Biological Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomato Caused by Alternaria alternata with Bacillus velezensis T3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fruits
2.2. Pathogen
2.3. Bacterial Antagonist
2.4. Efficacy of B. velezensis T3 in the Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomatoes
2.5. Inhibition of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomatoes by Cell-Free Filtrate of B. velezensis T3
2.5.1. In Vitro
2.5.2. In Vivo
2.6. Effect of B. velezensis T3 on Resistance-Related Enzyme Activities of Cherry Tomatoes
2.6.1. Determination of Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO) Activity
2.6.2. Determination of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase (PAL) Activity
2.6.3. Determination of β-1,3-glucanase (GLU) Activity
2.6.4. Determination of Chitinase (CHI) Activity
2.7. Effect of B. velezensis T3 on O2− Production Rate, H2O2 Content, and MDA Content of Cherry Tomatoes
2.8. Effect of B. velezensis T3 on the Activity of Antioxidant-Related Enzymes (Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Peroxidase (POD), Catalase (CAT), and Ascorbate Peroxidase (APX)) in Cherry Tomatoes
2.9. RT-qPCR for Detection of Expression Levels of Disease Resistance-Related Genes
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
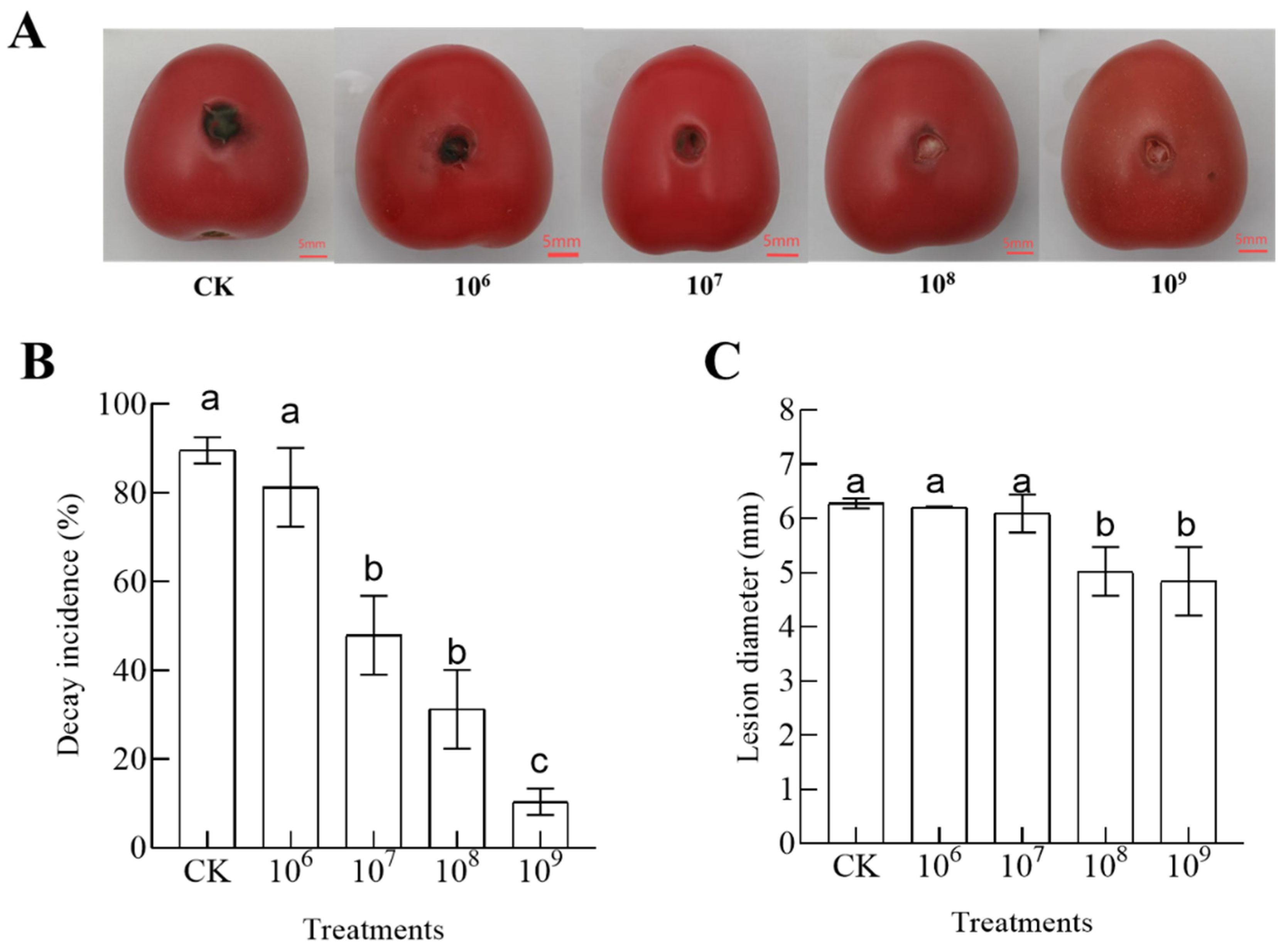
3.1. Efficacy of B. velezensis T3 in the Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomatoes
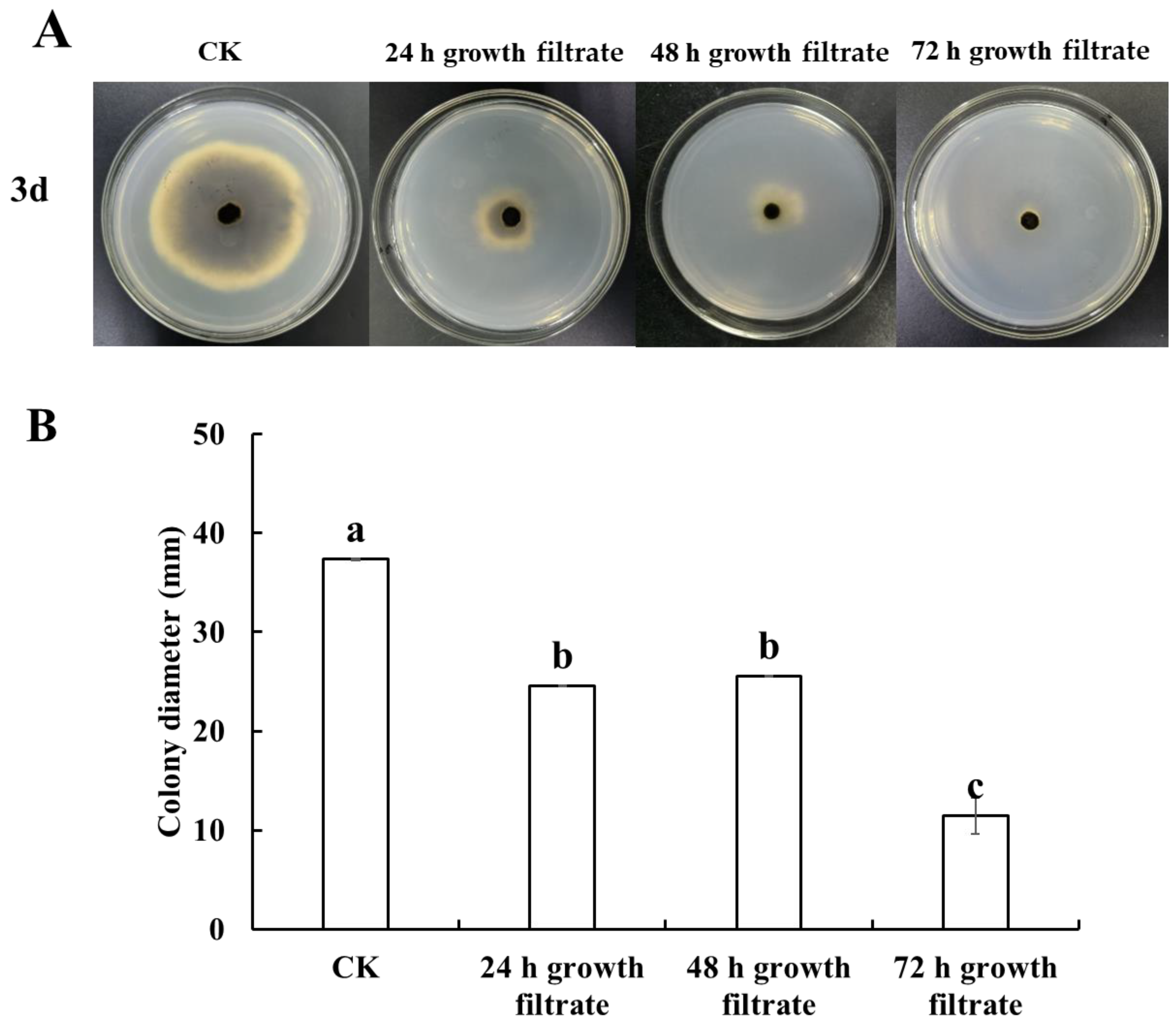
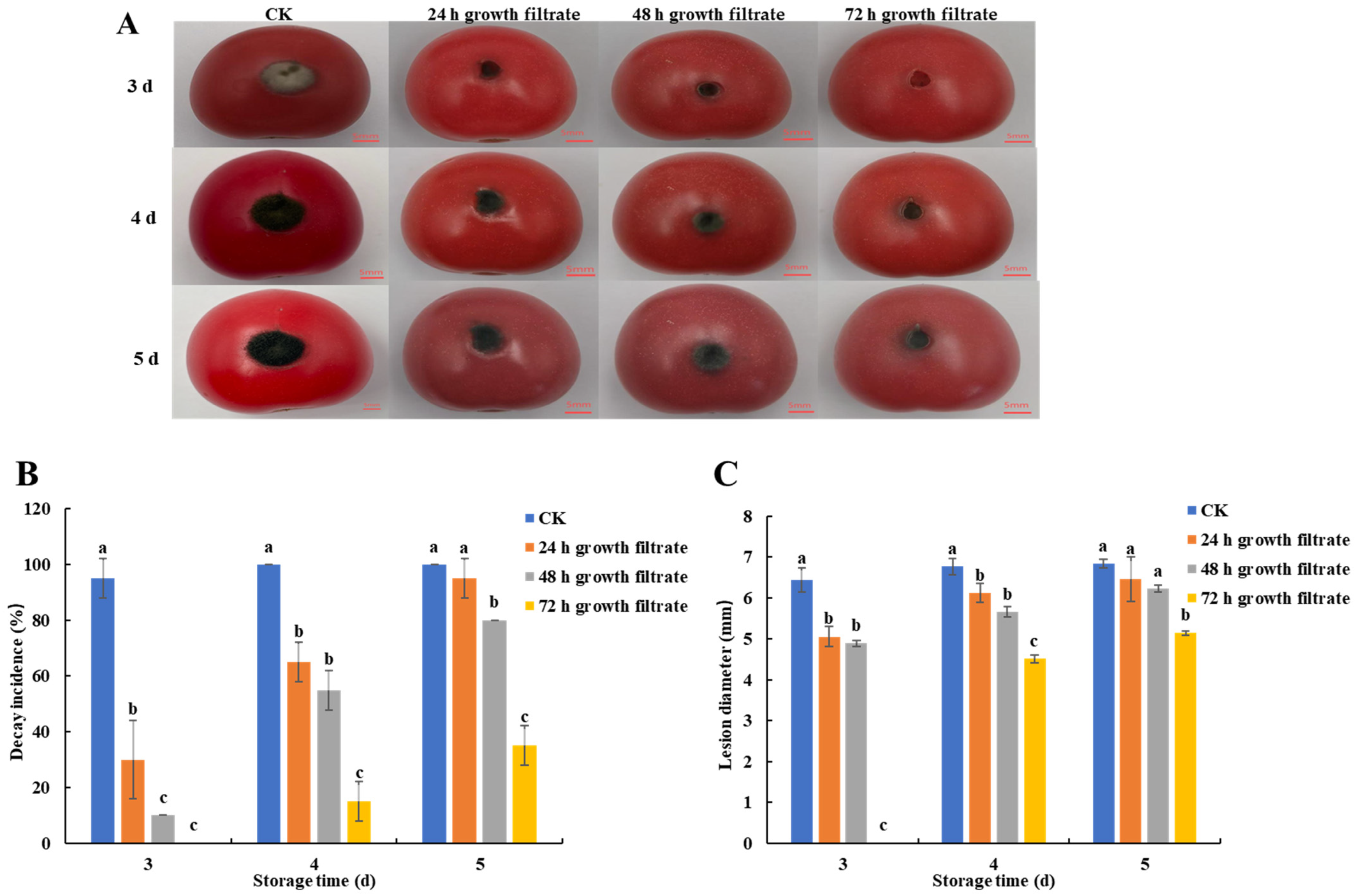
3.2. Inhibition of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomatoes by Cell-Free Filtrate of B. velezensis T3
3.2.1. In Vitro
3.2.2. In Vivo
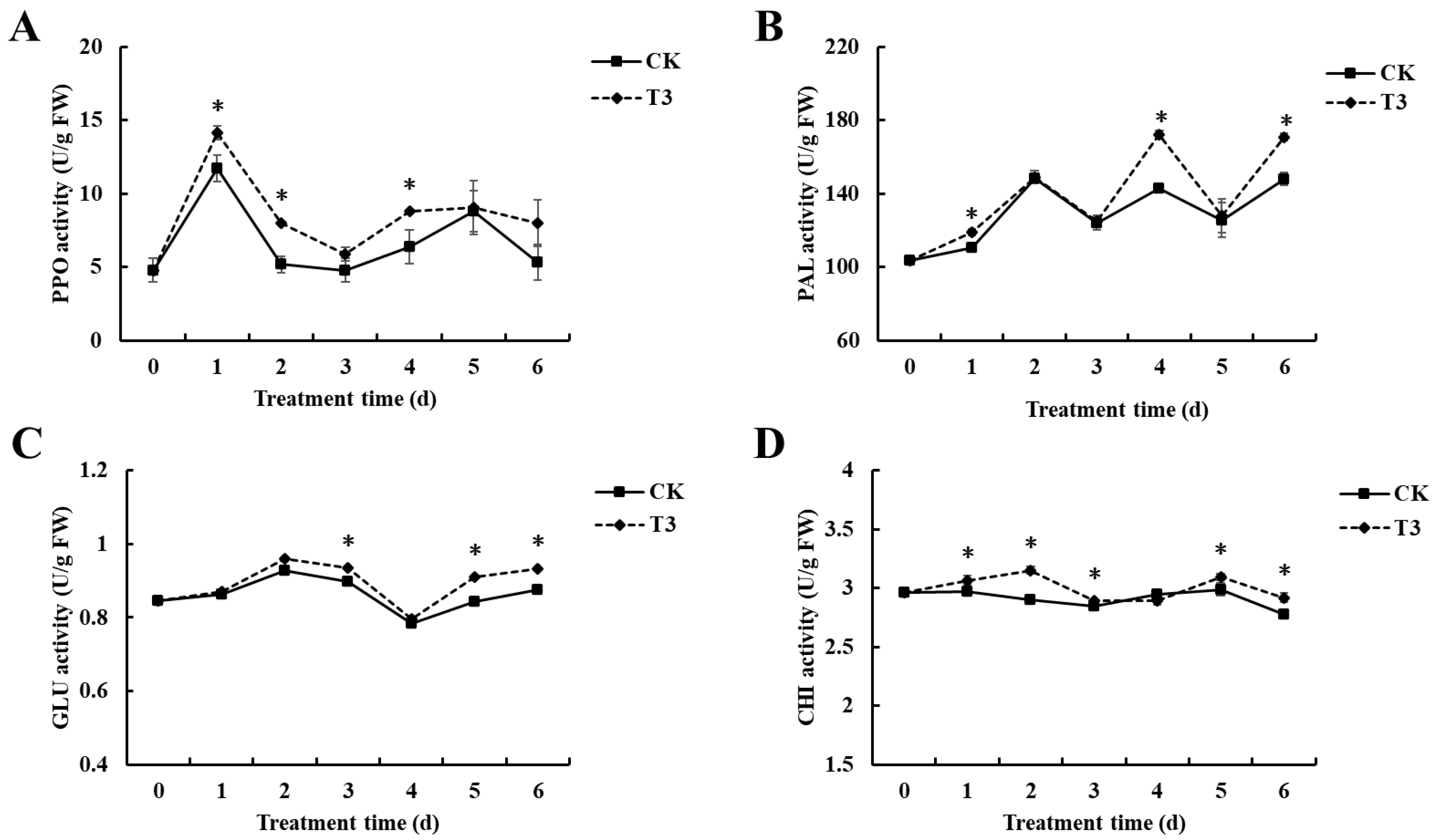
3.3. Effect of B. velezensis T3 on Resistance-Related Enzyme (PPO, PAL, GLU, and CHI) in Cherry Tomatoes
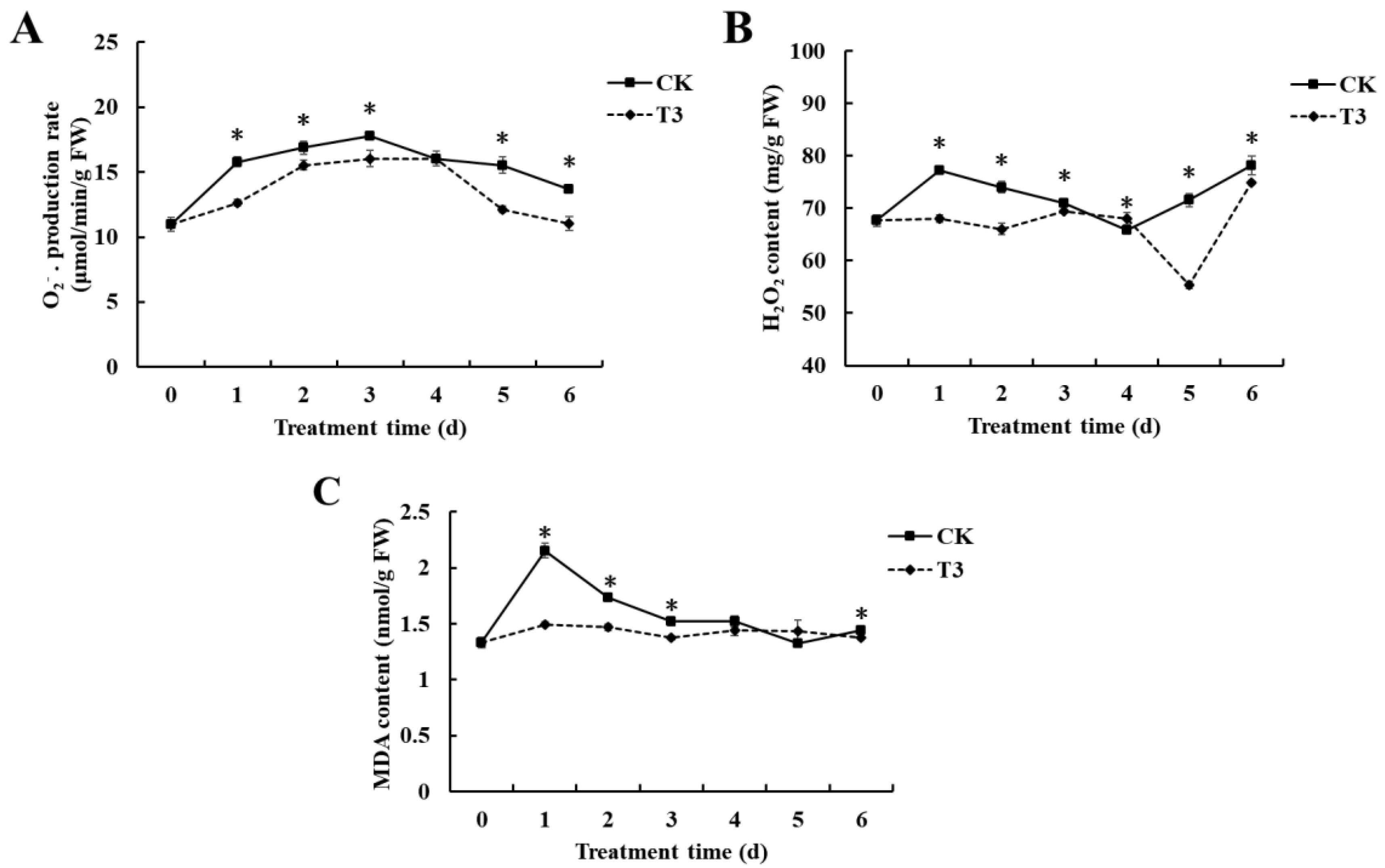
3.4. Effect of B. velezensis T3 on O2− Production Rate, H2O2 Content, and MDA Content of Cherry Tomatoes
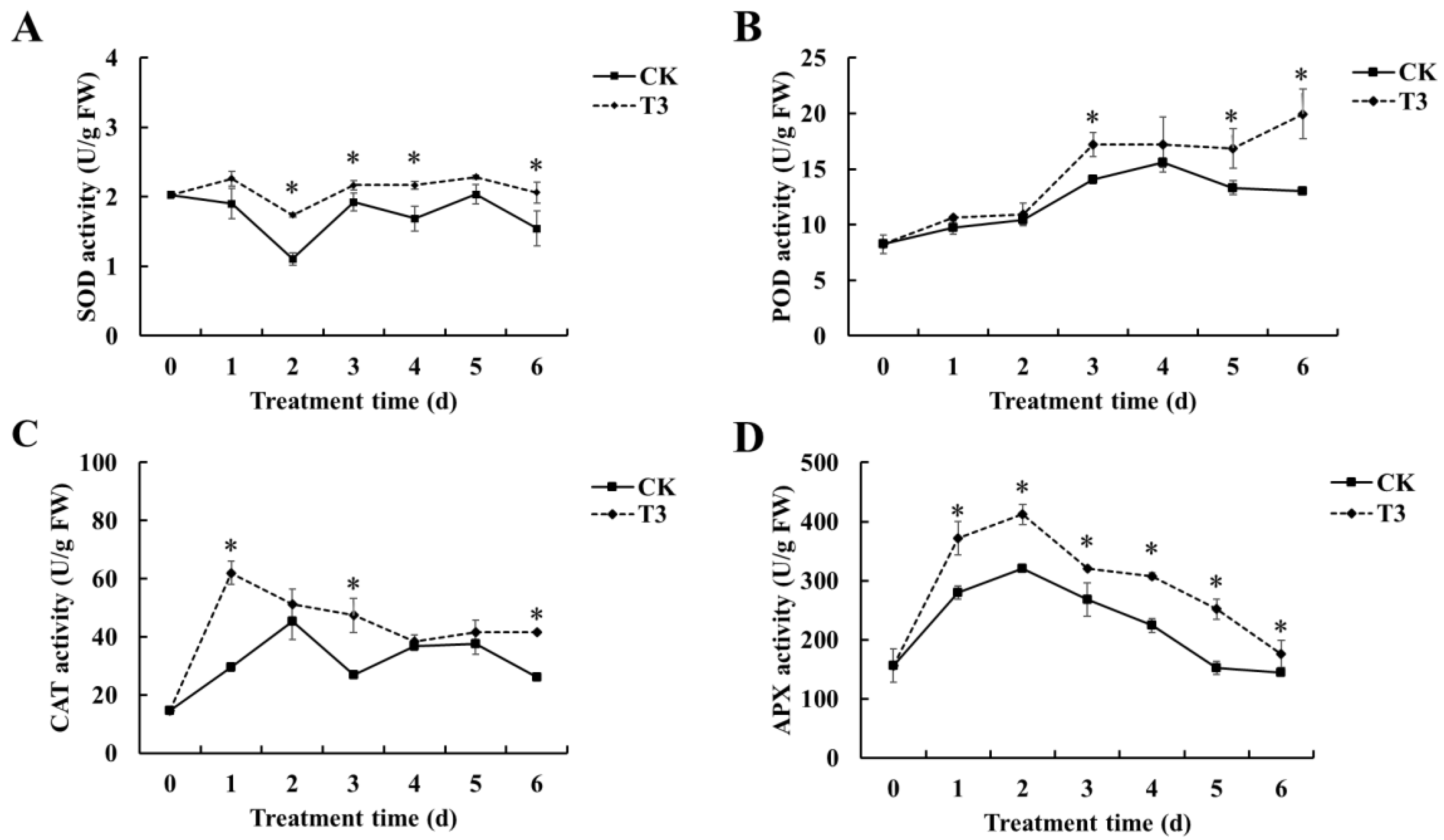
