The Preparation of W/O/W High-Internal-Phase Emulsions as Coagulants for Tofu: The Effect of the Addition of Soy Protein Isolate in the Internal Water Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Soy Protein Isolate (SPI)
2.3. Fabrication of W/O/W HIPE
2.4. Evaluation of the Stability
2.5. Characterization of W/O/W HIPE
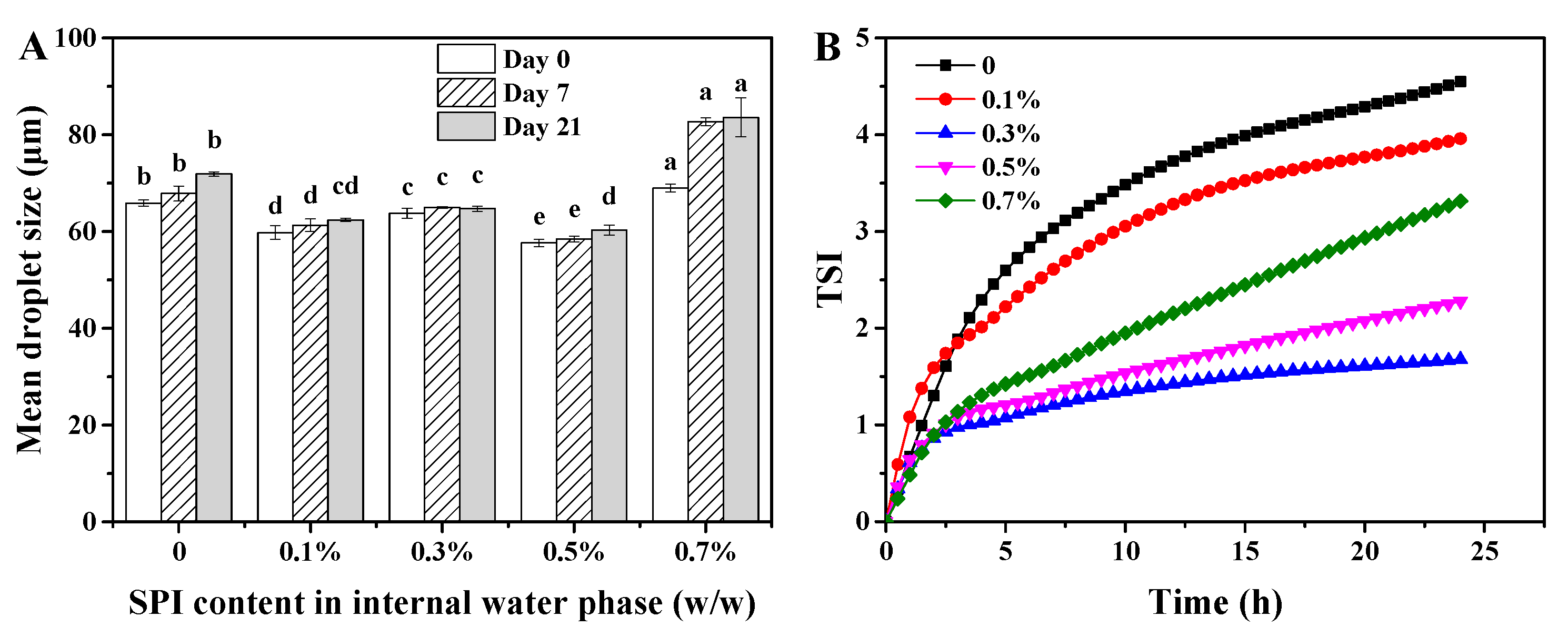
2.5.1. Measurement of Droplet Size
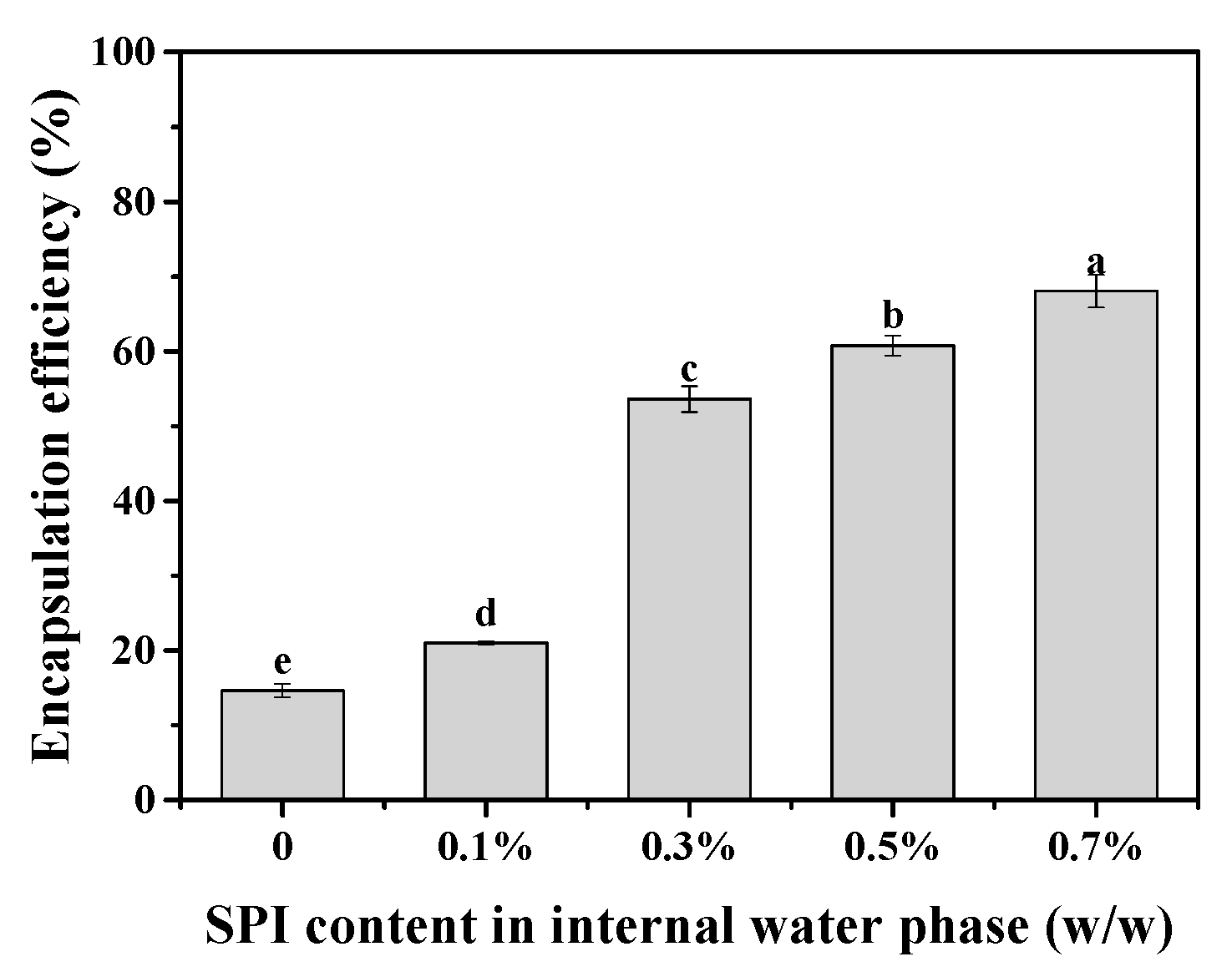
2.5.2. Encapsulation Efficiency of Magnesium Chloride
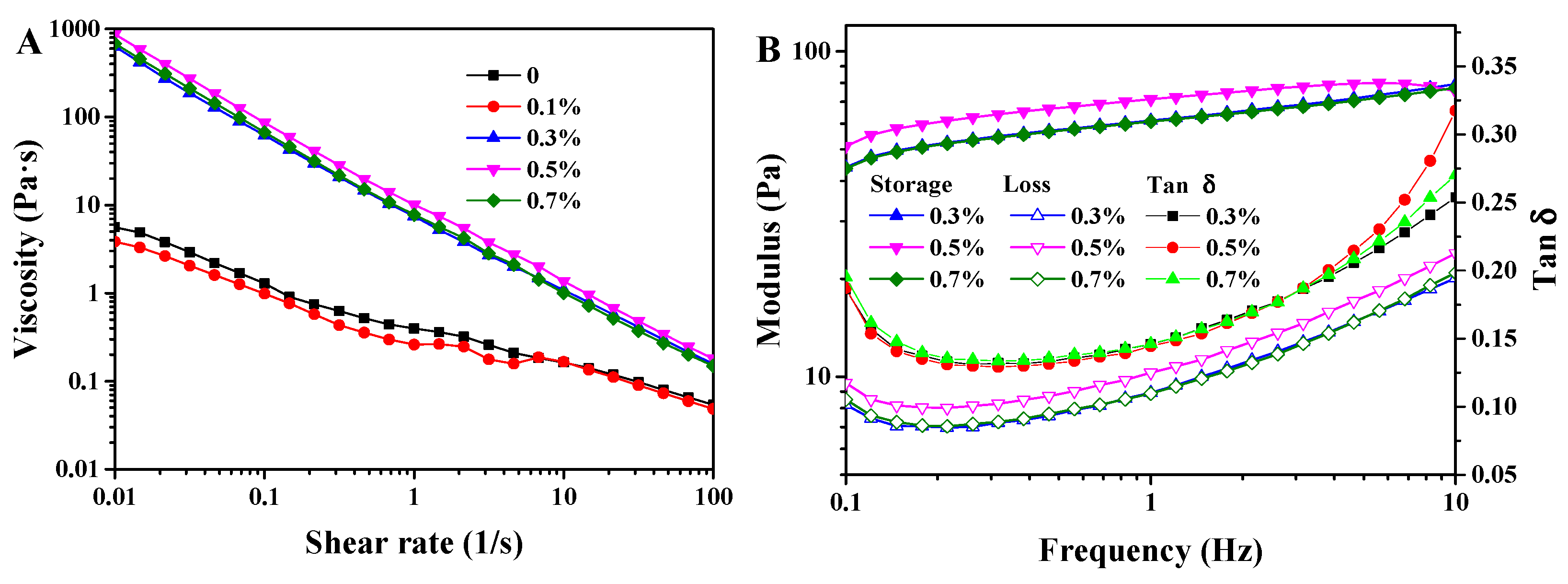
2.5.3. Rheological Behavior
2.5.4. Microstructure Observation
2.6. Application of W/O/W HIPE as a Coagulant for Tofu
2.6.1. Gelation Process Investigation
2.6.2. Tofu Preparation
2.6.3. Measurement of Tofu Yield and Tofu Water Content
2.6.4. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC) Determination
2.6.5. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
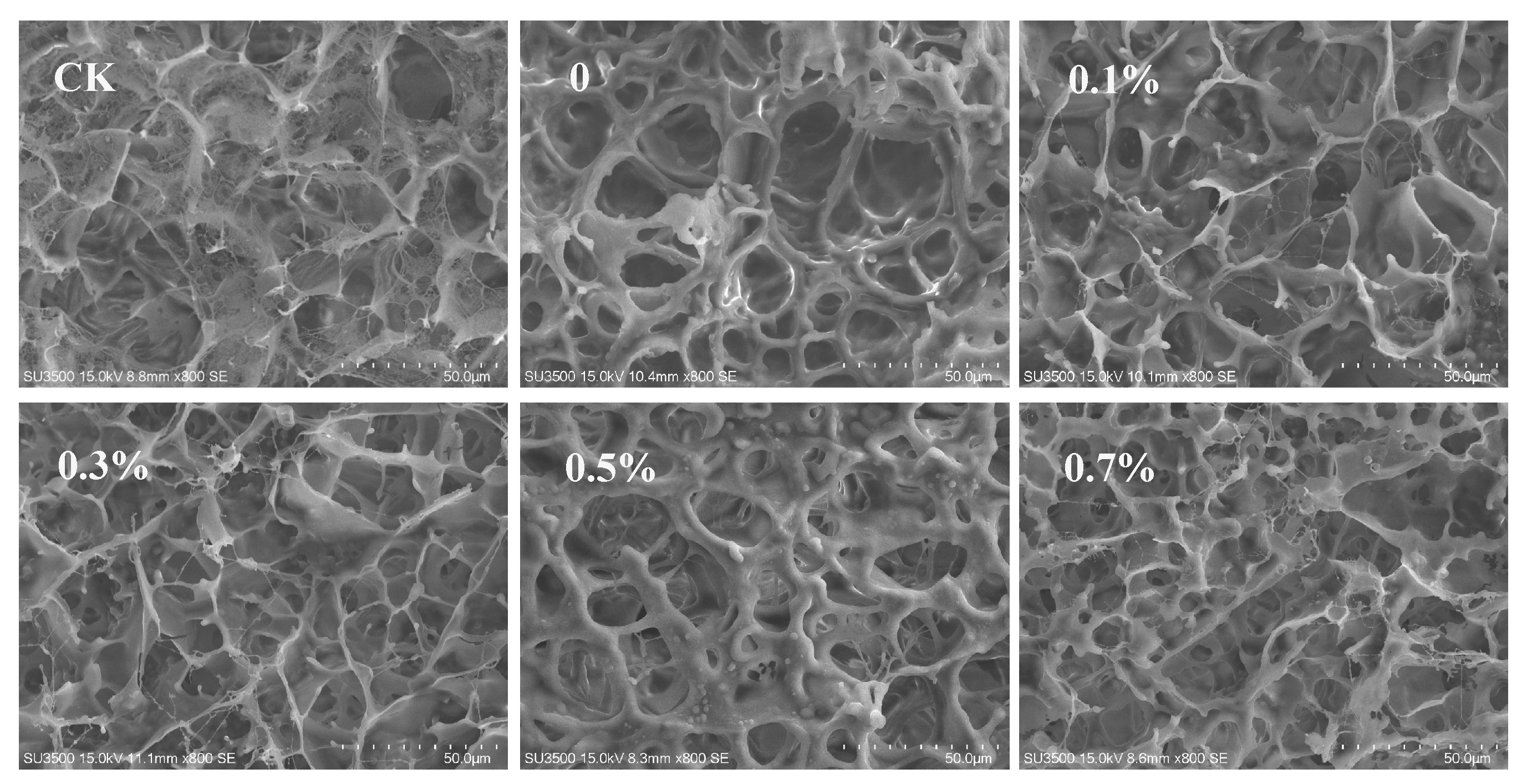
2.6.6. Scanning Electron Microscopic Observation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
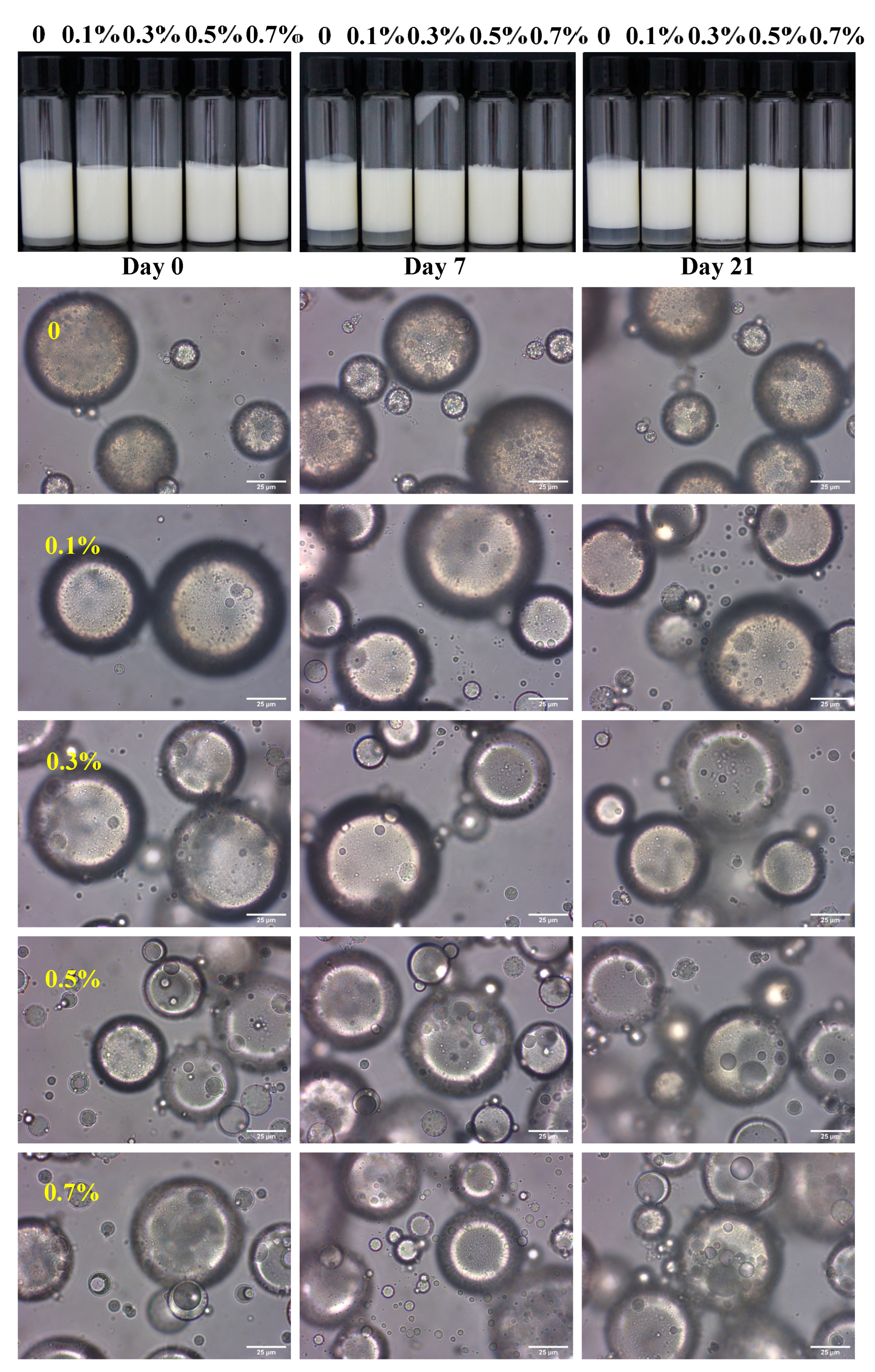
3.1. Storage Stability of W/O/W HIPE
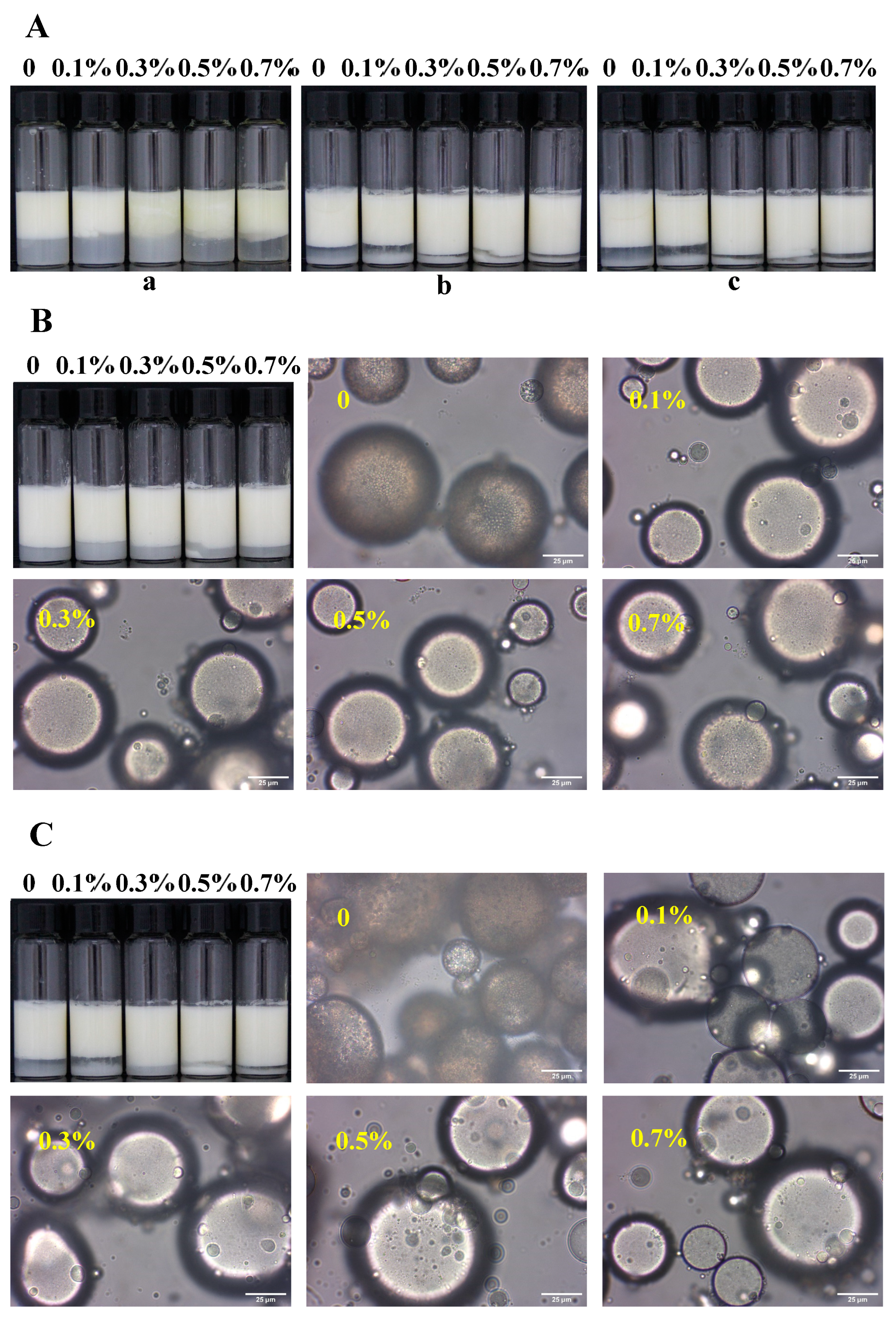
3.2. Freeze–Thaw Stability of W/O/W Emulsions
3.3. Rheological Behavior of W/O/W Emulsions
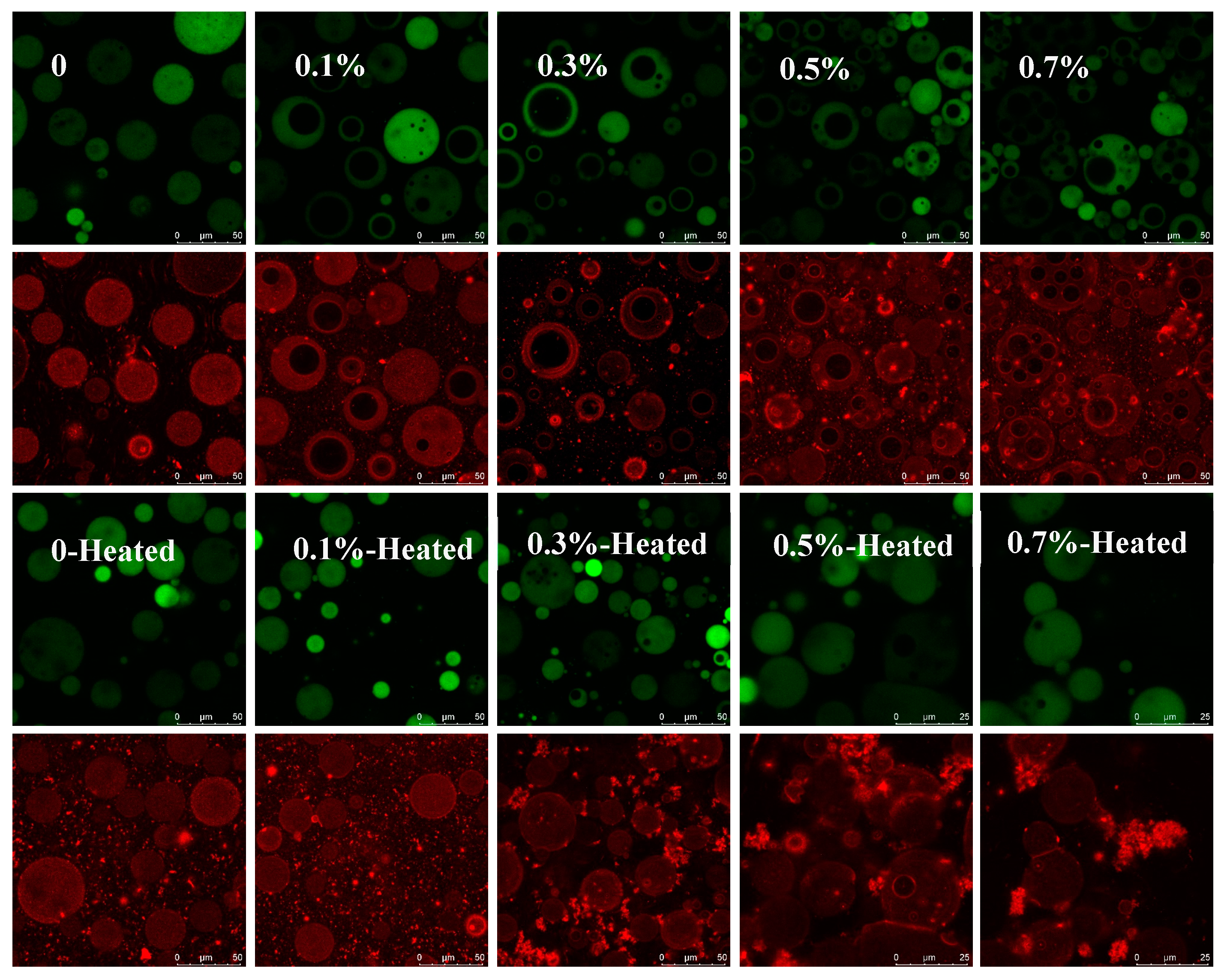
3.4. Microstructure of W/O/W Emulsions
