Sensory-Guided Isolation, Identification, and Active Site Calculation of Novel Umami Peptides from Ethanol Precipitation Fractions of Fermented Grain Wine (Huangjiu)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
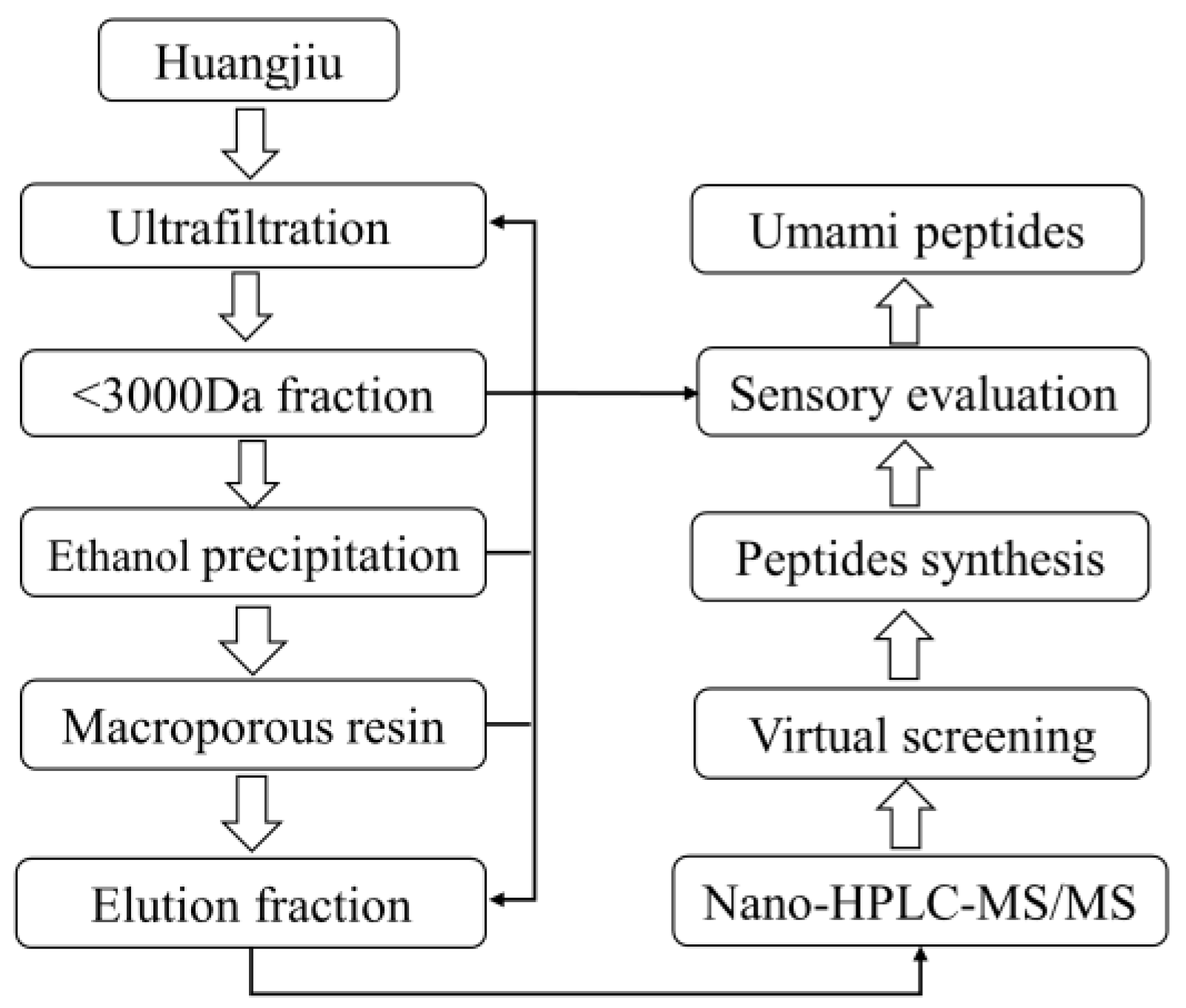
2.2. Separation of Huangjiu Umami Peptide Fractions
2.3. Identification of Peptides via Nano-HPLC-MS/MS
2.4. Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking
2.5. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Umami Peptides
2.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.6.1. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
2.6.2. Taste Thresholds of Synthetic Peptides
2.6.3. Umami Enhancement Effects of Synthetic Peptides
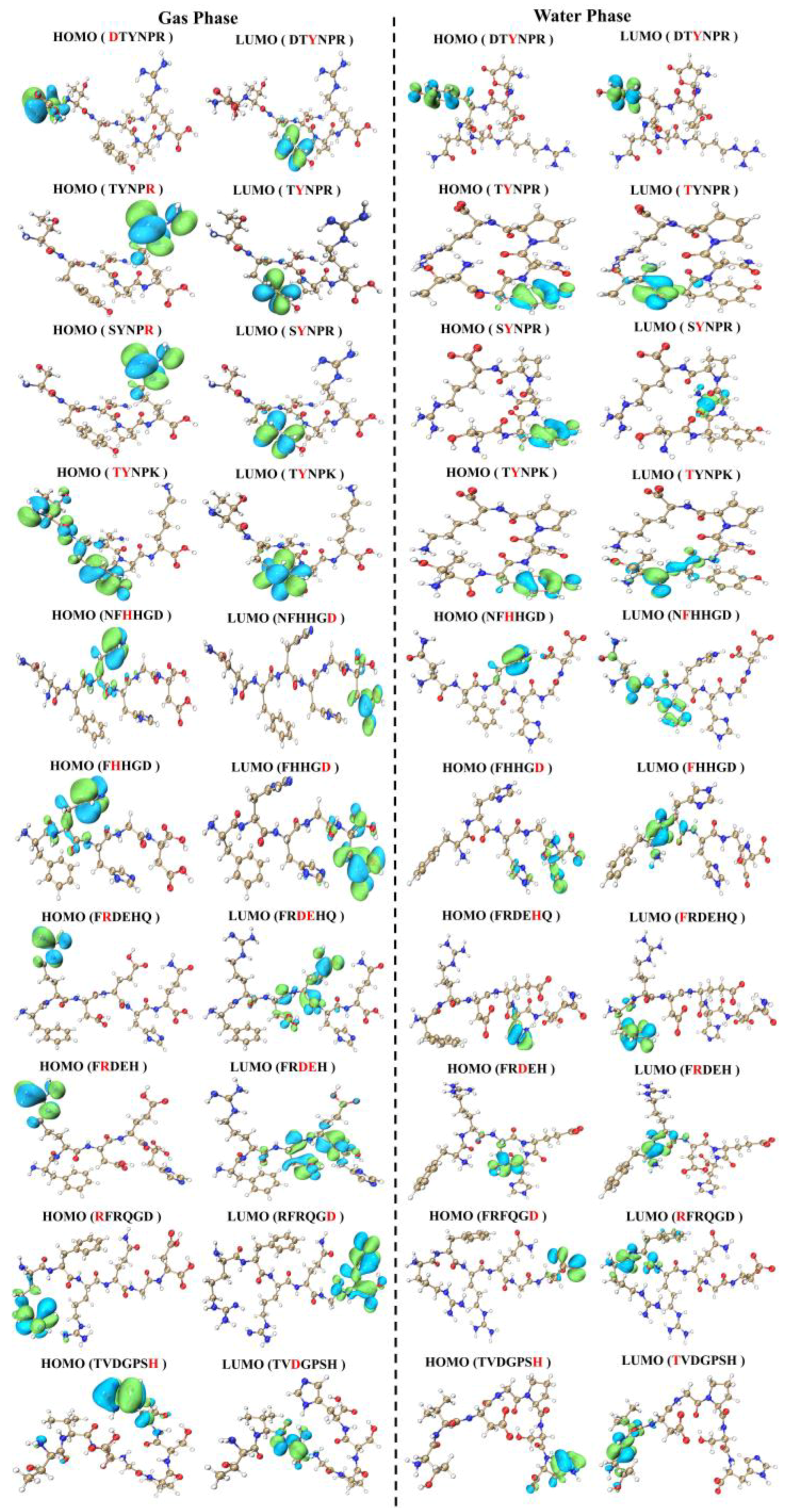
2.7. Theoretical Calculation of Active Sites
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensory-Guided Separation of Huangjiu Peptides
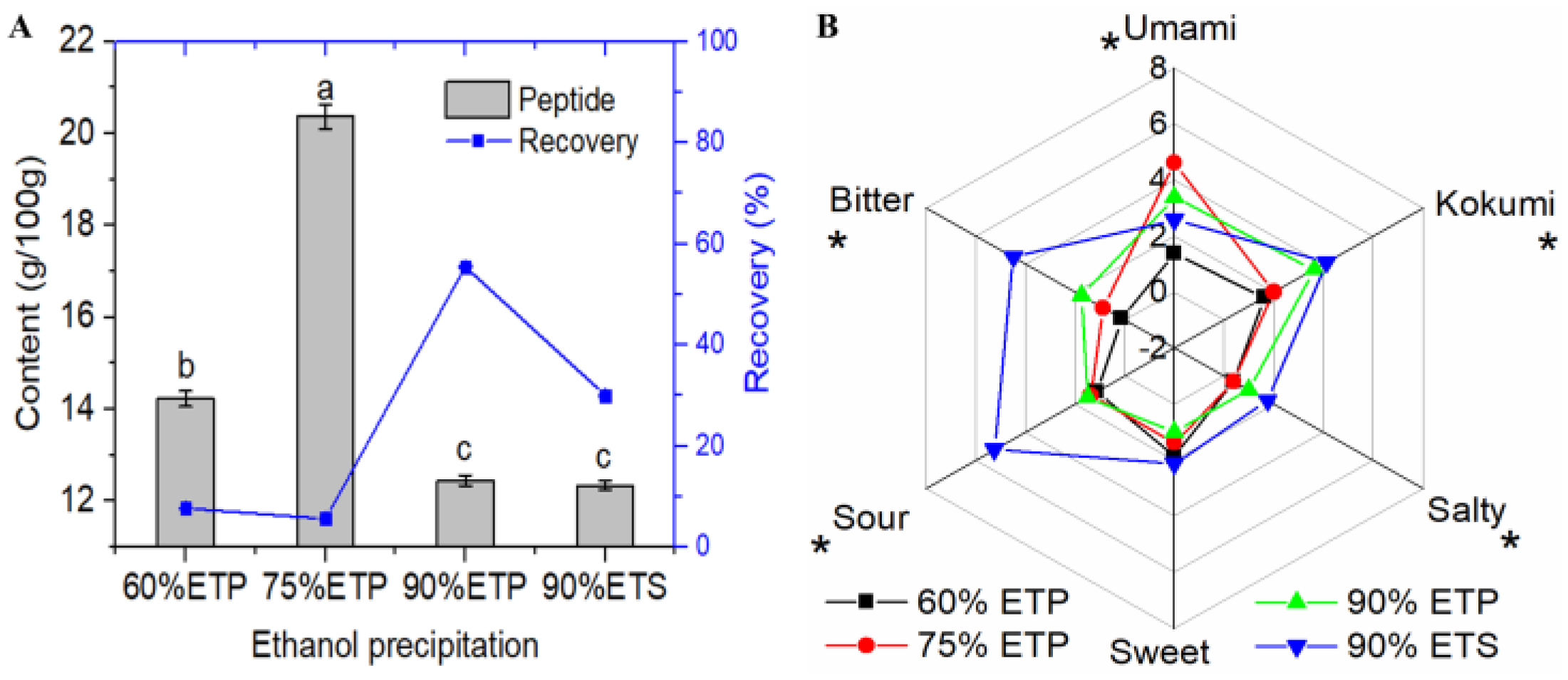
3.1.1. Ultrafiltration and Ethanol Precipitation Fractions
3.1.2. Macroporous Resin Separation Fractions
3.2. Virtual Screening of Umami Peptides
3.3. Synthetic Peptide Umami Characteristics and Composition Analysis
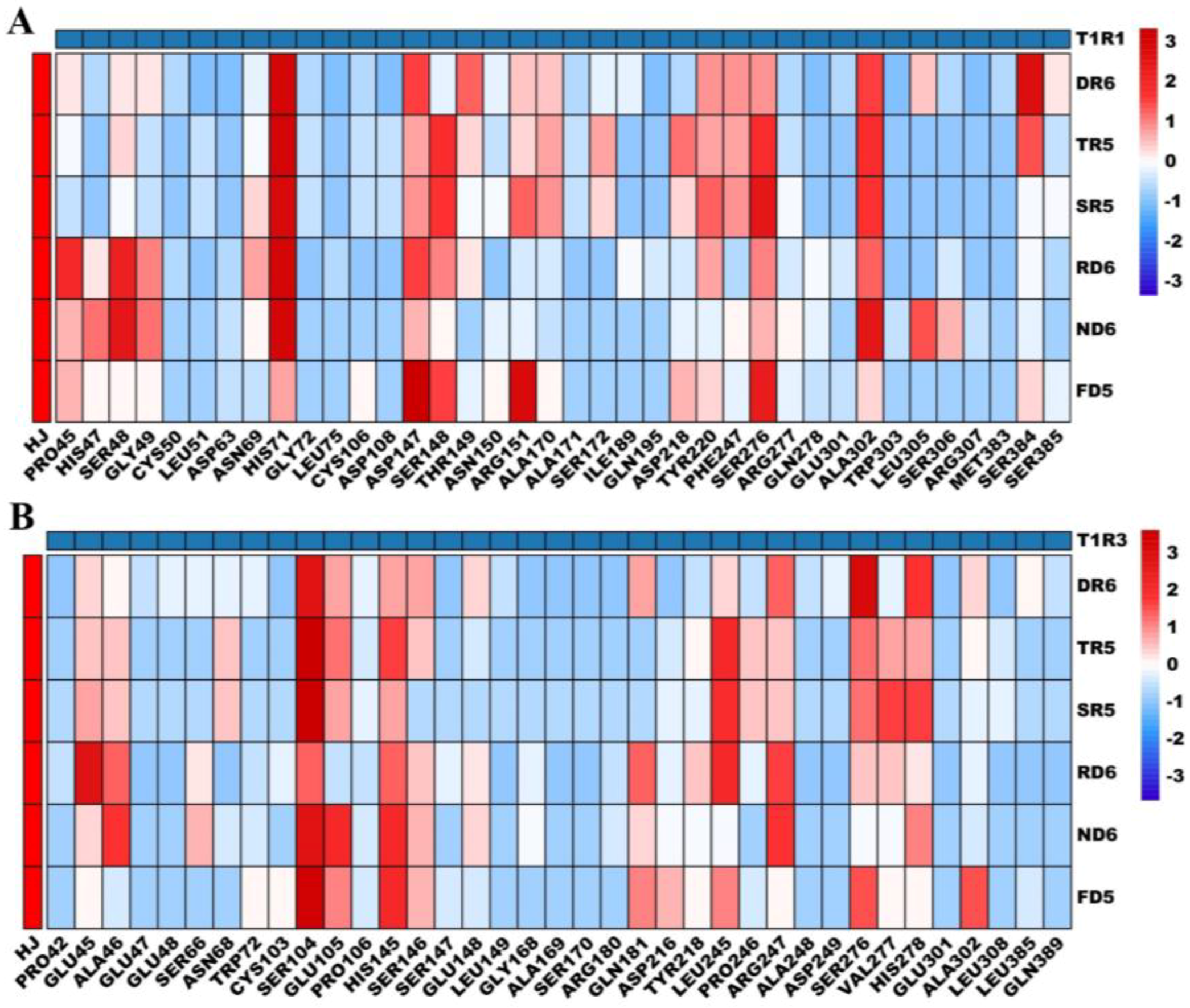
3.4. Molecular Docking Interactions of Peptides with T1R1-T1R3
3.4.1. Molecular Docking Interactions of Peptides with T1R1
3.4.2. Molecular Docking Interactions of Peptides with T1R3
3.5. Theoretical Calculation of Umami Peptides’ Active Sites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurihara, K. Glutamate: From discovery as a food flavor to role as a basic taste (umami). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 719S–722S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, M. Six categories of amino acid derivatives with potential taste contributions: A review of studies on soy sauce. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Maekawa, K. A peptide with delicious taste. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. A TastePeptides-Meta system including an umami/bitter classification model Umami_YYDS, a TastePeptidesDB database and an open-source package Auto_Taste_ML. