Citrinin Exposure Induced Testicular Damage and Spermatogenesis Disorder by Triggering Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Animals and Treatment
2.4. Calculation of the Testicular Index
2.5. Histopathological Examination
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscope Examination
2.7. Sperm Viability Test
2.8. Testosterone Concentration Measurement
2.9. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.10. Oxidation-Antioxidant Index Detection
2.11. TUNEL Assay
2.12. Western Blotting Assay
2.13. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of CTN on Testicular Damage
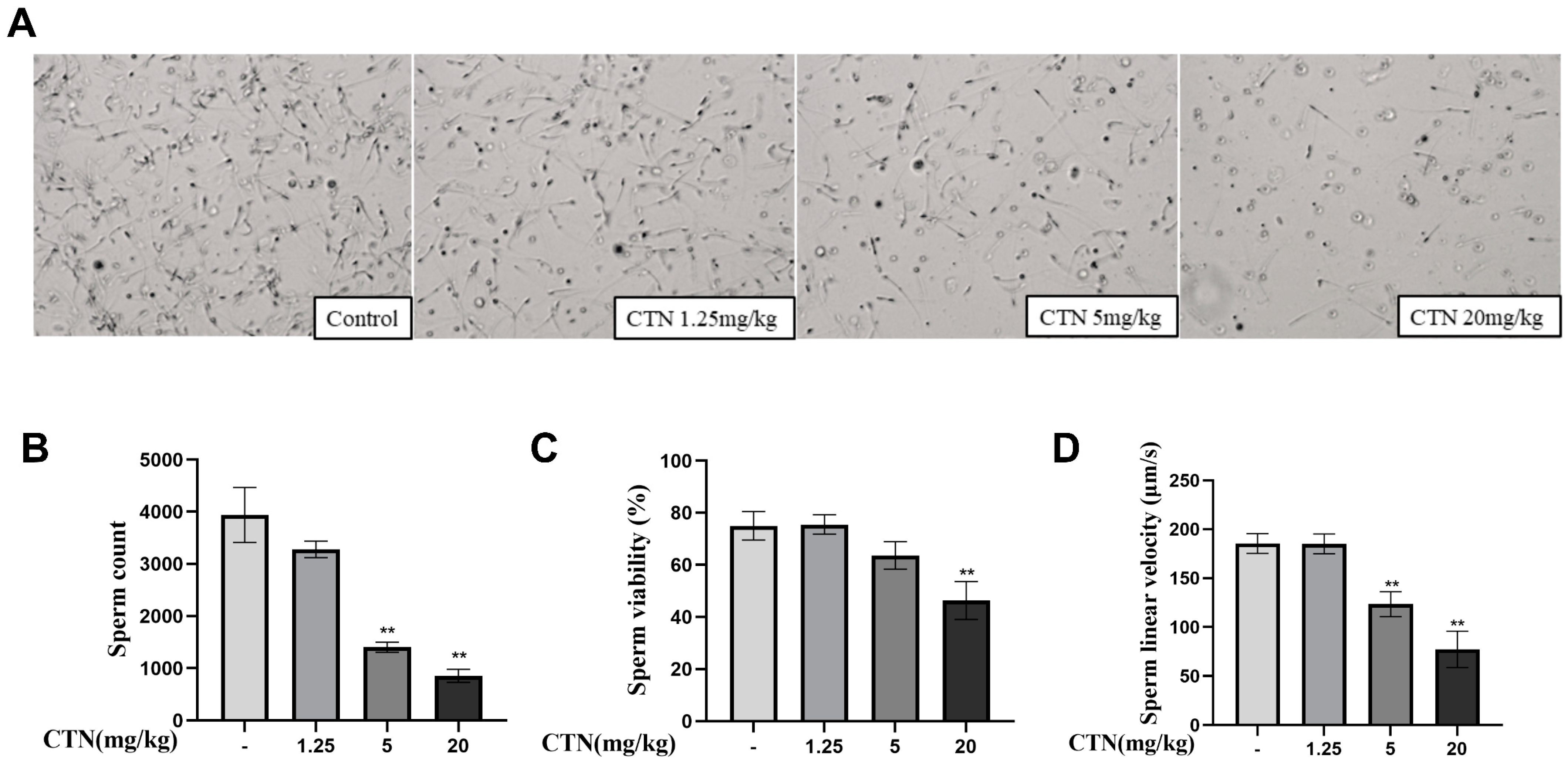
3.2. The Effects of CTN on Spermatogenesis
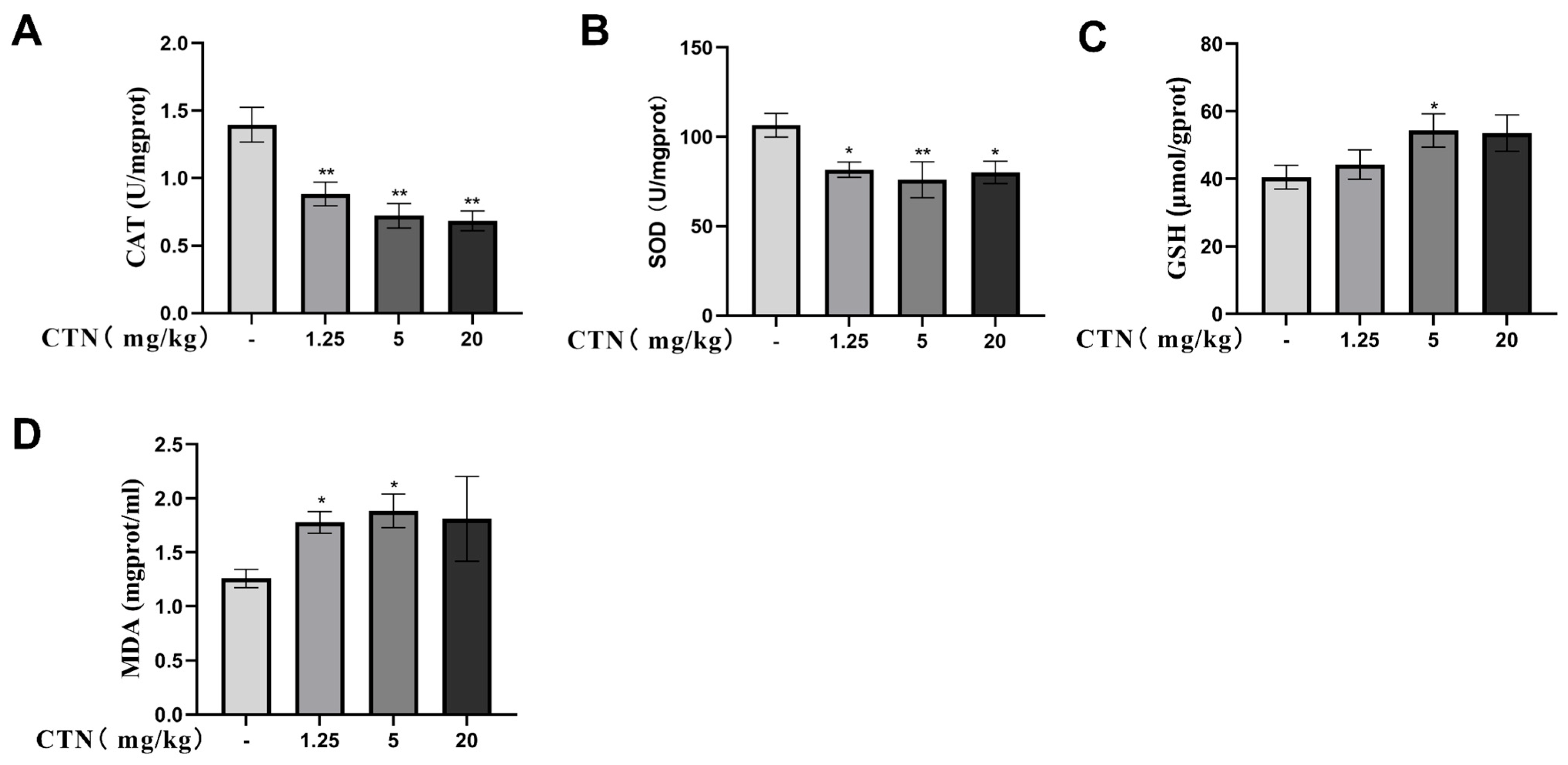
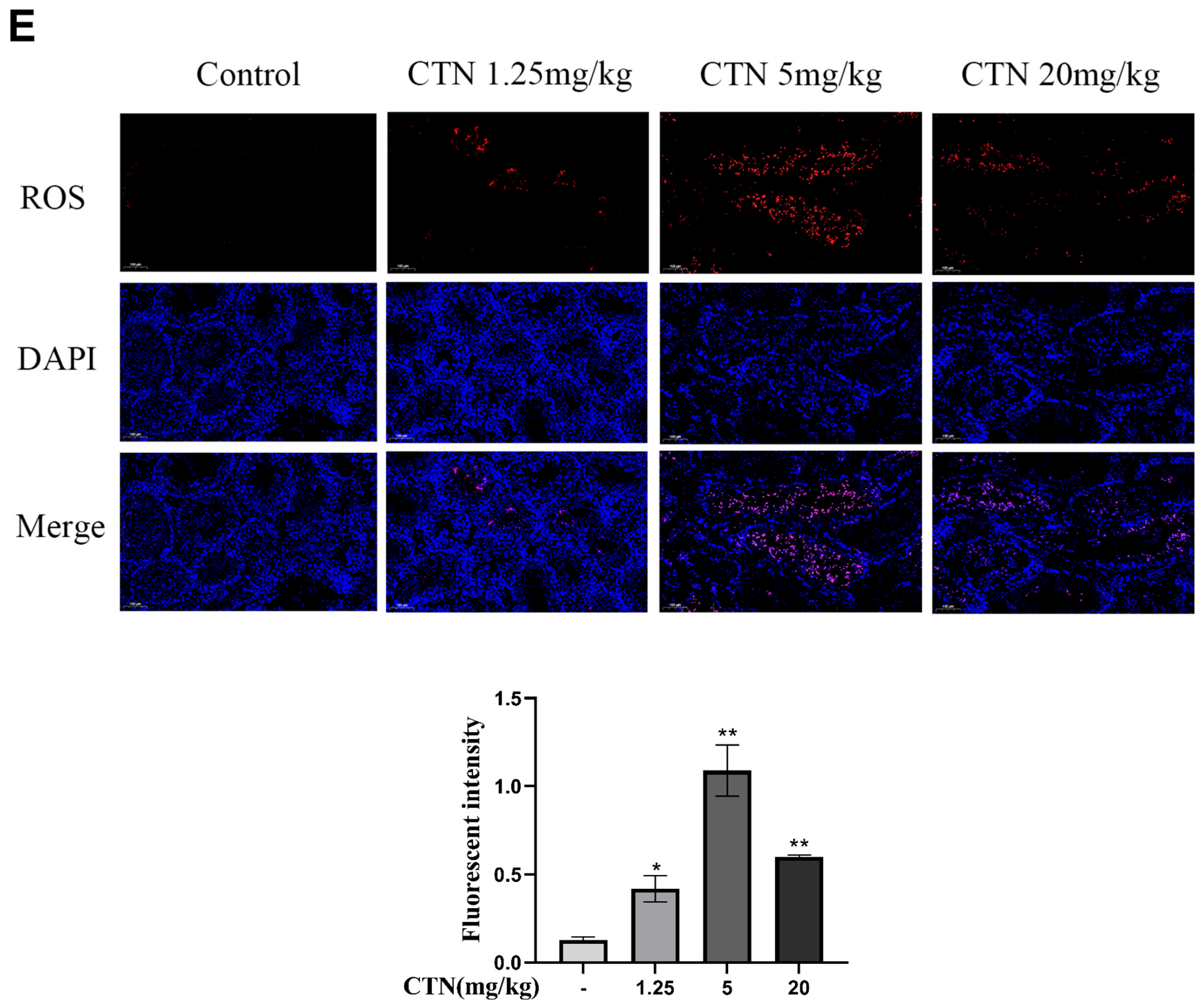
3.3. The Effects of CTN on Testicular Oxidative Damage
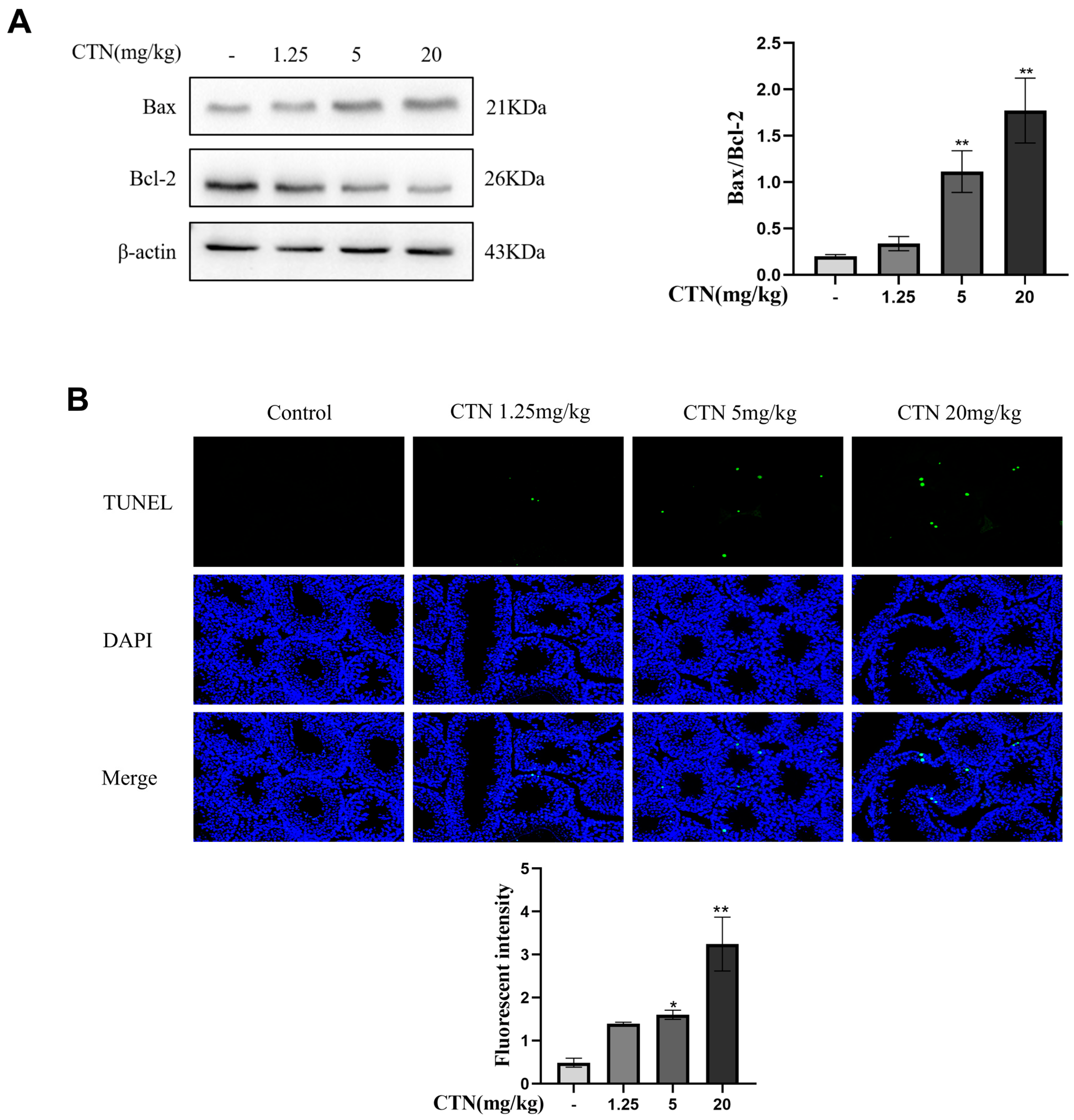
3.4. The Effects of CTN on Apoptosis of Testicle Cells
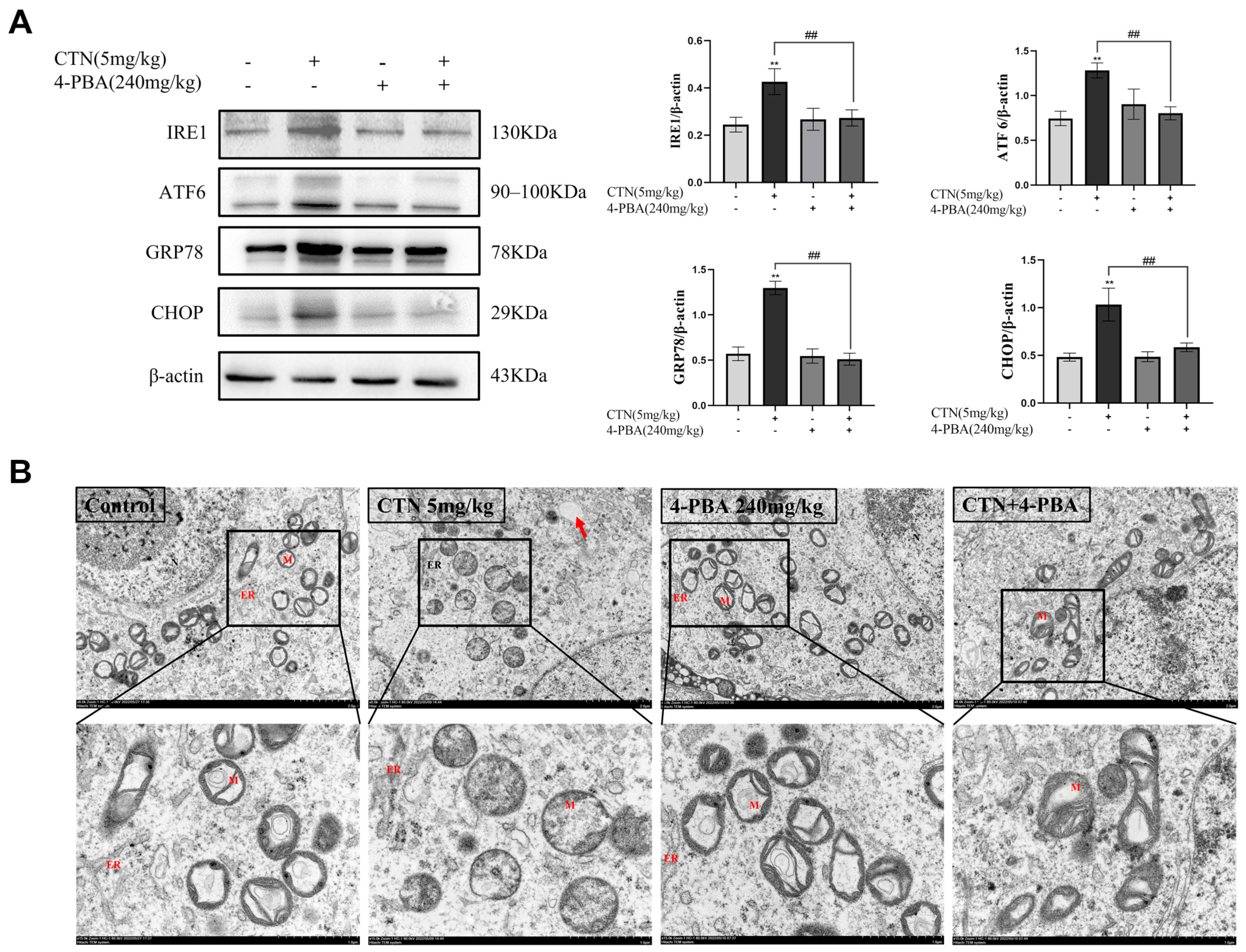
3.5. Effects of 4-PBA on Testicular ERS and Ultrastructural Changes after CTN Exposure
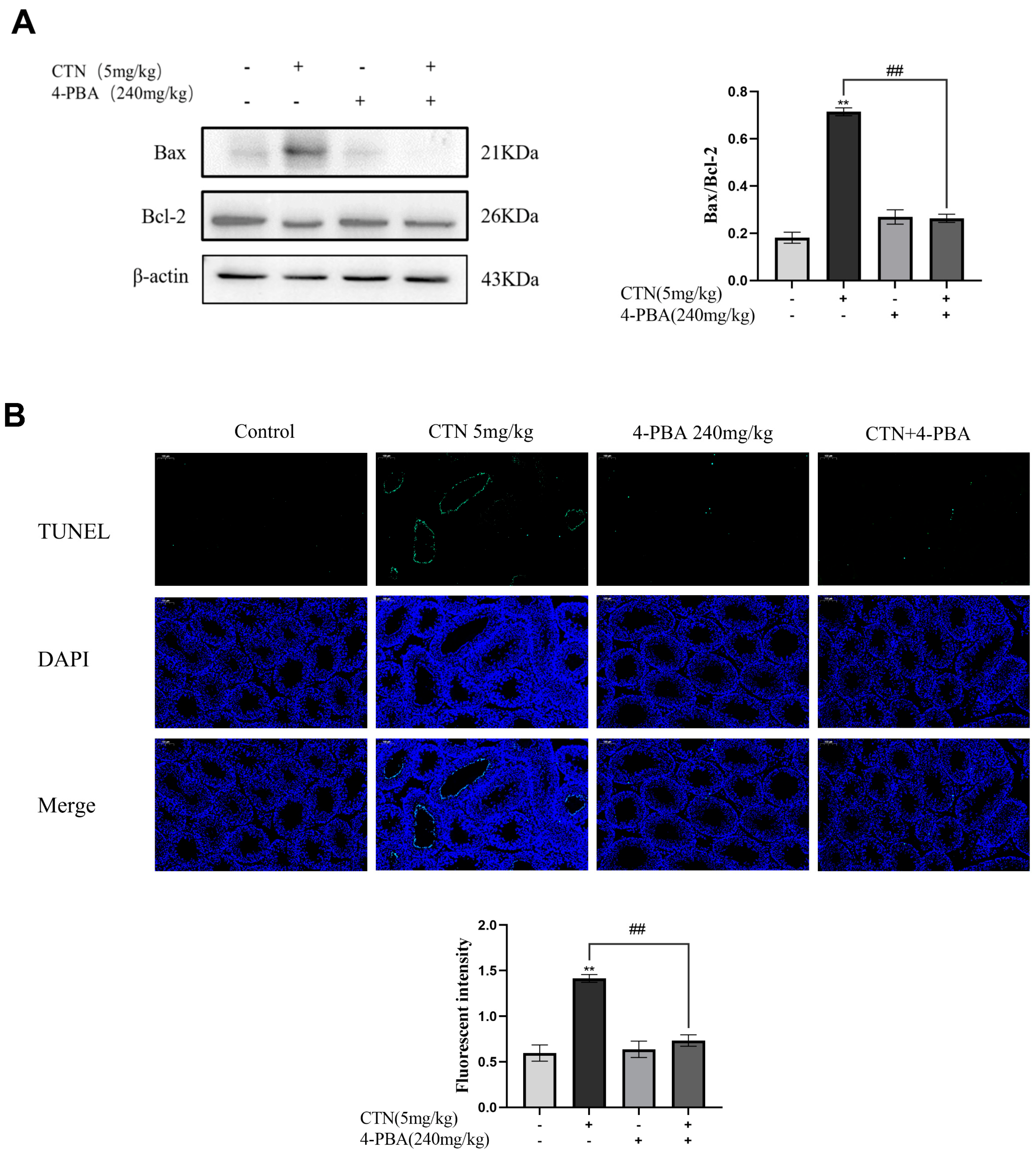
3.6. Effects of 4-PBA on Testis Cells Apoptosis after CTN Exposure
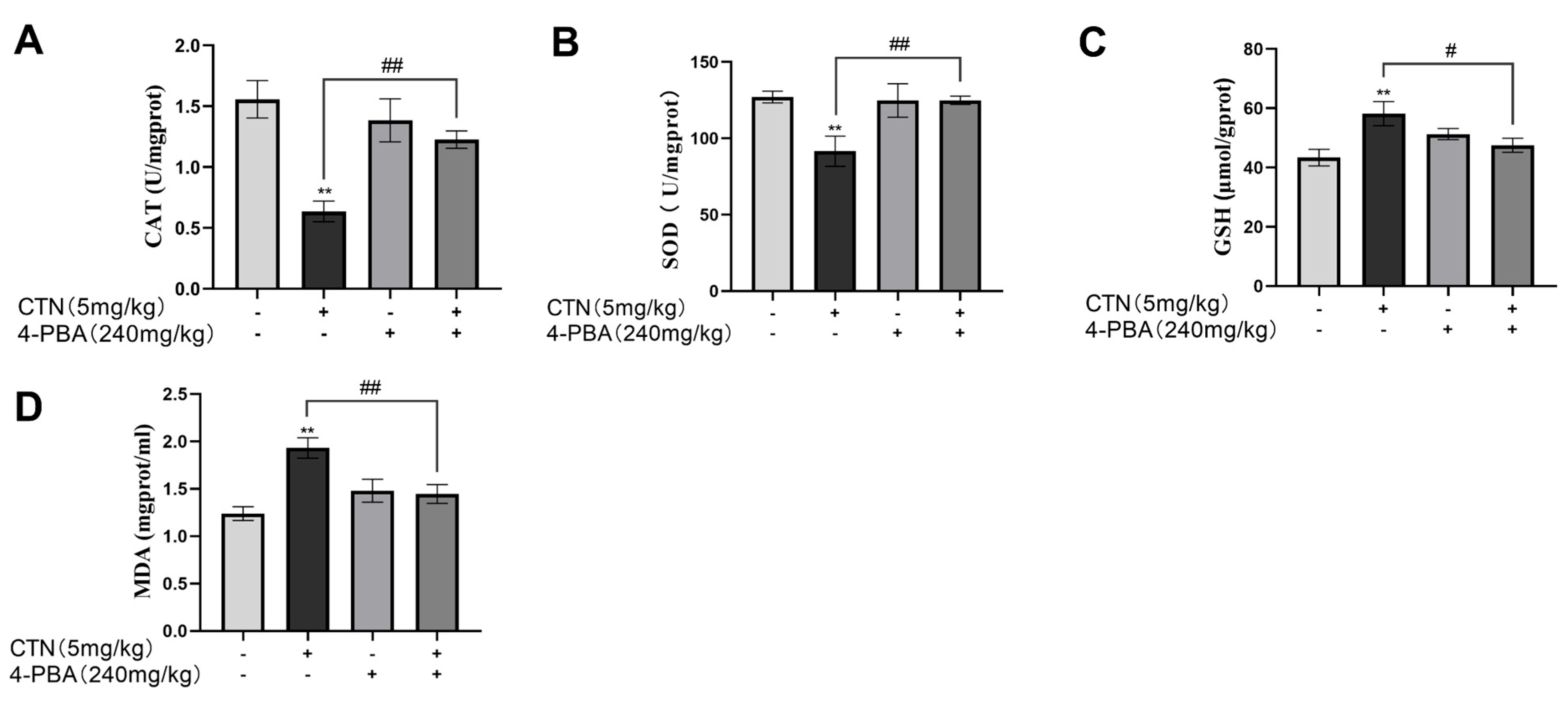
3.7. Effects of 4-PBA on Testicular Oxidative Damage after CTN Exposure
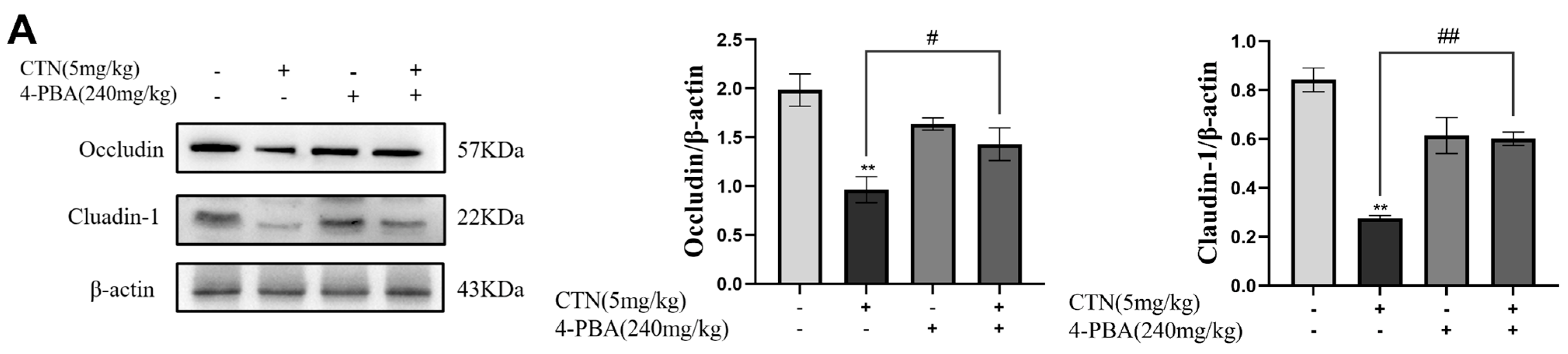
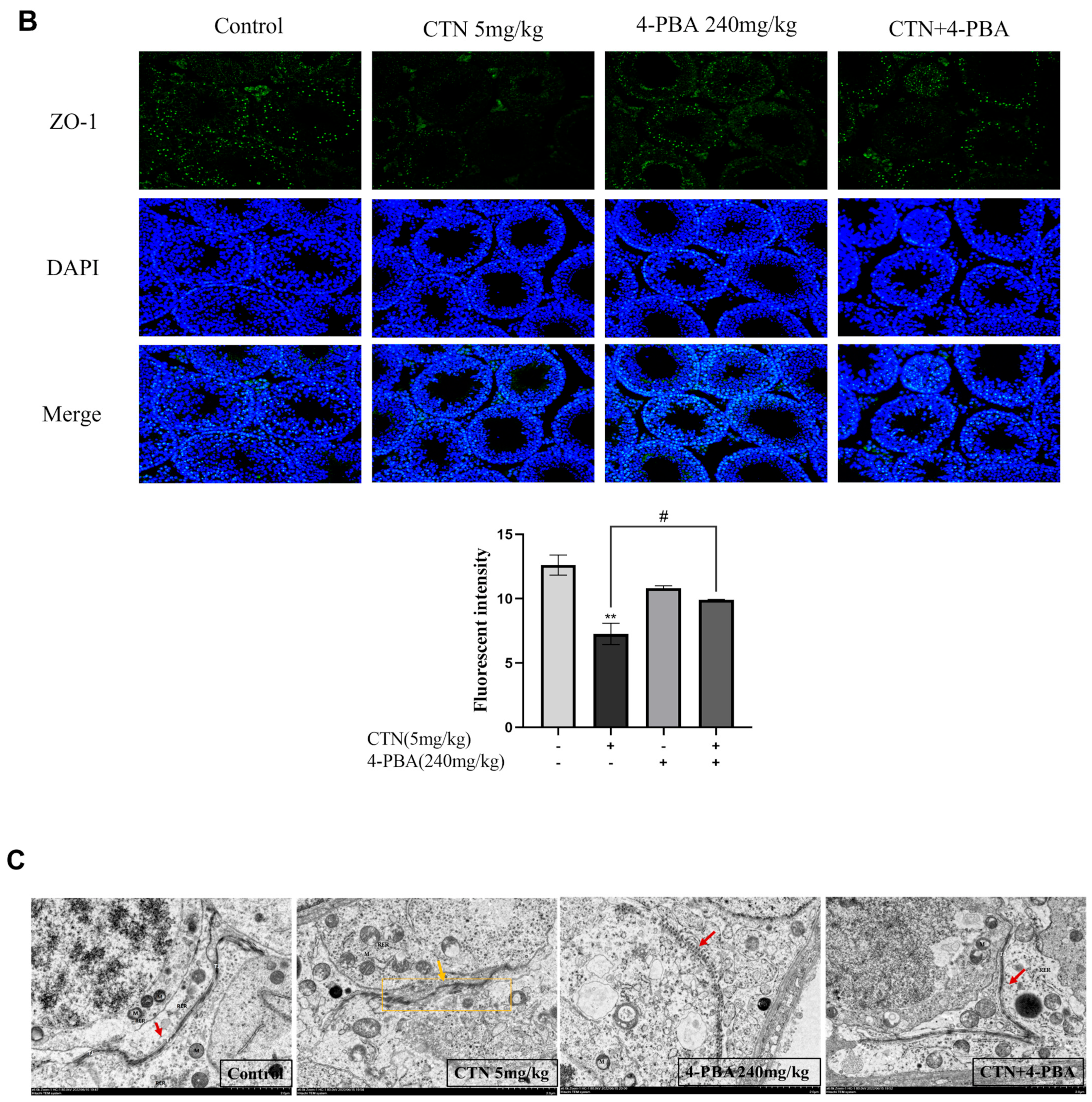
