The Protein Composition Changed the Quality Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogues Produced by a Single-Screw Extruder: Four Main Soybean Varieties in China as Representatives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Soybean Varieties and Preparation of Defatted Soybean Flour (DSF)
2.2. Analysis of Soybean Protein Composition by SDS-PAGE
2.3. The Structure of PBMs
2.3.1. The Basic Composition of Four Kinds of PBMs
2.3.2. The Sulfhydryl Content of Four Kinds of PBMs
2.3.3. Circular Dichroism Spectrum (CD)
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. The Processing Characteristics of PBMs
2.4.1. Water-Absorption Capacity (WAC), Water-Holding Capacity (WHC), and Water-Swelling Capacity (WSC)
2.4.2. The Tensile Strength (TS) and Breaking Elongation (BE) of Four Kinds of PBMs
2.4.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.5. The Nutritional Characteristics of PBMs
2.5.1. The Dietary Fiber, Reducing Sugar, Phytic Acid, Trypsin Inhibitor, Plant Lectin, and Isoflavone Content of Four Kinds of PBMs
2.5.2. The Amino Acid Composition
2.6. The Flavor Characteristics of PBMs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Protein Composition on the Structural Characteristics of PBMs
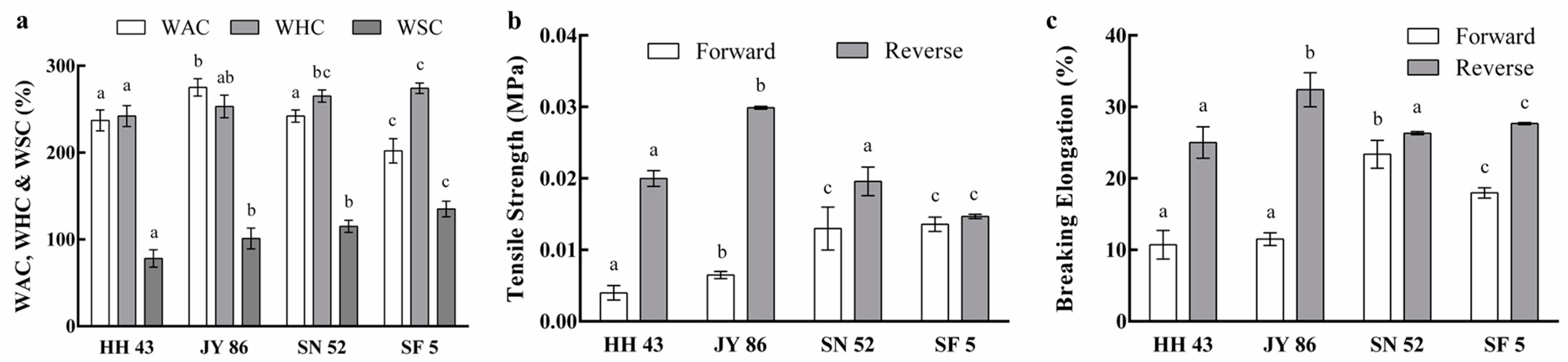
3.2. Effect of Protein Composition on the Processing Characteristics of PBMs
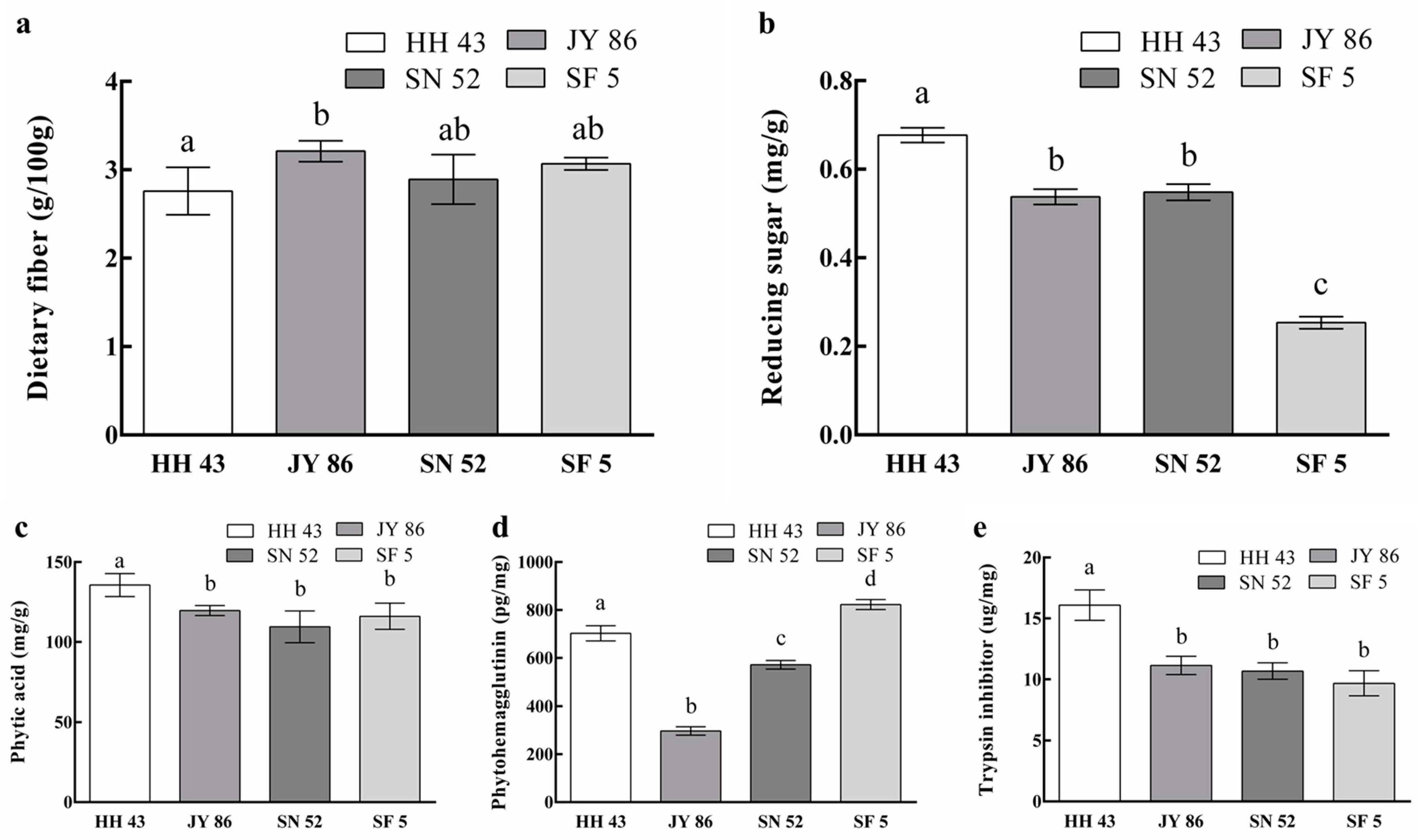
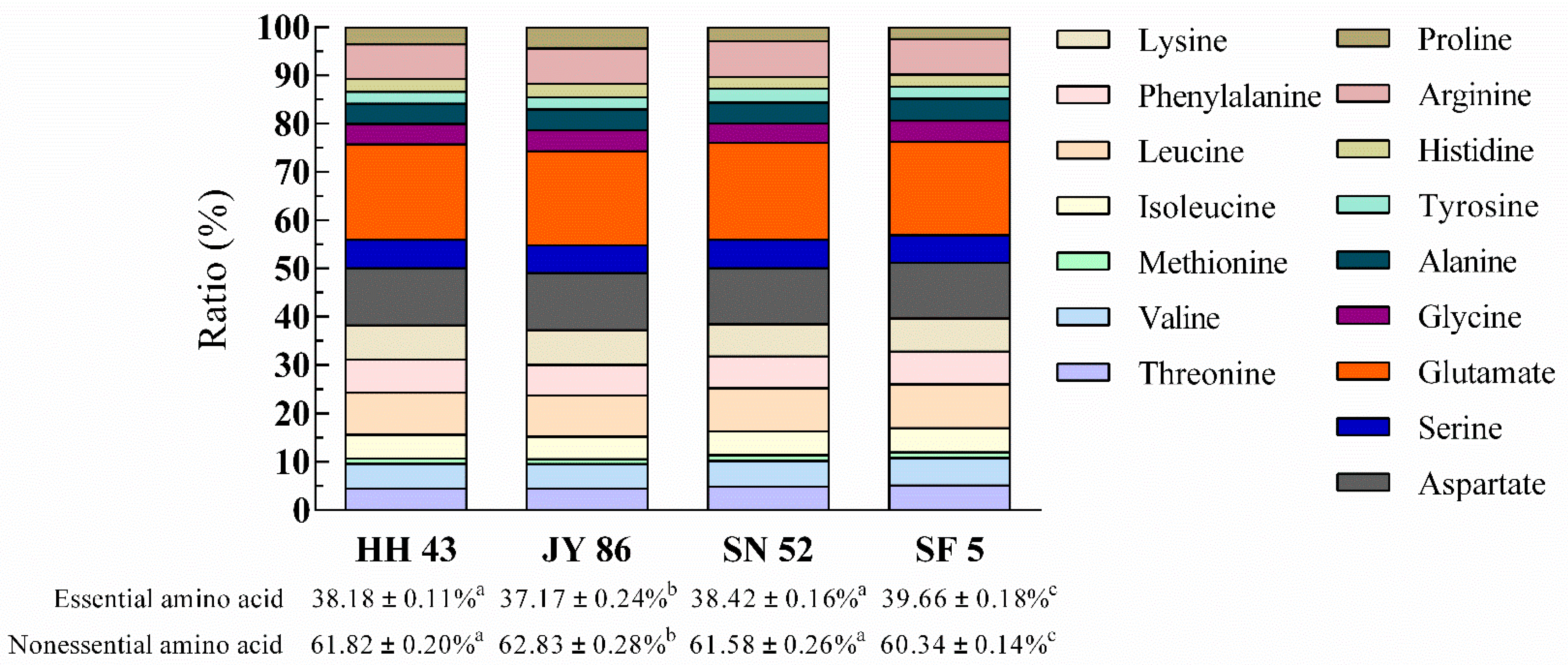
3.3. Effect of Protein Composition on the Nutritional Properties of PBMs
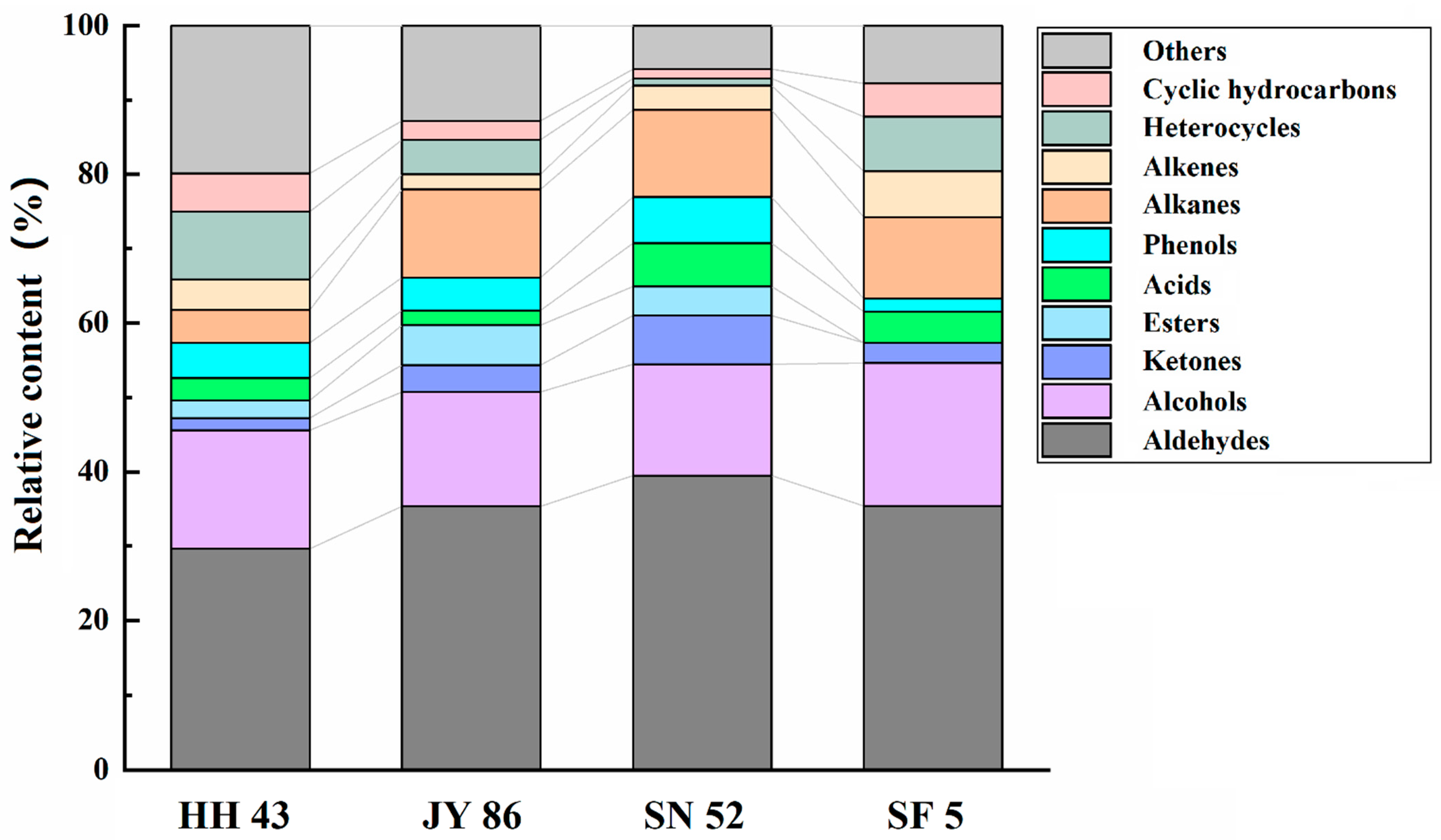
3.4. Effect of Protein Composition on the Flavor of PBMs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, X.; Yu, X. Using semiparametric models to study nutrition improvement and dietary change with different indices: The case of China. Food Policy 2015, 53, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.S.; Park, E.J.; Bae, J.W. Strict vegetarian diet improves the risk factors associated with metabolic diseases by modulating gut microbiota and reducing intestinal inflammation. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Ansorena, D.; Van Hecke, T.; Astiasarán, I.; De Smet, S.; Estévez, M. Meat lipids, NaCl and carnitine: Do they unveil the conundrum of the association between red and processed meat intake and cardiovascular diseases? _Invited Review. Meat Sci. 2021, 171, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Pan, A.; Manson, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B. Dairy fat and risk of cardiovascular disease in 3 cohorts of US adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacanlı, M.; Başaran, N. Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, D.; Pimentel, M. Sustainability of meat-based and plant-based diets and the environment. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 660S–663S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, J.; Brightwell, G. Safety of Alternative Proteins: Technological, environmental and regulatory aspects of cultured meat, plant-based meat, insect protein and single-cell protein. Foods 2021, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sharma, G.; Goyal, S.; Manivannan, B. Key Attributes for Success of Plant-Based Meat Alternative-Nutritional Values, Functional Properties, Suitability for Diverse Use and Price Parity. J. Nutr. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Boukid, F. Plant-based meat analogues: From niche to mainstream. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, S.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Sun, H. High-moisture Extrusion Technology Application in the Processing of Textured Plant Protein Meat Analogues: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.-J.; Kowalski, R.J.; Ganjyal, G.M. Food Extrusion Processing: An Overview; Washington State University Extension: Pullman, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Samard, S.; Gu, B.-Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Ryu, G.-H. Influences of extrusion parameters on physicochemical properties of textured vegetable proteins and its meatless burger patty. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Nieblas, C.; Zazueta-Morales, J.; Gallegos-Infante, J.; Aguilar-Palazuelos, E.; Camacho-Hernández, I.; Ordorica-Falomir, C.; Pires de Melo, M.; Carrillo-López, A. Elaboration of functional snack foods using raw materials rich in carotenoids and dietary fiber: Effects of extrusion processing. CyTA-J. Food 2015, 13, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.L.; Wei, Y.M.; Zhang, B. Chemical cross-linking and molecular aggregation of soybean protein during extrusion cooking at low and high moisture content. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. The development history and recent updates on soy protein-based meat alternatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L. Soy protein: Molecular structure revisited and recent advances in processing technologies. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 119–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Swallah, M.S.; Fu, H.; Ji, L.; Meng, X.; Yu, H.; Lyu, B. Soy protein isolate: An overview on foaming properties and air–liquid interface. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Soy protein isolates: A review of their composition, aggregation, and gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Liu, H. Oil-water interfacial behavior of soy β-conglycinin–soyasaponin mixtures and their effect on emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Du, M. Effect of partial replacement of water-soluble cod proteins by soy proteins on the heat-induced aggregation and gelation properties of mixed protein systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, E.M.; Scha, S.; Terjung, N.