Agricultural Food System Transformation on China’s Food Security
Abstract
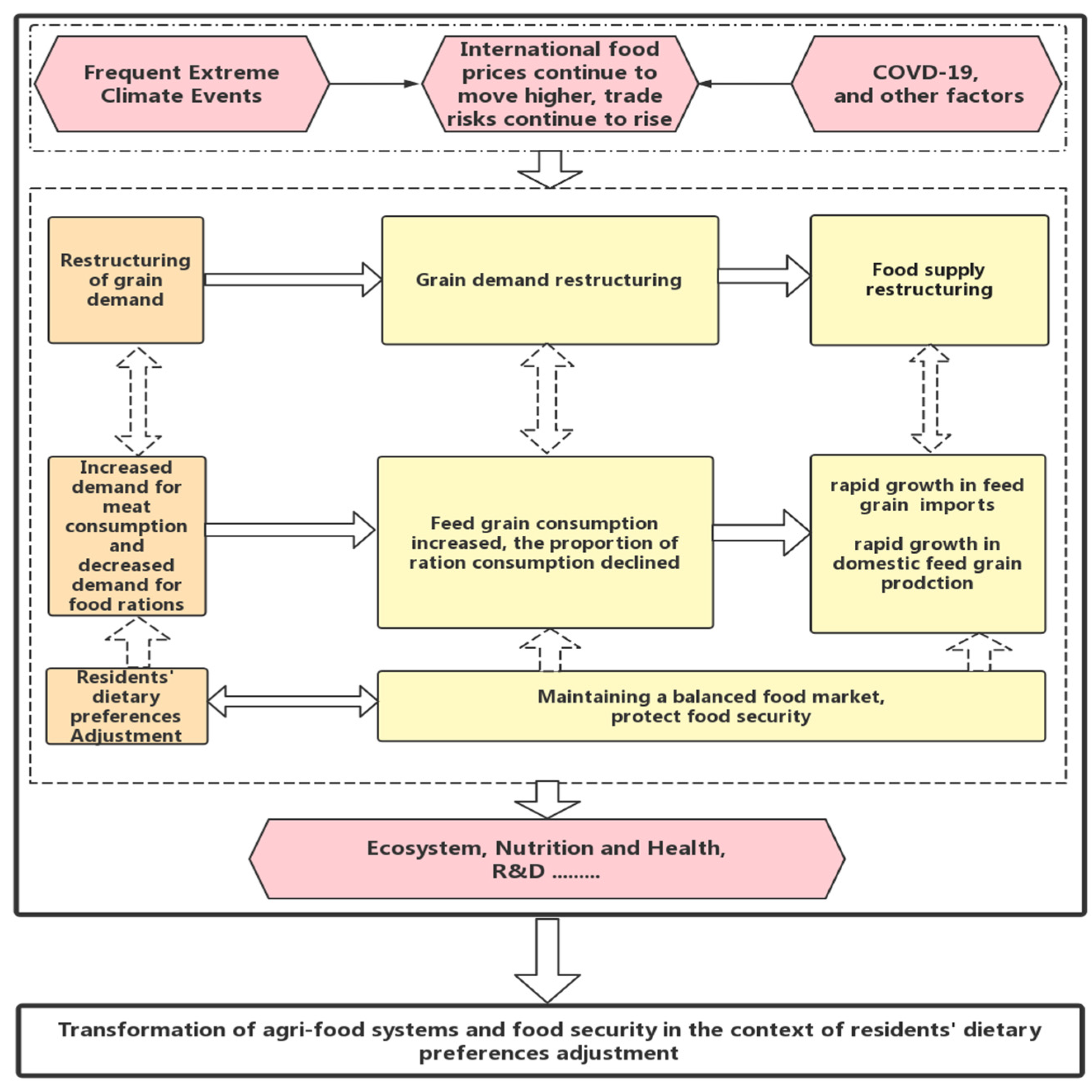
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Food Security Indicator System
3.2. Index Measurement Method
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
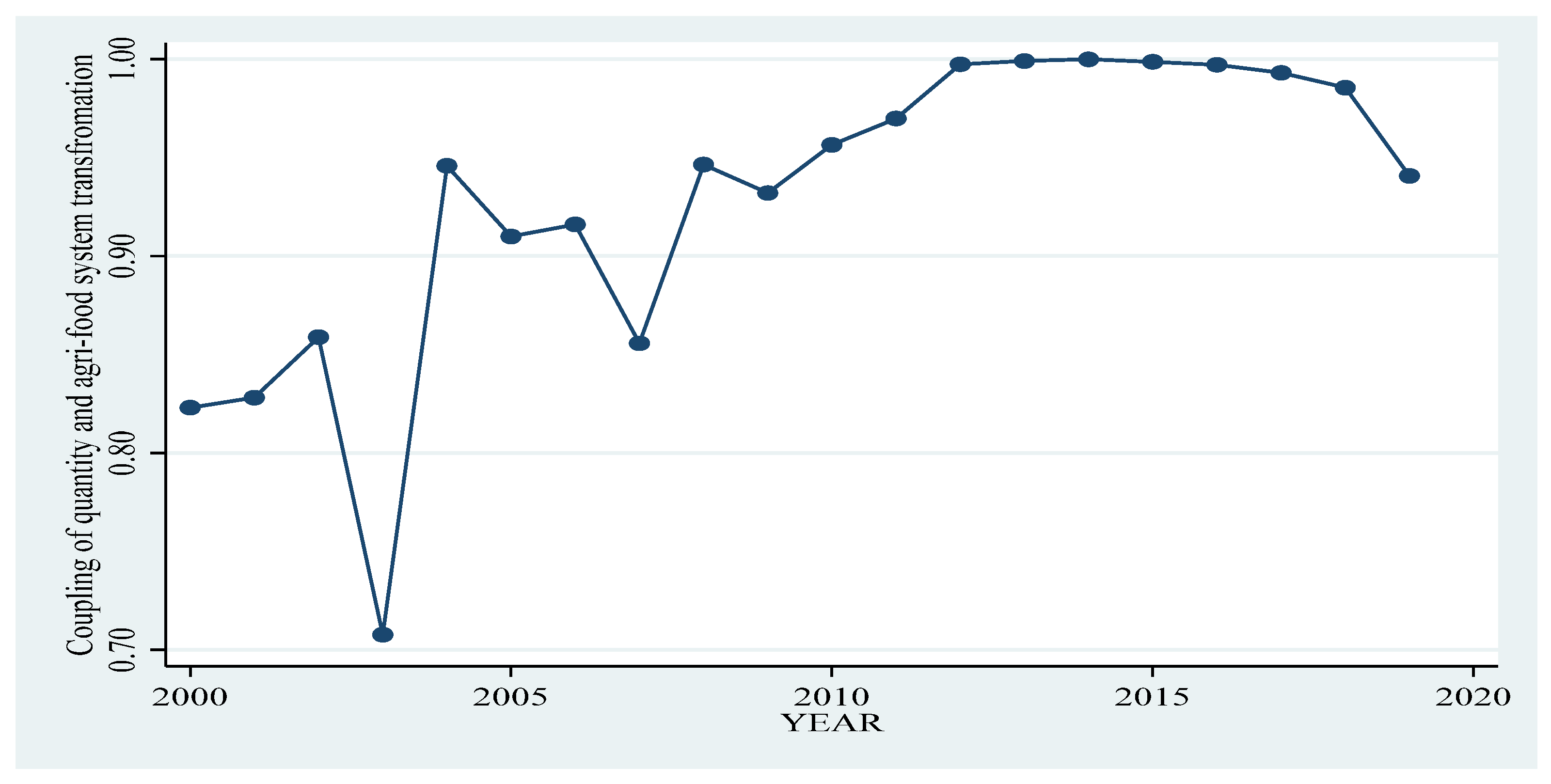
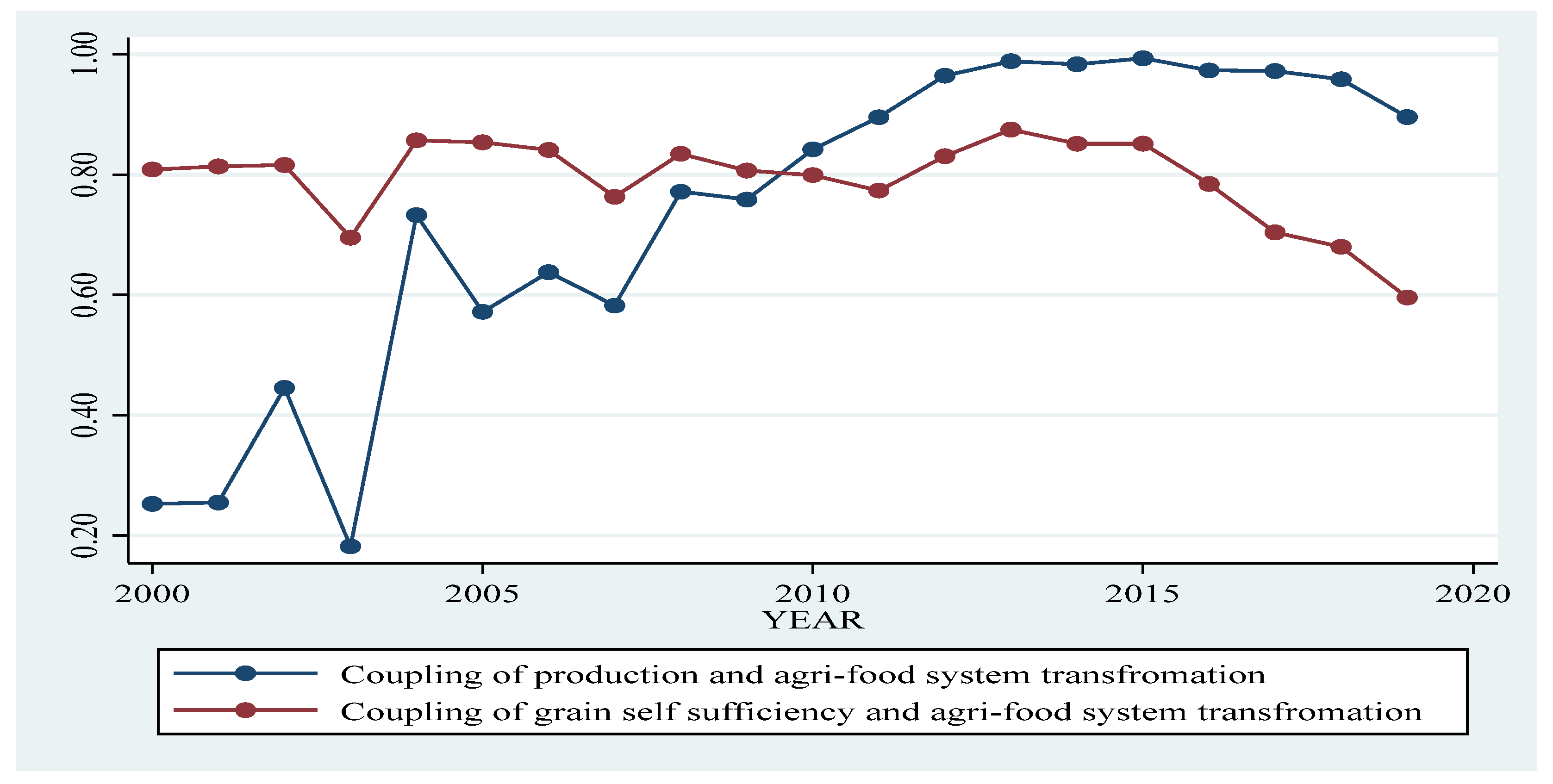
4.2. Food Security Index Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, S.; Headey, D.; Rue, C.; Thomas, T. Food systems for human and planetary health: Economic perspectives and challenges. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2021, 13, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S. Economics in food systems transformation. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidy, S. Biofuels Industry Tackles COVID-19, War Challenges. Available online: https://www.world-grain.com/articles/16799-biofuels-industry-tackles-covid-19-war-challenges (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022–2031; OECD Agriculture Statistics (Database): Paris, France, 2022; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/agriculture-and-food/data/oecd-agriculture-statistics_agr-data-en (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- OECD. “MeatConsumption” (Indicator). 2023. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/agriculture-and-food/meat-consumption/indicator/english_fa290fd0-en (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- FAOSTAT. “Meat Consumption” (Indicator). 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Maxwell, S. Food security: A post-modern perspective. Food Policy 1996, 21, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headey, D.; Ecker, O. Rethinking the measurement of food security: From first principles to best practice. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Build it back better: Deconstructing food security for improved measurement and action. Glob. Food Secur. 2013, 2, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.D.; Ngure, F.M.; Pelto, G.; Young, S.L. What are we assessing when we measure food security? A compendium and review of current metrics. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilan, Y.; Lyeonov, S.; Stoyanets, N.; Vysochyna, A. The impact of environmental determinants of sustainable agriculture on country food security. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2018, 21, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, A.S.; Abbas, A.; Padmaja, S.S.; Kaechele, H.; Ranjit, K.; Muller, K. Linking food security with household’s adaptive capacity and drought risk: Implications for sustainable rural development. Soc. Indic. Res. 2019, 142, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeana-Pizana, J.M.; Couturier, S.; Monsivais-Huertero, A. Assessing food security and environmental protection in Mexico with a GIS-based food environmental efficiency index. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venghaus, S.; Dieken, S. From a few security indices to the FEW Security Index: Consistency in global food, energy and water security assessment. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2019, 20, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.D.; Bassi, N.; Singh, O.P. Rethinking on the methodology for assessing global water and food challenges. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, M.; Hanganu, A.; Dumitriu, R.; Tociu, M.; Ivanov, G.; Stavarache, C.; Popescu, L.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Sturza, R.; Deleanu, C.; et al. Saponification value of fats and oils as determined from 1H-NMR data: The Case of Dairy Fats. Foods 2022, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanganu, A.; Chira, N.A. When detection of dairy food fraud fails: An alternative approach through proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8454–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezza, A.; Tasciotti, L. Urban agriculture, poverty, and food security: Empirical evidence from a sample of developing countries. Food Policy 2010, 35, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruane, J.; Sonnino, A. Agricultural biotechnologies in developing countries and their possible contribution to food security. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 156, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broeck, G.; Maertens, M. Horticultural exports and food security in developing countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2016, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Cline, S.A. Global food security: Challenges and policies. Science 2003, 302, 1917–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, L.J.; Hubbard, C. Food security in the United Kingdom: External supply risks. Food Policy 2013, 43, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, C.; Hubbard, L. External supply risks in the context of food security: An index borrowed from the energy security literature. Eurochoices 2014, 13, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. Meat consumption in China and its impact on international food security: Status quo, trends, and policies. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2021: Transforming Food Systems for Food Security, Improved Nutrition and Affordable Healthy Diets for All; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Economist Intelligence Unit. Global Food Security iIndex 2012. Available online: https://www.eiu.com/public/topical_report.aspx?campaignid=FoodSecurity2012 (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Abete, I.; Romaguera, D.; Vieira, A.R.; de Munain, A.L.; Norat, T. Association between total, processed, red and white meat consumption and all-cause, CVD and IHD mortality: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray HC, J.; Aveyard, P.; Garnett, T.; Hall, J.W.; Key, T.J.; Lorimer, J.; Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Scarborough, P.; Springmann, M.; Jebb, S.A. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science 2018, 361, eaam5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Shoemaker, S.P. A look at food security in China. NPJ Sci. Food 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First-Level Indicators | Second-Level Indicators | No. | Third-Level Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity safety dimension | Grain production levels | 1 | Grain output per unit area |
| 2 | Grain per capita | ||
| Self-sufficiency in grain | 3 | Grain self-sufficiency rate | |
| 4 | Grain ration self-sufficiency rate | ||
| 5 | Level of grain reserves | ||
| Quality safety dimension | Quality level | 6 | Food sampling inspection qualified rate |
| 7 | Food loss ratio | ||
| 8 | Proportion of highly processed grain | ||
| Natural disaster dimension | Extent of disaster | 9 | Areas affected by floods |
| 10 | Drought-stricken areas | ||
| Disaster management | 11 | Flood relief rate | |
| 12 | Drought relief rate | ||
| 13 | Soil erosion control area | ||
| Factor input dimension | Development and utilization of water resources | 14 | Effective irrigated area |
| 15 | Reservoir capacity | ||
| Land investment | 16 | Proportion of grain sown area to total sown area | |
| Input of labor force | 17 | Labor force in primary industry | |
