Dietary Pleurotus citrinopileatus Polysaccharide Improves Growth Performance and Meat Quality Associated with Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Arbor Acre Broilers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparing for PCP
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Production Performance and Sample Collection
2.4. Determination of Meat Quality
2.5. Composition of Free Amino Acids in Muscle
2.6. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. 16S rRNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.8. Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFAs) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Production Performance Analysis
3.2. Breast Meat Quality and Muscle Composition
3.2.1. Analysis of Basic Indicators
3.2.2. Free Amino Acid Analysis
3.3. Metabolomic Analysis
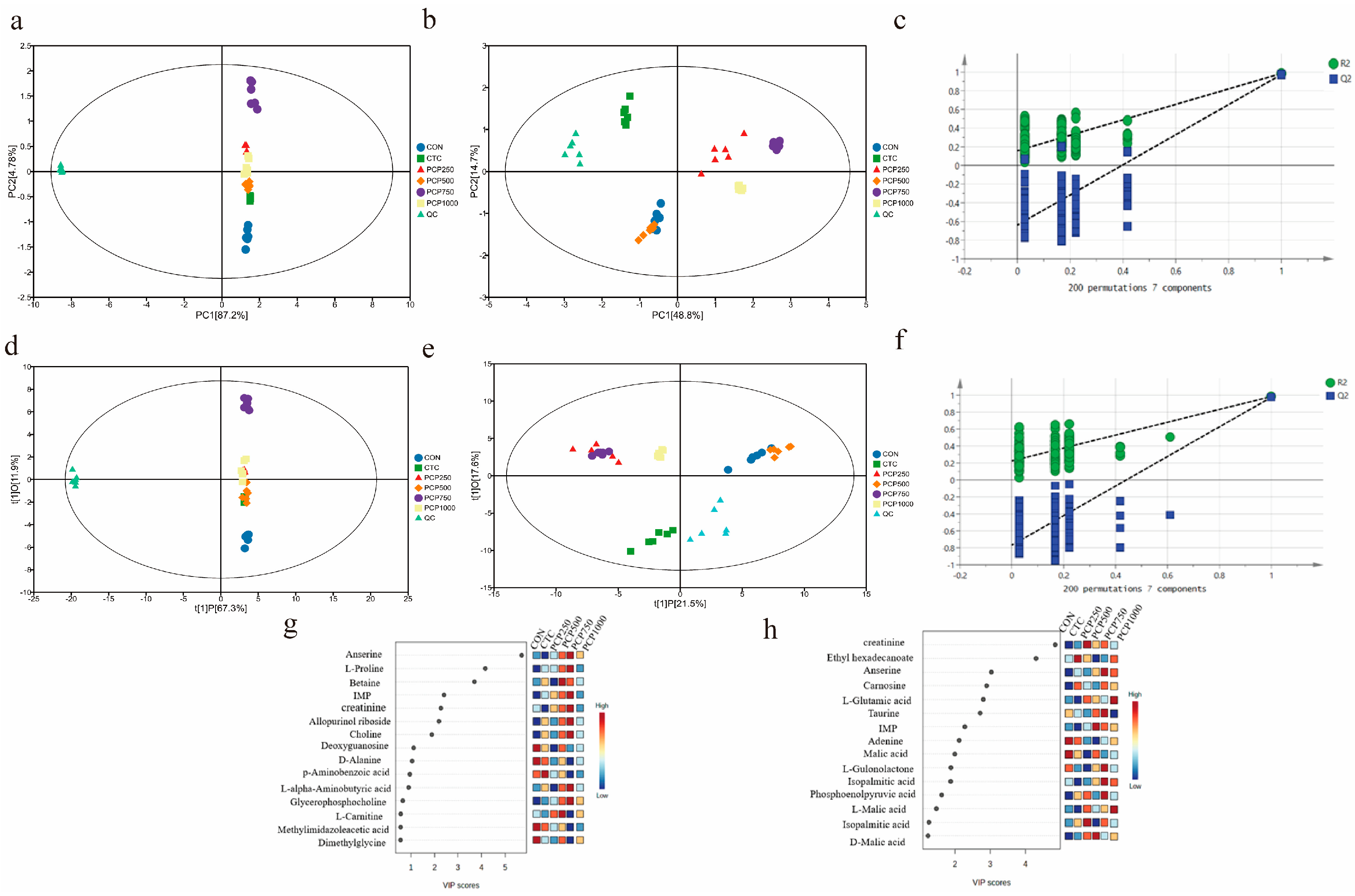
3.3.1. PCA and PLS-DA Analysis
3.3.2. Analysis of Differential Metabolites
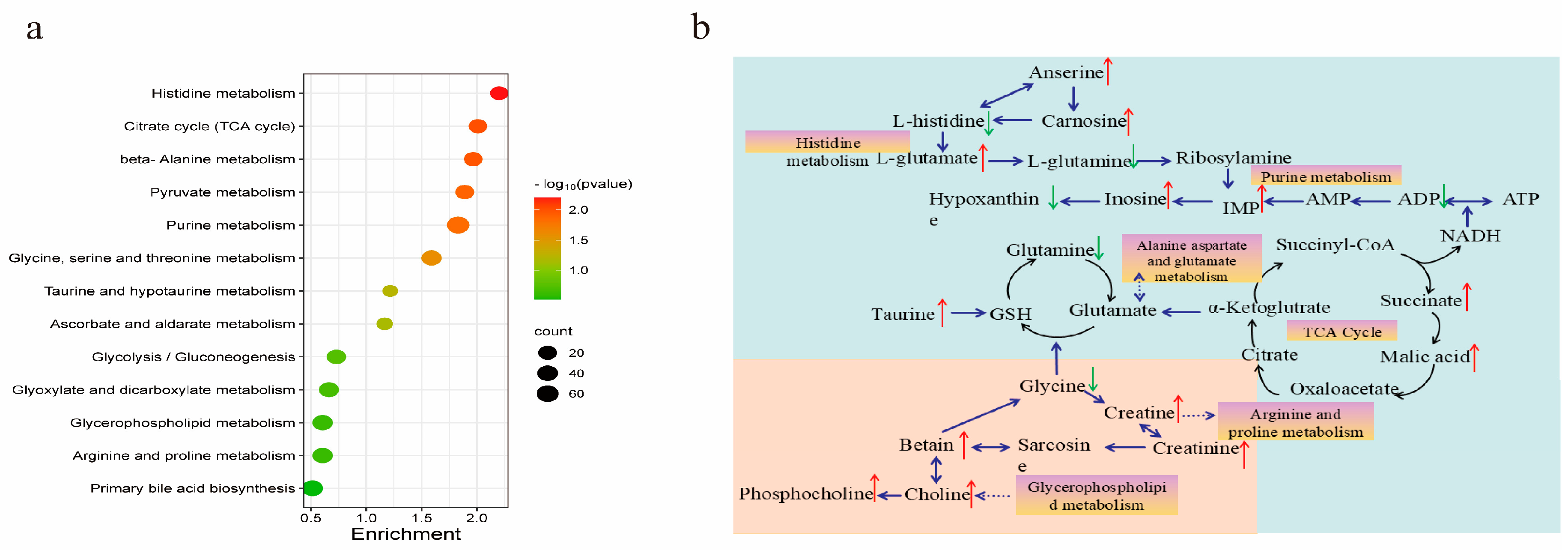
3.3.3. KEGG Pathway Analysis
3.4. Microbiota Diversity and SCFA Composition in the Caecum
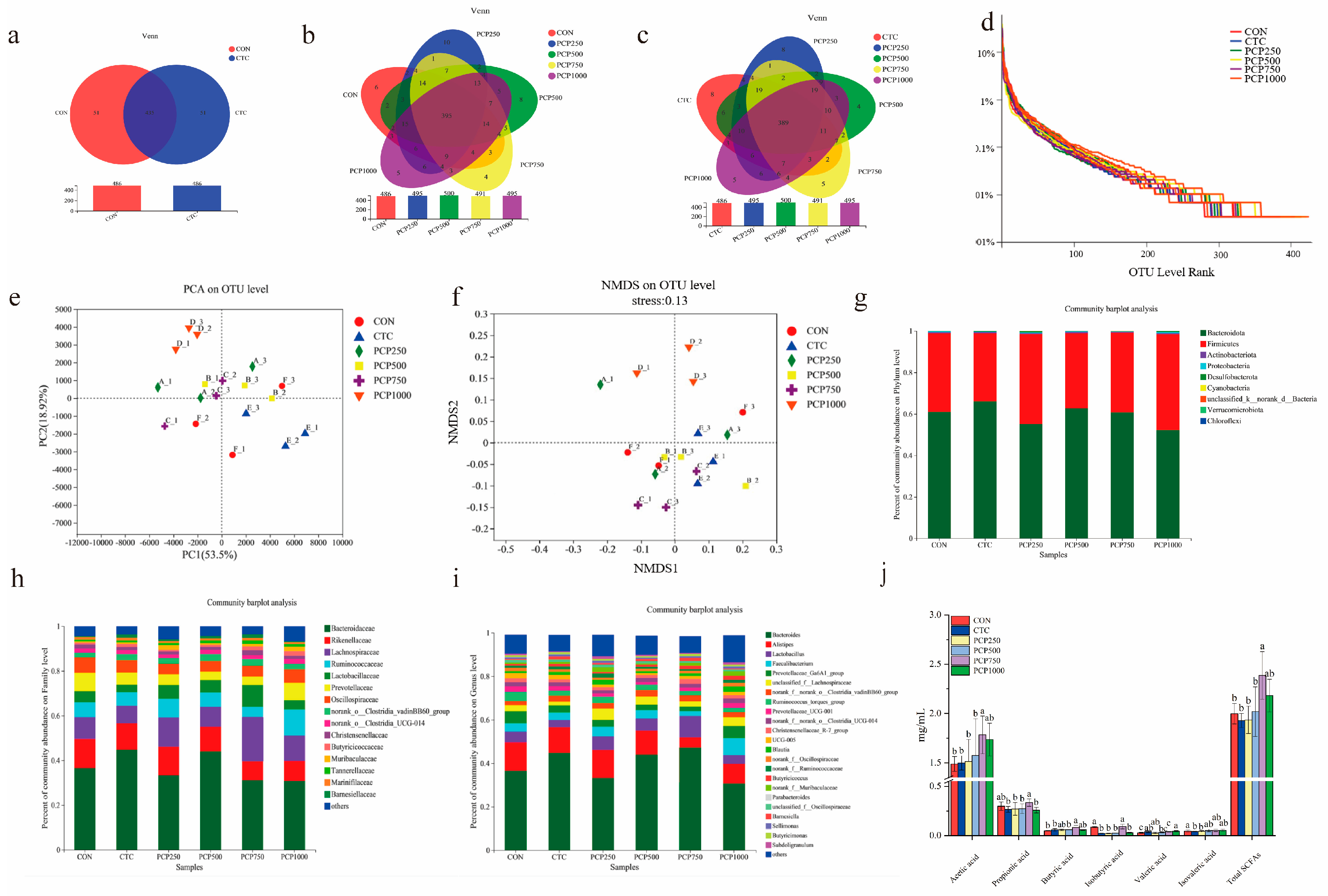
3.4.1. Analysis of the Microbial Composition of the Caecum
3.4.2. Microbial Community Structure Analysis
3.4.3. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Analysis
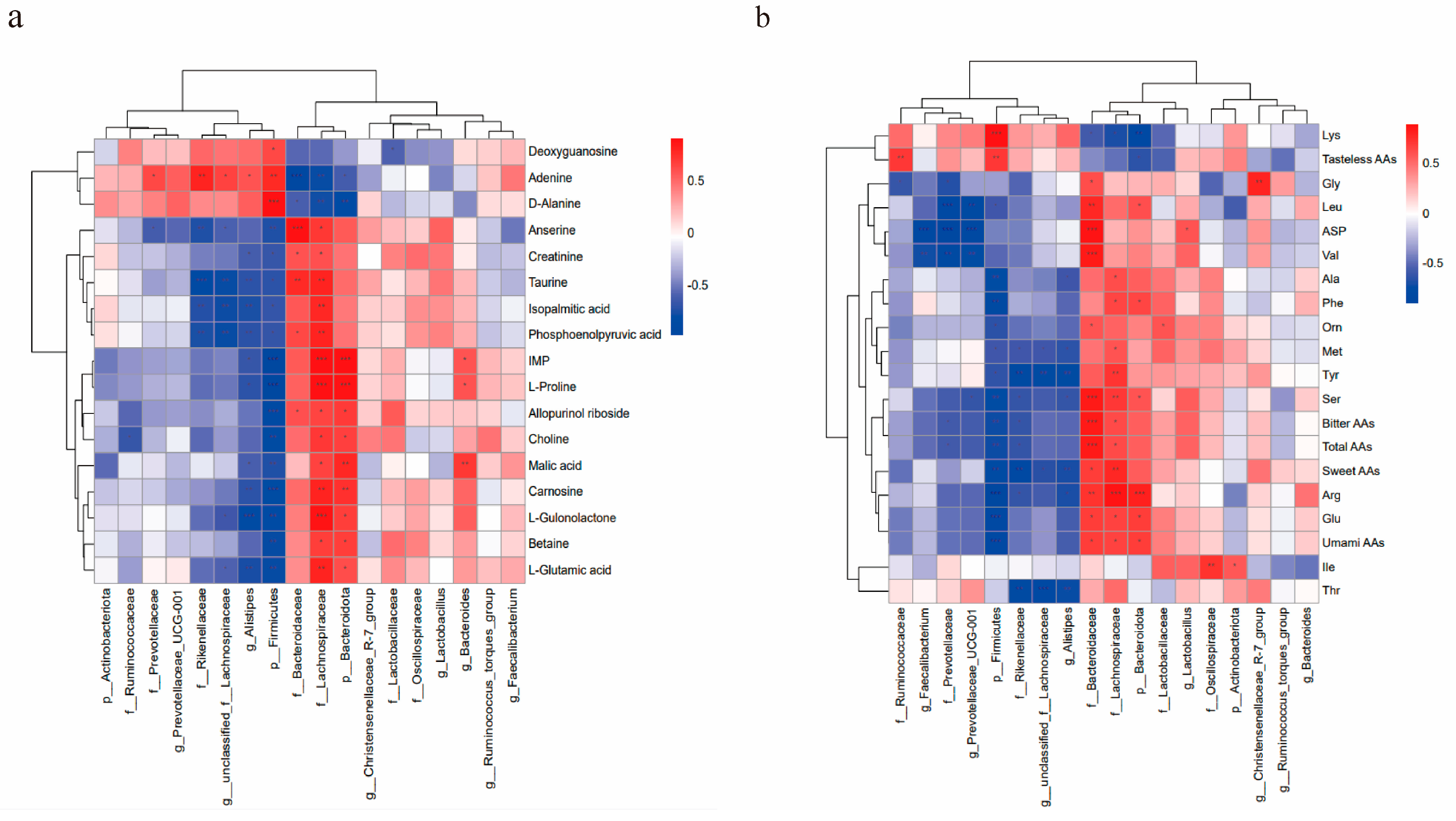
3.4.4. Correlation Analysis Between Gut Microbiota and Meat Quality Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, Z.C.; Luo, Y.T.; Wang, G.Y.; Ge, C.R.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G.; Liao, G.Z. 1H-NMR-based water-soluble low molecular weight compound characterization and fatty acid composition of boiled Wuding chicken during processing. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 99, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Xiao, Q.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, B.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Aroma Compounds in Chicken Broths of Beijing Youji and Commercial Broilers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10242–10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ying, G.G.; Deng, W.J. Antibiotic Residues in Food: Extraction, Analysis, and Human Health Concerns. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7569–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, J. Emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant foodborne pathogens from farm to table. