Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional Quality of Zizania latifolia Cultivars Harvested in Different Growing Seasons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Determination of Moisture, Fiber, Total Soluble Solids, Reducing Sugar, Soluble Protein, and Vitamin C
2.3. Determination of Amino Acid Contents
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Difference Analysis for Physicochemical Parameters in Z. latifolia
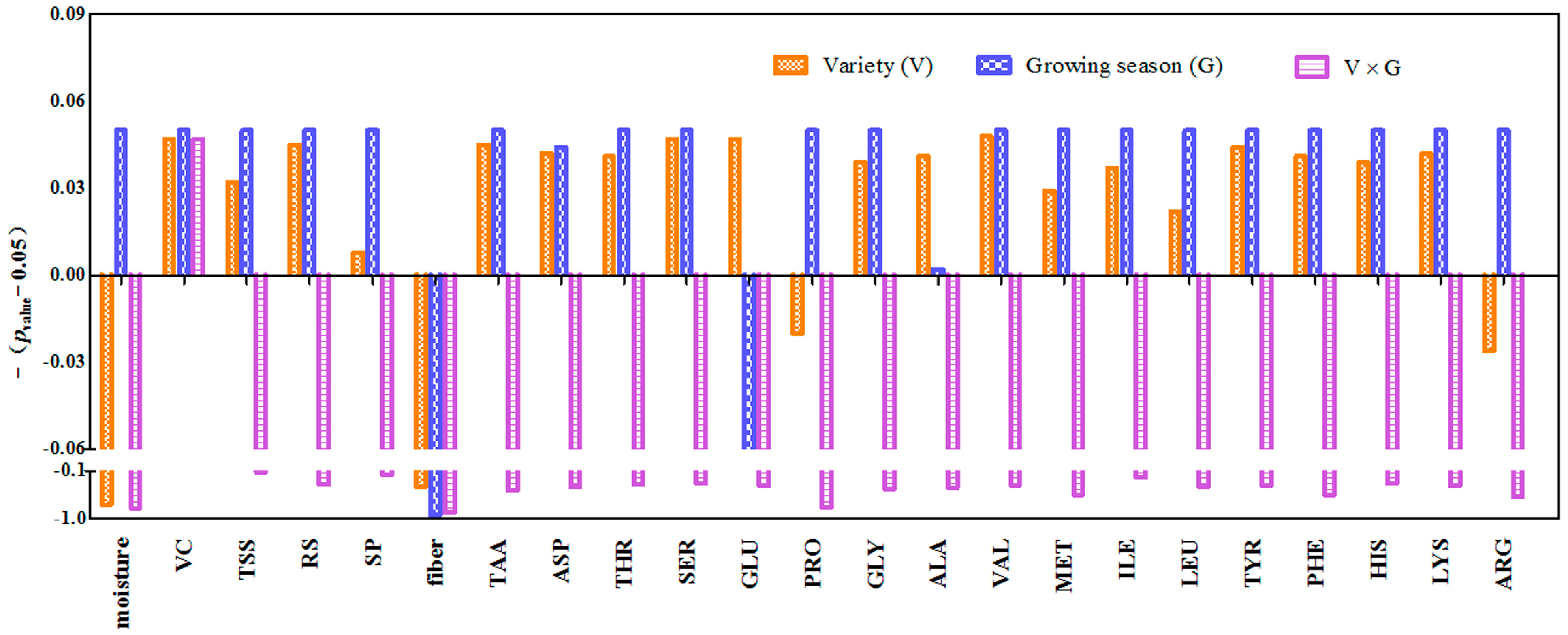
3.1.1. ANOVA for the Quality Parameters
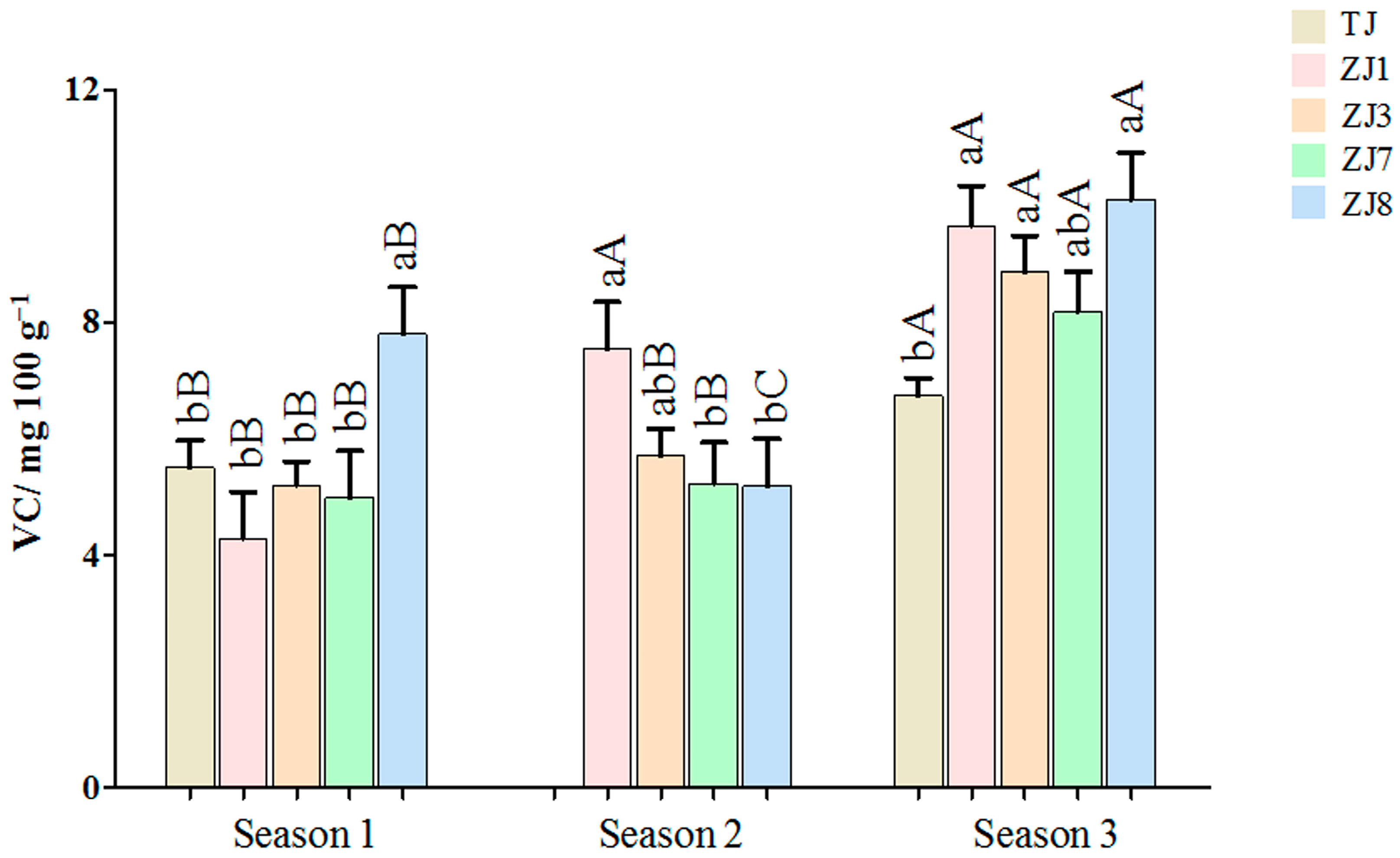
3.1.2. VC Content Variations between Different Varieties and Growing Seasons
3.1.3. Effect of Variety and Growing Season on the Contents of Moisture, SP, TSS, and RS
3.1.4. Effect of Variety and Growing Season on the Values of Amino Acids
3.2. Multivariate Analysis
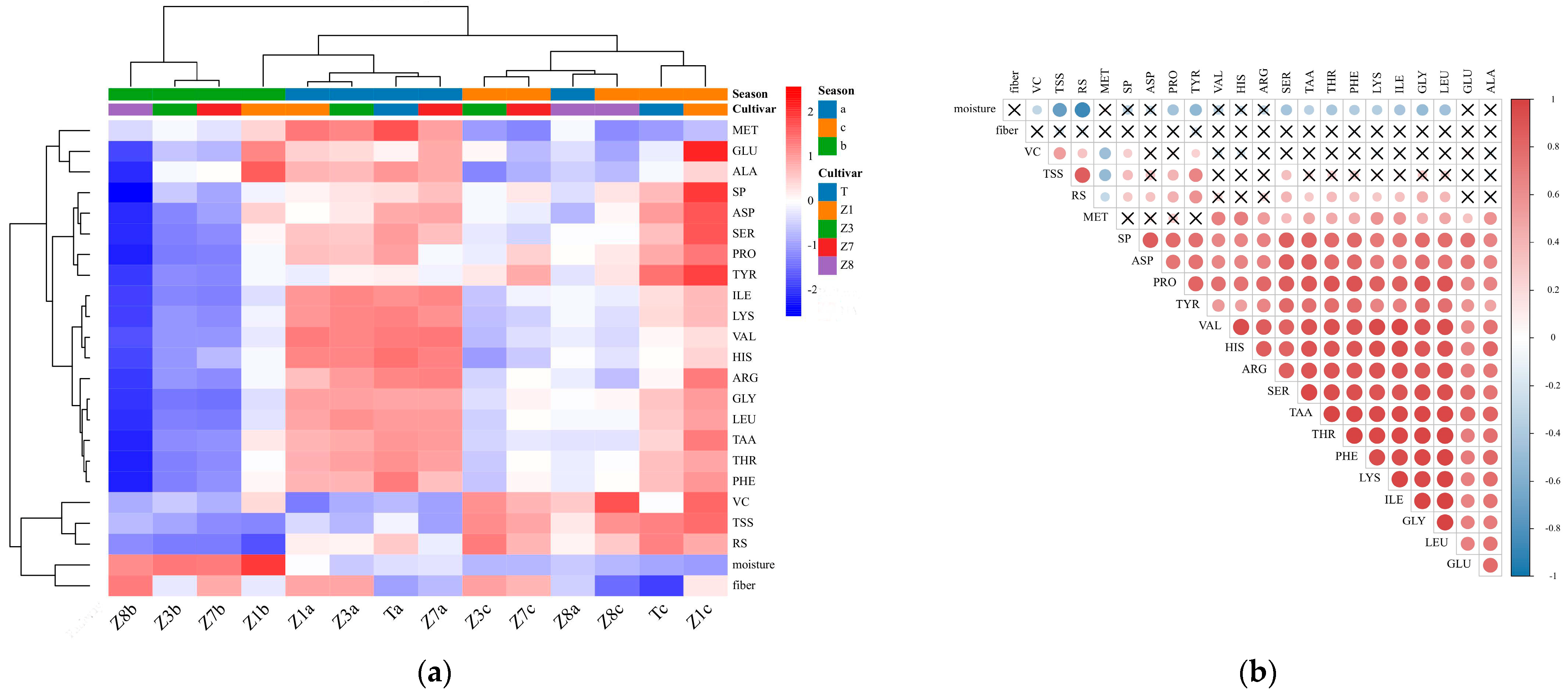
3.2.1. Hierarchical Clustering Heatmap Analysis and Pearson’s Correlation Analysis
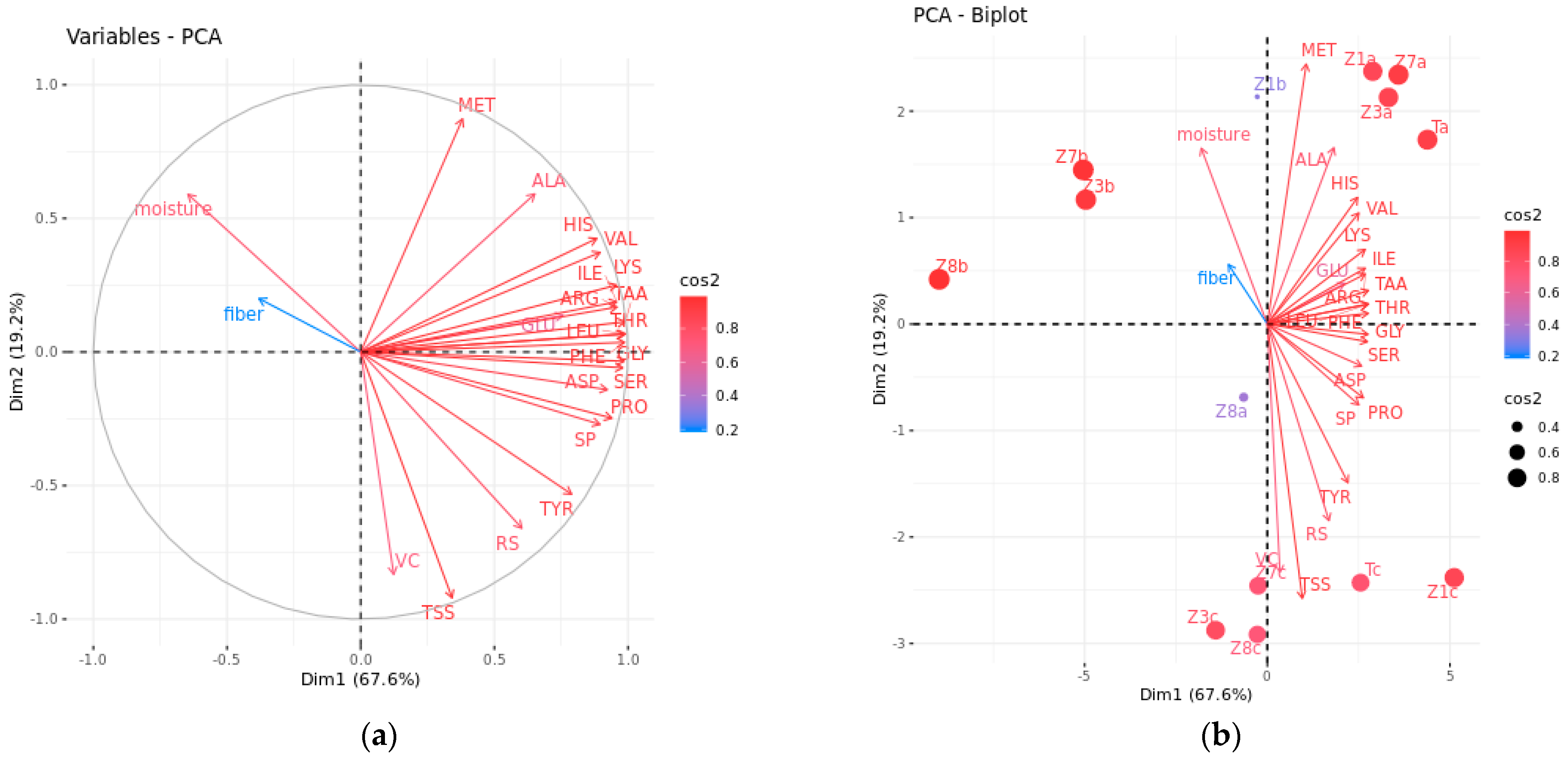
3.2.2. Comprehensive Evaluation by PCA and MLR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, R.; Wu, W.; Mu, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, H.; Gao, H. Ameliorating effects of water bamboo shoot (Zizania latifolia) on acute alcoholism in a mice model and its chemical composition. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Chu, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Morphological Characteristics, Nutrients, and Bioactive Compounds of Zizania latifolia, and Health Benefits of Its Seeds. Molecules 2018, 23, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Boon-Ek, Y.; Wongs-Aree, C.; Supapanich, S. Ultraviolet-C treatment maintains physicochemical quality of water bamboo (Zizania latifolia) shoots during postharvest storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 152, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Yuan, L.; Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhu, S. Effects of exogenous IAA in regulating photosynthetic capacity, carbohydrate metabolism and yield of Zizania latifolia. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 253, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, P.; Nie, C.; Ma, S.; Wang, N.; Du, X.; Zhou, Y. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of water extractable polysaccharides from the swollen culms of Zizania latifolia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Bang, M.-H.; Jo, S.K.; Jhee, K.-H.; Yang, S.-A. Protection against UVB-induced damages in human dermal fibroblasts: Efficacy of tricin isolated from enzyme-treated Zizania latifolia extract. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2019, 83, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.B.; Li, S.M.; Ke, J. Zizania latifolia Turcz. cultivated in China. Genet. Resour. Crop Environ. 2007, 54, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yao, Y. Research Progress on Breeding and Efficient Cultivation Technology of New Zizania latifolia Cultivars in China. J. Chang. Veg. 2012, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Chen, H.; Han, Y.; Niu, B.; Gao, H. Zizania latifolia Cell Wall Polysaccharide Metabolism and Changes of Related Enzyme Activities during Postharvest Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diel, M.I.; Lúcio, A.D.C.; Schmidt, D.; Valera, O.V.S.; Fontana, D.C.; Tartaglia, F.d.L.; Tischler, A.L.; Lambrecht, D.M.; Zemolin, J.A. Relations between fruit chemical components of biquinho pepper cultivars in different crop seasons. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, D.M.; Durán-Soria, S.; Allwood, J.W.; Pont, S.; Gordon, S.L.; Jennings, N.; Austin, C.; Stewart, D.; Brennan, R.M.; Masny, A.; et al. Dissecting the impact of environment, season and genotype on blackcurrant fruit quality traits. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Shehzad, Q.; Kong, W.; Wu, G.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. A comprehensive comparison of Chinese olive oils from different cultivars and geographical origins. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Gao, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, H. Comprehensive Quality Evaluation of Different Varieties of Water Bamboo Shoot Based on Principal Components Analysis. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.S.N.d.; Schmidt, H.d.O.; Pagno, C.; Rodrigues, E.; Silva, M.A.S.d.; Flôres, S.H.; Rios, A.d.O. Influence of cultivar and season on carotenoids and phenolic compounds from red lettuce influence of cultivar and season on lettuce. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Analysis of differences in the accumulation of tea compounds under various processing techniques, geographical origins, and harvesting seasons. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Yamada, S.; Hu, D.; Ito, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Yamaguchi, A. Microbial Diversity in the Edible Gall on White Bamboo Formed by the Interaction between Ustilago esculenta and Zizania latifolia. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, K.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Sun, J.; Bai, W. Modeling and application of sensory evaluation of blueberry wine based on principal component analysis. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Park, B.; Kang, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q. Physicochemical indicators coupled with multivariate analysis for comprehensive evaluation of matcha sensory quality. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5009.3; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Moisture in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T5009.10; Determination of Crude Fiber in Vegetable Foods. Ministry of Public Health & Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- GB5009.7; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Reducing Sugar in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Shi, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhang, H.; Gan, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hao, J.; et al. Physiological and biochemical changes during fruit maturation and ripening in highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhou, M.; Le, L.; Gong, X.; Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Cao, X.; Shi, Z.; Tan, M.; Cao, Y.; et al. Evaluation of morphology, nutrients, phytochemistry and pigments suggests the optimum harvest date for high-quality quinoa leafy vegetable. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 304, 111240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alañón, M.E.; Ivanović, M.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A. Choline chloride derivative-based deep eutectic liquids as novel green alternative solvents for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaf. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Han, Y.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Chen, H.; Gao, H. Impact of melatonin application on lignification in water bamboo shoot during storage. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, H.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Crosby, K.; Yoo, K.S.; Leskovar, D.I.; Jifon, J.; Patil, B.S. Ascorbic acid, capsaicinoid, and flavonoid aglycone concentrations as a function of fruit maturity stage in greenhouse-grown peppers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 33, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, S.; Hang, J.; Neufeld, J.; Zhao, S.; House, J.D. Effects of Genotype, Environment and Their Interaction on Protein and Amino Acid Contents in Soybeans. Plant Sci. 2023, 337, 111891. [Google Scholar]
- Mourtzinis, S.; Gaspar, A.P.; Naeve, S.L.; Conley, S.P. Planting Date, Maturity, and Temperature Effects on Soybean Seed Yield and Composition. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, I.S.; Melo, C.A.F.d.; Nunes, G.H.d.S.; Holanda, I.S.A.; Grangeiro, L.C.; Corrêa, R.X. Phenotypic variability, diversity and genetic-population structure in melon (Cucumis melo L.) Associated with total soluble solids. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 278, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckles, D.M. Factors affecting the postharvest soluble solids and sugar content of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 63, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Wang, B. Analysis of physicochemical characteristics, antioxidant activity, and key aroma compounds of five flat peach cultivars grown in Xinjiang. LWT 2023, 176, 114550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Metrani, R.