Abstract
The myofibrillar protein (MP) of duck meat is prone to excessive oxidation during thermal processing, resulting in a decline in its overall quality. In this paper, the effect of shikimic acid on the oxidative structure of duck muscle fibrin was studied. The findings showed that, at a mass ratio of 1:50,000 (g/g) between shikimic acid and MP, the carbonyl content of MP was reduced by 74.20%, while the sulfhydryl content was increased by 73.56%. MP demonstrated the highest denaturation temperature, whereas its thermal absorption was the lowest. The percentage of α-helixes and β-sheets increased by 16.72% and 24.74%, respectively, while the percentage of irregular structures decreased by 56.23%. In addition, the surface hydrophobicity index of MP exhibited a significant decrease (p < 0.05), while there was a significant increase in its free radical-scavenging ability (p < 0.05). Molecular fluorescence spectrum analysis showed that shikimic acid could bind to MP, altering the internal environment of MP and enhancing its thermal stability. FTIR analysis showed that shikimic acid could enhance the distribution of protein particle sizes by reducing irregular structures, the proportion of β-rotation, and the degree of protein aggregation. It is hoped that this research can offer scientific support for improving meat processing technology.
1. Introduction
Duck meat is a high protein, low fat, and low cholesterol food [1]. Heat treatment is a common and important method of processing duck meat to improve food safety, texture, and flavour and increase its storage life, providing a better eating experience. Some studies have found that high temperatures destroy the nutrients in duck meat, such as vitamins and antioxidant substances, reducing its nutritional value [2,3]. It has also been shown that excessive heat treatment leads to changes in the texture of duck meat, significantly reducing its tenderness and flavour [4]. These specific changes were closely related to myofibrillar protein in duck meat.
Myofibrillar protein plays a significant role in meat composition, constituting approximately 50–55% of the overall muscle protein content. Studies have shown that myofibrillar proteins make the connections between muscle fibres tighter. It increases tensile strength and adhesion of muscle fibres, which affect the tenderness of the muscles [5,6]. Myofibrillar proteins are susceptible to oxidation during heat treatment. The oxidation of proteins has been reported to reduce the water-holding capacity and texture of processed meat products, which affects their tenderness and juiciness [7,8]. Oxidation exposes the sulfhydryl groups of myofibrillar proteins, which, in turn, cross-link with other proteins, leading to protein aggregation [9]. Oxidation also affects the conformation and function of myofibrillar proteins. Myofibrillar proteins with a higher degree of oxidation exhibit stronger hydrophobicity, resulting in enhanced protein interactions and further decreasing tenderness [10]. Therefore, taking into account consumers’ demand for products with good flavour and high nutritional value, it is necessary to solve the problem of adverse changes in meat during hot processing.
It is widely accepted that the addition of appropriate antioxidants can reduce the extent of myofibrillar protein oxidation and maintain meat product tenderness [11,12,13]. As the demand for healthy food and natural ingredients increases, the research and application of natural antioxidants are gradually gaining attention. Among them are spices commonly used in culinary processes. These can bring a unique flavour to the taste buds and also have antioxidant properties. Studies have shown that flavonoids in spices can improve the sensory quality of meat products by inhibiting oxidative damage to myofibrillar protein [14]. Star anise (Illicium verum) is a spice widely used in meat products, and its main active component is shikimic acid [15]. Previous laboratory studies have found that Star anise extract can improve the tenderness of meat products. When duck meat was braised for 45 min, the shear force in the Star anise extract group was reduced by 40.87%, and the myofibrillar fracture index increased by 16.13% compared with the blank group. The content of shikimic acid in Star anise can reach 6.28%~11.57% [16]. The reason why the extract of Star anise can improve the tenderness of duck meat may be that shikimic acid can change the structure of duck myofibrillar protein (MP) and improve its processing quality. In this study, spectral analysis and other methods were used to determine the interaction between shikimic acid and duck myofibrillar proteins. The effect of shikimic acid on the structure of myofibrillar protein during heat treatment and its mechanism were investigated. The purpose of this study was to provide a theoretical basis for the application of shikimic acid in meat processing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
