The Potential Mechanisms of Catechins in Tea for Anti-Hypertension: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
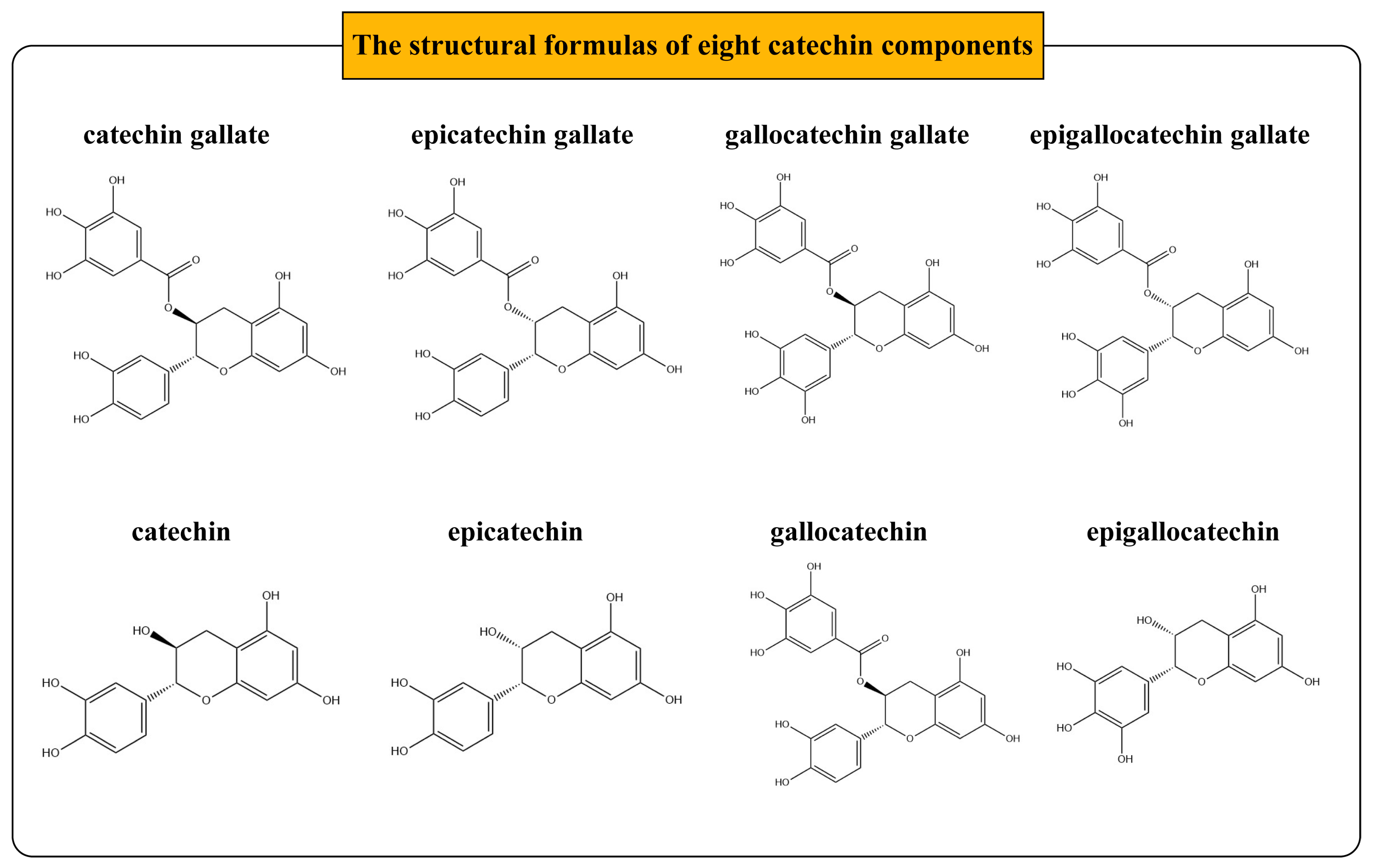
2.1. Collection of Catechin Targets
2.2. Screening of Hypertension-Related Targets
2.3. Screening of Key Targets and Construction and Analysis of the Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.4. GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Results
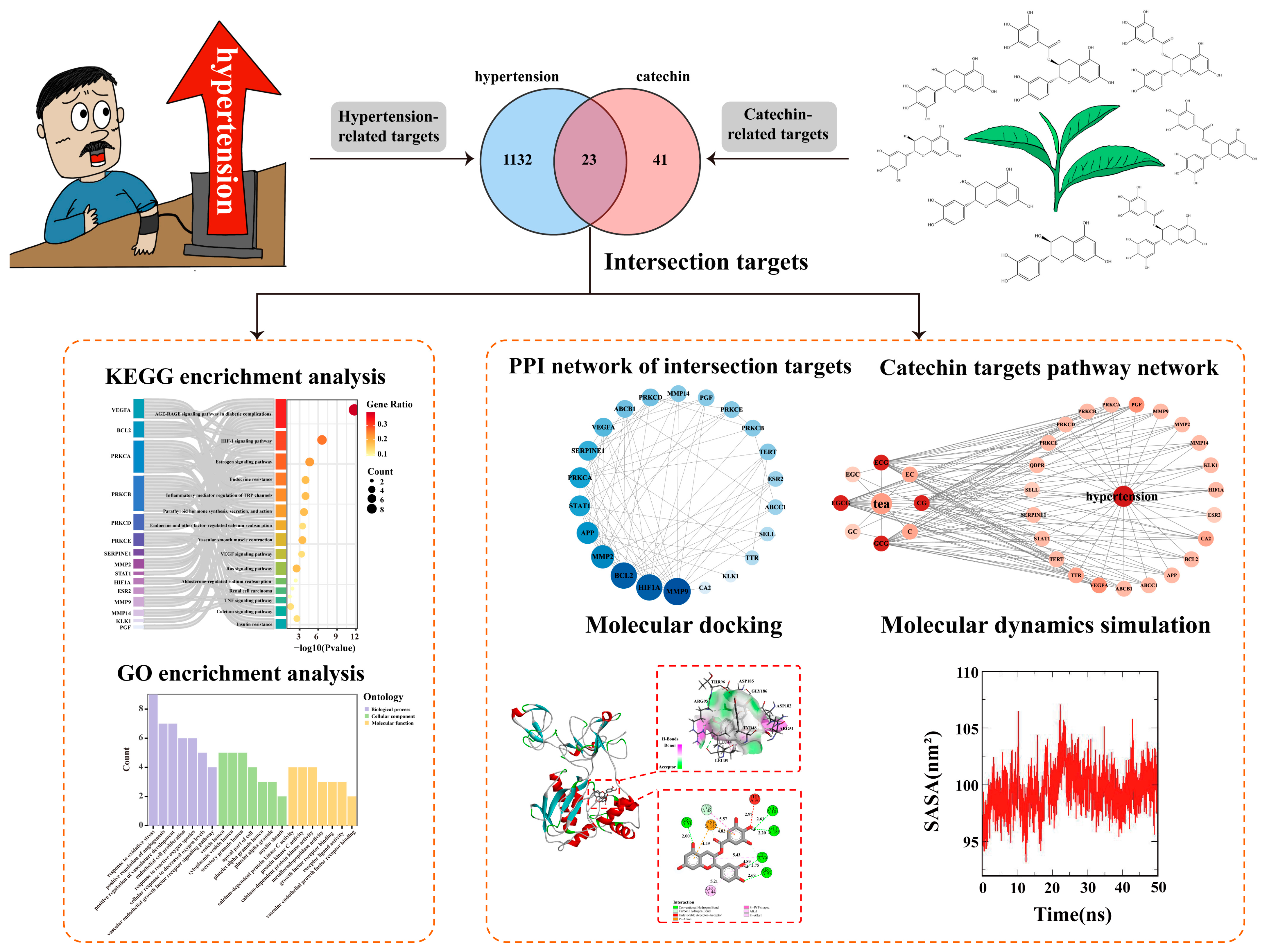
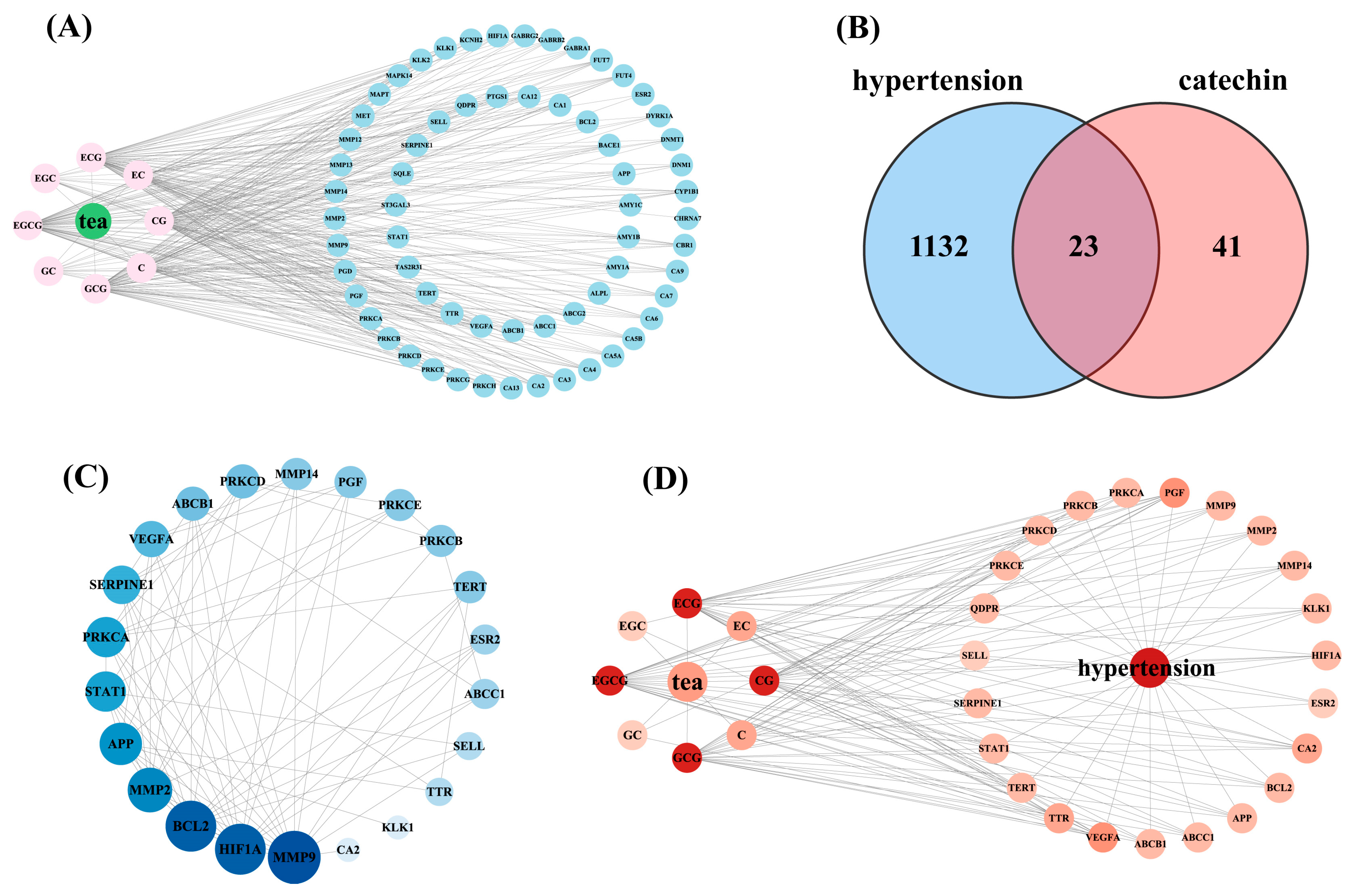
3.1. Screening of Potential Targets for the Anti-Hypertensive Effects of Catechin Components
3.2. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis and Key Target Screening
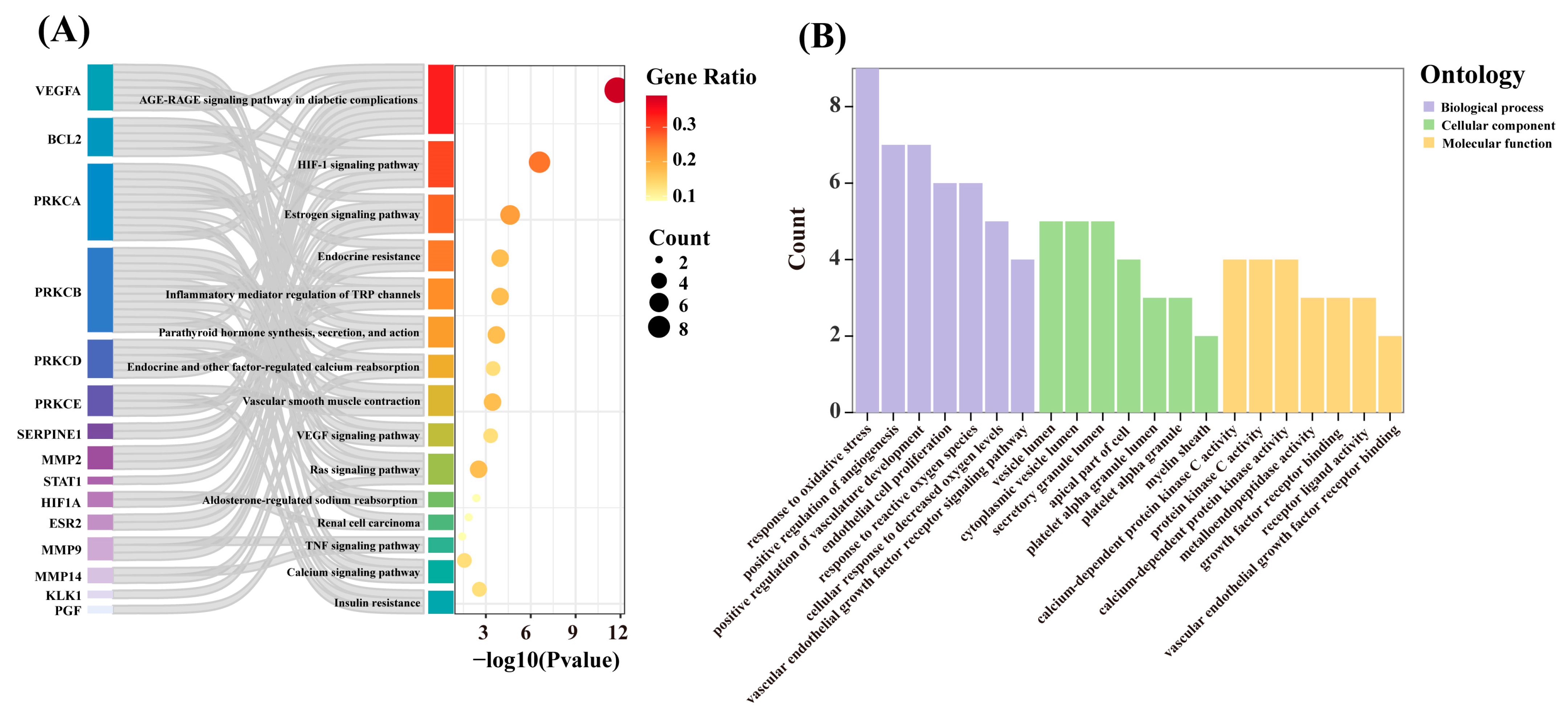
3.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Key Targets
3.4. Molecular Docking Verification
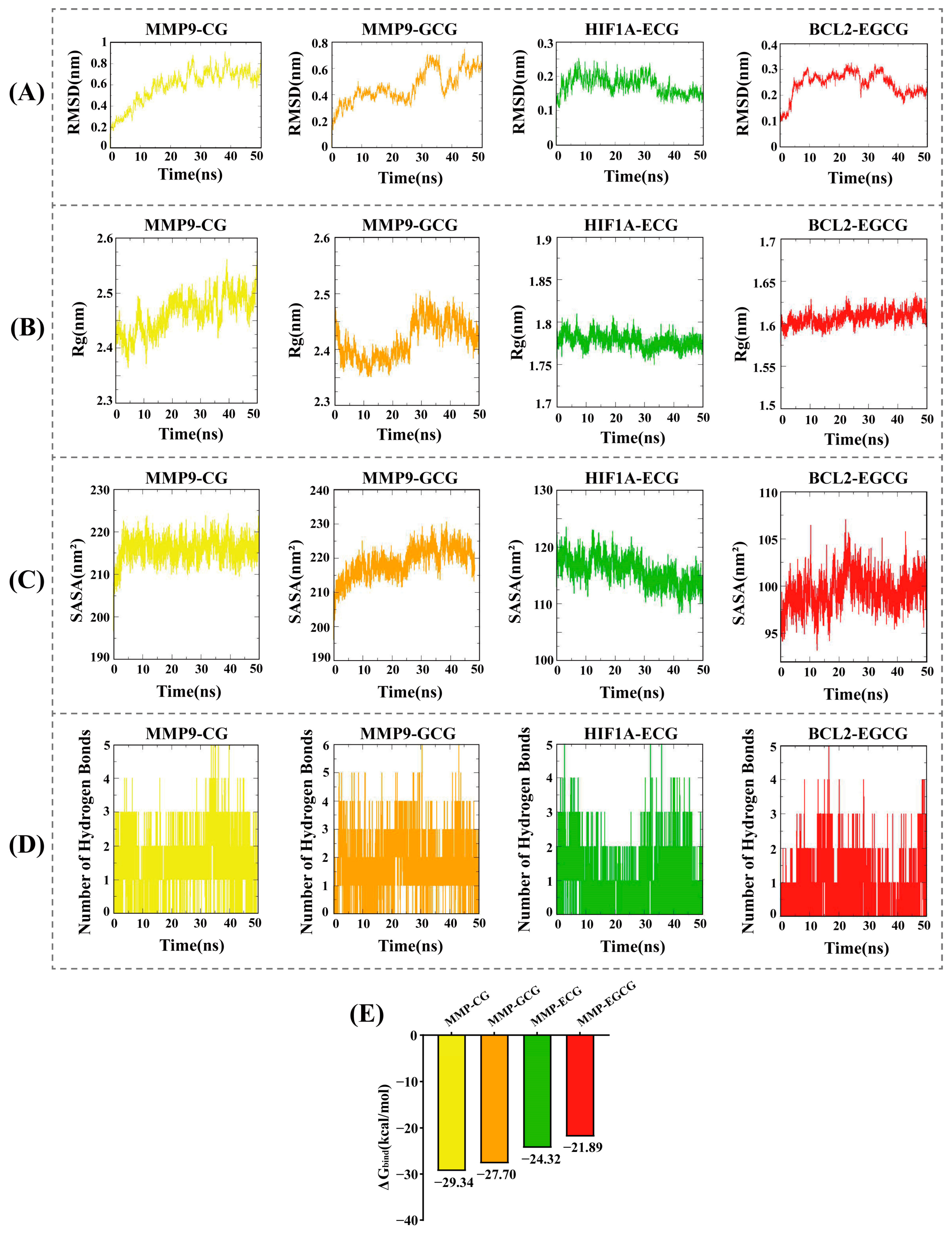
3.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Binding Free Energy Calculations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Major Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full name |
| HTN | hypertension |
| C | catechin |
| EC | epicatechin |
| GC | gallocatechin |
| EGC | epigallocatechin |
| CG | catechin gallate |
| ECG | epicatechin gallate |
| GCG | gallocatechin gallate |
| EGCG | epigallocatechin gallate |
| RMSD | root mean square deviation |
| Rg | radius of gyration |
| SASA | solvent-accessible surface area |
| MD | molecular dynamics |
| BP | biological process |
| CC | cellular component |
| MF | molecular function |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| ΔGbind | binding free energies |
References
