Descriptive Sensory Profile and Consumer Study Impact of Different Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Descriptive, Temporal Profile, and Consumer Acceptance in a Peach Juice Matrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Participants
2.2.2. Quantitative Descriptive Analysis—QDA®
2.2.3. Time–Intensity Analysis
Training and Selection of Assessors to Time–Intensity
Sweetness and Bitterness Time–Intensity Analysis
2.2.4. Consumer Test
3. Results and Discussion
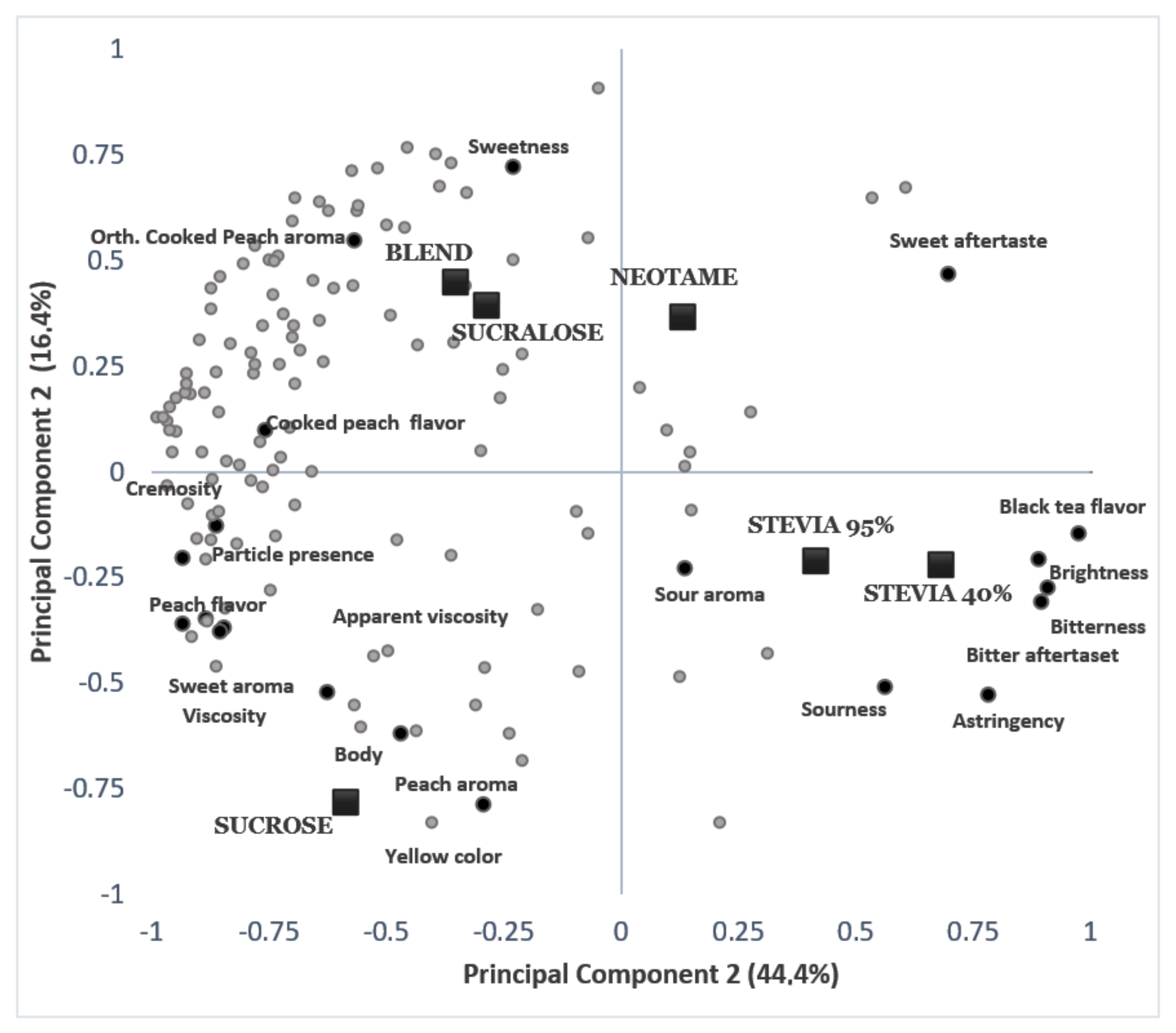
3.1. Descriptive Quantitative Analysis
3.2. Time–Intensity Analysis
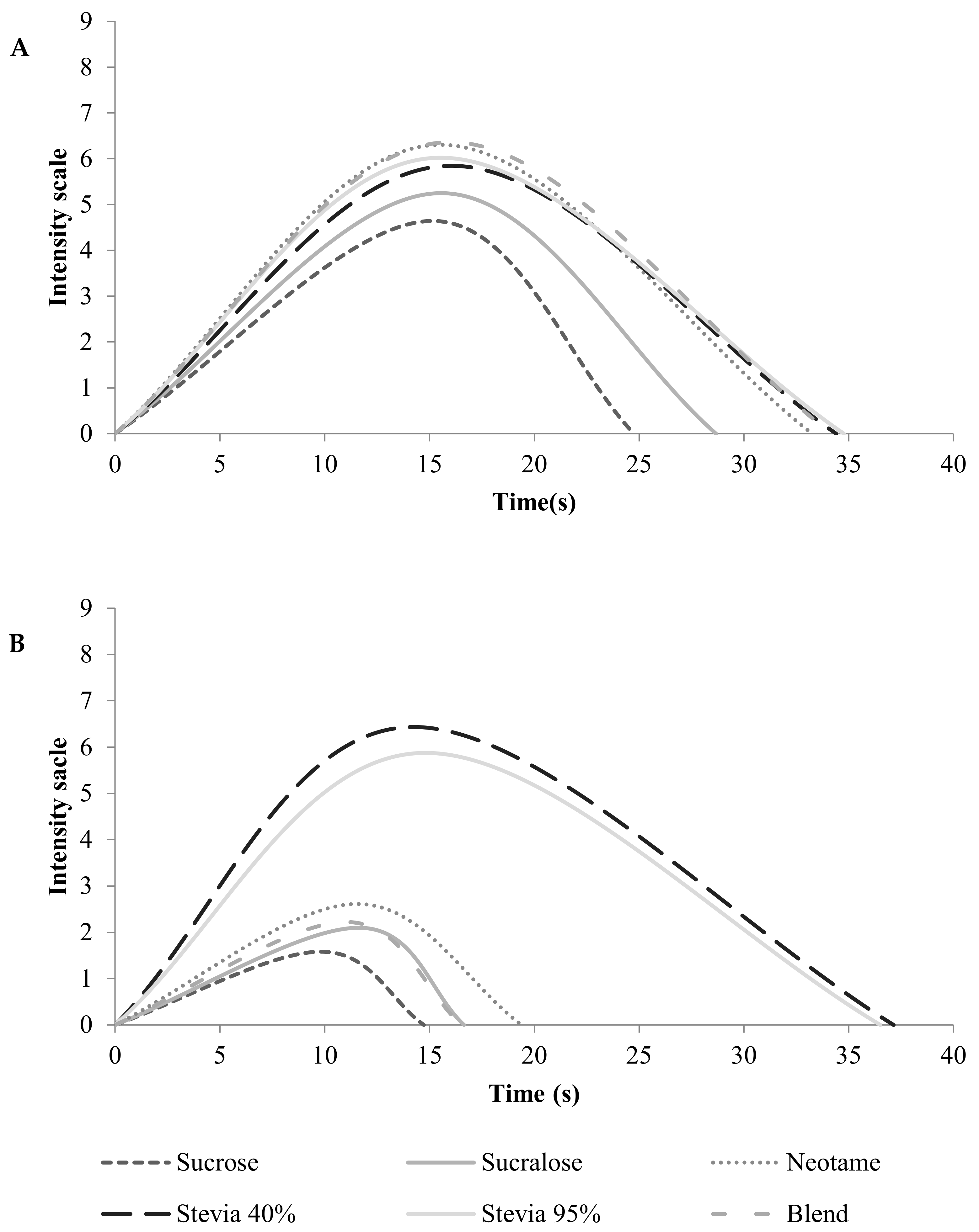
3.2.1. Sweet Taste
3.2.2. Bitter Taste
3.3. Consumer Analysis
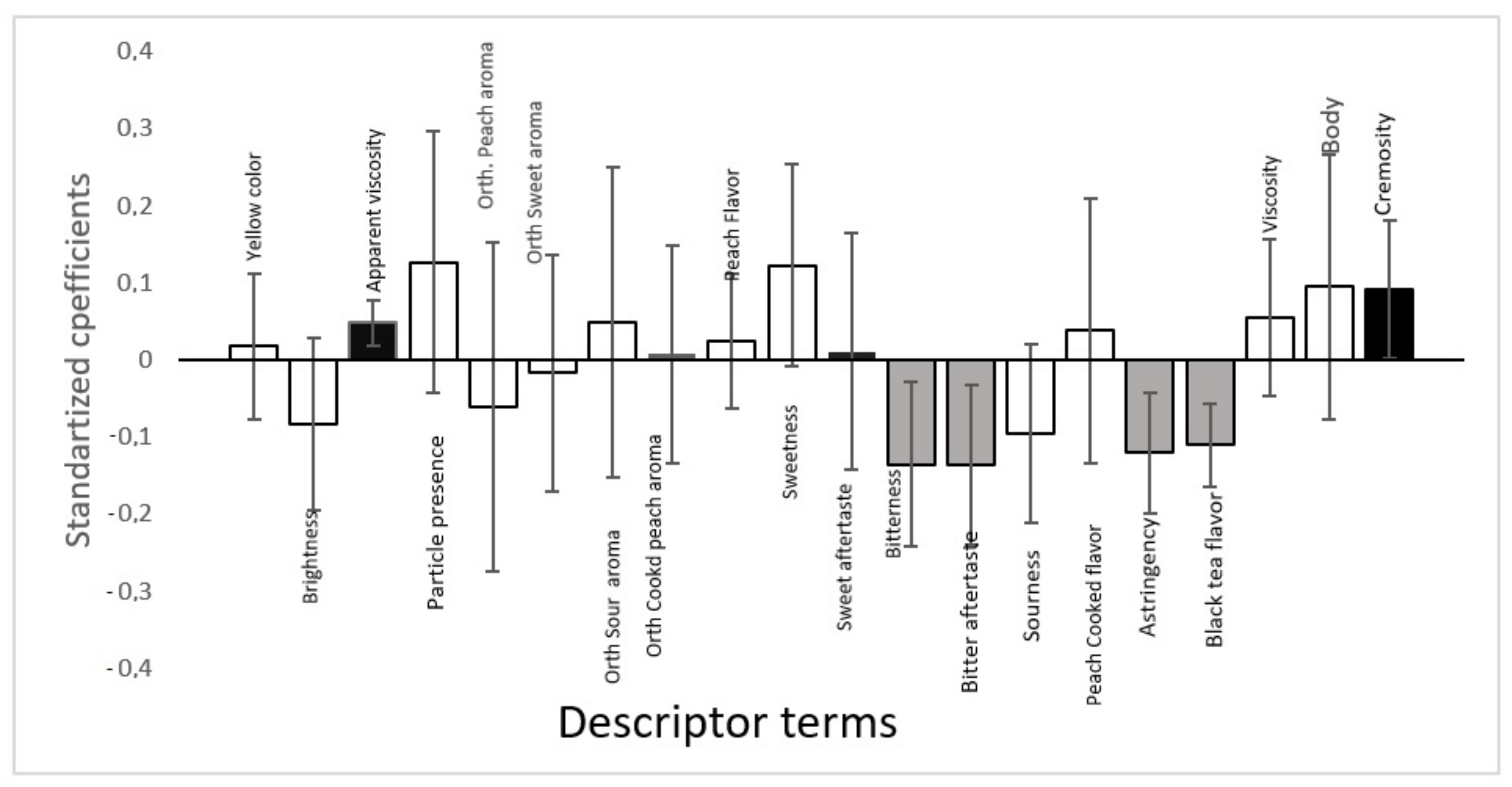
3.4. ADQ and Acceptance Data Correlation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Toxicological Terms. In Thirty-Eighth Meeting of JECFA; WHO Technical Report Series; No. 815; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, M.I.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant Capacities, Phenolic Compounds, Carotenoids and Vitamin C Contents of Nectarines, Peach and Plum Cultivars from California. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4976–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunini, M.A.; Durigan, J.F.; Oliveira, A.L. Avaliação Das Alterações Em Polpa De Manga Tommy-Atkins Congeladas. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2002, 24, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ros-Chumillas, M.; Belissario, Y.; Iguaz, A.; López, A. Quality and Shelf Life of Orange Juice Aseptically Packaged in Pet Bottles. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotz, V.L.; Munro, I.C. An Overview of the Safety of Sucralose. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiban, N.; Pilizota, N.; Subaric, V.; Milicevic, D.; Kopjar, M. Influence of Hydrocolloids and Sweeteners on Flow Behaviour of Peach Juice. Acta Aliment. 2003, 32, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Fao/Who Expert Committee On Food Additives (JECFA). Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants. In Thirty Seventh Meeting of JECFA; WHO Food Additives Series; No. 28; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991; p. 219. [Google Scholar]