Duck meat was purchased from Guangxi Dongxin Duck Co., Ltd. (Liuzhou, China). Shikimic acid was purchased from Guilin Rhein Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Guilin, China). Golden Arowana soybean oil was purchased from Yihai Kerry Grain and Oil Industry Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). Spices purchased at Zhongbai Supermarket (Wuhan, China). Magnesium chloride, potassium chloride, disodium glycolate tetraacetic acid, ethanol, trifluoroacetic acid, Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, formic acid, and β-mercaptoethanol were manufactured by Sinopath Chemical Reagents Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All chemicals and reagents were analytical grade.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Duck Meat Myofibrillar Protein
Duck myofibrillar protein was prepared using a modified version of the previously reported method [17]. We washed the fresh duck thoroughly under water, wiped the water off the surface of the duck with absorbent paper, and, finally, cut it into appropriately sized pieces. A 2 g sample of the duck meat was taken and added to 20 mL buffer (150 mmol/L sodium chloride, 25 mmol/L potassium chloride, 3 mmol/L magnesium chloride, 4 mmol/L disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate, and 1 mmol/L protease inhibitor, pH 6.50). It was homogenised for 30 s at 10,000 rpm and centrifuged for 30 min. The sample containing the myofibrillar protein precipitate was rinsed three times. The aforementioned procedures were carried out at 4 °C. The concentration of the protein mass was determined using the biuret assay, and the isolated protein was kept at 4 °C and utilised within 12 h. The precipitated MP was resuspended in a phosphate buffer, and the concentration of the resulting solution was set to 1 mg/mL. After dissolving, it was put into a polyethylene bag, sealed by vacuum (100 mL/bag), and heated at a constant vacuum temperature of 70 °C for 8 h.
2.2.2. Sample Preparation
According to the laboratory treatment method, MP was placed in a water bath at 100 °C for 10 min, and different amounts of shikimic acid were added to it. The mass-specific concentrations of shikimic acid and MP were 1:50,000, 1:25,000, 1:12,500, and 1:6250 (g/g). They were placed in a 100 °C water bath for an additional 30 min. The blank group consisted of an MP solution without shikimic acid. Samples were taken from the final prepared mixed solution as well as the blank group sample solution in each water bath for a duration of 10 min.
2.2.3. Determination of Carbonyl Content
A method referred to by Rodriguez-Carpena et al. was slightly modified to determine the carbonyl content [18]. A standard curve was constructed using bovine serum protein, and absorbance readings were taken at 280 nm. Additionally, the absorbance of the treated sample was quantified at a wavelength of 370 nm. The molar absorption coefficient of 22,000 L/mol.cm was used to determine the content of carbonyl groups, and Vitamin C (VC) served as a positive control.
2.2.4. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl Content
The free sulfhydryl content was determined using the method developed by Zakrys-Waliwander et al. [19]. The absorbance at 412 nm was measured after 2 mL of sample solution was added to Tris buffer (4 mL, pH = 8) at room temperature for 30 min. The absorption coefficient of the sulfhydryl molecule was 13,600 L/mol.cm, and vitamin C (VC) served as a positive control.
2.2.5. Hydroxyl Radical-Scavenging Activity
A method by Shen et al. was referenced and slightly modified to determine the capacity to neutralise hydroxyl radicals [20]. Sequentially, 1 mL of the sample solution, salicylic acid–ethanol solution (6 mmol/L), ferrous sulfate solution (6 mmol/L), and hydrogen peroxide solution (6 mmol/L) were added to a test tube and mixed well. The absorbance was measured at 510 nm after being held in a water bath maintained at 37 °C for a duration of 30 min. The rate of hydroxyl radical scavenging was calculated using the following formula:
Hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity (%) = [1 − (A1 − A2) A0] × 100%
- A0—Distilled water instead of blank group and experimental group sample solution absorbance value;
- A1—Absorbance at 510 nm;
- A2—The absorbance value of anhydrous ethanol instead of salicylic acid–ethanol solution.