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1481–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z. Efficient physical extraction of active constituents from edible fungi and their potential bioactivities: A review. Trends. Food. Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, X.; Baran, A.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.E. Effects of dietary incorporation of Radix rehmanniae praeparata polysaccharide on growth performance, digestive physiology, blood metabolites, meat quality, and tibia characteristics in broiler chickens. Poultry Sci. 2023, 102, 103150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Yu, W.; Yu, T.; Ding, C.; Liu, W. Research progress of natural plant polysaccharides inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways and regulating intestinal flora and metabolism to protect inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Effect of dietary Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide on the growth performance and immunity of juvenile broilers. Poultry Sci. 2018, 97, 3489–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, X.; Mesalam, N.; Elsadek, M.; Abdel-Moneim, A. The impact of dietary supplementation of polysaccharide derived from polygonatum sibiricum on growth, antioxidant capacity, meat quality, digestive physiology, and gut microbiota in broiler chickens. Poultry Sci. 2024, 103, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Williams, B.A.; Kwakkel, R.P.; Li, H.S.; Li, X.P.; Luo, J.Y.; Li, W.K.; Verstegen, M.W.A. Effects of mushroom and herb polysaccharides, as alternatives for an antibiotic, on the cecal microbial ecosystem in broiler chickens. Poultry Sci. 2004, 83, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, G.; Miao, X.; Zhong, D.W. Optimization extraction of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides and its immunity and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.-T.; Meng, L.-Z.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lv, G.-P.; Cheong, K.-L.; Hu, D.-J.; Guan, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.-P. Chain conformation and immunomodulatory activity of a hyperbranched polysaccharide from Cordyceps sinensis. Carbohyd Polym. 