3.5. Application of W/O/W HIPE as a Coagulant for Tofu
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Lin, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Research progress in tofu processing: From raw materials to processing conditions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1448–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Tian, K.; Wang, Z.X. Modern techniques efficacy on tofu processing: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 766–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Tofu products: A review of their raw materials, processing conditions, and packaging. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3683–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, M.P.; Perera, C.O.; Valiyaveettil, S. Effect of different coagulants on the isoflavone levels and physical properties of prepared firm tofu. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Tokita, M. Viscoelastic properties and microstructures of 11S globulin and soybean protein isolate gels: Magnesium chloride-induced gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.; Ritzoulis, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Liu, W. In vitro digestion of tofu with different textures using an artificial gastric digestive system. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, F.; Yang, B.; Lai, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, K.; Bu, G.; Fu, C.; Deng, Y. Preparation of organic tofu using organic compatible magnesium chloride incorporated with polysaccharide coagulants. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, Z.; Tatsumi, E.; Saito, M.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, L. A novel approach to improving the quality of bittern-solidified tofu by W/O controlled-release coagulant. 2: Using the improved coagulant in tofu processing and product evaluation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wu, F.; Saito, M.; Tatsumi, E.; Yin, L. Effect of magnesium salt concentration in water-in-oil emulsions on the physical properties and microstructure of tofu. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Tatsumi, E.; Saito, M.; Yin, L. The use of W/O/W controlled-release coagulants to improve the quality of bittern-solidified tofu. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Saito, M.; Yin, L. Impact of the release rate of magnesium ions in multiple emulsions (water-in-oil-in-water) containing BSA on the resulting physical properties and microstructure of soy protein gel. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, B.; Tong, L.T.; Lu, C.