The Blue Treasure: Comprehensive Biorefinery of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
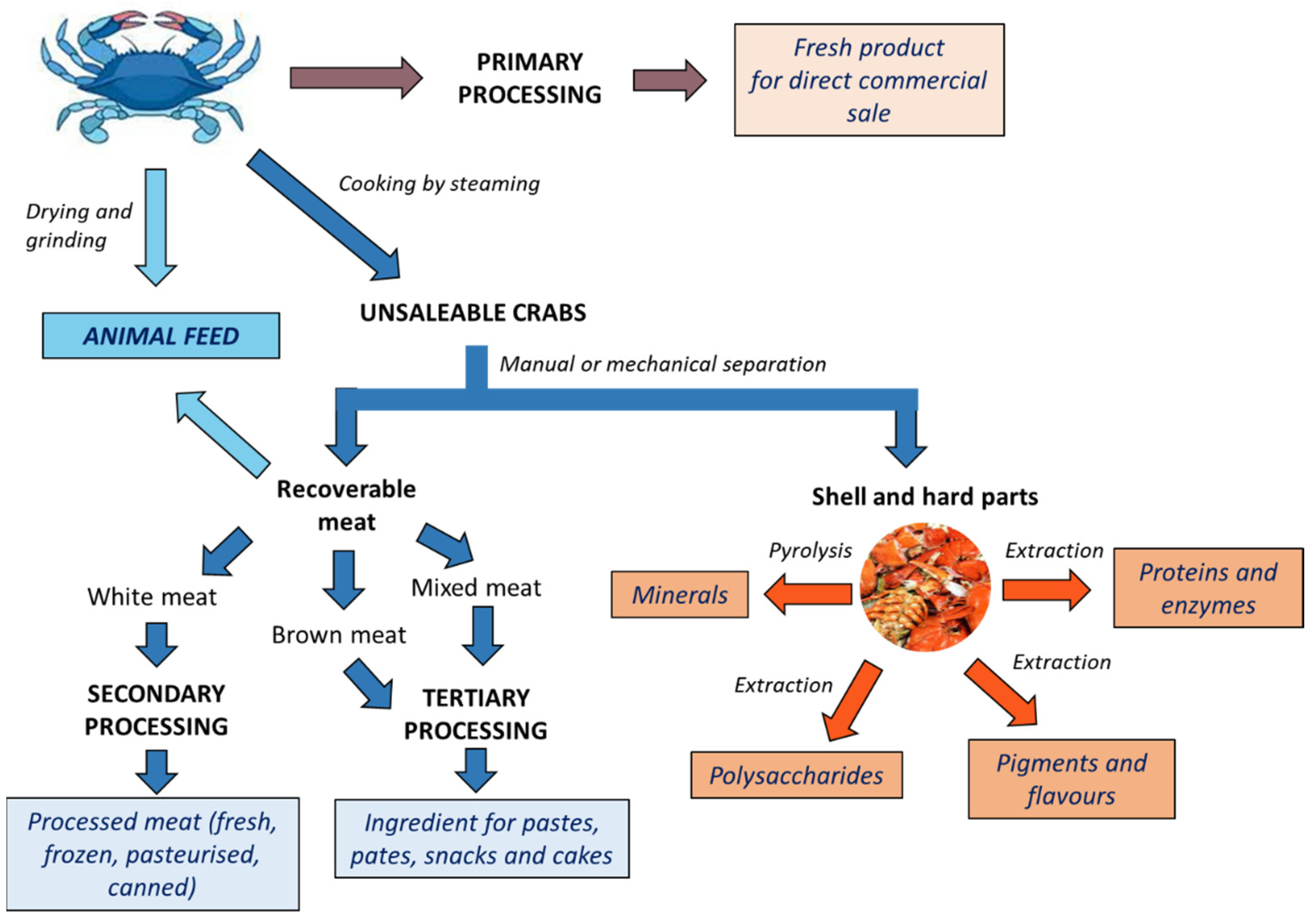
2. C. sapidus Product and Processing Overview
- -
- Primary products, e.g., cooked whole or dressed crab;
- -
- Secondary products, e.g., white picking meat (fresh, frozen, pasteurised, or canned);
- -
- Tertiary products, e.g., white, brown, or mixed picking meat used as an ingredient in another product, including pâtés, pastes, and crab cakes.