2014, 110, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, L.; Yu, L.; He, J.; Zhu, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; et al. Moringa oleifera leaf improves meat quality by modulating intestinal microbes in white feather broilers. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, B.W.; Zhao, P.; Ge, C.R.; Li, S.J.; Xiao, Z.C. The effect of the improvement technology on the quality of Midu pork roll. Foods 2022, 11, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Uparse: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tang, J.; Feng, F. Glycerol monolaurate improves performance, intestinal development, and muscle amino acids in yellow-feathered broilers via manipulating gut microbiota. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10279–10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.X.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Pan, D.D.; Ou, C.R. The effect of dry-cured salt contents on accumulation of non-volatile compounds during dry-cured goose processing. Poultry Sci. 2016, 95, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritota, M.; Casciani, L.; Failla, S.; Valentini, M. HRMAS-NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis meat characterisation. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.R.; Zaefarian, F.; Ravindran, V. Feed intake response of broilers: Impact of feed processing. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2018, 237, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Shao, Q.; Chen, W.; Ma, L.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Ma, Y. Effects of Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide in diet on growth performance, serum antioxidant capacity, and biochemistry of broilers. Poultry Sci. 2021, 100, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, B.C.; Eastridge, J.S.; Solomon, M.B. Use of gelatin gels as a reference material for performance evaluation of meat shear force measurements. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, S210–S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, G.M.; Alowaimer, A.N.; Al-Mufarrej, S.I.; Hussein, E.O.S.; Fazea, E.H.