2.2.6. DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity
The total free radical-scavenging activity of DPPH was determined using the previously reported method with some modifications [21]. A total of 2 mL of the sample solution was thoroughly mixed with 2 mL of a 0.2 mM/L DPPH solution and left to stand away from light (30 min). The absorbance at 517 nm was measured three times for each sample, using methanol as a blank control. The absorption value of 2 mL water and 2 mL DPPH was measured as A0. The absorption value of the sample solution (2 mL) mixed with 2 mL DPPH was denoted as Ai. The absorption value of the sample solution (2 mL) mixed with 2 mL methanol was denoted as Aj. DPPH free radical clearance was calculated according to the following formula:
DPPH scavenging activity (%) = [1 − (Ai − Aj) A0] × 100%
2.2.7. Surface Hydrophobicity
The molecular fluorescence was determined according to Turgut et al. [22]. A mixture of shikimic acid and myofibrillar proteins was prepared in a water bath for 15 min, with ratios of 1:50,000, 1:25,000, 1:12,500, and 1:6500 (g/g). The water bath was set at 90 °C for 30 min, and 2 mL of the final mixture and the blank group were taken for fluorescence scanning every 10 min during heating. Fluorescence scanning conditions included a fixed excitation wavelength of 296 nm, an emission wavelength range of 270–350 nm, an excitation and emission slit width of 2.5 nm, and a scanning rate of 12,000 nm/min.
2.2.8. Molecular Fluorescence Assay
Surface hydrophobicity was determined using a previously established method with some modifications [23]. The compound 1-Benzoic acid-8-sulfonic acid was used as a fluorescent probe, and 2 mL of the sample solution was added to the phosphate buffer. The fluorescence intensity at 470 nm was used to plot the protein concentration, and the gradient of the line corresponded to the protein’s degree of surface hydrophobicity.
2.2.9. Particle Size Determination
The method of Huang was referred to and slightly modified for determining the particle size [24]. We measured 1.5 mL of the sample solution and centrifuged it at a speed of 10,000 rpm for 10 min. The particle size distribution of myofibrillar protein in the sample solution was determined using a nanoparticle size analyser (Malvern Instrument Company, Worcester, UK). The temperature measured during the analysis was 25 °C.
2.2.10. DSC Analysis
DSC analyses were performed according to the method of Kocher et al. [25] with minor modifications. A mixture of shikimic acid and myofibrillar proteins was prepared in a water bath for 15 min, with ratios of 1:50,000, 1:25,000, 1:12,500, and 1:6500 (g/g). The samples from each group were analysed using DSC. Hesheng Instrument Technology Company (Shanghai, China) was used.
2.2.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Analysis
The approach employed by Nguyen et al. [26] was used and slightly modified in order to perform Fourier transform infrared absorption spectroscopy. A mixture of shikimic acid and myofibrillar proteins was prepared in a water bath for 15 min, with ratios of 1:50,000, 1:25,000, 1:12,500, and 1:6500 (g/g). The water bath was set at 90 °C for 30 min, and 2 mL of the final mixture and the blank group were taken for infrared spectroscopy analysis every 10 min during the water bath. Infrared spectrometry parameters were as follows: the wavelength range was 500–4500 cm−1, and the signal acquisition mode was Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR) mode.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Microsoft Excel 2016 and Origin 2018 were used for data analysis and plotting purposes. The variance method in SPSS 19.0 was used to analyse all data. Univariate analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan test were used to analyse the significant differences between the mean values (p < 0.05). All data were independently tested for three replicates and expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydroxyl Radical- and DPPH Radical-Scavenging Rate
Figure 1 shows that the scavenging rates of Hydroxyl radicals and DPPH radicals in the blank group both decreased during heating. The findings indicated that high temperatures could induce the formation of Hydroxyl and DPPH radicals within meat products. These radicals were highly active, which would lead to oxidative damage of proteins and further degradation of proteins [27]. At 20 min and 30 min of heating, the scavenging activities of Hydroxyl and DPPH radicals were significantly increased in all experimental groups compared to the blank group (p < 0.05). The results showed that shikimic acid can effectively enhance the scavenging ability of MP against Hydroxyl and DPPH radicals during heat treatment, thus preventing further oxidation of proteins. Some studies have found that plant bioactive compounds can enhance the clearance activity of reactive oxygen species in meat during heating processes, thereby inhibiting the degradation of proteins [28]. At the same heat treatment time, the hydroxyl radical-scavenging capacity was significantly higher in the 1:50,000 group than in other experimental groups (p < 0.05). The results may be due to the excess of shikimic acid forming complexes or condensates that prevent free radicals from binding to them, resulting in decreased free radical clearance.
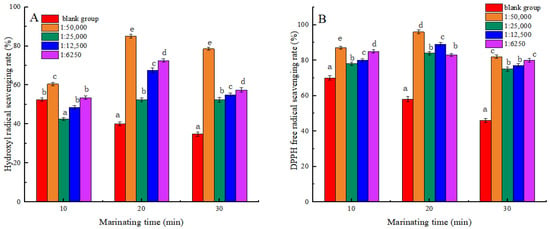
Figure 1.
