Visual Detection of Chicken Adulteration Based on a Lateral Flow Strip-PCR Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Meat Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.3.1. CTAB Method
2.3.2. Salt Method
2.3.3. Urea Method
2.3.4. SDS Method
2.3.5. Guanidine Isothiocyanate Method
2.3.6. Tiangen Method
2.4. Primer Design
2.5. PCR Amplification
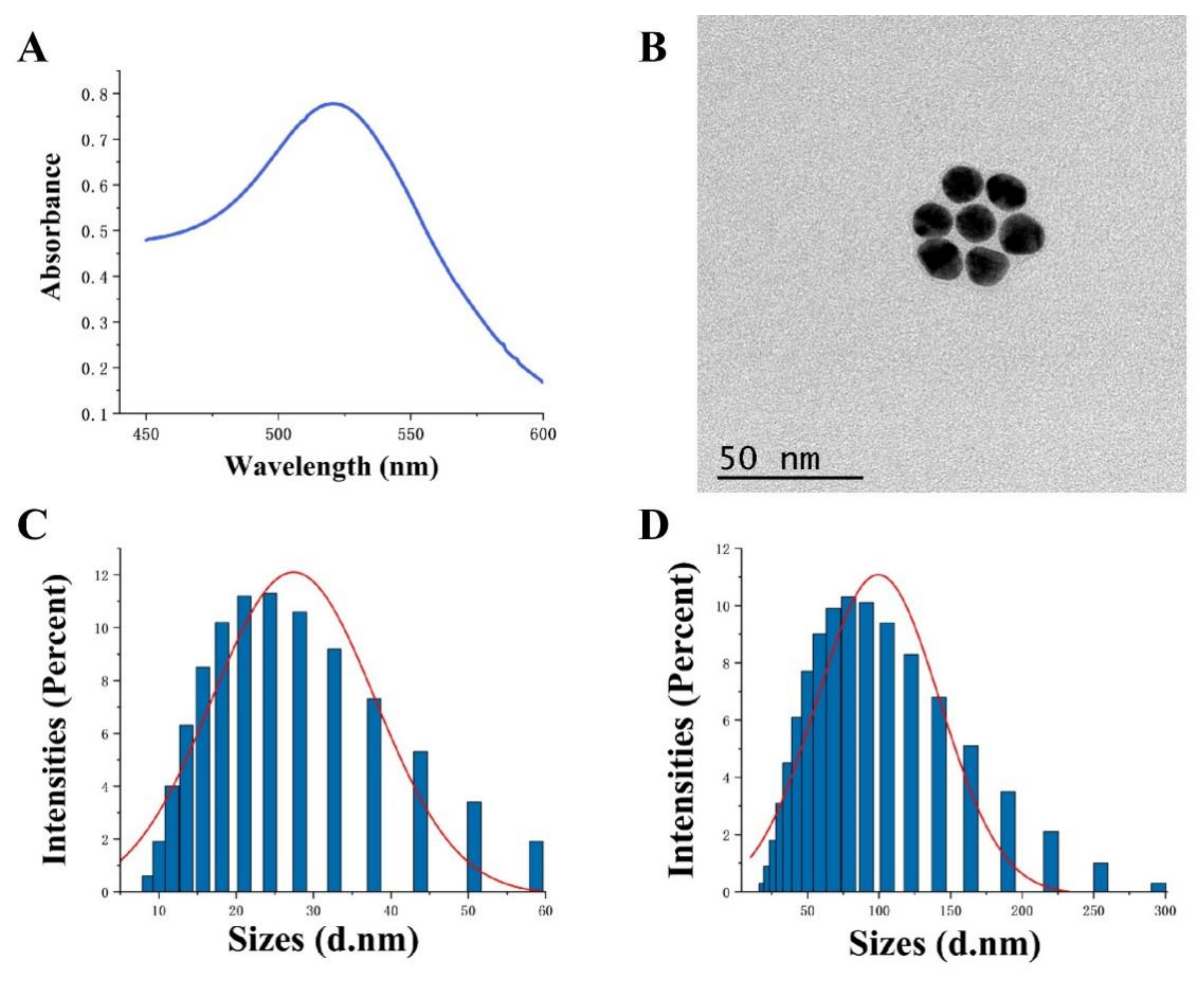
2.6. Synthesis of AuNPs and AuNPs-SA
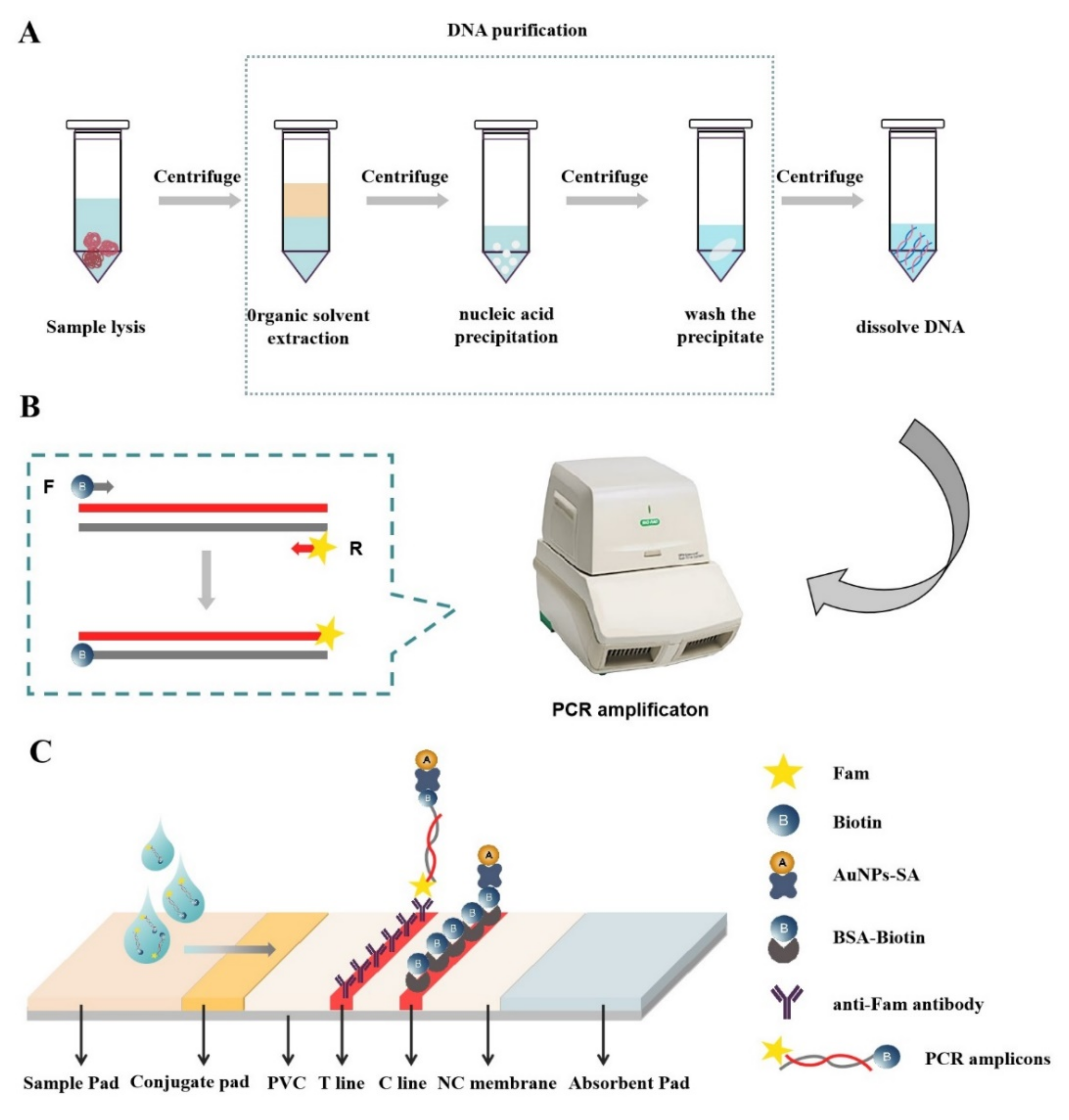
2.7. Test Strip Fabrication
2.8. PCR-LFS Assay
2.9. Specificity and Sensitivity Detection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
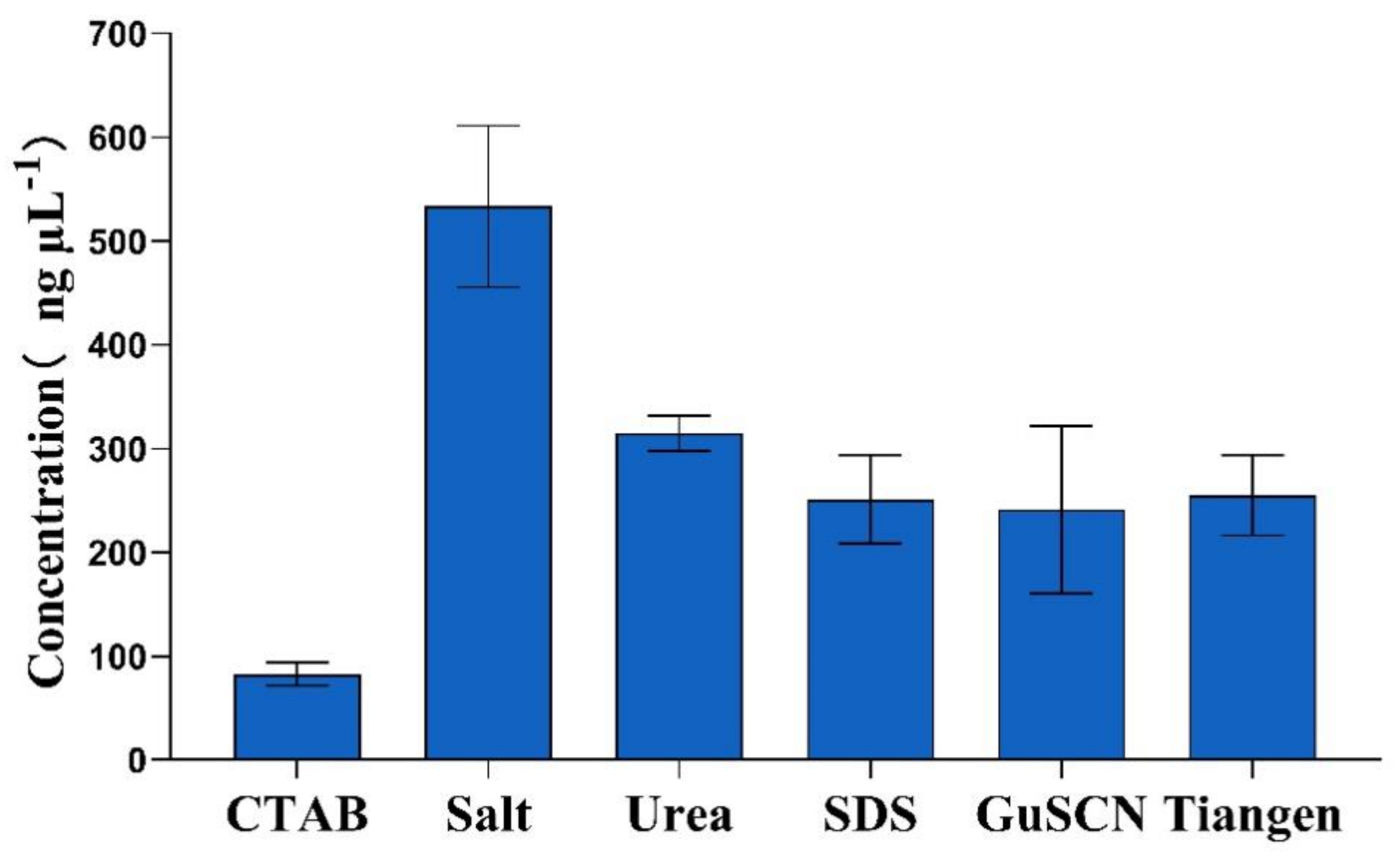
3.1. DNA Concentration and Purity
3.2. Characterization of AuNPs
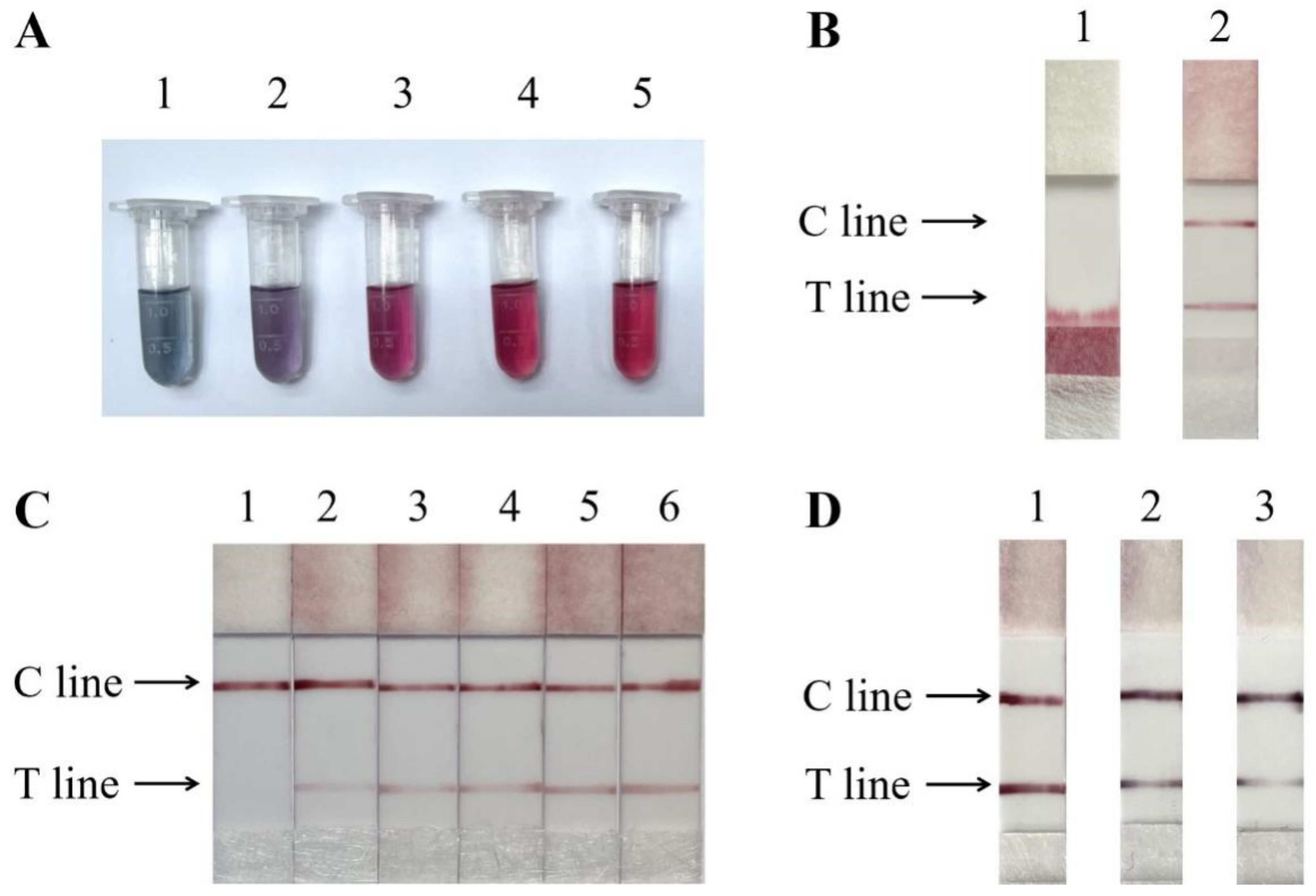
3.3. Optimization of Lateral Flow Strips
3.4. Specificity of the Test Strip Method
3.5. Sensitivity of the Test Strip Method
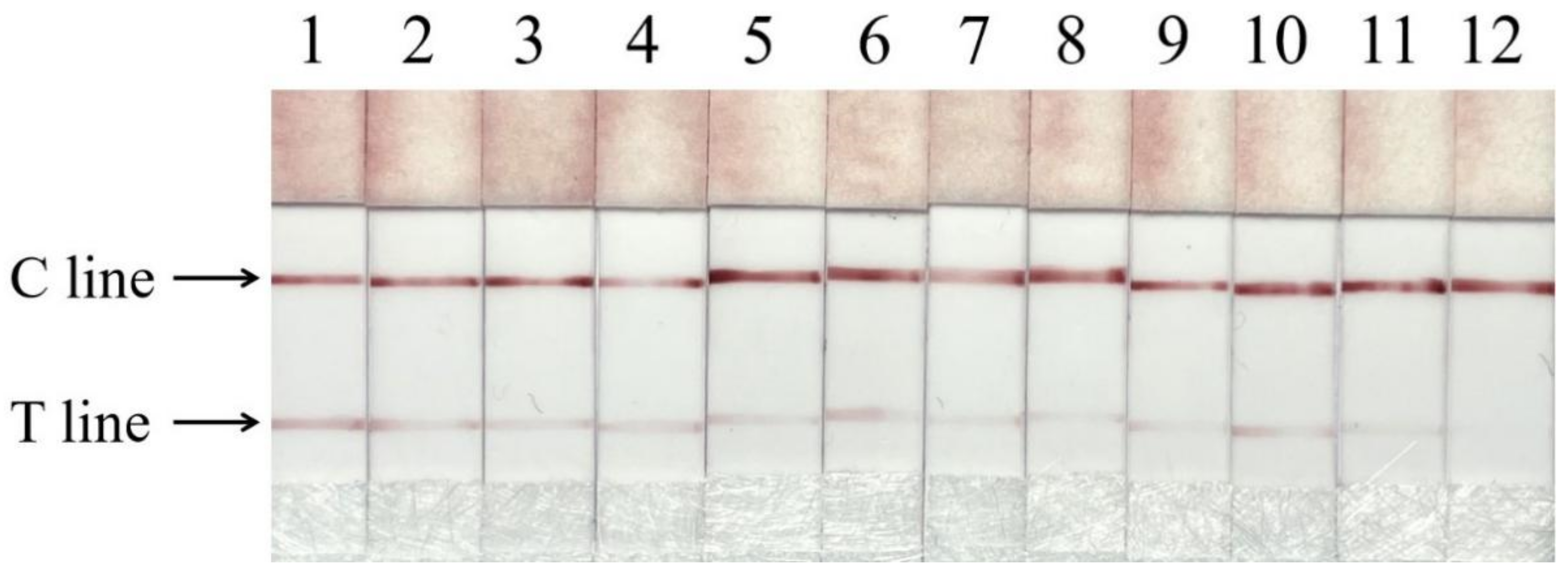
3.6. Meat Sample Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Mahony, P.J. Finding horse meat in beef products—A global problem. QJM 2013, 106, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, C.; Zhao, W.; Ren, N.; Guo, W.; Wang, S. Rapid LC-MS/MS method for the detection of seven animal species in meat products. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Choi, Y.; Oh, H.; Yoon, Y. Identification of Pork Adulteration in Processed Meat Products Using the Developed Mitochondrial DNA-Based Primers. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, P.; Qu, W.; Xu, J.; Qiao, D.; Yao, L.; Xue, F.; Chen, W. A sensitive multiplex PCR protocol for simultaneous detection of chicken, duck, and pork in beef samples. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Meng, F.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.M. Comparative review and the recent progress in detection technologies of meat product adulteration. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2256–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Fuller, D.; Hsieh, Y.P.; Rao, Q. Monoclonal antibody-based ELISA for the quantification of porcine hemoglobin in meat products. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengou, L.-C.; Lianou, A.; Tsakanikas, P.; Mohareb, F.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Detection of Meat Adulteration Using Spectroscopy-Based Sensors. Foods 2021, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, B.; Bjelak, A.; Velioglu, H.M.; Boyaci, I.H. Protein based evaluation of meat species by using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Brunius, C.; Chevallier, O.; Dervilly, G.; Elliott, C.; Guitton, Y.; Prenni, J.E.; Savolainen, O.; Hemeryck, L.; Vidkjaer, N.H.; et al. Making complex measurements of meat composition fast: Application of rapid evaporative ionisation mass spectrometry to measuring meat quality and fraud. Meat Sci. 2021, 181, 108333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachniuk, A.; Sumara, A.; Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Bottom-up Proteomic Methods in Animal Species Analysis of Processed Meat for Food Authentication and the Detection of Adulterations. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 40, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai-Kastoori, L.; Schutz-Geschwender, A.R.; Harford, J.A. A systematic approach to quantitative Western blot analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 593, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Feng, N.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M. Development of a PCR-based lateral flow strip assay for the simple, rapid, and accurate detection of pork in meat and meat products. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.M.K.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Johan, M.R.B. Short targeting multiplex PCR assay to detect and discriminate beef, buffalo, chicken, duck, goat, sheep and pork DNA in food products. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benli, H.; Barutçu, E. Sequential use of real-time polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques verifies adulteration of fermented sausages with chicken meat. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Peng, C.; Xu, X.; Pei, X.; Xu, J.; Li, L. Development of a Duck Genomic Reference Material by Digital PCR Platforms for the Detection of Meat Adulteration. Foods 2021, 10, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhong, G.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Molecular Authentication of Twelve Meat Species Through a Promising Two-Tube Hexaplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Technique. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 813962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jainonthee, C.; Chaisowwong, W.; Ngamsanga, P.; Wiratsudakul, A.; Meeyam, T.; Pichpol, D. A Cutoff Determination of Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for End-Point Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in Chicken Meat. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Feng, T.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, J. Cross-priming isothermal amplification combined with nucleic acid test strips for detection of meat species. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 597, 113672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jalbani, Y.M.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, A. Rapid authentication of mutton products by recombinase polymerase amplification coupled with lateral flow dipsticks. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 290, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Ji, Y.; Wei, W.; Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Sun, M.; Xu, J. Development and Application of a Visual Duck Meat Detection Strategy for Molecular Diagnosis of Duck-Derived Components. Foods 2022, 11, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q.; Ma, H.; Yuan, X.; Gao, J.; Cao, J.; Pan, D. A Simple and Reliable Single Tube Septuple PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Seven Meat Species. Foods 2021, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Leng, Y.; Hao, L.; Duan, H.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Self-assembled colloidal gold superparticles to enhance the sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassays with sandwich format. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3737–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, K.; Yamakoshi, Y.; Futo, S. Single-Laboratory Validation of Rapid and Easy DNA Strip for Porcine DNA Detection in Beef Meatballs. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiati, M.; Myridaki, V.M.; Christopoulos, T.K.; Kalogianni, D.P. Lateral flow test for meat authentication with visual detection. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Wei, S.; Yang, H.; Yin, R. Polymerase chain reaction with lateral flow sensor assay for the identification of horse meat in raw and processed meat products. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseneau, J.R.; Steeves, R.; Laflamme, M. Modified low-salt CTAB extraction of high-quality DNA from contaminant-rich tissues. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçınkaya, B.; Yumbul, E.; Mozioğlu, E.; Akgoz, M. Comparison of DNA extraction methods for meat analysis. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Du, M.; Ming, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, Y. Comparison of the effects of two methods for four animal musclar tissue DNA extraction. Shipin Gongye Keji 2011, 32, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Qiao, D.; Xu, J.; Song, Q.; Yao, L.; Lu, J.; Chen, W. Rapid visual sensing and quantitative identification of duck meat in adulterated beef with a lateral flow strip platform. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MozİOĞLu, E.; AkgÖZ, M.; Tamerler, C.; KocagÖZ, Z.T. A simple guanidinium isothiocyanate method for bacterial genomic DNA isolation. Turk. J. Biol. 2014, 38, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Mason, M.G.; Wang, Y.; Wee, E.; Turni, C.; Blackall, P.J.; Trau, M.; Botella, J.R. Nucleic acid purification from plants, animals and microbes in under 30 seconds. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2003916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.A.; Khlebtsov, N.G. Biomedical Applications of Multifunctional Gold-Based Nanocomposites. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min-xuan, L.; Xing-ran, Z.; Lu, Y.; Hao-zhi, L.; Xiang-hong, W. A gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic assay for rapid determination of cephalexin in animal-derived foods. Shipin Yanjiu Yu Kaifa 2020, 41, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Cascade-Enhanced Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Sensitive Detection of Okadaic Acid in Seawater, Fish, and Seafood. Foods 2022, 11, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Touchdown Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018, 2018, pdb. prot095133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, H.A.; Fathi, M.M.; Sadek, M.A. Using cytochrome b gene of mtDNA as a DNA barcoding marker in chicken strains. Mitochondrial DNA 2015, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Vostrikova, N.L.; Chernukha, I.M.