- Li, H.; Guo, H.; Luo, Q.; Wu, D.-T.; Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.-B.; Gan, R.-Y. Current extraction, purification, and identification techniques of tea polyphenols: An updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 63, 3912–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.-F.; Jiang, C.-L.; Kong, Y.-S.; Luo, J.-L.; Yin, P.; Guo, G.-Y. Recent Advances in Analytical Methods for Determination of Polyphenols in Tea: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaghi, M.; Hoseyni, S.Z.; Tavasoli, S.; Mozafari, M.; Katouzian, I. Strategies of confining green tea catechin compounds in nano-biopolymeric matrices: A review. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Xia, G.; Liu, S. Modeling and comparison of extraction kinetics of 8 catechins, gallic acid and caffeine from representative white teas. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Hwang, K.; Lee, J.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, E.-M.; Park, J.; Cho, J.Y. Skin Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounekti, T.; Joubert, E.; Hernández, I.; Munné-Bosch, S. Improving the Polyphenol Content of Tea. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2012, 32, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cao, R. Angiogenesis inhibited by drinking tea. Nature 1999, 398, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orita, T.; Chogahara, S.; Okuda, M.; Sakao, K.; Miyata, T.; Hou, D.-X. Extraction Efficiency and Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities of Green Tea Catechins by Different Infusion Methods. Foods 2023, 12, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, A.; Braunwald, E. Treatment of hypertension addressing a global health problem. JAMA 2018, 320, 