Effects of Shikimic acid on the scavenging rate of myofibrillar protein hydroxyl radicals (A) and the scavenging rate of myofibrillar protein DPPH active free radicals (B). Note: different letters in the figure indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.2. Carbonyl and Free Sulfhydryl Groups
Measuring the content of carbonyl groups and free sulfhydryl groups allows for a comprehensive assessment of protein oxidative status [29]. As seen in Figure 2, the carbonyl content of MP tended to increase, while the sulfhydryl content exhibited a downward trend in all groups with prolonged heat treatment duration. The results showed that the oxidation degree of MP increased with the extension of heat treatment time. The carbonylation of amino acid side chains in protein increased the content of carbonyl groups at high temperatures. The free sulfhydryl groups between the polypeptide chains reacted to form disulfide bonds, resulting in a decrease in the free sulfhydryl group content [30]. At the same heat treatment time, a noticeable reduction in carbonyl content and a considerable elevation in free sulfhydryl content were observed among the experimental groups relative to the blank group (p < 0.05). The findings demonstrated that shikimic acid significantly mitigated the oxidative state of myofibrillar proteins. This finding was consistent with the outcomes observed in the aforementioned study regarding the activity of scavenging free radicals. When the mass ratio of shikimic acid to myofibrillar protein was 1:50,000 (g/g), and the heat treatment was for 30 min, the carbonyl content of myofibrillar protein reduced by 74.20%, while the sulfhydryl content increased by 73.56% compared to the blank group. The findings indicated that the degree of oxidation of MP was the lowest under these conditions. However, the elevated levels of shikimic acid may disrupt the structure of MP and further increase the degree of protein oxidation.
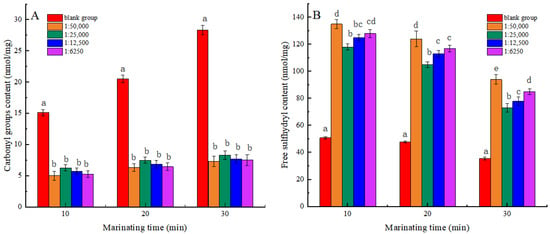
Figure 2.
Effects of Shikimic acid on the carbonyl content of myofibrillar protein (A) and the free sulfhydryl content of myofibrillar protein (B). Note: different letters in the figure indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.3. DSC Analysis
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) is a thermal analysis technique that serves as an important indicator for evaluating the structural changes of proteins [31]. It was used in this experiment for measuring the energy changes during protein denaturation. As shown in Table 1 and Figure 3A, the denaturation temperature and initial denaturation temperature exhibited an increase across all treatment groups compared to the blank group. This could be due to the interaction between shikimic acid and molecules in myofibrillar protein, which enhances the stability of its internal structure, allowing it to withstand higher temperatures. This was similar to the results of Xu et al. [32]. At a mass ratio of 1:50,000 (g/g) between shikimic acid and protein, the myofibrillar protein exhibited the highest denaturation temperature of 107.35 °C, an initial denaturation temperature of 115.68 °C, and a thermal absorption value as low as 118.42 J·g−1. The findings showed that the thermal degeneration of myofibrillar protein was minimal under these conditions. During heat treatment, the incorporation of shikimic acid was found to reduce thermal absorption by myofibrillar protein and mitigate the extent of chemical bond disruption in myofibrillar protein. At the same time, the thermal stability of myofibrillar protein was enhanced to increase its denaturation temperature. However, the high shikimic acid content may disrupt the internal chemical bonds of myofibrillar protein, thereby reducing its thermal stability.

Table 1.
Effect of the shikimic acid on the denaturation temperature and heat absorption of muscle fibrin.
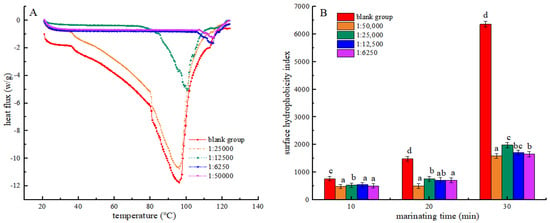
Figure 3.