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Bu, T.; Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Wu, J. Peptides in brewed wines: Formation, structure, and function. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, R.; Mao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, Z.; Chen, S.; Mao, J. Structural characterization of peptides from huangjiu and their regulation of hepatic steatosis and gut microbiota dysbiosis in hyperlipidemia mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.V.; Olsen, K.; Mouritsen, O.G. Umami potential of fermented beverages: Sake, wine, champagne, and beer. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 128971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosse, P. Umami in wine. Res. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 2, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Watanabe, U.; Fujimoto, M.; Sako, N. Taste preference and nerve response to 5′-inosine monophosphate are enhanced by glutathione in mice. Chem. Senses 2009, 34, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Kan, J. Isolation and identification of flavor peptides from douchi (traditional Chinese soybean food). Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1982–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhao, M.; Lin, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, H.; Feng, M.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Su, G. Macroporous resin purification of peptides with umami taste from soy sauce. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.H.; Liu, T.T.; Wan, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xia, N.; Wang, Q.Z.; Chen, D.W. Enrichment of the umami-taste-active amino acids and peptides from crab sauce using ethanol precipitation and anion-exchange resin. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15390. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. Identification and virtual screening of novel umami peptides from chicken soup by molecular docking. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134414. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Xiang, H. Taste mechanism of umami peptides from Chinese traditional fermented fish (Chouguiyu) based on molecular docking using umami receptor T1R1/T1R3. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Toldrá, F.; Zhang, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, Z. Study on the effects and mechanisms of ultrasound on the peptide profile and taste of unsmoked bacon using peptidomics and bioinformatics. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135764. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Chi, H.; Ma, S.; Zhao, L.; Cai, S. Identification of novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides in rice wine and their antioxidant activities using in silico and in vitro analyses. LWT 2023, 178, 114629. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Gao, X.; Pan, D.; Sun, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Dang, Y. Research progress in the screening and evaluation of umami peptides. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1462–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Hua, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, Y.; Pan, D.; Liu, Z.; Dang, Y. Umami peptides screened based on peptidomics and virtual screening from Ruditapes philippinarum and Mactra veneriformis clams. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133504. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono, T.; Hirooka, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kuniishi, S.; Ohtsuka, M.; Kimura, S.; Park, E.Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, K. Identification of pyroglutamyl peptides in Japanese rice wine (sake): Presence of hepatoprotective pyroGlu-Leu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11660–11667. [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume, K.; Ito, T.; Nagae, Y.; Tokiwano, T. Quantitation and sensory properties of three newly identified pyroglutamyl oligopeptides in sake. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, F.L.; Xu, Y. Identification of low molecular weight peptides in Chinese rice wine (Huang Jiu) by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 238–250. [Google Scholar]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: Current opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenkwan, P.; Nantasenamat, C.; Hasan, M.M.; Moni, M.A.; Manavalan, B.; Shoombuatong, W. UMPred-FRL: A new approach for accurate prediction of umami peptides using feature representation learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Da, L.