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J. Influence of Transglutaminase on Glucono-δ-lactone-Induced Soy Protein Gels. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čosić, A.; Karić, A.; Šabanović, K.; Šutković, J.; Yildirim, A. Determination of GMO soy products in processed food from Bosnian market. Bioeng. Stud. 2020, 1, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, K.; Zhang, L.; Duan, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z. Compositional differences between conventional Chinese and genetically modified Roundup Ready soybeans. Crop Pasture Sci. 2019, 70, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şurcă, E. Evaluating the Potential for Soybean Culture in Romania Compared with the European Union. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj Napoca Hortic. 2018, 75, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, O.M.; Cortes, H.N.; Jenks, B.H.; Maki, K.C. Naturally occurring hormones in foods and potential health effects. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2020, 4, 2397847320936281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Critical reviews and recent advances of novel non-thermal processing techniques on the modification of food allergens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Qiu, Z.; Li, M.; Luo, T.; Wu, Q.; Krishnan, H.B.; Wu, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S. Breeding of ‘DND358’: A new soybean cultivar for processing soy protein isolate with a hypocholesterolemic effect similar to that of fenofibrate. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotti, M.J.; Loyeau, P.A.; Marangón, A.; Noir, H.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Carrara, C.R. Influence of Maillard reaction extent on acid induced gels of whey proteins and dextrans. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Sui, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, D. Effect of secondary structure determined by FTIR spectra on surface hydrophobicity of soybean protein isolate. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 4819–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, B.; Wang, H.; Swallah, M.S.; Fu, H.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Tong, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, L. Structure, properties and potential bioactivities of high-purity insoluble fibre from soybean dregs (Okara). Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppo, C.; Chapleau, N.; Speroni, F.; de Lamballerie-Anton, M.; Michel, F.; Añón, C.; Anton, M. Physicochemical modifications of high-pressure-treated soybean protein isolates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Handa, C.L.; Xu, J. Effects of ultrasound pre-treatment on the structure of β-conglycinin and glycinin and the antioxidant activity of their hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, W.