(−)-Gallocatechin Gallate: A Novel Chemical Marker to Distinguish Triadica cochinchinensis Honey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Palynological Identification and Physicochemical Analysis
2.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Construction of Flavonoid Standard Curves and Determination of Linearity Range
2.7. Determination of Qualitative and Quantitative Parameters of the LC-MS/MS Method
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Palynological and Physicochemical Characterization of Honey
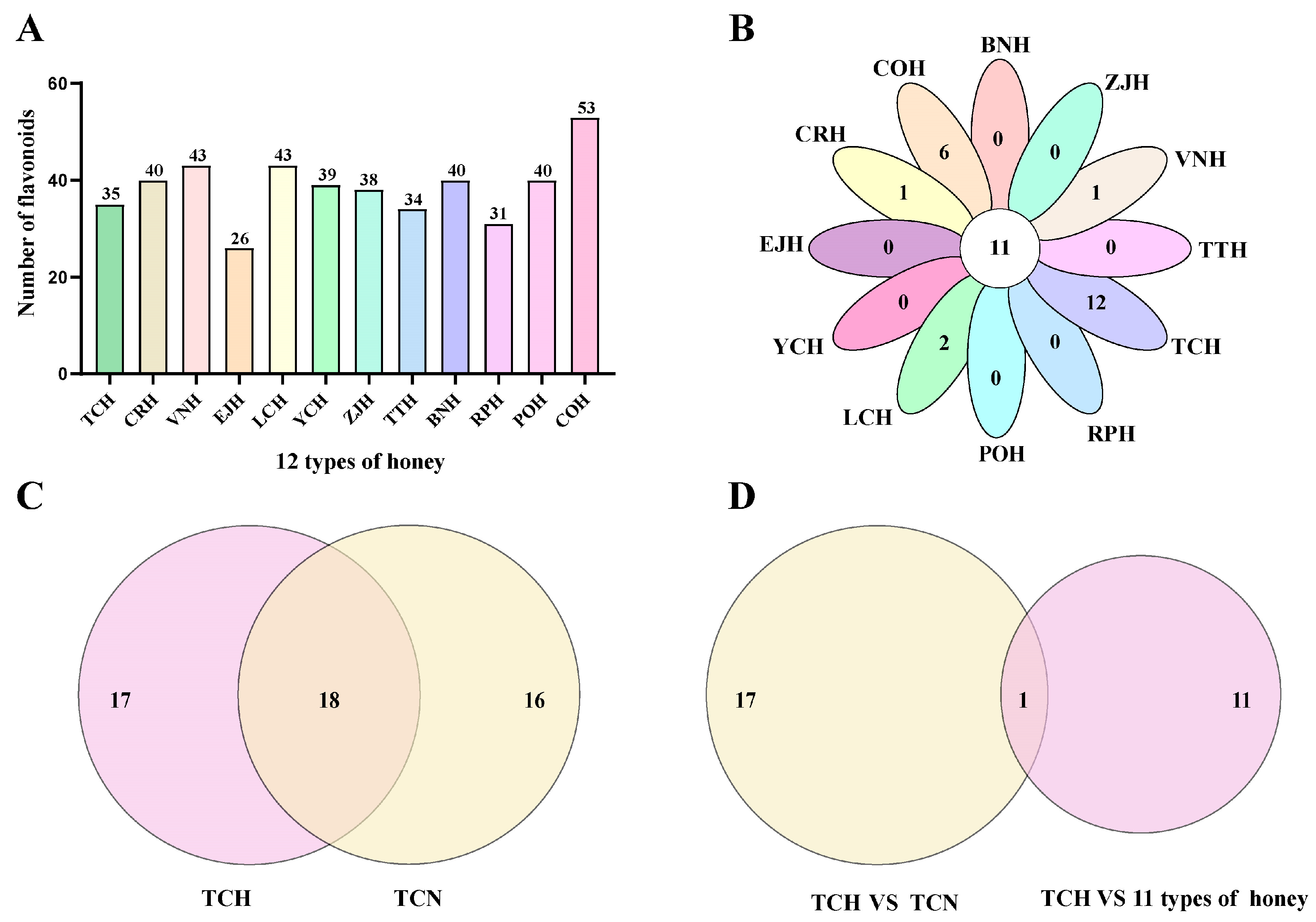
3.2. Screening and Identification of Unique Flavonoid Markers in TCH
3.3. Method Validation and Quantification of (−)-Gallocatechin Gallate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becerril-Sánchez, A.L.; Quintero-Salazar, B.; Dublán-García, O.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Relationship with Antioxidant Activity, Botanical Origin, and Color. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, F.D.; Andrecan, A.F.; Călugăr, A.; Bunea, C.I.; Popescu, M.; Petrescu-Mag, I.V.; Bunea, A. Comprehensive Elemental Profiling of Romanian Honey: Exploring Regional Variance, Honey Types, and Analyzed Metals for Sustainable Apicultural and Environmental Practices. Foods 2024, 13, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, A.; Zacometti, C.; Bragolusi, M.; Buček, J.; Piro, R.; Tata, A. Authentication of the botanical origin of monofloral honey by dielectric barrier discharge ionization high resolution mass spectrometry (DBDI-HRMS). Breaching the 6 s barrier of analysis time. Food Control 2024, 160, 110330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, L.; Lin, X.; Bai, W.; Xiao, G.; Liu, G. Composition, functional properties and safety of honey: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6767–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciucure, C.T.; Geană, E.I. Phenolic compounds profile and biochemical properties of honeys in relationship to the honey floral sources. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawag, I.L.; Lim, L.-Y.; Joshi, R.; Hammer, K.A.; Locher, C. A comprehensive survey of phenolic constituents reported in Monofloral honeys around the globe. Foods 2022, 11, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Morales, M.; Huertas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C. A Comprehensive Review of the Effect of Honey on Human Health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.M.; Miguel, M.G.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Figueiredo, A.C. Honey Volatiles as a Fingerprint for Botanical Origin—A Review on their Occurrence on Monofloral Honeys. Molecules 2020, 25, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanzmann, H.; Augustini, A.; Sanders, D.; Dahlheimer, M.; Wigger, M.; Zech, P.M.; Sielemann, S. Differentiation of Monofloral Honey Using Volatile Organic Compounds by HS-GCxIMS. Molecules 2022, 27, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Giampieri, F. The Composition and Biological Activity of Honey: A Focus on Manuka Honey. Foods 2014, 3, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Daniels, B.J.; Middleditch, M.J.; Furkert, D.P.; Brimble, M.A.; Bong, J.; Stephens, J.M.; Loomes, K.M. Utility of the Leptospermum scoparium Compound Lepteridine as a Chemical Marker for Manuka Honey Authenticity. