Effects of Roughage on the Lipid and Volatile-Organic-Compound Profiles of Donkey Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Management and Sample Collection
2.2. Lipid Analysis
2.3. HS–SPME–GC–MS Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
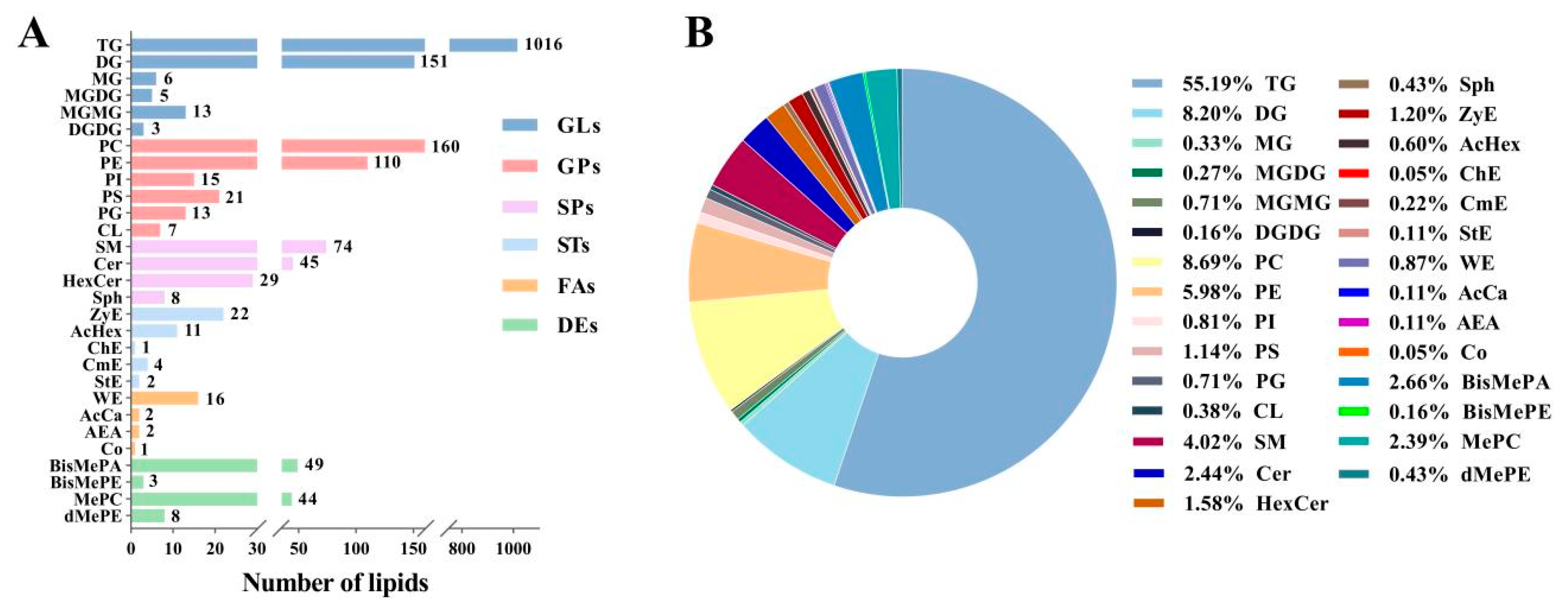
3.1. Lipid Profiles of Donkey Milk
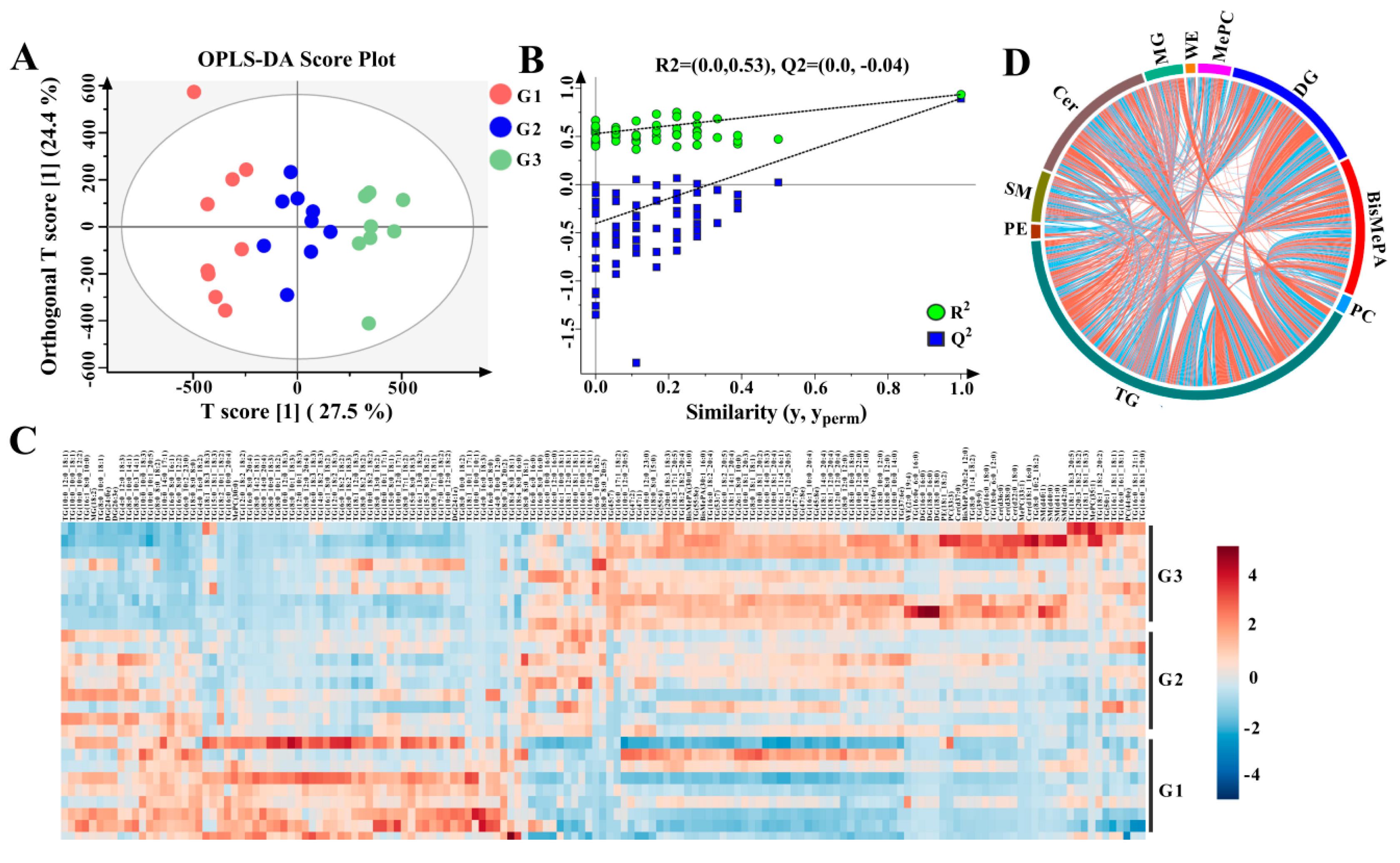
3.2. Differential Analysis of Lipids
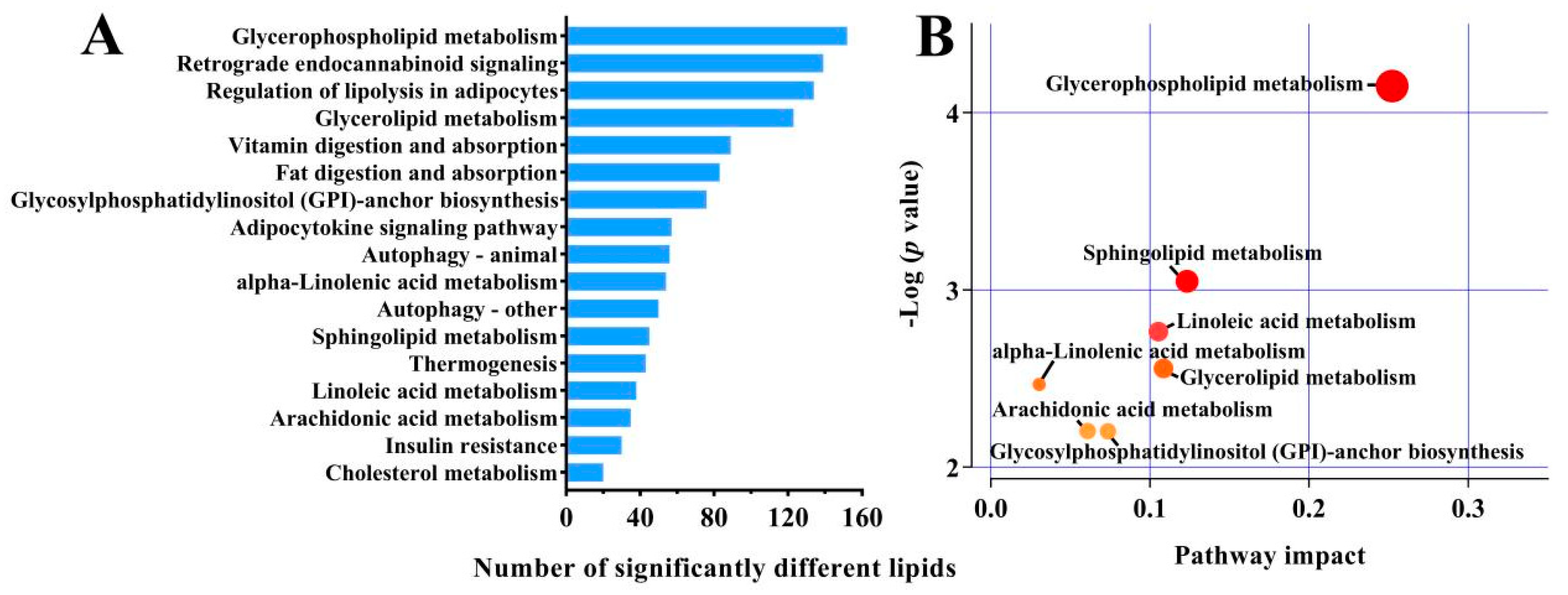
3.3. Lipid Metabolism Pathways
3.4. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of VOCs
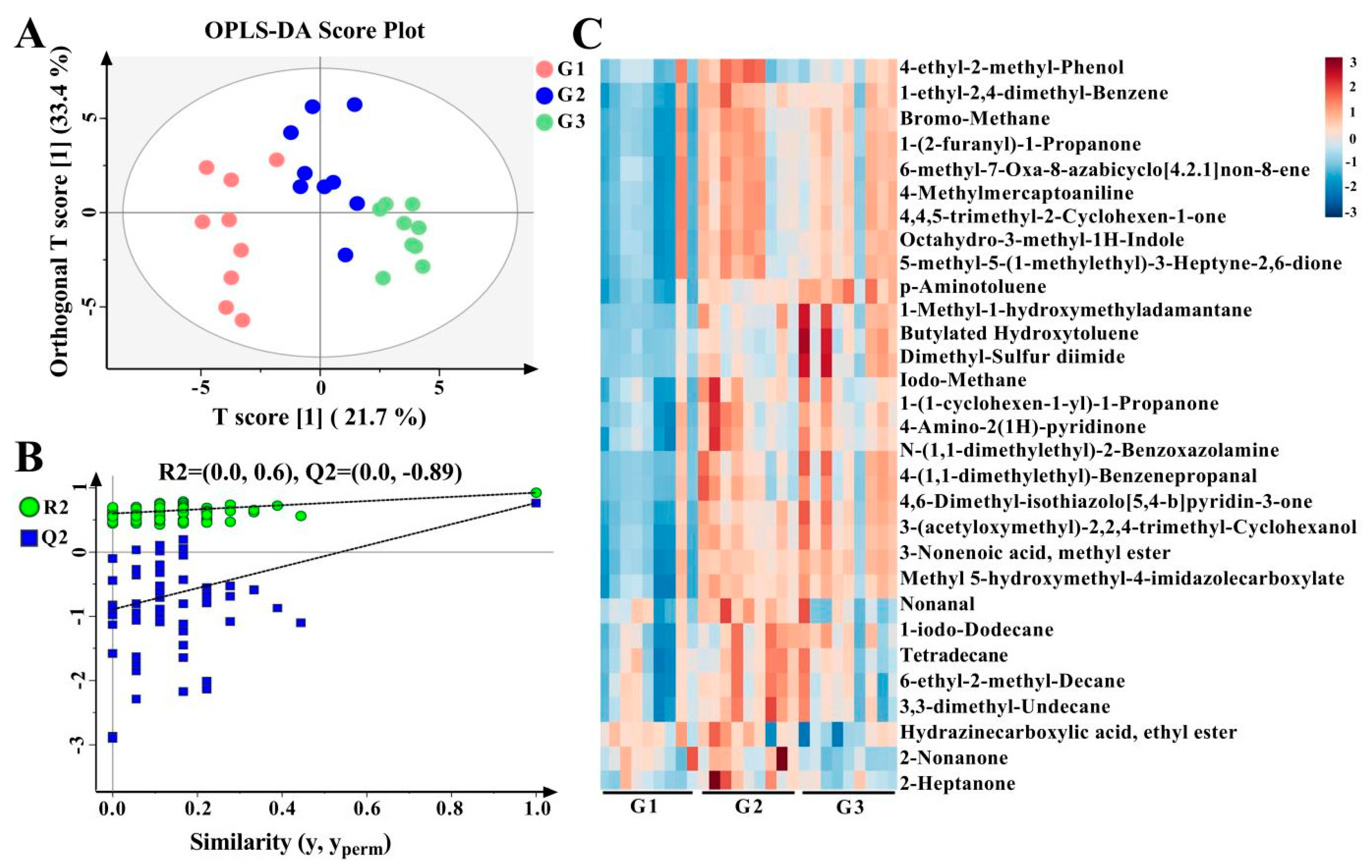
3.5. Differential VOCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magan, J.B.; O’ Callaghan, T.F.; Kelly, A.L.; Mccarthy, N.A. Compositional and functional properties of milk and dairy products derived from cows fed pasture or concentrate-based diets. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2769–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silanikove, N.; Leitner, G.; Merin, U. The interrelationships between lactose intolerance and the modern dairy industry: Global perspectives in evolutional and historical backgrounds. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7312–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspri, M.; Economou, N.; Papademas, P. Donkey milk: An overview on functionality, technology, and future prospects. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, H.F.; Visentin, S. Nutrients and neurodevelopment: Lipids. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2016, 114, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Trinchese, G.; Cavaliere, G.; De Filippo, C.; Aceto, S.; Prisco, M.; Chun, J.T.; Penna, E.; Negri, R.; Muredda, L.; Demurtas, A.; et al. Human milk and donkey milk, compared to cow milk, reduce inflammatory mediators and modulate glucose and lipid metabolism, acting on mitochondrial function and oleylethanolamide levels in rat skeletal muscle. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, W.F.; Duivenvoorden, I.; Voshol, P.J.; Rensen, P.C.N.; van Duyvenvoorde, W.; Romijn, J.A.; Emeis, J.J.; Havekes, L.M. Dietary sphingolipids lower plasma cholesterol and triacylglycerol and prevent liver steatosis. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küllenberg, D.; Taylor, L.A.; Schneider, M.; Massing, U. Health effects of dietary phospholipids. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Aida, K.; Duan, J.; Hirata, T. Analysis of glucosylceramides from various sources by liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Oleo Sci. 2010, 59, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, W.W. The Composition and Structure of Milk Lipids; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- George, A.D.; Gay, M.C.L.