Effects of the Shikimic acid on the thermal denaturation of myofibrillar protein (A) and effects of Shikimic acid on the surface hydrophobicity of myofibrillar protein (B). Note: different letters in the figure indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.4. Surface Hydrophobicity
The hydrophobicity of the myofibrillar protein surface reflects both the thermal-induced degradation of its hydrophobic region and the extent of protein cross-linking [33]. In Figure 3B, the surface hydrophobicity index of myofibrin increased in each group with the duration of heat treatment. This result may be attributed to the breakdown of the hydrophobic areas within myofibrillar proteins under elevated temperature conditions, which exposes more hydrophobic groups and, thus, increases the hydrophobicity index. Moreover, high temperatures also increased the interactions between protein molecules, resulting in the formation of larger aggregates, leading to an increase in surface hydrophobicity. This trend is in accordance with the results reported by Mitra et al. [34]. Furthermore, all experimental groups exhibited a significant decrease in the surface hydrophobicity index compared to the blank group after undergoing identical heat treatment durations (p < 0.05). The results suggest that shikimic acid may interact with proteins to form polymers that inhibit the unfolding of protein structures. The myofibrillar protein structure prevents the exposure of hydrophobic amino acids, resulting in a decrease in its surface hydrophobicity [35]. Compared with the group with a mass ratio of shikimic acid to myofibrillar protein of 1:50,000 (g/g), the surface hydrophobicity index of myofibrillar protein increased in all experimental groups. This may be because excess shikimic acid increases the active oxidising free radicals in the protein, resulting in an increased protein oxidation degree.
3.5. Endogenous Amino Acids
Molecular fluorescence spectroscopy is an analytical method used for studying the fluorescence properties of molecules. It can better reflect the oxidative deterioration of proteins and the degradation of internal amino acids [36]. The intensity of the fluorescent signal is related to the environment in which endogenous tryptophan and endogenous tyrosine reside, which, in turn, is closely related to the tertiary structure of the protein [37]. Figure 4 shows that the endogenous fluorescence intensity of myofibrillar protein decreased in all groups during the heat treatment process (10–30 min). It is shown that heat treatment may result in the disruption of protein structure, leading to changes in protein conformation and exposure of some chromophore groups containing tryptophan and tyrosine. These groups may be more inclined to cluster together rather than to interact with the surrounding water molecules, thus resulting in a decrease in fluorescence intensity. Under the same heat treatment time condition, the fluorescence intensity of myofibrillar protein in each experimental group at the emission wavelength of 300 nm was significantly enhanced compared to that of the blank group. Shikimic acid may alter the structure of myofibrillar protein, making it easier for tryptophan and tyrosine residues to interact with surrounding water molecules. This finding was consistent with the research conducted by Kumari et al. [38]. When the heat treatment time was the same, the endogenous fluorescence intensity of myofibrillar protein in the 1:50,000 (g/g) group was the highest. The results showed that excess shikimic acid induced amino acid deamination and decarboxylation, which increased the amino acid degradation rate.
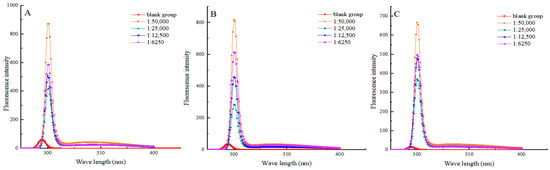
Figure 4.
Effects of shikimic acid at 10 min (A), 20 min (B), and 30 min (C) of heat treatment on the endogenous amino acids of myofibrillar protein.
3.6. Secondary Structure of Myofibrillar Protein
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) can measure the absorption and scattering spectra of proteins in the near-infrared spectral region. In turn, the characteristic peaks of the protein secondary structure were analysed to assess the extent of protein structural denaturation [39]. In Figure 5 and Table 2, the percentage of α-helixes, β-sheets and β-turn structures decreased, and the percentage of irregular structures increased in the blank group with the prolongation of heat treatment time. The results showed that, during heat treatment, the α-helix structure loosened and the β-sheet structure expanded or relaxed. This caused the proteins to lose their original stable structure. Then, the α-helix structure and β-sheet structure were progressively transitioned into more disordered β-turns and irregular structures [40]. Also, heat treatment might induce an expansion of the proportion of disorganised structures in proteins, making them looser and more random. Compared with the blank group, when the ratio of shikimic acid to myofibrillar protein was 1:50,000 (g/g), and the heat treatment was for 30 min, the proportion of α-helixes and β-sheets in the myofibrillar proteins increased by 16.72% and 24.74%, respectively, and the proportion of irregular structure decreased by 56.23%. This showed that moderate amounts of shikimic acid can maintain the overall stability of protein secondary structure by reducing the proportion of irregular structures. The above results were similar to those of Serson [41] and Carbas [42] et al. At an equivalent duration of heat treatment, the proportion of irregular structures increased in other experimental groups where the mass ratio of shikimic acid to protein exceeded 1:50,000 (g/g). The results showed that, when the mass ratio of shikimic acid to myofibrillar protein was 1:50,000 (g/g), the protective effect was the best. Therefore, excessive content of shikimic acid may break the chemical bonds in proteins and thus increase the degree of protein degradation.