1751–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Aziz, S.; Akram, T.; Amjad, F.; Iqtidar, K.; Nam, Y.; Khan, M.A. Expert Hypertension Detection System Featuring Pulse Plethysmograph Signals and Hybrid Feature Selection and Reduction Scheme. Sensors 2021, 21, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, S.M.; Reynier, P.; Platt, R.W.; Basso, O.; Filion, K.B. The timing of onset of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy and the risk of incident hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 270, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On-Nom, N.; Khaengamkham, K.; Kettawan, A.; Rungruang, T.; Suttisansanee, U.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Prangthip, P.; Chupeerach, C. Parboiled Germinated Brown Rice Improves Cardiac Structure and Gene Expression in Hypertensive Rats. Foods 2022, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Montaniel, K.R.C.; Saleh, M.A.; Xiao, L.; Chen, W.; Owens, G.K.; Humphrey, J.D.; Majesky, M.W.; Paik, D.T.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; et al. The Origin of Matrix-Producing Cells That Contribute to Aortic Fibrosis in Hypertension. Hypertension 2016, 67, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.-F.; Qiu, C.-S.; Wang, S.-L.; Huang, L.-F.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G. A Cross-sectional Study of the Relationship Between Habitual Tea Consumption and Arterial Stiffness. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 35, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.M.; Croft, K.D. Tea flavonoids and cardiovascular health. Mol. Asp. Med. 2010, 31, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Kroon, P.A.; Rimm, E.B.; Cohn, J.S.; Harvey, I.; Le