Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Geographic Origin Discrimination of Greek Beans “Gigantes-Elefantes” (Phaseolus coccineus L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
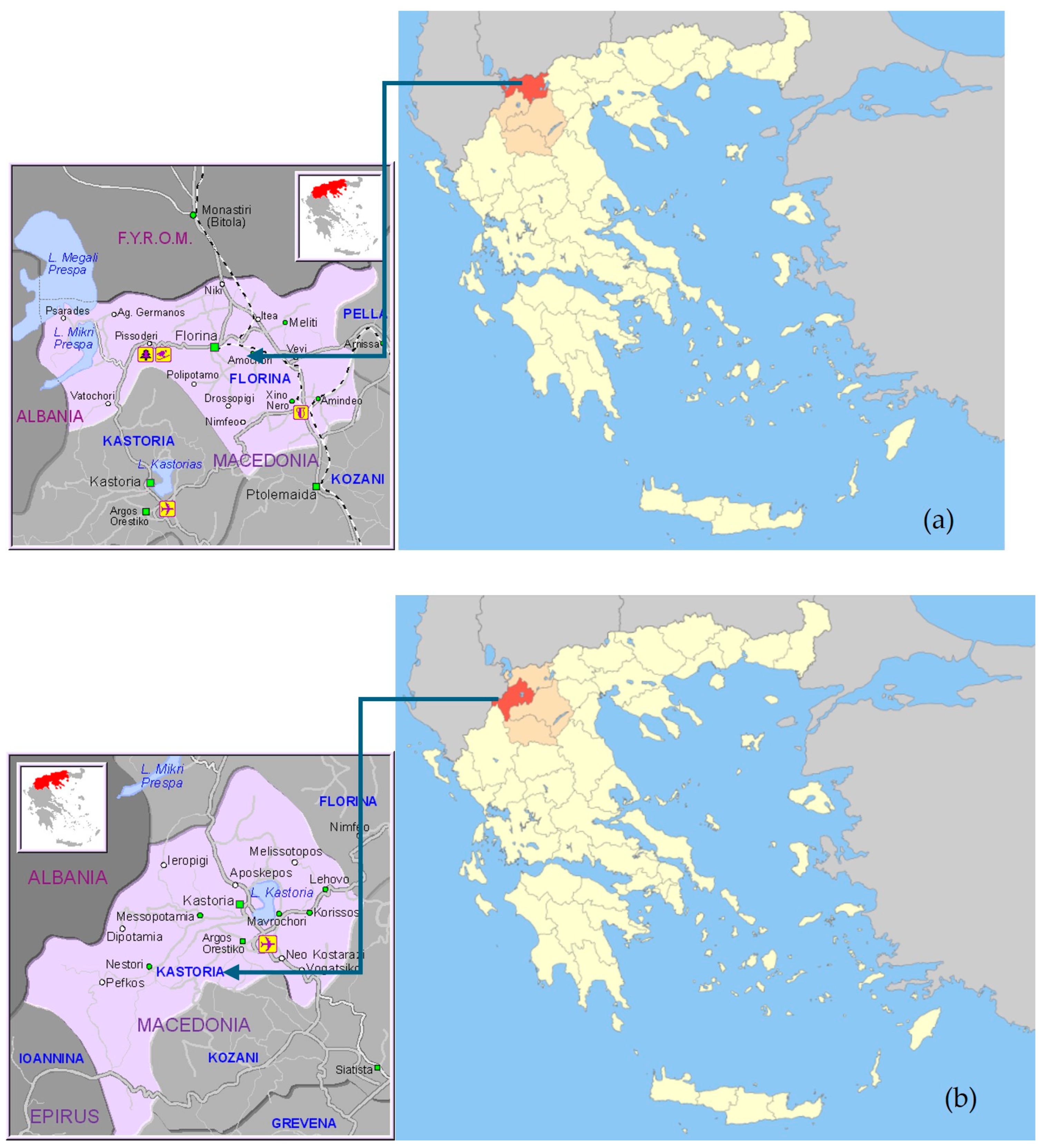
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Sample Treatment
2.3. EA-IRMS Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
Stable Isotope Results for Giant Beans
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camin, F.; Boner, M.; Bontempo, L.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Kelly, S.D.; Riedl, J.; Rossmann, A. Stable isotope techniques for verifying the declared geographical origin of food in legal cases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulou, M.E.; Vantarakis, A. Does Traceability Lead to Food Authentication? A Systematic Review from A European Perspective. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Bontempo, L.; Perini, M.; Piasentier, E. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for Assessing the Authenticity of Food of Animal Origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomatou, A.A.; Mazarakioti, E.C.; Zotos, A.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Patakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Application of Stable Isotope Analysis for Detecting the Geographical Origin of the Greek Currants “Vostizza”: A Preliminary Study. Foods 2023, 12, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosmali, I.; Ganopoulos, I.; Madesis, P.; Tsaftaris, A. Microsatellite and DNA-barcode regions typing combined with High Resolution Melting (HRM) analysis for food forensic uses: A case study on lentils (Lens culinaris). Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharanathan, R.N.; Mahadevamma, S. Grain legumes—A boon to human nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.E.A.; Queiroz-Monici, K.S.; Reis, S.M.P.M.; Oliveira, A.C. Chemical composition, dietary fibre and resistant starch contents of raw and cooked pea, common bean, chickpea and lentil legumes. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Z.; Harnly, J.M.; Pastor-Corrales, M.S.; Luthria, D.L. The polyphenolic profiles of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.L. The glycemic index: Looking back 25 years. Cereal Foods World 2007, 52, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.J.; Liu, Q.; Pauls, K.P.; Fan, M.Z.; Yada, R. In vitro starch digestibility, expected glycemic index and some physicochemical properties of starch and flour from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties grown in Canada. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Hillen, C.; Garden Robinson, J. Composition, nutritional value, and health benefits of pulses. Cereal. Chem. J. 2017, 94, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Mitchell, S.; Sahye-Pudaruth, S.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Chiavaroli, L.; Mirrahimi, A.; Ireland, C.; Bashyam, B.; et al. Effect of legumes as part of a low glycemic index diet on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, V. Nutritional and health benefits of dried beans: Discovery service for Endeavour College of Natural Health Library. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duenas, M.; Sarmento, T.; Aguilera, Y.; Benitez, V.; Molla, E.; Esteban, R.M.; Martin-Cabrejas, M.A. Impact of cooking and germination on phenolic composition and dietary fibre fractions in dark beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and lentils (Lens culinaris L.). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverri, E.J.; Randolph, J.M.; Kappagoda, C.T.; Park, E.; Edirisinghe, I.; Burton-Freeman, B.M. Assessing beans as a source of intrinsic fiber on satiety in men and women with metabolic syndrome. Appetite 2017, 118, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, L.; Luna-vital, D.A.; Gonzalez, E.; Mejia, D. Characterization of peptides from common bean protein isolates and their potential to inhibit markers of type-2 diabetes, hypertension and oxidative stress. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Bioactive constituents in pulses and their health benefits. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, K.H.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Olesen, J.E.; Askegaard, M.; Halekoh, U.; Husted, S. Multielemental Fingerprinting as a Tool for Authentication of Organic Wheat, Barley, Faba Bean, and Potato. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4385–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longobardi, F.; Casiello, G.; Cortese, M.; Perini, M.; Camin, F.; Catucci, L.; Agostiano, A. Discrimination of geographical origin of lentils (Lens culinaris Medik.) using isotope ratio mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganopoulos, I.; Madesis, P.; Darzentas, N.; Argiriou, A.; Tsaftaris, A. Barcode High Resolution Melting (Bar-HRM) analysis for detection and quantification of PDO ‘‘Fava Santorinis’’ (Lathyrus clymenum) adulterants. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganopoulos, I.; Bosmali, I.; Madesis, P.; Tsaftaris, A. Microsatellite genotyping with HRM (High Resolution Melting) analysis for identification of the PGI common bean variety Plake Megalosperma Prespon. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Beta, T. Discrimination of geographical origin of Napirira bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) based on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 62, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.P.C.; Santos, D.C.M.B.; Fernandes, A.P.; Castro, J.T.; Korn, M.G.A. Geographical Characterization of Beans Based on Trace Elements After Microwave-Assisted Digestion Using Diluted Nitric Acid. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, P.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Millaire, J.F.; White, C.D. Large variation in nitrogen isotopic composition of a fertilized legume. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 45, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics, 11th Edition|Wiley. Wiley.com. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-ie/Statistics%2C+11th+Edition-p-9781119254515 (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Du, C.-J.; Sun, D.-W. Object Classification Methods. In Computer Vision Technology for Food Quality Evaluation, Food Science and Technology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS; SAGE Publication: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Pramesh, C.S. Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: Odds versus risk. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2015, 6, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niu, L. A review of the application of logistic regression in educational research: Common issues, implications, and suggestions. Educ. Rev. 2018, 72, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerinopoulou, K.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Salmas, C.E.; Patakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Geographical Origin Authentication of Agri-Food Products: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.; Heaton, K.; Hoogewerff, J. Tracing the geographical origin of food: The application of multi-element and multi-isotope analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food authentication: Techniques, trends & emerging approaches. TrAC 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opatic, A.M.; Necemer, M.; Lojen, S. Determination of the geographical origin of Slovenian potato and garlic, based on stable isotope and elemental analyses—Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 2nd IMEKOFOODS Promoting Objective and Measurable Food Quality & Safety, Benevento, Italy, 2–5 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, I.M.; Kim, J.K.; Han, J.G.; Kong, W.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; An, Y.J.; Kwon, C.; Chi, H.Y.; Jung, M.Y.; et al. Potential geo-discriminative tools to trace the origins of the dried slices of shiitake (Lentinula edodes) using stable isotope ratios and OPLS-DA. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Bong, Y.S. Geographical origin authentication of onions using stable isotope ratio and compositions of C, H, O, N, and S. Food Control 2019, 101, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Area | N (Samples) | Mean δ15NAIR (‰)/ (S.D.) | Mean δ13CV-PDB (‰)/ (S.D.) | Mean δ34SV-CDT (‰)/ (S.D.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||
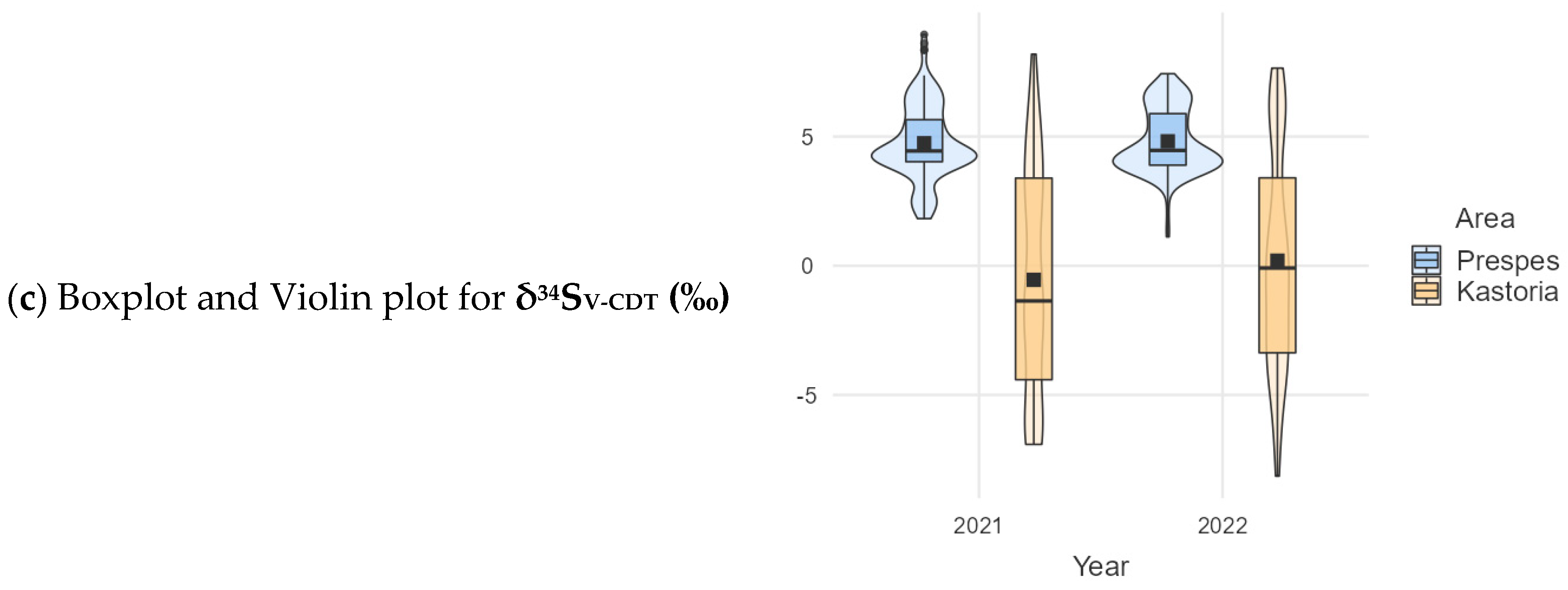
| Prespes | 160 | 1.88 (2.26) | −25.6 (0.97) | 4.74 (1.43) |
| Kastoria | 120 | 1.59 (1.07) | −26.2 (1.23) | −0.54 (4.45) |
| 2022 | ||||
| Prespes | 160 | 1.78 (1.68) | −25.4 (0.795) | 4.82 (1.23) |
| Kastoria | 120 | 1.72 (1.61) | −25.7 (0.985) | 0.196 (4.21) |
| δ (‰) | Area | N | Mean δ (‰) | Std. Error | ANOVA F Value | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ15NAIR (‰) | Prespes | 320 | 1.875 | 0.111 | 2.44 | 0.119 |
| Kastoria | 240 | 1.654 | 0.087 | |||
| δ13CV-PDB (‰) | Prespes | 320 | −25.483 | 0.049 | 25.12 | <0.001 |
| Kastoria | 240 | −25.928 | 0.073 | |||