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T. The importance of infants’ lipid intake in human milk research. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores, G.; Virto, M. Total and free fatty acids analysis in milk and dairy fat. Separations 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldi, D.; Bertino, E.; Monti, G.; Baro, C.; Fabris, C.; Lezo, A.; Medana, C.; Baiocchi, C.; Mussap, M.; Galvano, F.; et al. Donkey’s milk detailed lipid composition. Front. Biosci.-Elite 2010, 2, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, Q.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, X.; Yang, M. Quantitative lipidomics reveals alterations in donkey milk lipids according to lactation. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Recent progress in food flavor analysis using gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry (GC–IMS). Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, R.; Bosset, J.O. Relationships between micro-organisms and formation of aroma compounds in fermented dairy products. Z. Lebensm.-Unters. Forsch. 1994, 198, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, U.; Berger, R.G. Biotechnological production of flavours and fragrances. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 1998, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Cecchi, T.; Perinelli, D.R.; Pucciarelli, S.; Polzonetti, V.; Bonacucina, G.; Ariani, A.; Parrocchia, L.; Spera, D.M.; Ferretti, E.; et al. Effects of freeze-drying and spray-drying on donkey milk volatile compounds and whey proteins stability. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 88, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurka, V.; Rankin, S. The effect of feedstuff on milk flavor. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, M.; Kasavi, C.; Toksoy Öner, E. Developments in effective use of volatile organic compound analysis to assess flavour formation during cheese ripening. J. Dairy Res. 2021, 88, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.M.; Reigan, P.; Mayle-Combs, K.D.; Orlicky, D.J.; Mcmanaman, J.L. Determinants of adipophilin function in milk lipid formation and secretion. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, D.E.; Griinari, J.M. Nutritional regulation of milk fat synthesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2003, 23, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, J.G. Aroma compounds of fresh milk from new zealand cows fed different diets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, F.; Bell, N. Donkey nutrition and malnutrition. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2019, 35, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shingfield, K.J.; Salo-Väänänen, P.; Pahkala, E.; Toivonen, V.; Jaakkola, S.; Piironen, V.; Huhtanen, P. Effect of forage conservation method, concentrate level and propylene glycol on the fatty acid composition and vitamin content of cows’ milk. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Bu, D.P.; Wang, J.Q.; Khas-Erdene; Zhou, L.Y.; Loor, J.J. Duodenal infusion of α-linolenic acid affects fatty acid metabolism in the mammary gland of lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5821–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipe, W.F.; Ledford, R.A.; Peterson, R.D.; Scanlan, R.A.; Geerken, H.F.; Dougherty, R.W.; Morgan, M.E. Physiological mechanisms involved in transmitting flavors and odors to milk. II. Transmission of some flavor components of silage1. J. Dairy Sci. 1962, 45, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havemose, M.S.; Weisbjerg, M.R.; Bredie, W.L.P.; Poulsen, H.D.; Nielsen, J.H. Oxidative stability of milk influenced by fatty acids, antioxidants, and copper derived from feed. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierlita, D. Effects of diets containing hemp seeds or hemp cake on fatty acid composition and oxidative stability of sheep milk. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 48, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, S.; Mallia, S.; La Terra, S.; Melilli, C.; Licitra, G.; Acree, T.E.; Barbano, D.M.; Van Soest, P.J. Composition and aroma compounds of ragusano cheese: Native pasture and total mixed rations*. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picariello, G.; Sacchi, R.; Addeo, F. One-step characterization of triacylglycerols from animal fat by MALDI-TOF MS. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.; Korte, N.; Dyk, M.; Wenninger, O.; Schreiter, P.; Hiller, E. Rapid animal species identification of feta and mozzarella cheese using MALDI-TOF mass-spectrometry. Food Control 2020, 117, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Rochfort, S.; Cocks, B. Milk lipidomics: What we know and what we don’t. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 71, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ren, W.; Chai, W.; Zhu, M.; Man, L.; Zhan, Y.; Qin, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. Comparing the profiles of raw and cooked donkey meat by metabonomics and lipidomics assessment. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 851761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, L.; Ren, W.; Qin, H.; Sun, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Characterization of the relationship between lipids and volatile compounds in donkey, bovine, and sheep meat by UHPLC–ESI–MS and SPME–GC–MS. LWT 2023, 175, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasilva, G.; Muñoz, S.; Lois, S.; Medina, I. Non-Targeted LC-MS/MS Assay for Screening Over 100 Lipid Mediators from ARA, EPA, and DHA in Biological Samples Based on Mass Spectral Fragmentations. Molecules 2019, 24, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, G. UPLC-ESI-MS/MS-Based widely targeted metabolomics analysis of wood metabolites in teak (Tectona grandis). Molecules 2020, 25, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contarini, G.; Pelizzola, V.; Scurati, S.; Povolo, M. Polar lipid of donkey milk fat: Phospholipid, ceramide and cholesterol composition. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 57, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniacke-Lowe, T.; Fox, P.F. Equid milk: Chemistry, biochemistry and processing. In Food Biochemistry and Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell Ams: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 491–530. [Google Scholar]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Santini, G.; Polzonetti, V.; Pucciarelli, S.; Klimanova, Y.; Polidori, P. Vitamins in human and donkey milk: Functional and nutritional role. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souroullas, K.; Aspri, M.; Papademas, P. Donkey milk as a supplement in infant formula: Benefits and technological challenges. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, L.; Cavaliere, G.; Bergamo, P.; Trinchese, G.; De Filippo, C.; Gifuni, G.; Gaita, M.; Pignalosa, A.; Donizzetti, I.; Putti, R.; et al. Diet supplementation with donkey milk upregulates liver mitochondrial uncoupling, reduces energy efficiency and improves antioxidant and antiinflammatory defences in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.A.; Sadaf, N.; Mohd, A.; Zulfiqarur, R.A.A.A. UPLC-MS: An emerging novel technology and its application in food safety. In Analytical Chemistry; Abhay, N.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; p. 92455. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Jiang, G.; Ji, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, F. Comparative lipidomics profiling of donkey milk with cow and human milk by UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 101, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Leng, Y.