Effect of Sinapine on Microstructure and Anti-Digestion Properties of Dual-Protein-Based Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Gel
2.2.2. Determination of Drug Loading and Entrapment Efficiency of Double Protein Composite Gel
2.2.3. Size Distribution and Zeta Potential Measurement
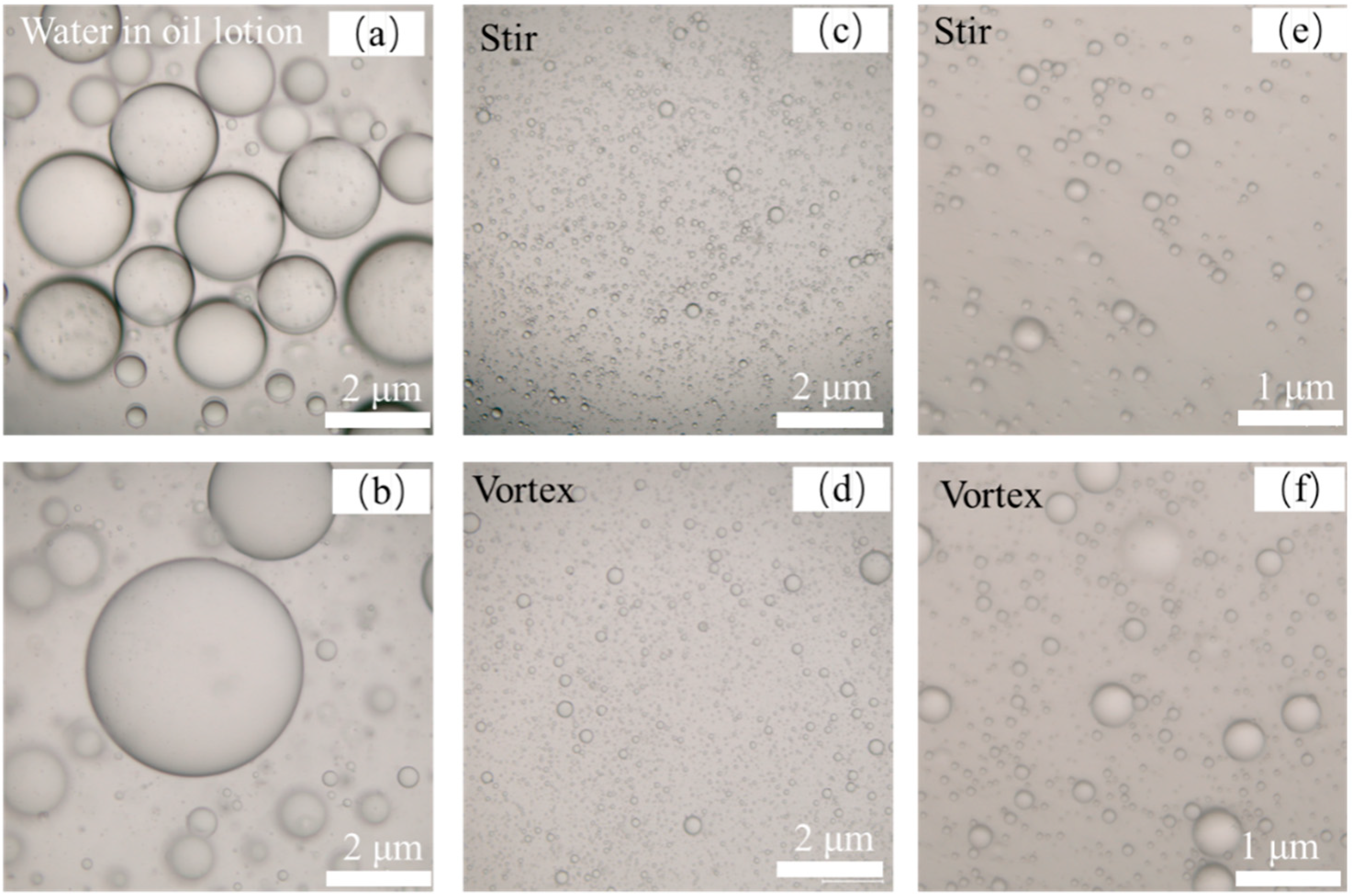
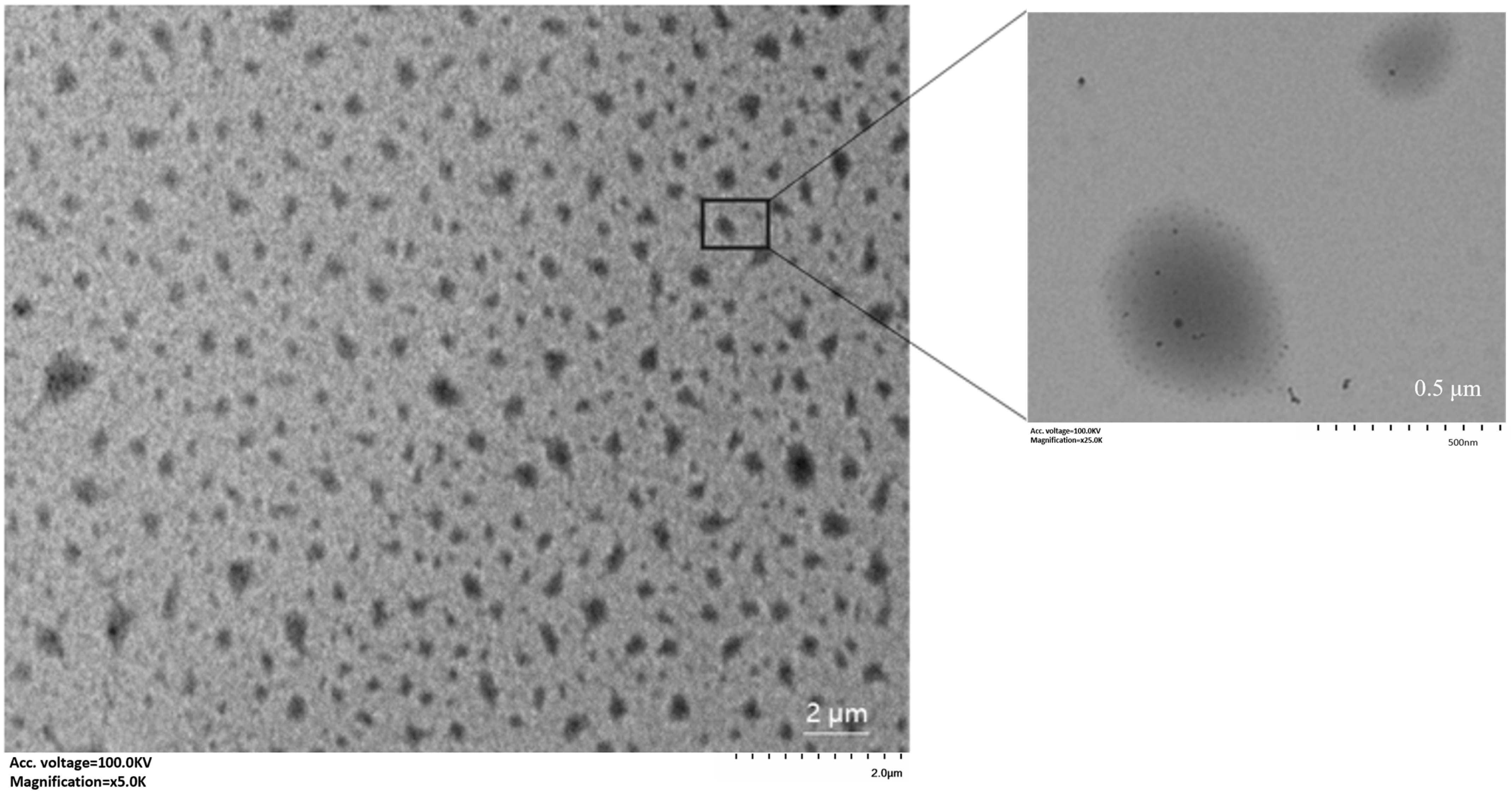
2.2.4. Morphological Analysis of Double Protein Composite Gel
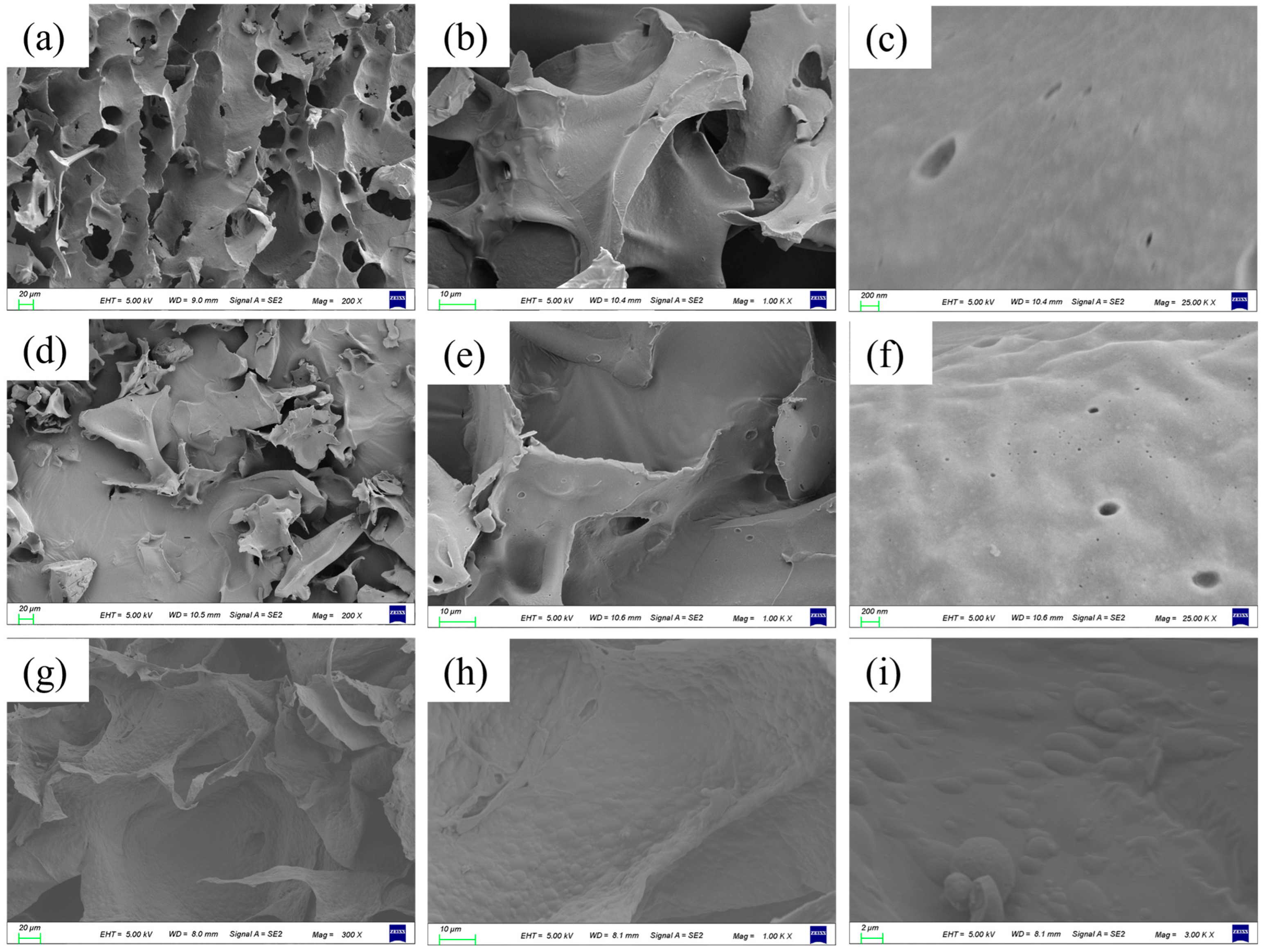
2.2.5. Determination of Morphology of Double Protein Composite Gel
2.2.6. Determination of the Internal Structure of Double Protein Composite Gel
2.2.7. Swelling Degree of Gel
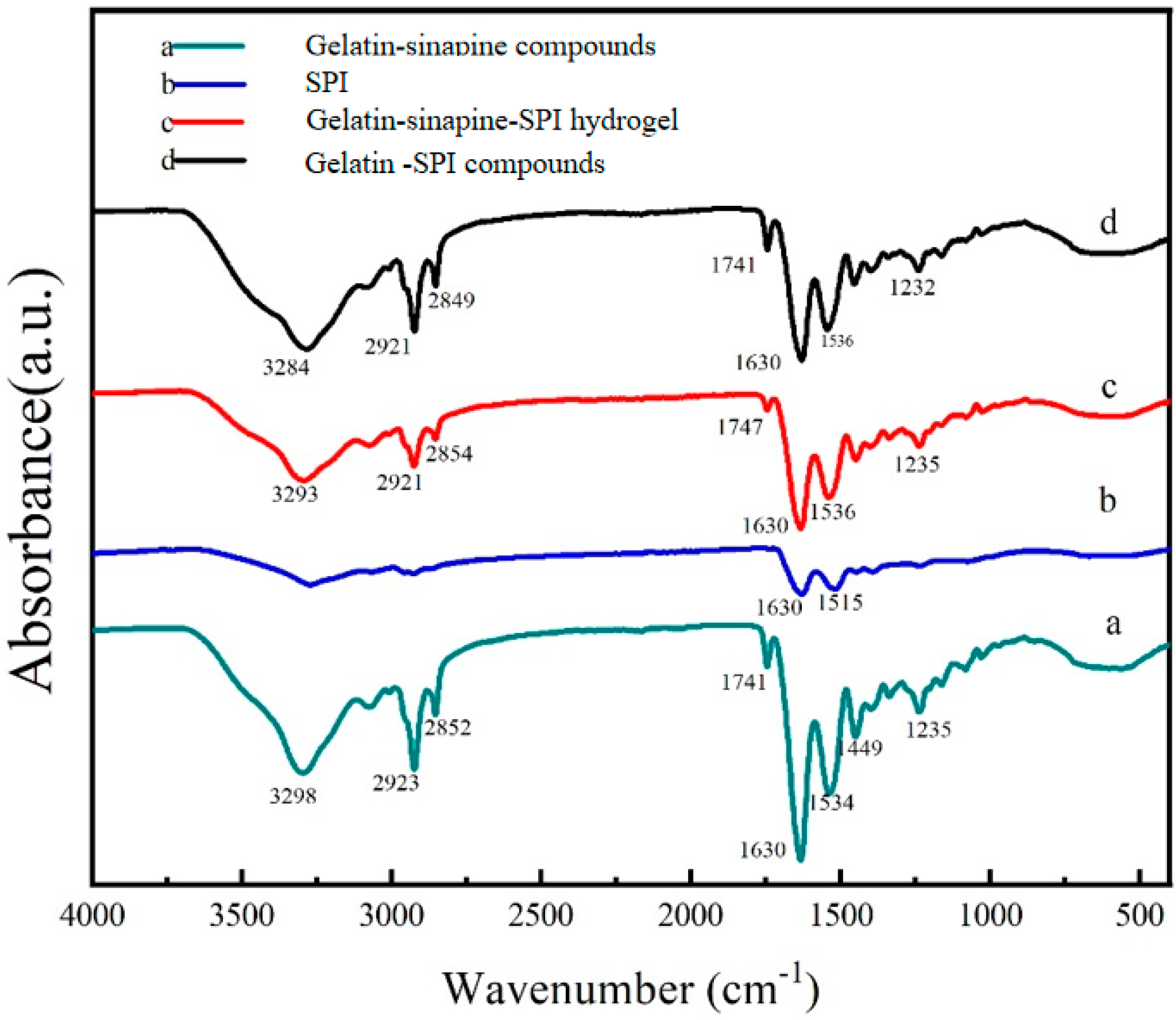
2.2.8. FT-IR Analysis
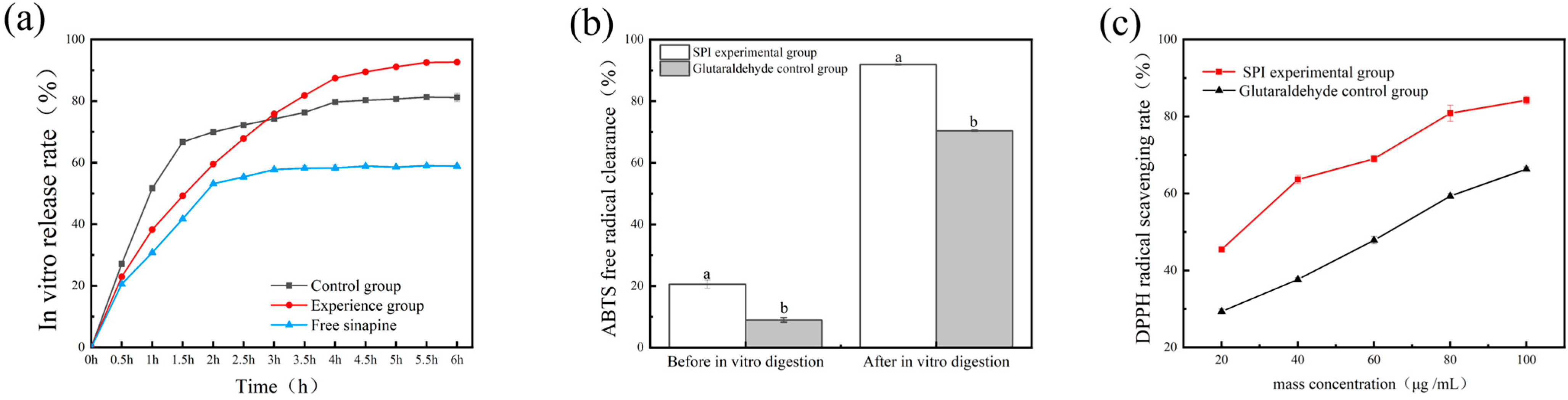
2.2.9. Determination of Sinapine Release Rate In Vitro
2.2.10. In Vitro Antioxidant Analysis of Double Protein Composite Gel
2.2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Result and Discussion
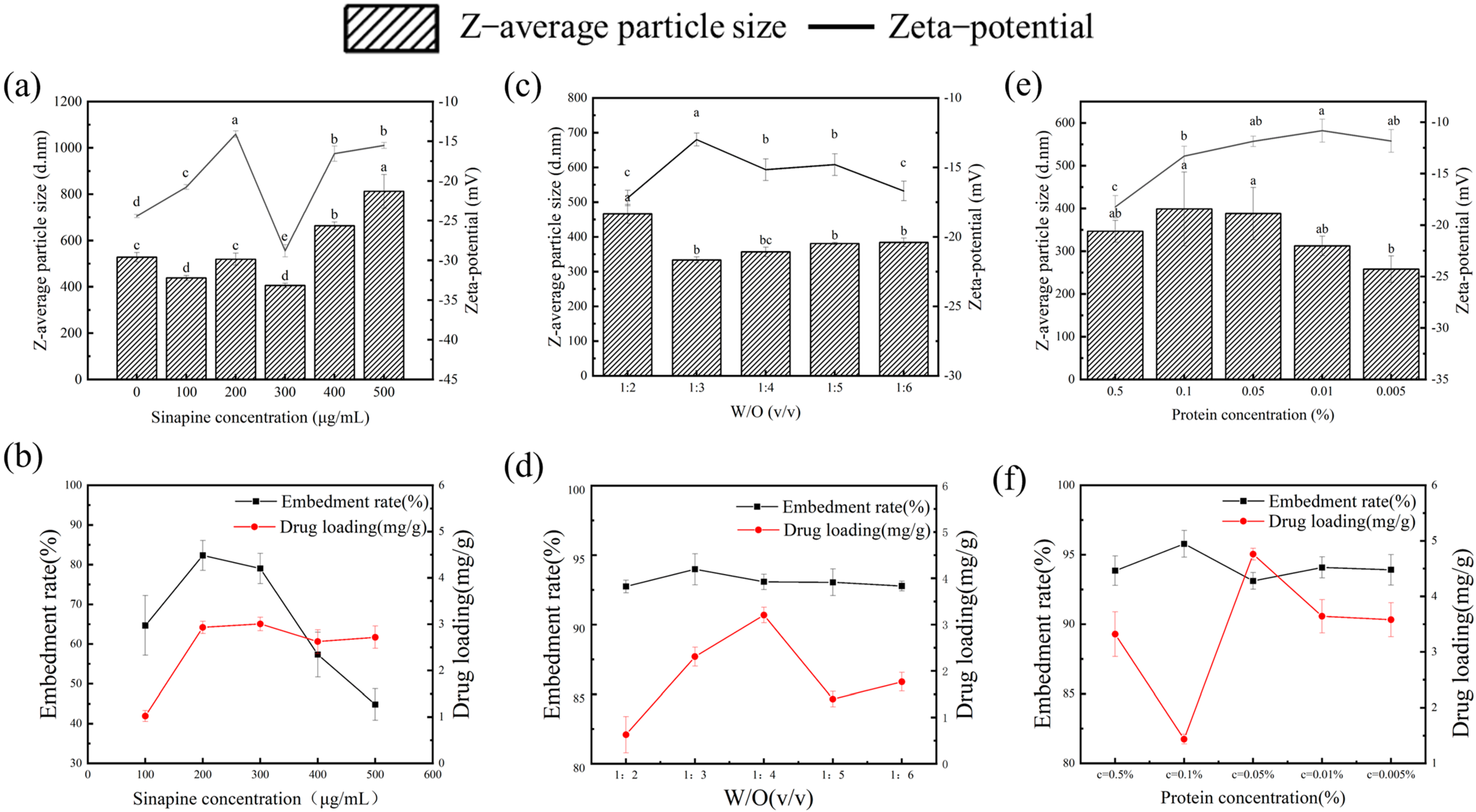
3.1. Effect of Sinapine Concentration on the Particle Size of Gel
3.2. Effect of Water-Oil Ratio on Particle Size of Gel
3.3. Effect of Protein Concentration on Gel
3.4. Determination of Particle Size
3.5. The Internal Structure of the Gel
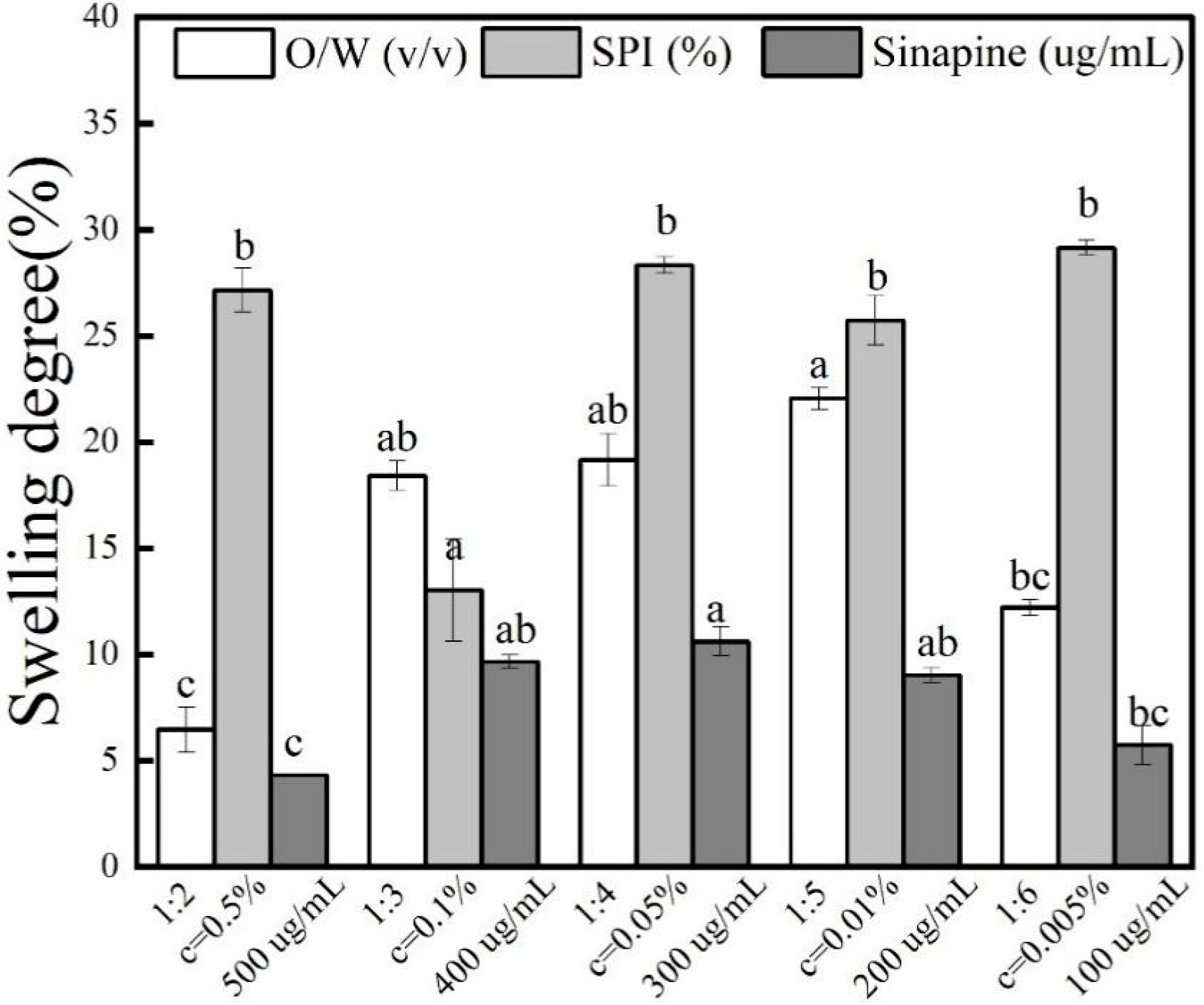
3.6. Effect of Swelling Degree of Gel
3.7. Cross Linking Mechanism between Sinapine, Gelatin, and Soy Protein Isolate