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Alhotan, R.A.; Swelum, A.A. The effects of clove seed (Syzygium aromaticum) dietary administration on carcass characteristics, meat quality, and sensory attributes of broiler chickens. Poultry Sci. 2021, 100, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.F.; Bertram, H.C.; Rosenvold, K.; Lindahl, G.; Oksbjerg, N. Dietary creatine monohydrate affects quality attributes of Duroc but not Landrace pork. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Fletcher, D.L.; Smith, D.P.; Northcutt, J.K. The effect of broiler breast meat color on pH, moisture, water-holding capacity, and emulsification capacity. Poultry Sci. 2001, 80, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Zang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yang, H.; Jin, S.; Qi, X.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Quality of chicken breast meat improved by dietary pterostilbene referring to up-regulated antioxidant capacity and enhanced protein structure. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 0308–8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cho, W.-Y.; Seo, H.G.; Jeon, B.-T.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.H.B.; Wang, Y.; Lee, C.-H. Effect of L-cysteine, Boswellia serrata, and whey protein on the antioxidant and physicochemical properties of pork patties. Foods 2020, 9, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D.; Brown, S.N.; Nute, G.R.; Whittington, F.M.; Perry, A.M.; Johnson, S.P.; Enser, M. Effects of breed, feed level and conditioning time on the tenderness of pork. Meat Sci. 1996, 44, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajíc, T.; Mráz, J.; Pickova, J. Evaluation of the effect of dietary sesamin on white muscle lipid composition of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) juveniles. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagawa, Y.; Katayama, A.; Funamoto, M.; Shimizu, K.; Shimizu, S.; Sari, N.; Katanasaka, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Hosomi, R.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. The polyunsaturated fatty acids, EPA and DHA, ameliorate myocardial infarction-induced heart failure by inhibiting p300-HAT activity in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 106, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, M.