- Soejarto, D.D. Biodiversity Prospecting and Benefit Sharing: From The Field. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1996, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, H.; Matos, A.F.J. Plantas Medicinais No Brasil: Nativas E Exóticas; Plantarum: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002; 544p. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, I.; Dubois, G.; Clos, J.; Wilkens, K.; Fosdick, L. Development of Rebiana, A Natural, Non-Caloric Sweetener. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, R. Sugar Substitutes. In Low Calorie Foods Handbook; Altschul, A.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 139–170. [Google Scholar]
- Parpinello, G.P.; Versari, A.; Castellari, M.; Galassi, S. Stevioside as a Replacement of Sucrose in Peach Juice: Sensory Evaluation. J. Sens. Stud. 2001, 16, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriocanal, L.; Palacios, M.; Benitez, G.; Benitez, S.; Jimenez, J.; Jimenez, N. Apparent Lack of Pharmacological Effect of Steviol Glycosides Used as Sweeteners In Humans, a Pilot Study of Repeated Exposures in Some Normatensive and Hypotensive Individuals and in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetics. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 51, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Hong, J.-H. Sweetness profiles of glycosylated rebaudioside A and its binary mixtures with allulose and maltitol. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, L. High-Intensity, Low-Calorie Sweeteners. In Low-Calorie Foods and Food Ingredients; Khan, R., Ed.; Blackie Academic & Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1996; pp. 138–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bakal, A.I. Mixed Sweetener Functionality. In Alternatives Sweeteners; Nabors, L.O., Gelardi, R.C., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 71–95. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, M.I.; Vincken, J.P.; Sanders, M.; Castro, C.; Stieger, M.; Agosin, E. Identification, Quantification, and Sensory Characterization of Steviol Glycosides from Differently Processed Stevia Rebaudiana Commercial Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11797–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.K.; Singh, S.; Dhyani, D.; Et Ahuja, P.S. L’amélioration Génétique Du Stévia [Stevia Rebaudiana (Bertoni)], Tour D’horizon. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2011, 91, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.M.; Castura, J.C.; Hayes, J.E. Characterizing Dynamic Sensory Properties of Nutritive and Nonnutritive Sweeteners with Temporal Check-All-That-Apply. J. Sens. Stud. 2017, 32, e12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, V.W.K.; Wee, M.S.M.; Forde, O.T.C.G. Temporal Sweetness and Side Tastes Profiles of 16 Sweeteners Using Temporal Check-All-That-Apply (TCATA). Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, M.; Tan, V.; Forde, C. A Comparison of Psychophysical Dose-Response Behaviour across 16 Sweeteners. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujimaru, T.; Park, J.H.; Lim, J. Sensory Characteristics and Relative Sweetness of Tagatose and Other Sweeteners. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, S323–S329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antenucci, R.G.; Reyes, J.E. Nonnutritive Sweeteners Are Not Supernormal Stimuli. Int J. Obes. 2015, 39, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.C.M.L.S. Determinação Do Perfil Sensorial Descritivo, Perfil Tempo-Intensidade E Estudo De Consumidor De Néctar De Pêssego (Prunus Persica (L.) Batsch) Adoçado Com Sacarose E Diferentes Edulcorantes. Master’s Thesis, University of Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2014; 112p. [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz, H.R. Product Testing and Sensory Evaluation of Foods; Food & Nutrition Press: Westport, WA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Damásio, M.H.; Costell, E. Análisis Sensorial Descriptivo: Generación De Descriptores Y Selección De Catadores. Rev. Agroquím. Tecnol. Aliment. 1991, 3, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.; Bleibaum, R.N.; Thomas, H.A. Sensory Evaluation Practices; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials International—ASTM International. E1909-11: Standard Guide for Time-Intensity Evaluation of Sensory Attributes, 3rd ed.; American Society for Testing and Materials International—ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Civille, G.V.; Carr, B.T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 5th ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bolini, H.M.A. Time–Intensity Analysis of Flavors and Tastes TIAF –Register INPI 12445–5; Revista Da Propriedade Industrial; Institute National of Property Industry: St. Paul, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hough, G.; Wakeling, I.; Mucci, A.; Chambers, I.V.E.; Gallardo, I.M.; Alves, L.R. Number Of Consumers Necessary For Sensory Acceptability Tests. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenhaus, M.; Pagès, J.; Ambroisine, L.; Guinot, C. PLS Methodology to Study Relationships between Hedonic Judgments and Products Characteristics. Food Qual. Pref. 2005, 16, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Farias Silva, C.E.; De Oliveira Moura, E.M.; De Souza, J.E.A.; Abud, A.K.S. Quality Control of Tropical Fruit Pulp in Brazil. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 44, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Cadena, R.S.; Bolini, H.M.A. Ideal and Relative Sweetness of High Intensity Sweeteners in Mango Nectar. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.L.F.; De Dutra, M.B.L.; Bolini, H.M.A. Time–Intensity Profile of Pitanga Nectar (Eugenia Uniflora L.) with Different Sweeteners: Sweetness and Bitterness. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2015, 22, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, A.C.; Bolini, H.M.A. Plant-Based Frozen Desserts: Temporal Sensory Profile and Preference. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dutra, M.B.L.; Bolini, H.M.A. Sensory and Physicochemical Evaluation of Acerola Nectar Sweetened with Sucrose and Different Sweeteners. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voorpostel, C.R.; De Dutra, M.B.L.; Bolini, H.M.A. Sensory Profile and Drivers of Liking for Grape Nectar among Smoker and Nonsmoker Consumers. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Rocha, I.F.O.; Bolini, H.M.A. Passion Fruit Juice with Different Sweeteners: Sensory Profile by Descriptive Analysis and Acceptance. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 3, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sweeteners Added to Peach Juice | Peach Pulp (g)/100 mL | Water (mL) | Sweetener (w/v) g/100 mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | 40.00 | 60.00 | 8.60 |
| Sucralose | 40.00 | 60.00 | 0.0169 |
| Neotame | 40.00 | 60.00 | 0.0018 |
| Stevia Rebaudioside A 40% | 40.00 | 60.00 | 0.1055 |
| Stevia Rebaudioside A 95% | 40.00 | 60.00 | 0.1055 |
| Acesulfame, sucralose, and neotame (100:50:1) blend | 40.00 | 60.00 | 0.0332 |
| Descriptor Terms | Definitions | References |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow color | Yellow color characteristic of products made with peach | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Pure concentrate peach juice Maguary® |
| Brightness | Light reflection capability | Weak: boiled egg yolk Strong: Gelatina peach flavor Dr. Oetker® |
| Apparent Viscosity | Flow velocity on the wall glass cup | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Peach pulp DeMarchi® |