3.8. In Vitro Release and Antioxidant Analysis of Gel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.M.; Afzaal, M.; Tufail, T.; Bashir, M.S.; Ishtiaq, A.; Hussain, S.; Suleria, H.A.R. Natural polyphenols: An overview. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 20, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N.; Rubini, K. Stabilization of gelatin films by crosslinking with genipin. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4827–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, X.; Chen, Q.; Ye, X.; Zeng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Su, D. Hydrogel with the network structure fabricated by anthocyanin–gelatin crosslinking and improved mineral encapsulation ability. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7143–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shan, Z.H.; Woo, M.W.; Chen, X.D. Preparation and characteristic of gelatine/oxidized corn starch and gelatin/corn starch blend microspheres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tang, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X. The dose-dependent effects of poly-phenols and malondialdehyde on the emulsifying and gel properties of myofibrillar protein-mulberry polyphenol complex. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo-Santaella, T.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Molina-Bolivar, J.A.; Galisteo-Gonzalez, F. Effect of cross-linker glutaraldehyde on gastric digestion of emulsified albumin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Meng, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X.; Wang, D.-A.; Fan, C. Progress of gelatin-based microspheres (GMSs) as delivery vehicles of drug and cell. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, T.; Madadlou, A. Fabrication methods of biopolymeric microgels and microgel-based hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chang, S.; Jing, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Qin, G. Transdermal delivery of sinapine thiocyanate by gelatin microspheres and hyaluronic acid microneedles for allergic asthma in guinea pigs. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.; Sehgal, P.K.; Mandal, A.B.; Sadulla, S. Novel collagen scaffolds prepared by using unnatural D-amino acids assisted EDC/NHS crosslinking. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 344–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Du, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Zheng, H.; Yang, A.; Li, H.; Lv, G. Preparation and the hemostatic property study of porous gelatin microspheres both in vitro and in vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 187, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.