3.5. Effect of B. velezensis T3 on the Activity of Antioxidant-Related Enzymes (SOD, POD, CAT, and APX) in Cherry Tomatoes
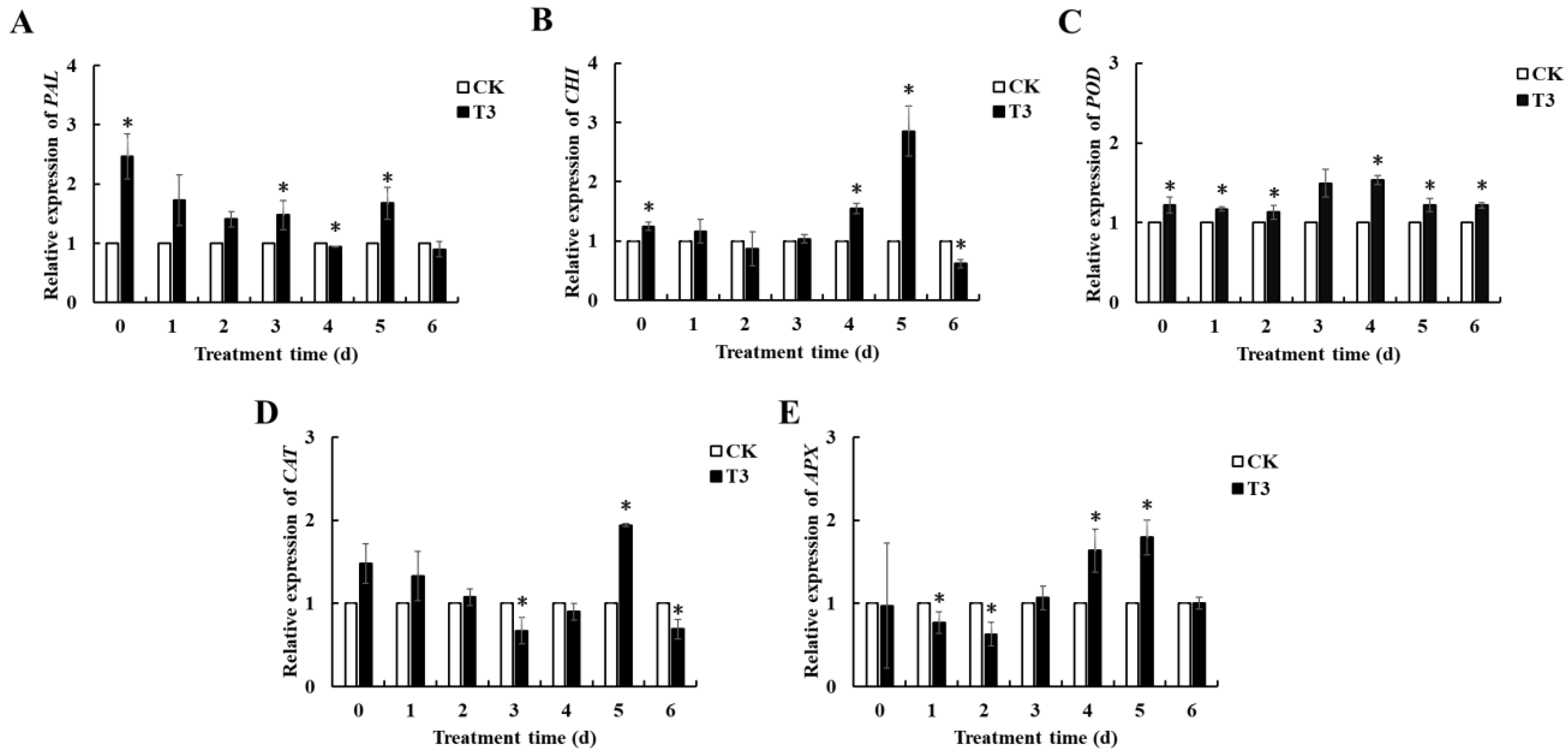
3.6. Expression Levels of Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, W. Curcumin: An innovative approach for postharvest control of Alternaria alternata induced black rot in cherry tomatoes. Fungal Biol. 2024, 128, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.-Y.; Yang, S.; Ding, K.-X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Yu, Y.-Z.; Huang, Y.-X.; Qin, S.; Xing, K. 2-Methylbutyric acid functions as a potential antifungal fumigant by inhibiting Botrytis cinerea and inducing resistance to gray mold in cherry tomatoes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 222, 113343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H. Antifungal activity of Bacillus mojavensis D50 against Botrytis cinerea causing postharvest gray mold of tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 312, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwana, H.; Bokahri, N.A.; Alsahli, S.A.; Al Showiman, A.S.; Alzahrani, R.M.; Aldehaish, H.A. Postharvest disease management of Alternaria spots on tomato fruit by Annona muricata fruit extracts. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.; Lee, Y.; Balaraju, K.; Jeon, Y. Characterization and evaluation of Bacillus subtilis GYUN-2311 as a biocontrol agent against Colletotrichum spp. on apple and hot pepper in Korea. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1322641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Song, H.; Shi, H.; Gao, Z.; Mao, J.; Cao, Y.; Huo, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, M. Postharvest treatment with Bacillus velezensis LX mitigates disease incidence and alters the microbiome on kiwifruit surface. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 211, 112843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Munir, S.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Kong, B.; He, P.; He, Y. Bacillus subtilis L1-21 as a biocontrol agent for postharvest gray mold of tomato caused by Botrytis cinerea. Biol. Control. 