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Mu, D.; Zheng, Z. Formation of macromolecules in wheat gluten/starch mixtures during twin-screw extrusion: Effect of different additives. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 5131–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Lv, C.; Gao, J.; Yuan, J.; Shan, L.; Chen, H. Effect of extrusion on the modification of wheat flour proteins related to celiac disease. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. Effect of extrusion on the polymerization of wheat glutenin and changes in the gluten network. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3814–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li-Chan, E.C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S. Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Imamura, H. Universal model for α-helix and β-sheet structures in protein. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2003, 321, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Xiao, Z.; Huo, J.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Su, S.; Duan, Y.; Gao, Y. Effects of rice bran content on plant-based simulated meat: From the aspects of apparent properties and structural characteristics. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 131842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Teng, F.; Huang, Z.; Lv, B.; Lv, X.; Babich, O.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L. Effects of material characteristics on the structural characteristics and flavor substances retention of meat analogs. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samard, S.; Ryu, G.H. A comparison of physicochemical characteristics, texture, and structure of meat analogue and meats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhao, L.; He, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, B. Analysis of the gel properties, microstructural characteristics, and intermolecular forces of soybean protein isolate gel induced by transglutaminase. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Jia, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Effect of extrusion temperature on the protein aggregation of wheat gluten with the addition of peanut oil during extrusion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wu, C.; Regenstein, J.M.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Different commercial soy protein isolates and the characteristics of Chiba tofu. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.J.; Li, Y.P.; Qu, X.Q.; Kang, Z.L. Effects of combined high pressure and temperature on solubility, foaming, and rheological properties of soy 11S globulin. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, e14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Plant protein-based alternatives of reconstructed meat: Science, technology, and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, W.; Chen, Y.; Navicha, W.B.; Wu, D.; Du, M. The water holding capacity and storage modulus of chemical cross-linked soy protein gels directly related to aggregates size. LWT 2019, 103, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.j.; Zou, X.L.; Li, Y.p.; Kang, Z.L.; Ma, H.j. Effects of high-pressure-modified soy 11S globulin on the gel properties and water-holding capacity of pork batter. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gamlath, S.; Wakeling, L. Nutritional aspects of food extrusion: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiyama, I.; Kikuchi, M.; Harada, K.; Fukushima, D. 2S globulins of soybean seeds. 1. Isolation and characterization of protein components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajos, G.; Gelencser, E.; Pusztai, A.; Grant, G.; Sakhri, M.; Bardocz, S. Biological effects and survival of trypsin inhibitors and the agglutinin from soybean in the small intestine of the rat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.-S.; Ying-Yuan, N.; Gan, C.-Y. A comparative study of physicochemical characteristics and functionalities of pinto bean protein isolate (PBPI) against the soybean protein isolate (SPI) after the extraction optimisation. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, A.; Das, M.; Jain, S.; Dwivedi, P.D. Leucoagglutinating phytohemagglutinin: Purification, characterization, proteolytic digestion and assessment for allergenicity potential in BALB/c mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 36, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Sachdev, A. Molecular cloning, characterization and bacterial overexpression of D-‘myo’-inositol 3-phosphate synthase (‘MIPS1’) gene from soybean (‘Glycine max’[L.] Merr.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Raboy, V. Approaches and challenges to engineering seed phytate and total phosphorus. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.L.; Wolf, W.J. Compositional changes in trypsin inhibitors, phytic acid, saponins and isoflavones related to soybean processing. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 581S–588S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahungu, S.; Diaz-Mercado, S.; Li, J.; Schwenk, M.; Singletary, K.; Faller, J. Stability of isoflavones during extrusion processing of corn/soy mixture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, K.; Amin, P. Meltlets® of soy isoflavones: Process optimization and the effect of extrusion spheronization process parameters on antioxidant activity. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 450. [Google Scholar]
