Protective Effect of Ginsenoside CK against Autoimmune Hepatitis Induced by Concanavalin A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
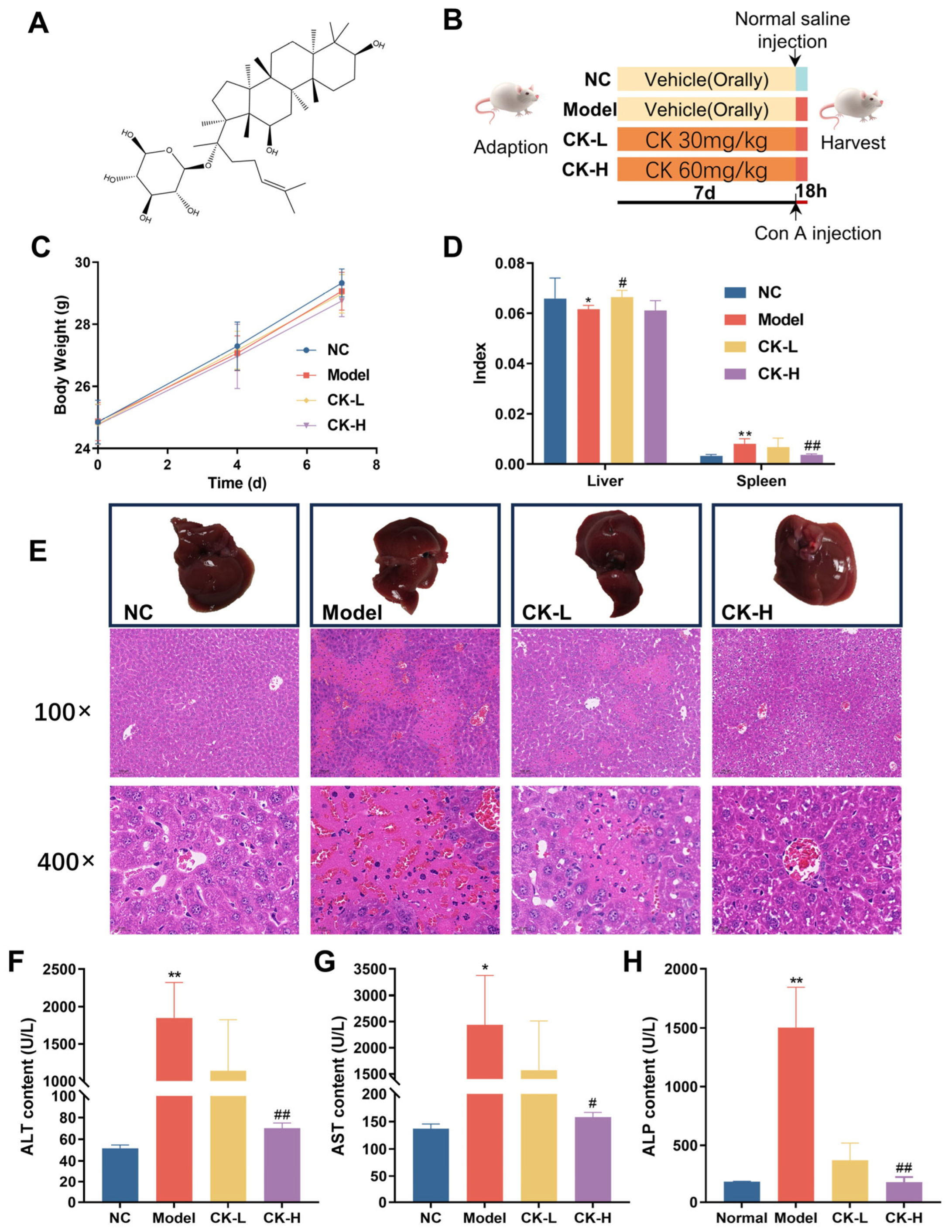
2.3. Experimental Design
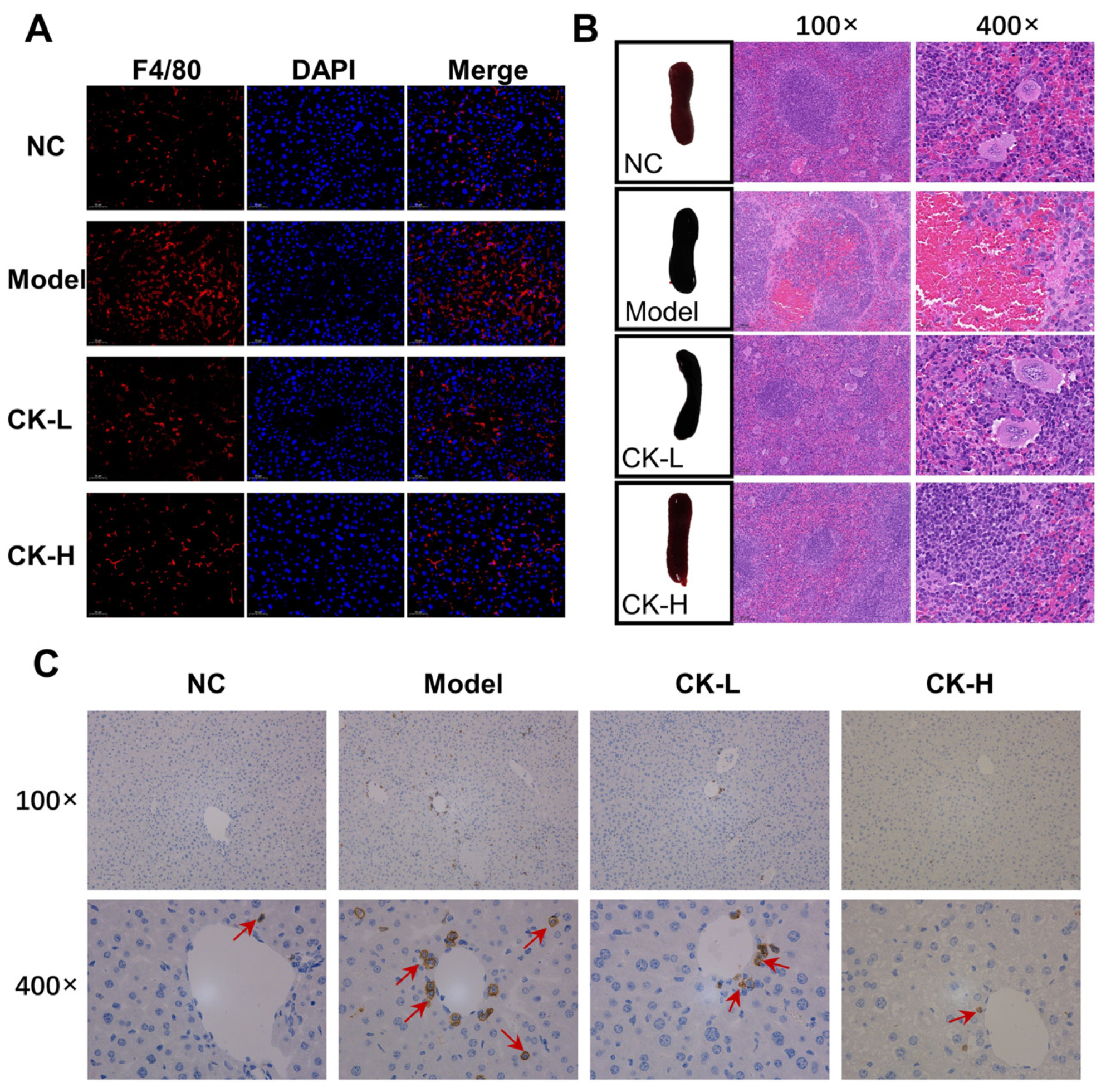
2.4. Histopathological Examination of Liver and Spleen
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
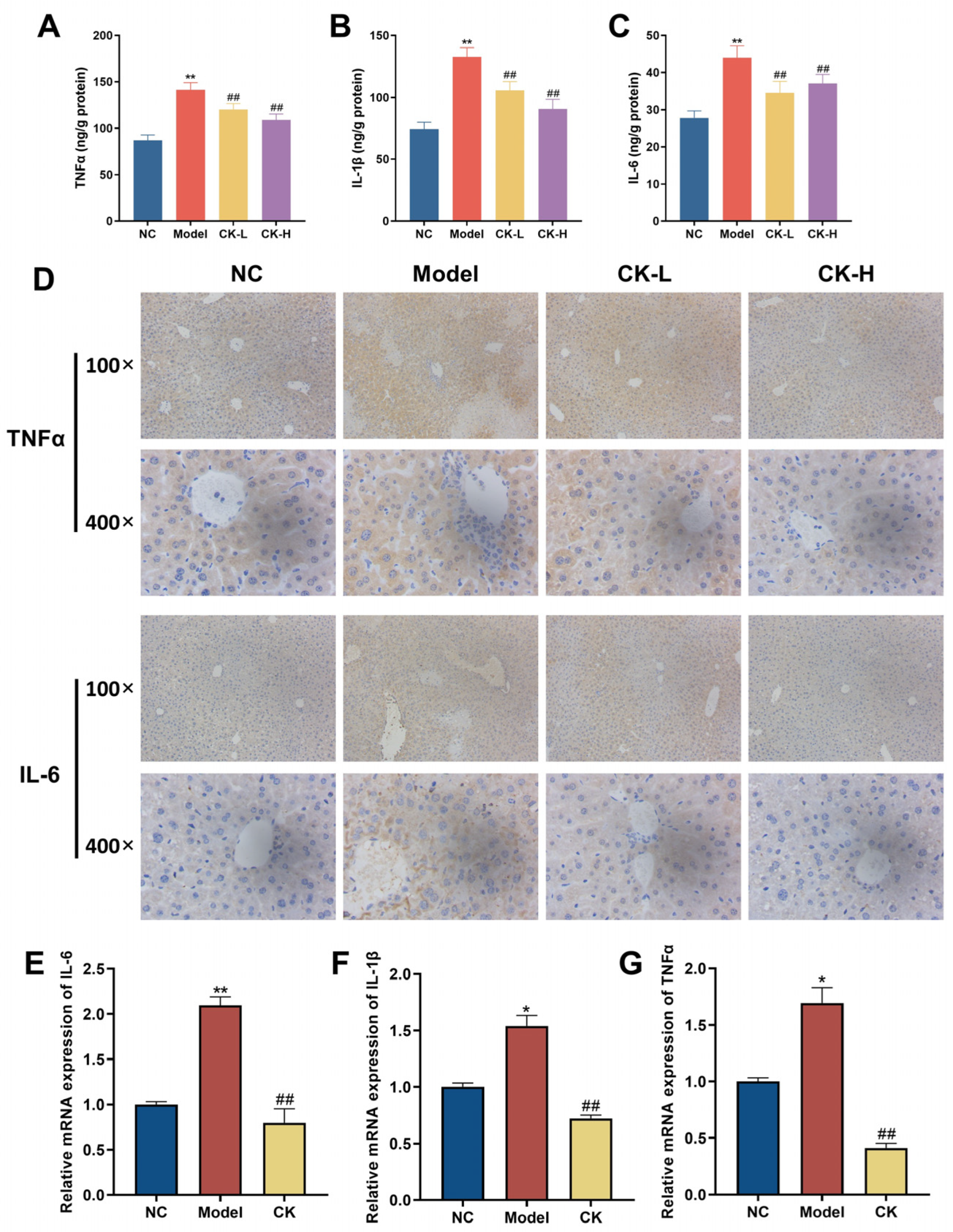
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
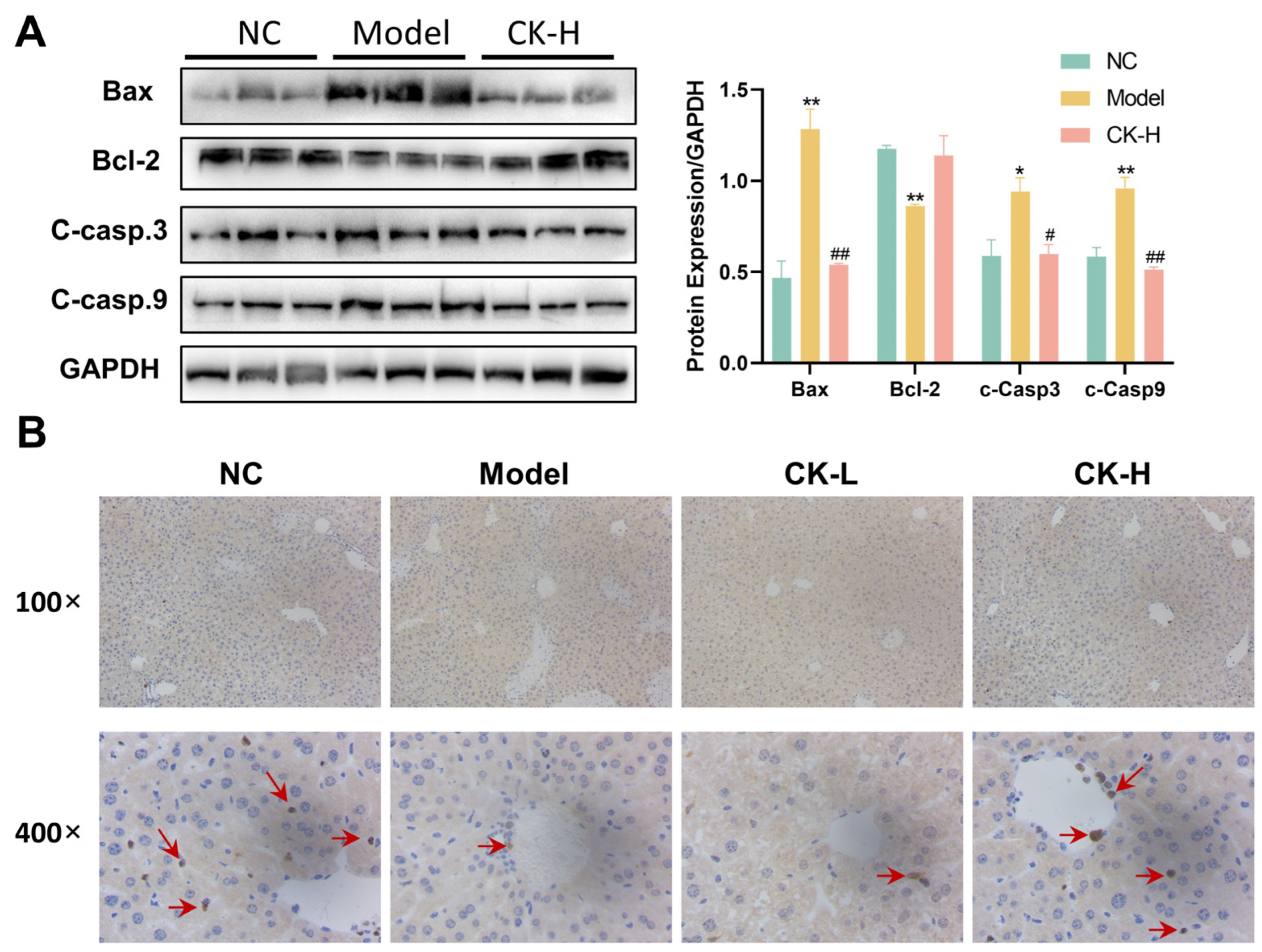
2.7. Immunoblotting Analysis
2.8. Inflammatory Markers Assessment
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ginsenoside CK Ameliorated Hepatic Injury Induced by Con A
3.2. Ginsenoside CK Pretreatment Inhibited Cell Apoptosis in Mice with Hepatitis
3.3. Ginsenoside CK Regulated Immune Imbalance Caused by Con A
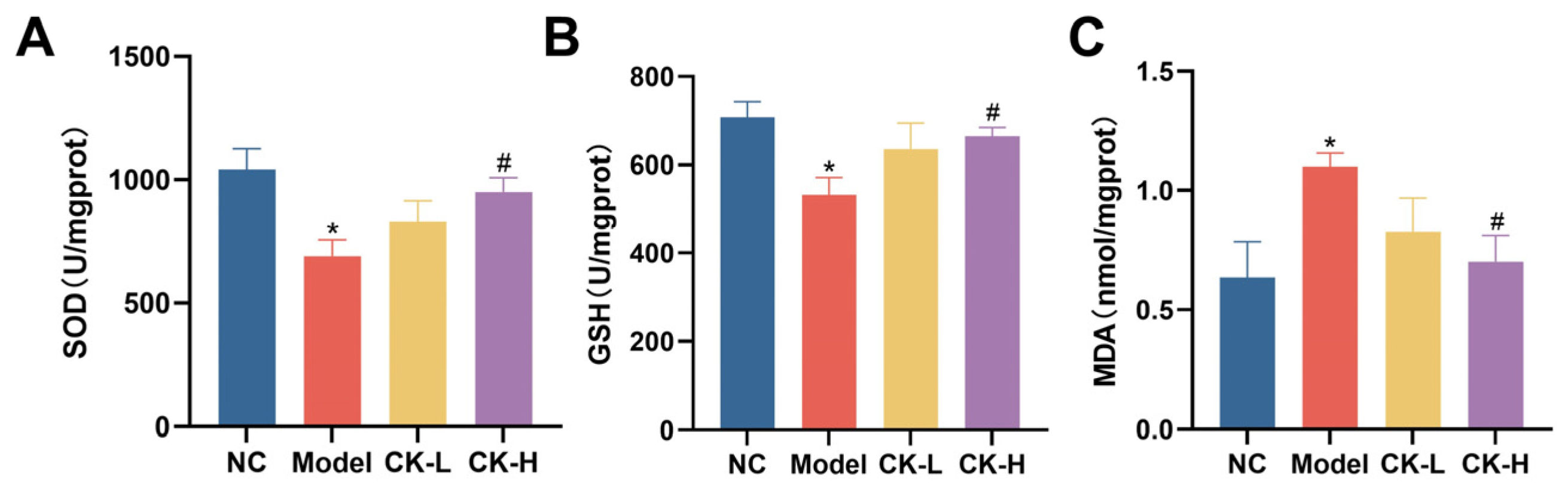
3.4. Effects of Ginsenoside CK on Oxidative Stress Caused by Con A
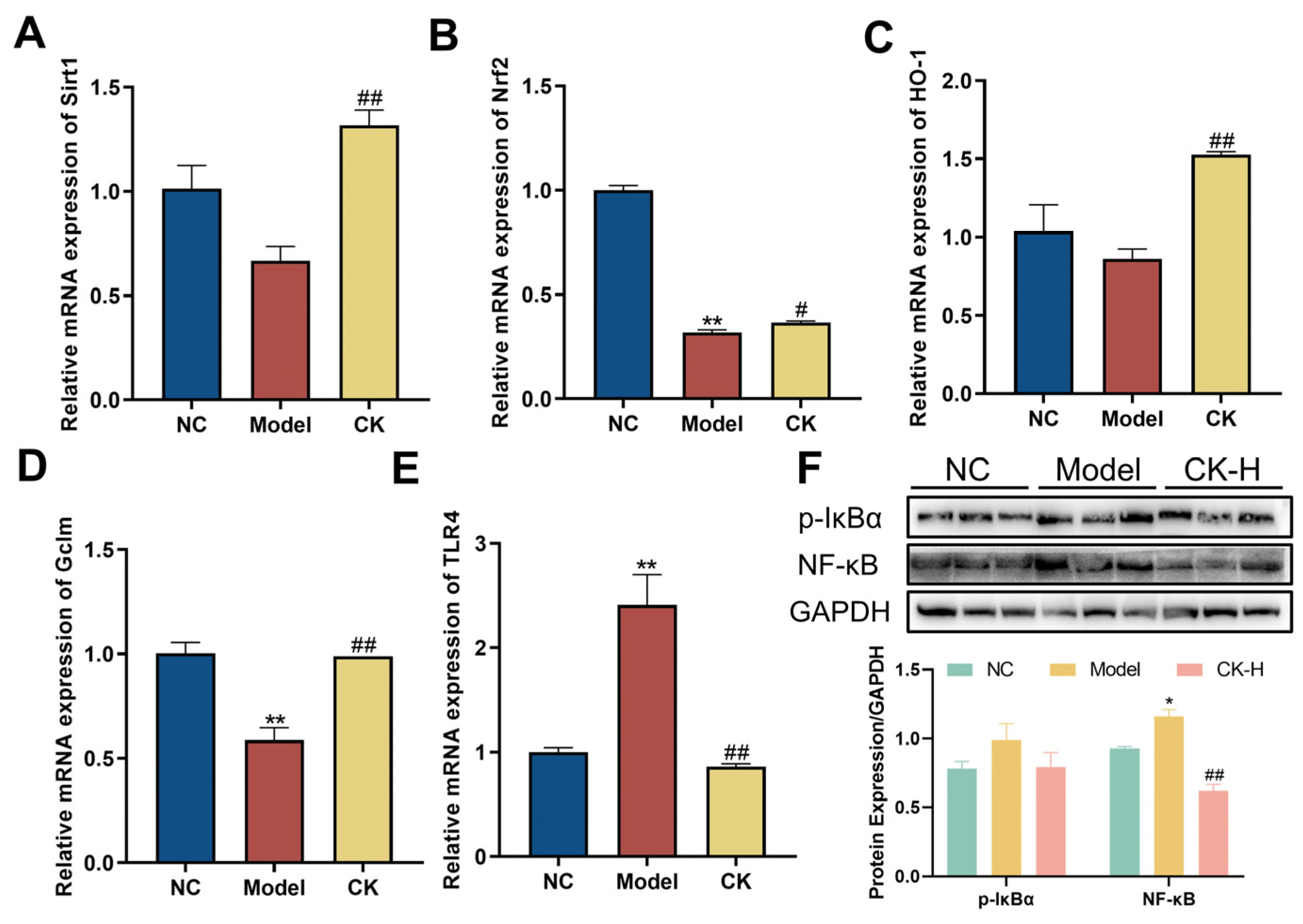
3.5. Effects of Ginsenoside CK on Sirt1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in the Liver
3.6. Ginsenoside CK Targeted TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Safeguard Hepatocytes from Damaged by Con A
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Remmer, H. The role of the liver in drug metabolism. Am. J. Med. 1970, 49, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Czaja, A.J.; Manns, M.P.; Krawitt, E.L.; Vierling, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Autoimmune hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, G.; Hirschfield, G.; Krawitt, E.; Gershwin, M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 