Contamination of Streptococcus suis and S. suis Serotype 2 in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs: A Public Health Concern in Chiang Mai, Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
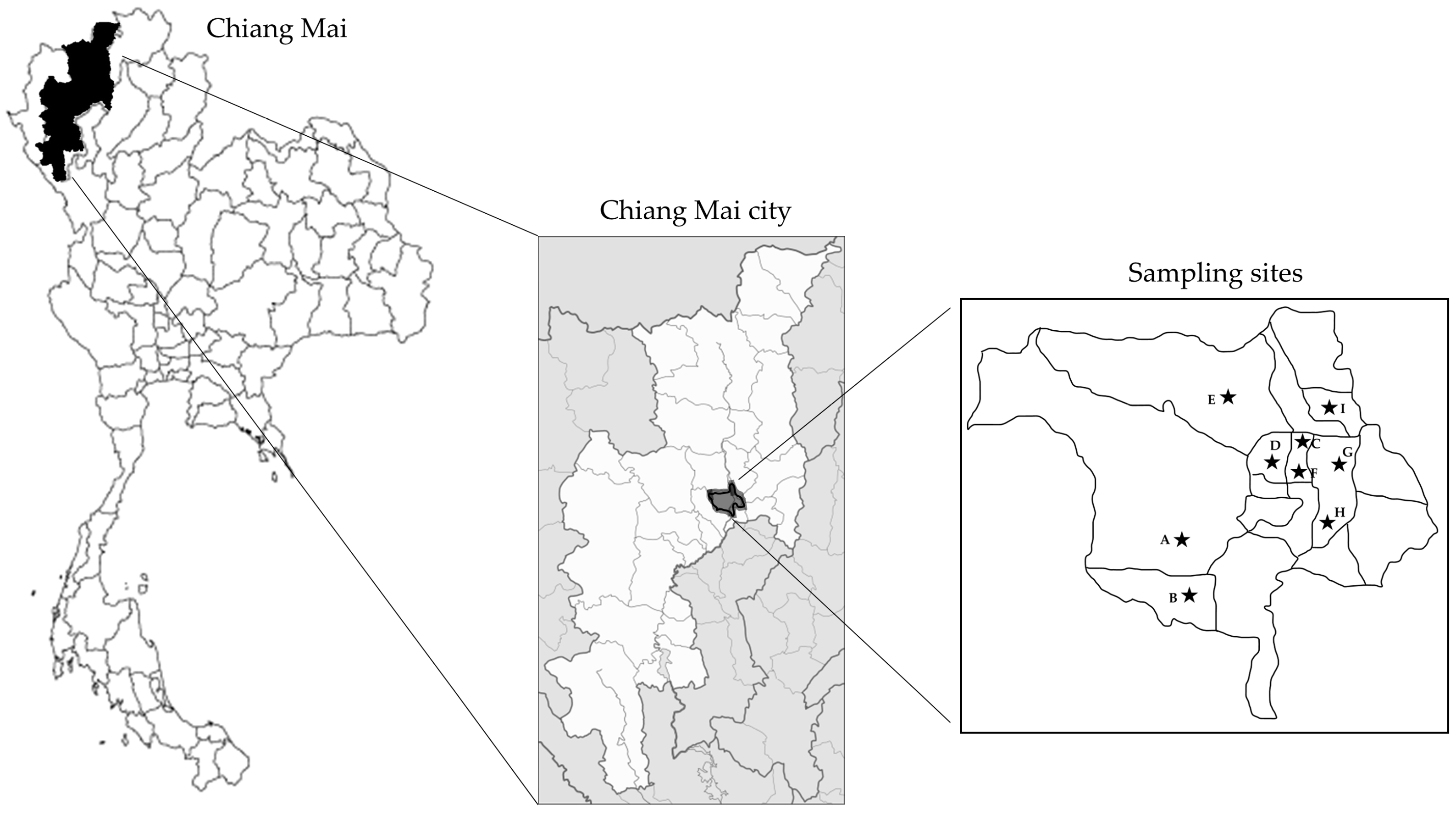
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Bacterial DNA Extraction
2.3. Detections of S. suis and S. suis Serotype 2 by LAMP Techniques
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LAMP Results for S. suis and S. suis Serotype 2 Detection
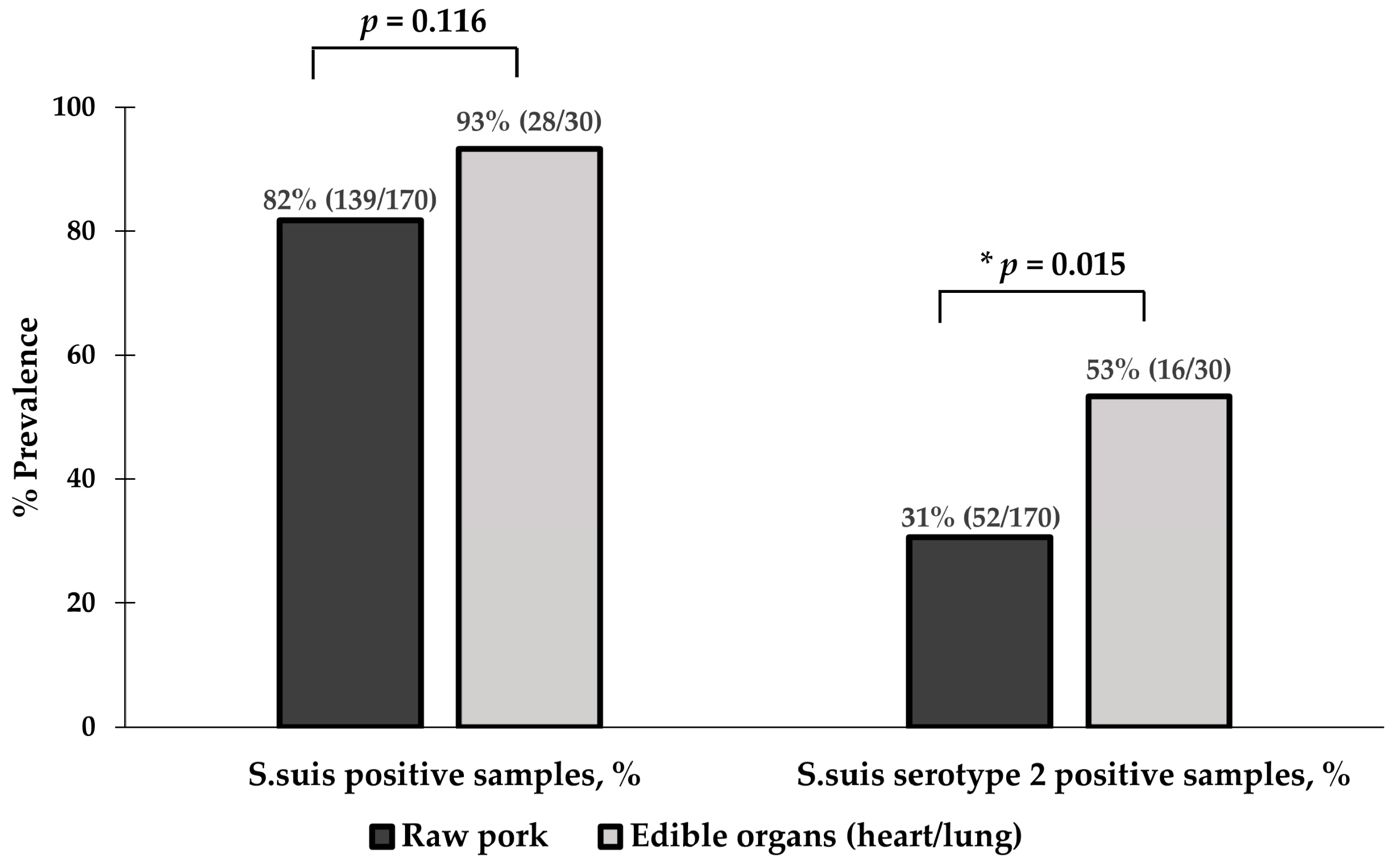
3.2. Prevalence of S. suis and S. suis Serotype 2 Contamination in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs
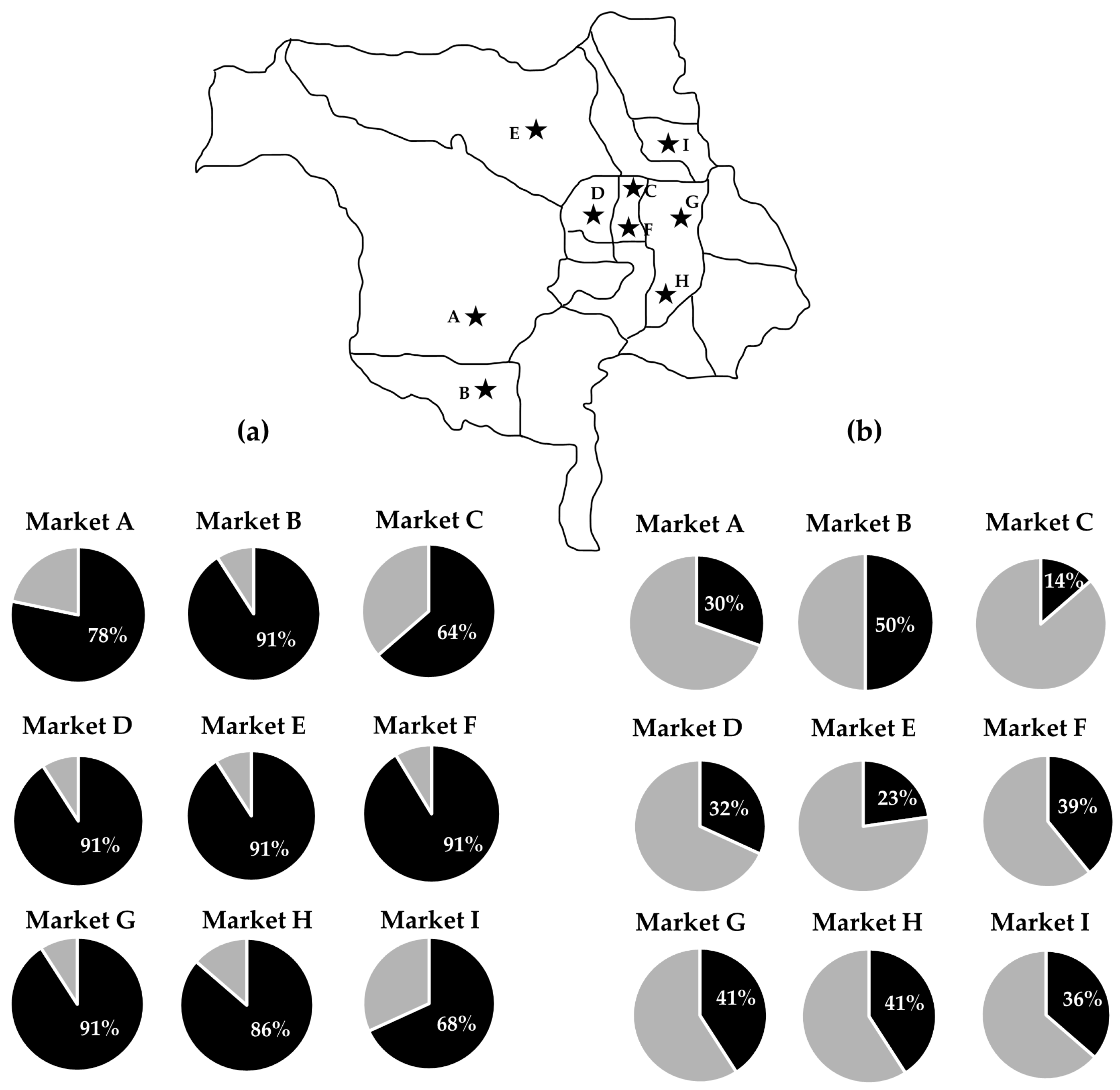
3.3. Prevalence of S. suis and S. suis Serotype 2 Contamination from Fresh Markets
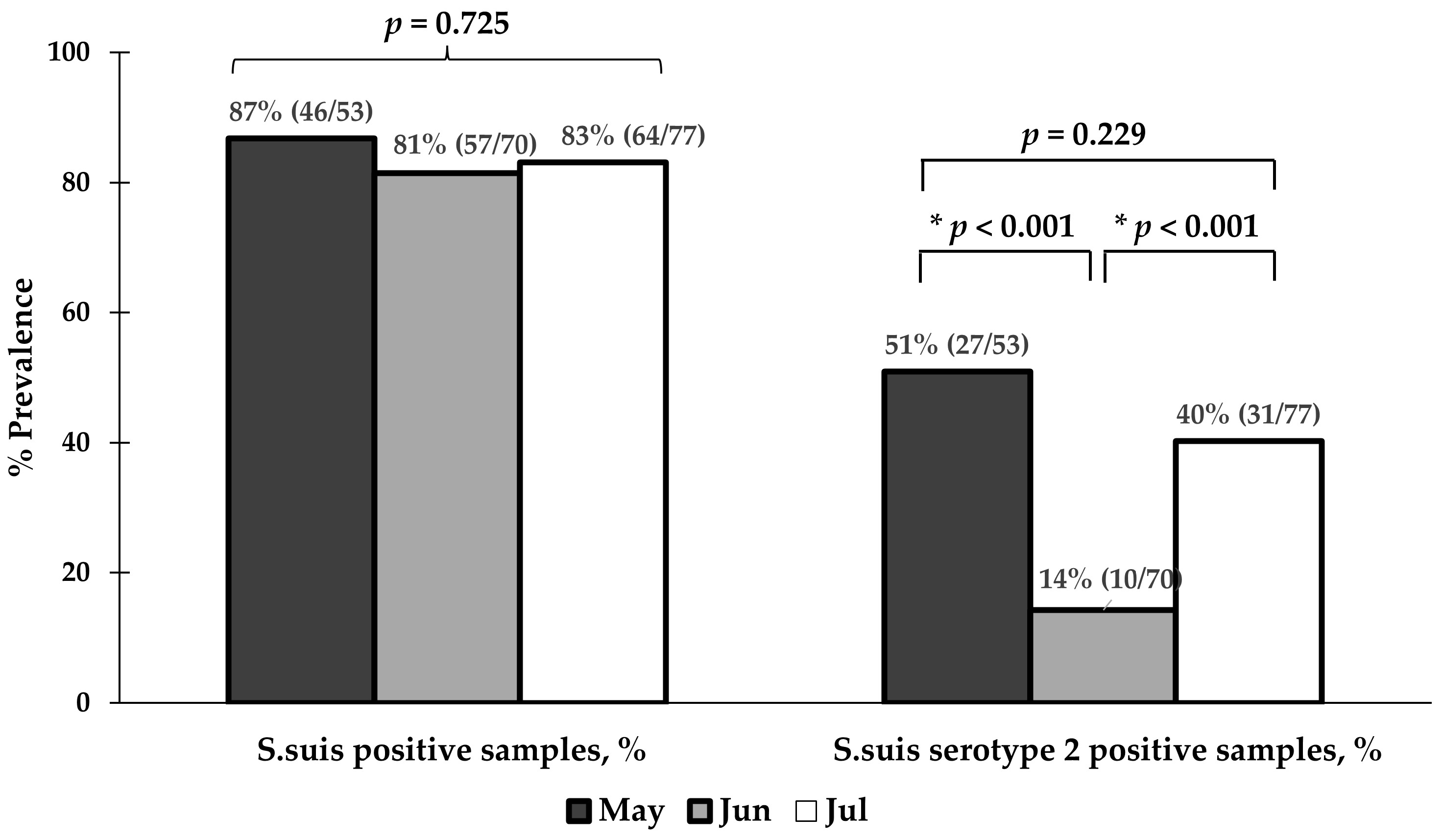
3.4. Prevalence of S. suis and S. suis Serotype 2 Contamination According to the Month of Sample Collection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, V.T.; Ha, N.; Huy, N.T.; Horby, P.; Nghia, H.D.; Thiem, V.D.; Zhu, X.; Hoa, N.T.; Hien, T.T.; Zamora, J.; et al. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and outcomes of Streptococcus suis infection in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdsin, A. Human Streptococcus suis Infections in Thailand: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Genotypes, and Susceptibility. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, D.; Kerdsin, A.; Pienpringam, A.; Loetthong, P.; Samerchea, S.; Luangsuk, P.; Khamisara, K.; Wongwan, N.; Areeratana, P.; Chiranairadul, P.; et al. Population-based study of Streptococcus suis infection in humans in Phayao Province in northern Thailand. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, C.; Varaldo, P.E.; Facinelli, B. Streptococcus suis, an Emerging Drug-Resistant Animal and Human Pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarradas, C.; Arenas, A.; Maldonado, A.; Luque, I.; Miranda, A.; Perea, A. Identification of Streptococcus suis isolated from swine: Proposal for biochemical parameters. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatrongjit, R.; Kerdsin, A.; Gottschalk, M.; Hamada, S.; Oishi, K.; Akeda, Y. Development of a multiplex PCR assay to detect the major clonal complexes of Streptococcus suis relevant to human infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Tienle, H.T.; Osawa, R.; Tohya, M.; Nomoto, R.; Kawamura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kikuchi, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Sekizaki, T. Development of an appropriate PCR system for the reclassification of Streptococcus suis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 107, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdsin, A.; Akeda, Y.; Hatrongjit, R.; Detchawna, U.; Sekizaki, T.; Hamada, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Oishi, K. Streptococcus suis serotyping by a new multiplex PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marois, C.; Bougeard, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Kobisch, M. Multiplex PCR assay for detection of Streptococcus suis species and serotypes 2 and 1/2 in tonsils of live and dead pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3169–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Fukunari, K.; Tada, S.; Ichimura, S.; Chiba, Y.; Suzuki, T. A multiplex real-time RT-PCR system to simultaneously diagnose 16 pathogens associated with swine respiratory disease. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Tohya, M.; Yamada, R.; Osawa, R.; Nomoto, R.; Kawamura, Y.; Sekizaki, T. Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to detect Streptococcus suis and its application to retail pork meat in Japan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 208, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, F.; Lv, H.; Hu, D.; Hao, L.; Geng, M.; et al. Rapid visual detection of highly pathogenic Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolates by use of loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3250–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.; Kreitlow, A.; Rohn, K.; Hennig-Pauka, I.; Abdulmawjood, A. Rapid Diagnostic of Streptococcus suis in Necropsy Samples of Pigs by thrA-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Chu, P.; Zhai, S.; Yang, D.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Accelerated loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of Streptococcus suis serotypes 2 and 14 based on single nucleotide polymorphisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1034762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, M.; Liu, Y. Development of Two Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays for Rapid Detection of ermB and mefA Genes in Streptococcus suis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyong, N.; Kaewmongkol, S.; Khunbutsri, D.; Satchasataporn, K.; Meekhanon, N. Contamination of Streptococcus suis in pork and edible pig organs in central Thailand. Vet. World 2019, 12, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongcom, A.; Pruksakorn, S.; Mongkol, R.; Tharavichitkul, P.; Yoonim, N. Streptococcus suis infection in northern Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. Chotmaihet Thangphaet 2001, 84, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Khadthasrima, N.; Hannwong, T.; Thammawitjaya, P.; Pingsusean, D.; Akkanij, B.; Jaikhar, A.; Paungmali, P.; Yudee, P.; Wongyai, S.; Samerchea, S.; et al. Human Streptococcus suis outbreak in Phayao province, Thailand, 2007. Outbreak Surveill. Investig. Response J. 2007, 1, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangkaew, S.; Chaiwarith, R.; Tharavichitkul, P.; Supparatpinyo, K. Streptococcus suis infection: A series of 41 cases from Chiang Mai University Hospital. J. Infect. 