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, F. High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by soy protein isolate. J. Food Eng. 2022, 318, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, S.; Zhu, S. High internal phase emulsion with double emulsion morphology and their templated porous polymer systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 483, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Saito, M.; Tatsumi, E.; Yin, L. Development of stable water-in-oil emulsions using polyglycerol polyricinoleate and whey protein isolate and the impact on the quality of bittern-tofu. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 21st ed.; Latimer, G.W., Jr., Ed.; AOAC International: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 123–158. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.P.; Tang, C.H. Outstanding antioxidant Pickering high internal phase emulsions by co-assembled polyphenol-soy β-conglycinin nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V. Encapsulation of vitamin E in edible orange oil-in-water emulsion beverages: Influence of heating temperature on physicochemical stability during chilled storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, F.J.; Su, N.W.; Lee, M.H. Effect of calcium sulfate concentration in soymilk on the microstructure of firm tofu and the protein constitutions in tofu whey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6211–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppo, M.C.; Anon, M.C. Structural properties of heat-induced soy protein gels as affected by ionic strength and pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3583–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Kuo, M.I. Effect of γ-polyglutamate on the rheological properties and microstructure of tofu. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, C.; Khalid, N.; Qiu, S.; Yin, L. Effect of protein molecules and MgCl2 in the water phase on the dilational rheology of polyglycerol polyricinoleate molecules adsorbed at the soy oil-water interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Calderon, F.; Homer, S.; Goh, A.; Lundin, L. W/O/W emulsions with high internal droplet volume fraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, L. Physical stability, microstructure and micro-rheological properties of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions stabilized by porcine gelatin. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidts, T.; Dobler, D.; Nissing, C.; Runkel, F. Influence of hydrophilic surfactants on the properties of multiple W/O/W emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhaninia, M.; Nasirpour, A.; Shahedi, M.; Golkar, A. Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein aggregates: Effect of aggregate size, pH of aggregation and emulsion pH. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Ma, W.; Yu, P.; Li, T.; Wang, L. Assemble behavior of ultrasound-induced quinoa protein nanoparticles and their roles on rheological properties and stability of high internal phase emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Liu, F. Cold, gel-like soy protein emulsions by microfluidization: Emulsion characteristics, rheological and microstructural properties, and gelling mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, J.; Prakash, S. Rheological and textural properties of emulsion-filled gel based on enzymatically hydrolyzed rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapčíková, B.; Lapčík, L.; Valenta, T.; Chvatíková, M. Plant-Based Emulsions as Dairy Cream Alternatives: Comparison of Viscoelastic Properties and Colloidal Stability of Various Model Products. Foods 2024, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Hu, Y.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; Din, Z.U.; Huang, Q.; Liu, R. Influence of okara dietary fiber with varying particle sizes on gelling properties, water state and microstructure of tofu gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Xu, D.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y. Gelation of κ-carrageenan/Konjac glucommanan compound gel: Effect of cyclodextrins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, A.; Remondetto, G.E.; Subirade, M. Mechanisms involved in the formation and structure of soya protein cold-set gels: A molecular and supramolecular investigation. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Coagulant | CK | 0 | 0.1% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.7% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (g/500 mL) | 167.20 ± 9.71 d | 201.53 ± 4.31 bc | 187.21 ± 9.76 cd | 201.84 ± 6.86 bc | 222.17 ± 18.80 ab | 233.78 ± 16.14 a |
| Moisture (%) | 77.91 ± 0.22 d | 79.16 ± 0.48 bc | 78.03 ± 1.05 d | 78.22 ± 0.43 cd | 80.09 ± 0.71 b | 81.85 ± 0.35 a |
| WHC (%) | 58.76 ± 5.03 a | 55.18 ± 3.08 ab | 58.53 ± 3.85 a | 58.44 ± 1.02 a | 50.31 ± 2.70 b | 50.06 ± 4.42 b |
| Hardness | 211.02 ± 8.39 a | 86.02 ± 1.64 e | 138.94 ± 6.92 b | 112.76 ± 9.18 c | 101.48 ± 1.89 d | 88.06 ± 4.12 e |
| Cohesion | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 0.80 ± 0.02 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 0.79 ± 0.01 ab | 0.79 ± 0.02 ab | 0.76 ± 0.01 b |
| Springiness (%) | 93.25 ± 0.42 ab | 91.91 ± 3.12 ab | 93.52 ± 0.72 ab | 94.10 ± 0.54 a | 93.32 ± 0.32 ab | 91.12 ± 0.67 b |
| Gumminess | 170.40 ± 4.12 a | 68.57 ± 1.25 e | 112.24 ± 6.52 b | 88.97 ± 8.33 c | 79.83 ± 1.33 d | 67.17 ± 2.94 e |
| Chewiness | 158.89 ± 3.15 a | 63.02 ± 2.07 e | 104.98 ± 6.63 b | 83.70 ± 7.44 c | 74.49 ± 1.25 d | 61.20 ± 2.42 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. The Preparation of W/O/W High-Internal-Phase Emulsions as Coagulants for Tofu: The Effect of the Addition of Soy Protein Isolate in the Internal Water Phase. Foods 2024, 13, 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172748
Wang Y, Liu X, Zhang Q. The Preparation of W/O/W High-Internal-Phase Emulsions as Coagulants for Tofu: The Effect of the Addition of Soy Protein Isolate in the Internal Water Phase. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172748
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yongquan, Xuanbo Liu, and Qiang Zhang. 2024. "The Preparation of W/O/W High-Internal-Phase Emulsions as Coagulants for Tofu: The Effect of the Addition of Soy Protein Isolate in the Internal Water Phase" Foods 13, no. 17: 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172748
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, X., & Zhang, Q. (2024). The Preparation of W/O/W High-Internal-Phase Emulsions as Coagulants for Tofu: The Effect of the Addition of Soy Protein Isolate in the Internal Water Phase. Foods, 13(17), 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172748