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8858–8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Wang, K.; Luo, T.; Xue, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, L.; Zhao, L. Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside as a marker for authenticating Lespedeza bicolor Turcz. monofloral honey. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Shi, W.K.; Zeng, Z.J. Kaempferitrin: A Flavonoid Marker to Distinguish Camellia oleifera Honey. Nutrients 2023, 15, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.W.; Ren, C.J.; Xue, X.F.; Lu, H.X.; Wang, K.; Wu, L.M. Safflomin A: A novel chemical marker for Carthamus tinctorius L. (Safflower) monofloral honey. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Qi, S.; Xue, X.; Wu, L.; Li, Q. Identification of characteristic markers for monofloral honey of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus Hsiao: A combined untargeted and targeted MS-based study. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134312. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, H.-J. A revision of Triadica Lour. (euphorbiaceae). Harv. Pap. Bot. 2002, 7, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, R.C. Phylogenetic relationships and natural hybridization in Triadica inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA analyses. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 64, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H. DNA Barcode Sequence of Lingnan Chinese Herbs; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2017; p. 219. [Google Scholar]
- Sabandar, C.; Jalil, J.; Ahmat, N.; Aladdin, N.-A. Assessment of antioxidant and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Triadica cochinchinensis stem bark. Curr. Res. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2019, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.B.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Li, C.H.; Song, H.N.; Fan, P.H. Genus Sapium (Euphorbiaceae): A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 277, 114206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Qiu, S.; Yi, S.; Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Huang, X.; Ning, F. Monofloral Triadica cochinchinensis Honey Polyphenols Improve Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease by Regulating the Gut Microbiota of Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 673903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qiao, N.; Ning, F.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Luo, L.P. Identification and characterization of plant-derived biomarkers and physicochemical variations in the maturation process of Triadica cochinchinensis honey based on UPLC-QTOF-MS metabolomics analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.P. The Mechanism of Triadica cochinchinensis Honey Ameliorating Alcohol Liver Damage of Mice by Adjusting the Gut Microbiota. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.P.; Qiao, N.; Guo, L.M.; Liu, T. Analysis of volatile components of Triadica cochinchinensis honey by HS-SPME-GC-MS. J. Nanchang Univ. 2022, 46, 320–326+333. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.J. Apiculture, 4th ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2023; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wu, L. Bee Products: The Challenges in Quality Control. Foods 2023, 12, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, X. Systematic review of the characteristic markers in honey of various botanical, geographic, and entomological origins. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Lu, M.; Li, J.; Ma, C. Metabolomics Reveals Distinctive Metabolic Profiles and Marker Compounds of Camellia (Camellia sinensis L.) Bee Pollen. Foods 2023, 12, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Albujja, M.; Bakar, M.F.A. Honey and its nutritional and anti-inflammatory value. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchado, P.; Ferreres, F.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry reveals the widespread occurrence of flavonoid glycosides in honey, and their potential as floral origin markers. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7241–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.Y.; Yao, Y.F.; Yang, W.D. Pollen analysis of natural honeys from the central region of Shanxi, North China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Mao, L.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, B.; Li, J. Pollen atlas for selected subfamilies of Euphorbiaceae from Southern China: A complementary contribution to Quaternary pollen analysis. Palynology 2020, 44, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W. Nectar and Pollen Plants of China; Heilongjiang Science & Technology Press: Harbin, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. International Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Suo, Z.; Zhao, P.; Cheng, N.; Gao, H.; Zhao, J.; Cao, W. Jujube honey from China: Physicochemical characteristics and mineral contents. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C387–C394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicudo de Almeida-Muradian, L.; Monika Barth, O.; Dietemann, V.; Eyer, M.; Freitas, A.d.S.d.; Martel, A.-C.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Marchese, C.M.; Mucignat-Caretta, C.; Pascual-Maté, A. Standard methods for Apis mellifera honey research. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živkov Baloš, M.; Popov, N.; Jakšić, S.; Mihaljev, Ž.; Pelić, M.; Ratajac, R.; Ljubojević Pelić, D. Sunflower Honey—Evaluation of Quality and Stability during Storage. Foods 2023, 12, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council, E. Council Directive 2001/110/EC of 20 December 2001 relating to honey. Off. J. Eur. Communities L 2002, 10, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Du, B.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Xue, X. Recent advancements in detecting sugar-based adulterants in honey—A challenge. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 86, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, S.; Turhan, K.N.; Turhan, M. Correlation between water activity and moisture content of Turkish flower and pine honeys. Ciência Tecnol. Aliment. 2018, 38, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapla, U.M.; Solayman, M.; Alam, N.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) levels in honey and other food products: Effects on bees and human health. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Melo, A.A.M.; Almeida-Muradian, L.B.D.; Sancho, M.T.; Pascual-Maté, A. Composition and properties of Apis mellifera honey: A review. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, P.M.; Gauche, C.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.; Fett, R. Honey: Chemical composition, stability and authenticity. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solayman, M.; Islam, M.A.; Paul, S.; Ali, Y.; Khalil, M.I.; Alam, N.; Gan, S.H. Physicochemical properties, minerals, trace elements, and heavy metals in honey of different origins: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, I.; Lestari, A.E. Effectiveness of Honey in Increasing Hemoglobin Levels of Mothers Post Sectio Caesarea; Humanistic Network for Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Waili, N.S. Effects of daily consumption of honey solution on hematological indices and blood levels of minerals and enzymes in normal individuals. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Ntoupa, P.-S.A.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Recent aspects of the effects of zinc on human health. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Z.; Jiang, W.J.; Li, Z.; Zhong, S.Q.; He, X.J.; Yan, W.Y.; Xi, F.G.; Wu, W.M.; Zeng, Z.J. Production and composition analysis of high quality Triadica cochinchinensis honey. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2023, 45, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Masad, R.J.; Haneefa, S.M.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Al-Sbiei, A.; Bashir, G.; Fernandez-Cabezudo, M.J.; Al-Ramadi, B.K. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Honey and Associated Flavonoids in Cancer. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P.P.; Zhang, J.; Bravo Lamas, L.; Martínez Flórez, S.; Agudo Toyos, P.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Associated Health Benefits: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Zhou, X.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, X.R.; Han, X.Q.; Shi, X.G.; Song, X.H.; Ye, C.X.; Ko, C.H. Preparative separation of gallocatechin gallate from Camellia ptilophylla using macroporous resins followed by sephadex LH-20 column chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1011, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, H.J.; Baik, J.H. GCG-rich tea catechins are effective in lowering cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations in hyperlipidemic rats. Lipids 2008, 43, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Di, T.; Wang, W.; Jiang, H. EGCG, GCG, TFDG, or TSA Inhibiting Melanin Synthesis by Downregulating MC1R Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.; Hotta, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Wakida, Y.