Enhancement of Carbon Conversion and Value-Added Compound Production in Heterotrophic Chlorella vulgaris Using Sweet Sorghum Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of HSE
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Microalgae Biomass and pH
2.4.2. Nutrient Analysis of the Medium
2.4.3. Chemical Composition Analysis of the Microalgae
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Compositions of SE and HSE
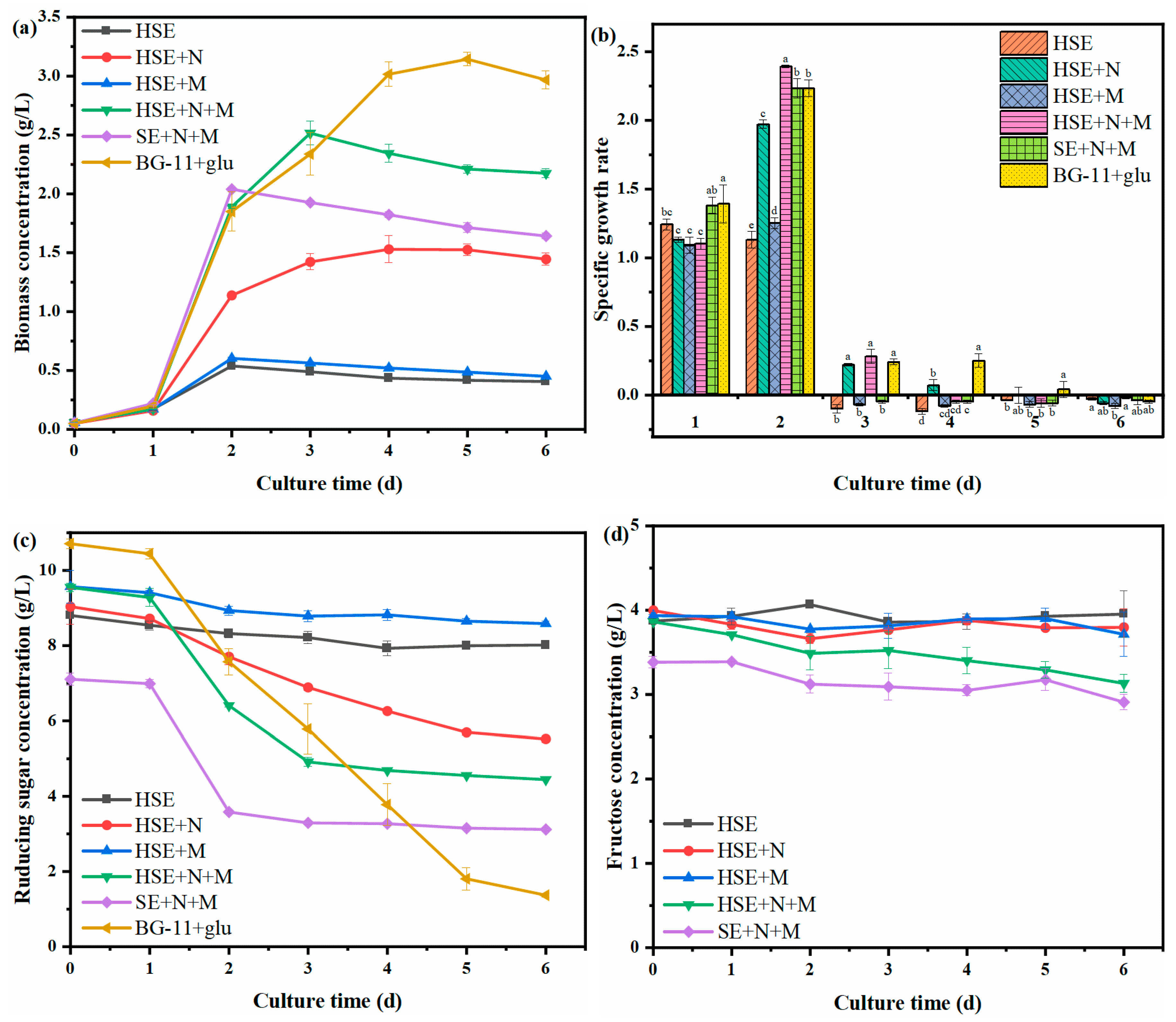
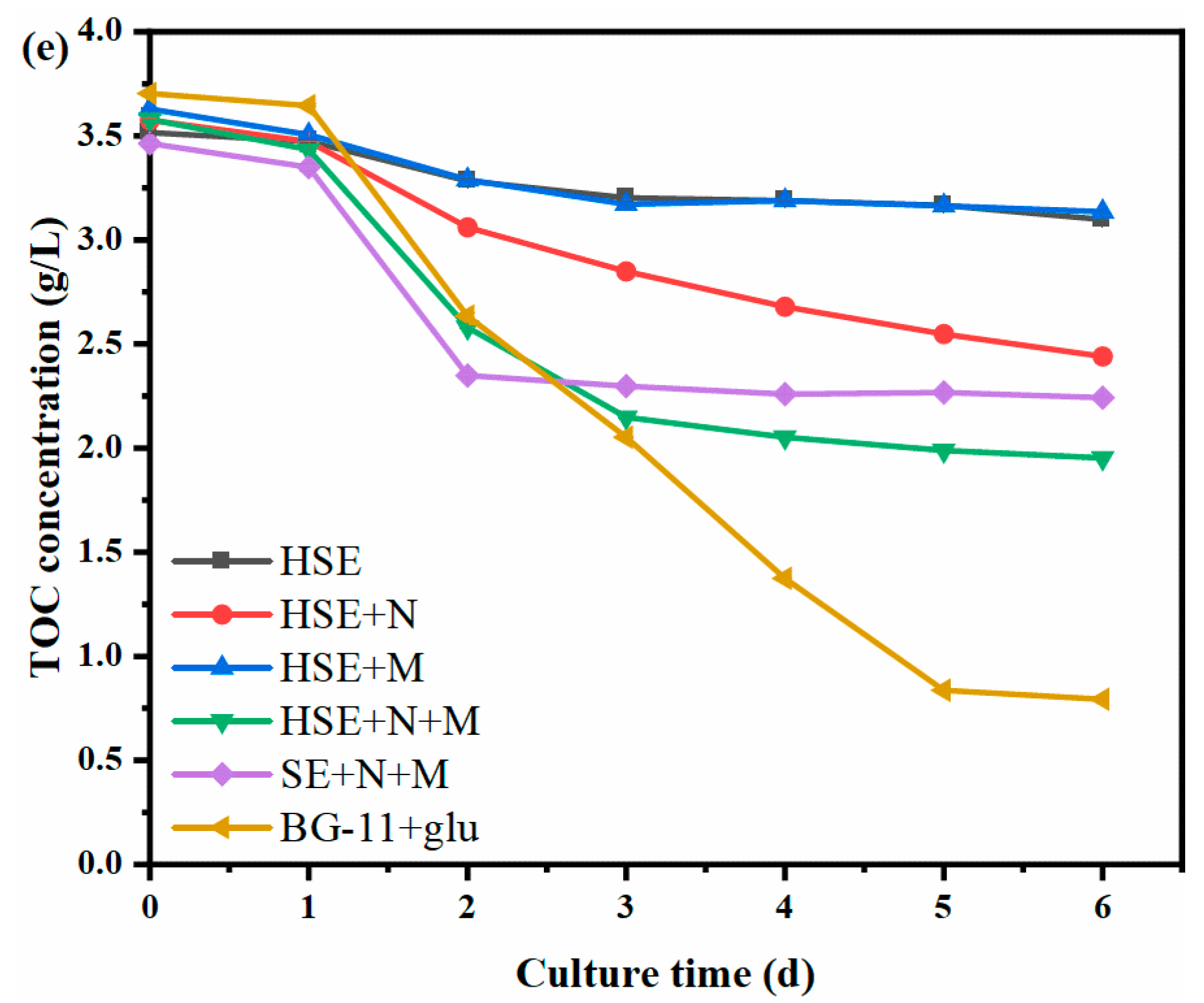
3.2. Changes in Biomass and Organic Carbon during the Cultivation of Chlorella Vulgaris
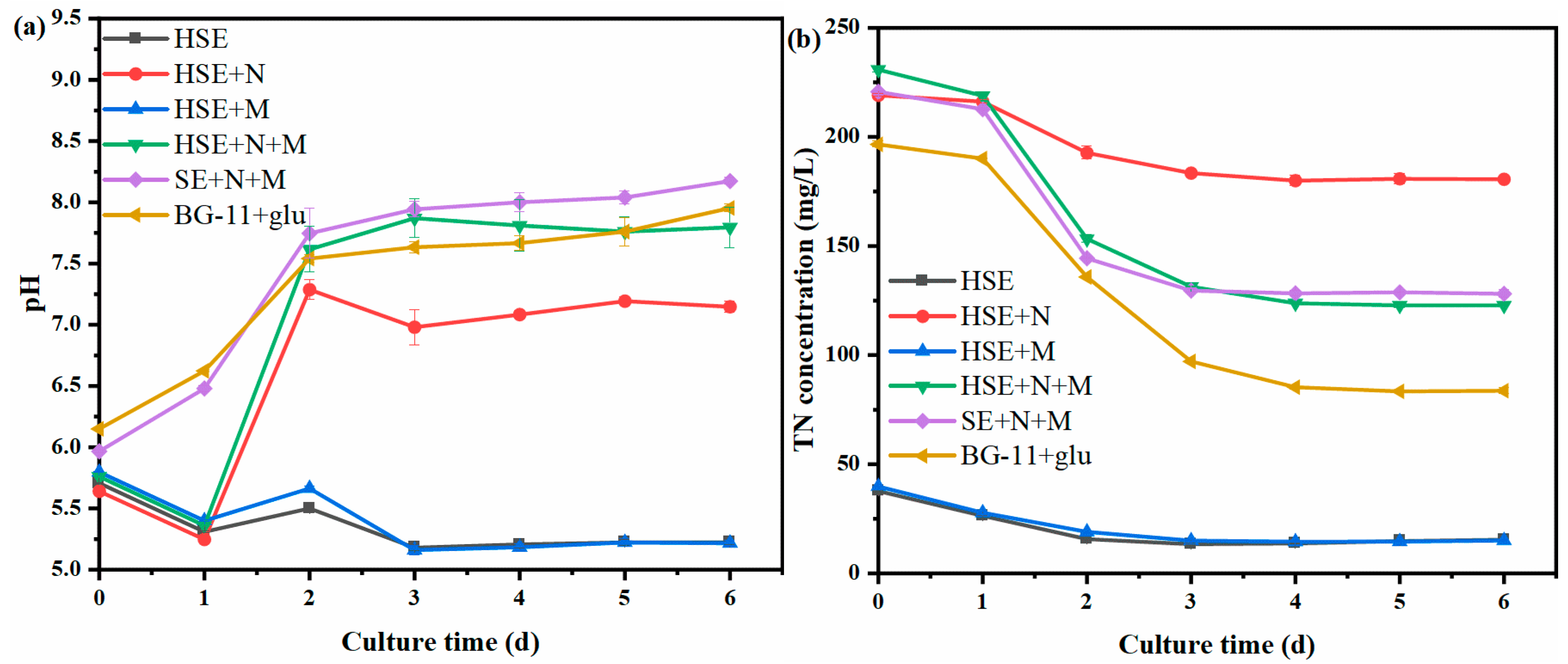
3.3. Changes in the pH and Total Nitrogen during the Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris
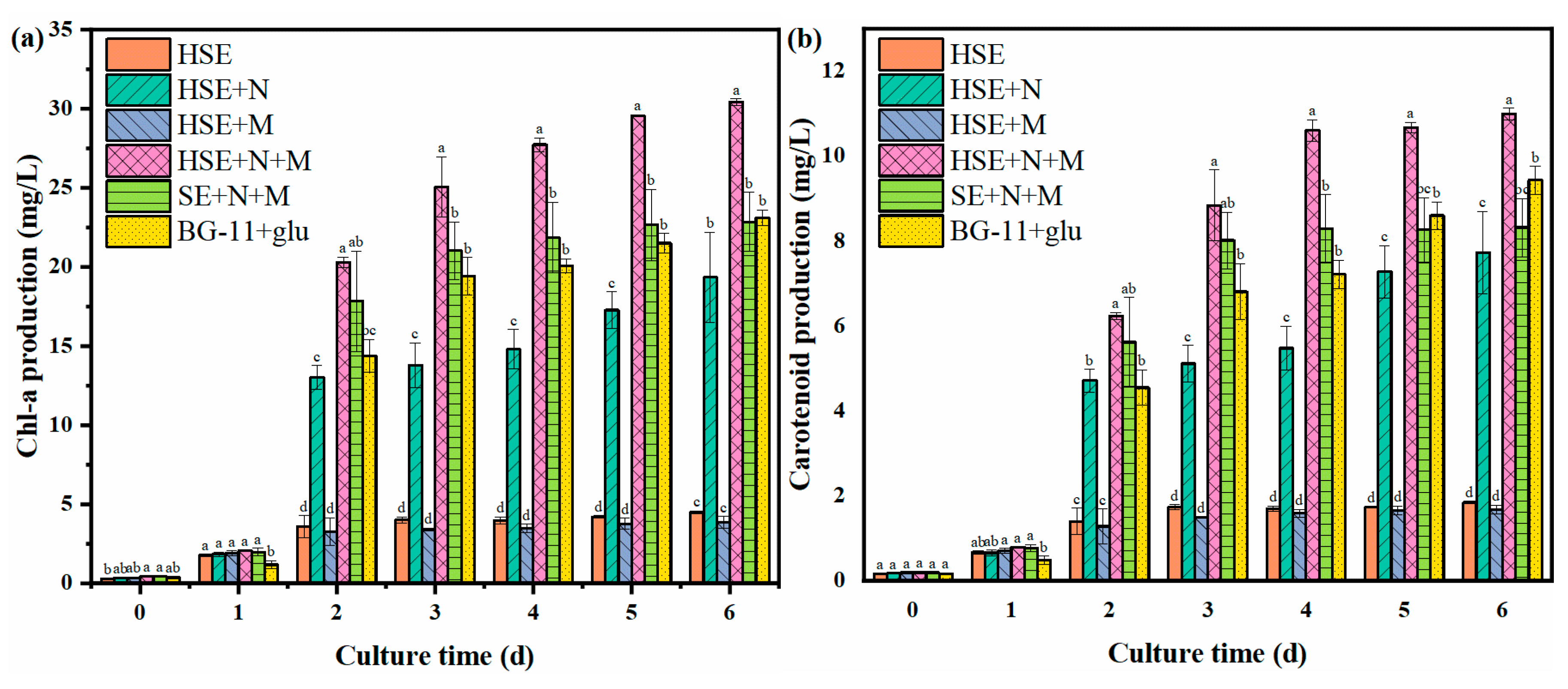
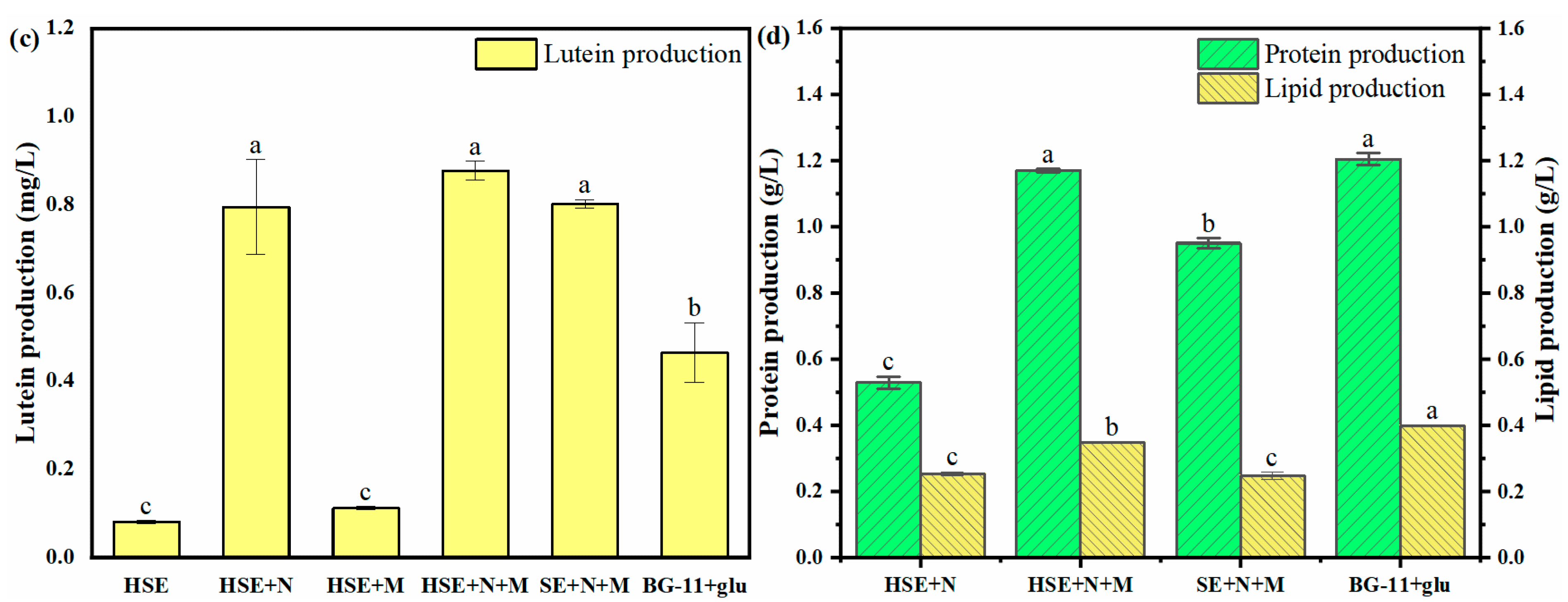
3.4. Chemical Composition of Chlorella vulgaris
3.5. Cost Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Amorim, W.S.; Deggau, A.B.; Do Livramento Gonçalves, G.; Da Silva Neiva, S.; Prasath, A.R.; De Andrade, J.B.S.O. Urban challenges and opportunities to promote sustainable food security through smart cities and the 4th industrial revolution. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, O.; Dolganyuk, V.; Andreeva, A.; Katserov, D.; Matskova, L.; Ulrikh, E.; Ivanova, S.; Michaud, P.; Sukhikh, S. Isolation of Valuable Biological Substances from Microalgae Culture. Foods 2022, 11, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejike, C.E.; Collins, S.A.; Balasuriya, N.; Swanson, A.K.; Mason, B.; Udenigwe, C.C. Prospects of microalgae proteins in producing peptide-based functional foods for promoting cardiovascular health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F. Microalgae metabolites: A rich source for food and medicine. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, D.M.; Cahú, T.B.; Oliveira, C.Y.B.; Abadie Guedes, R.; Roberto, N.A.; Santana, W.M.; Gálvez, A.O.; Guedes, R.C.; Bezerra, R.S. Chlorella vulgaris functional alcoholic beverage: Effect on propagation of cortical spreading depression and functional properties. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, H.; Nunes, M.C.; Prista, C.; Raymundo, A. Innovative and Healthier Dairy Products through the Addition of Microalgae: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelli, G.; Tevere, S.; Jaquenod, L.; Dionisi, F.; Rohfritsch, Z.; Bolten, C.J.; Neutsch, L.; Mathys, A. A novel strategy to simultaneously enhance bioaccessible lipids and antioxidants in hetero/mixotrophic Chlorella vulgaris as functional ingredient. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, D.; Melo, T.; Conde, T.A.; Moreira, A.S.; Ferreira, P.; Costa, M.; Silva, J.; Domingues, R.; Domingues, P. Food grade extraction of Chlorella vulgaris polar lipids: A comparative lipidomic study. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avinash, A.; Sasikumar, P.; Pugazhendhi, A. Analysis of the limiting factors for large scale microalgal cultivation: A promising future for renewable and sustainable biofuel industry. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2020, 134, 110250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Nagarajan, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.J. Heterotrophic cultivation of microalgae for pigment production: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-S.; Wu, J.-Y. Effect of carbon sources on growth and lipid accumulation of newly isolated microalgae cultured under mixotrophic condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sánchez, D.; Martinez-Rodriguez, O.A.; Kyndt, J.; Martinez, A. Heterotrophic growth of microalgae: Metabolic aspects. World J. Microb. Biot. 2015, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Wang, X.; Tao, H.H.; Sun, X.S.; Tian, Y.T. Heterotrophic culture of Chlorella pyrenoidosa using sucrose as the sole carbon source by co-culture with immobilized yeast. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Han, J.-I.; Yang, J.-W.; Chang, Y.K.; Ryu, B.-G. Carbon balance of major volatile fatty acids (VFAs) in recycling algal residue via a VFA-platform for reproduction of algal biomass. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Garcia, O.; Bashan, Y.; Esther Puente, M. Organic carbon supplementation of sterilized municipal wastewater is essential for heterotrophic growth and removing ammonium by the microalga Chlorella vulgaris. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menetrez, M.Y. An overview of algae biofuel production and potential environmental impact. Enciron. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7073–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberkorn, I.; Walser, J.C.; Helisch, H.; Böcker, L.; Belz, S.; Schuppler, M.; Fasoulas, S.; Mathys, A. Characterization of Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae) associated microbial communities. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Song, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Su, K.; Liu, N.; Mou, Y.; Lu, T. Comparison of heterotrophic and mixotrophic Chlorella pyrenoidosa cultivation for the growth and lipid accumulation through acetic acid as a carbon source. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tang, T.; Umagiliyage, A.L.; Siddaramu, T.; McCarroll, M.; Choudhary, R. Utilization of sorghum bagasse hydrolysates for producing microbial lipids. Appl. Energ. 2012, 91, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wen, H.; Zheng, J.; Fu, C.; Chen, C.; Cai, D.; Qin, P.; Wang, Z. A combination of evaporation and chemical preservation for long-term storage of fresh sweet sorghum juice and subsequent bioethanol production. J. Food. Process. Pres. 2018, 42, e13825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xiong, J.; Yang, X.; Siddique, K.H.; Du, T. Carbon footprint analysis of sweet sorghum-based bioethanol production in the potential saline-Alkali land of northwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Nkansah, N.B.; Li, J.; Rooney, W.; Wang, D. A review of sweet sorghum as a viable renewable bioenergy crop and its techno-economic analysis. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphy, M.P.; Anjali, K.B.; Vivek, N.; Thirumalesh, B.V.; Sindhu, R.; Pugazhendi, A.; Pandey, A.; Binod, P. Sweet sorghum juice as an alternative carbon source and adaptive evolution of Lactobacillus brevis NIE9. 3.3 in sweet sorghum juice and biodiesel derived crude glycerol to improve 1,3 propanediol production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Lu, I.-C.; Nagarajan, D.; Chang, C.-H.; Ng, I.-S.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. A highly efficient two-stage cultivation strategy for lutein production using heterotrophic culture of Chlorella sorokiniana MB-1-M12. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Gao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, H.; Peng, H. Heterotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using broken rice hydrolysate as carbon source for biomass and pigment production. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zou, G.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, R.; Yan, H.; Cao, L.; Liu, T.; Ruan, R. Enhancement of nutrients removal and biomass accumulation of Chlorella vulgaris in pig manure anaerobic digestate effluent by the pretreatment of indigenous bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ruan, R.; Zhang, Q. Effects of microalgae-bacteria inoculation ratio on biogas slurry treatment and microorganism interactions in the symbiosis system. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiang, S.; Cao, L.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Characterization of additional zinc ions on the growth, biochemical composition and photosynthetic performance from Spirulina platensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovchenko, A.; Merzlyak, M.N.; Khozin Goldberg, I.; Cohen, Z.; Boussiba, S. Coordinated carotenoid and lipid syntheses induced in Parietochloris incisa (chlorophyta, trebouxiophyceae) mutant deficient in δ5 desaturase by nitrogen starvation and high light. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, J. Breeding of high protein Chlorella sorokiniana using protoplast fusion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, G.; Rao, X.; Chen, L.; Jian, H.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z.; Chen, B. Microalga Isochrysis galbana in feed for Trachinotus ovatus: Effect on growth performance and fatty acid composition of fish fillet and liver. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cui, Q.; Lu, Y. Artificial creation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa mutants for economic sustainable food production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Erickson, J.; Sollenberger, L.; Woodard, K.; Vendramini, J.; Fedenko, J. Mineral composition and biomass partitioning of sweet sorghum grown for bioenergy in the southeastern USA. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Sun, H.; Chen, M.; Lu, S.; Li, P. Effects of various organic carbon sources on the growth and biochemical composition of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 173, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Gao, S.; Lopez, P.A.; Ogden, K.L. Effects of pH on cell growth, lipid production and CO2 addition of microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana. Algal. Res. 2017, 28, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, O.; Escalante, F.M.; De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products. Water Res. 2011, 45, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lin, W.; Liu, J.; Luo, J. Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella for biomass production by using pH-stat culture medium: Glucose-Acetate-Phosphorus (GAP). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: Status and prospects. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jing, F.; Wu, D.; Xiao, B.; Hu, Z. Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus by a novel aerobic denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating bacterium, Pseudomonas stutzeri ADP-19. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Singh, D. Photosynthetic efficiency and compositional alterations in microalgae Chlorella vulgaris in response to changes in the pH condition. Vegetos 2021, 34, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Waller, P.; Khawam, G.; Attalah, S.; Huesemann, M.; Ogden, K. Incorporation of salinity, nitrogen, and shading stress factors into the Huesemann algae biomass growth model. Algal Res. 2018, 35, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ogden, K. Nitrogen balances and impacts on the algae cultivation-extraction-digestion-cultivation process. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Wei, L.; Huang, S.; Xu, J. Genome editing of model oleaginous microalgae Nannochloropsis spp. by CRISPR/Cas9. Plant J. 2016, 88, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, P.; Chen, T.; Chen, F. Microalgal carotenoids: Beneficial effects and potential in human health. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Yan, W.; Jin, Y.; Chen, F.