Cornu, K.A.; Ryder, J.J.; Hall, W.L.; Cassidy, A. Flavonoids, flavonoid-rich foods, and cardiovascular risk: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.L.; Pontes, R.B.; Nishi, E.E.; Ibuki, F.K.; Oliveira, V.; Sawaya, A.; Carvalho, P.O.; Nogueira, F.N.; Franco, M.D.; Campos, R.R.; et al. The antioxidant effects of green tea reduces blood pressure and sympathoexcitation in an experimental model of hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Seppia, C.; Federighi, G.; Lapi, D.; Gerosolimo, F.; Scuri, R. Effects of a catechins-enriched diet associated with moderate physical exercise in the prevention of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.A.M.; Lee, S.-K.; Murugan, D.D.; Ling, W.C. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) alleviates vascular dysfunction in angiotensin II-infused hypertensive mice by modulating oxidative stress and eNOS. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zheng, J.-H.; Li, S. TCM network pharmacology: A new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Long, X.; Yin, S.; Hu, G.; Yang, X.; Jian, W.; Yu, R. Study on the mechanism of action of colchicine in the treatment of coronary artery disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1147360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, G.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Teng, W.; Jin, G.; Geng, F.; Cao, J. Research advances of molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation in recognizing interaction between muscle proteins and exogenous additives. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.H.; Jeong, S.; Ahn, D.