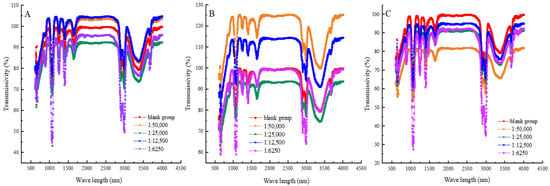
Figure 5.
Effects of shikimic acid at 10 min (A), 20 min (B), and 30 min (C) on the secondary structure of myofibrillar protein.

Table 2.
Near-infrared spectroscopy parameters of unconjugated and conjugated shikimate myofibrillar protein. Note: different letters in the figure indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.7. Particle Size
During the process of heat treatment, proteins undergo cross-linking and form larger aggregates. The size of these aggregates can be characterised by the particle size of MP. It visually reflects the degree of protein crosslinking during heat treatment, thereby elucidating the effect of shikimic acid on the thermal denaturation of MP under high-temperature conditions [43]. As can be seen from Figure 6, with the prolongation of heat processing time, the protein particle size enlarged in both the blank and experimental groups. This may be because, at high temperatures, the non-covalent interactions between protein molecules are destroyed, which makes the protein molecules lose their stability, thus leading to aggregation. This aggregation increases the particle size of the protein. This was in line with the results of Ince-Coskun et al. [44]. When the mass ratio of shikimic acid to myofibrillar protein was 1:5000 (g/g), and the heating time was 10 min, the myofibrillar protein exhibited the smallest particle size and the narrowest range of particle size distributions. This indicated that shikimic acid could significantly inhibit protein aggregation and enhance protein particle size distribution, thus maintaining protein stability. When heating for 10 min, the particle size of the experimental group was larger than that of the blank group when the mass ratio of shikimic acid to myofibrillar protein was 1:6250 (g/g). It is possible that the excessive presence of shikimic acid facilitated an elevation in the content of protein disulfide bonds, consequently leading to an augmentation in the size of protein particles. A similar phenomenon was observed by Li [45] and Saleem [46] in the study of fish myofibrillar proteins and chicken actinomyosin.
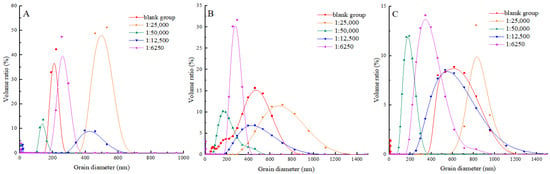
Figure 6.
Effects of shikimic acid at 10 min (A), 20 min (B), and 30 min (C) on the particle size of myofibrillar protein.
4. Conclusions
This study employed multispectral analysis, DSC, and near-infrared spectroscopy to investigate the structural changes of duck myofibrillar protein after the addition of shikimic acid during heat treatment. These changes included a decrease in protein surface hydrophobicity, a significant increase in disulfide bonds, and a decrease in its random coil content. Shikimic acid can effectively inhibit the formation of carbonyl groups and the loss of sulfhydryl groups, as well as increase the scavenging rate of free radicals when undergoing thermal processing. These findings reveal that shikimic acid could efficiently decrease the oxidative damage to MP caused by thermal processing. The addition of shikimic acid increased the denaturation temperature and initial denaturation temperature of MP while decreasing heat absorption. The findings demonstrated that the addition of shikimic acid significantly enhanced the thermal stability of myofibrillar protein. The NIR analysis further confirmed a reduction in random structure proportion and an increase in particle size. These results suggested that shikimic acid facilitated the formation and clumping of protein structures. Therefore, the addition of shikimic acid in duck meat processing is essential for improving the stability of processed duck meat products. This study is expected to furnish scientific backing for the enhancement of duck meat product processing techniques.