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, S. Comparative Lipidomic Analysis of Human, Bovine and Caprine milk. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J. Lipidomics analysis for identifying the geographical origin and lactation stage of goat milk. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiofalo, B.; Dugo, P.; Bonaccorsi, I.L.; Mondello, L. Comparison of major lipid components in human and donkey milk: New perspectives for a hypoallergenic diet in humans. Immunopharm. Immunot. 2011, 33, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugo, P.; Kumm, T.; Lo Presti, M.; Chiofalo, B.; Salimei, E.; Fazio, A.; Cotroneo, A.; Mondello, L. Determination of triacylglycerols in donkey milk by using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. Lipids in human milk. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 32, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarlińska, J.; Piaścik, M.; Sikorski, A.F.; Czogalla, A. Phosphatidic acid—A simple phospholipid with multiple faces. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, A.; Souchet, S.; Gelé, M.; Le Provost, F.; Boutinaud, M. Effect of feed restriction on dairy cow milk production: A review. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, b130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, B.M.; Da Silva, F.F.; Silva, R.R.; Costa, E.G.L.; Porto Junior, A.F.; Costa, E.N.; de Souza, D.D. Effect of different roughages sources on performance, milk composition, fatty acid profile, and milk cholesterol content of feedlot feed crossbred cows (Holstein × Zebu). Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suharoschi, R.; Pop, O.L.; Vlaic, R.A.; Muresan, C.I.; Muresan, C.C.; Cozma, A.; Sitar-Taut, A.V.; Vulturar, R.; Heghes, S.C.; Fodor, A.; et al. Dietary fiber and metabolism. In Dietary Fiber: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 59–77. [Google Scholar]
- Beyero, N.; Kapoor, V.; Tewatia, B.S. Effect of different Roughage: Concentrate Ratio on Milk Yield and its Fatty Acid Profile in Dairy Cows. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2015, 5, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Cazita, P.M.; Castilho, L.N.; Carvalho, M.D.; Sesso, A.C.; Oliveira, H.C.; Quintão, E.C. Reversible flow of cholesteryl ester between high-density lipoproteins and triacylglycerol-rich particles is modulated by the fatty acid composition and concentration of triacylglycerols. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, R.; Suzuki, K.; Cui, L.; Mcclements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Impact of association colloids on lipid oxidation in triacylglycerols and fatty acid ethyl esters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10161–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.P.; Drackley, J.K.; Weigel, D.J. Digestibility and effects of hydrogenated palm fatty acid distillate in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Manan, S.F.; Li, J.; Hsieh, C.; Faubion, J.; Shi, Y. Extraction of non-starch lipid from protease-treated wheat flour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumeistere, L.; Ciproviča, I.; Zavadska, D.; Andersons, J.; Volkovs, V.; Ceļmalniece, K. Impact of maternal diet on human milk composition among lactating women in latvia. Medicina 2019, 55, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobiński, R.; Mikulska, M.; Mojska, H.; Ulman-Włodarz, I.; Sodowska, P. Pregnant women’s diet composition and transitional milk fatty acids: Factor analysis. Ginekol. Pol. 2015, 86, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunick, M.H.; Iandola, S.K.; Van Hekken, D.L. Comparison of SPME methods for determining volatile compounds in milk, cheese, and whey powder. Foods 2013, 2, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Tong, L.; Chi, X.; Ai, N.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B. Comparison of sensory and electronic tongue analysis combined with HS-SPME-GC-MS in the evaluation of skim milk processed with different preheating treatments. Molecules 2019, 24, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tao, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Luan, D.; Ni, L.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Effect of four types of thermal processing methods on the aroma profiles of acidity regulator-treated tilapia muscles using E-nose, HS-SPME-GC-MS, and HS-GC-IMS. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Zachariadis, G.A. Determination of volatile compounds in Nut-Based milk alternative beverages by HS-SPME prior to GC-MS analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wei-Jun, D. Analysis on volatile compositions of donkey milk powder by simultaneous distillation extraction and solid phase micro extraction. J. Xinjiang Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 36, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Debong, M.W.; Loos, H.M. Diet-Induced flavor changes in human milk: Update and perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10275–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, H.; Bredie, W.L.P.; Mølgaard, C.; Petersen, M.A.; Møller, P. Differential transfer of dietary flavour compounds into human breast milk. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 95, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eknæs, M.; Skeie, S. Effect of different level of roughage availability and contrast levels of concentrate supplementation on flavour of goat milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2006, 66, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Marrazzo, A.; De Luca, L.; Romano, R.; Manzo, N.; Masucci, F.; Di Francia, A.; Sacchi, R. Volatile Organic Compound and Fatty Acid Profile of Milk from Cows and Buffaloes Fed Mycorrhizal or Nonmycorrhizal Ensiled Forage. Molecules 2019, 24, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppa, M.; Martin, B.; Pradel, P.; Leotta, B.; Priolo, A.; Vasta, V. Effect of a hay-based diet or different upland grazing systems on milk volatile compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4947–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcock, C.J. Feed flavors in milk and milk products. J. Dairy Sci. 1938, 21, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, E.; Ramos, M.; Polo, C.; Juárez, M.; Olano, A. Enzyme accelerated ripening of Spanish hard cheese. Food Chem. 1988, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | G1 | G2 | G3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients (%) | |||
| Corn | 15.50 | 15.50 | 15.50 |
| Soybean | 3.10 | 3.10 | 3.10 |
| Salt | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Premix 1 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| Corn straw | 80.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Wheat hulls | 0.00 | 80.00 | 0.00 |
| Wheat straw | 0.00 | 0.00 | 80.00 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Proximate composition (% dry matter) | |||
| Dry matter | 95.49 | 93.53 | 91.48 |
| Crude protein | 6.30 | 6.50 | 6.12 |
| Crude fat | 2.66 | 2.33 | 2.31 |
| Crude ash | 11.50 | 11.14 | 12.06 |
| Major fatty acids (% total fatty acid) | |||
| C16:0 | 18.26 | 20.96 | 19.90 |
| C18:0 | 3.27 | 3.47 | 5.39 |
| C18:1 | 24.03 | 23.95 | 26.68 |
| C18:2n-6 | 49.16 | 46.60 | 43.43 |
| C18:3n-6 | 4.46 | 4.18 | 4.28 |
| Lipid | Diet (%) | Donkey Milk (%) | SEM | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | |||
| TG | 68.10 | 68.21 | 66.17 | 96.06 a | 95.86 a | 94.34 b | 0.23 | 0.001 |
| DG | 3.13 | 3.58 | 3.27 | 1.83 | 2.02 | 1.83 | 0.05 | 0.184 |
| MG | 0.0445 | 0.0346 | 0.0366 | 0.0935 a | 0.0820 ab | 0.0631 b | 0.0052 | 0.047 |
| PC | 10.48 | 9.49 | 14.16 | 0.40 b | 0.38 b | 0.77 a | 0.05 | 0.001 |