- Rostagno, M.A.; Palma, M.; Barroso, C.G. Pressurized liquid extraction of isoflavones from soybeans. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 522, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.R.; Fernández, P.C.R.; Rodríguez, E.O.C.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rochín, S.M. Changes in nutritional properties and bioactive compounds in cereals during extrusion cooking. In Extrusion of Metals, Polymers and Food Products; BoD Publishers: Stoughton, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 104–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Kan, J. Isolation and identification of flavor peptides from douchi (traditional Chinese soybean food). Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1982–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilić, S.M.; Barać, M.B.; Pešić, M.B.; Mladenović Drinić, S.D.; Ignjatović-Micić, D.D.; Srebrić, M.B. Characterization of proteins from kernel of different soybean varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y.; Xu, B. Flavor profiles of soymilk processed with four different processing technologies and 26 soybean cultivars grown in China. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2887–S2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Xie, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.; Qin, X. Study on the relevance between beany flavor and main bioactive components in Radix Astragali. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5568–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Ao, Q. Functional, nutritional and flavor characteristic of soybean proteins obtained through reverse micelles. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Heihe 43 | Jiyu 86 | Suinong 52 | Shengfeng 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 46.76 ± 0.07 c | 46.68 ± 0.07 c | 48.10 ± 0.03 b | 49.18 ± 0.04 a |
| Oil | 4.02 ± 0.01 b | 3.94 ± 0.04 c | 3.97 ± 0.01 c | 4.17 ± 0.01 a |
| Ash | 5.28 ± 0.01 b | 4.92 ± 0.07 d | 5.19 ± 0.05 c | 5.46 ± 0.01 a |
| Moisture | 7.26 ± 0.01 b | 6.91 ± 0.06 c | 7.77 ± 0.01 a | 6.24 ± 0.01 d |
| Soybeans | α′ | α | β | 7S | A3 | A1aA1bA2A4 | B1aB1bB2B3B4 | 11S | 11S/7S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heihe 43 | 13.53 ± 1.25 b | 14.26 ± 0.63 b | 7.98 ± 0.05 c | 35.77 ± 1.66 b | 3.03 ± 0.33 d | 17.39 ± 1.24 c | 17.37 ± 0.82 b | 37.79 ± 0.43 d | 1.05 ± 0.05 d |
| Jiyu 86 | 11.88 ± 0.85 a | 12.02 ± 0.85 a | 9.83 ± 0.47 a | 33.73 ± 1.32 a | 4.69 ± 0.27 c | 27.48 ± 0.67 b | 20.70 ± 1.73 b | 52.87 ± 2.24 b | 1.56 ± 0.20 c |
| Suinong 52 | 9.69 ± 0.85 b | 8.90 ± 0.57 c | 8.08 ± 0.35 c | 26.67 ± 0.46 c | 4.66 ± 0.18 b | 24.65 ± 0.55 c | 22.19 ± 0.09 b | 51.50 ± 0.61 c | 1.94 ± 0.05 b |
| Shengfeng 5 | 9.62 ± 0.85 c | 8.80 ± 0.85 b | 9.88 ± 0.14 b | 28.30 ± 0.14 b | 5.44 ± 0.30 a | 37.85 ± 1.53 a | 27.30 ± 0.34 a | 70.59 ± 2.07 a | 2.50 ± 0.11 a |
| α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heihe 43 | 24.49 ± 0.19 a | 45.72 ± 0.31 a | 17.50 ± 0.32 b | 12.31 ± 0.15 a |
| Jiyu 86 | 25.30 ± 0.19 c | 44.98 ± 0.34 c | 17.29 ± 0.31 c | 12.54 ± 0.15 b |
| Suinong 52 | 24.79 ± 0.16 b | 45.20 ± 0.32 b | 17.32 ± 0.31 c | 12.66 ± 0.14 c |
