Effects of Emulsifiers on Physicochemical Properties and Carotenoids Bioaccessibility of Sea Buckthorn Juice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. DHPM Treatment of Sea Buckthorn Juice
2.3. Particle Size Measurement
2.4. ζ-Potential Measurement
2.5. Turbidity, Total Soluble Solids Content and pH Measurement
2.6. Physical Stability
2.7. Observation of Microstructure
2.8. Color
2.9. Determination of Carotenoids Content
2.10. In Vitro Digestion
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
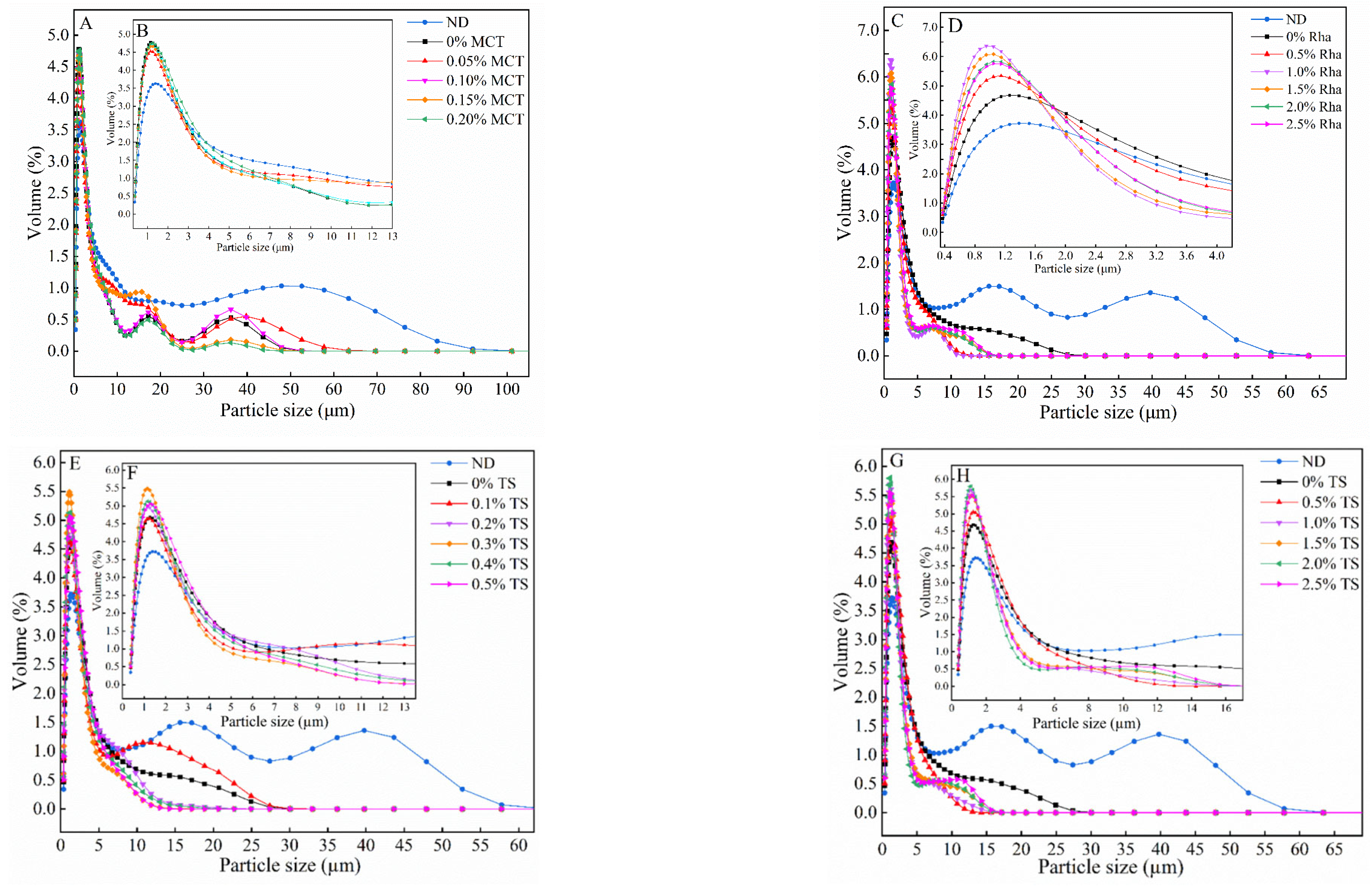
3.1. The Particle Size Distribution of Sea Buckthorn Juice
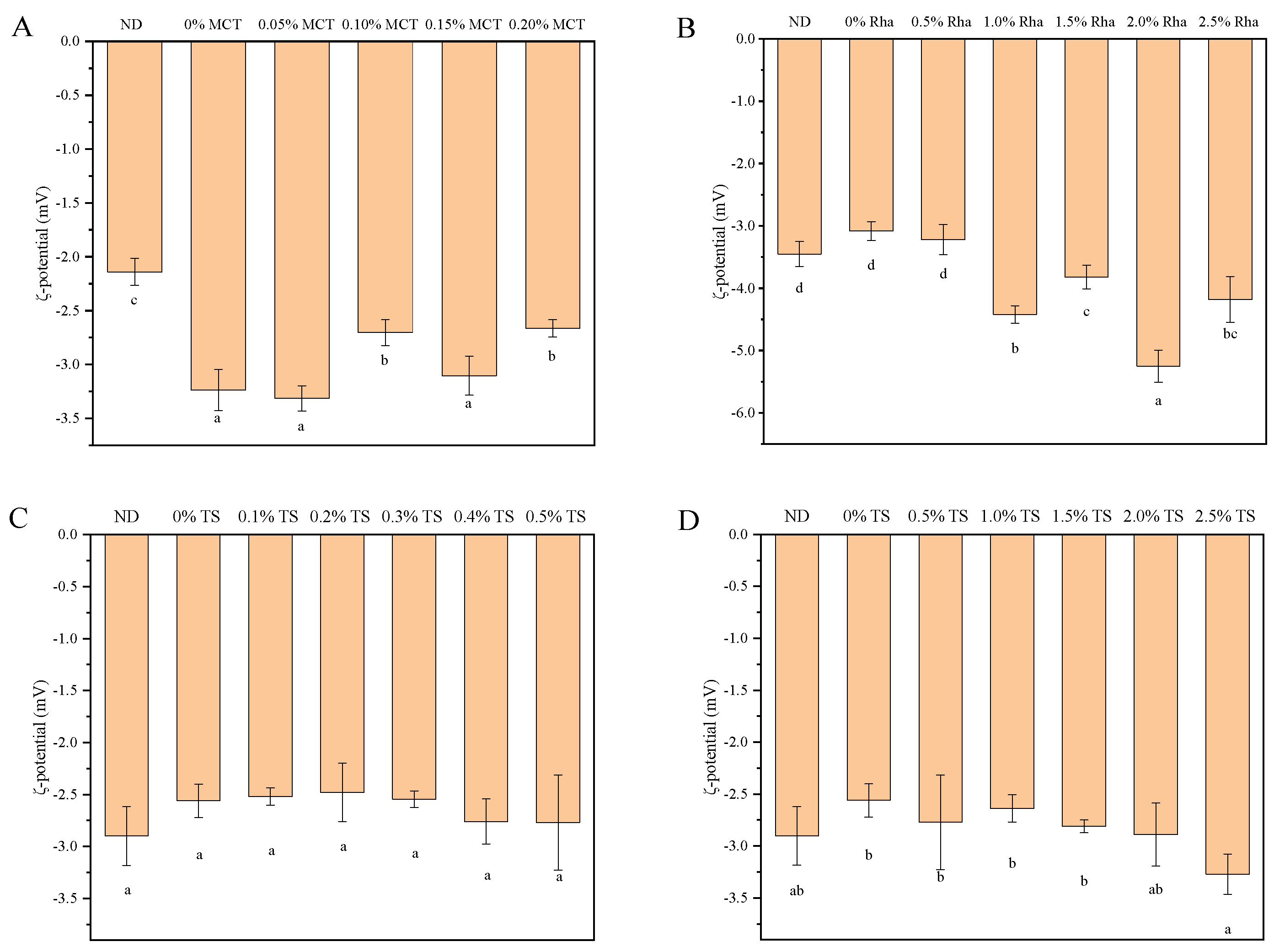
3.2. ζ-Potential
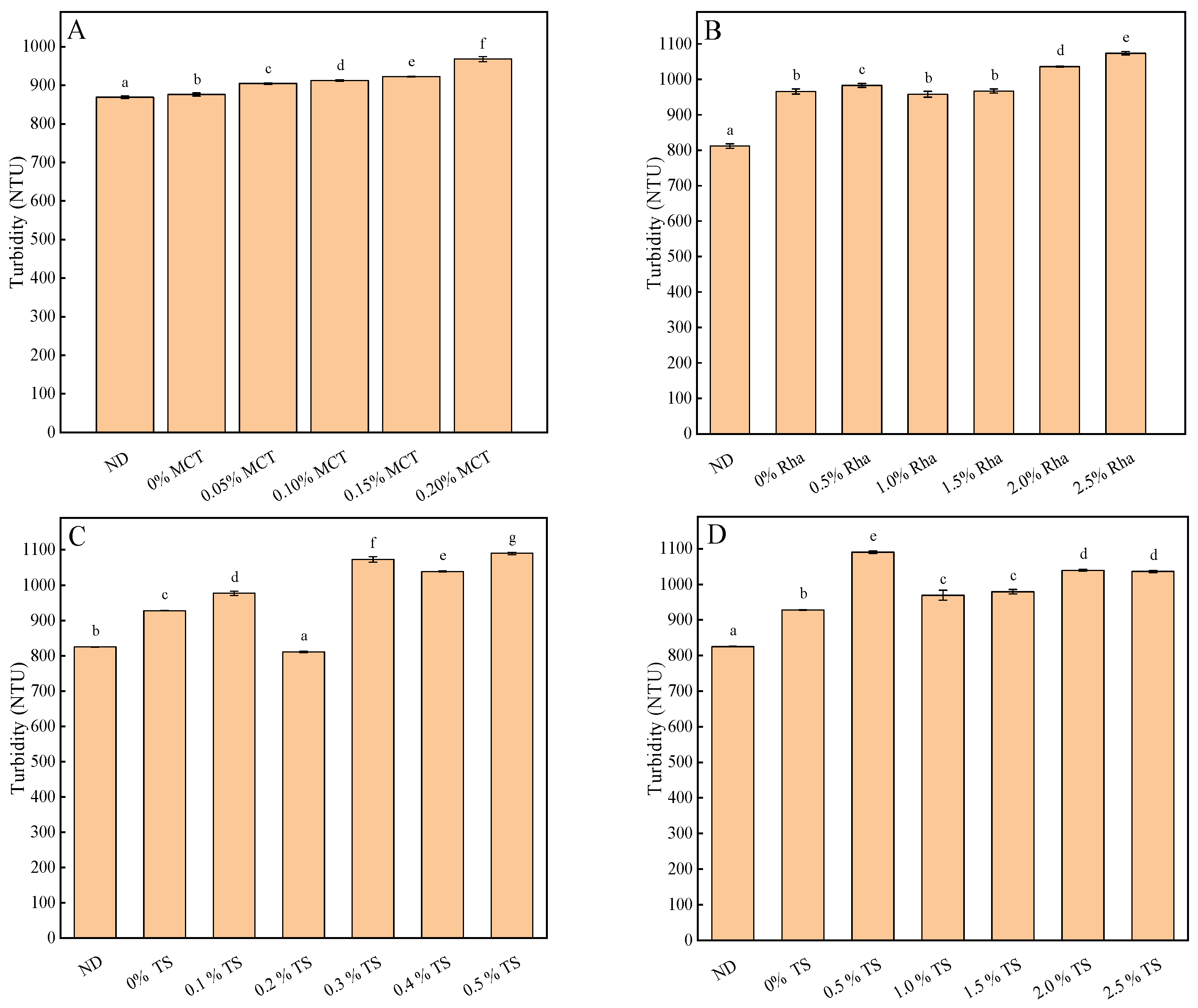
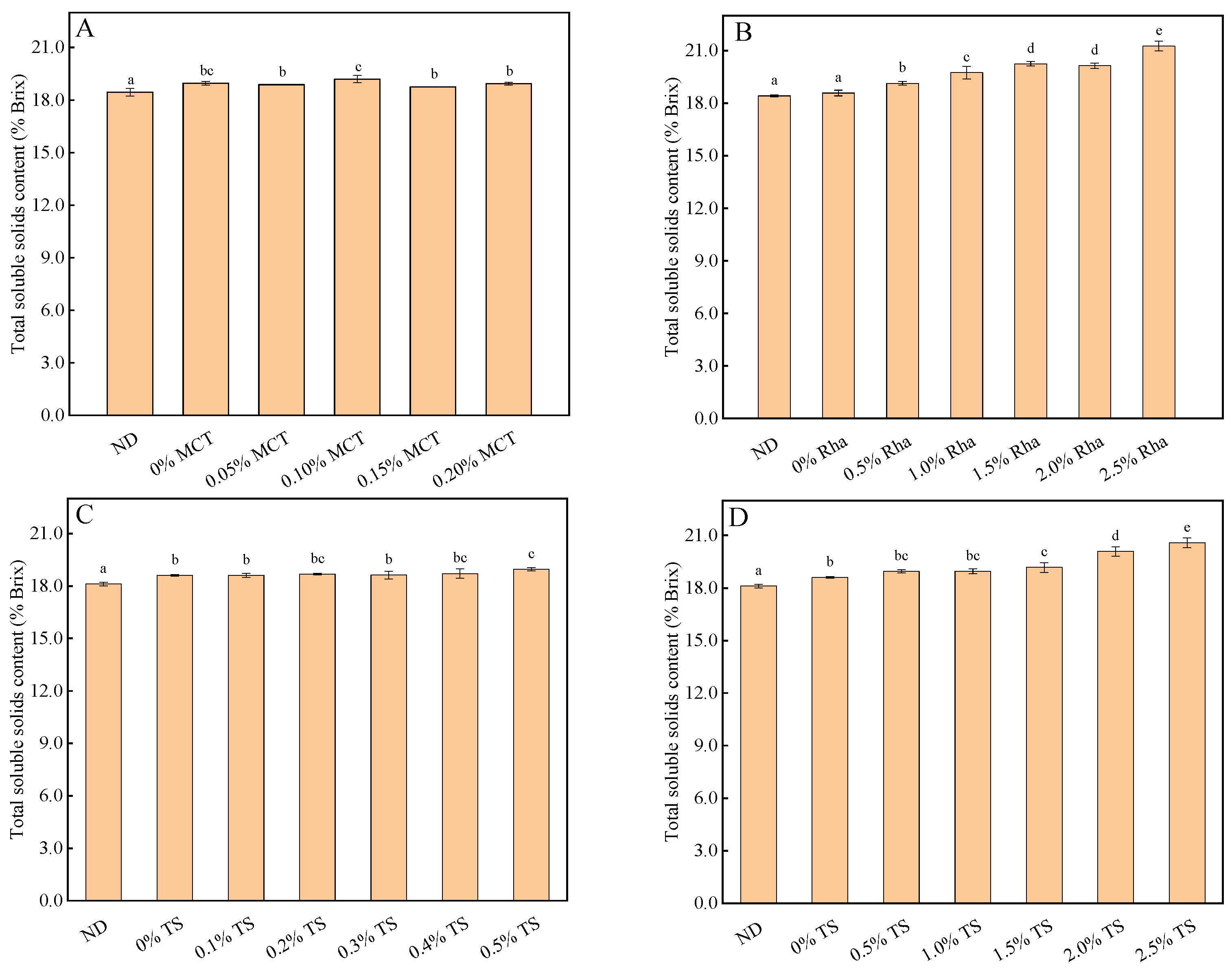
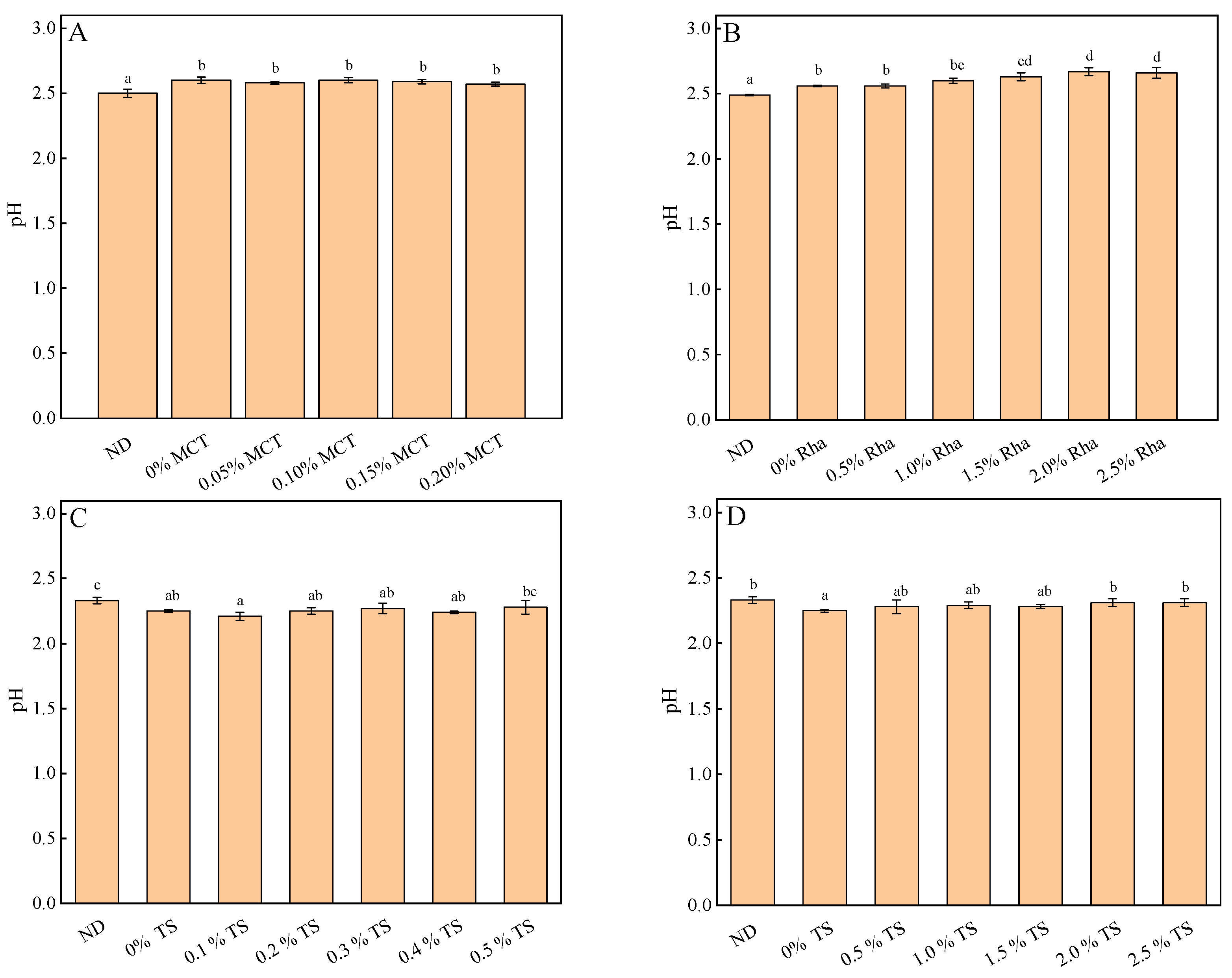
3.3. Turbidity, pH and Total Soluble Solids Content
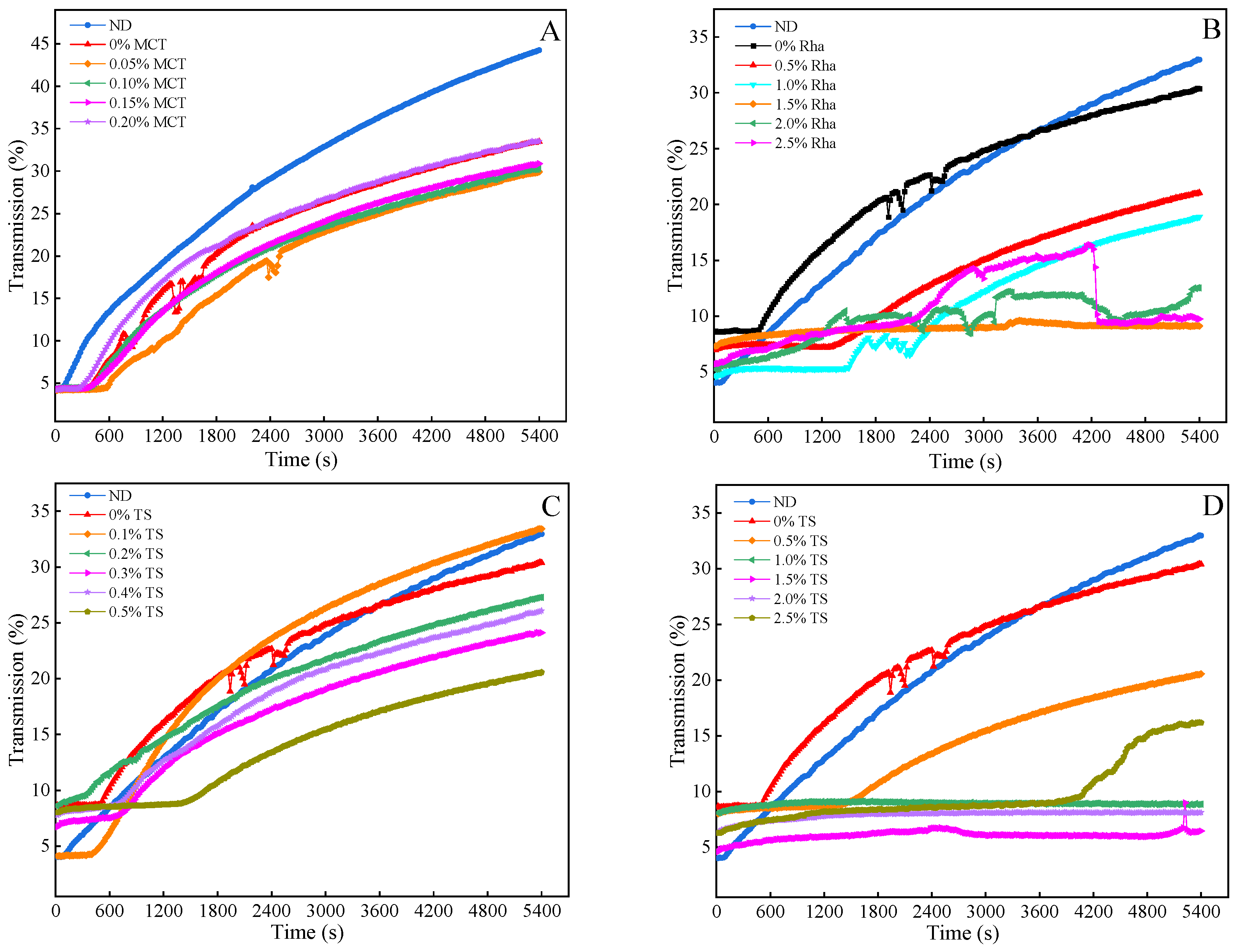
3.4. Physical Stability
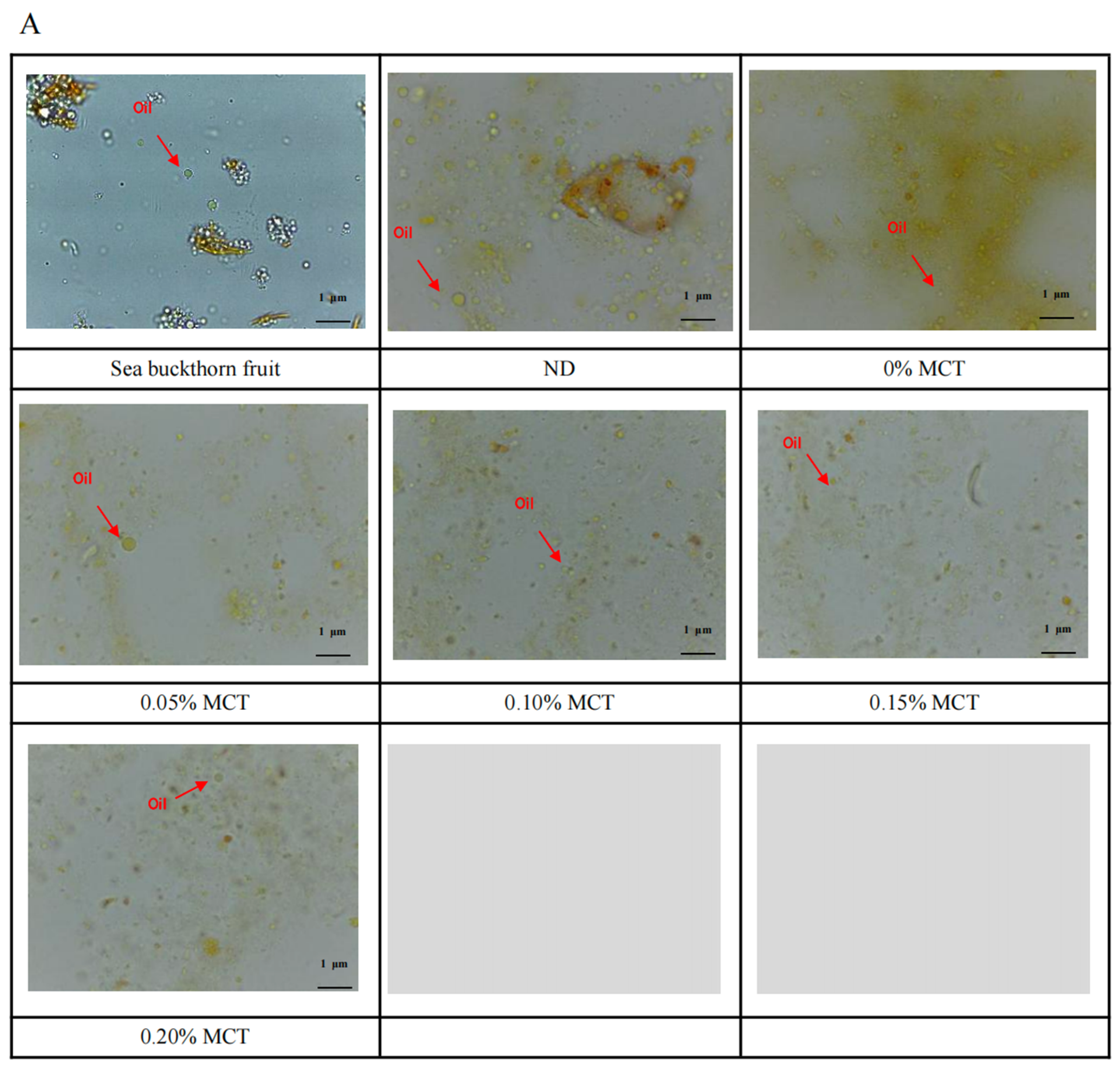
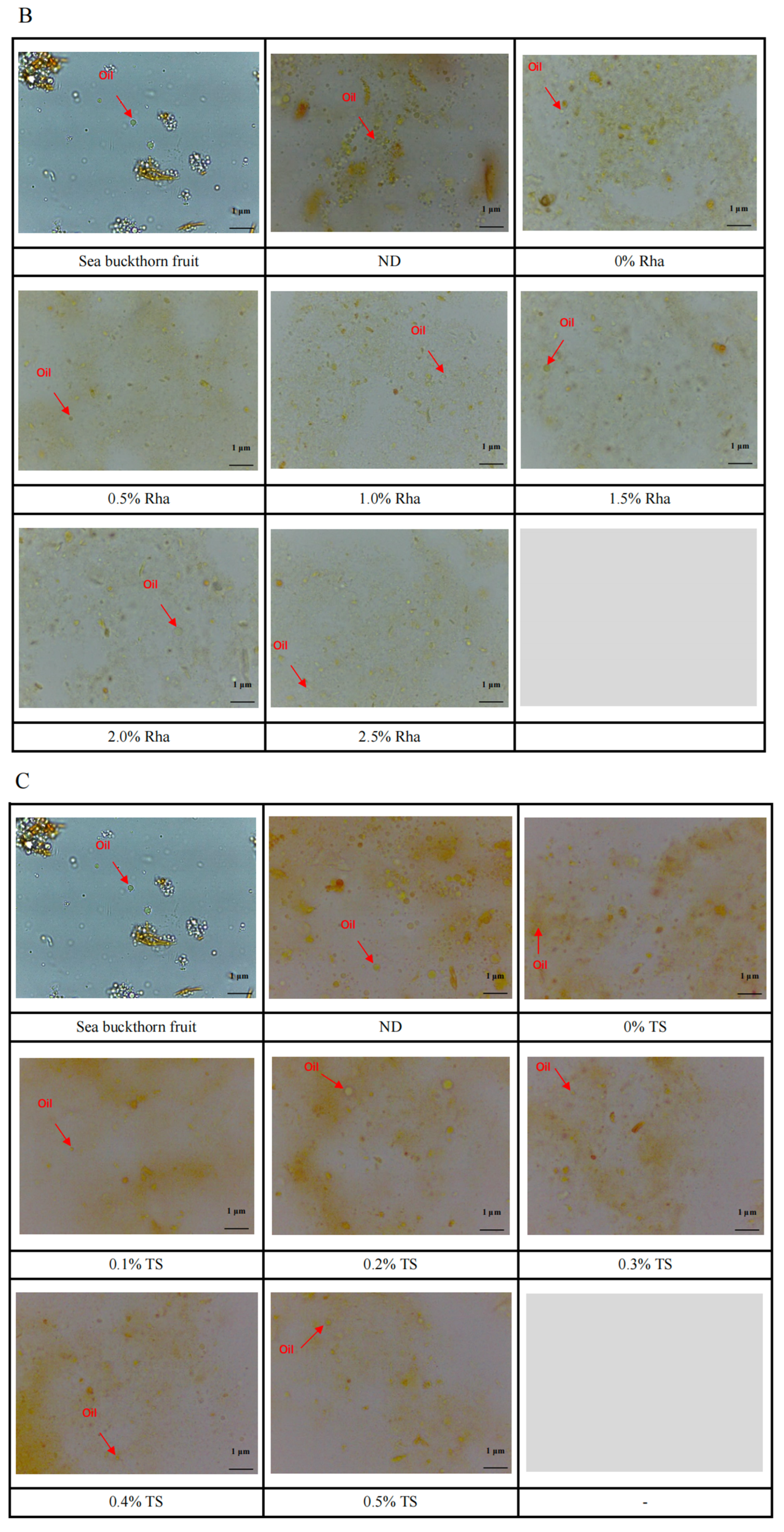
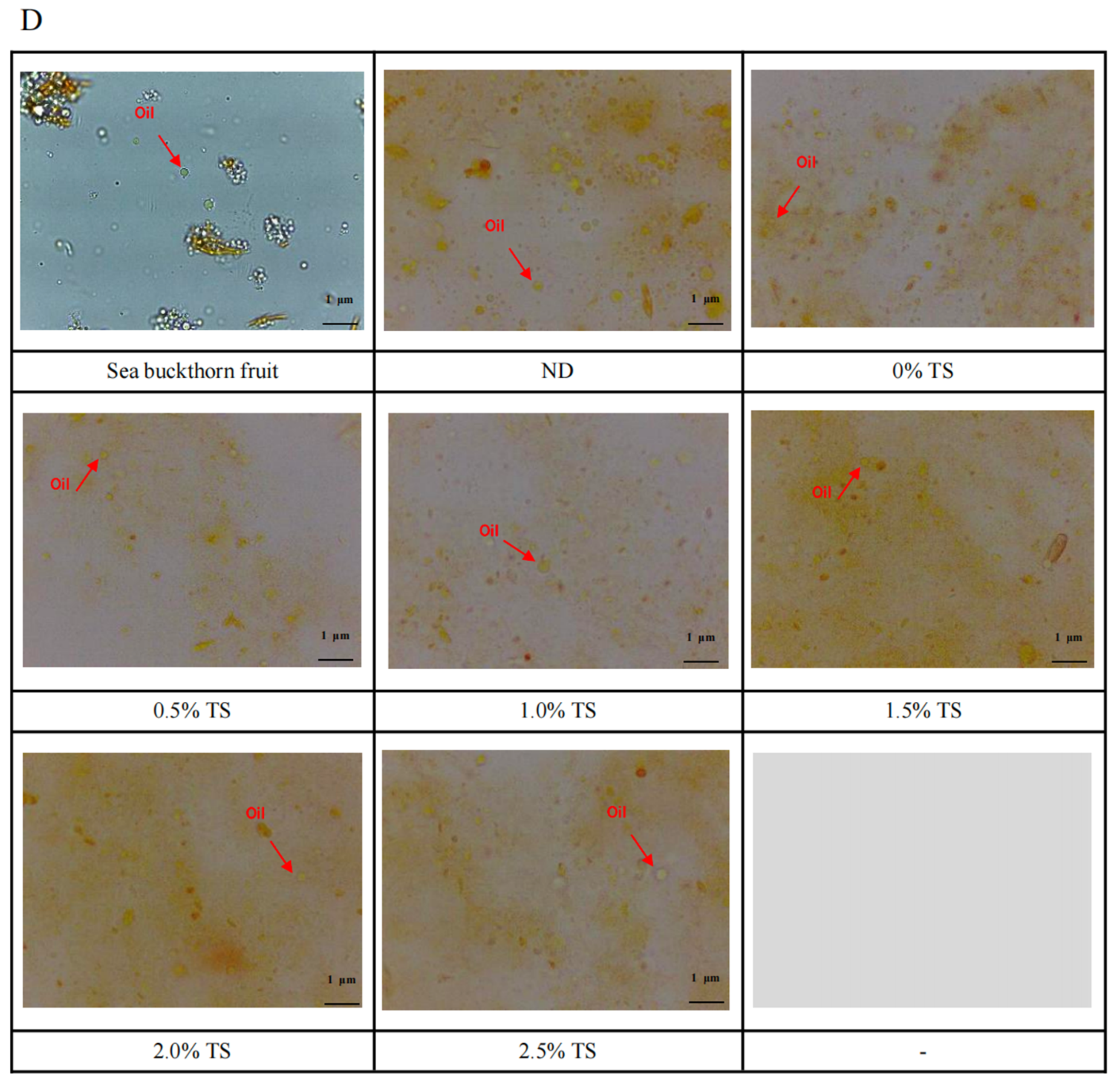
3.5. Microstructure
3.6. Color Analysis
3.7. Carotenoids Content
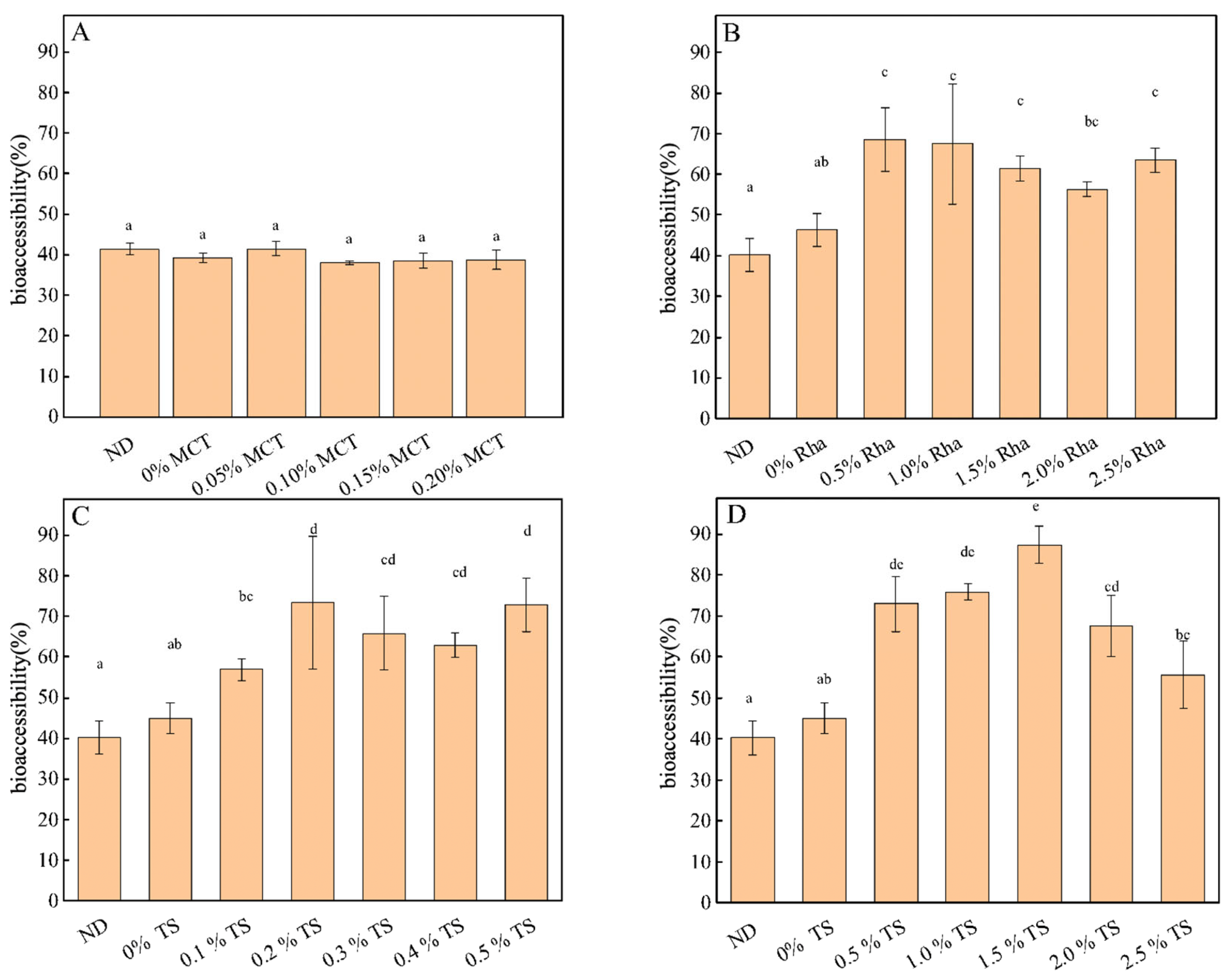
3.8. Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, K.; Fernando, W.; Durham, R.; Stockmann, R.; Jayasena, V. Nutritional Value, Health-promoting Benefits and Food Application of Sea Buckthorn. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 2122–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Xu, D.X.; Chen, S.; Yuan, F.; Mao, L.K.; Gao, Y.X. Superfruits in China: Bioactive phytochemicals and their potential health benefits—A Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6892–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.R.; Li, N.; Su, C.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhao, X.J.; Yang, L.L.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.Y.; Ma, X.Q. The bioactive components as well as the nutritional and health effects of sea buckthorn. Rsc Adv. 2020, 10, 44654–44671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.T.; Liao, X.J. High pressure processing for sea buckthorn juice with higher superoxide dismutase activity. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 252–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. Update on natural food pigments—A mini-review on carotenoids, anthocyanins, and betalains. Food Res. Int. 2019, 124, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukin, T.P.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Gensh, K.V.; Tulysheva, E.A.; Salnikova, O.I.; Grazhdannikov, A.E.; Kolosova, E.A. Bioactive Components of Sea Buckthorn Hippophae rhamnoides L. Foliage. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2017, 43, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkacz, K.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Medina, S.; Turkiewicz, I.P.; Domínguez-Perles, R.; Nowicka, P.; Wojdylo, A. Phytoprostanes, phytofurans, tocopherols, tocotrienols, carotenoids and free amino acids and biological potential of sea buckthorn juices. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhkheil, A.; Naghdi Badi, H.; Mehrafarin, A.; Abdossi, V. Chemical constituents of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) fruit in populations of central Alborz Mountains in Iran. Res. J. Pharmacogn. (RJP) 2017, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Aaby, K.; Martinsen, B.K.; Borge, G.I.A.; Roen, D. Bioactive compounds and color of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) purees as affected by heat treatment and high-pressure homogenization. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentsendavaa, C.; Székély, D.; Furulyás, D.; Végvári, G.; Gonelimali, F.; Kumar, P.; Steger-Máté, M. Stability of Carotene and Phenols of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Juice with Pomace during Storage. Period. Polytech.-Chem. Eng. 2021, 65, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Chen, M.S.; Li, Y.T.; Dai, T.T.; Shuai, X.X.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.M. Modification of food macromolecules using dynamic high pressure microfluidization: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.K.; Mert, B. Characterization and evaluation of emulsifying properties of high pressure microfluidized and pH shifted corn gluten meal. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, A.; Guamis, B. Opportunities for Ultra-High-Pressure Homogenisation (UHPH) for the Food Industry. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Li, J.Y.; Guo, T.T.; Li, Y.J.; Ni, Y.D.; Zhou, Q.C. Effect of dynamic high-pressure microfluidization on structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of pea albumin. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Ren, M.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, L. Modification of insoluble dietary fiber from rice bran with dynamic high pressure microfluidization: Cd(II) adsorption capacity and behavior. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 73, 102765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, F.; Lan, X.H.; Gong, S.X.; Wang, Z.W. Characteristics of pectin from black cherry tomato waste modified by dynamic high-pressure microfluidization. J. Food Eng. 2018, 216, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, A.; Kaur, B.P.; Pareek, S. Effect of Microfluidization on Deteriorative Enzymes, Sugars, Chlorophyll, and Color of Sugarcane Juice. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, W.J.; Ge, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.H.; Li, C.W.; Zhang, B.; Zong, W. Comparison of the effects of dynamic high-pressure microfluidization and conventional homogenization on the quality of peach juice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5994–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, B. Using high pressure microfluidization to improve physical properties and lycopene content of ketchup type products. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Wang, Y.; Selomulya, C. Dairy and plant proteins as natural food emulsifiers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Dong, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Ren, J.N.; Pan, S.Y.; Fan, G. Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release. Molecules 2016, 21, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergenståhl, B. Physicochemical aspects of an emulsifier functionality. In Food Emulsifiers and Their Applications, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 173–194. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Wellala, C.K.D.; Zhang, B. Effects of high pressure homogenization and addition of oil on the carotenoid bioaccessibility of carrot juice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneiwa Kubo, M.T.; Augusto, P.E.D.; Cristianini, M. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on the physical stability of tomato juice. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abliz, A.; Liu, J.F.; Mao, L.K.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y.X. Effect of dynamic high pressure microfluidization treatment on physical stability, microstructure and carotenoids release of sea buckthorn juice. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, S.; Oszmianski, J.; Kolniak-Ostek, J. Influence of different pectinolytic enzymes on bioactive compound content, antioxidant potency, colour and turbidity of chokeberry juice. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hespeler, D.; Knoth, D.; Keck, C.M.; Müller, R.H.; Pyo, S.M. smartPearls® for dermal bioavailability enhancement—Long-term stabilization of suspensions by viscoelasticity. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, A.P.; Hung, Y.C.; Adhikari, K. Optimization of Emulsifier and Stabilizer Concentrations in a Model Peanut-Based Beverage System: A Mixture Design Approach. Foods 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Bi, X.F.; Guo, D.D.; Xing, Y.G.; Che, Z.M. The effect of high-power ultrasound on the quality of carrot juice. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2019, 25, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinco, C.M.; Fernández-Vázquez, R.; Escudero-Gilete, M.L.; Heredia, F.J.