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Crosby, K.M.; Jifon, J.L.; Ravishankar, S.; Brierley, P.; Leskovar, D.L.; Turini, T.A.; Schultheis, J.; et al. Profiling carotenoid and sugar contents in unique Cucumis melo L. cultigens harvested from different climatic regions of the United States. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbou, S.; Maatallah, S.; Antonelli, A.; Montevecchi, G. Variation of amino acids in Prunus persica cultivars leaves with regard to leaf age. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 110001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; He, Z. Simultaneous determination of 49 amino acids, B vitamins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids in commonly consumed vegetables by ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Xu, H.; Xin, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Zhi, Y.; Li, B.; Shen, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of Actinidia arguta fruit based on the nutrition and taste: 67 germplasm native to Northeast China. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2022, 11, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Ma, T. Comprehensive evaluation of the effect of five sterilization methods on the quality of black carrot juice based on PCA, TOPSIS and GRA models. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, W.; Moussa, S.-A.; Ottoni, M.M.N.; Dubois-Laurent, C.; Huet, S.; Aubert, C.; Desnoues, E.; Navez, B.; Cottet, V.; Chalot, G.; et al. Evaluation of pedoclimatic factors and cultural practices effects on carotenoid and sugar content in carrot root. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 140, 126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Han, G.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, X. Nutrient composition and quality traits of dried jujube fruits in seven producing areas based on metabolomics analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cultivars | Moisture (%) | SP (g 100 g−1) | TSS (%) | RS (g 100 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJ | 92.34 ± 0.61 a | 1.33 ± 0.16 a | 6.20 ± 0.78 a | 3.90 ± 0.49 a |
| ZJ1 | 92.98 ± 0.96 a | 1.35 ± 0.15 a | 5.51 ± 1.13 b | 2.97 ± 0.89 b |