2006, 52, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangsomboonsiri, W.; Luksananun, T.; Saksornchai, S.; Ketwong, K.; Sungkanuparph, S. Streptococcus suis infection and risk factors for mortality. J. Infect. 2008, 57, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsawat, S. Streptococcus suis serotype 2 outbreak at Chomthong district, Chiang Mai province, June–July, 2008. Lanna Public Health J. 2010, 6, 322–336. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C., Jr. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppon, B.; Khaeng, S.; Sopa, A.; Phuaram, P.; Wongsan, R.; Laohasinnurak, T. Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in Uncooked Pork Meat Products in Khon Kaen, Northeastern Thailand, and their Antimicrobial Profiles. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Lunha, K.; Chumpol, W.; Samngamnim, S.; Jiemsup, S.; Assavacheep, P.; Yongkiettrakul, S. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Streptococcus suis Isolated from Diseased Pigs in Thailand, 2018–2020. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojkovic, A.; Astojic-andric, D.; Petrovic, M.; Stanisic, N.; Gogic, M.; Stanojkovic-Sebic, A.; Radovic, C. Prevalence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strains isolated from major parts of fresh pork meat. Sci. Works. Ser. C Vet. Med. 2016, LXII, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, M.; Aragon, V.; Brockmeier, S.L.; Gebhart, C.; Greeff, A.; Kerdsin, A.; O’Dea, M.A.; Okura, M.; Saléry, M.; Schultsz, C.; et al. Update on Streptococcus suis Research and Prevention in the Era of Antimicrobial Restriction: 4th International Workshop on S. suis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdsin, A.; Dejsirilert, S.; Puangpatra, P.; Sripakdee, S.; Chumla, K.; Boonkerd, N.; Polwichai, P.; Tanimura, S.; Takeuchi, D.; Nakayama, T.; et