3. Composition of Crab Meat and Shell
4. Use as Animal Feed
5. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Crab Shell Waste
5.1. Polysaccharides
5.2. Carotenoids, Flavours, and Pigments
6. Valorisation of Shell as Carbonaceous Material
6.1. Applications as Bio-Absorbent
6.2. Applications in Medicine
6.3. Applications as Bio-Catalyst
7. Crab Shells as Bio-Filler for Polymers and Bio-Carbon Material
8. Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Crab Shell towards Zero-Waste Processing
9. Conclusions and Implications of This Review
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant Peptides from Marine By-Products: Isolation, Identification and Application in Food Systems. A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Verma, A.K.; Patel, R. Collagen Extraction and Recent Biological Activities of Collagen Peptides Derived from Sea-Food Waste: A Review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, C.; Bacenetti, J.; Bezama, A.; Blok, V.; Goglio, P.; Koukios, E.G.; Lindner, M.; Nemecek, T.; Siracusa, V.; Zabaniotou, A.; et al. The Potential Roles of Bio-Economy in the Transition to Equitable, Sustainable, Post Fossil-Carbon Societies: Findings from This Virtual Special Issue. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Sairash, S.; Hussain, N.; Baqar, Z.; Sumrin, A.; Bilal, M. Current Challenges of Biomass Refinery and Prospects of Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Bioproducts and Bioeconomy. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2022, 16, 1478–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. A Systematic Review on Marine Umami Peptides: Biological Sources, Preparation Methods, Structure-Umami Relationship, Mechanism of Action and Biological Activities. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, P.K.; Singh, A.K.; Sonkar, S.; Shadangi, K.P.; Srivastava, R.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Parikh, J.; Sahoo, U.K.; Govarthanan, M. Biorefinery Solutions for Food Processing Wastes: A Sustainable Bioeconomic Perspective. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 205, 117488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, G.; Chainho, P.; Cilenti, L.; Falco, S.; Kapiris, K.; Katselis, G.; Ribeiro, F. The Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in Southern European Coastal Waters: Distribution, Impact and Prospective Invasion Management Strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, N.; Williamson, A.; Aguero, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Geeves, W. Marine Invasive Alien Species: A Threat to Global Biodiversity. Mar. Policy 2003, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, H.; Polito, M.J. Trophic Ecology of the Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus as an Invasive Non-Native Species in the Aegean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türeli, C.; Miller, T.J.; Gündoğdu, S.; Yeşilyurt, İ.N. Growth and Mortality of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) in the North-Eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 10, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Rifi, M.; Basti, L.; Rizzo, L.; Tanduo, V.; Radulovici, A.; Jaziri, S.; Uysal, İ.; Souissi, N.; Mekki, Z.; Crocetta, F. Tackling Bioinvasions in Commercially Exploitable Species through Interdisciplinary Approaches: A Case Study on Blue Crabs in Africa’s Mediterranean Coast (Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 291, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini-Foka, M.; Abdulghani, A.; Al Mabruk, S.A.A.; Abdulrraziq, A.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Scannella, D.; Zava, B.; Deidun, A.; Gianguzza, P. Invasive Portunid Crabs in Libyan Waters: First Record of the Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 and Range Expansion of the Swimming Blue Crab Portunus segnis (Forskål, 1775). BioInvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, T. Recent Expansion of the Alien Invasive Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun, 1896)(Decapoda, Crustacea) along the Bulgarian Coast of the Black Sea. Hist. Nat. Bulg. 2021, 42, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; Franch, N.; Bernardo-Madrid, R.; López, V.; Abelló, P.; Queral, J.M.; Mancinelli, G. Severe, Rapid and Widespread Impacts of an Atlantic Blue Crab Invasion. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfrin, C.; Comisso, G.; Dall’Asta, A.; Bettoso, N.; Chung, J.S. The Return of the Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896, after 70 Years from Its First Appearance in the Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy (Decapoda: Portunidae). Check List 2016, 12, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaria, G.; Pierucci, A.; Zanello, P.; Fanelli, E.; Chiesa, S.; Azzurro, E. Percnon Gibbesi (H. Milne Edwards, 1853) and Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun, 1896) in the Ligurian Sea: Two Additional Invasive Species Detections Made in Collaboration with Local Fishermen. BioInvasions Rec. 2017, 6, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchioni, L.; Russotto, S.; Arculeo, M.; Marrone, F. On the Occurrence of the Invasive Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun 1896 (Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunidae) in Sicilian Inland Waters. Nat. Hist. Sci. 2022, 9, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, P.; Esposito, G.; Meloni, D. On the Occurrence of the Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun, 1896) in Sardinian Coastal Habitats (Italy): A Present Threat or a Future Resource for the Regional Fishery Sector? BioInvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalici, M.; Chiesa, S.; Mancinelli, G.; Rontani, P.M.; Voccia, A.; Nonnis Marzano, F. Euryhaline Aliens Invading Italian Inland Waters: The Case of the Atlantic Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Fernández, M.; Cordero, D.; Saavedra, C.; Carella, F.; Alcaraz, C.; Gairin, I. Molecular Identification, Life Cycle Characterization, and Hatchery Seed Production of Dwarf Oysters from the Ebro Delta (Spain). Aquat. Living Resour. 