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, H. Network pharmacology and molecular docking approaches to elucidate the potential compounds and targets of Saeng-Ji-Hwang-Ko for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.G.; Kantevari, S.; Guru, S.K.; Naik, P.K. Combination of docetaxel and newly synthesized 9-Br-trimethoxybenzyl-noscapine improve tubulin binding and enhances antitumor activity in breast cancer cells. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 139, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wen, R.; Liu, D.; Yan, L.; Gong, Q.; Yu, H. Assessment of the Potential of Sarcandra glabra (Thunb.) Nakai. in Treating Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rats Based on Metabolomics and Network Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 810344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.; Mitro, A.; Hoque, H.; Hasan, N.; Jewel, G.N.A. Identification of potential novel therapeutic drug target against Elizabethkingia anophelis by integrative pan and subtractive genomic analysis: An in silico approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 165, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, A.; Kotynia, A.; Szkatuła, D.; Krzyżak, E. The 2-hydroxy-3-(4-aryl-1-piperazinyl)propyl Phthalimide Derivatives as Prodrugs—Spectroscopic and Theoretical Binding Studies with Plasma Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, G. Advances in the Anti-Atherosclerotic Mechanisms of Epigallocatechin Gallate. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.-L.; Xiao, H.-B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hu, L.-K.; Chen, N.; Chu, X.; Dong, J.; Yan, Y.-X. Association between systemic immune inflammatory/inflammatory response index and hypertension: A cohort study of functional community. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 34, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Owusu, L.; Duan, W.; Jiang, T.; Zang, S.; Ahmed, A.; Xin, Y. Anti-metastatic and differential effects on protein expression of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in HCCLM6 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, B. Cellular antioxidant, methylglyoxal trapping, and anti-inflammatory activities of cocoa tea (Camellia ptilophylla Chang). Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, T.; Mohri, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Kashima, A.; Kamo, T.; Hirota, M.; Kiyota, H.; Makabe, H. Synthesis of (−)-Epicatechin 3-(3-O-Methylgallate) and (+)-Catechin 3-(3-O-Methylgallate), and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, I. Multifunctional effects of green tea catechins on prevention of the metabolic syndrome. Asia Pac. J. Clin Nutr. 2008, 17, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Redford, K.E.; Rognant, S.; Jepps, T.A.; Abbott, G.W. KCNQ5 Potassium Channel Activation Underlies Vasodilation by Tea. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mims, P.N.; Zhu, T.; Fan, F.; Roman, R.J. Abstract 097: Knockout of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Protects Against Hypertension-induced Renal Disease in Hypertensive Dahl S Rats. Hypertension 2017, 70, A097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunova, A.Y.; Blagonravov, M.L.; Neborak, E.V.; Syatkin, S.P.; Sklifasovskaya, A.P.; Semyatov, S.M.; Agostinelli, E. BCL2-regulated apoptotic process in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 47, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerraty, M.A.; Szapary, H.J.; Berrido, A.; Arany, Z.P.; Rader, D.J. Abstract 