3.8. Effects of 4-PBA on Blood Testis Barrier (BTB) Damage after CTN Exposure
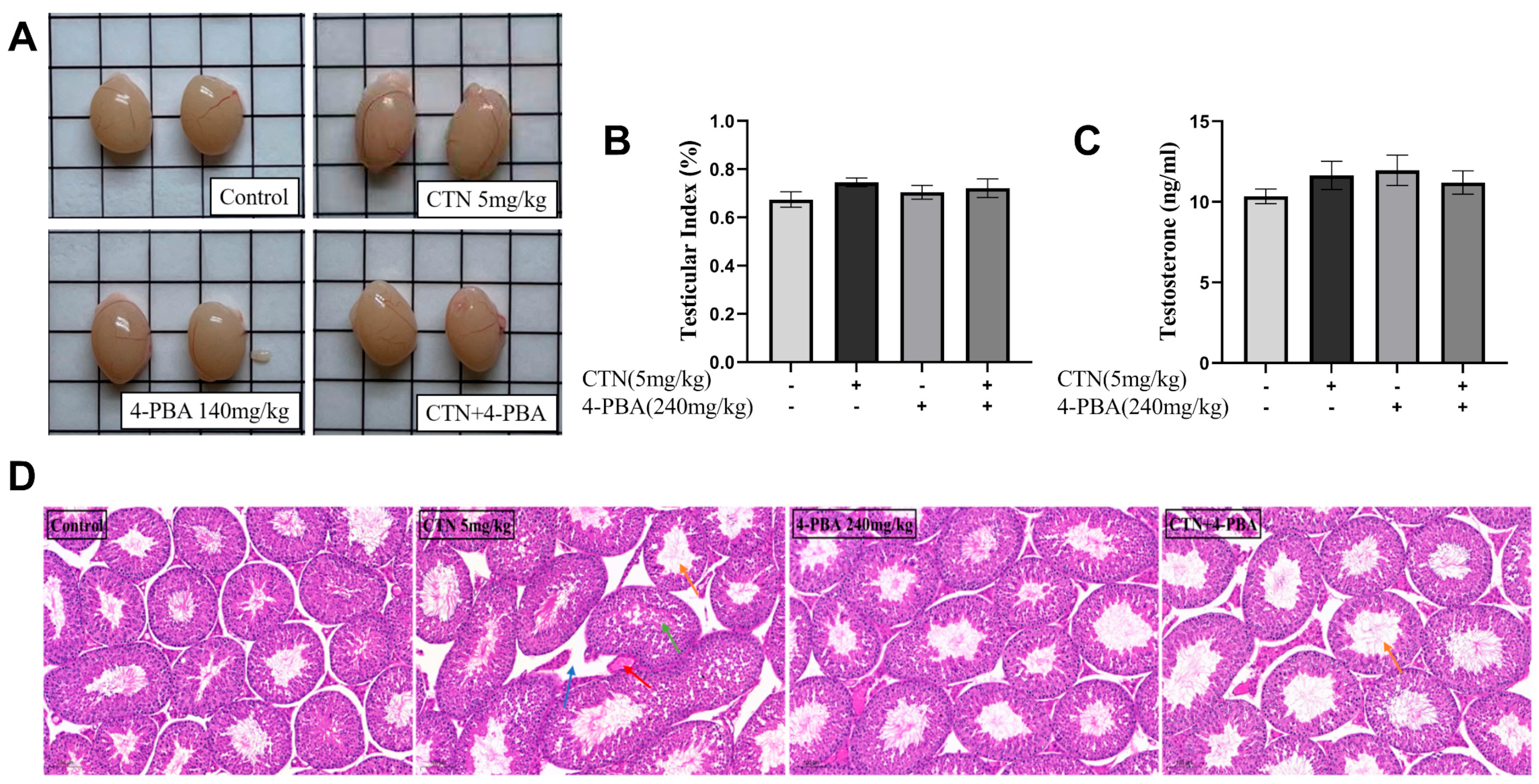
3.9. Effects of 4-PBA on Testicular Damage after CTN Exposure
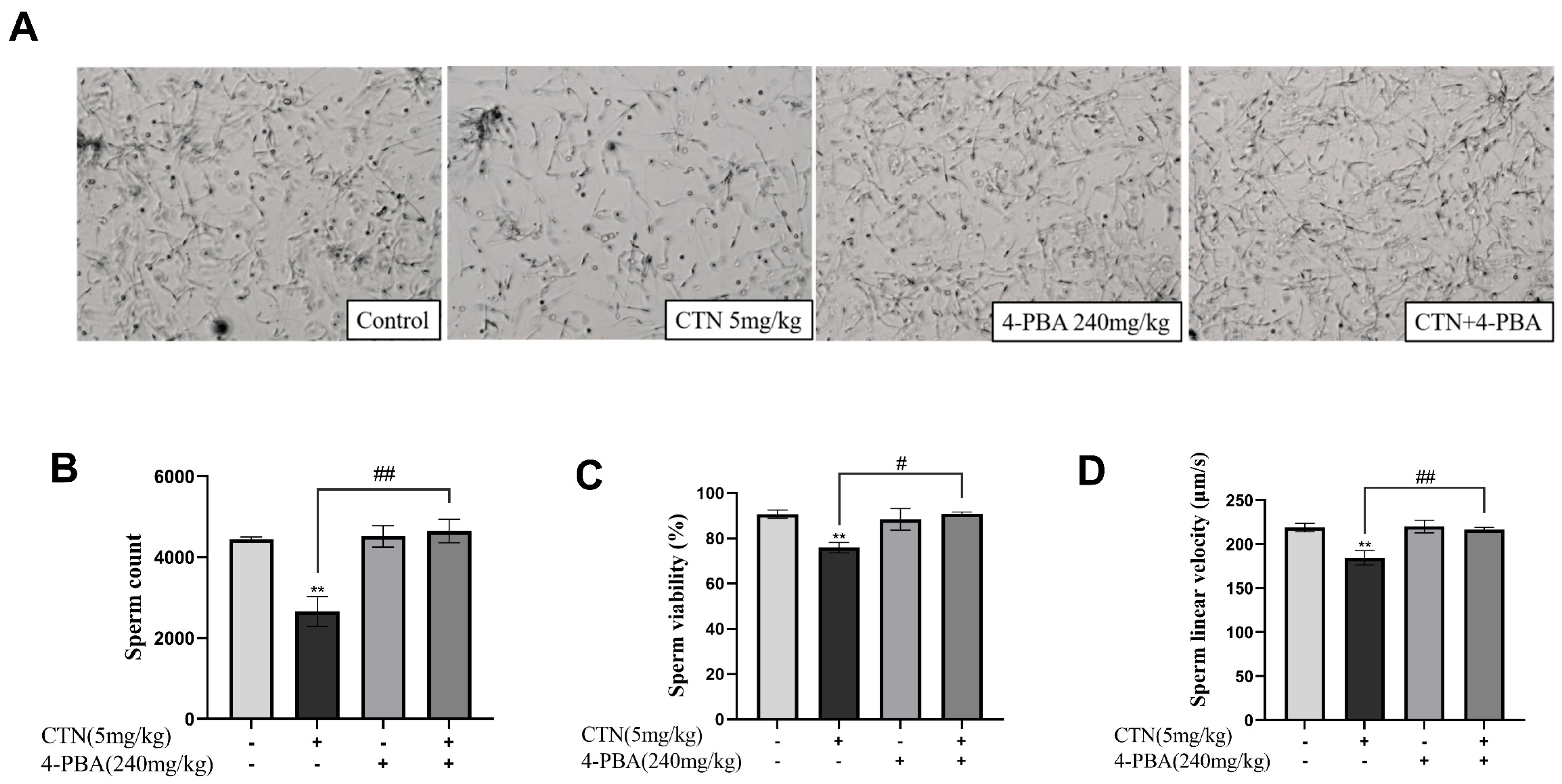
3.10. Effects of 4-PBA on Spermatogenesis Disorder after CTN Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kepinska-Pacelik, J.; Biel, W. Alimentary Risk of Mycotoxins for Humans and Animals. Toxins 2021, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.; Pereira, A.; Pena, A.; Lino, C. Citrinin in Foods and Supplements: A Review of Occurrence and Analytical Methodologies. Foods 2021, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamle, M.; Mahato, D.; Gupta, A.; Pandhi, S.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, B.; Mishra, S.; Arora, S.; Selvakumar, R.; Saurabh, V.; et al. Citrinin Mycotoxin Contamination in Food and Feed: Impact on Agriculture, Human Health, and Detection and Management Strategies. Toxins 2022, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.; Islam, M.; Ali, E.; Uddin, S.; Santos, J.; de Alencar, M.; Gomes, A.; Paz, M.; de Brito, M.; Sousa, J.; et al. A comprehensive review on biological properties of citrinin. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Sun, S. Citrinin exposure disrupts organelle distribution and functions in mouse oocytes. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, C.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, J. Citrinin-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice Is Regulated by the Ca2+/Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2022, 14, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pan, W.; Cai, W.; Ju, J.; Sun, S. Exposure to citrinin induces DNA damage, autophagy, and mitochondria dysfunction during first cleavage of mouse embryos. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fainberg, J.; Kashanian, J. Recent advances in understanding and managing male infertility. F1000Research 2019, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarikwu, S. Causes and risk factors for male-factor infertility in Nigeria: A review. Afr. J. Reprod. Health 2013, 17, 150–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, H.; Itahashi, M.; Taniai, E.; Yafune, A.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Mitsumori, K.; Shibutani, M. Induction of ovarian toxicity in a subchronic oral toxicity study of citrinin in female BALB/c mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S. Toxic effects of citrinin on the male reproductive system in mice. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 465–469. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, Y.; Yilmaz, B.; Yildizbayrak, N.; Korkut, A.; Kursun, M.; Irez, T.; Erkan, M. Evaluation of citrinin-induced toxic effects on mouse Sertoli cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 44, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, M.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Kong, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, S.; Ning, C.; Xiao, W.; et al. The role of ER stress and ATP/AMPK in oxidative stress meditated hepatotoxicity induced by citrinin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Bouaziz, C.; Prola, A.; Da Silva, J.; Bacha, H.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Lemaire, C. Citrinin induces apoptosis in human HCT116 colon cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2017, 80, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M. Testosterone and sexual function in men. Maturitas 2018, 112, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Minhas, S.; Dhillo, W.; Jayasena, C. Male infertility due to testicular disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e442–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Gong, M.; Wang, C.; Wei, N.