| Particle Presence | Presence of particles/residues after draining the glass cup | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Peach pulp DeMarchi® |
| Orthonasal Peach Aroma | Characteristic orthonasal aroma of fresh peach natural fruit | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Peach pulp DeMarchi® |
| Orthonasal Sweet Aroma | Orthonasal sweet aroma from aromatic compounds that provide a sweet sensation | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:10) with sucrose (4%—União®) Strong: Juice peach (1:10) with sucrose (50%—União®) |
| Orthonasal Sour Aroma | Orthonasal sour aroma characteristic of the fermentation of peach juice | None: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:10) Strong: Pure concentrate peach juice Maguary® at 22 °C by 4 days |
| Orthonasal Cooked peach aroma | Orthonasal peach aroma after the peach natural fruit by thermal processing | None: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:10) Strong: Canned peach in syrup Schramm® |
| Peach flavor | Orthonasal peach ripe flavor | None: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:10) Strong: Peach pulp DeMarchi® |
| Sweetness | Sweet taste characteristic of sucrose or sweetener | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) with sucrose (4%—União®) Strong: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) with sucrose (25%—União®) |
| Sweet aftertaste | Sweet taste that remains in the mouth after swallowing | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) sweetened with neotame 0.010% Sweetmix ® |
| Bitterness | Characteristic bitter taste of caffeine | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water with caffeine 0.10% Ecibra® |
| Bitter Aftertaste | Bitter taste that remains in the mouth after swallowing | Weak: Peach juice and water (1:2) Strong: Peach juice and water (1:2) with caffeine 0.20%, Stevia 40% Rebaudioside A Sweetmix® |
| Sourness | Sour taste characteristic of unripe peach | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) with citric acid 0.10% |
| Cooked peach flavor | Peach flavor after thermal processing | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) Strong: Canned peach Schramm® |
| Astringency | Sensation of tannins in the mouth (such as green cashew) | Weak: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:10) Strong: Strong: peach pulp DeMarchi® |
| Black tea flavor | Characteristic flavor of black tea | None: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:10) Strong: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® and water (1:2) with 25% black tea Nestea® |
