Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Standardized Oral Pomegranate Extract on the Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
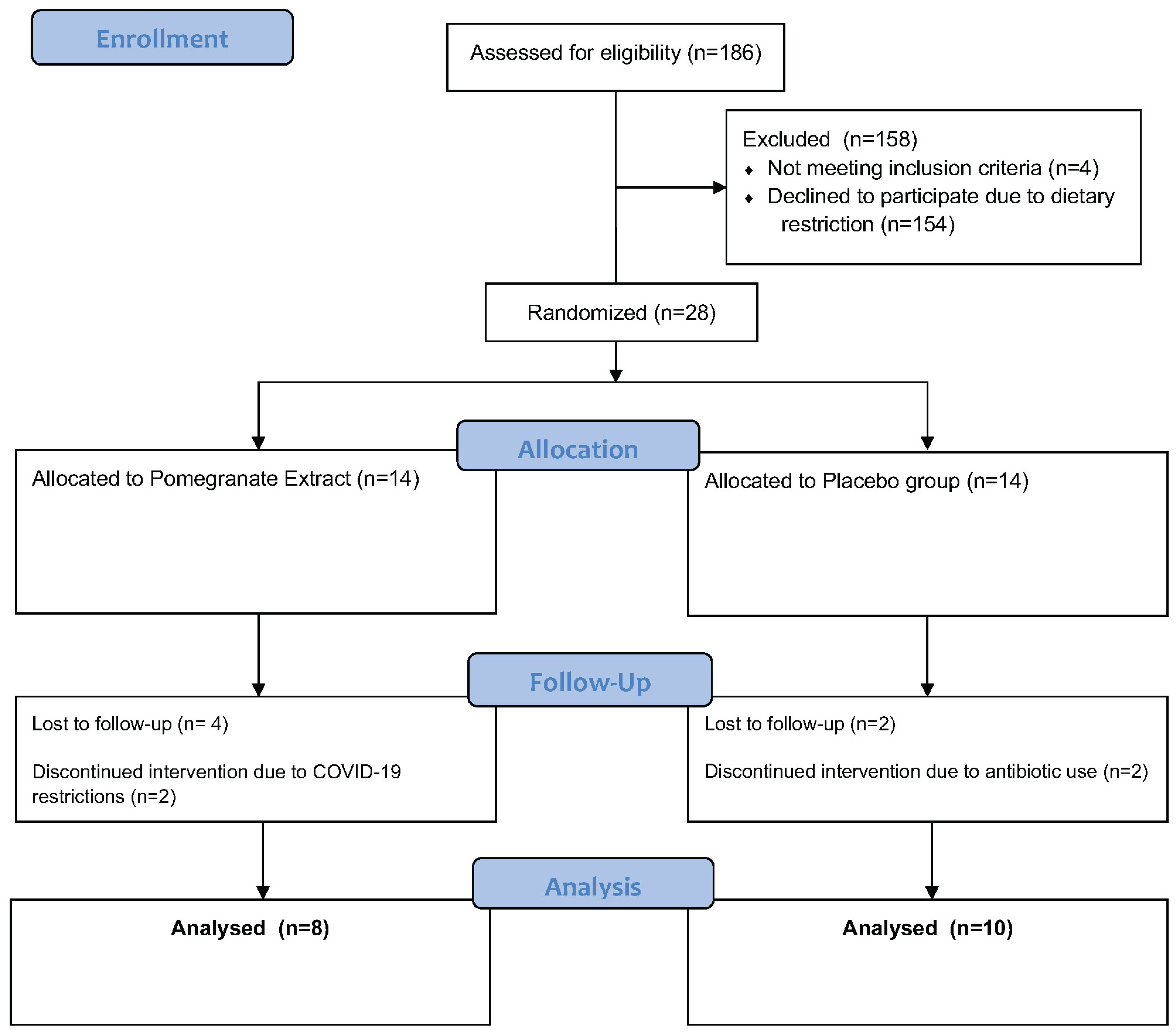
2.1. Study Design and Recruitment
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Dietary Restrictions and Microbiome Sampling
2.4. Stool DNA Extraction and Whole Genome Sequencing
2.4.1. Library Preparation
2.4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis of Stool Samples
2.5. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Measurements
2.6. Urolithin a Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Demographics
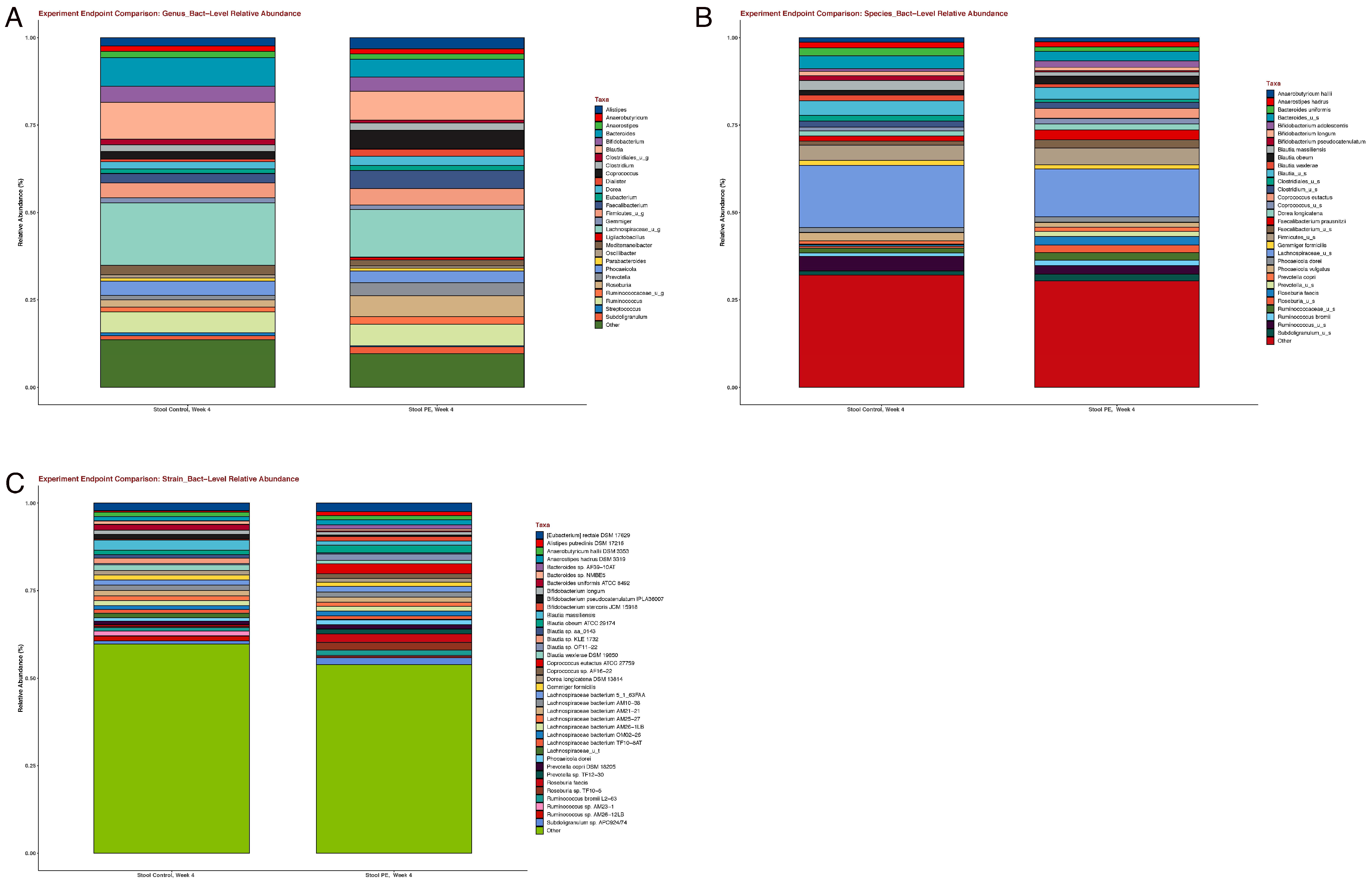
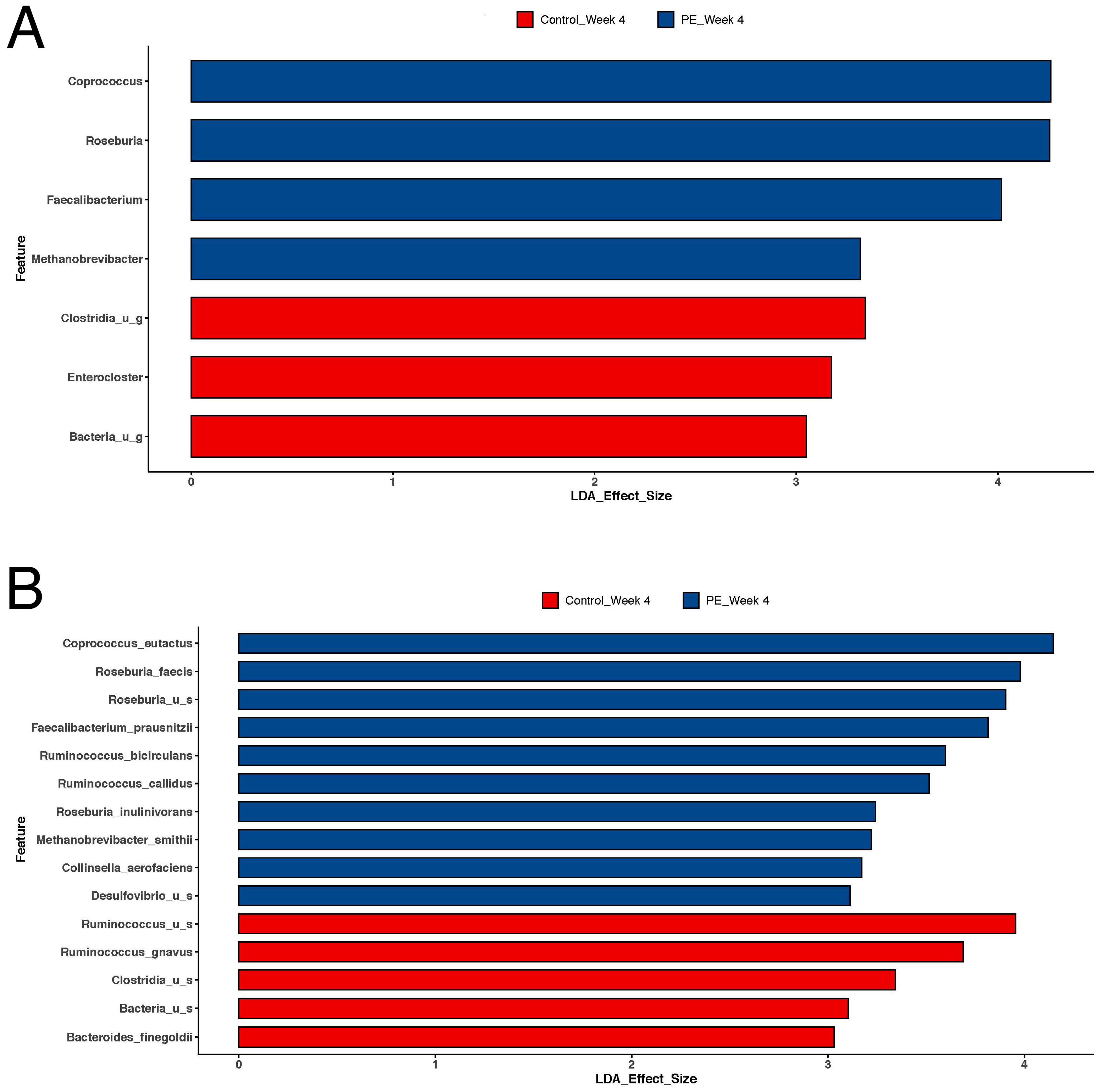
3.2. Gut Microbiome
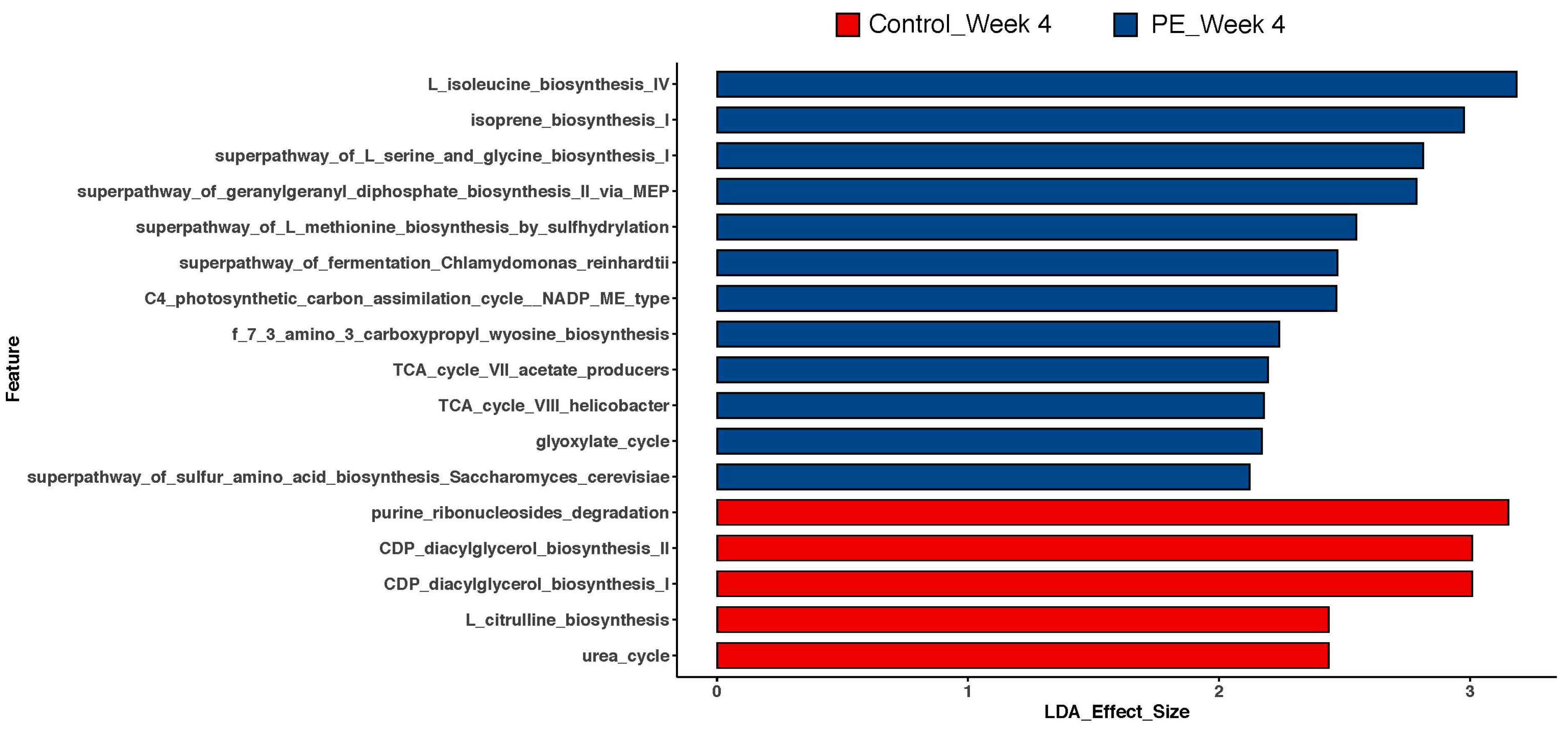
3.3. Gut Microbiome Functional Analysis
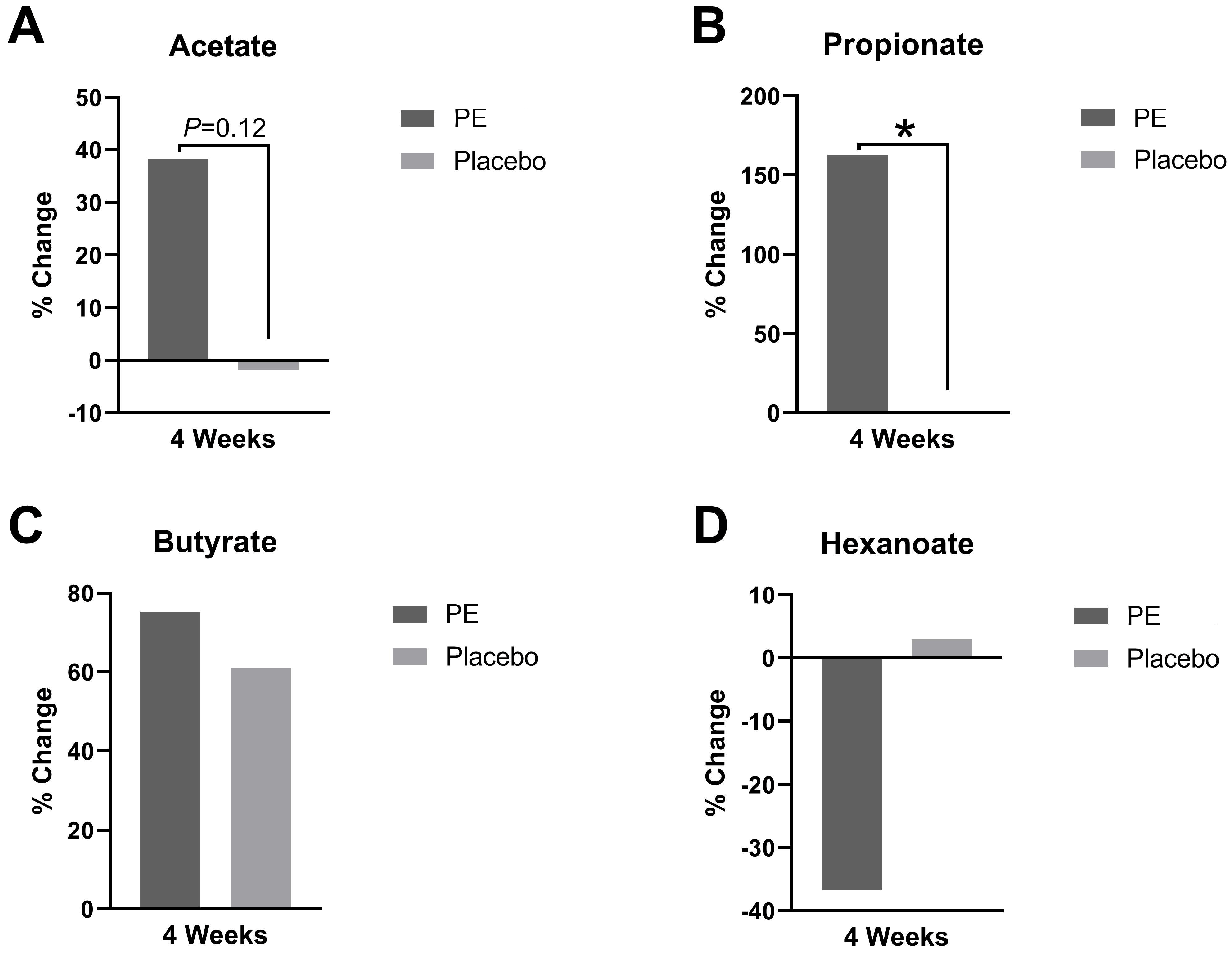
3.4. Plasma Short-Chain Fatty Acids
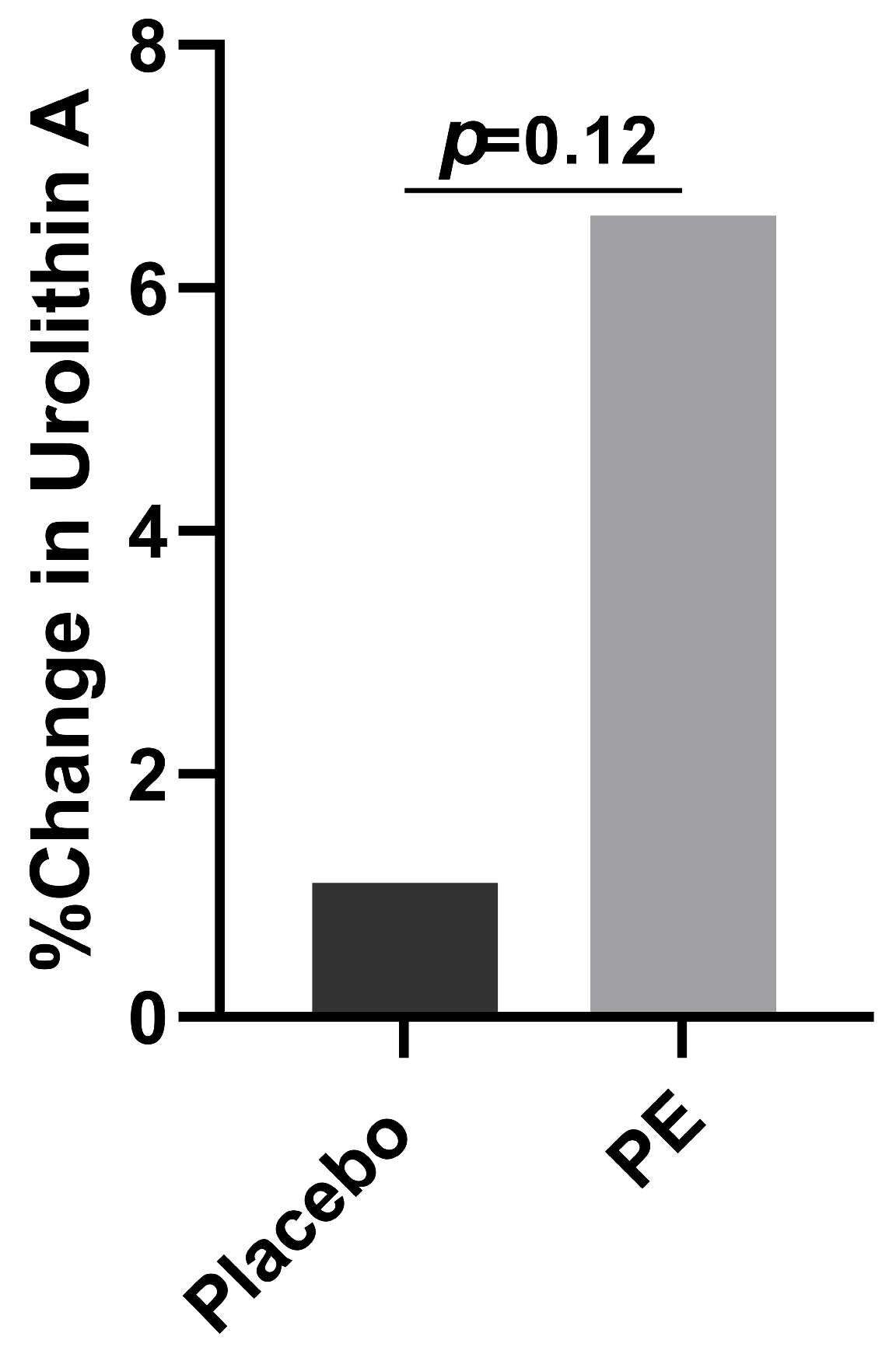
3.5. Plasma Urolithin A
4. Discussion
4.1. Gut Microbiome Shifts
4.2. Functional Predictive Shifts in the Gut Microbiome
4.3. Implications of Gut-Microbiome-Related Secondary Metabolites or Co-Factor Synthesis
4.4. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Augmentation
4.5. Urolithin A
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colombo, E.; Sangiovanni, E.; Dell’agli, M. A review on the anti-inflammatory activity of pomegranate in the gastrointestinal tract. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 247145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawska, M.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Potential of the ellagic acid-derived gut microbiota metabolite—Urolithin A in gastrointestinal protection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3170–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoro, A.; Falzone, L.; Gattuso, G.; Salemi, R.; Cultrera, G.; Leone, G.M.; Scandurra, G.; Candido, S.; Libra, M. Pomegranate: A promising avenue against the most common chronic diseases and their associated risk factors (Review). Int. J. Funct. Nutr. 2021, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Van Hee, V.F.; Bindels, L.B.; De Backer, F.; Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. Polyphenol-rich extract of pomegranate peel alleviates tissue inflammation and hypercholesterolaemia in high-fat diet-induced obese mice: Potential implication of the gut microbiota. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Dunngalvin, G.; Kern, T.; Blanco-Bose, W.; Auwerx, J.; Aebischer, P.; Rinsch, C. Direct supplementation with Urolithin A overcomes limitations of dietary exposure and gut microbiome variability in healthy adults to achieve consistent levels across the population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakkalakal, M.; Nadora, D.; Gahoonia, N.; Dumont, A.; Burney, W.; Pan, A.; Chambers, C.J.; Sivamani, R.K. Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study of Oral Pomegranate Extract on Skin Wrinkles, Biophysical Features, and the Gut-Skin Axis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottesen, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Reed, E.; White, J.R.; Hasan, N.; Subramanian, P.; Ryan, G.; Jarvis, K.; Grim, C.; Daquiqan, N.; et al. Enrichment dynamics of Listeria monocytogenes and the associated microbiome from naturally contaminated ice cream linked to a listeriosis outbreak. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, D.; Kozlova, E.V.; Sha, J.; Erova, T.E.; Azar, S.R.; Fitts, E.C.; Kirtley, M.L.; Tiner, B.L.; Andersson, J.A.; Grim, C.J.; et al. Cross-talk among flesh-eating Aeromonas hydrophila strains in mixed infection leading to necrotizing fasciitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, S.; Smith, D.P.; Hampton-Marcell, J.; Owens, S.M.; Handley, K.M.; Scott, N.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Larsen, P.; Shogan, B.D.; Weiss, S.; et al. Longitudinal analysis of microbial interaction between humans and the indoor environment. Science 2014, 345, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.A.; Young, B.A.; Minard-Smith, A.T.; Saeed, K.; Li, H.; Heizer, E.M.; McMillan, N.J.; Isom, R.; Abdullah, A.S.; Bornman, D.M.; et al. Microbial community profiling of human saliva using shotgun metagenomic sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleu, S.; Machiels, K.; Raes, J.; Verbeke, K.; Vermeire, S. Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, E.T.; Kozik, A.J.; Hooker, C.A.; Burnett, J.L.; Heo, Y.; Kiesel, V.A.; Nevins, C.J.; Oshiro, J.; Robins, M.M.; Thakkar, R.D.; et al. Comparative genomics of the genus Roseburia reveals divergent biosynthetic pathways that may influence colonic competition among species. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinolo, M.A.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Nachbar, R.T.; Curi, R. Regulation of inflammation by short chain fatty acids. Nutrients 2011, 3, 858–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, A.; Bruhs, A.; Schwarz, T. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Sodium Butyrate Functions as a Regulator of the Skin Immune System. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dujaili, E.A.S.; Casey, C.; Stockton, A. Antioxidant Properties and Beneficial Cardiovascular Effects of a Natural Extract of Pomegranate in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Preliminary Single-Blind Controlled Study. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockton, A.; Farhat, G.; McDougall, G.J.; Al-Dujaili, E.A.S. Effect of pomegranate extract on blood pressure and anthropometry in adults: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial. J. Nutr. Sci. 2017, 6, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviram, M.; Rosenblat, M. Pomegranate Protection against Cardiovascular Diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 382763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, A.P.; Al Zaidan, S.; Bangarusamy, D.K.; Al-Shamari, S.; Elhag, W.; Terranegra, A. Increased Relative Abundance of Ruminoccocus Is Associated with Reduced Cardiovascular Risk in an Obese Population. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 849005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Surdin-Kerjan, Y. Metabolism of sulfur amino acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1997, 61, 503–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; Koshland, D.E., Jr. Determination of flux through the branch point of two metabolic cycles. The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the glyoxylate shunt. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 9646–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: Metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, H.; Shimbo, K.; Inoue, Y.; Takino, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Importance of amino acid composition to improve skin collagen protein synthesis rates in UV-irradiated mice. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohnalova, L.; Lundgren, P.; Carty, J.R.E.; Goldstein, N.; Wenski, S.L.; Nanudorn, P.; Thiengmag, S.; Huang, K.P.; Litichevskiy, L.; Descamps, H.C.; et al. A microbiome-dependent gut-brain pathway regulates motivation for exercise. Nature 2022, 612, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torregrosa-Garcia, A.; Avila-Gandia, V.; Luque-Rubia, A.J.; Abellan-Ruiz, M.S.; Querol-Calderon, M.; Lopez-Roman, F.J. Pomegranate Extract Improves Maximal Performance of Trained Cyclists after an Exhausting Endurance Trial: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, I.; Haas, K.N.; Dhaliwal, S.K.; Burney, W.A.; Pourang, A.; Sandhu, S.S.; Maloh, J.; Newman, J.W.; Crawford, R.; Sivamani, R.K. Prospective Placebo-Controlled Assessment of Spore-Based Probiotic Supplementation on Sebum Production, Skin Barrier Function, and Acne. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita-Mindrican, C.B.; Ziani, K.; Mititelu, M.; Oprea, E.; Neacsu, S.M.; Morosan, E.; Dumitrescu, D.E.; Rosca, A.C.; Draganescu, D.; Negrei, C. Therapeutic Benefits and Dietary Restrictions of Fiber Intake: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatian, A.; Bordbar, S.; Sarkissian, S.; Woods, J.A.; Cains, G.D.; Chong, C.W.; Marino, E.; Frew, J.W. Adalimumab therapy is associated with increased faecal short chain fatty acids in hidradenitis suppurativa. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1872–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between gut microbiota and diet in cardio-metabolic health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1897212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Valdes, P.; Singh, A.; Rinsch, C.; Auwerx, J. Impact of the Natural Compound Urolithin A on Health, Disease, and Aging. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, S.A.; Abdulrahman, A.O.; Zamzami, M.A.; Khan, M.I. Urolithins: The Gut Based Polyphenol Metabolites of Ellagitannins in Cancer Prevention, a Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 647582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, O.; Kujawska, M. Urolithin A in Health and Diseases: Prospects for Parkinson’s Disease Management. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.R.; Zhang, M.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Gao, Z.M.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, G.P.; Qin, Y.; Dai, X.Y.; Yu, X.Y.; et al. Urolithin A ameliorates obesity-induced metabolic cardiomyopathy in mice via mitophagy activation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Madani, B.; Burzangi, A.S.; Alsieni, M.; Bazuhair, M.A.; Jamal, M.; Daghistani, H.; Barasheed, M.O.; Alkreathy, H.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Urolithin A’s Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antiapoptotic Activities Mitigate Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Injury in Wistar Rats. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Villalba, R.; Gimenez-Bastida, J.A.; Cortes-Martin, A.; Avila-Galvez, M.A.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Selma, M.V.; Espin, J.C.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A. Urolithins: A Comprehensive Update on their Metabolism, Bioactivity, and Associated Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sivamani, R.K.; Chakkalakal, M.; Pan, A.; Nadora, D.; Min, M.; Dumont, A.; Burney, W.A.; Chambers, C.J. Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Standardized Oral Pomegranate Extract on the Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods 2024, 13, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010015
Sivamani RK, Chakkalakal M, Pan A, Nadora D, Min M, Dumont A, Burney WA, Chambers CJ. Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Standardized Oral Pomegranate Extract on the Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods. 2024; 13(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleSivamani, Raja K., Mincy Chakkalakal, Adrianne Pan, Dawnica Nadora, Mildred Min, Ashley Dumont, Waqas A. Burney, and Cindy J. Chambers. 2024. "Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Standardized Oral Pomegranate Extract on the Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids" Foods 13, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010015
APA StyleSivamani, R. K., Chakkalakal, M., Pan, A., Nadora, D., Min, M., Dumont, A., Burney, W. A., & Chambers, C. J. (2024). Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Standardized Oral Pomegranate Extract on the Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods, 13(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010015