2021, 157, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Tian, Z.; He, H.; Long, C.-A.; Jiang, F. Bacillus species as potential biocontrol agents against citrus diseases. Biol. Control. 2020, 151, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, Q.; Godana, E.A.; Huo, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, H. Efficacy of Wickerhamomyces anomalus in the biocontrol of black spot decay in tomatoes and investigation of the mechanisms involved. Biol. Control. 2023, 186, 105356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.L.; Borges, Á.V.; da Silva, H.A.O.; Leite, I.C.H.L.; Alves, K.S.; de Medeiros, L.S.; Abreu, L.M.d. Lipopeptide-enriched extracts of Bacillus velezensis B157 for controlling tomato early blight. Crop Prot. 2023, 172, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Xing, F.; Nie, C.; Cao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, X.; Moosa, A.; Liu, Y. Biocontrol potential of lipopeptides produced by the novel Bacillus subtilis strain Y17B against postharvest Alternaria fruit rot of cherry. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1150217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, J.; Tian, H.; Ji, M. Bacillus species as versatile weapons for plant pathogens: A review. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2017, 31, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, L.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Mei, R.; Wang, Q. Biological Control of Apple Ring Rot on Fruit by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 9001. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 29, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.-N.; Ye, W.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Zhou, W.-W. Antifungal Activity of Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by Bacillus methylotrophicus and Bacillus thuringiensis against Five Common Spoilage Fungi on Loquats. Molecules 2020, 25, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.; Xu, M. Isolation and Identification of Bacillus subtilis LY-1 and Its Antifungal and Growth-Promoting Effects. Plants 2023, 12, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethapathy, P.; Gurudevan, T.; Subramanian, K.S.; Kuppusamy, P. Bacterial antagonists and hexanal-induced systemic resistance of mango fruits against Lasiodiplodia theobromae causing stem-end rot. J. Plant Interact. 2016, 11, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Rosales, P.U.; Ochoa-Jiménez, V.A.; Casas-Junco, P.P.; Balois-Morales, R.; Rubio-Melgarejo, A.; Díaz-Jasso, Á.E.; Berumen-Varela, G. Bacillus mojavensis enhances the antioxidant defense mechanism of soursop (Annona muricata L.) fruits during postharvest storage. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Zhang, X.; Godana, E.A.; Ngolong Ngea, G.L.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Gao, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H. Control of postharvest soft rot of green peppers by Bacillus subtilis through regulating ROS metabolism. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 131, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wei, H.; Ding, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Biological control efficacy of Bacillus licheniformis HG03 against soft rot disease of postharvest peach. Food Control. 2022, 145, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, J. Identification of the Fungal Pathogens of Postharvest Disease on Peach Fruits and the Control Mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis JK-14. Toxins 2019, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.-L.; Peng, S.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.-P.; Zhu, F. Induced resistance in nectarine fruit by Bacillus licheniformis W10 for the control of brown rot caused by Monilinia fructicola. Food Microbiol. 2020, 92, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Xin, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Yue, Q.R.; Feng, F.P.; Gu, X.Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, L.N.; Zhang, H.Y. Characterization of a Bacillus velezensis strain as a potential biocontrol agent against soft rot of eggplant fruits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 410, 110480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynaldo, F.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Ngea, G.L.N.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Investigating the biocontrol potentiality of Wickerhamomyces anomalus against postharvest gray mold decay in cherry tomatoes. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 285, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, M.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H. The effect of ε-poly-l-lysine treatment on molecular, physiological and biochemical indicators related to resistance in longan fruit infected by Phomopsis longanae Chi. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Cao, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lu, H. Effect of Cryptococcus laurentii on inducing disease resistance in cherry tomato fruit with focus on the expression of defense-related genes. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.C.; de Miranda, R.F.; Costa, F.A.; Ulhoa, C.J. Potential of Trichoderma piluliferum as a biocontrol agent of Colletotrichum musae in banana fruits. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; Hung, Y.-C.; Lin, Y. Inhibitory effect of propyl gallate on pulp breakdown of longan fruit and its relationship with ROS metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Ding, C.; Li, P.; Fu, L. Combined application of the endophyte Bacillus K1 and sodium dehydroacetate alleviates postharvest gray mold in grapes. Food Microbiol. 2024, 125, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yan, X. Inhibition of potassium cinnamate to blueberry Alternaria fruit rot. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 106, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yan, F.; Ni, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, X. In vitro and in vivo control of Alternaria alternata in cherry tomato by essential oil from Laurus nobilis of Chinese origin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 94, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osdaghi, E.; Jones, J.B.; Sharma, A.; Goss, E.M.; Abrahamian, P.; Newberry, E.A.; Potnis, N.; Carvalho, R.; Choudhary, M.; Paret, M.L.; et al. A centenary for bacterial spot of tomato and pepper. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1500–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Tian, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Long, C.-A. Antagonistic Activity and the Mechanism of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DH-4 Against Citrus Green Mold. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastochkina, O.; Seifikalhor, M.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Baymiev, A.; Pusenkova, L.; Garipova, S.; Kulabuhova, D.; Maksimov, I. Bacillus Spp.: Efficient Biotic Strategy to Control Postharvest Diseases of Fruits and Vegetables. Plants 2019, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbee, M.F.; Ali, M.S.; Choi, J.; Hwang, B.S.; Jeong, S.C.; Baek, K. Bacillus velezensis: A Valuable Member of Bioactive Molecules within Plant Microbiomes. Molecules 2019, 24, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Qiao, M.; Yang, Y.; Luo, K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Kuznetsova, N.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Q. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens M73 reduces postharvest decay and promotes anthocyanin accumulation in Tarocco blood orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) during cold storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 182, 111698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Wang, H.X.; Lv, Z.H.; Shi, Y.R.; Wang, Z.G. Antifungal activity and functional components of cell-free supernatant from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LZN01 inhibit Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum growth. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Cai, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J. Physiological and transcriptomics analysis of the effect of recombinant serine protease on the preservation of loquat. Genomics 2021, 113, 3750–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Li, N.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, B.; Cao, K.; Hu, T. An endophytic strain Bacillus velezensis JZ51 controlled pink mold rot of postharvest apple fruit via antagonistic action and disease resistance induction. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 210, 112793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, M.; Chen, J. Effect of exogenous methyl jasmonate treatment on disease resistance of postharvest kiwifruit. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, L.; Yan, S.; Xiao, L. Relationship between activated oxygen metabolism and browning of “Yali” pears during storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, 14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, D.; Shao, Y.; Li, R.; Li, W. Bacillus siamensis N-1 improves fruit quality and disease resistance by regulating ROS homeostasis and defense enzyme activities in pitaya. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 329, 112975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Kong, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Identification of a new Bacillus sonorensis strain KLBC GS-3 as a biocontrol agent for postharvest green mould in grapefruit. Biol. Control. 2020, 151, 104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Inhibitory effects of propyl gallate on browning and its relationship to active oxygen metabolism in pericarp of harvested longan fruit. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, R.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Li, W.; Shao, Y. Combined effect of Debaryomyces hansenii and Bacillus atrophaeus on the physicochemical attributes, defense-related enzyme activity, and transcriptomic profile of stored litchi fruit. Biol. Control. 2022, 172, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Pang, X.; Liu, H.; Lin, F.