High-Yield Expressed Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain Nanoparticles in K. marxianus for Functional Food Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of a Kluyveromyces marxianus Strain Expressing Recombinant Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain (KM-rhFTH)
2.2. Fermentation of KM-rhFTH Strain
2.3. Analysis of rhFTH
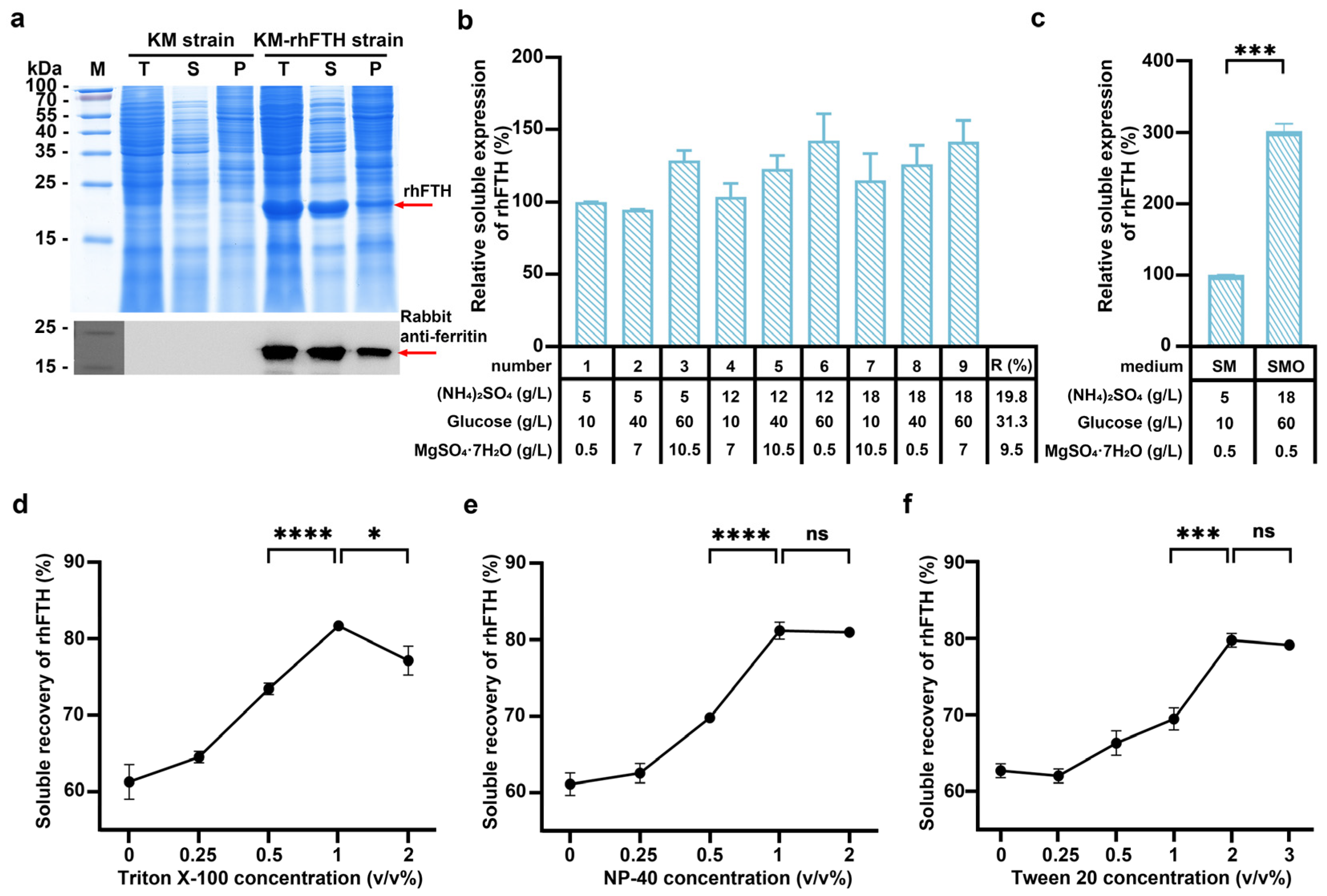
2.4. Orthogonal Design Experiment
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Analysis
2.6. Purification of rhFTH
2.7. Measurement of Iron Uptake and Release Kinetics
2.8. Cell Proliferation and Cytokine Assays
2.9. Experimental Nematodes, Culture, and Lifespan Analysis
2.10. Locomotion, Pharyngeal Pumping, and Egg-Laying Assay
2.11. Analysis of T-SOD, CAT, ROS, and Lipofuscin in C. elegans
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression of Recombinant Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain in K. marxianus
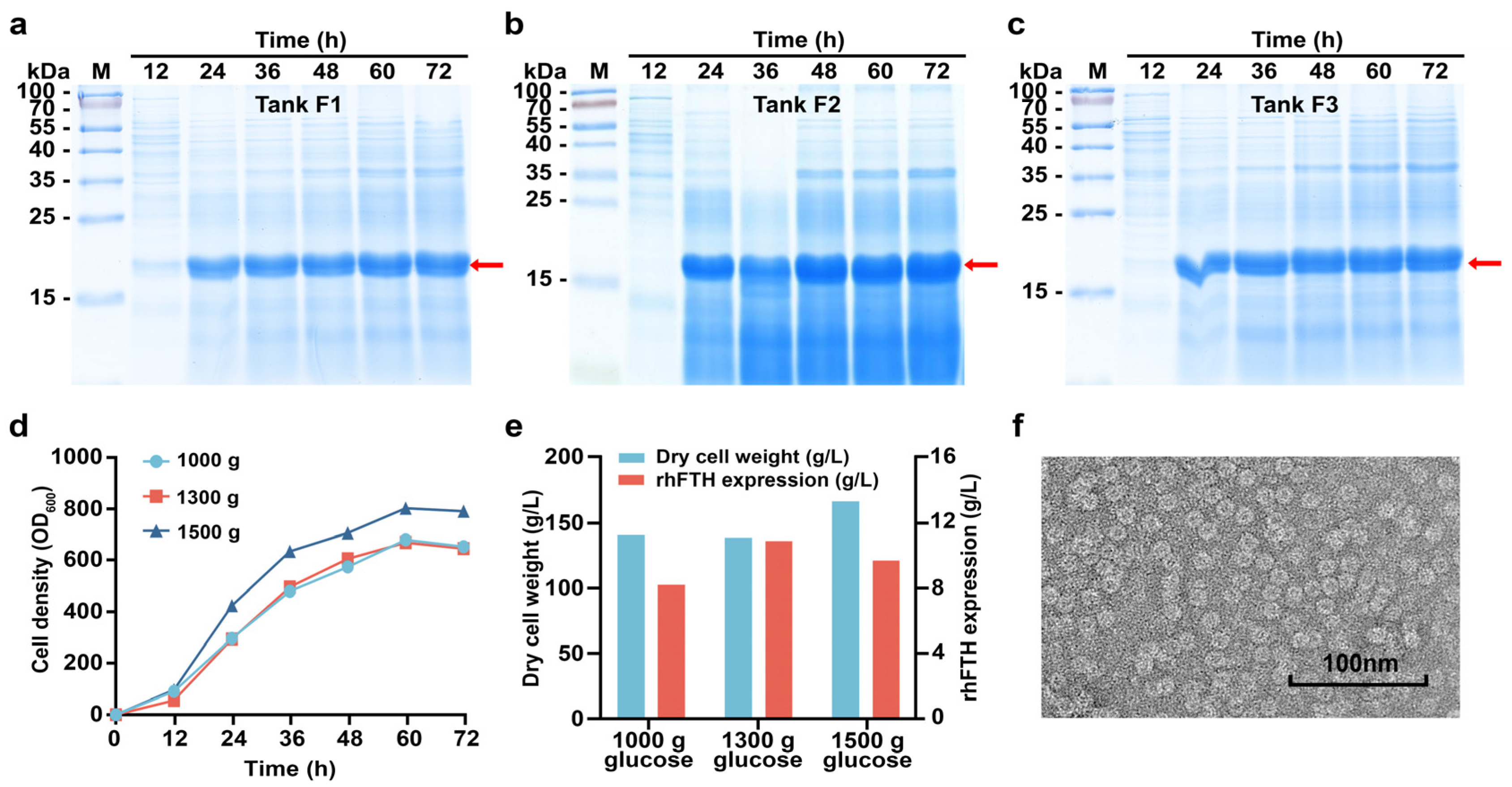
3.2. Fed-Batch Fermentation of KM-rhFTH in 5 L Fermenters
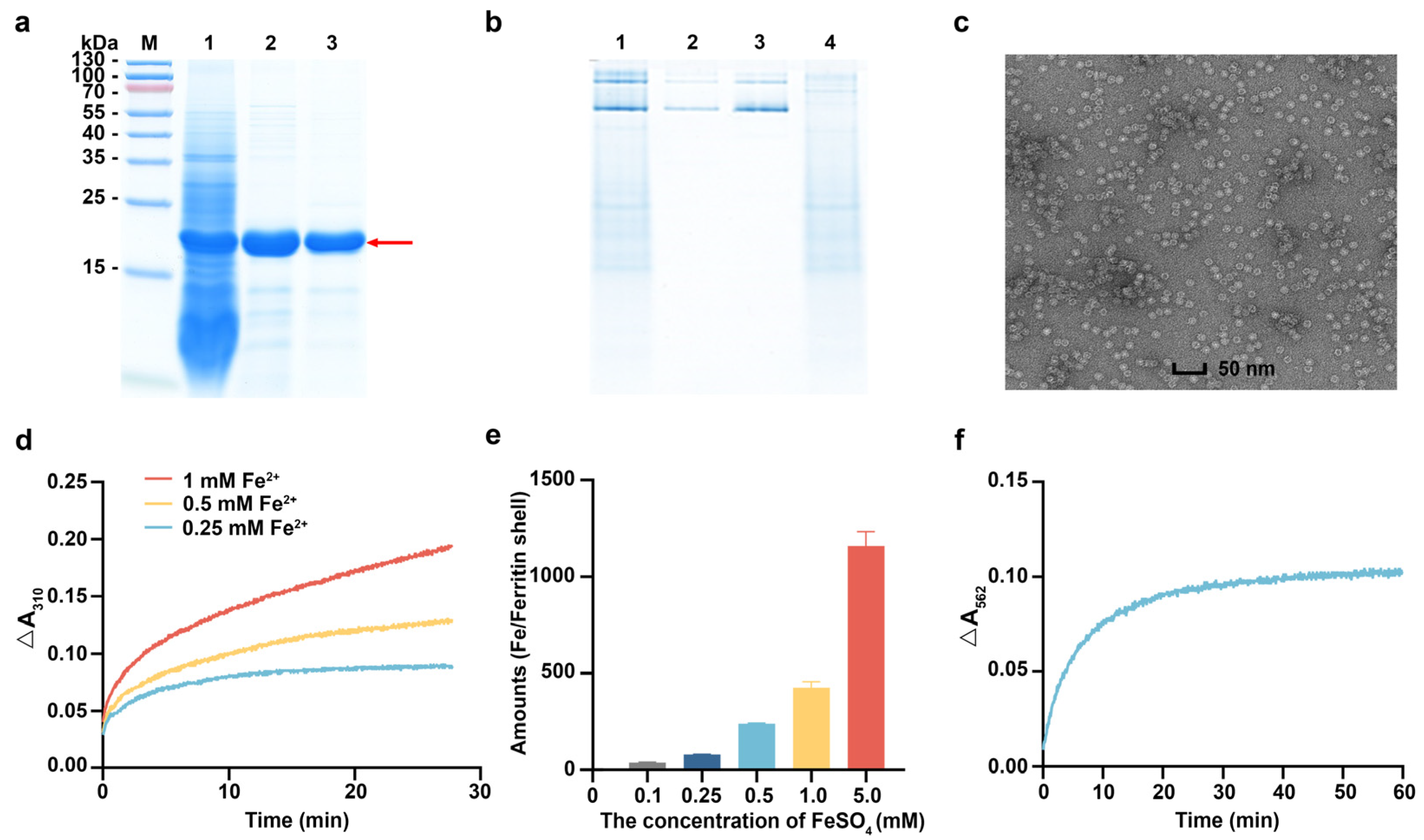
3.3. Characterization of rhFTH Expressed in K. marxianus
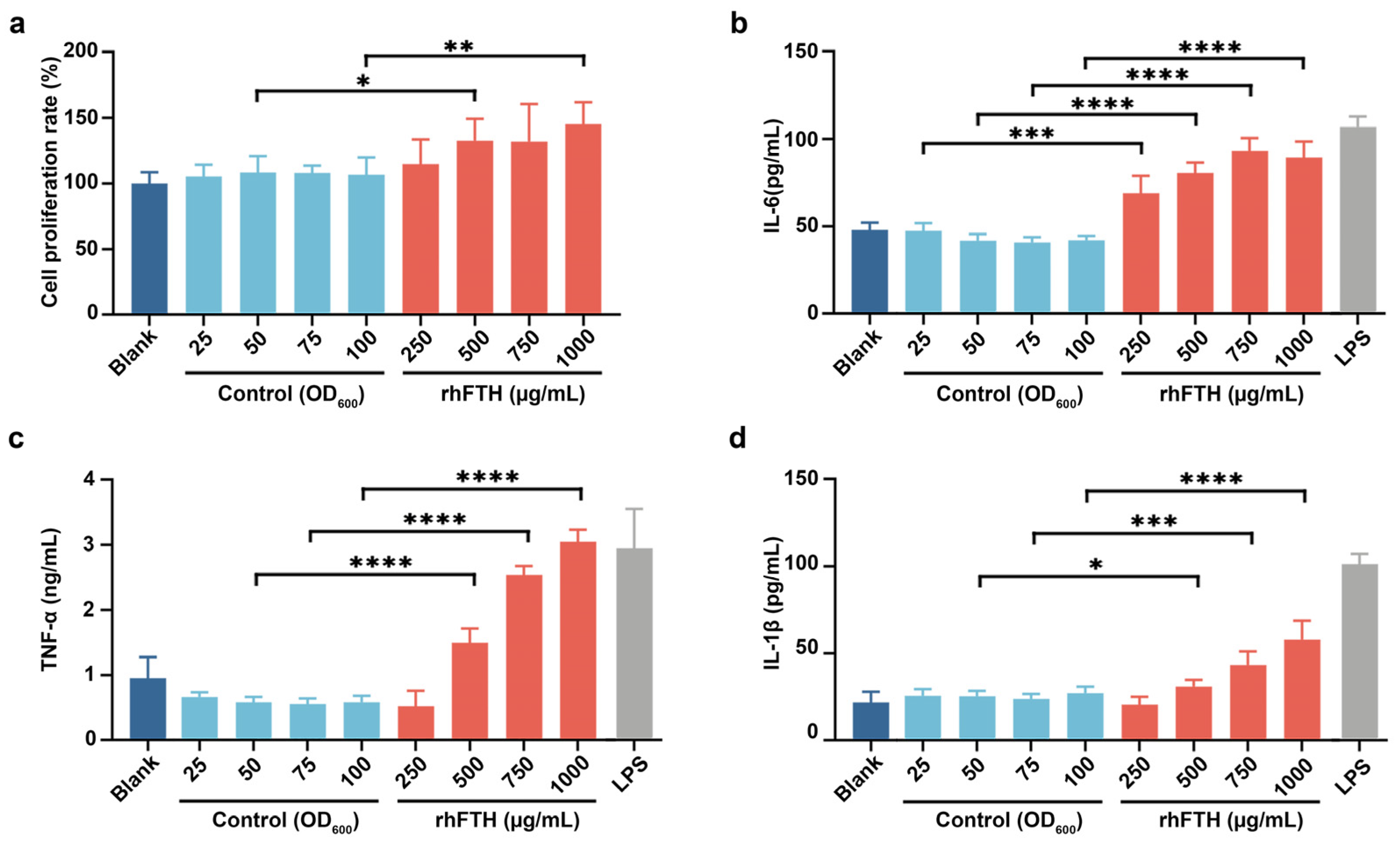
3.4. Analysis of Cytokine Secretion in RAW264.7 Mouse Macrophage Cell Line
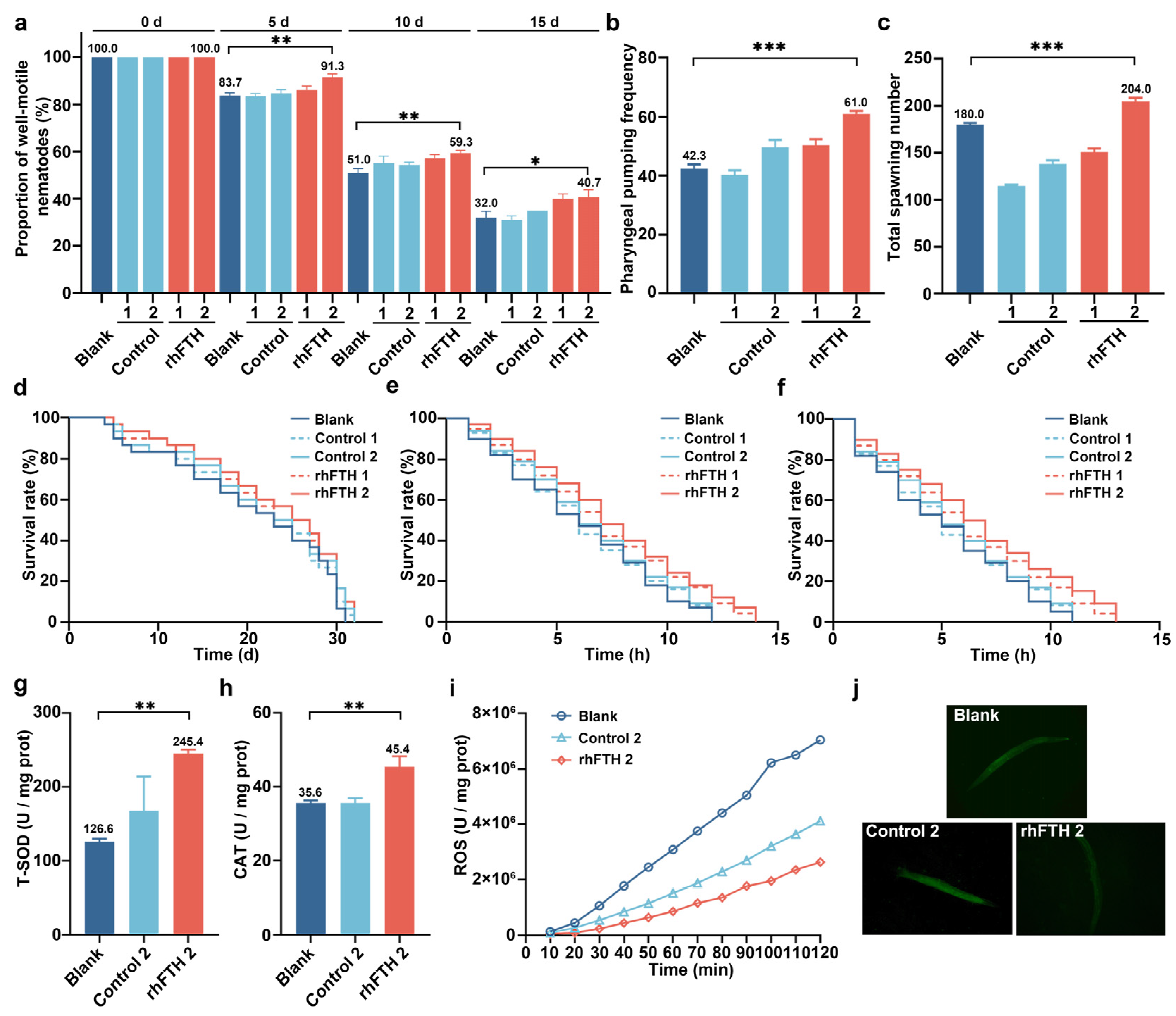
3.5. Analysis of Biological Functions of rhFTH-Containing Cell Lysates in C. elegans Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Hong, J.; Tang, A.; Liu, Y.; Xie, N.; Nie, G.; Yan, X.; Liang, M. Biochemistry of mammalian ferritins in the regulation of cellular iron homeostasis and oxidative responses. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lid, S.; Carmona, D.; Maas, M.; Treccani, L.; Colombi Ciacchi, L. Anchoring of Iron Oxyhydroxide Clusters at H and L Ferritin Subunits. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucignano, R.; Stanzione, I.; Ferraro, G.; Di Girolamo, R.; Cané, C.; Di Somma, A.; Duilio, A.; Merlino, A.; Picone, D. A new and efficient procedure to load bioactive molecules within the human heavy-chain ferritin nanocage. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1008985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, S.; Fujita, H.; Tanaka, Y.K.; Ogra, Y.; Iwai, K. Iron-induced NCOA4 condensation regulates ferritin fate and iron homeostasis. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Zang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, G. Redesign of protein nanocages: The way from 0D, 1D, 2D to 3D assembly. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 3957–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, S.; Chakrabarti, P. Self-Assembly of Ferritin: Structure, Biological Function and Potential Applications in Nanotechnology. In Biological and Bio-Inspired Nanomaterials: Properties and Assembly Mechanisms; Perrett, S., Buell, A.K., Knowles, T.P.J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 313–329. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, B.; Connor, J.R. Emerging and Dynamic Biomedical Uses of Ferritin. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffi, M.; Fiandra, L.; Sorrentino, L.; Monieri, M.; Corsi, F.; Mazzucchelli, S. Ferritin nanocages: A biological platform for drug delivery, imaging and theranostics in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Muñoz-Culla, M.; Carmona, U.; Lopez, M.P.; Yang, F.; Trigueros, C.; Otaegui, D.; Zhang, L.; Knez, M. Ferritin-mediated siRNA delivery and gene silencing in human tumor and primary cells. Biomaterials 2016, 98, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhai, M.