| ZJ3 | 92.91 ± 0.76 a | 1.25 ± 0.12 b | 5.02 ± 0.81 c | 2.95 ± 0.83 b |
| ZJ7 | 92.94 ± 0.70 a | 1.25 ± 0.10 ab | 5.10 ± 0.95 c | 2.87 ± 0.74 b |
| ZJ8 | 92.82 ± 0.78 a | 1.15 ± 0.18 b | 5.62 ± 0.92 d | 2.94 ± 0.71 b |
| Harvest Seasons | Moisture (%) | SP (g 100 g−1) | TSS (%) | RS (g 100 g−1) |
| Season 1 | 92.56 ± 0.34 b | 1.29 ± 0.11 a | 5.02 ± 0.51 b | 3.25 ± 0.35 b |
| Season 2 | 93.85 ± 0.36 a | 1.15 ± 0.16 b | 4.52 ± 0.37 c | 2.01 ± 0.31 c |
| Season 3 | 92.24 ± 0.55 c | 1.34 ± 0.14 a | 6.54 ± 0.48 a | 3.94 ± 0.44 a |
| Amino Acid Composition | Cultivars | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJ | ZJ1 | ZJ3 | ZJ7 | ZJ8 | |
| ASP | 0.158 ± 0.03 a | 0.156 ± 0.017 a | 0.134 ± 0.02 b | 0.137 ± 0.02 b | 0.123 ± 0.03 b |
| THR | 0.053 ± 0.01 a | 0.052 ± 0.005 ab | 0.048 ± 0.01 c | 0.048 ± 0.01 bc | 0.044 ± 0.01 c |
| SER | 0.061 ± 0.01 a | 0.062 ± 0.008 a | 0.054 ± 0.01 b | 0.053 ± 0.01 b | 0.050 ± 0.01 b |
| GLU | 0.123 ± 0.02 b | 0.148 ± 0.019 a | 0.124 ± 0.02 b | 0.120 ± 0.02 bc | 0.108 ± 0.02 c |
| PRO | 0.051 ± 0.01 a | 0.050 ± 0.005 ab | 0.045 ± 0.01 c | 0.045 ± 0.01 bc | 0.043 ± 0.01 c |
| GLY | 0.057 ± 0.01 a | 0.057 ± 0.007 a | 0.052 ± 0.01 b | 0.051 ± 0.01 b | 0.047 ± 0.01 b |
| ALA | 0.070 ± 0.01 a | 0.074 ± 0.007 a | 0.069 ± 0.01 a | 0.068 ± 0.01 ab | 0.062 ± 0.01 b |
| VAL | 0.064 ± 0.01 a | 0.064 ± 0.008 ab | 0.060 ± 0.01 bc | 0.058 ± 0.01 cd | 0.052 ± 0.01 d |
| MET | 0.009 ± 0.00 bc | 0.010 ± 0.003 ab | 0.011 ± 0.00 a | 0.009 ± 0.00 bc | 0.008 ± 0.00 c |
| ILE | 0.047 ± 0.01 a | 0.046 ± 0.006 ab | 0.043 ± 0.01 bc | 0.042 ± 0.01 cd | 0.038 ± 0.01 d |
| LEU | 0.085 ± 0.01 a | 0.084 ± 0.009 ab | 0.077 ± 0.01 bc | 0.076 ± 0.01 bc | 0.070 ± 0.01 c |
| TYR | 0.038 ± 0.01 a | 0.036 ± 0.006 a | 0.031 ± 0.00 b | 0.032 ± 0.01 b | 0.030 ± 0.01 b |
| PHE | 0.051 ± 0.01 a | 0.050 ± 0.005 ab | 0.046 ± 0.01 c | 0.046 ± 0.01 bc | 0.043 ± 0.01 c |
| HIS | 0.033 ± 0.01 a | 0.033 ± 0.003 a | 0.031 ± 0.01 a | 0.031 ± 0.00 ab | 0.028 ± 0.00 b |
| LYS | 0.077 ± 0.01 a | 0.076 ± 0.009 ab | 0.072 ± 0.01 bc | 0.068 ± 0.01 cd | 0.063 ± 0.01 d |
| ARG | 0.056 ± 0.01 a | 0.058 ± 0.007 a | 0.052 ± 0.01 ab | 0.052 ± 0.01 ab | 0.045 ± 0.01 b |
