N.; Farooq, M. Strategies for reducing cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Wei, S.; Jia, P.; Liu, T.; Hou, D.; Xie, R.; Lin, Z.; Ge, J.; Qiao, Y.; Chang, X.; et al. Biochar significantly alters rhizobacterial communities and reduces Cd concentration in rice grains grown on Cd-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Liao, X.; Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Ji, X. Remediation of Cd contaminated paddy fields by intercropping of the high- and low- Cd-accumulating rice cultivars. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabagala, F.S.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, X.; He, C.; Shan, H.; Qiu, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, N.; Su, S. A review of amendments for simultaneously reducing Cd and As availability in paddy soils and rice grain based on meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Lin, X.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Guan, M.Y.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.X. Gene identification and transcriptome analysis of low cadmium accumulation rice mutant (lcd1) in response to cadmium stress using MutMap and RNA-seq. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H.; Li, S.; Deng, H.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Robust identification of low-Cd rice varieties by boosting the genotypic effect of grain Cd accumulation in combination with marker-assisted selection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Dong, J.; Tan, L.; Ji, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; Lv, Q.; Mao, B.; Hu, Y.; et al. Overexpression of OsLCT2, a Low-Affinity Cation Transporter Gene, Reduces Cadmium Accumulation in Shoots and Grains of Rice. Rice 2021, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guan, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y. Screening Rice Germplasm with Different Genetic Backgrounds for Cadmium Accumulation in Brown Rice in Cadmium-Polluted Soils. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.D.; Zhao, D.; Ren, F.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal variation of soil heavy metals in China: The pollution status and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Tian, G.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L. Cadmium (Cd) distribution and contamination in Chinese paddy soils on national scale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17941–17952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Long, T.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Mi, N.; Xia, F.; Wang, X.; Deng, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, F. Meta-analysis of Cd input-output fluxes in agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2022, 303 Pt 2, 134974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.T.; Zhao, R.; Hu, B.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Novel framework for modelling the cadmium balance and accumulation in farmland soil in Zhejiang Province, East China: Sensitivity analysis, parameter optimisation, and forecast for 2050. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, F.J. Dietary cadmium exposure, risks to human health and mitigation strategies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 939–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Ma, L.; Shang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Exposure to Lead and Cadmium in the Sixth Total Diet Study—China, 2016–2019. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.P.; Yang, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, F.-J. Dietary cadmium intake from rice and vegetables and potential health risk: A case study in Xiangtan, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Deng, X.; Zhou, H.; Long, J.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Hou, H.-B.; Peng, P.-Q.; Liao, B.-H. Health risk assessment of Cd pollution in irrigated paddy field system: A field investigation in Hunan Province, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C. Health Risk Assessment of Dietary Cadmium Intake: Do Current Guidelines Indicate How Much is Safe? Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Tahir, A.; Rashid, H.U.; ur Rehman, T.; Danish, S.; Hussain, B.; Akca, H. Strategies for reducing Cd concentration in paddy soil for rice safety. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128116. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Pan, J.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Guan, M. Water management affects arsenic uptake and translocation by regulating arsenic bioavailability, transporter expression and thiol metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S. A New Model for Effective Remediation and Comprehensive Utilization of Cd–Pb Composite Contaminated Farmland by Ornamental Plants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, F. Phytoexclusion of heavy metals using low heavy metal accumulating cultivars: A green technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Ito, M.; Takahashi, R.; Honma, T.; Kuramata, M.; Ishikawa, S. QTL Pyramiding and Its Use in Breeding for Increasing the Phytoextraction Efficiency of Soil Cd via High-Cd-Accumulating Rice. Plants 2022, 11, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Z.; Kang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiu, R.; Qin, J.; Li, H. Interplanting of rice cultivars with high and low Cd accumulation can achieve the goal of “repairing while producing” in Cd-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Fu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, X. Sustainable remediation of Cd-contaminated farmland through the rotation of rapeseed-rice varieties with different Cd accumulation potentials. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, A.W.; Chi, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Effects of cultivar, water condition and their interactions on Cd accumulation in rice grains. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, L.; Yang, M.; Zou, X.; Yin, C.; Lin, Y. Research Advances in Cadmium Uptake, Transport and Resistance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Cells 2022, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.A.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, P.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M. Exploring the mechanism of Cd uptake and translocation in rice: Future perspectives of rice safety. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H.; Ogawa, I.; Ishimaru, Y.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2006, 52, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xiong, J.; Chen, R.; Fu, G.; Chen, T.; Tao, L. Excessive nitrate enhances cadmium (Cd) uptake by up-regulating the expression of OsIRT1 in rice (Oryza Sativa). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 122, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, H.; Ye, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T. Comparative transcriptomics reveals the key pathways and genes of cadmium accumulation in the high cadmium-accumulating rice (Oryza Sativa L.) line. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, P.G.; Kuruvilla, S.; Mathew, M.K. Functional characterization of a transition metal ion transporter, OsZIP6 from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 97, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Qu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Chen, C. ZINC TRANSPORTER5 and ZINC TRANSPORTER9 Function Synergistically in Zinc/Cadmium Uptake. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramata, M.; Abe, T.; Tanikawa, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Ishikawa, S. A weak allele of OsNRAMP5 confers moderate cadmium uptake while avoiding manganese deficiency in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 6475–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Senoura, T.; Shimo, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. The OsNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in Cd accumulation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4843–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.D.; Huang, S.; Yamaji, N.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F. OsNRAMP1 transporter contributes to cadmium and manganese uptake in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 2476–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Liu, H.; Fu, M.-J.; Zhang, L.-W.; Yin, S.-F.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, F.-J.; Huang, X.-Y. The cation/H plus exchanger OsCAX2 is involved in cadmium uptake and contributes to differential grain cadmium accumulation between Indica and Japonica rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.L.; Xu, W.; Xie, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Dai, C.; et al. Variation of a major facilitator superfamily gene contributes to differential cadmium accumulation between rice subspecies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Bashir, K.; Shimo, H.; Senoura, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Ono, K.; Yano, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T.; et al. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in Manganese, Iron and Cadmium Transport. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Guan, M.; Chen, M.; Lin, X.; Xu, P.; Cao, Z. Mutation of reduces cadmium xylem and phloem transport in rice plants and its physiological mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Wang, W.; Yamaji, N.; Fukuoka, S.; Che, J.; Ueno, D.; Ando, T.; Deng, F.; Hori, K.; Yano, M.; et al. Duplication of a manganese/cadmium transporter gene reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grain. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.K.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xie, H.; Song, S.; Qiu, M.; Wen, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, G.; Tian, Y.; et al. Mutation at Different Sites of Metal Transporter Gene OsNRAMP5 Affects Cd Accumulation and Related Agronomic Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Dong, J.; Qu, M.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, Z.; Mao, B.; et al. Knockout of enhances rice tolerance to cadmium toxicity in response to varying external cadmium concentrations via distinct mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.M.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Xie, H.; Long, Q.; Cai, Y. Effects of external Mn2+ activities on OsNRAMP5 expression level and Cd accumulation in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Mao, D.; Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Tan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, H.; Peng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. CF1 reduces grain-cadmium levels in rice (Orzya sativa). Plant J. 2022, 110, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.D.; Huang, S.; Konishi, N.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F.-J. Overexpression of the manganese/cadmium transporter OsNRAMP5 reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grain. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5705–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.L.; Chen, J.; Meng, L.; Chen, D.; He, H.; Ye, G. The Rice Cation/H Exchanger Family Involved in Cd Tolerance and Transport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyadate, H.; Adachi, S.; Hiraizumi, A.; Tezuka, K.