Effective Adsorption of Colorants from Sugarcane Juice by Bagasse-Based Biochar-Hydroxyapatite Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bagasse Biochar (BBC)
2.2. Synthesis of Bagasse Biochar Coated Hydroxyapatite (BBC-HAP) Composite
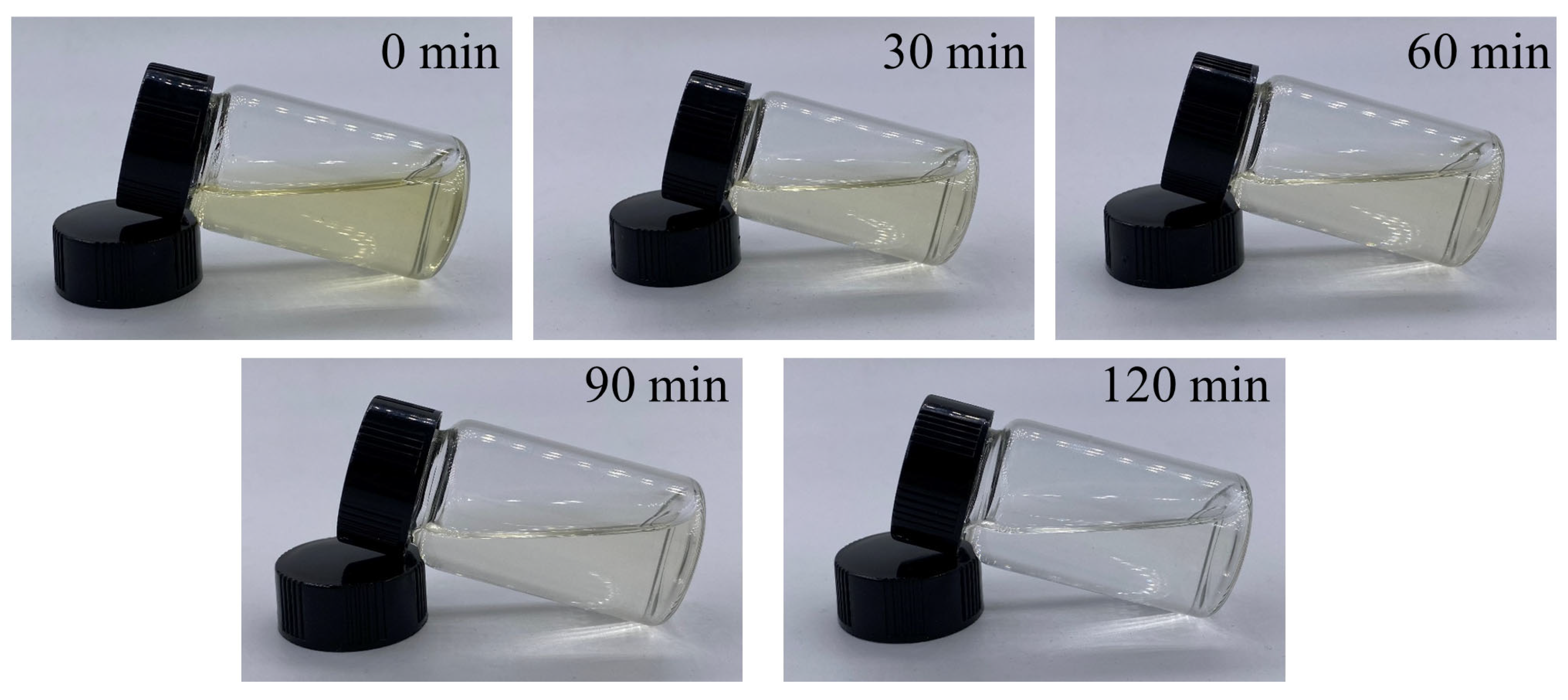