| Shengfeng 5 | 24.44 ± 0.18 a | 45.12 ± 0.34 a | 17.36 ± 0.31 a | 12.26 ± 0.16 c |
| Heihe 43 | Jiyu 86 | Suinong 52 | Shengfeng 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resilience | 0.32 ± 0.03 a | 0.35 ± 0.02 a | 0.35 ± 0.03 a | 0.39 ± 0.04 a |
| Springiness | 0.80 ± 0.02 a | 0.83 ± 0.03 a | 0.87 ± 0.04 a | 0.92 ± 0.09 a |
| Hardness (g) | 606.29 ± 21.74 b | 658.03 ± 19.11 a | 693.82 ± 18.88 c | 748.10 ± 20.38 d |
| Adhesiveness (g·sec) | 0.15 ± 0.02 ab | 0.22 ± 0.06 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 b | 0.29 ± 0.01c |
| Chewiness | 510.34 ± 12.66 b | 554.46 ± 12.11 a | 578.33 ± 13.53 c | 634.01 ± 10.91 d |
| Heihe 43 | Jiyu 86 | Suinong 52 | Shengfeng 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daidzin | 0.413 ± 0.03 b | 0.456 ± 0.02 a | 0.418 ± 0.02 b | 0.389 ± 0.03 c |
| Glycitin | 0.113 ± 0.03 b | 0.106 ± 0.02 b | 0.118 ± 0.03 b | 0.236 ± 0.05 a |
| Genistin | 0.911 ± 0.07 a | 0.821 ± 0.08 a | 0.877 ± 0.08 a | 0.668 ± 0.05 b |
| Daidzein | 0.019 ± 0.01 a | 0.017 ± 0.01 a | 0.024 ± 0.01 a | 0.018 ± 0.01 a |
| Glycitein | 0.432 ± 0.06 a | 0.302 ± 0.04 b | 0.254 ± 0.05 c | 0.312 ± 0.03 b |
| Genistein | 0.117 ± 0.01 a | 0.095 ± 0.01 b | 0.136 ± 0.01 a | 0.098 ± 0.00 b |
| Total | 2.005 ± 0.13 a | 1.797 ± 0.16 b | 1.827 ± 0.15 c | 1.721 ± 0.10 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, B.; Li, J.; Meng, X.; Fu, H.; Wang, W.; Ji, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yu, H. The Protein Composition Changed the Quality Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogues Produced by a Single-Screw Extruder: Four Main Soybean Varieties in China as Representatives. Foods 2022, 11, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081112
Lyu B, Li J, Meng X, Fu H, Wang W, Ji L, Wang Y, Guo Z, Yu H. The Protein Composition Changed the Quality Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogues Produced by a Single-Screw Extruder: Four Main Soybean Varieties in China as Representatives. Foods. 2022; 11(8):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081112
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Bo, Jiaxin Li, Xiangze Meng, Hongling Fu, Wei Wang, Lei Ji, Yi Wang, Zengwang Guo, and Hansong Yu. 2022. "The Protein Composition Changed the Quality Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogues Produced by a Single-Screw Extruder: Four Main Soybean Varieties in China as Representatives" Foods 11, no. 8: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081112
APA StyleLyu, B., Li, J., Meng, X., Fu, H., Wang, W., Ji, L., Wang, Y., Guo, Z., & Yu, H. (2022). The Protein Composition Changed the Quality Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogues Produced by a Single-Screw Extruder: Four Main Soybean Varieties in China as Representatives. Foods, 11(8), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081112