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Wen, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, S. Effect of anhydrous betaine and hydrochloride betaine on growth performance, meat quality, postmortem glycolysis, and antioxidant capacity of broilers. Poultry Sci. 2022, 101, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.C.; Ge, C.R.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G.; Liao, G.Z. 1H-NMR-based metabolic characterization of Chinese Wuding chicken meat. Food Chem. 2018, 274, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Tamura, Y.; Tanabe, K.; Ishimoto, T.; Thomas, J.; Inaba, S.; Kitagawa, W.; et al. Umami: The taste that drives purine intake. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1794–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Cai, C.; Ni, X.-Q.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, J.-L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.-S.; Xue, C.-D.; Zhao, J.; et al. Taurine alleviates schistosoma-induced liver injury by inhibiting the TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway and pyroptosis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00732-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, W.; Quan, S.; Sheng, T.; Tu, J.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K. Effects of probiotics on cecal microbiome profile altered by duck Escherichia coli 17 infection in Cherry Valley ducks. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torok, V.A.; Allison, G.E.; Percy, N.J.; Ophel-Keller, K.; Hughes, R.J. Influence of antimicrobial feed additives on broiler commensal posthatch gut microbiota development and performance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3380–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cesare, A.; Sala, C.; Castellani, G.; Astolfi, A.; Indio, V.; Giardini, A.; Manfreda, G. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus D2/CSL (CECT4529) supplementation in drinking water on chicken crop and caeca microbiome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Xiang, Q.; Chen, N.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, J.; He, Q. Antibiotic-induced disruption of gut microbiota alters local metabolomes and immune responses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Yu, Z. Intestinal microbiome of poultry and its interaction with host and diet. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastro. Hepat. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-S.; Cha, J.; Sim, M.; Jung, S.; Chun, W.Y.; Baik, H.W.; Shin, D.-M.; Cha, L. Probiotic supplementation improves cognitive function and mood with changes in gut microbiota in community-dwelling older adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Mu, C.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhu, W. Marked response in microbial community and metabolism in the ileum and cecum of suckling piglets after early antibiotics exposure. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhong, H.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y. Effect of probiotics on the meat flavour and gut microbiota of chicken. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group 2 | CON | CTC | PCP250 | PCP500 | PCP750 | PCP1000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items 1 | |||||||
| 1–21 days of age | |||||||
| ADFI (g) | 52.46 ± 0.69 c | 54.85 ± 0.96 ab | 53.07 ± 0.23 bc | 54.15 ± 0.99 abc | 56.22 ± 1.65 a | 55.22 ± 0.82 ab | |
| ADG (g) | 38.51 ± 1.30 b | 39.96 ± 1.48 ab | 39.05 ± 1.79 ab | 40.41 ± 0.64 ab | 41.59 ± 0.72 a | 41.77 ± 0.73 a | |
| F/G | 1.362 ± 0.029 | 1.372 ± 0.030 | 1.36 ± 0.058 | 1.34 ± 0.009 | 1.352 ± 0.019 | 1.323 ± 0.037 | |
| BW (g) | 849.22 ± 27.14 b | 882.92 ± 31.24 ab | 860.93 ± 38.00 b | 891.70 ± 13.41 ab | 921.60 ± 16.30 a | 929.28 ± 10.65 a | |
| Mortality (%) | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 21–42 days of age | |||||||
| ADFI (g) | 137.74 ± 3.70 c | 159.01 ± 2.98 a | 137.91 ± 2.78 c | 149.00 ± 3.70 b | 164.29 ± 1.71 a | 152.22 ± 2.22 b | |
| ADG (g) | 73.01 ± 5.91 c | 88.28 ± 2.02 a | 72.36 ± 0.56 c | 80.87 ± 3.66 b | 91.19 ± 2.85 a | 79.00 ± 1.50 bc | |
| F/G | 1.895 ± 0.108 | 1.803 ± 0.071 | 1.906 ± 0.028 | 1.845 ± 0.075 | 1.802 ± 0.070 | 1.972 ± 0.034 | |
| BW (g) | 2572.50 ± 92.34 b | 2775.67 ± 32.78 a | 2363.19 ± 100.23 c | 2678.08 ± 54.62 ab | 2838.67 ± 71.87 a | 2607.89 ± 63.26 b | |
| Mortality (%) | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0.045 | 0 | 0.045 | |
| Items 2 | pH45min | pH24h | Shear Force (kgf) | Cooking Loss (%) | Drip Loss (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | ||||||
| CON | 6.22 ± 0.193 | 5.76 ± 0.183 | 2.97 ± 0.316 a | 14.67 ± 1.198 b | 3.55 ± 0.238 b | |
| CTC | 6.22 ± 0.089 | 5.76 ± 0.100 | 2.44 ± 0.273 b | 17.28 ± 1.716 a | 3.93 ± 0.351 a | |