| Capital investment | 18 | Agricultural machinery power station | |
| 19 | Amount of fertilizer used | ||
| Energy consumption | 20 | Rural electricity consumption | |
| 21 | Number of rural hydropower stations | ||
| Agri-food system transformation | Adjustment of grain consumption structure | 22 | Proportion of grain ration |
| 23 | Proportion of feed grain | ||
| 24 | Ratio of meat consumption to food consumption | ||
| Meat consumption structure adjustment | 25 | Proportion of pork consumption | |
| 26 | Proportion of beef and mutton consumption | ||
| 27 | Proportion of poultry consumption | ||
| Adjustment of grain import structure | 28 | Grain ration import adjustment degree | |
| 29 | Share of grain imports | ||
| 30 | Market concentration of grain imports |
| (N = 20) | (N = 20) | (N = 20) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Min Max | Mean (Std) | w_j | |
| Grain output per unit area | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.436 (0.357) | 0.052 |
| Grain per capita | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.547 (0.358) | 0.034 |
| Grain self-sufficiency rate | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.520 (0.330) | 0.032 |
| Grain ration self-sufficiency rate | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.585 (0.244) | 0.014 |
| Level of grain reserves | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.552 (0.230) | 0.014 |
| Food sampling inspection qualified rate | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.738 (0.294) | 0.015 |
| Food loss ratio | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.300 (0.239) | 0.038 |
| Proportion of highly processed grain | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.471 (0.270) | 0.024 |
| Areas affected by floods | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.793 (0.235) | 0.009 |
| Drought-stricken areas | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.699 (0.273) | 0.014 |
| Flood relief rate | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.434 (0.304) | 0.034 |
| Drought relief rate | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.466 (0.299) | 0.031 |
| Soil erosion control area | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.424 (0.280) | 0.032 |
| Effective irrigated area | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.437 (0.365) | 0.053 |