2.3. Extraction of Colorant from Sugarcane Juice
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Colorant
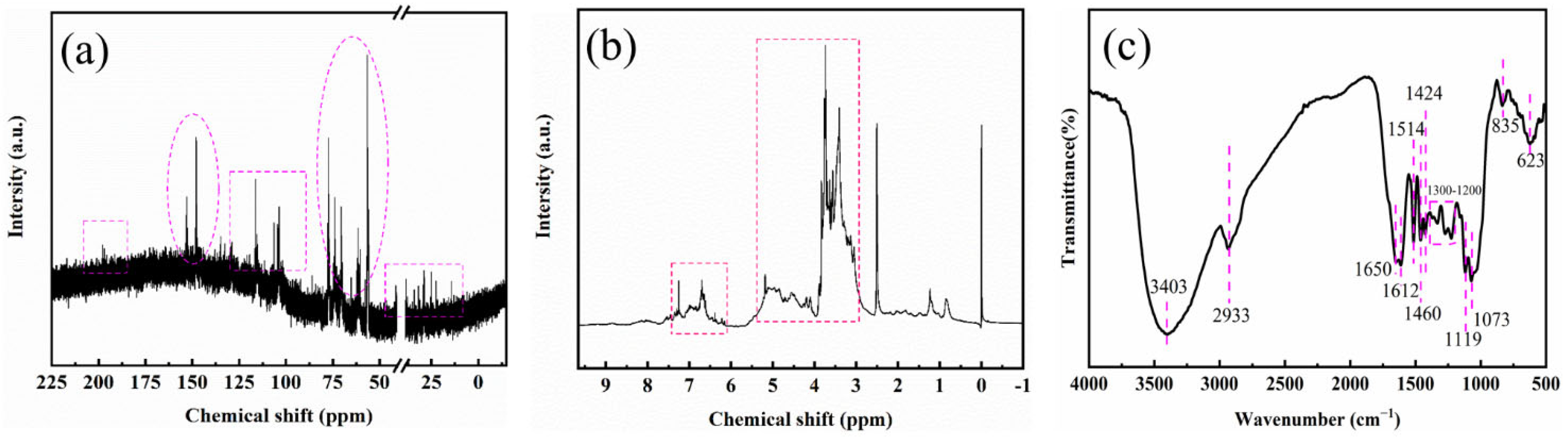
3.1.1. NMR Analysis
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis of Colorant
3.2. Characterization of BBC-HAP