| EAA | 0.387 ± 0.06 a | 0.360 ± 0.08 ab | 0.357 ± 0.06 ab | 0.346 ± 0.06 ab | 0.318 ± 0.05 b |
| CEAA | 0.648 ± 0.09 a | 0.625 ± 0.14 a | 0.593 ± 0.09 ab | 0.588 ± 0.08 ab | 0.536 ± 0.09 b |
| TAA | 1.035 ± 0.14 a | 1.056 ± 0.101 a | 0.950 ± 0.14 b | 0.934 ± 0.14 bc | 0.854 ± 0.14 c |
| Amino Acid Composition | Harvest Seasons | ||||
| Season 1 | Season 2 | Season 3 | |||
| ASP | 0.147 ± 0.02 a | 0.121 ± 0.02 b | 0.154 ± 0.03 a | ||
| THR | 0.053 ± 0.00 a | 0.042 ± 0.01 c | 0.051 ± 0.01 b | ||
| SER | 0.060 ± 0.01 a | 0.047 ± 0.01 b | 0.059 ± 0.01 a | ||
| GLU | 0.130 ± 0.01 a | 0.116 ± 0.02 b | 0.125 ± 0.03 ab | ||
| PRO | 0.049 ± 0.01 a | 0.040 ± 0.00 b | 0.050 ± 0.01 a | ||
| GLY | 0.059 ± 0.01 a | 0.043 ± 0.01 c | 0.055 ± 0.01 b | ||
| ALA | 0.073 ± 0.01 a | 0.068 ± 0.01 b | 0.066 ± 0.01 b | ||
| VAL | 0.071 ± 0.01 a | 0.049 ± 0.01 c | 0.059 ± 0.01 b | ||
| MET | 0.014 ± 0.00 a | 0.009 ± 0.00 b | 0.006 ± 0.00 c | ||
| ILE | 0.050 ± 0.01 a | 0.035 ± 0.00 c | 0.044 ± 0.01 b | ||
| LEU | 0.087 ± 0.01 a | 0.065 ± 0.01 c | 0.081 ± 0.01 b | ||
| TYR | 0.033 ± 0.00 b | 0.027 ± 0.00 c | 0.039 ± 0.01 a | ||
| PHE | 0.051 ± 0.01 a | 0.041 ± 0.01 b | 0.049 ± 0.01 a | ||
| HIS | 0.036 ± 0.00 a | 0.027 ± 0.00 c | 0.030 ± 0.00 b | ||
| LYS | 0.081 ± 0.01 a | 0.061 ± 0.01 c | 0.072 ± 0.01 b | ||
| ARG | 0.059 ± 0.01 a | 0.044 ± 0.01 c | 0.053 ± 0.01 b | ||
| EAA | 0.407 ± 0.04 a | 0.301 ± 0.04 c | 0.362 ± 0.05 b | ||
| CEAA | 0.646 ± 0.06 a | 0.533 ± 0.09 b | 0.631 ± 0.09 a | ||
| TAA | 1.054 ± 0.10 a | 0.834 ± 0.12 c | 0.993 ± 0.14 b | ||
| Parameters | Component Matrix | Component Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC1 | |
| Moisture (X1) | −0.646 | 0.590 |
| VC (X2) | 0.124 | −0.833 |
| TSS (X3) | 0.342 | −0.920 |
| RS (X4) | 0.603 | −0.660 |
| SP (X5) | 0.896 | −0.271 |
| Fiber (X6) | −0.381 | 0.200 |
| TAA (X7) | 0.989 | 0.113 |
| ASP (X8) | 0.923 | −0.141 |
| THR (X9) | 0.991 | 0.068 |
| SER (X10) | 0.981 | −0.059 |
| GLU (X11) | 0.757 | 0.137 |
| PRO (X12) | 0.940 | −0.248 |
| GLY (X13) | 0.986 | −0.034 |
| ALA (X14) | 0.652 | 0.592 |
| VAL (X15) | 0.896 | 0.373 |
| MET (X16) | 0.381 | 0.872 |