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Katou, K.; Kodama, I.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.L.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.; Yang, M.; Lian, X.; Tang, Z.; Huang, C.; Salt, D.E.; Zhao, F. A loss-of-function allele of associated with high cadmium accumulation in shoots and grain of rice cultivars. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.J.; Jiao, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H.; Liang, W.; Liu, C. Knockout of OsHMA3 in an rice increases cadmium sensitivity and inhibits plant growth. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 103, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.J.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Lv, K.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of variation of cadmium accumulation in rice and detection of a new weak allele of OsHMA3. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6389–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Gao, Z.Y.; Shang, L.G.; Yang, C.H.; Ruan, B.P.; Zeng, D.L.; Guo, L.B.; Zhao, F.J.; Huang, C.F.; Qian, Q. Natural variation in the promoter of contributes to differential grain cadmium accumulation between and rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Z.; Fu, S.; Huang, J.; Li, L.; Long, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xia, J. The tonoplast-localized transporter OsABCC9 is involved in cadmium tolerance and accumulation in rice. Plant Sci. 2021, 307, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.D.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.-J. The vacuolar transporter OsNRAMP2 mediates Fe remobilization during germination and affects Cd distribution to rice grain. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Hu, R.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Dong, J.; Yang, T.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; et al. OsNRAMP2 facilitates Cd efflux from vacuoles and contributes to the difference in grain Cd accumulation between japonica and indica rice. Crop J. 2023, 11, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, M.; Baldoni, E.; Lucchini, G.; Vigani, G.; Valè, G.; Sacchi, G.A.; Nocito, F.F. Analysis of Cadmium Root Retention for Two Contrasting Rice Accessions Suggests an Important Role for OsHMA2. Plants 2021, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, N.; Xia, J.; Mitani-Ueno, N.; Yokosho, K.; Ma, J.F. Preferential Delivery of Zinc to Developing Tissues in Rice Is Mediated by P-Type Heavy Metal ATPase OsHMA2. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Shimo, H.; Ogo, Y.; Senoura, T.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimo, H.; Ishimaru, Y.; An, G.; Yamakawa, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. Low cadmium (LCD), a novel gene related to cadmium tolerance and accumulation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 5727–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Ye, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Sun, C.; Li, F.; Yi, J. Generation of low-cadmium rice germplasms via knockout of OsLCD using CRISPR/Cas9. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Lee, Y.; An, G. Rice P-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Sun, D.; Yang, Z.M. OsPDR20 is an ABCG metal transporter regulating cadmium accumulation in rice. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 136, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.S.; Feng, S.J.; Zhang, B.Q.; Wang, M.Q.; Cao, H.W.; Rono, J.K.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.M. OsZIP1 functions as a metal efflux transporter limiting excess zinc, copper and cadmium accumulation in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, T.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, C. OsZIP7 functions in xylem loading in roots and inter-vascular transfer in nodes to deliver Zn/Cd to grain in rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 512, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.H.; Zeng, M.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Dai, J.; Xie, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tian, L.; Chen, L.; Li, D. A Node-Expressed Transporter OsCCX2 Is Involved in Grain Cadmium Accumulation of Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Chao, D.; Wang, Z.; Shi, M.; Chen, J.; Chao, D.-Y.; Li, R.; et al. The ABC transporter ABCG36 is required for cadmium tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5909–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.N.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z.; Huang, X.-Y.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F.-J. Producing cadmium-free rice by overexpressing OsHMA3. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, S.; Kamiya, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Kasai, K.; Sato, Y.; Nagamura, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kyozuka, J.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, T. Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20959–20964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, S.; Kamiya, T.; Clemens, S.; Fujiwara, T. Characterization of OsLCT1, a cadmium transporter from indica rice (Oryza sativa). Physiol. Plant. 2014, 151, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Huang, X. The OsZIP2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation and intervascular transfer of cadmium in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 3865–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, K.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, F.-J.; Huang, C.-F.; et al. OsNRAMP5 contributes to manganese translocation and distribution in rice shoots. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, H.; Mao, D.; Liang, G.; et al. The metal tolerance protein OsMTP11 facilitates cadmium sequestration in the vacuoles of leaf vascular cells for restricting its translocation into rice grains. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 1733–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.N.; Cheng, H.F.; Tao, S. The Challenges and Solutions for Cadmium-contaminated Rice in China: A Critical Review. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.P.; Xu, D.; Yue, J.; Ma, Y.; Dong, S.; Feng, J. Recent advances in soil remediation technology for heavy metal contaminated sites: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.H.; Li, F.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Liu, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations and screening for stable low-accumulating rice cultivars from multi-environment trials. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Ishimaru, Y.; Igura, M.; Kuramata, M.; Abe, T.; Senoura, T.; Hase, Y.; Arao, T.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H. Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19166–19171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, V.E.; Pegoraro, C.; Busanello, C.; de Oliveira, A.C. Mutagenesis in Rice: The Basis for Breeding a New Super Plant. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Yamaji, N.; Yokosho, K.; Ma, J.F. Nramp5 Is a Major Transporter Responsible for Manganese and Cadmium Uptake in Rice. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2155–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.K.; Fu, Y.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Bai, L.; Li, L. Xizi 3: A new rice variety with stable low-cadmium-accumulation characteristics. Mol. Breed. 2025, 45, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.L.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, W.; He, Z. Cadmium Minimization in Crops: A Trade-Off with Mineral Nutrients in Safe Breeding. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 48, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.N.; Ning, W.; Su, L.; Wei, Z.; Shi, D.; Liao, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Fang, B.; Mao, B.; Chang, S. Reducing cadmium uptake without compromising nitrogen uptake, photosynthesis, or yield in low-Cd hybrid rice. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Tang, L.; Huang, G.; Liu, L.; Dong, C.; Liu, H.; Mao, B.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, Y. The Indica Hybrid Rice Containing an OsNRAMP5 Knockout Exhibit Better Adaptability Compared to Its Paternal Parent in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Meng, J.; Xu, S.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Shu, Q.; Huang, J. Characterization and Evaluation of OsLCT1 and OsNRAMP5 Mutants Generated Through CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Mutagenesis for Breeding Low Cd Rice. Rice Sci. 2019, 26, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Miao, Z.; Kong, D.; Zhang, A.; Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; Liu, Y. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Rice Germplasm Innovation and Genetic Improvement. Genes 2024, 15, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Mao, B.; Li, Y.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; He, H.; Wang, W.; Zeng, X.; Shao, Y.; et al. Knockout of using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating rice without compromising yield. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.J.; Teo, J.; Tian, D.; Yin, Z. Genetic engineering low-arsenic and low-cadmium rice grain. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 2143–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.; Brini, F.; Rouached, H.; Masmoudi, K. Genetically engineered crops for sustainably enhanced food production systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1027828. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Liang, R.; Wang, G.; Ma, S.; Liu, N.; Gong, Y.; Mccouch, S.R.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Design of rice with low cadmium accumulation in grain using single segment substitution line. New Crops 2025, 2, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Ding, S.; Zhang, A.; Hong, K.; Jiang, H.; Yang, S.; Ruan, B.; Zhang, B.; Dong, G.; Guo, L.; et al. Development of nutritious rice with high zinc/selenium and low cadmium in grains through QTL pyramiding. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.J.; Hua, H.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.; Gong, J.; Wei, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q. Whole-Genome Sequencing of 117 Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines for Genetic Analyses of Complex Traits in Rice. Rice 2022, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard: Limits of Contaminants in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; Cao, Z. A Review of Reducing Cadmium Pollution in the Rice–Soil System in China. Foods 2025, 14, 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101747
Guan M, Xia Y, Zhang W, Chen M, Cao Z. A Review of Reducing Cadmium Pollution in the Rice–Soil System in China. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101747
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Meiyan, Yuchun Xia, Weixing Zhang, Mingxue Chen, and Zhenzhen Cao. 2025. "A Review of Reducing Cadmium Pollution in the Rice–Soil System in China" Foods 14, no. 10: 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101747
APA StyleGuan, M., Xia, Y., Zhang, W., Chen, M., & Cao, Z. (2025). A Review of Reducing Cadmium Pollution in the Rice–Soil System in China. Foods, 14(10), 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101747