3.2.1. SEM-EDX and TEM Analysis
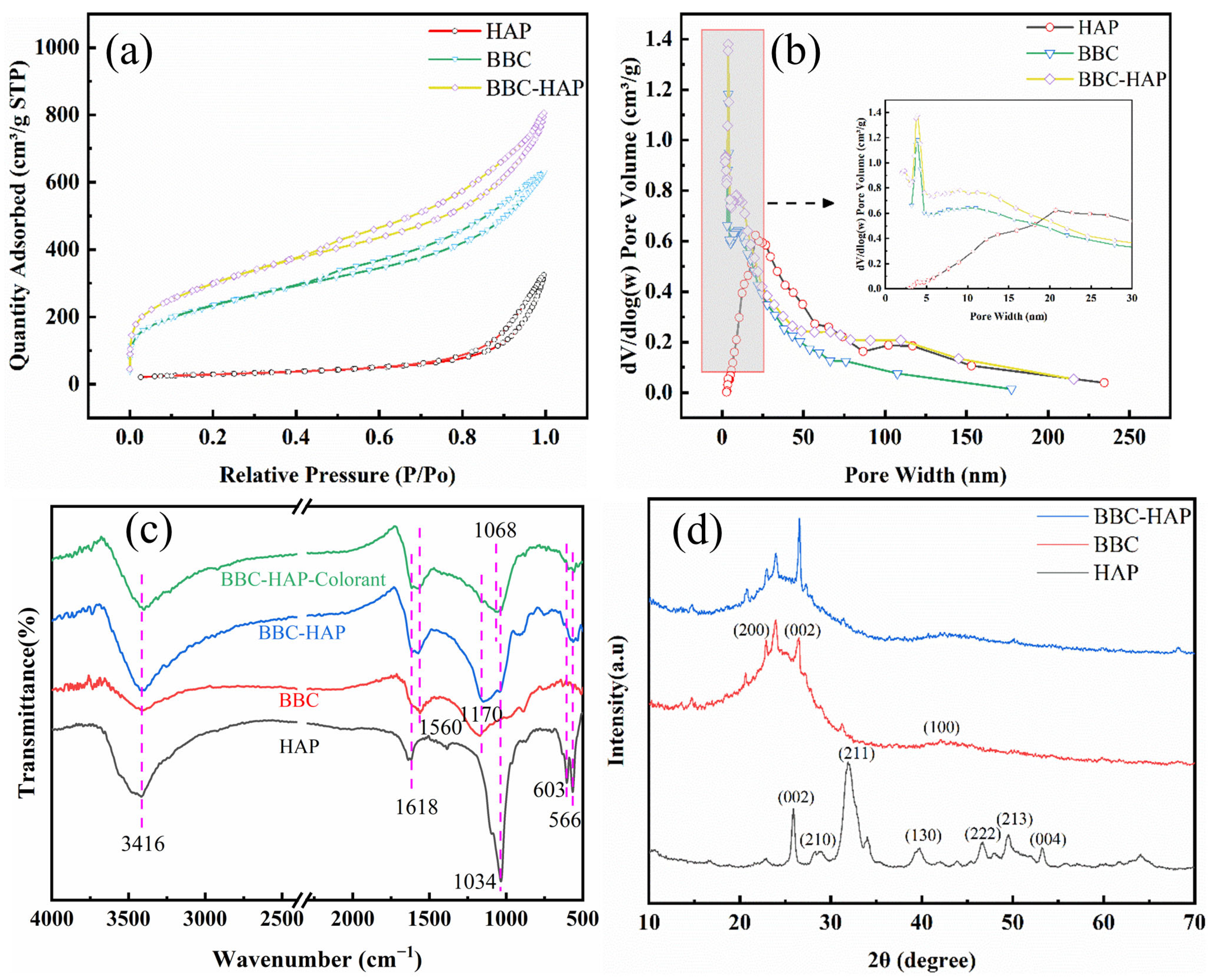
3.2.2. N2 Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
3.2.3. FTIR Analysis of HAP, BBC, BBC-HAP and BBC-HAP-Colorant
3.2.4. XRD Analysis
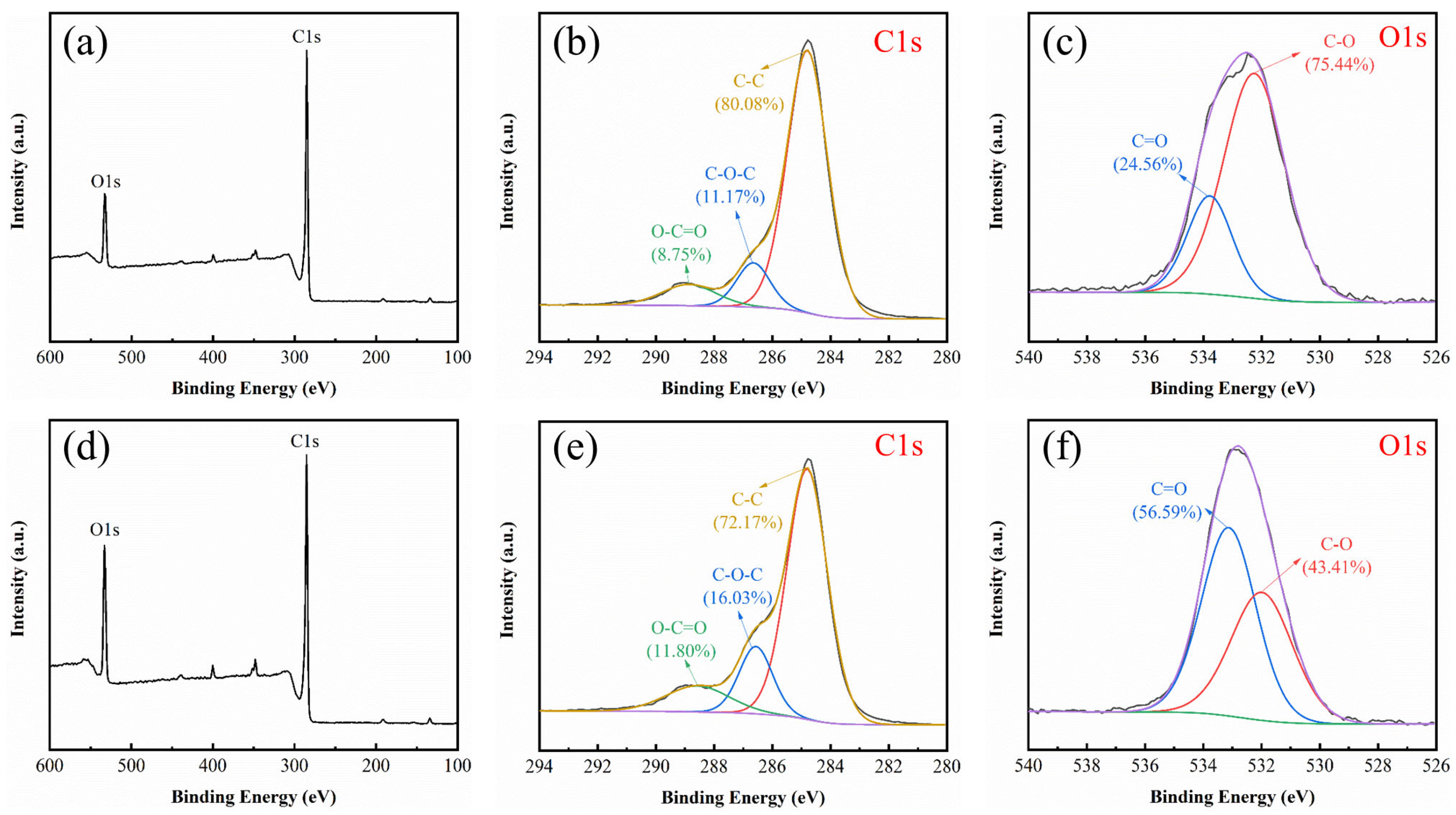