-J.; Tan, C.P.; Liu, Y. Sinapine improves LPS-induced oxidative stress in hepatocytes by down-regulating MCJ protein expression. Life Sci. 2022, 306, 120828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, M.; Liu, G.; Liang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Xu, X. Effects of sinapine on structure, rheology, stability, and antioxidant properties of protein-based capillary bridging oleogels. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Meng, H.; Guo, X.; Yu, S. Enhancing the Emulsification and Photostability Properties of Pectin from Different Sources Using Genipin Crosslinking Technique. Foods 2022, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yu, S.; Ai, C.; Zhang, T.; Guo, X. Emulsion stability of sugar beet pectin increased by genipin crosslinking. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.-C.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Ding, W.; Xiao, X.-H.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Xiong, L.-X. Fish gelatin: The novel potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.H.; Kuang, Y.Z.; Hao, X.Z.; Gu, N. Preparation and characterization of tea polyphenols and vitamine loaded nanoscale complex liposome. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Ensenberger, S.; Irmscher, S.B.; Weiss, J. Glutaraldehyde induced cross-linking of oppositely charged oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağlam, D.; Venema, P.; de Vries, R.; van den Berg, M.; van der Linden, E. Whey protein particles modulate mechanical properties of gels at high protein concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gao, Y.; Lee, L.; Song, T.; Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; Li, Y. Adaptive Gelatin Microspheres Enhanced Stem Cell Delivery and Integration with Diabetic Wounds to Activate Skin Tissue Regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 813805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, B.; Xu, S.; Li, L. Characteristics of inflammation process in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Hong, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Hua, Q.; Liu, L.; Ying, D. Urea Controlled-Release Fertilizer Based on Gelatin Microspheres. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 26, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Fan, S.; Hu, D. A multifunctional poly(acrylic acid)/gelatin hydrogel. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 24, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirgarian, B.; Farmani, J.; Milani, J.M. Edible oleofilms with high vegetable oil content obtained from novel soy protein isolate/gelatin/chitosan nanofiber emulgels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Mi, Y.; Meng, Q.; Mu, D.; Hou, Y. Biomimetic cell membrane vesicles as promising delivery carriers for dietary polyphenols