-T.; Liu, Y. Understanding the molecular mechanism of umami recognition by T1R1-T1R3 using molecular dynamics simulations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 967–973. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Seven novel umami peptides from Takifugu rubripes and their taste characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127204. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Miao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, Z.; Dong, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, L. Umami polypeptide detection system targeting the human T1R1 receptor and its taste-presenting mechanism. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Chen, J.; Cui, C.; Wang, W. Comparative study on the novel umami-active peptides of the whole soybeans and the defatted soybeans fermented soy sauce. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Chen, J.; Cui, C.; Wang, W. Bitter-tasting hydrophobic peptides prepared from soy sauce using aqueous ethanol solutions influence taste sensation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 146–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liao, S.; Bi, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Ding, W.; Che, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lin, H. Isolation, identification and characterization of taste peptides from fermented broad bean paste. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 8730–8740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zong, X.; Cui, C.; Mu, L.; Zhao, H. Wheat gluten hydrolysates separated by macroporous resins enhance the stress tolerance in brewer’s yeast. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhyu, M.-R.; Kim, E.-Y. Umami taste characteristics of water extract of Doenjang, a Korean soybean paste: Low-molecular acidic peptides may be a possible clue to the taste. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Gao, P.; Lei, L.; Liang, H.; Zhang, S.; Dong, L. Modification of a Novel Umami Octapeptide with Trypsin Hydrolysis Sites via Homology Modeling and Molecular Docking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5326–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, B. Inhibitory effects of oat peptides on lipolysis: A physicochemical perspective. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Hao, L.; Cao, J.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Molecular docking and simulation of the synergistic effect between umami peptides, monosodium glutamate and taste receptor T1R1/T1R3. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Guo, R.; Yang, B.; You, G.; Zhao, M.; Liu, X. Taste, umami-enhance effect and amino acid sequence of peptides separated from silkworm pupa hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Su, G. Two-stage selective enzymatic hydrolysis generates protein hydrolysates rich in Asn-Pro and Ala-His for enhancing taste attributes of soy sauce. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gao, X.; Pan, D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Dang, Y. Taste characteristics and umami mechanism of novel umami peptides and umami-enhancing peptides isolated from the hydrolysates of Sanhuang Chicken. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, S.; Nagata, K. Isolation and characterization of acidic peptides in soy sauce. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1974, 38, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yi, S.; Zhu, W.; Mi, H.; Li, T.; Li, J. Identification, taste characteristics and molecular docking study of novel umami peptides derived from the aqueous extract of the clam Meretrix meretrix Linnaeus. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Son, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Misaka, T.; Rhyu, M.-R. Umami–bitter interactions: The suppression of bitterness by umami peptides via human bitter taste receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Dai, B.; Ayed, C.; Liu, Y. Comparing the metabolic profiles of raw and cooked pufferfish (Takifugu flavidus) meat by NMR assessment. Food Chem. 2019, 290, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Hu, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Screening of characteristic umami substances in preserved egg yolk based on the electronic tongue and UHPLC-MS/MS. LWT 2021, 152, 112396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cui, Z.; Ning, M.