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X. Biochemical wastewater from landfill leachate pretreated by microalgae achieving algae’s self-reliant cultivation in full wastewater-recycling chain with desirable lipid productivity. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, M.B.; Chinn, M.S.; Veal, M.W. Processing of materials derived from sweet sorghum for biobased products. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 37, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netsun Raw Material Trading Center. Available online: https://www.rawmex.cn/ (accessed on 18 August 2022).
| Ingredient | Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSE | HSE+N | HSE+M | HSE+N+M | SE+N+M | BG-11+glu | |
| Nitrogen source and mineral | ||||||
| NaNO3 (g/L) | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 | ||
| K2HPO4 (g/L) | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.040 | ||
| MgSO4·7H2O (g/L) | 0.075 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 0.075 | ||
| CaCl2·2H2O (g/L) | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.036 | ||
| Citric acid (g/L) | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||
| Ferric ammonium citrate (g/L) | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||
| EDTA·2Na (g/L) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| Na2CO3 (g/L) | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 | ||
| A5 (mL/L) a | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Carbon source | ||||||
| Glucose (g/L) | 10.000 | |||||
| SE (g/L) | 11.400 | |||||
| HSE (g/L) | 10.700 | 10.700 | 10.700 | 10.700 | ||
| Component | Treatment | |
|---|---|---|
| SE | HSE | |
| Reducing sugar (g/L) | 56.75 ± 2.41 b | 86.69 ± 2.18 a |
| Fructose (g/L) | 31.28 ± 2.09 b | 42.25 ± 0.52 a |
| Total carbon (g/L) | 32.39 ± 0.00 b | 34.21 ± 0.00 a |
| Total organic carbon (g/L) | 32.05 ± 0.00 b | 34.04 ± 0.00 a |
| Inorganic carbon (g/L) | 0.34± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.05 b |
| Total nitrogen (g/L) | 0.18 ± 0.00 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 a |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 62.15 ± 0.15 a | 61.40 ± 1.20 a |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 632.30 ± 2.90 a | 658.40 ± 8.00 a |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 177.75 ± 7.65 a | 170.25 ± 2.55 a |