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; et al. Apoferritin Nanocage for Brain Targeted Doxorubicin Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Yang, T.; Yang, S.; Yang, M.; Mao, C. Protein nanoparticles directed cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.K.; Sahoo, B.R.; Pattnaik, A.K. Protein Nanoparticles as Vaccine Platforms for Human and Zoonotic Viruses. Viruses 2024, 16, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.-C. Ferritin-based nanomedicine for disease treatment. Med. Rev. 2023, 3, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, N.; Yao, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, R.; Li, J.-W. Efficient expression of recombinant human heavy chain ferritin (FTH1) with modified peptides. Protein Expr. Purif. 2017, 131, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.L.; Song, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Chung, D.K.; Park, C.S.; Jeoung, D.; Kim, H.Y. Functional expression and production of human H-ferritin in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilert, E.; Hollenberg, C.P.; Piontek, M.; Suckow, M. The use of highly expressed FTH1 as carrier protein for cytosolic targeting in Hansenula polymorpha. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 159, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Ji, L.; Hua, Z. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant human L-chain ferritin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 119, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, M. Expression, purification, and characterisation of recombinant ferritin in insect cells using the baculovirus expression system. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitia, L.; Galbiati, V.; Bonizzi, A.; Sevieri, M.; Truffi, M.; Pinori, M.; Corsini, E.; Marinovich, M.; Corsi, F.; Mazzucchelli, S. In Vitro Immunoreactivity Evaluation of H-Ferritin-Based Nanodrugs. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhu, P.; Hu, X.; Lu, H.; Yu, Y. Improved secretory expression of lignocellulolytic enzymes in Kluyveromyces marxianus by promoter and signal sequence engineering. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonklang, S.; Abdel-Banat Babiker, M.A.; Cha-aim, K.; Moonjai, N.; Hoshida, H.; Limtong, S.; Yamada, M.; Akada, R. High-Temperature Ethanol Fermentation and Transformation with Linear DNA in the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU3-1042. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7514–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ji, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Cheng, H. Bioprospecting Kluyveromyces marxianus as a Robust Host for Industrial Biotechnology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 851768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H. Efficient production of porcine circovirus virus-like particles using the nonconventional yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Chen, L.; Duan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H. Investigation of Kluyveromyces marxianus as a novel host for large-scale production of porcine parvovirus virus-like particles. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Duan, J.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H. A Single Vaccination of IBDV Subviral Particles Generated by Kluyveromyces marxianus Efficiently Protects Chickens against Novel Variant and Classical IBDV Strains. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mo, W.-J.; Shi, T.-F.; Wang, M.-Z.; Zhou, J.-G.; Yu, Y.; Yew, W.-S.; Lu, H. Mutational Mtc6p attenuates autophagy and improves secretory expression of heterologous proteins in Kluyveromyces marxianus. Microb. Cell Factories 2018, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensing, M.; Vrouwenvelder, H.; Hellinga, C.; Baartmans, R.; Vandijken, H. Production of extracellular inulinase in high-cell-density fed-batch cultures of Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 42, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Luzzago, A.; Cesareni, G.; Cozzi, A.; Franceschinelli, F.; Albertini, A.; Arosio, P. Mechanism of ferritin iron uptake: Activity of the H-chain and deletion mapping of the ferro-oxidase site. A study of iron uptake and ferro-oxidase activity of human liver, recombinant H-chain ferritins, and of two H-chain deletion mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 18086–18092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Asakawa, H.; Katayama, T. Colorimetric Determination of Ferritin Iron. Anal. Sci. 1992, 8, 881–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta-de-la-Riva, M.; Fontrodona, L.; Villanueva, A.; Cerón, J. Basic Caenorhabditis elegans Methods: Synchronization and Observation. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 64, 4019. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, S.; Firlar, E.; Rasul, M.G.; Foroozan, T.; Farajpour, N.; Covnot, L.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R.; Shokuhfar, T. On the structure and chemistry of iron oxide cores in human heart and human spleen ferritins using graphene liquid cell electron microscopy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16868–16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, P.; Elia, L.; Poli, M. Ferritin, cellular iron storage and regulation. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struyf, N.; Laurent, J.; Verspreet, J.