| Reservoir capacity | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.507 (0.369) | 0.041 |
| Proportion of grain sown area to total sown area | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.675 (0.289) | 0.016 |
| Labor force in primary industry | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.502 (0.355) | 0.038 |
| Agricultural machinery power station | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.542 (0.330) | 0.030 |
| Amount of fertilizer used | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.593 (0.342) | 0.028 |
| Rural electricity consumption | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.555 (0.354) | 0.033 |
| Number of rural hydropower stations | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.580 (0.445) | 0.052 |
| Proportion of grain ration | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.322 (0.316) | 0.064 |
| Proportion of feed grain | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.531 (0.305) | 0.026 |
| Ratio of meat consumption to food consumption | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.515(0.253) | 0.019 |
| Proportion of pork consumption | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.182 (0.246) | 0.094 |
| Proportion of poultry consumption | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.757 (0.261) | 0.011 |
| Proportion of beef and mutton consumption | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.422 (0.263) | 0.028 |
| Grain ration import adjustment degree | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.400 (0.317) | 0.048 |
| Share of grain imports | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.542 (0.330) | 0.029 |
| Market concentration of grain imports | 0.000, 1.000 | 0.409 (0.305) | 0.043 |
| Year | Food Security Index | Score | % | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity Safety | Quality Safety | Natural Disaster | Factor Input | Agri-Food System Transformation | Quantity Safety | Quality Safety | Natural Disasters | Factor Inputs | Agri-Food System Transformation | ||
| 2000 | 0.298 | 0.046 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.057 | 0.167 | 0.154 | 0.042 | 0.055 | 0.191 | 0.559 |
| 2001 | 0.272 | 0.041 | 0.007 | 0.022 | 0.058 | 0.144 | 0.149 | 0.025 | 0.081 | 0.214 | 0.531 |
| 2002 | 0.330 | 0.046 | 0.054 | 0.028 | 0.060 | 0.142 | 0.139 | 0.164 | 0.086 | 0.182 | 0.430 |