al. Genotypic profile of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and clinical features of infection in humans, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayanakorn, A.; Katip, W.; Goh, B.H.; Oberdorfer, P.; Lee, L.H. Clinical Manifestations and Risk Factors of Streptococcus suis Mortality Among Northern Thai Population: Retrospective 13-Year Cohort Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3955–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayanakorn, A.; Goh, B.-H.; Lee, L.-H.; Khan, T.M.; Saokaew, S. Risk factors for Streptococcus suis infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.S.; Kim, W.; Jo, G.; Yang, K.Y. Rapid detection of a downy mildew pathogen, Peronospora destructor, in infected onion tissues and soils by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Phytopathology 2024, 114, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebregziabher, S.M.; Yalew, A.W.; Sime, H.; Abera, A. Molecular detection of waterborne pathogens in infants’ drinking water and their relationship with water quality determinants in eastern Ethiopia: Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-based study. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielba-Fernández, A.; Dowling, M.; Schnabel, G.; Fernández-Ortuño, D. A Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for the Identification of Botrytis fragariae in Strawberry. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 3414–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabatake, R.; Kagiya, Y.; Futo, S.; Minegishi, Y.; Soga, K.; Shibata, N.; Kondo, K. Rapid Screening Detection of Genetically Modified Papaya by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 46, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, D.; Kerdsin, A.; Akeda, Y.; Chiranairadul, P.; Loetthong, P.; Tanburawong, N.; Areeratana, P.; Puangmali, P.; Khamisara, K.; Pinyo, W.; et al. Impact of a Food Safety Campaign on Streptococcus suis Infection in Humans in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdsin, A.; Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Gottschalk, M. Sociocultural Factors Influencing Human Streptococcus suis Disease in Southeast Asia. Foods 2022, 11, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guntala, R.; Khamai, L.; Srisai, N.; Ounjaijean, S.; Khamduang, W.; Hongjaisee, S. Contamination of Streptococcus suis and S. suis Serotype 2 in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs: A Public Health Concern in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Foods 2024, 13, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132119
Guntala R, Khamai L, Srisai N, Ounjaijean S, Khamduang W, Hongjaisee S. Contamination of Streptococcus suis and S. suis Serotype 2 in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs: A Public Health Concern in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132119
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuntala, Ratchadakorn, Likhitphorn Khamai, Nattawara Srisai, Sakaewan Ounjaijean, Woottichai Khamduang, and Sayamon Hongjaisee. 2024. "Contamination of Streptococcus suis and S. suis Serotype 2 in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs: A Public Health Concern in Chiang Mai, Thailand" Foods 13, no. 13: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132119
APA StyleGuntala, R., Khamai, L., Srisai, N., Ounjaijean, S., Khamduang, W., & Hongjaisee, S. (2024). Contamination of Streptococcus suis and S. suis Serotype 2 in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs: A Public Health Concern in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Foods, 13(13), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132119