| Viscosity | Perceived flow during swallowing of substances, such as Bordo syrup | None: deionized water Strong: Concentrate peach juice Maguary® |
| Body | Mouth-filling capacity, consistency of a drink | Weak: Peach juice and water (1:10) Strong: Peach pulp DeMarchi® |
| Cremosity | Flow of peach juice with a high proportion of pulp | Weak: Peach nectar and water (1:10) Strong: Vigor® Greek yogurt yellow fruits flavor |
| Attributes | Sucrose | Sucralose | Neotame | Stevia 40% | Stevia 95% | Blend | HSD ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow color | 5.63 a | 5.29 b | 5.45 ab | 5.38 ab | 5.40 ab | 5.33 ab | 0.31 |
| Brightness | 5.87 b | 5.86 b | 5.94 ab | 6.22 a | 6.01 ab | 5.90 b | 0.32 |
| Apparent viscosity | 4.58 a | 4.24 ab | 4.06 ab | 3.93 b | 4.06 ab | 4.29 ab | 0.6 |
| Particle presence | 3.93 a | 3.79 ab | 3.50 abc | 3.44 bc | 3.20 c | 3.64 abc | 0.44 |
| Orthonasal peach aroma | 5.52 a | 5.32 a | 5.23 a | 5.12 a | 5.42 a | 5.18 a | 0.52 |
| Orthonasal sweet aroma | 4.23 a | 4.06 a | 3.93 a | 3.90 a | 4.05 a | 4.13 a | 0.54 |
| Orthonasal sour aroma | 2.52 a | 2.28 a | 2.55 a | 2.54 a | 2.41 a | 2.53 a | 0.42 |
| Orthonasal cooked peach aroma | 4.24 a | 4.35 a | 4.21 a | 4.18 a | 4.27 a | 4.44 a | 0.41 |
| Peach flavor | 5.38 a | 4.76 bc | 4.62 c | 4.43 c | 4.71 bc | 5.11 ab | 0.46 |
| Sweetness | 4.16 b | 4.32 b | 5.17 a | 4.16 b | 4.18 b | 5.24 a | 0.53 |
| Sweet aftertaste | 0.66 d | 1.53 c | 4.48 a | 3.14 b | 3.17 b | 2.56 b | 0.66 |
| Bitterness | 0.33 c | 0.42 c | 0.52 c | 4.04 a | 2.76 b | 0.33 c | 0.59 |
| Bitter aftertaste | 0.22 c | 0.52 c | 0.60 c | 4.22 a | 2.97 b | 0.31 c | 0.6 |
| Sourness | 2.05 ab | 1.71 b | 2.08 ab | 2.11 a | 2.18 a | 1.95 ab | 0.39 |
| Cooked peach flavor | 4.30 a | 4.12 ab | 4.22 a | 3.77 b | 4.19 ab | 4.32 a | 0.43 |
| Astringency | 2.09 ab | 1.73 b | 2.12 ab | 2.41 a | 2.37 a | 1.91 b | 0.4 |
| Black tea flavor | 2.03 b | 2.04 b | 2.24 ab | 2.50 a | 2.40 ab | 2.09 b | 0.37 |
| Viscosity | 3.93 a | 3.61 ab | 3.46 b | 3.50 b | 3.43 b | 3.75 ab | 0.35 |
| Body | 3.80 a | 3.35 b | 3.41 ab | 3.43 ab | 3.18 b | 3.46 ab | 0.41 |
| Cremosity | 2.91 a | 2.66 abc | 2.51 bc | 2.45 bc | 2.38 c | 2.76 ab | 0.37 |
| (A) Sweetness | ||||||
| Parameter | Sucrose | Sucralose | Neotame | Stevia 40% Reb. A | Stevia 95% Reb. A | Blend |
| IMAX | 4.64 d | 5.25 c | 6.31 a | 5.85 b | 6.02 ab | 6.36 a |
| TIMAX (s) | 15.15 a | 15.56 a | 15.53 a | 16.05 a | 15.54 a | 16.00 a |