| Cuprum (mg/L) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Zine (mg/L) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Treatment | Generation Time (d) | Biomass Productivity (g/L/d) | Max Biomass (g/L) | Growth Yield (g Biomass/g TOC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSE | 0.56 ± 0.02 a | 0.09 ± 0.00 e | 0.54 ± 0.02 e | 0.85 ± 0.01 d |
| HSE+N | 0.35 ± 0.01 b | 0.25 ± 0.02 d | 1.53 ± 0.14 d | 1.23 ± 0.03 b |
| HSE+M | 0.55 ± 0.02 a | 0.10 ± 0.00 e | 0.60 ± 0.02 e | 0.79 ± 0.01 d |
| HSE+N+M | 0.29 ± 0.00 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 b | 2.51 ± 0.15 b | 1.30 ± 0.02 a |
| SE+N+M | 0.31 ± 0.01 c | 0.34 ± 0.00 c | 2.04 ± 0.02 c | 1.30 ± 0.02 a |
| BG-11+glu | 0.31 ± 0.01 c | 0.52 ± 0.01 a | 3.14 ± 0.07 a | 1.00 ± 0.03 c |
| Treatment | Chl-a Content (mg/g) | Carotenoid Content (mg/g) | Lutein Content (mg/g) | Protein Content (g/g) | Lipid Content (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSE | 11.09 ± 0.36 b | 4.56 ± 0.12 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 c | - | - |
| HSE+N | 13.33 ± 1.53 ab | 5.33 ± 0.49 a | 0.55 ± 0.07 a | 0.37 ± 0.01 d | 0.18 ± 0.01 a |
| HSE+M | 8.59 ± 0.88c | 3.74 ± 0.27 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 c | - | - |
| HSE+N+M | 13.99 ± 0.16 a | 5.05 ± 0.15 a | 0.40 ± 0.01 b | 0.54 ± 0.00 b | 0.16 ± 0.00 ab |
| SE+N+M | 13.90 ± 1.03 a | 5.07 ± 0.38 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 ab | 0.58 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 b |
| BG-11+glu | 7.79 ± 0.24 c | 3.18 ± 0.13 b | 0.15 ± 0.02 c | 0.41 ± 0.01 c | 0.13 ± 0.00 c |
| Estimate | Unit Price (USD/kg) | HSE+N+M | SE+N+M | BG-11+glu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass yield (kg/103 L medium) | 2.175 | 1.642 | 2.967 | |
| NaNO3 amount (kg/103 L medium) | 0.537 a | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 |
| K2HPO4 amount (kg/103 L medium) | 2.385 a | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.040 |
| MgSO4·7H2O amount (kg/103 L medium) | 0.146 a | 0.075 | 0.075 | 0.075 |
| CaCl2·2H2O amount (kg/103 L medium) | 0.188 a | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.036 |