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Vicario, I.M. Effect of Orange Juice’s Processing on the Color, Particle Size, and Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assuncao, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixé-Roig, J.; Oms-Oliu, G.; Ballesté-Muñoz, S.; Odriozola-Serrano, I.; Martín-Belloso, O. Improving the In Vitro Bioaccessibility of β-Carotene Using Pectin Added Nanoemulsions. Foods 2020, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.R.; Pulikkal, A.K. Nano emulsions stabilized by natural emulsifiers: A comprehensive review on feasibility, stability and bio-applicability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 92, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenhuettl, G.L. Future Trends of Emulsifiers and Other Food Ingredients. In Food Emulsifiers and Their Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural emulsifiers—Biosurfactants, phospholipids, biopolymers, and colloidal particles: Molecular and physicochemical basis of functional performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammak, I.; Sobral, P.J.D.; Aquino, A.; das Neves, M.A.; Conte, C.A. Nanoemulsions: Using emulsifiers from natural sources replacing synthetic ones-A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2721–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, F.Y.; Han, L.; Li, L.; Jiang, L.Z.; Qi, B.K.; Li, Y. Soy/whey protein isolates: Interfacial properties and effects on the stability of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Yuan, M.; Cao, Y.; Tang, J.L.; Zhao, J.C.; Zheng, H.Y.; Zhu, L.Q.; Cai, Z.P.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Tea saponin, a natural emulsifier, performs better in preparation of cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsion. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, L.E.; Siva, S.P.; Ho, Y.K.; Chan, E.S.; Tey, B.T. Recent advances of characterization techniques for the formation, physical properties and stability of Pickering emulsion. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 277, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Bayram, I.; Zhang, W.T.; Su, J.Q.; Shu, X.; Yuan, F.; Mao, L.K.; Gao, Y.X. Fabrication and characterization of curcumin-loaded pea protein isolate-surfactant complexes at neutral pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, D.; Mackie, A.; Yang, S.F.; Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Mao, L.K.; Gao, Y.X. Stability, Interfacial Structure, and Gastrointestinal Digestion of β-Carotene-Loaded Pickering Emulsions Co-stabilized by Particles, a Biopolymer, and a Surfactant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reineccius, G.A. Factors controlling the turbidity of submicron emulsions stabilized by food biopolymers and natural surfactant. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Cao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, K.; Xie, L.; Li, X. Does binary blend emulsifier enhance emulsifier performance? Preparation of baicalin nanoemulsions using tea saponins and glycyrrhizic acid as binary blend emulsifier. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.; Abliz, A.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, S. Effect of dynamic high pressure microfluidization on physical properties of goji juice, mango juice and carrot puree. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 189, 02027. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, T.H.J.; Harrison, J.E. Centrifugal yield and further microscopic characterization of sea buckthorn juice products. J. Food Qual. 2005, 28, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, T.; Harrison, J.E. Microscopic structural components of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) juice prepared by centrifugation. Lebensm.-Wiss. Und-Technol. -Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lele, V.; Monstaviciute, E.; Varinauskaite, I.; Peckaityte, G.; Paskeviciute, L.; Plytnikaite, M.; Tamosiunaite, V.; Pikunaite, M.; Ruzauskas, M.; Stankevicius, R.; et al. Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) and Quince (Cydonia oblonga L.) Juices and Their By-Products as Ingredients Showing Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties for Chewing Candy: Nutraceutical Formulations. J. Food Qual. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgerel, U.; Islam, M.Z.; Kitamura, Y.; Kokawa, M.; Odbayar, T.O. Effect of micro wet milling process on particle sizes, antioxidants, organic acids, and specific phenolic compounds of whole sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) juices. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva-Estrada, S.D.; García, O.; Mendoza, M.R.; Jiménez, M. Characterization of O/W emulsions of carotenes in blackberry juice performed by ultrasound and high-pressure homogenization. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tydeman, E.A.; Parker, M.L.; Faulks, R.M.; Cross, K.L.; Fillery-Travis, A.; Gidley, M.J.; Rich, G.T.; Waldron, K.W. Effect of Carrot (Daucus carota) Microstructure on Carotene Bioaccessibility in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. 2. In Vivo Digestions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9855–9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinco, C.M.; Sentandreu, E.; Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Navarro, J.L.; Vicario, I.M.; Melendez-Martinez, A.J. Influence of high pressure homogenization and pasteurization on the in vitro bioaccessibility of carotenoids and flavonoids in orange juice. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Bi, J.; Liu, X.; Lyu, Y.; Verkerk, R.; Dekker, M. Micelle separation conditions based on particle size strongly affect carotenoid bioaccessibility assessment from juices after in vitro digestion. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, E.T.; Maráz-Szabó, L.; Varga, J. Examination of the protein-emulsifier-carbohydrate interactions in amaranth based pasta products. Acta Aliment. 2001, 30, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shi, A.; Zhong, J.; Rao, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H. Correlation between interfacial layer properties and physical stability of food emulsions: Current trends, challenges, strategies, and further perspectives. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 313, 102863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total Carotenoids Content mg/100 g fw | Total Carotenoids Content mg/100 g fw | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MCT | Low-concentration tea saponion | ||
