Mechanisms of Degradation of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Coconut Chips by Ultra-High Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. UHP Pre-Treatment and Preparation with Coconut Chips
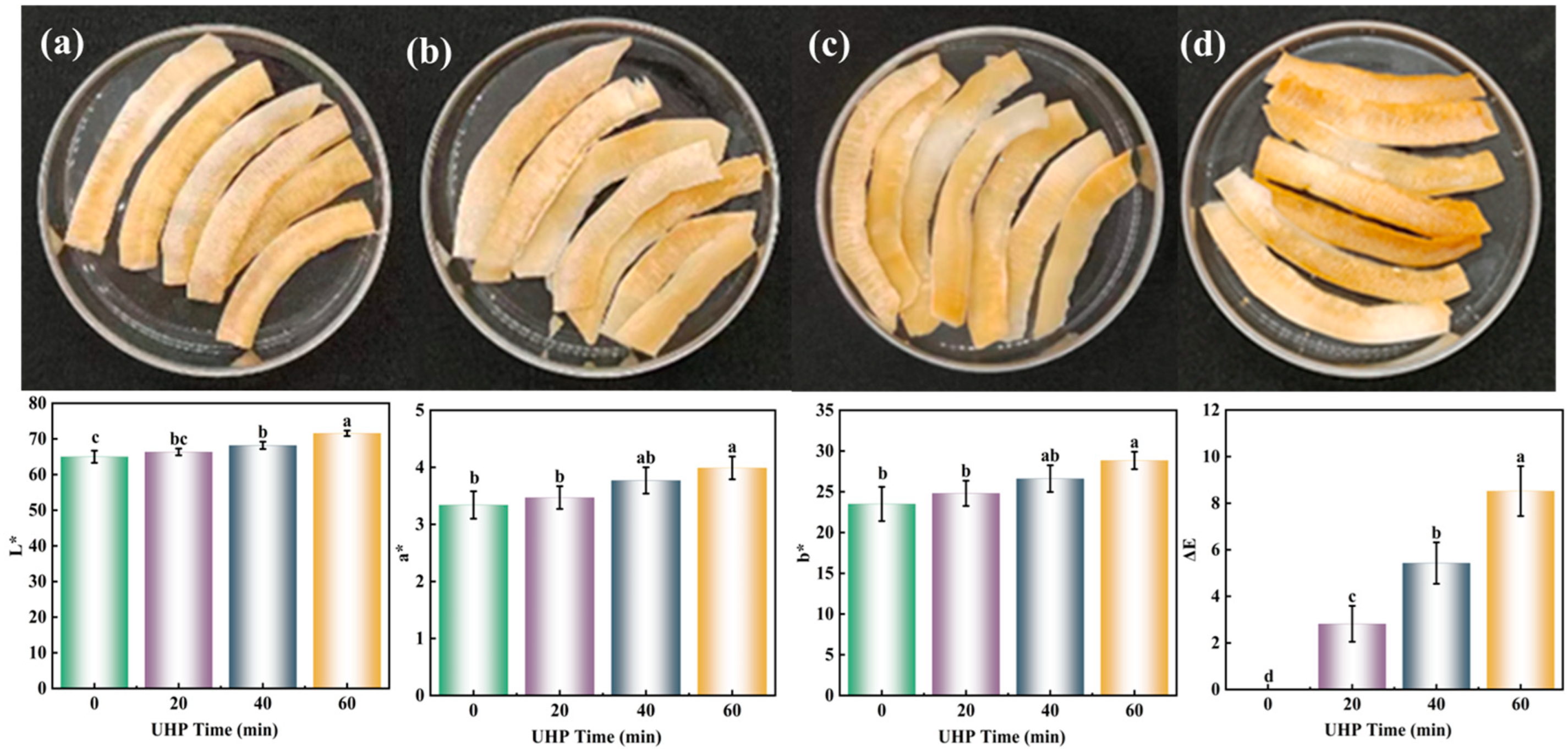
2.3. Color
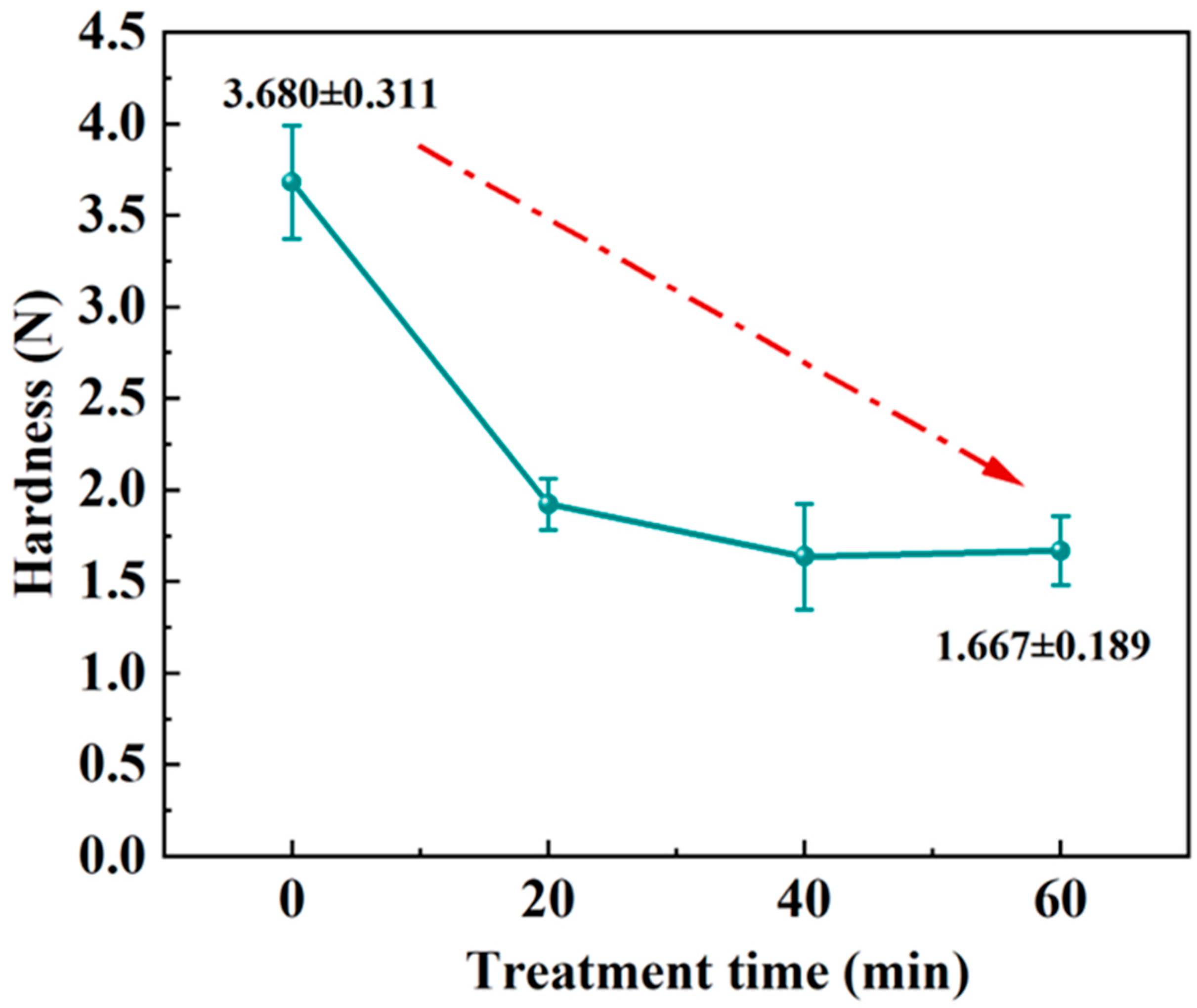
2.4. Hardness
2.5. Determination of Major Components
2.5.1. Moisture
2.5.2. Fat
2.5.3. Protein
2.6. The Extraction of Insoluble and Soluble Dietary Fiber
2.7. Structural Characterisation
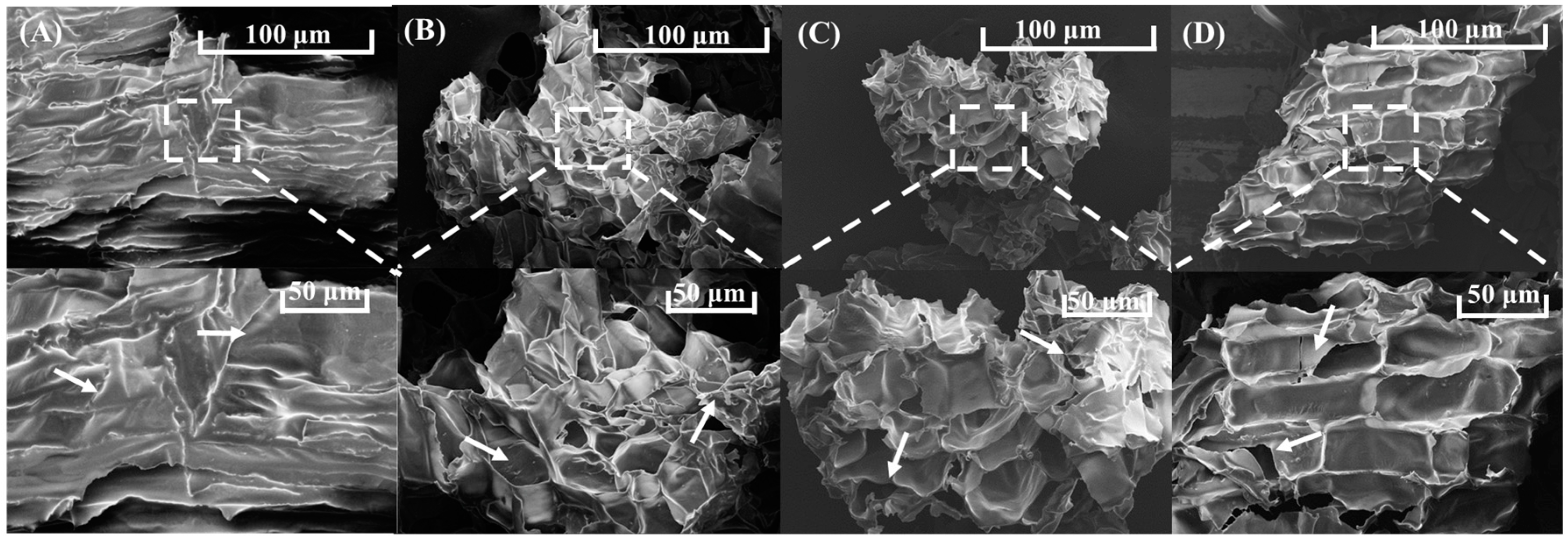
2.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
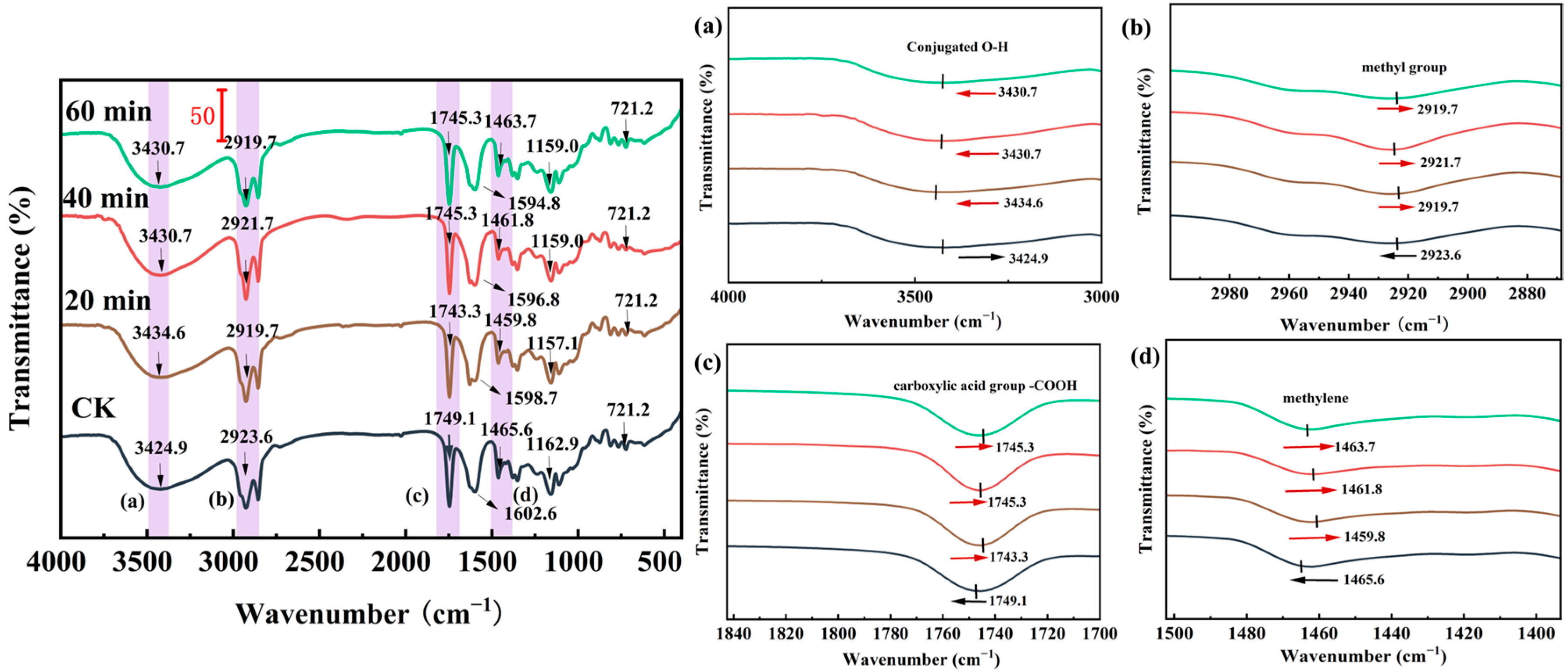
2.7.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.8. Thermal Gravimetry (TG)
2.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.10. The Monosaccharide Composition of IDF
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color
3.2. Statistical Analysis of the Hardness Results
3.3. Determination of Major Components
3.4. Dietary Fiber Fraction
3.5. Structural Characterisation of IDFs
3.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.5.2. Fourier-Infrared (FTIR)
3.5.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.6. TG and DSC
3.7. The Monosaccharide Composition of IDF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Chan, J.X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.Q. Pre-treatment of Coconut Kernels by Proteases to Modulate the Flavour of Coconut Oil. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Cake Dietary Fibres: Effects of Cellulase Hydrolysis, Acid treatment and Particle Size Distribution. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O‘Grady, J.; O‘Connor, E.M.; Shanahan, F. Review Article: Dietary Fibre in the era of Microbiome Science. Aliment. Pharm Ther. 2019, 49, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, G.A. Dietary Fiber, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.W.; Yu, E.Z.; Feng, Q. Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lei, H.; Zhen, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, W.; Tang, Q.; Gou, D.; Zhao, J. Advancements in Modifying Insoluble Dietary Fiber: Exploring the Microstructure, Physicochemical Properties, Biological Activity, and Applications in Food Industry—A review. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Xie, L.; Peng, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q. Systematic Review on Modification Methods of Dietary Fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader Ul Ain, H.; Saeed, F.; Khan, M.A.; Niaz, B.; Khan, S.G.; Anjum, F.M.; Tufail, T.; Hussain, S. Comparative Study of Chemical Treatments in Combination with Extrusion for the Partial Conversion of Wheat and Sorghum Insoluble Fiber into Soluble. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, P.; Yadav, R.B.; Yadav, B.S. Influence of Chemical Modification Approaches on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Dietary Fiber from Oat. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 111, 103688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yi, C.; Quan, K.; Lin, B. Chemical Composition, Structure, Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Rice Bran Dietary Fiber Modified by Cellulase Treatment. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Bei, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Cheng, C. Modification of Carrot (Daucus carota Linn. var. Sativa Hoffm.) Pomace Insoluble Dietary Fiber with Complex Enzyme Method, Ultrafine Comminution, and High Hydrostatic Pressure. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, X.; Lv, X. Characterisation of Alkaline and Enzymatic Modified Insoluble Dietary Fibre from Undaria Pinnatifida. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhou, X.J.; Ma, R.; Lin, H.; Wu, J.L.; Peng, X.; Tanokura, M.; Xue, Y.L. Hydrogen Peroxide Modification Affects the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Dietary Fibers from White Turnip (Brassica rapa L.). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Qiao, C.C.