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y. In-silico investigation of umami peptides with receptor T1R1/T1R3 for the discovering potential targets: A combined modeling approach. Biomaterials 2022, 281, 121338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Ning, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. A rational tool for the umami evaluation of peptides based on multi-techniques. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pu, D.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. Identification of novel umami peptides in chicken breast soup through a sensory-guided approach and molecular docking to the T1R1/T1R3 taste receptor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7803–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of umami peptides identified from porcine bone soup and molecular docking to the taste receptor T1R1/T1R3. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, G.; Zhao, T.; Fan, J.; Ho, C.-T.; Zhao, M. Preparation, Sensory Characterization, and Umami-Enhancing Mechanism of Novel Peptide Glycoconjugates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8043–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Chattaraj, P.K. Conceptual density functional theory based electronic structure principles. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 6264–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, M.; Zhao, H.; Lv, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhang, B. A novel insight into screening for antioxidant peptides from hazelnut protein: Based on the properties of amino acid residues. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Miao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. The structure features of umami hexapeptides for the T1R1/T1R3 receptor. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

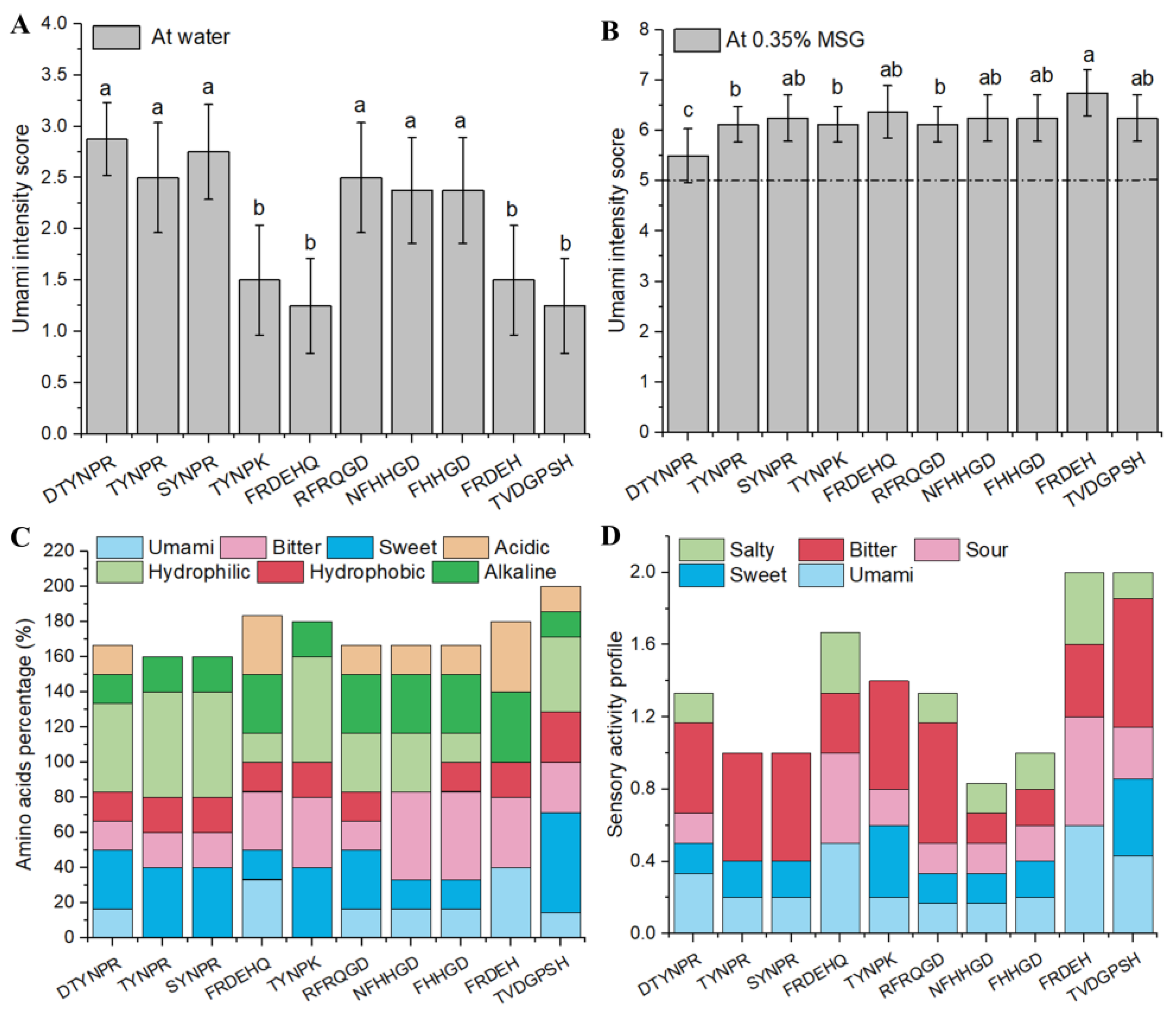