247–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Sirwi, A.; Eid, B.G.; Mohamed, S.G.A.; Mohamed, G.A. Summary of Natural Products Ameliorate Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury: Structures, Sources, Pharmacological Effects, and Mechanisms of Action. Plants 2021, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Sun, W.; Xu, H. Pathogenesis of Concanavalin A induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cao, L.; Luo, Y.; Feng, X.; Sun, L.; Wen, M.; Peng, S. Paeoniflorin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 24, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Shanura Fernando, I.P.; Wang, L.; Abetunga, D.T.U.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, D.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Fucoidan isolated from Padina commersonii inhibit LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages blocking TLR/NF-kappaB signal pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Hong, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.-O.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y. Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, W.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, T. Pharmacological properties, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 975784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cheng, Y. Role of ginsenoside Rh2 in tumor therapy and tumor microenvironment immunomodulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113912. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Lyu, W.; Duan, C.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Li, D. Preparation and bioactivity of the rare ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2: An updated review. Fitoterapia 2023, 167, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lee, H.-J. Ginsenoside Compound K: Insights into Recent Studies on Pharmacokinetics and Health-Promoting Activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, L.; Zeng, X.; Liao, J.; Ouyang, D. Ginsenoside compound K alleviates sodium valproate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via antioxidant effect, regulation of peroxisome pathway and iron homeostasis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 386, 114829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.U.; Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Hepatoprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Lin, M.; Chen, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhang, F.; Gao, D.; Ma, X.; Lv, L.; et al. Salvianolic acid A preconditioning confers protection against concanavalin A-induced liver injury through SIRT1-mediated repression of p66shc in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 273, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, H.; Kang, X.; Tian, H.; Kang, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. A Synbiotic Ameliorates Con A-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis in Mice through Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune Imbalance. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 2200428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Qu, L.; Duan, Z.