Author Contributions
Y.N.: formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft. Y.Z.: formal analysis, data curation. Y.W.: data curation, visualisation, formal analysis. W.H.: data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. D.G.: writing—review and editing. W.X.: conceptualisation, project administration, writing—review and editing. H.W.: conceptualisation, methodology, formal analysis. Y.Y.: writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. G.T.: conceptualisation, methodology, formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Hubei Province (grant number 2023BBB143).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available because a paper based on this part of the data is being submitted.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| ANS | 8-anilino-1-naphthalene sulfonic acid |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| MP | Myofibrillar protein |
| NIR | Near-infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Slobodyanik, V.S.; Ilina, N.M.; Suleymanov, S.M.; Polyanskikh, S.V.; Maslova, Y.F.; Galin, R.F. Study of composition and properties of duck meat. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 640, 032046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Shi, W.; Huang, H.; Shen, S.; Yang, F.; Chen, S. Changes of the flavor substances and protein degradation of black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) pickled products during steaming. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, S.; Abid, M.; Cao, J.; Jabbar, S.; Tume, R.K.; Zhou, G. Improved duck meat quality by application of high pressure and heat: A study of water mobility and compartmentalization, protein denaturation and textural properties. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Bian, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W. Changes in actomyosin dissociation and endogenous enzyme activities during heating and their relationship with duck meat tenderness. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of oxidation on the physicochemical properties and degradation of mutton myofibrillar proteins. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2932–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Wu, B.; Fu, B.; Jiang, P.; Liu, Y.; Qi, L.; Du, M.; Dong, X. Enzyme treatment-induced tenderization of puffer fish meat and its relation to physicochemical changes of myofibril protein. LWT 2022, 155, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, L.J.; Maddock, K.R.; Lonergan, S.M.; Huff-Lonergan, E. Influence of early postmortem protein oxidation on beef quality. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Huff-Lonergan, E.; Sebranek, J.G.; Lonergan, S.M. High-oxygen modified atmosphere packaging system induces lipid and myoglobin oxidation and protein polymerization. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xiong, Y.L. Electrophoretic pattern, thermal denaturation, and in vitro digestibility of oxidized myosin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delles, R.M.; Xiong, Y.L. The effect of protein oxidation on hydration and water-binding in pork packaged in an oxygen-enriched atmosphere. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Fu, C.; Limsila, B.; Li, R.; Liao, W. Extraction, structural characterization and antioxidant activity of turmeric polysaccharides. LWT 2022, 154, 112805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Du, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Dao, X.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; He, H. Arginine as a regulator of antioxidant and gel formation in yak Myofibrillar proteins: Efficacy and mechanistic insights. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, F.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Kong, B. Investigating the effect of catechin on the emulsification and oxidation stability of myofibrillar protein-diacylglycerol emulsions. Meat Sci. 2024, 210, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fan, Y.; Kou, T. Effect of flavonoids from Lycium barbarum leaves on the oxidation of myofibrillar proteins in minced mutton during chilled storage. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, H.; Sun, P. Optimization and comparison of ultrasound-assisted extraction and microwave-assisted extraction of shikimic acid from Chinese star anise. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qu, S.; Tan, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, P.; Zheng, X. Exploiting the synergistic antibacterial activity of shikimic acid and ceftiofur against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Huang, M.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Influence of heat on protein degradation, ultrastructure and eating quality indicators of pork. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Carpena, J.G.; Morcuende, D.; Estevez, M. Avocado by-products as inhibitors of color deterioration and lipid and protein oxidation in raw porcine patties subjected to chilled storage. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrys-Waliwander, P.I.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; O’Neill, E.E.; Kerry, J.P. The effects of high oxygen modified atmosphere packaging on protein oxidation of bovine M. longissimus dorsi muscle during chilled storage. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Ou, A.; Liu, S.; Elango, J.; Wang, S.; Henriques da Silva, T.; Wu, W.; Robinson, J.; Bao, B. Effects of ion concentrations on the hydroxyl radical scavenging rate and reducing power of fish collagen peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braca, A.; Fico, G.; Morelli, I.; De Simone, F.; Tome, F.; De Tommasi, N. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of flavonol glycosides from different Aconitum species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 86, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, S.S.; Isikci, F.; Soyer, A. Antioxidant activity of pomegranate peel extract on lipid and protein oxidation in beef meatballs during frozen storage. Meat Sci. 2017, 129, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, Z.; Wu, S.