2022, 35, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchessaux, G.; Mangano, M.C.; Bizzarri, S.; M’Rabet, C.; Principato, E.; Lago, N.; Veyssiere, D.; Garrido, M.; Scyphers, S.B.; Sarà, G. Invasive Blue Crabs and Small-Scale Fisheries in the Mediterranean Sea: Local Ecological Knowledge, Impacts and Future Management. Mar. Policy 2023, 148, 105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.L.; Ihde, T.; Knoche, S.; Townsend, H.; Lewis, K.A. Simulated Climate Change Impacts on Striped Bass, Blue Crab and Eastern Oyster in Oyster Sanctuary Habitats of Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 292, 108465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, H.M.; Anderson, J.; Collins, L. Status and Management of the Blue Crab Fishery in the Gulf of Mexico. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2022, 42, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, P.K.; Das, A.K.; Dandapat, P.; Dhar, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Dib, A.L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gagaoua, M. Nutritional Aspects, Flavour Profile and Health Benefits of Crab Meat Based Novel Food Products and Valorisation of Processing Waste to Wealth: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obatolu, V.A.; Skonberg, D.I.; Camire, M.E.; Dougherty, M.P. Effect of Moisture Content and Screw Speed on the Physical Chemical Properties of an Extruded Crab-Based Snack. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2005, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.Y.; Cadwallader, K.R. Volatile Components in Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Meat and Processing By-Product. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department—Yearbook of Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics—Aquaculture Production. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/static/Yearbook/YB2019_USBcard/navigation/index_content_aquaculture_e.htm#B (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Rudovica, V.; Rotter, A.; Gaudêncio, S.P.; Novoveská, L.; Akgül, F.; Akslen-Hoel, L.K.; Alexandrino, D.A.M.; Anne, O.; Arbidans, L.; Atanassova, M.; et al. Valorization of Marine Waste: Use of Industrial By-Products and Beach Wrack Towards the Production of High Added-Value Products. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 723333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.L.; Jin, T.; Lam, E.; Kerton, F.; Moores, A. Blue Is the New Green: Valorization of Crustacean Waste. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, J.A.; Fellers, C.R.; Parkhurst, R.T. Crab Meal in Poultry Rations*: I. Nutritive Properties. Poult. Sci. 1943, 22, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, T.P.; Wheaton, F.W.; Brinsfield, R.B. Optimizing Variables Affecting Composting of Blue Crab Scrap. Agric. Wastes 1986, 15, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.C.; Islam, M.R.; Sadia, S.; Yeasmin, M.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Chun, B.-S. Trash to Treasure: An Up-to-Date Understanding of the Valorization of Seafood By-Products, Targeting the Major Bioactive Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimat, V.; Rathod, N.B.; Čagalj, M.; Hamed, I.; Generalić Mekinić, I. Astaxanthin from Crustaceans and Their Byproducts: A Bioactive Metabolite Candidate for Therapeutic Application. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S. Antioxidants from Crustaceans: A Panacea for Lipid Oxidation in Marine-Based Foods. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.P.; Domingues, M.R.; Calado, R. Marine Animal Co-Products—How Improving Their Use as Rich Sources of Health-Promoting Lipids Can Foster Sustainability. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V. Green Processing of Seafood Waste Biomass towards Blue Economy. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 4, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azelee, N.I.W.; Dahiya, D.; Ayothiraman, S.; Noor, N.M.; Rasid, Z.I.A.; Ramli, A.N.M.; Ravindran, B.; Iwuchukwu, F.U.; Selvasembian, R. Sustainable Valorization Approaches on Crustacean Wastes for the Extraction of Chitin, Bioactive Compounds and Their Applications—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, H. Literature Review as a Research Methodology: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMOFA. Available online: https://eumofa.eu/ (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Çelik, M.; Türeli, C.; Çelik, M.; Yanar, Y.; Erdem, Ü.; Küçükgülmez, A. Fatty Acid Composition of the Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896) in the North Eastern Mediterranean. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, T.J.; DuPaul, W.D. Feasibility of Crab Meal Processing in the Chesapeake Bay Region; Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary: Gloucester Point, VA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zeng, C.; Wang, C.; Feng, L. Comparison of Gender Differences in Biochemical Composition and Nutritional Value of Various Edible Parts of the Blue Swimmer Crab. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.R.; Biesiot, P.M.; Perry, H.M.; Trigg, C. Biochemical Composition of Embryonic Blue Crabs Callinectes sapidus Rathbun 1896 (Crustacea: Decapoda) from the Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2003, 72, 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khafaji, K.K.; Al-Malki, G.M.; Karim, R.M. Biochemical Composition and Heavy Metal Accumulation in Tissues of the Blue Crab Portunus Pelagicus (Linnaeus, 1766) from NW of Arabian Gulf, South Iraq. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 8, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tufan, B. Biochemical Composition of Different Sex and Body Parts of Blue Crabs (Callinectes sapidus) Caught from the Middle Black Sea Coast. Mar. Sci. Technol. Bull. 2023, 12, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farragut, R.N. Proximate Composition of Chesapeake Bay Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus). J. Food Sci. 1965, 30, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuley, E.; Özoğul, F.; Özogul, Y.; Olgunoglu, A.I. Comparison of Fatty Acid and Proximate Compositions of the Body and Claw of Male and Female Blue Crabs (Callinectes sapidus) from Different Regions of the Mediterranean Coast. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 59, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökoðlu, N.; Yerlikaya, P. Determinaton of Proximate Composition and Mineral Contents of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) and Swim Crab (Portunus Pelagicus) Caught off the Gulf of Antalya. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükgülmez, A.; Çelik, M.; Yanar, Y.; Ersoy, B.; Çikrikçi, M. Proximate Composition and Mineral Contents of the Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Breast Meat, Claw Meat and Hepatopancreas. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamassi, F.; Bahri, W.R.; Bhouri, A.M.; Chaffai, A.; Kechaou, E.S.; Ghanem, R.; Souissi, J.B. Biochemical Composition, Nutritional Value and Socio-Economic Impacts of the Invasive Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 in Central Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, B.; Kapoor, D.; Gautam, S.; Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, S. Dietary Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs): Uses and Potential Health Benefits. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2021, 10, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umer, A.; Syed, M.N.; Tarar, O.M.; Mushtaq, S.; Jalbani, N.; Saleem, N.; Haider, M.S.; Ahmad, N. Biochemical Evaluation with Reference to Nutritional Aspects of Edible Species of Crabs Collected from the Coastal Waters of Pakistan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 100, 103877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, K.; Kobylińska, M.; Antosik, K. Folic Acid—Importance for Human Health and Its Role in COVID-19 Therapy. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2023, 74, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Melo-Cavalcante, A.A.; da Rocha Sousa, L.; Alencar, M.V.O.B.; de Oliveira Santos, J.V.; da Mata, A.M.O.; Paz, M.F.C.J.; de Carvalho, R.M.; Nunes, N.M.F.; Islam, M.T.; Mendes, A.N.; et al. Retinol Palmitate and Ascorbic Acid: Role in Oncological Prevention and Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyh, C.; Krüger, K.; Peeling, P.; Castell, L. The Role of Minerals in the Optimal Functioning of the Immune System. Nutrients 2022, 14, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, N.; Shakila, R.J.; Jeyasekaran, G.; P, P.; N, N.; Shalini, R.; Arisekar, U.; Patel, A.; Kumar, U.; Malini, A.H.; et al. Variation in the Nutritional Composition of Soft and Hard Blue Swimming Crabs (Portunus Pelagicus) Having Good Export Potential. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2021, 30, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.M.; Hassanien, F.R.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Sulieman, A.M. Biochemical Quality Indices of Blue Swimmer Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Meat. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2020, 8, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, C.; Alparslan, Y.; Baygar, T.; Baygar, T. Physicochemical, Microstructural and Thermal Characterization of Chitosan from Blue Crab Shell Waste and Its Bioactivity Characteristics. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaweera, B.O.; Wijesundara, W.M.N.M. Use of Seafood Processing by-Products in the Animal Feed Industry. In Seafood Processing by-Products: Trends and Applications; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 315–339. ISBN 978-1-4614-9590-1. [Google Scholar]
- Safamehr, A.; Langille, M.L.; Anderson, D.M.; MacIsaac, J.L. Evaluation of Composition and in Vitro Solubility Rate of By-Products of the Atlantic Shellfish Industry as Alternative Calcium Sources. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2013, 22, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundage, A.L.; Husby, F.M.; Herlugson, M.L.; Simpson, W.L.; Burton, V.L. Acceptability of Tanner Crab Meal in Concentrates for Lactation1, 2. J. Dairy Sci. 1984, 67, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbile, O.A.; Fontenot, J.P.; Graham, P.P.; Kirk, D.J.; Allen, V.G. Nutrient Utilization by Sheep and Performance and Carcass Characteristics of Steers Fed Crab Waste-Straw Silage. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Romero, J.; Ginés, R.; Vargas, R.; Izquierdo, M.; Robaina, L. Marine and Freshwater Crab Meals in Diets for Red Porgy (Pagrus Pagrus): Digestibility, Ammonia-N Excretion, Phosphorous and Calcium Retention. Aquaculture 2014, 428–429, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, S.M.; Lall, S.P.; Milley, J.E. Apparent Digestibility of Common Feed Ingredients by Juvenile Haddock, Melanogrammus aeglefinus L. Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppe, J.; Aksnes, A.; Hope, B.; Albrektsen, S. Inclusion of Fish Bone and Crab By-Products in Diets for Atlantic Cod, Gadus Morhua. Aquaculture 2006, 253, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, Ø.; Amlund, H.; Berg, A.; Olsen, R.E. The Effect of Dietary Chitin on Growth and Nutrient Digestibility in Farmed Atlantic Cod, Atlantic Salmon and Atlantic Halibut. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowska, M.A.; Drazen, J.C.; Robison, B.H. Digestive Chitinolytic Activity in Marine Fishes of Monterey Bay, California. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 139, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, A. Assessing the Presence of Chitinases in the Digestive Tract and Their Relationship to Diet and Morphology in Freshwater Fish. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University Ghent, Gent, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi, S.; Montero, D.; Torrecillas, S.; Serradell, A.; Acosta, F.; Haffray, P.; Hostins, B.; Fontanillas, R.; Allal, F.; Bajek, A.; et al. Genetically superior European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and nutritional innovations: Effects of functional feeds on fish immune response, disease resistance, and gut microbiota. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goytortúa-Bores, E.; Civera-Cerecedo, R.; Rocha-Meza, S.; Green-Yee, A. Partial Replacement of Red Crab (Pleuroncodes planipes) Meal for Fish Meal in Practical Diets for the White Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei. Effects on Growth and in Vivo Digestibility. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V. Valorization of Seafood Processing Discards: Bioconversion and Bio-Refinery Approaches. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 611835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Lv, X.; Ma, M.; Oh, D.-H.; Jiang, Z.; Fu, X. Chitin and Chitin-Based Biomaterials: A Review of Advances in Processing and Food Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgey, K.K.; Bahekar, A. Studies on Extraction Methods of Chitin from Crab Shell and Investigation of Its Mechanical Properties. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol 2017, 8, 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan Preparation from Marine Sources. Structure, Properties and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seenuvasan, M.; Sarojini, G.; Dineshkumar, M. Chapter 6—Recovery of Chitosan from Natural Biotic Waste. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Varjani, S., Pandey, A., Gnansounou, E., Khanal, S.K., Raveendran, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 115–133. ISBN 978-0-444-64321-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zargar, V.; Asghari, M.; Dashti, A. A Review on Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Structure, Chemistry, Solubility, Derivatives, and Applications. ChemBioEng Rev. 2015, 2, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.-H.; Vo, T.-S.; Ngo, D.-N.; Thuong, N.T.L.; Kim, S.-K. Chitosan and Its Derivatives as Potential Biomaterials. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2509–2527. ISBN 978-1-119-14380-2. [Google Scholar]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Abdou, E.S. Chitosan Based Edible Films and Coatings: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1819–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtoom, T.; Chinnan, M.S. Preparation and Properties of Rice Starch–Chitosan Blend Biodegradable Film. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Sands, R.D.; Brunelle, T.; Cui, Y.; Frank, S.; Fujimori, S.; Popp, A. Food Security under High Bioenergy Demand toward Long-Term Climate Goals. Clim. Change 2020, 163, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, K.; Sionkowska, A.; Kaczmarek, B.; Furtos, G. Mechanical and Morphological Studies of Chitosan/Clay Composites. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 590, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, H.; Ha, H.C.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Physical Properties of Silk Fibroin/Chitosan Blend Films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Wisniewski, M.; Skopinska, J.; Kennedy, C.J.; Wess, T.J. Molecular Interactions in Collagen and Chitosan Blends. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.D.; Pérez, L.L.; Salcedo, J.M.; Córdoba, L.P.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J. Production and Characterization of Films Based on Blends of Chitosan from Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Waste and Pectin from Orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) Peel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafiq, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Ilyas, R.A.; Nazrin, A.; Sherwani, S.F.K.; Khalina, A. Antimicrobial Activities of Starch-Based Biopolymers and Biocomposites Incorporated with Plant Essential Oils: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abugoch, L.E.; Tapia, C.; Villamán, M.C.; Yazdani-Pedram, M.; Díaz-Dosque, M. Characterization of Quinoa Protein–Chitosan Blend Edible Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Dudakli, F.; Asan-Ozusaglam, M.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Baran, T.; Mentes, A.; Erdogan, S. Porous and Nanofiber α-Chitosan Obtained from Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Tested for Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, W.; Arbia, L.; Adour, L.; Amrane, A. Chitin Extraction from Crustacean Shells Using Biological Methods—A Review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hajji, S.; Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O.; Younes, I.; Jellouli, K.; Nasri, M. Chitin Extraction from Crab Shells by Bacillus Bacteria. Biological Activities of Fermented Crab Supernatants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, H.V.; Yamaka, S.; Pornsopin, P.; Jaturasitha, S.; Faggio, C. Proximate and Nutritional Content of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Flesh Cultured in a Tropical Highland Area. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, e20180234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Guerrero-Legarreta, I.; Bórquez, R. Chitin Extraction from Allopetrolisthes Punctatus Crab Using Lactic Fermentation. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 20, e00287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Goswami, P.; Paritosh, K.; Kumar, M.; Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V. Seafood Waste: A Source for Preparation of Commercially Employable Chitin/Chitosan Materials. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixto-Berrocal, A.M.; Vázquez-Aldana, M.; Miranda-Castro, S.P.; Martínez-Trujillo, M.A.; Cruz-Díaz, M.R. Chitin/Chitosan Extraction from Shrimp Shell Waste by a Completely Biotechnological Process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, N.S.; Ghaly, A.E.; Arab, F. Unconventional Approach for Demineralization of Deproteinized Crustacean Shells for Chitin Production. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Hammami, A.; Hajji, S.; Jridi, M.; Nasri, M.; Nasri, R. Chitin Extraction from Blue Crab (Portunus segnis) and Shrimp (Penaeus kerathurus) Shells Using Digestive Alkaline Proteases from P. Segnis Viscera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Yu, S.; Wu, D.; Xia, M.; Wen, Z.; Yao, Z.; Tang, J.; Wu, W. A Critical Review of Cast-off Crab Shell Recycling from the Perspective of Functional and Versatile Biomaterials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31581–31591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, F.; Maziati Akmal, M.H.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, K.; Samat, N. Biopolymer Chitosan: Potential Sources, Extraction Methods, and Emerging Applications. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Mengibar, M.; Harris, R.; Miralles, B.; Acosta, N.; Calderon, L.; Sanchez, A.; Heras, A. Role of Physicochemical Properties of Chitin and Chitosan on Their Functionality. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2014, 8, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, U.; Bajić, M.; Kõrge, K.; Oberlintner, A.; Murn, J.; Lokar, K.; Triler, K.V.; Likozar, B. From Waste/Residual Marine Biomass to Active Biopolymer-Based Packaging Film Materials for Food Industry Applications—A Review. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2020, 5, 20190099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenuvasan, M.; Malar, C.G.; Growther, L. Production of a Biopolymer Film from Biological Wastes and Its Statistical Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 13, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, W.; Dave, D.; Cheema, S.K.; Ramakrishnan, V.V.; Pohling, J. Biorefinery Approach and Environment-Friendly Extraction for Sustainable Production of Astaxanthin from Marine Wastes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.M.; Velazco Mata, S.; Acosta, J.L.; Herrera Cabrera, B.E.; López Valdez, L.G.; Reyes, C.; Barrales Cureño, J.H. Obtaining of Astaxanthin from Crab Exosqueletons and Shrimp Head Shells. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem 2021, 11, 13516–13523. [Google Scholar]
