Impact of Germination on the Edible Quality and Nutritional Properties of Brown Rice Noodles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Germinated Brown Rice
2.3. Preparation of Germinated Brown Rice Noodles
2.4. Determination of Cooking Quality
2.5. Determination of Texture Properties
2.6. Appearance and Microscopic Structure of Germinated Brown Rice Noodles
2.7. Odor and Flavor of Germinated Brown Rice Noodles
2.8. Basic Components of Germinated Brown Rice Noodles
2.9. Determination of γ-Aminobutyric Acid in Brown Rice Noodles
2.10. Polyphenols in Germinated Brown Rice Noodles
2.10.1. Extraction of Free Polyphenols
2.10.2. Extraction of Bound Polyphenols
2.10.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.11. Resistant Starch Content
2.12. Statistics Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Germination on the Cooking, Textural, and Sensory Quality of Brown Rice Noodles
3.1.1. Cooking and Textural Properties
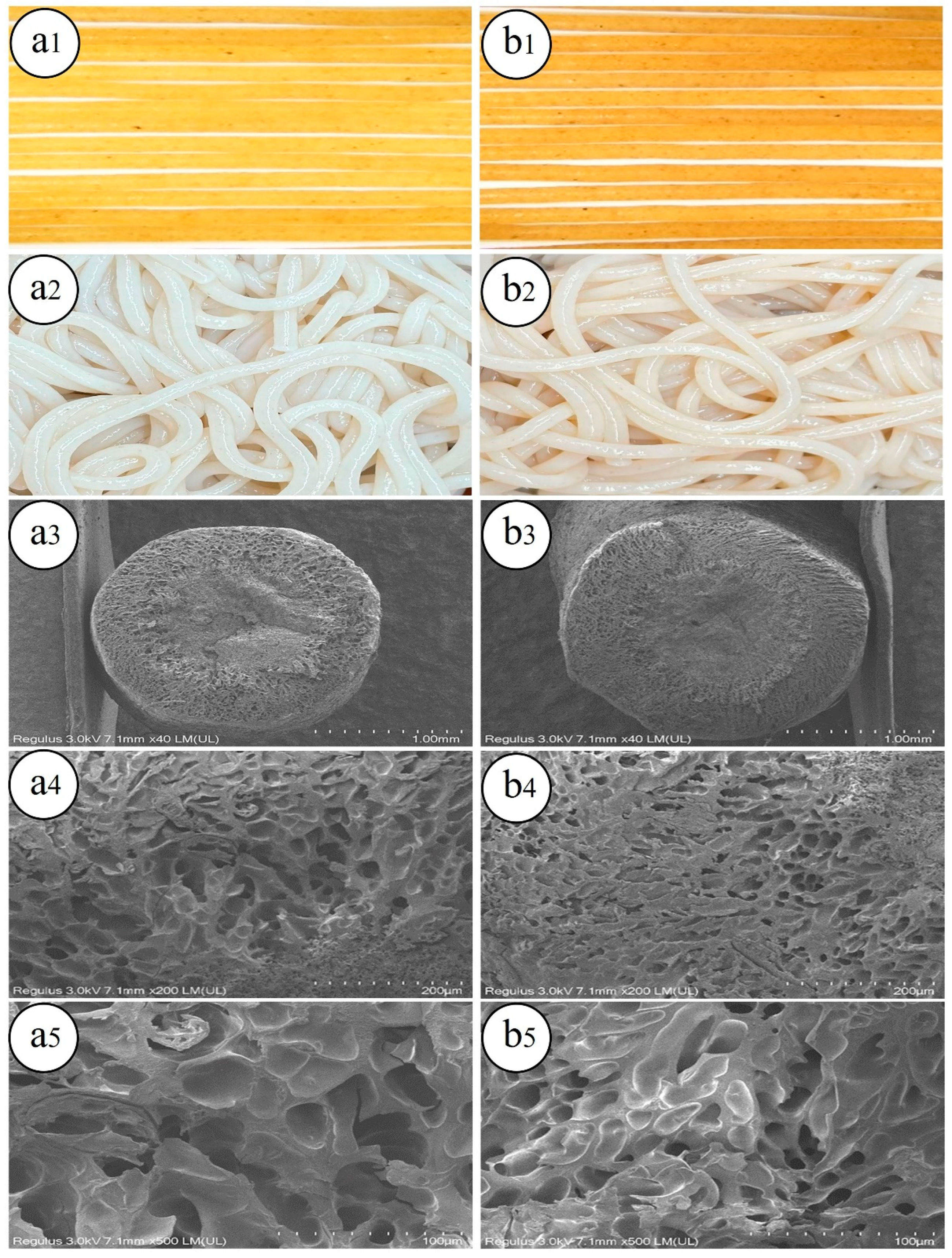
3.1.2. Appearance and Color
3.1.3. Microstructure
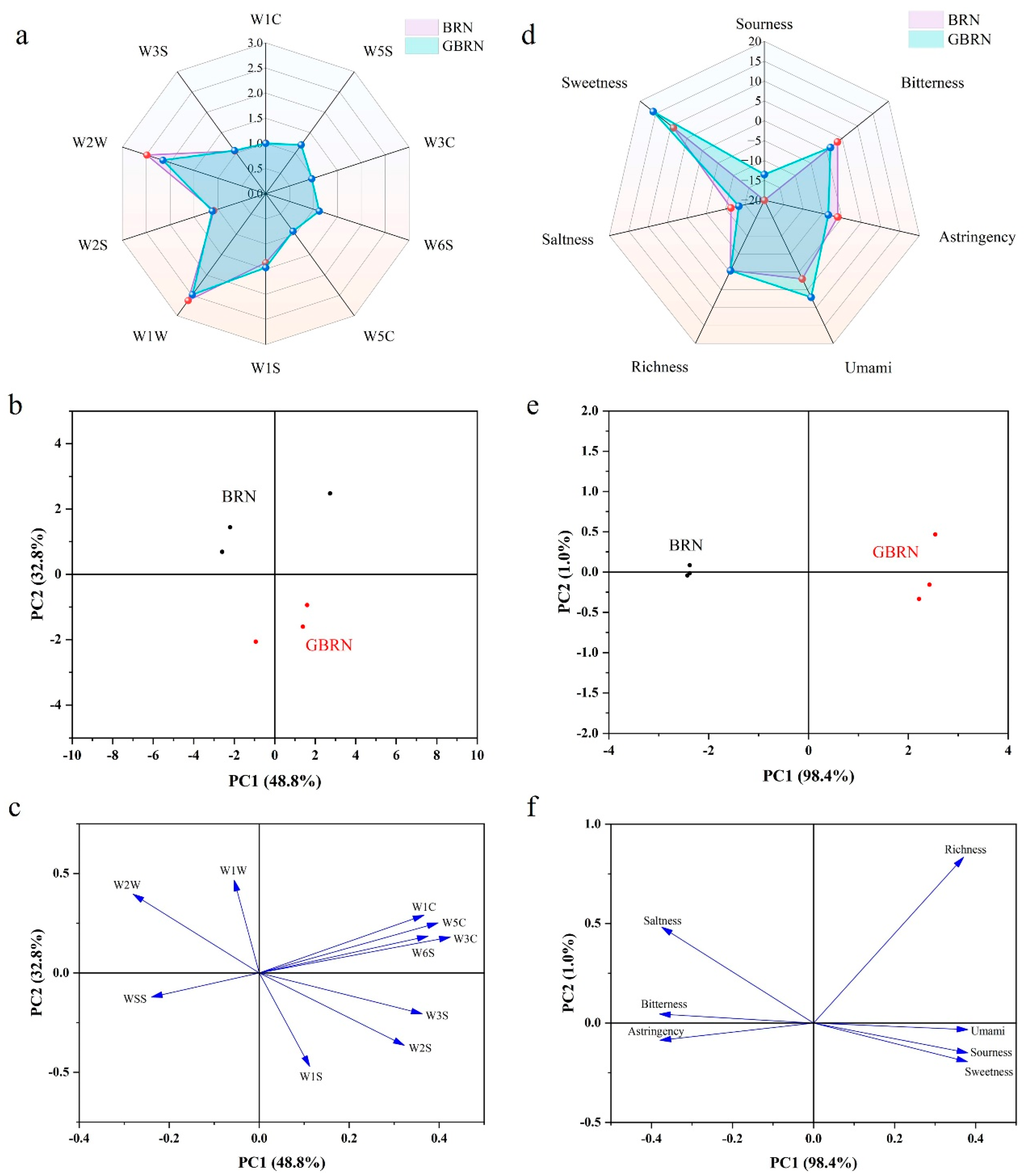
3.1.4. Smell and Taste
3.2. Effect of Germination on the Nutritional Quality of Brown Rice Noodles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.M.; You, Y.X.; Chen, D.; Gu, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Holler, T.P.; Ban, X.F.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.F. A systematic review of rice noodles: Raw material, processing method and quality improvement. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.D.; Liu, C.M.; Huang, A.; Chen, R.Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, S.J. The nutritional components and physicochemical properties of brown rice flour ground by a novel low temperature impact mill. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 92, 102927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lyu, Q.; Zhuang, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, W. Impact of different preparation methods on the properties of brown rice flour and the cooking stability of brown rice noodles and the underlying mechanism: Microstructure, starch-protein distribution, moisture migration. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 181, 114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Xie, L.; Cao, Z.; Quan, K.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, J. Effects of rice bran fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum on palatability, volatile profiles, and antioxidant activity of brown rice noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 5048–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.H.; Lin, Z.X.; Liu, L.; Qin, W.Y.; Wang, A.X.; Wang, F.Z.; Tong, L.T. Effects of ultrasound-assisted cellulase enzymatic treatment on the textural properties and in vitro starch digestibility of brown rice noodles. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. New perspectives on physiological, biochemical and bioactive components during germination of edible seeds: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, L.