3.2.5. XPS Analysis of BBC-HAP and BBC-HAP-Colorant
3.3. Adsorption Experiments
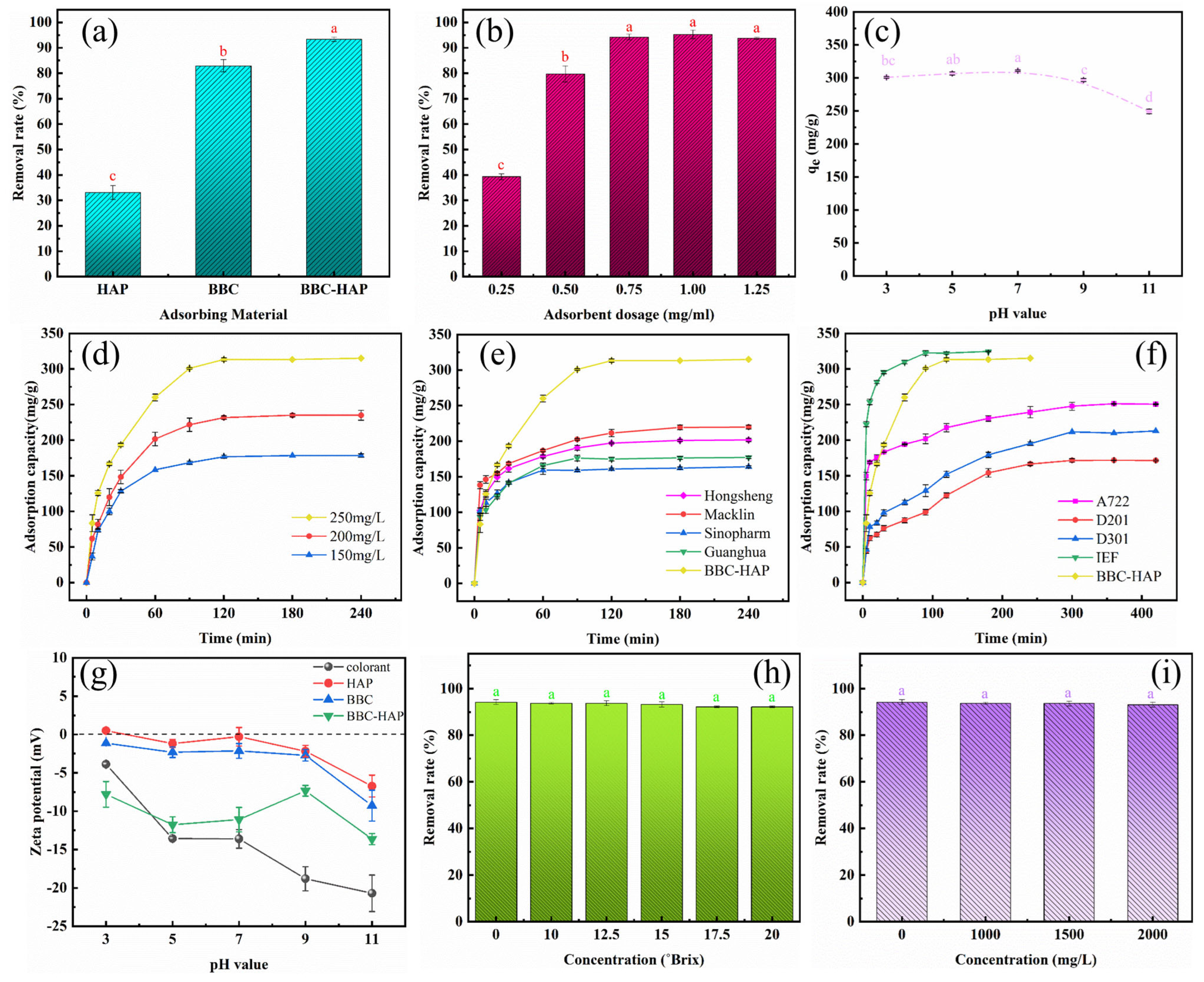
3.3.1. Effect of Adsorbing Materials
3.3.2. Effect of BBC-HAP Dosage
3.3.3. Effect of pH
3.3.4. Effects of Contact Time and Initial Colorant Concentration