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J. Effects of concentration of flavor compounds on interaction between soy protein isolate and flavor compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; Xiong, S.; Li, A. Property and structure changes of myofibril protein in pork treated by high pressure combined with heat. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2016, 22, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, P.N.; Foegeding, E.A. Microcentrifuge-Based Method for Measuring Water-Holding of Protein Gels. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.G. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy to quantify the met-myoglobin proportion and meat oxygenation inside of pork and beef. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Sarkar, S.; Mazumder, S.; Adhikari, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Synthesis and biological evaluation of primaquine–chloroquine twin drug: A novel heme-interacting molecule prevents free heme and hydroxyl radical-mediated protein degradation. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korimová, Ľ.; Máté, D.; Turek, P. Influence of natural antioxidants on heat-untreated meat products quality. Czech J. Food Sci. 2000, 18, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado, G.; Cava, R. The incorporation of a pomegranate peel extract in the formulation of uncured dry sausages protects lipids and proteins from oxidation during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. LWT 2023, 184, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Fang, R.; Huang, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, G. Oxidation combined with Maillard reaction induced free and protein-bound Nε-carboxymethyllysine and Nε-carboxyethyllysine formation during braised chicken processing. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsenaidy, M.A.; Jain, N.K.; Kim, J.H.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B. Protein comparability assessments and potential applicability of high throughput biophysical methods and data visualization tools to compare physical stability profiles. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; He, W.; Yi, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Guo, D. The impacting mechanism of β-sanshool in Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim on the structure of myofibrillar protein in duck meat. LWT 2023, 182, 114838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Jia, R.; Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Tong, J.; Xia, G. Effects of innovative gelation and modified tapioca starches on the physicochemical properties of surimi gel during frozen storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 6591–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Rinnan, A.; Ruiz-Carrascal, J. Tracking hydrophobicity state, aggregation behaviour and structural modifications of pork proteins under the influence of assorted heat treatments. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Sun, J.; Qian, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, L. Effect of the frying process on the properties of gluten protein of you-tiao. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.D.; Monteiro, J.D.; Araujo, J.M.G.; Lima, K.M.G. Molecular fluorescence spectroscopy with multi-way analysis techniques detects spectral variations distinguishing uninfected serum versus dengue or chikungunya viral infected samples. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.I.; Rehman, M.T.; Sameena, F.; Hussain, T.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Lai, D.; Khan, M.K.A. Investigating the binding mechanism of topiramate with bovine serum albumin using spectroscopic and computational methods. J. Mol. Recognit. 2022, 35, e2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna Kumari, N.K.; Jagannadham, M.V. SDS induced molten globule state of heynein; a new thiol protease: Evidence of domains and their sequential unfolding. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Lin, M. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis Technology Based on Single Sample. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2021, 88, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, Q.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z. Effects of aldehyde products of lipid oxidation on the color stability and metmyoglobin reducing ability of bovine Longissimus muscle. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serson, W.; Armstrong, P.; Maghirang, E.; Al-Bakri, A.; Phillips, T.; Al-Amery, M.; Su, K.; Hildebrand, D. Development of Whole and Ground Seed Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Calibrations for Oil, Protein, Moisture, and Fatty Acids in Salvia hispanica. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 97, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbas, B.; Machado, N.; Oppolzer, D.; Ferreira, L.; Brites, C.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Barros, A. Comparison of near-infrared (NIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy for the determination of nutritional and antinutritional parameters in common beans. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, S.P.; Hong, Y.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Parker, J.K.; Faka, M.; Methven, L. Whey protein mouth drying influenced by thermal denaturation. Food Qual. Prefer. 2017, 56 Pt B, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, M.; Vasiljevic, T. Functional properties of whey proteins affected by heat treatment and hydrodynamic high-pressure shearing. J. Dairy. Sci. 2009, 92, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, B.; Guo, Z. Impact of combined ultrasound-microwave treatment on structural and functional properties of golden threadfin bream (Nemipterus virgatus) myofibrillar proteins and hydrolysates. Ultrason. Sonochem 2020, 65, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, R.; Ahmad, R. Effect of low frequency ultrasonication on biochemical and structural properties of chicken actomyosin. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).