Á.; Abhilasha, A.; Singh, J.; Elias, M.C.; Colussi, R. Rice Germination and Its Impact on Technological and Nutritional Properties: A Review. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, I.G.; Kim, T.M.; Wood, K.S.; Park, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.R.; Jeong, H.S. Chemical and functional components in different parts of rough rice (Oryza sativa L.) before and after germination. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, M.; Quílez, J.; Rafecas, M. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a bioactive compound in foods: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, L.K.; Bian, X.; Liu, X.F.; Chen, F.L.; Tan, B.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, N. Effects of germination time on the structural, physicochemical and functional properties of brown rice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 57, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, P.J.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Amigo, L.; Frias, J. Maximising the phytochemical content and antioxidant activity of Ecuadorian brown rice sprouts through optimal germination conditions. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, S.; Huang, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, C. Chinese rice noodles form the viscoelastic texture by dual high-temperature retrogradation: An insight into the mechanism. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 189, 115496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.F.; Meng, Y.P.; Yang, N.; Tao, H.; Xu, X.M. Effects of mung bean starch on quality of rice noodles made by direct dry flour extrusion. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.J.; Zhou, B.B.; Cheng, L.L.; Huang, J.Y.; Zou, P.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Huang, S.J.; Chen, T.T.; Liu, C.M.; Wu, J.Y. Pre-fermentation of rice flour for improving the cooking quality of extruded instant rice. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, M.N.; Shan, C.S.; Chen, Z.G. Effects of potato starch on the characteristics, microstructures and quality attributes of indica rice flour and instant rice noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.X.; Yi, C.; Xiao, T.; Qin, W.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.T. Volatile compounds, bacteria compositions and physicochemical properties of 10 fresh fermented rice noodles from southern China. Food Res. Int. 2019, 150, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Teng, C.; Zou, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Ren, G.; Qin, P. The gluten structure, starch digestibility and quality properties of pasta supplemented with native or germinated quinoa flour. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelp, B.J.; Bozzo, G.G.; Trobacher, C.P.; Chiu, G.; Bajwa, V.S. Strategies and tools for studying the metabolism and function of γ-aminobutyrate in plants. I. Pathway structure. Botany 2012, 90, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.C.; Hu, X.T.; McClements, D.J.; Luo, S.J.; Liu, C.M.; Gong, E.S.; Huang, K.C. Hydrothermal stability of phenolic extracts of brown rice. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Hudson, G.J. The classification and measurement of dietary carbohydrates. Food Chem. 1996, 57, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Ji, N.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, T.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. The effect of hydroxypropyl starch on the improvement of mechanical and cooking properties of rice noodles. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobha, D.; Vijayalakshmi, D.; Puttaramnaik; Asha, K.J. Effect of maize based composite flour noodles on functional, sensory, nutritional and storage quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2015, 52, 8032–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Hu, H.; Yang, J.; Wu, T.; Sun, X.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Q. Mechanistic study of the impact of germinated brown rice flour on gluten network formation, dough properties and bread quality. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 83, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-J.; Cho, A.; Lim, S.-T. Effect of heat-moisture treatment for utilization of germinated brown rice in wheat noodle. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Z.; Wei, Y.M.; Wang, C.; Kovacs, M.I.P. Quantitative assessment of protein fractions of Chinese wheat flours and their contribution to white salted noodle quality. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-J.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Wang, C.-F.; Liu, C.-X.; Qiao, Y.-J. Effect of ultrasound-assisted enzyme pretreatment on γ-aminobutyric acid content, eating quality and starch properties of germinated brown rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 117, 103904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Gao, C.; Cheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Shen, X.; Tang, X. Construction of starch-sodium alginate interpenetrating polymer network and its effects on structure, cooking quality and in vitro starch digestibility of extruded whole buckwheat noodles. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kovacs, M.I.P.; Fowler, D.B.; Holley, R. Effects of protein content and composition on white noodle making quality: Color. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcu, T.C.; Bilgicli, N. Effect of germinated and heat-moisture treated ancient wheat on some quality attributes and bioactive components of noodles. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Bareen, M.A.; Sahu, J.K.; Saha, S. Effect of high-pressure treatment and germination on the functional, rheological, and microstructural characteristics of red quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Tuo, Y.; Dang, J.; Wang, W.; You, H.; Du, S.; Wang, L.; Ding, L. Influence of germination and roasting on the characteristic volatile organic compounds of quinoa using sensory evaluation, E-nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.H.; Lim, S.T. Germinated brown rice and its bio-functional compounds. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Li, D.; Tao, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, R.; Han, Y. Effect of static magnetic field treatment on the germination of brown rice: Changes in α-amylase activity and structural and functional properties in starch. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Tao, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, D. Effect of static magnetic field treatment on γ-aminobutyric acid content and sensory characteristics of germinated brown rice cake. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaijan, M.; Panpipat, W. Nutritional composition and bioactivity of germinated Thai indigenous rice extracts: A feasibility study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, G.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H.S. Antioxidative and antidiabetic effects of germinated rough rice extract in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C57BLKS/J-db/db mice. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukpong, E.S.; Onyeka, E.U.; Oladeji, B.S. Bioactive compounds, nutrients and pasting properties of parboiled milled rice, brown rice and germinated brown rice of selected cultivars and the effects of germination durations. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.C.; Boue, S.M.; Goufo, P. Health-promoting germinated rice and value-added foods: A comprehensive and systematic review of germination effects on brown rice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 11570–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ti, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Deng, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y. Dynamic changes in the free and bound phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of brown rice at different germination stages. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Lim, S.T. Changes in phenolic acid composition and associated enzyme activity in shoot and kernel fractions of brown rice during germination. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.N.; Li, R.; Li, Z.J.; Tan, B. Effect of germination in the form of paddy rice and brown rice on their phytic acid, GABA, gamma-oryzanol, phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant capacity. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, S.A.; Rafiq, S.; Singh, J.; Mir, S.A.; Sharma, S.; Bakshi, P.; McClements, D.J.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Dar, B.N. Impact of germination on structural, physicochemical, techno-functional, and digestion properties of desi chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) flour. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 135011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Gao, J.; Feng, B. Effects of germination on the physicochemical, nutritional and in vitro digestion characteristics of flours from waxy and nonwaxy proso millet, common buckwheat and pea. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Dai, Z.; Nickerson, M.T.; Sopiwnyk, E.; Malcolmson, L.; Ai, Y. Impacts of short-term germination on the chemical compositions, technological characteristics and nutritional quality of yellow pea and faba bean flours. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinma, C.E.; Abu, J.O.; Asikwe, B.N.; Sunday, T.; Adebo, O.A. Effect of germination on the physicochemical, nutritional, functional, thermal properties and in vitro digestibility of Bambara groundnut flours. LWT 2021, 140, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | BRN | GBRN |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking times (s) | 709.67 ± 5.51 * | 667.33 ± 4.62 |
| Cooking loss (%) | 10.07 ± 0.68 * | 8.30 ± 0.30 |
| Breaking rate (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Hardness (g) | 493.71 ± 11.20 * | 438.15 ± 8.20 |
| Adhesiveness (g·s) | 1.25 ± 0.09 * | 0.82 ± 0.04 |
| Chewiness (g) | 624.88 ± 13.90 * | 473.46 ± 6.72 |
| Samples | L* | a* | b* | WI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncooked | ||||
| BRN | 48.36 ± 0.72 | 1.59 ± 0.03 | 8.41 ± 0.34 | 47.65 ± 0.68 |
| GBRN | 48.43 ± 0.33 | 2.29 ± 0.06 * | 10.43 ± 0.28 * | 47.33 ± 0.38 |
| Cooked | ||||
| BRN | 69.52 ± 0.40 * | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 10.67 ± 0.12 * | 67.71 ± 0.35 * |
| GBRN | 66.23 ± 0.16 | 0.70 ± 0.05 * | 9.66 ± 0.31 | 64.87 ± 0.17 |
| Samples | BRN | GBRN |
|---|---|---|
| Total starch (%) | 81.79 ± 0.37 * | 75.38 ± 0.63 |
| Dietary fiber (%) | 3.56 ± 0.13 | 6.15 ± 0.01 * |
| Lipids (%) | 0.65 ± 0.00 | 0.73 ± 0.00 * |
| Proteins | 6.90 ± 0.22 | 7.01 ± 0.16 |
| GABA (mg/100 g) | 33.63 ± 0.93 | 51.60 ± 0.54 * |
| Free phenolic acid (µg/g) | 129.13 ± 0.97 | 157.16 ± 5.41 * |
| Bound phenolic acid (µg/g) | 384.81 ± 10.68 | 412.28 ± 6.06 * |
| Resistant starch (%) | 27.61 ± 0.55 * | 21.66 ± 1.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, R.; Yan, X.; Cai, M.; Cai, J.; Dai, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Impact of Germination on the Edible Quality and Nutritional Properties of Brown Rice Noodles. Foods 2024, 13, 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132152
Chen R, Yan X, Cai M, Cai J, Dai T, Liu Y, Wu J. Impact of Germination on the Edible Quality and Nutritional Properties of Brown Rice Noodles. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132152
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ruiyun, Xudong Yan, Mingxi Cai, Jiamei Cai, Taotao Dai, Yunfei Liu, and Jianyong Wu. 2024. "Impact of Germination on the Edible Quality and Nutritional Properties of Brown Rice Noodles" Foods 13, no. 13: 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132152
APA StyleChen, R., Yan, X., Cai, M., Cai, J., Dai, T., Liu, Y., & Wu, J. (2024). Impact of Germination on the Edible Quality and Nutritional Properties of Brown Rice Noodles. Foods, 13(13), 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132152