- Yara-Varón, E.; Li, Y.; Balcells, M.; Canela-Garayoa, R.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Chemat, F. Vegetable Oils as Alternative Solvents for Green Oleo-Extraction, Purification and Formulation of Food and Natural Products. Molecules 2017, 22, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshmand, H.; Shabanpour, B.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Golmakani, M.T. Optimization of Carotenoids Extraction from Blue Crab (Portunus Pelagicus) and Shrimp (Penaeus Semisulcatus) Wastes Using Organic Solvents and Vegetable Oils. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, N.M. Studies on Some Crustaceans of Tropical Waters with Special Reference to Pigments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Mysore, Mysuru, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, H.J.; Kerton, F. Sequential Extraction of Valuable Bio-Products from Snow Crab (Chionoecetes opilio) Processing Discards Using Eco-Friendly Methods. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix-Valenzuela, L.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Goycoolea-Valencia, F.; Argüelles-Monal, W. Supercritical CO2/Ethanol extraction of astaxanthin from blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) shell waste. J. Food Process Eng. 2001, 24, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadkelayeh, S.; Hawboldt, K. Extraction of Lipids and Astaxanthin from Crustacean By-Products: A Review on Supercritical CO2 Extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.N.; Roda, A.; Gouveia, L.F.; Fernández, N.; Bronze, M.R.; Matias, A.A. Astaxanthin Extraction from Marine Crustacean Waste Streams: An Integrate Approach between Microwaves and Supercritical Fluids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, M.N.; Hamdi, S.A.; Elbaz, R.M.; Aloufi, A.S.; El Sayed, R.R.; Ghonaim, G.M.; Farahat, M.G. Development of a Microbial-Assisted Process for Enhanced Astaxanthin Recovery from Crab Exoskeleton Waste. Fermentation 2023, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, S.A.H.; Ghonaim, G.M.; El Sayed, R.R.; Rodríguez-Couto, S.; Abd El-Ghany, M.N. Bioprocess of Astaxanthin Extraction from Shrimp Waste via the Common Microorganisms Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Lactobacillus Acidophilus in Comparison to the Chemical Method. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 14, 8333–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, E. Flavor and Pigment Extraction from Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Processing by-Products. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.-T. Flavor Constituents in Enzyme Hydrolysates from Shore Swimming Crab and Spotted Shrimp. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 30, 787–795. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.-H.; Liu, T.-T.; Wan, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xia, N.; Wang, Q.-Z.; Chen, D.-W. Enrichment of the Umami-Taste-Active Amino Acids and Peptides from Crab Sauce Using Ethanol Precipitation and Anion-Exchange Resin. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, K.; Subbaiah, L.; Palanisamy, S. Exploring the Antimicrobial and Anticancer Potential of a Bioactive Peptide from T. Radiatus: A Comprehensive Study. Proceedings 2024, 100, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-D.; Xi, Q.-H.; Kong, J.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius Litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molchanov, V.; Yegorov, A.; Molchanov, M.; Timchenko, A.; Novikov, V.; Novojilov, N.; Timchenko, M. Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Hepatopancreas of the Red King Crab. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnedy, P.A.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Bioactive Proteins and Peptides from Macroalgae, Fish, Shellfish and Marine Processing Waste. In Marine Proteins and Peptides; Kim, S., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 5–39. ISBN 978-1-118-37506-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tincu, J.A.; Taylor, S.W. Antimicrobial Peptides from Marine Invertebrates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, L.; Robinette, D.W.; Noga, E.J. Callinectin, an Antibacterial Peptide from Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus, Hemocytes. Mar. Biotechnol. 1999, 1, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madende, M.; Hayes, M. Fish By-Product Use as Biostimulants: An Overview of the Current State of the Art, Including Relevant Legislation and Regulations within the EU and USA. Molecules 2020, 25, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebestyén, Z.; Jakab, E.; Domán, A.; Bokrossy, P.; Bertóti, I.; Madarász, J.; László, K. Thermal Degradation of Crab Shell Biomass, a Nitrogen-Containing Carbon Precursor. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 142, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekvapil, F.; Aluas, M.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Suciu, M.; Bortnic, R.-A.; Glamuzina, B.; Pinzaru, S.C. From Blue Bioeconomy toward Circular Economy through High-Sensitivity Analytical Research on Waste Blue Crab Shells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16820–16827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zheng, G.; Li, W.; McDowell, M.T.; Seh, Z.; Liu, N.; Lu, Z.; Cui, Y. Crab Shells as Sustainable Templates from Nature for Nanostructured Battery Electrodes. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3385–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Karlsson, A.M. Image Analyses of Two Crustacean Exoskeletons and Implications of the Exoskeletal Microstructure on the Mechanical Behavior. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2854–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasingha, N.; Kantavong, A.; Tunkijjanukij, S.; Aenglong, C.; Liu, H.-B.; Klaypradit, W. Effect of Calcination Temperature on Structure and Characteristics of Calcium Oxide Powder Derived from Marine Shell Waste. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, D.T.; MacQuarrie, S.; Hawboldt, K.A. Removal of Copper from Sulfate Solutions Using Biochar Derived from Crab Processing By-Product. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Foong, S.Y.; He, Y.; Liew, R.K.; Ma, N.L.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Ge, S.; Naushad, M.; Lam, S.S. Upcycling Crab Shell Waste into Biochar for Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent via Microwave Pyrolysis and Activation. Environ. Res. 2024, 248, 118282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Pandey, A.; Rosy; Sharma, Y.C. A Review on Sustainable Mesoporous Activated Carbon as Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Hazardous Dyes from Industrial Wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Biomass-derived renewable carbonaceous materials for sustainable chemical and environmental applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6458–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekvapil, F.; Mihet, M.; Lazar, G.; Pinzaru, S.C.; Gavrilović, A.; Ciorîță, A.; Levei, E.; Tamaș, T.; Soran, M.-L. Comparative Analysis of Composition and Porosity of the Biogenic Powder Obtained from Wasted Crustacean Exoskeletonsafter Carotenoids Extraction for the Blue Bioeconomy. Water 2023, 15, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Farjadfard, S.; Esmaeili, H.; Saberi, M.; Sahebi, S.; Dobaradaran, S.; Ramavandi, B. Characteristics and Performance of Cd, Ni, and Pb Bio-Adsorption Using Callinectes sapidus Biomass: Real Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6336–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, G.; Nekvapil, F.; Hirian, R.; Glamuzina, B.; Tamas, T.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Pinzaru, S.C. Novel Drug Carrier: 5-Fluorouracil Formulation in Nanoporous Biogenic Mg-Calcite from Blue Crab Shells—Proof of Concept. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27781–27790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekvapil, F.; Ganea, I.-V.; Ciorîță, A.; Hirian, R.; Tomšić, S.; Martonos, I.M.; Cintă Pinzaru, S. A New Biofertilizer Formulation with Enriched Nutrients Content from Wasted Algal Biomass Extracts Incorporated in Biogenic Powders. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Ilkaeva, M.; Vicente, F.; Vieira, R.; Sardo, M.; Lourenço, M.A.O.; Silvestre, A.; Marin-Montesinos, I.; Mafra, L. Valorization of Crab Shells as Potential Sorbent Materials for CO2 Capture. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 17956–17965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, D.J.; Yeom, S.H. Recycling Wasted Biomaterial, Crab Shells, as an Adsorbent for the Removal of High Concentration of Phosphate. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2646–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayuseno, A.P.; Prasetya, A.I.; Ismail, R.; Setiyana, B.; Jamari, J. Reuse of Waste Crab Shells for Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate as a Candidate Biomaterial. Medicine 2022, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, B.; Ravishankar, N. Controlled Synthesis of Plate-Shaped Hydroxyapatite and Implications for the Morphology of the Apatite Phase in Bone. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4855–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borciani, G.; Fischetti, T.; Ciapetti, G.; Montesissa, M.; Baldini, N.; Graziani, G. Marine Biological Waste as a Source of Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habashy, S.E.; El-Kamel, A.H.; Essawy, M.M.; Abdelfattah, E.-Z.A.; Eltaher, H.M. Engineering 3D-Printed Core–Shell Hydrogel Scaffolds Reinforced with Hybrid Hydroxyapatite/Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles for in Vivo Bone Regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4019–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, N.E.; Zhou, J.; Zadpoor, A.A. Sustainable Sources of Raw Materials for Additive Manufacturing of Bone-Substituting Biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2301837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ri, G.; Ri, O.-S.; Pang, M.-R. The Function of the Crab Shell Powder as Calcium Supplementary in the Treatment of Rickets. Pediatr. Med. 2020, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggernauth-Ali, P.; John, E.; Bridgemohan, P. The Application of Calcined Marlstones as a Catalyst in Biodiesel Production from High Free Fatty Acid Coconut Oil. Fuel 2015, 158, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-C.; Sun, L.; Yan, J. Carbon Sequestration via Shellfish Farming: A Potential Negative Emissions Technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 171, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.C.; Cavalcanti, A.S.; Silva, R.O.; Alves Junior, S.; Sousa, F.P.D.; Pasa, V.M.D.; Arias, S.; Pacheco, J.G.A. Residue-based CaO heterogeneous catalysts from crab and mollusk shells for FAME production via transesterification. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomman, T.; Boonwan, J.; Boonwan, Y.; Chareonwongsa, S.; Chaiyaporn, W. Kinetic Study of Biodiesel Synthesis from Palm Oil by Using Low-Cost Calcium Oxide Catalyst. Eng. Trans. A Res. Publ. Mahanakorn Univ. Technol. 2015, 18, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zheng, X.; Dong, A.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, J. Biont Shell Catalyst for Biodiesel Production. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boey, P.-L.; Maniam, G.P.; Hamid, S.A.; Ali, D.M.H. Crab and Cockle Shells as Catalysts for the Preparation of Methyl Esters from Low Free Fatty Acid Chicken Fat. J Am Oil Chem Soc 2011, 88, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Fu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X. Crab Shell-Derived Lotus Rootlike Porous Carbon for High Efficiency Isomerization of Glucose to Fructose under Mild Conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4466–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Pal, S. Promises in Direct Conversion of Cellulose and Lignocellulosic Biomass to Chemicals and Fuels: Combined Solvent–Nanocatalysis Approach for Biorefinary. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 62, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, İ.K.; Güngör, A.; Özdemir, T. Assessment of Blue Crab Shell (Callinectes sapidus) Particles as Bio-Based Filler to EPDM Rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, I.; Muniyadi, M.; Ismail, H. A Review on Clay-reinforced Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer Composites. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 1698–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athawale, A.A.; Joshi, A.M. Electronic Applications of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber and Its Composites. In Flexible and Stretchable Electronic Composites; Ponnamma, D., Sadasivuni, K.K., Wan, C., Thomas, S., Al-Ali AlMa’adeed, M., Eds.; Springer Series on Polymer and Composite Materials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 305–333. ISBN 978-3-319-23662-9. [Google Scholar]