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; et al. Citrinin reduces testosterone secretion by inducing apoptosis in rat Leydig cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N.; Kubo, K.; Onishi, T.; Kitakaze, T.; Goto, T.; Inui, H.; Yamaji, R. Androgen receptor suppresses beta-adrenoceptor-mediated CREB activation and thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue of male mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.; Roy, A.; Chainy, G. Rat testicular mitochondrial antioxidant defence system and its modulation by aging. Acta Biol. Hung. 2008, 59, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P.; Slama, P.; Roychoudhury, S. Oxidative Stress, Testicular Inflammatory Pathways, and Male Reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ghanghas, P.; Kaushal, N.; Kaur, J.; Kaur, P. Epigenetics and oxidative stress: A twin-edged sword in spermatogenesis. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, S.; Faiq, M.; Tolahunase, M.; Dada, R. Oxidative stress and male infertility. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasic, D.; Micek, V.; Klaric, M.; Peraica, M. Oxidative stress as a mechanism of combined OTA and CTN toxicity in rat plasma, liver and kidney. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, M.; Jin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H. Citrinin exposure affects oocyte maturation and embryo development by inducing oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34525–34533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Virk, G.; Ong, C.; Plessis, S. Effect of oxidative stress on male reproduction. World J. Men’s Health 2014, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, K.; Das, J.; Pal, P.; Sil, P. Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1157–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Ou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L. The Relationship between the Bcl-2/Bax Proteins and the Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Pathway in the Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells into Neurons. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.; Finnie, J. The Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Cell Survival and Death. J. Comp. Pathol. 2020, 181, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mruk, D.; Cheng, C. The Mammalian Blood-Testis Barrier: Its Biology and Regulation. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, 564–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wang, Z.; Xie, S.; Hu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Mruk, D.; Guan, Y. Testin regulates the blood-testis barrier via disturbing occludin/ZO-1 association and actin organization. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 6127–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z. Aflatoxin B1 disrupts blood-testis barrier integrity by reducing junction protein and promoting apoptosis in mice testes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 148, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Jiang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Jiao, R.; Peng, Z.; Li, Y.; Bai, W. Toxic effects of zearalenone on gametogenesis and embryonic development: A molecular point of review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, L.; Gao, X.; Kong, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wen, L.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; et al. Ameliorative effect of betulinic acid against zearalenone exposure triggers testicular dysfunction and oxidative stress in mice via p38/ERK MAPK inhibition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense activation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Huang, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Deoxynivalenol induced spermatogenesis disorder by blood-testis barrier disruption associated with testosterone deficiency and inflammation in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, C.; Tang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes blood-testis barrier impairment in mice with busulfan-induced oligospermia through PERK-eIF2α signaling pathway. Toxicology 2022, 473, 153193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, M.; Kong, X.; Ning, C.; Wang, S.; Xiao, W.; Wang, N.; et al. Citrinin Exposure Induced Testicular Damage and Spermatogenesis Disorder by Triggering Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Foods 2023, 12, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081616
Wu J, Wu Y, Fan H, Yang C, Yang M, Kong X, Ning C, Wang S, Xiao W, Wang N, et al. Citrinin Exposure Induced Testicular Damage and Spermatogenesis Disorder by Triggering Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Foods. 2023; 12(8):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081616
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, You Wu, Hui Fan, Chenglin Yang, Mengran Yang, Xiangyi Kong, Can Ning, Siqi Wang, Wenguang Xiao, Naidong Wang, and et al. 2023. "Citrinin Exposure Induced Testicular Damage and Spermatogenesis Disorder by Triggering Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress" Foods 12, no. 8: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081616
APA StyleWu, J., Wu, Y., Fan, H., Yang, C., Yang, M., Kong, X., Ning, C., Wang, S., Xiao, W., Wang, N., Yi, J., & Yuan, Z. (2023). Citrinin Exposure Induced Testicular Damage and Spermatogenesis Disorder by Triggering Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Foods, 12(8), 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081616





