Variations in the Multilevel Structure, Gelatinization and Digestibility of Litchi Seed Starches from Different Varieties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Starch Isolation
2.3. Granule Morphology
2.4. Particle Size Distribution
2.5. Crystalline Structure
2.6. Semi-Crystalline Structure
2.7. Molecular Structure
2.8. Thermo Properties
2.9. In Vitro Digestion
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characteristics
3.2. Particle Size Distribution
3.3. Crystalline Structure
3.4. Semi-Crystalline Structure
3.5. Molecular Structure
3.6. Thermal Properties
3.7. In Vitro Digestion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, K.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z. Nutrient components, health benefits, and safety of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.): A review. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2139–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Wang, K.; Lan, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, L. Effect of hybrid gelator systems of beeswax-carrageenan-xanthan on rheological properties and printability of litchi inks for 3D food printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S.; Kumar, M. Litchi (Litchi chinenis) seed: Nutritional profile, bioactivities, and its industrial applications. Trend. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, H.; Gao, A.; Zhu, M. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) seed by response surface methodology and their structural characteristics. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2011, 12, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Lu, F. Chemical composition and hypoglycaemic effect of polyphenol extracts from Litchi chinensis seeds. J. Funct. Food. 2016, 22, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. A-type proanthocyanidins from lychee seeds and their antioxidant and antiviral activities. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 58, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Xu, D.; Pan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, Q. Two flavanone compounds from litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) seeds, one previously unreported, and appraisal of their α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1760–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra Prasad, K.; Yang, B.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ashraf, M.; Jiang, Y. Identification of phenolic compounds and appraisal of antioxidant and antityrosinase activities from litchi (Litchi sinensis Sonn.) seeds. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lin, L.; Fan, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, C. Comparison of structural and functional properties of starches from five fruit kernels. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Hedayati, S.; Shahidi, F. Effects of mung bean (Vigna radiata) protein isolate on rheological, textural, and structural properties of native corn starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Liu, G.; Gu, Z. Recent advances of starch-based excipients used in extended-release tablets: A review. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, K.; Kamilah, H.; Shang, P.L.; Sulaiman, S.; Ariffin, F.; Alias, A.K. A review: Interaction of starch/non-starch hydrocolloid blending and the recent food applications. Food Biosci. 2017, 19, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J. The challenge of feeding 9–10 billion people equitably and sustainably. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 152, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thory, R.; Sandhu, K.S. A comparison of mango kernel starch with a novel starch from litchi (Litchi chinensis) kernel: Physicochemical, morphological, pasting, and rheological properties. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 20, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, P.; Kumar, K.J. Physicochemical properties and release characteristics of starches from seeds of Indian Shahi Litchi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K. Hierarchical structure, gelatinization, and digestion characteristics of starch from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) seeds. Molecules 2018, 23, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Xie, F. Supramolecular structure of jackfruit seed starch and its relationship with digestibility and physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hasjim, J.; Wu, A.C.; Henry, R.J.; Gilbert, R.G. Variation in amylose fine structure of starches from different botanical sources. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 62, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Dhital, S.; Junejo, S.A.; Ding, L.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, B. Starch retrogradation in potato cells: Structure and in vitro digestion paradigm. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 286, 119261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yuan, T.Z.; Ai, Y. Development, structure and in vitro digestibility of type 3 resistant starch from acid-thinned and debranched pea and normal maize starches. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuryev, V.P.; Krivandin, A.V.; Kiseleva, V.I.; Wasserman, L.A.; Genkina, N.K.; Fornal, J.; Blaszczak, W.; Schiraldi, A. Structural parameters of amylopectin clusters and semi-crystalline growth rings in wheat starches with different amylose content. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Man, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wei, W.; Wei, C. Relationship between structure and functional properties of normal rice starches with different amylose contents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Fu, X.; Dhital, S.; Zhai, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B. In vitro fecal fermentation outcomes of starch-lipid complexes depend on starch assembles more than lipid type. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeboom, N.; Chang, P.R.; Tyler, R.T. Analytical, biochemical and physicochemical aspects of starch granule size, with emphasis on small granule starches: A review. Starch-Starke 2004, 56, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corgneau, M.; Gaiani, C.; Petit, J.; Nikolova, Y.; Banon, S.; Ritié-Pertusa, L.; Le, D.T.L.; Scher, J. Digestibility of common native starches with reference to starch granule size, shape and surface features towards guidelines for starch-containing food products. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Q.; Jin, C.; Narayanamoorthy, S.; Zhang, T.; Sui, Z.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characterization of morphology and physicochemical properties of native starches isolated from 12 Lycoris species. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, F.M.; Riar, C.S. Effect of amylose, particle size & morphology on the functionality of starches of traditional rice cultivars. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Particle size distribution of wheat starch granules in relation to baking properties of frozen dough. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.-L.; Lu, Q.-Y. Effect of A- and B-granules of wheat starch on Chinese noodle quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 91, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, G.; Gao, H.; Ru, Z. Comparison of A and B starch granules from three wheat varieties. Molecules 2011, 16, 10570–10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Henry, R.J.; Gilbert, R.G. Causal relations between starch biosynthesis, structure and properties. Springe. Sci. Rev. 2014, 2, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blazek, J.; Gilbert, E.P. Application of small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering techniques to the characterisation of starch structure: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Pu, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, S. Supramolecular and molecular structures of potato starches and their digestion features. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.G.; Zhao, S.M.; Zhang, B.J.; Tan, M.M.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.H.; Huang, Q.L. Understanding the supramolecular structures and pasting features of adlay seed starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.L.; Tu, W.Y.; Zhang, B.J.; Wang, R.; Li, N.N.; Nishinari, K.; Riffat, S.; Jiang, F.T. Understanding the multi-scale structure and digestion rate of water chestnut starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wambugu, P.W.; Zhang, B.; Wu, A.C.; Henry, R.J.; Gilbert, R.G. The biosynthesis, structure and gelatinization properties of starches from wild and cultivated African rice species (Oryza barthii and Oryza glaberrima). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