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. Lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of undeclared chicken meat in meat products. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesmen, Z.; Yetiman, A.E.; Sahin, F.; Yetim, H. Detection of chicken and turkey meat in meat mixtures by using real-time PCR assays. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C167–C173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, R.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Ultrasensitive direct competitive FLISA using highly luminescent quantum dot beads for tuning affinity of competing antigens to antibodies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 972, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, M.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Jin, J.; Jiang, C.; Yu, W.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J. Ultrasensitive Competitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay with Visual Semiquantitative Inspection and Flexible Quantification Capabilities. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. A smartphone-based dual detection mode device integrated with two lateral flow immunoassays for multiplex mycotoxins in cereals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 158, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, C.; Li, S.; Yuan, L.; Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Wan, J.; Yu, C. Quantum dots’ size matters for balancing their quantity and quality in label materials to improve lateral flow immunoassay performance for C-reactive protein determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Xu, J.; Yao, L.; Wu, Q.; Yan, C.; Lu, J.; Yao, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, W. Simultaneous and accurate visual identification of chicken, duck and pork components with the molecular amplification integrated lateral flow strip. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, P.; Dong, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Zhu, H.; Dong, J.; Gao, S. An isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow strip combined method for rapid on-site detection of Vibrio vulnificus in raw seafood. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Yu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M. Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Three Foodborne Pathogens in Seafood. Foods 2020, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, S.; Kumar, R.R.; Mendiratta, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Rana, P.; Kumar, D.; Jawla, J. Species-specific loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for identification of tissue of cattle origin by targeting mitochondrial gene sequences. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

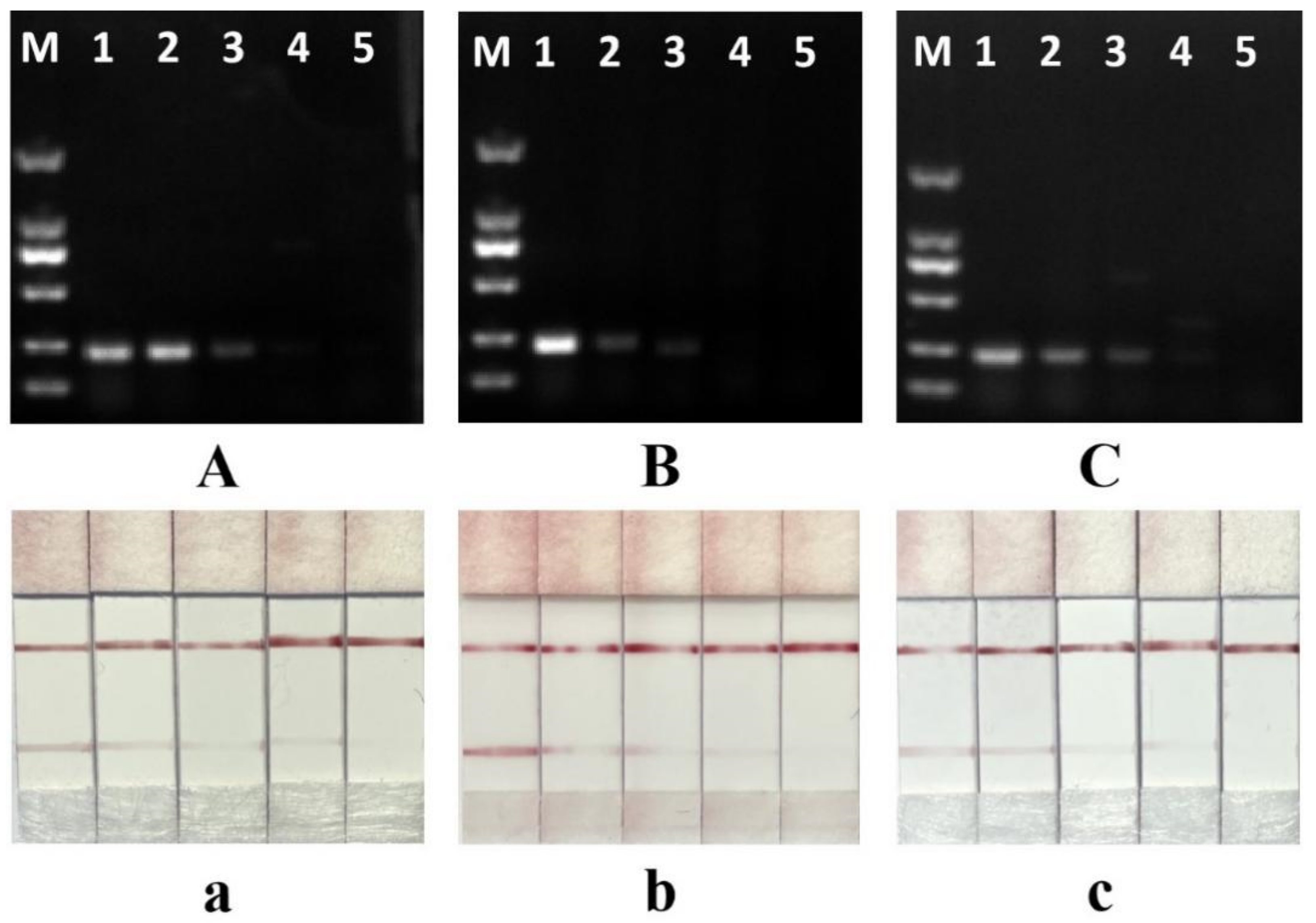
| Chicken Adulteration Ratio | 100% | 10% | 1% | 0.1% | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beef mixed with chicken | 300 mg chicken | 270 mg beef + 30 mg chicken | 297 mg beef + 3 mg chicken | 299.7 mg beef + 0.3 mg chicken | 300 mg beef |
| Lamb mixed with chicken | 300 mg chicken | 270 mg lamb + 30 mg chicken | 297 mg lamb + 3 mg chicken | 299.7 mg lamb + 0.3 mg chicken | 300 mg lamb |
| Beef, lamb and ostrich meat mixed with chicken | 300 mg chicken | 90 mg beef + 90 mg lamb + 90 mg ostrich + 30 mg chicken | 99 mg beef + 99 mg lamb + 99 mg ostrich + 3 mg chicken | 99.9 mg beef + 99.9 mg lamb + 99.9 mg ostrich + 0.3 mg chicken | 100 mg beef + 100 mg lamb + 100 mg ostrich |