in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 93, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Han, C.; Yang, C. Preparation and Properties of Fractionated Soybean Protein Isolate Films. Materials 2021, 14, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Hao, Y.; Yang, J.; Yao, W.; Xu, Y.; Yan, L.; Niu, Y.; Sun, T.; Yu, J.; Zhou, R. Protective effects of aloperine on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutani, R.; Morita, S.-Y.; Teraoka, R.; Kitagawa, S. Distribution of polyphenols and a surfactant component in skin during aerosol ot microemulsion-enhanced intradermal delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Acevedo, N.C. Effects of pre-heating soybean protein isolate and transglutaminase treat-ments on the properties of egg-soybean protein isolate composite gels. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z. Effects of gelatin-polyphenol and gelatin–genipin cross-linking on the structure of gelatin hydrogels. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 20, S2822–S2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Cao, Z.; Xu, B. Functional Hyper-Crosslinkers. Chemistry 2017, 23, 15844–15851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Ikoma, T.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Novel microsphere-packing synthesis, microstructure, formation mechanism and in vitro biocompatibility of porous gelatin/hydroxyapatite microsphere scaffolds. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32187–32194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test | Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| W/O (v/v) | SPI (%) | Sinapine Concentration (μg/mL) | |
| 1 | 1:2 | 0.5 | 100 |
| 2 | 1:3 | 0.1 | 200 |
| 3 | 1:4 | 0.05 | 300 |
| 4 | 1:5 | 0.01 | 400 |
| 5 | 1:6 | 0.005 | 500 |
| Sample | Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| Glutaraldehyde control group | 1780.03 ± 31.43 a | 4.86 ± 0.15 a |
| SPI experimental group | 500.53 ± 11.24 b | 3.69 ± 0.13 b |
| Sample | Sinapine Concentration | W/O | SPI Concentration | Swelling Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μg/mL) | (v/v) | (%) | ||
| 1 | 500 | 1:3 | 0.01 | 4.35 ± 1.03 c |
| 2 | 400 | 1:3 | 0.01 | 10.18 ± 0.32 ab |
| 3 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.01 | 8.17 ± 0.68 a |
| 4 | 200 | 1:3 | 0.01 | 6.32 ± 0.35 ab |
| 5 | 100 | 1:3 | 0.01 | 4.69 ± 0.91 bc |
| 6 | 300 | 1:2 | 0.5 | 5.6 ± 1.03 c |
| 7 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.5 | 17.73 ± 0.4 ab |
| 8 | 300 | 1:4 | 0.5 | 17.54 ± 0.4 ab |
| 9 | 300 | 1:5 | 0.5 | 16.52 ± 1.17 a |
| 10 | 300 | 1:6 | 0.5 | 17.95 ± 0.35 bc |
| 11 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.5 | 17.88 ± 1.06 b |
| 12 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.1 | 14.58 ± 0.7 a |
| 13 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.05 | 26.53 ± 1.24 b |
| 14 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.01 | 8.17 ± 0.68 b |
| 15 | 300 | 1:3 | 0.005 | 29.46 ± 0.37 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Duan, M.; Liu, G.; Liang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Xu, X. Effect of Sinapine on Microstructure and Anti-Digestion Properties of Dual-Protein-Based Hydrogels. Foods 2024, 13, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203237
Li Y, Duan M, Liu G, Liang L, Liu X, Zhang J, Wen C, Xu X. Effect of Sinapine on Microstructure and Anti-Digestion Properties of Dual-Protein-Based Hydrogels. Foods. 2024; 13(20):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203237
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Youdong, Mengxin Duan, Guoyan Liu, Li Liang, Xiaofang Liu, Jixian Zhang, Chaoting Wen, and Xin Xu. 2024. "Effect of Sinapine on Microstructure and Anti-Digestion Properties of Dual-Protein-Based Hydrogels" Foods 13, no. 20: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203237
APA StyleLi, Y., Duan, M., Liu, G., Liang, L., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Wen, C., & Xu, X. (2024). Effect of Sinapine on Microstructure and Anti-Digestion Properties of Dual-Protein-Based Hydrogels. Foods, 13(20), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203237