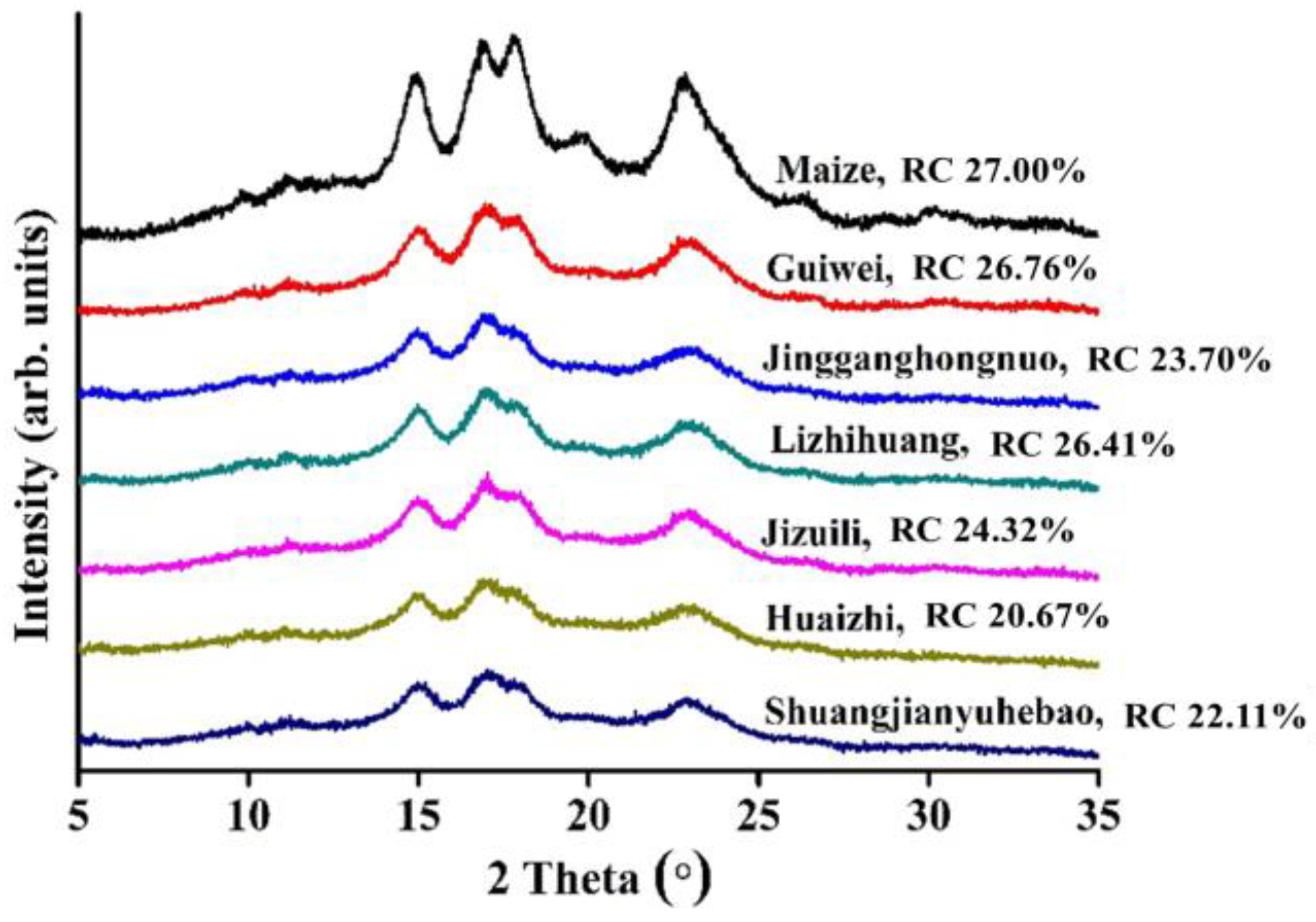
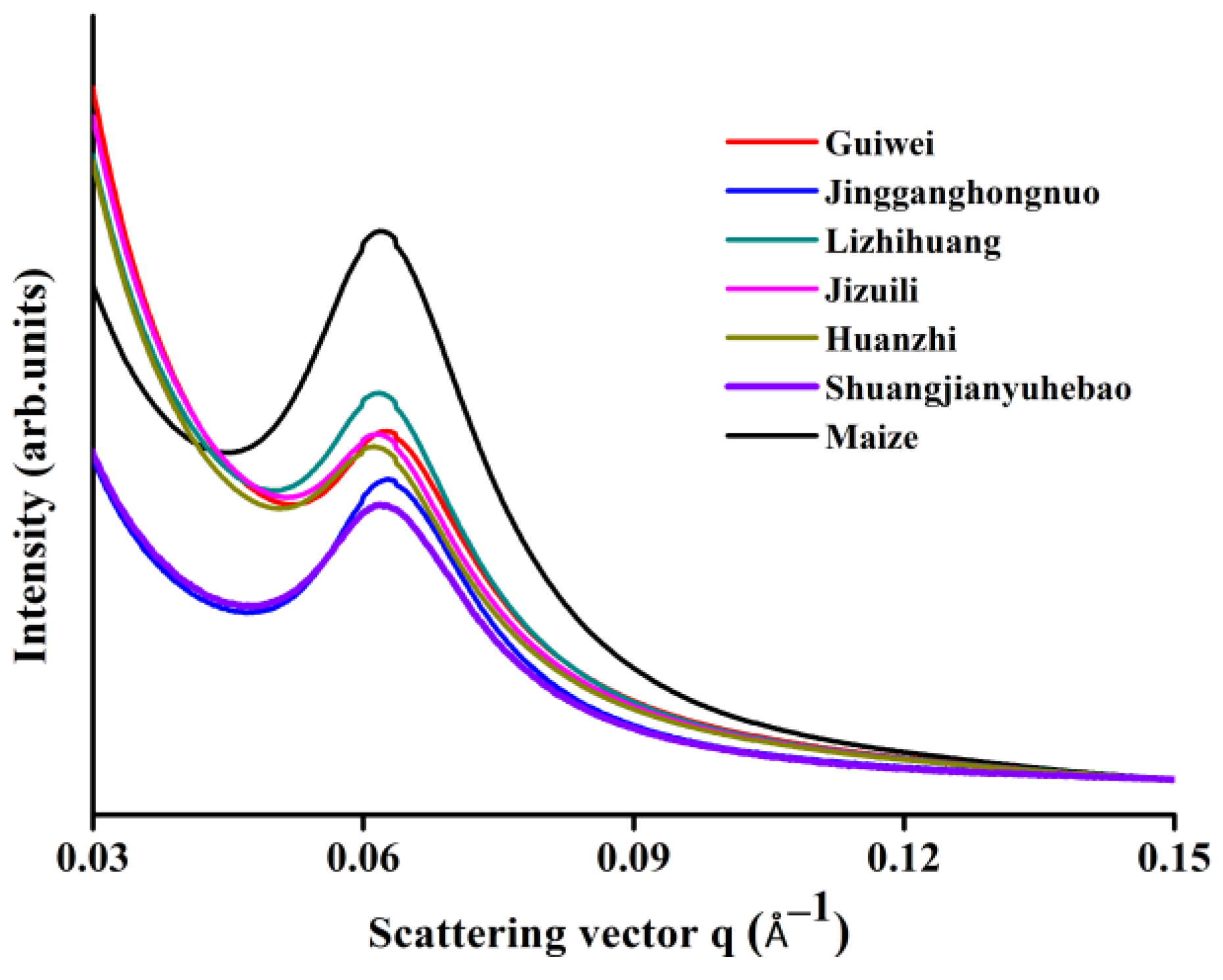


| Samples | Imax (Counts) | ΔS (Å−1) | Smax (Å−1) | D (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guiwei | 77.61 | 0.013 | 0.063 | 10.03 |
| Jingganghongnuo | 100.00 | 0.015 | 0.063 | 9.96 |
| Lizhihuang | 144.78 | 0.014 | 0.062 | 10.17 |
| Jizuili | 73.88 | 0.013 | 0.062 | 10.16 |
| Huaizhi | 68.28 | 0.014 | 0.061 | 10.27 |
| Shuangjianyuhebao | 83.21 | 0.017 | 0.062 | 10.17 |
| Maize | 174.25 | 0.019 | 0.062 | 10.19 |
| Samples | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | k (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guiwei | 74.27 ± 0.11 b | 78.40 ± 0.00 b | 83.24 ± 0.13 c | 9.41 ± 0.37 b | 0.039 ± 0.009 ab |
| Jingganghongnuo | 73.97 ± 0.04 b | 78.22 ± 0.01 b | 82.80 ± 0.00 c | 6.48 ± 0.03 c | 0.040 ± 0.000 ab |
| Lizhihuang | 73.85 ± 0.28 b | 78.32 ± 0.11 b | 82.96 ± 0.10 c | 7.08 ± 0.06 c | 0.034 ± 0.003 ab |
| Jizuili | 73.71 ± 0.25 b | 78.23 ± 0.01 b | 83.00 ± 0.18 c | 7.62 ± 0.60 c | 0.033 ± 0.006 ab |
| Huaizhi | 75.04 ± 0.25 a | 80.04 ± 0.22 a | 84.64 ± 0.24 a | 6.12 ± 0.86 c | 0.030 ± 0.004 b |
| Shuangjianyuhebao | 68.86 ± 0.3 c | 75.87 ± 0.48 c | 84.08 ± 0.46 b | 7.30 ± 0.09 c | 0.044 ± 0.004 a |
| Maize | 64.03 ± 0.07 d | 70.06 ± 0.25 d | 75.60 ± 0.17 d | 13.43 ± 0.33 a | 0.041 ± 0.007 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K. Variations in the Multilevel Structure, Gelatinization and Digestibility of Litchi Seed Starches from Different Varieties. Foods 2022, 11, 2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182821
Zhang X, Zhao L, Zhou W, Liu X, Hu Z, Wang K. Variations in the Multilevel Structure, Gelatinization and Digestibility of Litchi Seed Starches from Different Varieties. Foods. 2022; 11(18):2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182821
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin, Lei Zhao, Wanxia Zhou, Xuwei Liu, Zhuoyan Hu, and Kai Wang. 2022. "Variations in the Multilevel Structure, Gelatinization and Digestibility of Litchi Seed Starches from Different Varieties" Foods 11, no. 18: 2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182821
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhao, L., Zhou, W., Liu, X., Hu, Z., & Wang, K. (2022). Variations in the Multilevel Structure, Gelatinization and Digestibility of Litchi Seed Starches from Different Varieties. Foods, 11(18), 2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182821