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Courtin, C.M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces marxianus Cocultures Allow Reduction of Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, and Monosaccharides and Polyols Levels in Whole Wheat Bread. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8704–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.; Gerliani, N.; Aïder, M. Kluyveromyces marxianus: An emerging yeast cell factory for applications in food and biotechnology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Mo, W.J.; Ren, H.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Lu, W.L.; Luo, T.Y.; Zeng, J.Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Qi, J.; Lu, H. Comparative Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Specific Features of Gene Regulation in Kluyveromyces marxianus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 598060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Immune-Enhancing Effect of Heat-Treated Levilactobacillus brevis KU15159 in RAW 264.7 Cells. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jo, S.; Cho, M.J.; Cho, Y.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Byun, S. Immunomodulatory functional foods and their molecular mechanisms. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Wu, T.; Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Min, W. In vitro immunomodulatory effects of acidic exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus planetarium JLAU103 on RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; Cao, C.; Wang, J.; Gao, M. Recombinant ferritin nanoparticles can induce dendritic cell maturation through TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddell, R.G.; Hoang-Le, D.; Barwood, J.M.; Rutherford, P.S.; Piva, T.J.; Watters, D.J.; Santambrogio, P.; Arosio, P.; Ramm, G.A. Ferritin functions as a proinflammatory cytokine via iron-independent protein kinase C zeta/nuclear factor kappaB-regulated signaling in rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.; Jang, S.; Gu, D.H.; Park, J.M.; Ryu, J.A.; Yoon, S.R.; Jung, S.K. Curcuma longa L. extract increased immune responses in RAW 264.7 cells and cyclophosphamide-induced BALB/c mice. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Das, A.; Abir, M.H.; Nafiz, I.H.; Mahmud, A.R.; Sarker, M.R.; Emran, T.B.; Hassan, M.M. Cytokines and their role as immunotherapeutics and vaccine Adjuvants: The emerging concepts. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraynak, C.A.; Yan, D.J.; Suggs, L.J. Modulating inflammatory macrophages with an apoptotic body-inspired nanoparticle. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, S.; Cabreiro, F.; Ackerman, D.; Alam, M.M.; Kunze, M.B.A.; Kay, C.W.M.; Gems, D. Manipulation of in vivo iron levels can alter resistance to oxidative stress without affecting ageing in the nematode C. elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2012, 133, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, G.; He, J.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Ferritin nanocage: A promising and designable multi-module platform for constructing dynamic nanoassembly-based drug nanocarrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Fan, K.; Yan, X. Ferritin drug carrier (FDC) for tumor targeting therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 311–312, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, M.; Li, X.; Fan, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, F.; Choi, H.S.; Cheng, D.; et al. Bioengineered Magnetoferritin Nanoprobes for Single-Dose Nuclear-Magnetic Resonance Tumor Imaging. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4184–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenbacher, P.A.B.; Sanyal, M.; Friedland, N.; Tang, S.; Arunachalam, P.S.; Hu, M.; Kumru, O.S.; Morris, M.K.; Fontenot, J.; Shirreff, L.; et al. A ferritin-based COVID-19 nanoparticle vaccine that elicits robust, durable, broad-spectrum neutralizing antisera in non-human primates. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Tian, T.; Du, B.; Li, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H. High-Yield Expressed Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain Nanoparticles in K. marxianus for Functional Food Development. Foods 2024, 13, 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182919
Lu X, Liu L, Zhang H, Lu H, Tian T, Du B, Li P, Yu Y, Zhou J, Lu H. High-Yield Expressed Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain Nanoparticles in K. marxianus for Functional Food Development. Foods. 2024; 13(18):2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182919
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xinyi, Liping Liu, Haibo Zhang, Haifang Lu, Tian Tian, Bing Du, Pan Li, Yao Yu, Jungang Zhou, and Hong Lu. 2024. "High-Yield Expressed Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain Nanoparticles in K. marxianus for Functional Food Development" Foods 13, no. 18: 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182919
APA StyleLu, X., Liu, L., Zhang, H., Lu, H., Tian, T., Du, B., Li, P., Yu, Y., Zhou, J., & Lu, H. (2024). High-Yield Expressed Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain Nanoparticles in K. marxianus for Functional Food Development. Foods, 13(18), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182919