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, N.N.; Tan, B. Functional Properties and Structure of Soluble Dietary Fiber Obtained from Rice Bran with Steam Explosion Treatment. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 118, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Bai, S.; Zheng, J.; Hassan, N.A.; Lu, B.; Hu, A. Comparison of Structural, Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Dried Coconut Dietary Fiber by Steam Explosion and Extrusion Modification. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 218, 118916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, S.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q.; Liu, G.; Chen, Q. Influence of Three Modification Methods on the Structure, Physicochemical, and Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Rosa Roxburghii Tratt Pomace. Molecules 2024, 29, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zeng, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X. Improvement of the Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Corn Bran by Ultrasonic-microwave Synergistic Modification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 104, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Li, M.; Lan, X.; Zhang, W.; Gong, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Modification of Dietary Fibers From Purple-fleshed potatoes (Heimeiren) with High Hydrostatic Pressure and High Pressure Homogenization Processing: A Comparative Study. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 42, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Zeng, W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. Properties of Dietary Fiber from Citrus Obtained Through Alkaline Hydrogen Peroxide Treatment and Homogenization Treatment. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeager, S.E.; Batali, M.E.; Lim, L.X.; Liang, J.; Han, J.; Thompson, A.N.; Guinard, J.-X.; Ristenpart, W.D. Roast Level and Brew Temperature Significantly Affect the Color of Brewed Coffee. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.; Rincón, F.; García-Olmo, J. Cereal protein analysis via Dumas method: Standardization of a micro-method using the EuroVector Elemental Analyser. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, H.; Sharma, M.; Das, M.J.; Mahanta, C.L. Properties of Dietary Fibre From Passion Fruit Seed Obtained Through Individual and Combined Alkaline and Ultrasonication Extraction Techniques. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2024, 15, 2345–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, Y.A.; Deka, S.C. Effect of Processing on Structural, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties of Dietary Fiber of Culinary Banana Bracts. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, G.; Pan, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber-polysaccharide from Papaya Peel Obtained through Alkaline or Ultrasound-Assisted Alkaline Extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Jing, H.; Ye, X.; Gao, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, H. Effects of Different Extraction Methods on Structure and Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Defatted Coconut Flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 111031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Zheng, S.; Bai, T.; Chen, D.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Huang, Z.; et al. The Difference among Structure, Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Dietary Fiber Extracted from Triticale and Hull-less Barley. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, L.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, D.; An, K.; Hu, J. Effects of Ultrahigh Pressure and Ultrasound Pretreatments on Properties of Strawberry Chips Prepared by Vacuum-freeze Drying. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Z.; Wan, F.; Ma, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, B.; Huang, X. Enhancing Peach Slices Radio Frequency Vacuum Drying by Combining Ultrasound and Ultra-high Pressure as Pretreatments: Effect on Drying Characteristics, Physicochemical Quality, Texture and Sensory Evaluation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 103, 106786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, N.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Effect of Ultrahigh-pressure Treatment on the Structure and Allergenicity of Peach Allergenic Proteins. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Niu, L.; Song, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Xiao, L. Effect of Pretreatment and High Hydrostatic Pressure on Soluble Dietary Fiber in Lotus Root Residues. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 5565538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Gao, H.; Zhou, C.; Sun, P.; Wu, C.; Xia, Q.; Chen, J. Physicochemical Properties Improvement and Structural Changes of Bamboo Shoots (Phyllostachys praecox f. Prevernalis) Dietary Fiber Modified by Subcritical Water and High Pressure Homogenization: A comparative study. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pan, Z.; Azarakhsh, N.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Duan, H.; Wang, C. Effects of High-Pressure Processing on the Physicochemical and Adsorption Properties, Structural Characteristics, and Dietary Fiber Content of Kelp (Laminaria japonica). Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Q.; Ni, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, M. Effect of Ultra-High Pressure Treatment on Structural and Functional Properties of Dietary Fiber from Pomelo Fruitlets. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Effects of Modification Methods on Microstructural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Defatted Rice Bran Dietary Fiber. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honců, I.; Sluková, M.; Vaculová, K.; Sedláčková, I.; Wiege, B.; Fehling, E. The Effects of Extrusion on the Content and Properties of Dietary Fibre Components in Various Barley Cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 68, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhao, S.; Pi, Y.; Yue, X. Structural Characterization, A-glucosidase Inhibitory Activity and Antioxidant Activity of Neutral Polysaccharide from Apricot (Armeniaca Sibirica L. Lam) Kernels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettow, M.; Grabarics, M.; Mucha, E.; Thomas, D.A.; Polewski, Ł.; Freyse, J.; Rademann, J.; Meijer, G.; von Helden, G.; Pagel, K. IR Action Spectroscopy of Glycosaminoglycan Oligosaccharides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.L.; Huang, J.H.; Pan, L.; Hou, Y.C.; Li, X.X.; Zhao, P.H.; Dong, Y.Q.; Hu, Z.Y.; et al. Structural, Physicochemical, and Functional Properties of Wheat Bran Insoluble Dietary Fiber Modified with Probiotic Fermentation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 803440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, S. Production and Characterization of Okara Dietary Fiber Produced by Fermentation with Monascus Anka. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawas, P.; Deka, S.C. Isolation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibers from Culinary Banana Peel using High-intensity Ultrasonication Combined with Chemical Treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Z. Impact of Non-thermal Modifications on the Physicochemical Properties and Functionality of Litchi Pomace Dietary Fibre. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 182, 114878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Fang, D.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, C.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, Y. Modification of Insoluble Dietary Fibers from Bamboo Shoot Shell: Structural Characterization and Functional Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Glucose Adsorption and α-amylase Activity Inhibition Mechanism of Insoluble Dietary Fiber: Comparison of Structural and Microrheological Properties of Three Different Modified Coconut Residue Fibers. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.J.; Seo, Y.B. Thermogravimetric Study on Stem Biomass of Nicotiana Tabacum. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 486, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, E.; Yılmaz, E.; Tuncel, N.B. Physicochemical, Microstructural and Functional Characterization of Dietary Fibers Extracted from Lemon, Orange and Grapefruit Seeds Press meals. Bioact. 2017, 11, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Dong, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Peng, G.; Liao, W.; Xue, P.; Feng, L.; Yu, Q. Bound Polyphenols from Insoluble Dietary Fiber of Defatted Rice Bran by Solid-State Fermentation with Trichoderma viride: Profile, Activity, and Release Mechanism. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2021, 69, 5026–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, C. Structure, Physicochemical Properties and Effects on Nutrients Digestion of Modified Soluble Dietary Fiber Extracted from Sweet Potato Residue. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
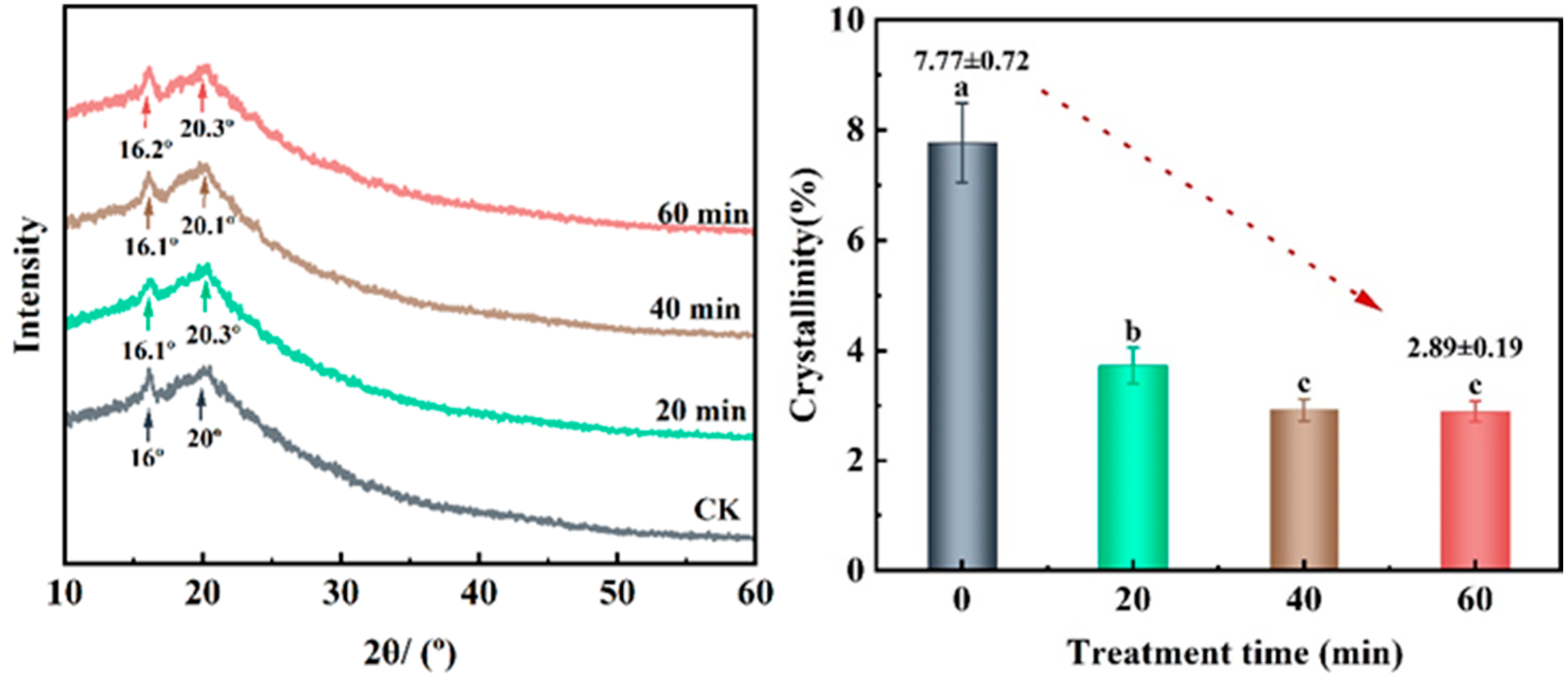
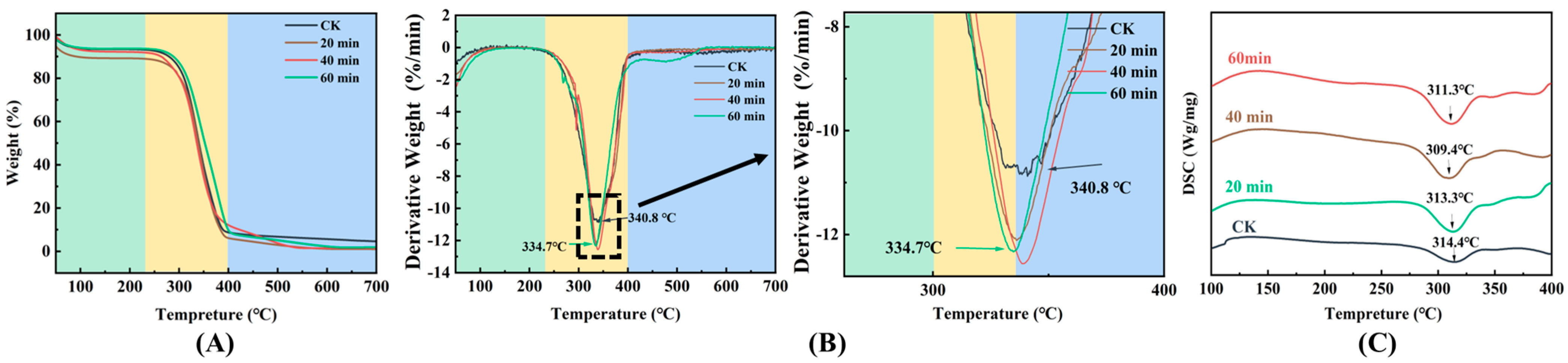
| Treatment Group | Moisture Content (%) | Protein (%) | Fat (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.81 ± 1.62 a | 7.57 ± 0.88 a | 41.37 ± 0.95 b |
| 100 MPa 20 min | 4.48 ± 0.65 b | 7.10 ± 0.87 a | 42.48 ± 0.78 ab |
| 100 MPa 40 min | 3.02 ± 0.37 b | 7.02 ± 0.69 a | 43.58 ± 2.14 a |
| 100 MPa 60 min | 3.08 ± 0.73 b | 7.8 ± 0.32 a | 44.67 ± 0.39 a |
| Treatment Group | IDF | SDF | TDF |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.67 ± 0.24 a | 1.47 ± 0.30 c | 9.23 ± 0.02 b |
| 100 MPa 20 min | 6.38 ± 0.12 b | 3.14 ± 0.11 b | 9.52 ± 0.17 a |
| 100 MPa 40 min | 6.13 ± 0.11 b | 3.31 ± 0.15 ab | 9.44 ± 0.14 ab |
| 100 MPa 60 min | 5.59 ± 0.15 c | 3.64 ± 0.21 a | 9.22 ± 0.06 b |
| Treatment Group (mol%) | CK | 20 min | 40 min | 60 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Guluronic acid | 0.010 ± 0.004 b | 0.024 ± 0.001 a | ND | ND |