| 2003 | 0.287 | 0.027 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 0.055 | 0.158 | 0.095 | 0.088 | 0.076 | 0.191 | 0.550 |
| 2004 | 0.307 | 0.055 | 0.020 | 0.060 | 0.063 | 0.109 | 0.181 | 0.066 | 0.195 | 0.205 | 0.354 |
| 2005 | 0.312 | 0.050 | 0.022 | 0.050 | 0.070 | 0.120 | 0.159 | 0.070 | 0.161 | 0.225 | 0.385 |
| 2006 | 0.351 | 0.059 | 0.032 | 0.037 | 0.085 | 0.137 | 0.167 | 0.092 | 0.106 | 0.243 | 0.391 |
| 2007 | 0.442 | 0.057 | 0.048 | 0.056 | 0.100 | 0.181 | 0.130 | 0.109 | 0.127 | 0.225 | 0.408 |
| 2008 | 0.461 | 0.074 | 0.031 | 0.053 | 0.159 | 0.144 | 0.160 | 0.068 | 0.115 | 0.344 | 0.313 |
| 2009 | 0.494 | 0.066 | 0.034 | 0.081 | 0.171 | 0.141 | 0.134 | 0.069 | 0.164 | 0.346 | 0.286 |
| 2010 | 0.475 | 0.070 | 0.034 | 0.062 | 0.182 | 0.127 | 0.147 | 0.071 | 0.131 | 0.383 | 0.268 |
| 2011 | 0.527 | 0.080 | 0.031 | 0.093 | 0.192 | 0.131 | 0.151 | 0.060 | 0.176 | 0.365 | 0.249 |
| 2012 | 0.526 | 0.090 | 0.044 | 0.076 | 0.213 | 0.104 | 0.171 | 0.083 | 0.145 | 0.404 | 0.197 |
| 2013 | 0.529 | 0.098 | 0.047 | 0.070 | 0.223 | 0.090 | 0.185 | 0.090 | 0.133 | 0.422 | 0.171 |
| 2014 | 0.537 | 0.100 | 0.037 | 0.068 | 0.231 | 0.100 | 0.187 | 0.069 | 0.127 | 0.431 | 0.186 |
| 2015 | 0.540 | 0.108 | 0.034 | 0.059 | 0.240 | 0.098 | 0.201 | 0.063 | 0.109 | 0.445 | 0.181 |
| 2016 | 0.564 | 0.104 | 0.033 | 0.066 | 0.240 | 0.121 | 0.185 | 0.058 | 0.116 | 0.426 | 0.215 |
| 2017 | 0.591 | 0.103 | 0.036 | 0.080 | 0.243 | 0.130 | 0.174 | 0.061 | 0.135 | 0.410 | 0.220 |
| 2018 | 0.608 | 0.101 | 0.046 | 0.083 | 0.236 | 0.142 | 0.166 | 0.075 | 0.137 | 0.387 | 0.234 |
| 2019 | 0.719 | 0.108 | 0.049 | 0.112 | 0.232 | 0.218 | 0.150 | 0.068 | 0.156 | 0.323 | 0.304 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Li, T.; Wang, G. Agricultural Food System Transformation on China’s Food Security. Foods 2023, 12, 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152906
Zhao S, Li T, Wang G. Agricultural Food System Transformation on China’s Food Security. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152906
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Sicheng, Tingyu Li, and Guogang Wang. 2023. "Agricultural Food System Transformation on China’s Food Security" Foods 12, no. 15: 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152906
APA StyleZhao, S., Li, T., & Wang, G. (2023). Agricultural Food System Transformation on China’s Food Security. Foods, 12(15), 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152906