| Peptide | Sensory Description | Umami Threshold (mol/L) | Protein | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| in Water in MSG | Accession | |||
| DTYNPR | umami, slightly sweet, sour | 1.63 ± 0.60 b | 0.81 ± 0.28 a | P07728 |
| TYNPR | umami, slightly bitter | 2.11 ± 0.80 ab | 0.63 ± 0.18 b | P14614 |
| SYNPR | umami, slightly bitter | 2.36 ± 0.84 ab | 0.64 ± 0.19 ab | Q02897 |
| FRDEHQ | weakly umami, sour | 3.02 ± 0.56 a | 0.65 ± 0.19 ab | P14614 |
| TYNPK | weakly umami, slightly bitter | 2.41 ± 1.11 ab | 0.53 ± 0.13 b | A0A3B6AZR2 |
| RFRQGD | umami, sour | 2.41 ± 0.45 ab | 0.53 ± 0.16 b | P07728 |
| NFHHGD | umami, weakly sour | 2.75 ± 1.28 a | 0.52 ± 0.17 b | P00925 |
| FHHGD | umami, weakly sour | 2.86 ± 0.75 a | 0.61 ± 0.20 ab | P00925 |
| FRDEH | weakly umami, sour | 3.02 ± 1.18 a | 0.44 ± 0.15 b | P14614 |
| TVDGPSH | weakly umami, weakly sour | 3.16 ± 0.99 a | 0.61 ± 0.16 ab | P00360 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Liu, S.; Mao, J. Sensory-Guided Isolation, Identification, and Active Site Calculation of Novel Umami Peptides from Ethanol Precipitation Fractions of Fermented Grain Wine (Huangjiu). Foods 2023, 12, 3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183398
Chang R, Zhou Z, Dong Y, Xu Y, Ji Z, Liu S, Mao J. Sensory-Guided Isolation, Identification, and Active Site Calculation of Novel Umami Peptides from Ethanol Precipitation Fractions of Fermented Grain Wine (Huangjiu). Foods. 2023; 12(18):3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183398
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Rui, Zhilei Zhou, Yong Dong, Yuezheng Xu, Zhongwei Ji, Shuangping Liu, and Jian Mao. 2023. "Sensory-Guided Isolation, Identification, and Active Site Calculation of Novel Umami Peptides from Ethanol Precipitation Fractions of Fermented Grain Wine (Huangjiu)" Foods 12, no. 18: 3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183398
APA StyleChang, R., Zhou, Z., Dong, Y., Xu, Y., Ji, Z., Liu, S., & Mao, J. (2023). Sensory-Guided Isolation, Identification, and Active Site Calculation of Novel Umami Peptides from Ethanol Precipitation Fractions of Fermented Grain Wine (Huangjiu). Foods, 12(18), 3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183398