| D-Mannuronic acid | 0.057 ± 0.031 b | 0.103 ± 0.041 c | 0.073 ± 0.004 a | 0.294 ± 0.002 bc |
| D-Mannose Man | 88.594 ± 0.151 b | 88.130 ± 0.540 c | 90.320 ± 0.007 a | 69.404 ± 0.251 d |
| L-Rhamnose Rham | 0.261 ± 0.003 b | 0.163 ± 0.003 b | 0.239 ± 0.001 b | 0.890 ± 0.141 a |
| D-Glucuronic acid | 0.121 ± 0.006 c | 0.12 ± 0.011 c | 0.190 ± 0.01 b | 11.830 ± 0.053 a |
| D-Galacturonic acid | 0.239 ± 0.006 a | 0.144 ± 0.006 c | 0.178 ± 0.0153 b | ND |
| D-glucose | 5.002 ± 0.009 c | 6.511 ± 0.0205 b | 3.925 ± 0.0175 d | 7.861 ± 0.115 a |
| D-galactose | 4.482 ± 0.001 a | 3.835 ± 0.012 c | 3.955 ± 0.065 b | 3.221 ± 0.013 d |
| D-xylulose | ND | 0.195 ± 0.002 b | ND | 1.096 ± 0.010 a |
| L-Arabinose | 1.234 ± 0.002 b | 0.776 ± 0.0065 d | 1.120 ± 0.0025 c | 3.469 ± 0.010 a |
| L-Fucose | ND | ND | ND | 1.934 ± 0.0410 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Q.; Cui, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, T. Mechanisms of Degradation of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Coconut Chips by Ultra-High Pressure. Foods 2024, 13, 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193174
Wei Q, Cui J, Zhang W, Jiang L, Li T. Mechanisms of Degradation of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Coconut Chips by Ultra-High Pressure. Foods. 2024; 13(19):3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193174
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Qiaozhu, Jingtao Cui, Weimin Zhang, Lianzhou Jiang, and Tian Li. 2024. "Mechanisms of Degradation of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Coconut Chips by Ultra-High Pressure" Foods 13, no. 19: 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193174
APA StyleWei, Q., Cui, J., Zhang, W., Jiang, L., & Li, T. (2024). Mechanisms of Degradation of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Coconut Chips by Ultra-High Pressure. Foods, 13(19), 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193174