| δ34SV-CDT (‰) | Prespes | 320 | 4.779 | 0.074 | 291.94 | <0.001 |
| Kastoria | 240 | −0.174 | 0.280 |
| δ (‰) | Years | N | Mean δ (‰) | Std. Error | ANOVA F Value | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ15NAIR (‰) | 2021 | 120 | 1.587 | 0.097 | 0.588 | 0.444 |
| 2022 | 120 | 1.722 | 0.146 | |||
| δ13CV-PDB (‰) | 2021 | 120 | −26.169 | 0.112 | 11.244 | <0.001 |
| 2022 | 120 | −25.687 | 0.089 | |||
| δ34SV-CDT (‰) | 2021 | 120 | −0.545 | 0.406 | 1.757 | 0.186 |
| 2022 | 120 | 0.196 | 0.384 |
| δ (‰) | Years | N | Mean δ (‰) | Std. Error | ANOVA F Value | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ15NAIR (‰) | 2021 | 160 | 1.88 | 0.178 | 0.005 | 0.941 |
| 2022 | 160 | 1.87 | 0.132 | |||
| δ13CV-PDB (‰) | 2021 | 160 | −25.58 | 0.077 | 3.805 | 0.052 |
| 2022 | 160 | −25.39 | 0.062 | |||
| δ34SV-CDT (‰) | 2021 | 160 | 4.74 | 0.113 | 0.251 | 0.616 |
| 2022 | 160 | 4.84 | 0.096 |
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | Z | p | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 21.562 | 3.9253 | 5.49 | <0.001 | 2.31 × 109 |
| δ15NAIR (‰) | −0.302 | 0.0693 | −4.37 | <0.001 | 0.739 |
| δ13CV-PDB (‰) | 0.872 | 0.1522 | 5.73 | <0.001 | 2.393 |
| δ34SV-CDT (‰) | 0.626 | 0.0574 | 10.90 | <0.001 | 1.871 |
| Year: | |||||
| 2022–2021 | −0.467 | 0.2476 | −1.89 | 0.059 | 0.627 |
| Observed | Predicted | Percentage Correct | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kastoria | Prespes | ||
| Kastoria | 188 | 52 | 78.3% |
| Prespes | 70 | 250 | 78.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomatou, A.-A.; Mazarakioti, E.C.; Zotos, A.; Kokkotos, E.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Patakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Geographic Origin Discrimination of Greek Beans “Gigantes-Elefantes” (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Foods 2024, 13, 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132107
Thomatou A-A, Mazarakioti EC, Zotos A, Kokkotos E, Kontogeorgos A, Patakas A, Ladavos A. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Geographic Origin Discrimination of Greek Beans “Gigantes-Elefantes” (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Foods. 2024; 13(13):2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132107
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomatou, Anna-Akrivi, Eleni C. Mazarakioti, Anastasios Zotos, Efthimios Kokkotos, Achilleas Kontogeorgos, Angelos Patakas, and Athanasios Ladavos. 2024. "Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Geographic Origin Discrimination of Greek Beans “Gigantes-Elefantes” (Phaseolus coccineus L.)" Foods 13, no. 13: 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132107
APA StyleThomatou, A.-A., Mazarakioti, E. C., Zotos, A., Kokkotos, E., Kontogeorgos, A., Patakas, A., & Ladavos, A. (2024). Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Geographic Origin Discrimination of Greek Beans “Gigantes-Elefantes” (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Foods, 13(13), 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132107