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Isobe, F.; Nakano, A.; Chiba, T.; Kawamura, N. Protective effects of EGCG or GCG, a green tea catechin epimer, against postischemic myocardial dysfunction in guinea-pig hearts. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, K.S.; Hwang, G.S. Neuroprotective effect of gallocatechin gallate on glutamate-induced oxidative stress in hippocampal ht22 cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
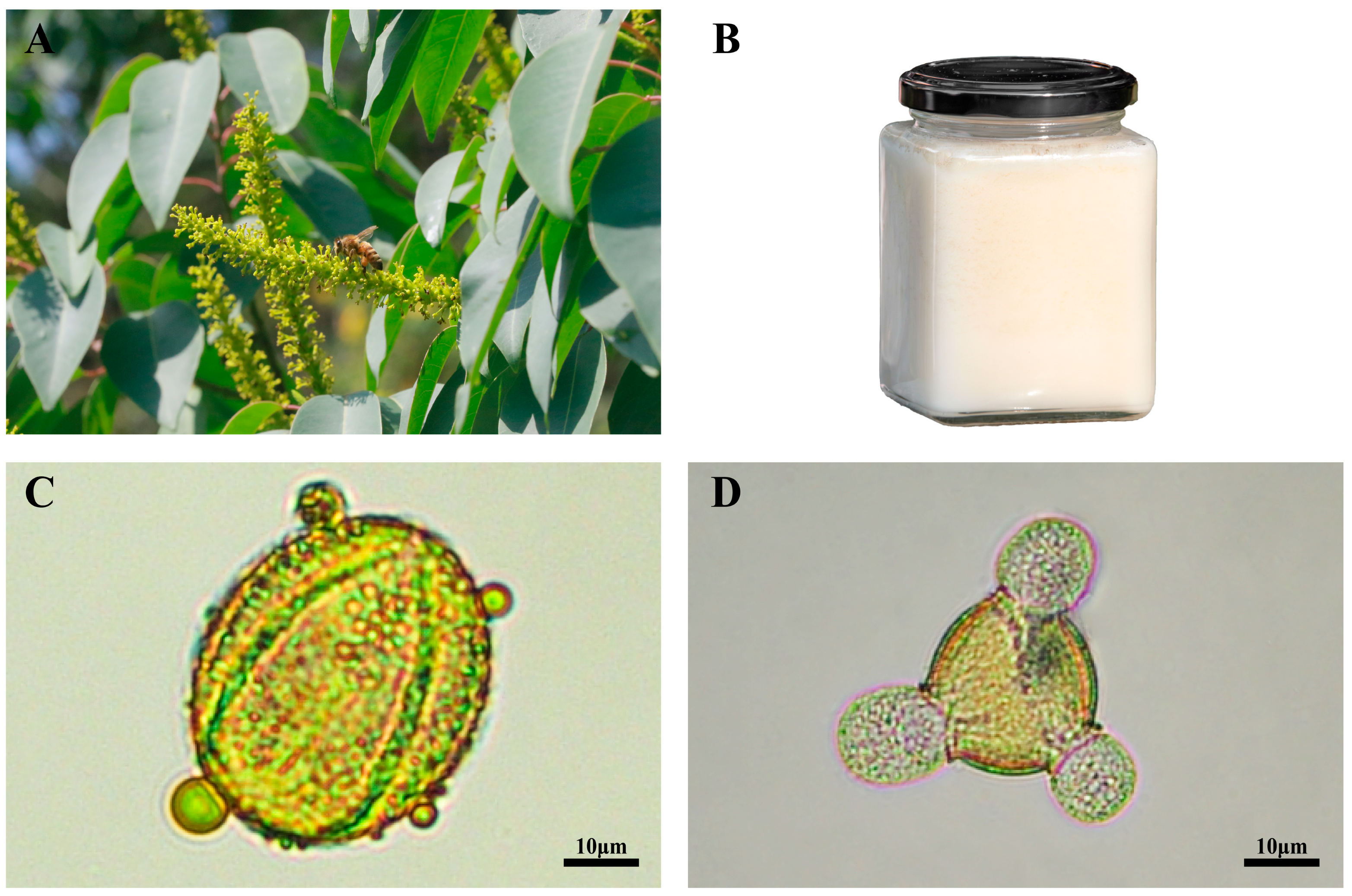
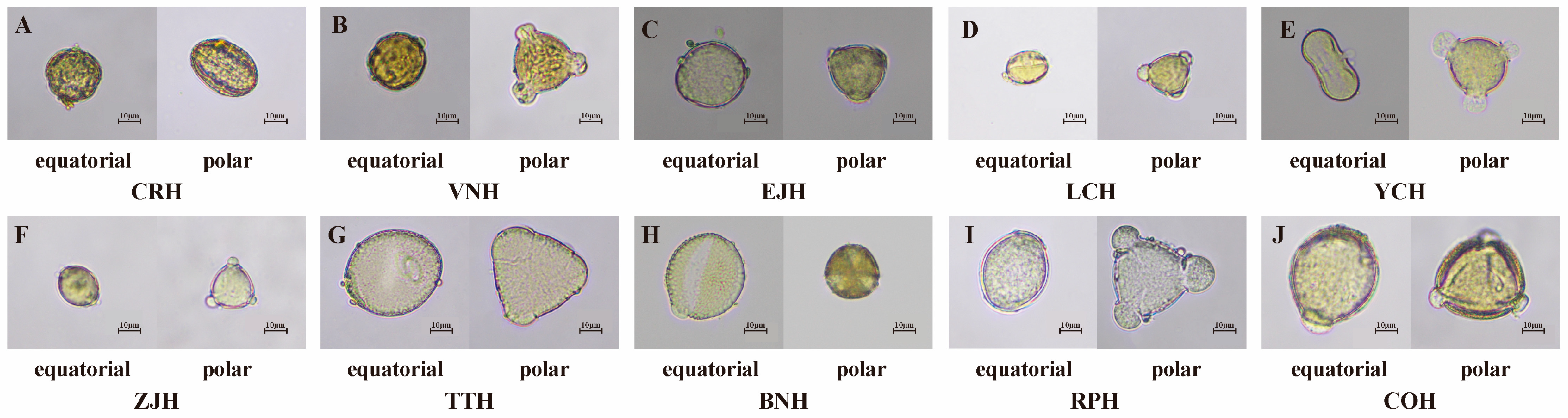

| Honey Variety | Native Pollen Rate (%) | Honey Variety | Native Pollen Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus reticulata honey (CRH) | 75.94 ± 5.22 | Ziziphus jujuba honey (ZJH) | 86.41 ± 2.22 |
| Vitex negundo honey (VNH) | 64.81 ± 5.50 | Tilia tuan honey (TTH) | 88.80 ± 1.25 |
| Eriobotrya japonica honey (EJH) | 76.82 ± 6.62 | Brassica napus honey (BNH) | 84.85 ± 2.08 |
| Litchi chinensis honey (LCH) | 85.51 ± 2.09 | Robinia pseudoacacia honey (RPH) | 71.47 ± 6.49 |
| Lycium chinense honey (YCH) | 81.08 ± 2.46 | Camellia oleifera honey (COH) | 87.76 ± 6.63 |
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Fructose | 37.42 ± 0.71 | % |
| Glucose | 37.32 ± 0.36 | % |
| Sucrose | 0.77 ± 0.10 | % |
| Water | 18.65 ± 0.56 | % |
| HMF | 1.87 ± 0.12 | mg/kg |
| Diastase activity | 2.55 ±0.32 | mL/(g·h) |
| Electrical conductivity | 0.14 ± 0.003 | mS/cm |
| ash content | 0.07 ±0.001 | g/100 g |
| Color value | 32.00 ± 0.00 | mm Pfund |
| Free acidity | 11.82 ± 0.22 | mL/kg |
| Pollen grains concentration | 18,025.00 ± 641.67 | grain/mL |
| Fe | 6.23 ± 0.05 | mg/kg |
| Cu | 105.31 ± 5.98 | μg/kg |
| Zn | 5.41 ± 0.29 | mg/kg |
| Compound | Standard Curve | LOD (nmol/kg) | LOQ (nmol/kg) | Regression (R2) | TCH (n = 3) | TCN (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (nmol/kg) | RSD (%) | Content (nmol/kg) | RSD (%) | |||||
| GCG | y = 1010.75160x − 2834.40065 | 1.14 | 3.43 | 0.9994 | 130.78 ± 4.44 | 3.40 | 96.33 ± 2.16 | 2.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhong, S.; Zeng, Z. (−)-Gallocatechin Gallate: A Novel Chemical Marker to Distinguish Triadica cochinchinensis Honey. Foods 2024, 13, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121879
Jiang H, Li Z, Zhong S, Zeng Z. (−)-Gallocatechin Gallate: A Novel Chemical Marker to Distinguish Triadica cochinchinensis Honey. Foods. 2024; 13(12):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121879
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Huizhi, Zhen Li, Shiqing Zhong, and Zhijiang Zeng. 2024. "(−)-Gallocatechin Gallate: A Novel Chemical Marker to Distinguish Triadica cochinchinensis Honey" Foods 13, no. 12: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121879
APA StyleJiang, H., Li, Z., Zhong, S., & Zeng, Z. (2024). (−)-Gallocatechin Gallate: A Novel Chemical Marker to Distinguish Triadica cochinchinensis Honey. Foods, 13(12), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121879