| ILE (X17) | 0.958 | 0.188 |
| LEU (X18) | 0.985 | 0.067 |
| TYR (X19) | 0.789 | −0.533 |
| PHE (X20) | 0.987 | 0.036 |
| HIS (X21) | 0.883 | 0.425 |
| LYS (X22) | 0.957 | 0.250 |
| ARG (X23) | 0.959 | 0.168 |
| Eigenvalue | 15.537 | 4.406 |
| Contribution rates (%) | 67.552 | 19.158 |
| Sample | F1 | F2 | F (Score) | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta | 16.65 | 3.50 | 13.75 | 2 |
| Tc | 9.70 | −4.91 | 6.47 | 6 |
| Z1a | 10.96 | 4.80 | 9.6 | 5 |
| Z1b | −1.04 | 4.32 | 0.14 | 7 |
| Z1c | 19.44 | −4.82 | 14.08 | 1 |
| Z3a | 12.60 | 4.31 | 10.77 | 4 |
| Z3b | −18.87 | 2.36 | −14.17 | 12 |
| Z3c | −5.38 | −5.82 | −5.47 | 11 |
| Z7a | 13.64 | 4.74 | 11.67 | 3 |
| Z7b | −19.14 | 2.93 | −14.26 | 13 |
| Z7c | −0.96 | −4.97 | −1.85 | 8 |
| Z8a | −2.45 | −1.39 | −2.22 | 10 |
| Z8b | −34.12 | 0.85 | −26.39 | 14 |
| Z8c | −1.04 | −5.90 | −2.11 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Li, X.; Lai, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Zhu, J.; Yang, M. Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional Quality of Zizania latifolia Cultivars Harvested in Different Growing Seasons. Foods 2024, 13, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010030
Hu G, Li X, Lai A, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Sun S, Zhu J, Yang M. Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional Quality of Zizania latifolia Cultivars Harvested in Different Growing Seasons. Foods. 2024; 13(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Guixian, Xue Li, Aiping Lai, Yan Liu, Yu Zhang, Junhong Wang, Suling Sun, Jiahong Zhu, and Mengfei Yang. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional Quality of Zizania latifolia Cultivars Harvested in Different Growing Seasons" Foods 13, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010030
APA StyleHu, G., Li, X., Lai, A., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Sun, S., Zhu, J., & Yang, M. (2024). Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional Quality of Zizania latifolia Cultivars Harvested in Different Growing Seasons. Foods, 13(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010030