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rh4 inhibits breast cancer growth through targeting histone deacetylase 2 to regulate immune microenvironment and apoptosis. Bioorg Chem. 2023, 135, 106537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, R.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Liu, M.-M.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Ginsenoside CK induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer HeLa cells by regulating autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5301–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, R.; Duan, Z.; Shen, S.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside CK induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting glutamine metabolism. Biochem. Pharm. 2022, 202, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Xia, J.; Yang, X.; Men, S.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, Y. Ginsenoside CK improves skeletal muscle insulin resistance by activating DRP1/PINK1-mediated mitophagy. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, Q.; Diao, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wu, Y.; Bai, Y.; et al. The Potential Protective Effect of Iridoid Glycosides Isolated From Osmanthus fragrans Seeds Against the Development of Immune Liver Injury in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 760338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, S.; Sun, X. Glycyrrhizic acid ammonium salt alleviates Concanavalin A-induced immunological liver injury in mice through the regulation of the balance of immune cells and the inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; El-Agamy, D.S.; Elsaed, W.M.; Sirwi, A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Koshak, A.E.; Elhady, S.S. Cucurbitacin E glucoside alleviates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis through enhancing SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting NF-ĸB/NLRP3 signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 292, 115223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Autoimmmune hepatitis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Lu, X.; Han, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, C. Ginseng polysaccharide reduces autoimmune hepatitis inflammatory response by inhibiting PI3K/AKT and TLRs/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscate, F.; Woestemeier, A.; Gagliani, N. Functional heterogeneity of CD4+ T cells in liver inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Men, R.; Fan, X.; Wang, T.; Huang, C.; Wang, H.; Ye, T.; Luo, X.; Yang, L. Total glucosides of paeony decreases apoptosis of hepatocytes and inhibits maturation of dendritic cells in autoimmune hepatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Guan, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Nobiletin Protects against Acute Liver Injury via Targeting c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK)-Induced Apoptosis of Hepatocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7112–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, Y. Eugenol attenuates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis through modulation of cytokine levels and inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2019, 71, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Bu, H.; Wang, H.; Guo, H. Correlation of vitamin D with inflammatory factors, oxidative stress and T cell subsets in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, K.V.; Nguyen, L.T. The role of vitamin d in autoimmune hepatitis. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2013, 5, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4350965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajuwon, O.R.; Marnewick, J.L.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Davids, L.M. Red Palm Oil Ameliorates Oxidative Challenge and Inflammatory Responses Associated with Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatic Injury by Modulating NF-kappabeta and Nrf2/GCL/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, W.O.; Yates, M.S.; Dolan, P.D.; Chen, S.; Liby, K.T.; Sporn, M.B.; Taguchi, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Genetic or pharmacologic amplification of nrf2 signaling inhibits acute inflammatory liver injury in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 104, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Z.; Du, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Tian, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, W. Diosmetin alleviated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting oxidative stress via the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Chen, C.C.; Liu, H.M.; Lee, T.Y.; Shieh, S.H. Resveratrol Pretreatment Attenuates Concanavalin A-induced Hepatitis through Reverse of Aberration in the Immune Response and Regenerative Capacity in Aged Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agamy, D.S.; Shaaban, A.A.; Almaramhy, H.H.; Elkablawy, S.; Elkablawy, M.A. Pristimerin as a Novel Hepatoprotective Agent Against Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Li, P.; Zhao, H.; Li, X. Maresin 1 alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis by regulating NRF2 and TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside CK ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation via activating the LKB1/AMPK pathway in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; An, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, H.; Shao, J.; Xue, W. Protective Effect of Ginsenoside CK against Autoimmune Hepatitis Induced by Concanavalin A. Foods 2023, 12, 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244379
Zhang J, Liu Y, An C, Liu C, Ma S, Zhang Q, Ding H, Shao J, Xue W. Protective Effect of Ginsenoside CK against Autoimmune Hepatitis Induced by Concanavalin A. Foods. 2023; 12(24):4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244379
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingjing, Yao Liu, Chao An, Chen Liu, Saijian Ma, Qiwen Zhang, Hao Ding, Jingjing Shao, and Wenjiao Xue. 2023. "Protective Effect of Ginsenoside CK against Autoimmune Hepatitis Induced by Concanavalin A" Foods 12, no. 24: 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244379
APA StyleZhang, J., Liu, Y., An, C., Liu, C., Ma, S., Zhang, Q., Ding, H., Shao, J., & Xue, W. (2023). Protective Effect of Ginsenoside CK against Autoimmune Hepatitis Induced by Concanavalin A. Foods, 12(24), 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244379