| Method | DNA Concentration ± SD 1 (ng µL−1) | Mean Ratio A260/A280 | Mean Ratio A260/A230 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTAB method | 70.0 ± 9.7 c | 1.5 ± 0.03 | 0.5 ± 0.10 |
| Salt method | 533 ± 84 a | 2.0 ± 0.09 | 2.8 ± 0.82 |
| Urea method | 314 ± 13 a,b | 1.9 ± 0.09 | 2.0 ± 0.19 |
| SDS method | 251 ± 58 b | 2.0 ± 0.01 | 2.4 ± 0.28 |
| Guanidine isothiocyanate method | 241 ± 75 b | 1.8 ± 0.15 | 1.8 ± 0.07 |
| Kit method | 289 ± 11 a,b | 2.0 ± 0.02 | 2.4 ± 0.34 |
| Type | Name | Samples Number | Adulteration Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef products | Beef skewers, beef rolls, beef meatballs | 30 | 6 |
| Lamb products | Lamb skewers, lamb rolls | 18 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Lan, H.; Pan, D.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Visual Detection of Chicken Adulteration Based on a Lateral Flow Strip-PCR Strategy. Foods 2022, 11, 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152351
Xu H, Lan H, Pan D, Xu J, Wang X. Visual Detection of Chicken Adulteration Based on a Lateral Flow Strip-PCR Strategy. Foods. 2022; 11(15):2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152351
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Haoyi, Hangzhen Lan, Daodong Pan, Junfeng Xu, and Xiaofu Wang. 2022. "Visual Detection of Chicken Adulteration Based on a Lateral Flow Strip-PCR Strategy" Foods 11, no. 15: 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152351
APA StyleXu, H., Lan, H., Pan, D., Xu, J., & Wang, X. (2022). Visual Detection of Chicken Adulteration Based on a Lateral Flow Strip-PCR Strategy. Foods, 11(15), 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152351