| ND | 9.1057 ± 1.1717 a | ND | 10.8329 ± 0.9316 ab |
| 0% MCT | 8.3488 ± 0.5982 a | 0% TS | 11.4504 ± 1.1880 b |
| 0.05% MCT | 7.8128 ± 0.2189 a | 0.1% TS | 8.0607 ± 0.5908 a |
| 0.10% MCT | 7.8057 ± 0.2256 a | 0.2% TS | 10.5680 ± 2.3076 ab |
| 0.15% MCT | 7.8106 ± 0.2145 a | 0.3% TS | 9.9941 ± 1.4994 ab |
| 0.20% MCT | 7.8081 ± 0.2246 a | 0.4% TS | 8.9610 ± 0.8435 ab |
| 0.5% TS | 10.7030 ± 2.7887 ab | ||
| Rha | High-concentration tea saponion | ||
| ND | 10.8329 ± 0.9316 a | ND | 10.8329 ± 0.9316 a |
| 0% Rha | 11.4504 ± 1.1880 a | 0% TS | 11.4504 ± 1.1880 a |
| 0.5% Rha | 11.5136 ± 0.9405 a | 0.5% TS | 10.7030 ± 2.7887 a |
| 1.0% Rha | 12.9001 ± 1.0776 ab | 1.0% TS | 11.4544 ± 0.3444 a |
| 1.5% Rha | 15.7299 ± 1.9474 b | 1.5% TS | 14.9443 ± 1.8581 b |
| 2.0% Rha | 15.5801 ± 2.9917 b | 2.0% TS | 11.6394 ± 1.4806 a |
| 2.5% Rha | 14.9905 ± 0.8207 b | 2.5% TS | 12.3089 ± 0.6041 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abliz, A.; Huang, Y.; Rouzi, R.; Xu, D.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J. Effects of Emulsifiers on Physicochemical Properties and Carotenoids Bioaccessibility of Sea Buckthorn Juice. Foods 2024, 13, 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131972
Abliz A, Huang Y, Rouzi R, Xu D, Gao Y, Liu J. Effects of Emulsifiers on Physicochemical Properties and Carotenoids Bioaccessibility of Sea Buckthorn Juice. Foods. 2024; 13(13):1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131972
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbliz, Arzigül, Yanan Huang, Reziwanguli Rouzi, Duoxia Xu, Yanxiang Gao, and Jinfang Liu. 2024. "Effects of Emulsifiers on Physicochemical Properties and Carotenoids Bioaccessibility of Sea Buckthorn Juice" Foods 13, no. 13: 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131972
APA StyleAbliz, A., Huang, Y., Rouzi, R., Xu, D., Gao, Y., & Liu, J. (2024). Effects of Emulsifiers on Physicochemical Properties and Carotenoids Bioaccessibility of Sea Buckthorn Juice. Foods, 13(13), 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13131972