| PE | 0.47 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.20 b | 0.19 b | 0.41 a | 0.03 | 0.003 |
| PS | 0.3331 | 0.3245 | 0.2632 | 0.0022 | 0.0012 | 0.0024 | 0.0004 | 0.409 |
| PG | 0.31 | 0.4849 | 0.2659 | 0.0072 b | 0.0088 b | 0.0163 a | 0.0012 | 0.001 |
| PI | 0.1685 | 0.1956 | 0.1232 | 0.0010 b | 0.0016 ab | 0.0019 a | 0.0001 | 0.013 |
| PA | 0.0262 | 0.0389 | 0.0234 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cer | 6.37 | 5.20 | 3.34 | 0.14 b | 0.26b | 0.47 a | 0.04 | 0.002 |
| HexCer | 3.518 | 1.9621 | 2.1496 | 0.0325 | 0.0255 | 0.0431 | 0.0033 | 0.079 |
| CL | 0.0324 | 0.0297 | 0.0195 | 0.0012 | 0.0004 | 0.0011 | 0.0003 | 0.49 |
| SM | 0.0368 | 0.0547 | 0.0761 | 0.3661 b | 0.3073 b | 0.7299 a | 0.06 | 0.001 |
| Sph | 0.0468 | 0.0466 | 0.0361 | 0.0079 | 0.0172 | 0.027 | 0.0036 | 0.094 |
| Co | 0.1827 | 0.1125 | 0.152 | 0.0008 ab | 0.0006 b | 0.0011 a | 0.0001 | 0.032 |
| WE | 0.1539 | 0.6102 | 0.5052 | 0.0754 | 0.1304 | 0.2161 | 0.0248 | 0.059 |
| AcHex | 4.8445 | 6.1485 | 7.2537 | 0.0327 a | 0.0230 b | 0.0339 a | 0.0019 | 0.027 |
| ZyE | 0.17 | 0.49 | 0.17 | 0.12 b | 0.15 a | 0.15 a | 0.00 | 0.003 |
| StE | 0.0346 | 0.1441 | 0.0383 | 0.0429 | 0.0376 | 0.0327 | 0.0028 | 0.534 |
| SiE | 0.0556 | 0.255 | 0.0776 | - | - | - | - | - |
| MePC | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.085 |
| BisMePA | 0.5683 | 0.6632 | 0.5937 | 0.0004 b | 0.0003 b | 0.0007 a | 0.0228 | 0.018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, W.; Sun, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of Roughage on the Lipid and Volatile-Organic-Compound Profiles of Donkey Milk. Foods 2023, 12, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112231
Ren W, Sun M, Shi X, Wang T, Wang Y, Wang X, Huang B, Kou X, Liang H, Chen Y, et al. Effects of Roughage on the Lipid and Volatile-Organic-Compound Profiles of Donkey Milk. Foods. 2023; 12(11):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112231
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Wei, Mengqi Sun, Xiaoyuan Shi, Tianqi Wang, Yonghui Wang, Xinrui Wang, Bingjian Huang, Xiyan Kou, Huili Liang, Yinghui Chen, and et al. 2023. "Effects of Roughage on the Lipid and Volatile-Organic-Compound Profiles of Donkey Milk" Foods 12, no. 11: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112231
APA StyleRen, W., Sun, M., Shi, X., Wang, T., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Huang, B., Kou, X., Liang, H., Chen, Y., Wang, C., & Li, M. (2023). Effects of Roughage on the Lipid and Volatile-Organic-Compound Profiles of Donkey Milk. Foods, 12(11), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112231