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Iturin A Induces Resistance and Improves the Quality and Safety of Harvested Cherry Tomato. Molecules 2021, 26, 6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | GeneBank Number | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (3′→5′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | AB199316.1 | acaccctgttctcctgactg | agagaaagcacagcctggat |
| PAL | Solycl0g086180.2 | gcatccggtgatcttgttcc | cgaagccaaaccagaaccaa |
| APX | LC203076.1 | gaggcccgaaaattcccatg | caaatgagcagcaggggaag |
| POD | NM_001247041.2 | acagctcctccgaattccaa | ggaatcacgagcagcaagag |
| CAT | M37151 | tgttgagggggttgtcactc | cgtgaagtccaggagcaagt |
| CHI | FJ849060.1 | tggtggtagtgcaggaacat | tgtccagctcgttcgtagtt |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Yang, Q.; Solairaj, D.; Godana, E.A.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Biological Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomato Caused by Alternaria alternata with Bacillus velezensis T3. Foods 2025, 14, 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101700
Wei X, Yang Q, Solairaj D, Godana EA, Zhang X, Li Y, Liu X, Zhang H. Biological Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomato Caused by Alternaria alternata with Bacillus velezensis T3. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101700
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xinmeng, Qiya Yang, Dhanasekaran Solairaj, Esa Abiso Godana, Xi Zhang, Yu Li, Xiaoyong Liu, and Hongyin Zhang. 2025. "Biological Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomato Caused by Alternaria alternata with Bacillus velezensis T3" Foods 14, no. 10: 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101700
APA StyleWei, X., Yang, Q., Solairaj, D., Godana, E. A., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Liu, X., & Zhang, H. (2025). Biological Control of Black Spot Disease in Cherry Tomato Caused by Alternaria alternata with Bacillus velezensis T3. Foods, 14(10), 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101700