- Valberg, P.A.; Long, C.M.; Sax, S.N. Integrating Studies on Carcinogenic Risk of Carbon Black: Epidemiology, Animal Exposures, and Mechanism of Action. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntoni, R.; Ceppi, M.; Gennaro, V.; Ugolini, D.; Puntoni, M.; La Manna, G.; Casella, C.; Franco Merlo, D. Occupational Exposure to Carbon Black and Risk of Cancer. Cancer Causes Control 2004, 15, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniyappan, S.; Sivakumar, N.K.; Sekar, V. Sustainable Approach to the Revalorization of Crab Shell Waste in Polymeric Filament Extrusion for 3D Printing Applications. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, N.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Feng, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Zheng, X. Effect of Crab Shell Particles on the Thermomechanical and Thermal Properties of Polybenzoxazine Matrix. Mater. Des. 2014, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaravelu, D.L.; M, R.R.; R, V.; Manoharan, S.; Kchaou, M. Development and Performance Evaluation of Eco-Friendly Crab Shell Powder Based Brake Pads for Automotive Applications. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2019, 16, 6502–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Ai, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Feng, W.; Huang, Y. Crab Shell-Derived Nitrogen-Doped Micro-/Mesoporous Carbon as an Effective Separator Coating for High Energy Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19892–19900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, D.; Guo, Z.; Tamirat, A.G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Crab-Shell Induced Synthesis of Ordered Macroporous Carbon Nanofiber Arrays Coupled with MnCo2O4 Nanoparticles as Bifunctional Oxygen Catalysts for Rechargeable Zn–Air Batteries. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11148–11157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-J.; Wang, X.-M.; Cui, W.-J.; Dou, Y.-Q.; Zhao, D.-Y.; Xia, Y.-Y. Highly Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Nanofiber Arrays from a Crab Shell Biological Template and Its Application in Supercapacitors and Fuel Cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Chen, W.; Ding, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Q. Biomass Waste Derived Multi-Hierarchical Porous Carbon Combined with CoFe2O4 as Advanced Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chang, B.; Yin, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, B.; Dong, X. Crab Shell-Derived Honeycomb-like Graphitized Hierarchically Porous Carbons for Satisfactory Rate Performance of All-Solid-State Supercapacitors. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Valcareggi, S.A.; Ferreira, S.R.; Hense, H. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Waste Processing to Obtain Chitin, Protein, and Astaxanthin-Enriched Extract. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2017, 3, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, G.M.; Huang, C.C.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Sirohi, R.; Awsathi, M.K.; Pillai, S.; Pandey, A. Enzymatic Approaches in the Bioprocessing of Shellfish Wastes. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Moisture (%) | Protein (%) | Lipids (%) | Ash (%) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body meat | 66.4–86.7 | 14.7–30.3 | 0.4–1.6 | 1.1–2.0 | [47,48,49] |
| Claw meat | 65.6–83.1 | 15.0–31.0 | 0.6–1.2 | 1.3–2.1 | [47,48,49] |
| Brown meat | 73.6 | 18.8 | 0.9 | 2.15 | [49] |
| Sample | Na (mg/100 g) | K (mg/100 g) | Ca (mg/100 g) | Mg (mg/100 g) | P (mg/100 g) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body meat | 326.9–723.6 | 62.8–244.4 | 64.9–455.4 | 37.1–85.5 | 165.4–202.2 | [48,49] |
| Claw meat | 266.8–663.9 | 69.1–256.3 | 149.2–398.2 | 35.1–117.7 | 135.2–176.2 | [48,49] |
| Brown meat | 1133.0 | 64.5 | 444.0 | 74.4 | 164.4 | [49] |
| Bioactive Category | Bioactive Molecule | Use | Field of Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharides | Chitin | Bio-film | Food packaging Pharma-biomed |
| Chitosan | Antioxidant Bio-film Bio-fibre | Food packaging Pharma-biomed | |
| Carotenoids | Astaxanthin | Antioxidant Pigment | Food/feed additive |
| Canthaxanthin, 4-hydroxiequinone, 3-ketocanthaxanthin | Natural pigments | Food/feed additive | |
| Protein | Free amino acids, i.e., arginine, alanine, glycine, taurine, glutamic acid taurine, glycine | Flavour Plant biostimulant | Food/feed additive Agriculture |
| Hydrolyzates | Flavour Functional ingredient | Food additive |
| Application | Use | Field of Application |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-sorbent | Wastewater treatment | Metal removal Antibiotics removal |
| CO2 capture | Industry | |
| Biogenic hydroxyapatite | Implant material | Medicine |
| Calcium supplementary | Pharmaceutical | |
| Bio-catalyst | Biodiesel production | Biofuels |
| Monosaccharides isomerization | Food | |
| Bio-filler | Polymer additive | Industry |
| Filaments | 3D printing | |
| Brake pads | Automotive | |
| Porous carbon material and nanofibers | High-tech electronic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamburini, E. The Blue Treasure: Comprehensive Biorefinery of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus). Foods 2024, 13, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132018
Tamburini E. The Blue Treasure: Comprehensive Biorefinery of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus). Foods. 2024; 13(13):2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132018
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamburini, Elena. 2024. "The Blue Treasure: Comprehensive Biorefinery of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus)" Foods 13, no. 13: 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132018
APA StyleTamburini, E. (2024). The Blue Treasure: Comprehensive Biorefinery of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus). Foods, 13(13), 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132018