| TTOTAL(s) | 24.76 b | 28.67 b | 33.26 a | 34.40 a | 34.77 a | 34.19 a |
| Area | 66.77 c | 92.88 b | 127.59 a | 118.03 a | 130.23 a | 129.28 a |
| (B) Bitterness | ||||||
| Parameter | Sucrose | Sucralose | Neotame | Stevia 40% Reb. A | Stevia 95% Reb. A | Blend |
| IMAX | 1.58 e | 2.10 d | 2.61 c | 6.43 a | 5.87 b | 2.22 dc |
| TIMAX (s) | 9.83 b | 11.62 b | 11.57 b | 14.25 a | 14.82 a | 11.03 b |
| TTOTAL(s) | 14.73 b | 16.65 b | 19.40 b | 37.15 a | 36.51 a | 16.53 b |
| Area | 23.67 d | 30.74 cd | 41.20 c | 143.33 a | 126.02 b | 31.34 cd |
| Parameter | Sucrose | Sucralose | Neotame | Stevia 40% Reb. A | Stevia 95% Reb. A | Blend | HSD ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | 5.89 a | 6.08 a | 6.20 a | 6.20 a | 6.05 a | 5.89 a | 0.57 |
| Aroma | 5.79 ab | 5.76 ab | 5.86 ab | 5.46 b | 5.44 b | 6.04 a | 0.58 |
| Flavor | 5.86 a | 5.36 a | 4.47 b | 2.58 c | 2.47 c | 5.54 a | 0.70 |
| Texture | 6.07 a | 5.94 a | 5.93 a | 5.05 b | 5.14 b | 6.08 a | 0.62 |
| Overall Liking | 5.83 a | 5.56 ab | 5.00 b | 3.24 c | 3.27 c | 5.66 a | 0.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medeiros, A.; Tavares, E.; Bolini, H.M.A. Descriptive Sensory Profile and Consumer Study Impact of Different Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Descriptive, Temporal Profile, and Consumer Acceptance in a Peach Juice Matrix. Foods 2022, 11, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020244
Medeiros A, Tavares E, Bolini HMA. Descriptive Sensory Profile and Consumer Study Impact of Different Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Descriptive, Temporal Profile, and Consumer Acceptance in a Peach Juice Matrix. Foods. 2022; 11(2):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020244
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedeiros, Alessandra, Elson Tavares, and Helena Maria Andre Bolini. 2022. "Descriptive Sensory Profile and Consumer Study Impact of Different Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Descriptive, Temporal Profile, and Consumer Acceptance in a Peach Juice Matrix" Foods 11, no. 2: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020244
APA StyleMedeiros, A., Tavares, E., & Bolini, H. M. A. (2022). Descriptive Sensory Profile and Consumer Study Impact of Different Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners on the Descriptive, Temporal Profile, and Consumer Acceptance in a Peach Juice Matrix. Foods, 11(2), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020244