| PCP250 | 6.29 ± 0.131 | 5.76 ± 0.093 | 2.44 ± 0.350 b | 18.98 ± 2.139 a | 2.47 ± 0.331 d | |
| PCP500 | 6.27 ± 0.160 | 5.80 ± 0.069 | 2.21 ± 0.429 b | 14.32 ± 1.500 b | 2.53 ± 0.253 d | |
| PCP750 | 6.31 ± 0.131 | 5.72 ± 0.117 | 2.08 ± 0.313 b | 11.82 ± 0.792 c | 2.42 ± 0.196 d | |
| PCP1000 | 6.20 ± 0.125 | 5.78 ± 0.100 | 2.31 ± 0.278 b | 14.13 ± 1.014 b | 2.95 ± 0.281 c | |
| Items 2 | Meat Color | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | L* | a* | b* | |
| CON | 42.77 ± 1.579 | 4.67 ± 0.084 bc | 18.25 ± 2.518 a | |
| CTC | 42.77 ± 1.457 | 3.61 ± 0.738 d | 17.31 ± 0.643 ab | |
| PCP250 | 44.19 ± 1.541 | 3.95 ± 0.349 cd | 16.90 ± 1.525 ab | |
| PCP500 | 43.87 ± 1.972 | 5.13 ± 0.701 ab | 15.69 ± 1.009 bc | |
| PCP750 | 41.60 ± 2.212 | 5.45 ± 0.723 a | 14.53 ± 1.306 c | |
| PCP1000 | 43.284 ± 2.112 | 4.38 ± 0.294 c | 16.99 ± 1.253 ab | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, N.; Song, X.; Wu, C.; Liang, S.; Yang, L.; Ge, C.; Xiao, Z. Dietary Pleurotus citrinopileatus Polysaccharide Improves Growth Performance and Meat Quality Associated with Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Arbor Acre Broilers. Foods 2024, 13, 3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213426
Zhou N, Song X, Wu C, Liang S, Yang L, Ge C, Xiao Z. Dietary Pleurotus citrinopileatus Polysaccharide Improves Growth Performance and Meat Quality Associated with Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Arbor Acre Broilers. Foods. 2024; 13(21):3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213426
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Nannan, Xiaoxiao Song, Changxi Wu, Shuangmin Liang, Liangyu Yang, Changrong Ge, and Zhichao Xiao. 2024. "Dietary Pleurotus citrinopileatus Polysaccharide Improves Growth Performance and Meat Quality Associated with Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Arbor Acre Broilers" Foods 13, no. 21: 3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213426
APA StyleZhou, N., Song, X., Wu, C., Liang, S., Yang, L., Ge, C., & Xiao, Z. (2024). Dietary Pleurotus citrinopileatus Polysaccharide Improves Growth Performance and Meat Quality Associated with Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Arbor Acre Broilers. Foods, 13(21), 3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213426