| Citric acid amount (kg/103 L medium) | 2.086 a | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| Ferric ammonium citrate amount (kg/103 L medium) | 7.452 a | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| EDTA·2Na amount (kg/103 L medium) | 4.322 a | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Na2CO3 amount (kg/103 L medium) | 0.402 a | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| Minerals cost for 1 kg biomass (USD) c | 0.454 | 0.601 | 0.333 | |
| Glucose amount (kg/103 L medium) | 0.715 a | 10.000 | ||
| Sweet sorghum stalk amount (kg/103 L medium) d | 0.019 b | 5.632 | 6.000 | |
| Carbon source cost for 1 kg biomass (USD) | 0.050 | 0.071 | 2.411 | |
| Sucrase amount (kg/103 L medium) | 23.845 a | 0.011 | ||
| Heating cost of enzymatic hydrolysis (USD) | 0.213 e | |||
| Other cost for 1 kg biomass (USD) | 0.330 | - | - | |
| Total cost for 1 kg biomass (USD) | 0.834 | 0.672 | 2.744 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Fang, Y.; Hong, B.; Cai, Y.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, R.; et al. Enhancement of Carbon Conversion and Value-Added Compound Production in Heterotrophic Chlorella vulgaris Using Sweet Sorghum Extract. Foods 2022, 11, 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172579
Wu K, Fang Y, Hong B, Cai Y, Xie H, Wang Y, Cui X, Yu Z, Liu Y, Ruan R, et al. Enhancement of Carbon Conversion and Value-Added Compound Production in Heterotrophic Chlorella vulgaris Using Sweet Sorghum Extract. Foods. 2022; 11(17):2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172579
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kangping, Yilin Fang, Biyuan Hong, Yihui Cai, Honglei Xie, Yunpu Wang, Xian Cui, Zhigang Yu, Yuhuan Liu, Roger Ruan, and et al. 2022. "Enhancement of Carbon Conversion and Value-Added Compound Production in Heterotrophic Chlorella vulgaris Using Sweet Sorghum Extract" Foods 11, no. 17: 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172579
APA StyleWu, K., Fang, Y., Hong, B., Cai, Y., Xie, H., Wang, Y., Cui, X., Yu, Z., Liu, Y., Ruan, R., & Zhang, Q. (2022). Enhancement of Carbon Conversion and Value-Added Compound Production in Heterotrophic Chlorella vulgaris Using Sweet Sorghum Extract. Foods, 11(17), 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172579