219: Role of Transcription Co-Factor Friend of GATA 2 (FOG2) in a Hypertensive-Diabetic Mouse Model of Coronary Microvascular Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, A455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Alves-Lopes, R.; Rios, F.J.; Camargo, L.L.; Anagnostopoulou, A.; Arner, A.; Montezano, A.C. Vascular smooth muscle contraction in hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.-Q.; Zhang, W.-M.; Liang, Z.; Piao, C.; Zhu, G. Identification of Signal Pathways and Hub Genes of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension by Bioinformatic Analysis. Can. Respir. J. 2022, 2022, 1394088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, R.; Poglitsch, M.; Davis, D.; Huang, H.; Schadler, A.; Patel, N.; Vignes, K.; Srinivasan, A.; Cockerham, C.; Bauer, J.A.; et al. Association of Elevated Serum Aldosterone Concentrations in Pregnancy with Hypertension. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.J.; Joiner, M.-L.A.; Singh, M.V.; Luczak, E.D.; Swaminathan, P.D.; Koval, O.M.; Kutschke, W.; Allamargot, C.; Yang, J.; Guan, X.; et al. Oxidation of CaMKII determines the cardiotoxic effects of aldosterone. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, M.A.F.; Grimm, D.; Bauer, J.; Wehland, M.; Wise, P.; Magnusson, N.E.; Infanger, M.; Krüger, M. Hypertension Caused by Lenvatinib and Everolimus in the Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X. MMP9 and IGFBP1 Regulate Tumor Immune and Drive Tumor Progression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yan, N.; Sun, W.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Hao, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. miR-4521-FAM129A axial regulation on ccRCC progression through TIMP-1/MMP2/MMP9 and MDM2/p53/Bcl2/Bax pathways. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound Name | Affinity (kcal/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP9 | HIF1A | BCL2 | Mean | |
| CG | −8.9 | −8.6 | −6.5 | −8.0 |
| GCG | −8.9 | −8.4 | −6.5 | −7.9 |
| ECG | −8.0 | −8.8 | −6.2 | −7.7 |
| EGCG | −8.0 | −8.5 | −6.7 | −7.7 |
| Mean | −8.5 | −8.6 | −6.5 | |
| enalapril | −7.1 | −6.7 | −6.0 | −6.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuo, Y.; Lu, X.; Tao, F.; Tukhvatshin, M.; Xiang, F.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, Y. The Potential Mechanisms of Catechins in Tea for Anti-Hypertension: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Foods 2024, 13, 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172685
Tuo Y, Lu X, Tao F, Tukhvatshin M, Xiang F, Wang X, Shi Y, Lin J, Hu Y. The Potential Mechanisms of Catechins in Tea for Anti-Hypertension: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172685
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuo, Yanming, Xiaofeng Lu, Fang Tao, Marat Tukhvatshin, Fumin Xiang, Xi Wang, Yutao Shi, Jinke Lin, and Yunfei Hu. 2024. "The Potential Mechanisms of Catechins in Tea for Anti-Hypertension: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation" Foods 13, no. 17: 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172685
APA StyleTuo, Y., Lu, X., Tao, F., Tukhvatshin, M., Xiang, F., Wang, X., Shi, Y., Lin, J., & Hu, Y. (2024). The Potential Mechanisms of Catechins in Tea for Anti-Hypertension: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Foods, 13(17), 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172685