3.3.5. Comparison of Performance with Activated Carbon, Commercial Resin and Ion Exchange Fiber
3.3.6. Effect of Sucrose Solution and Potassium Ion Concentration
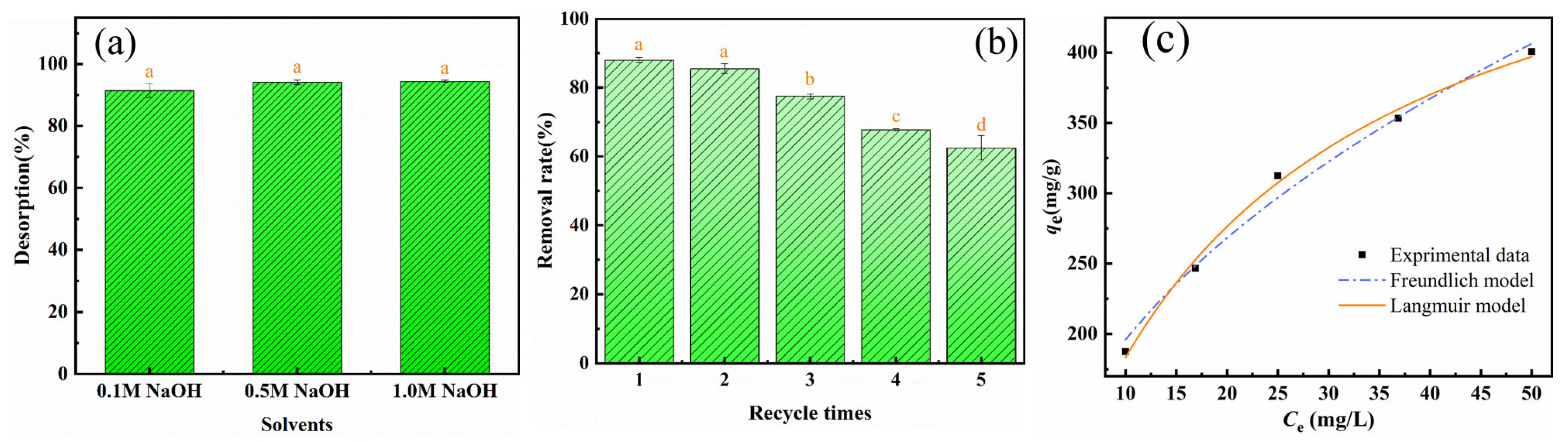
3.3.7. Desorption and Regeneration
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
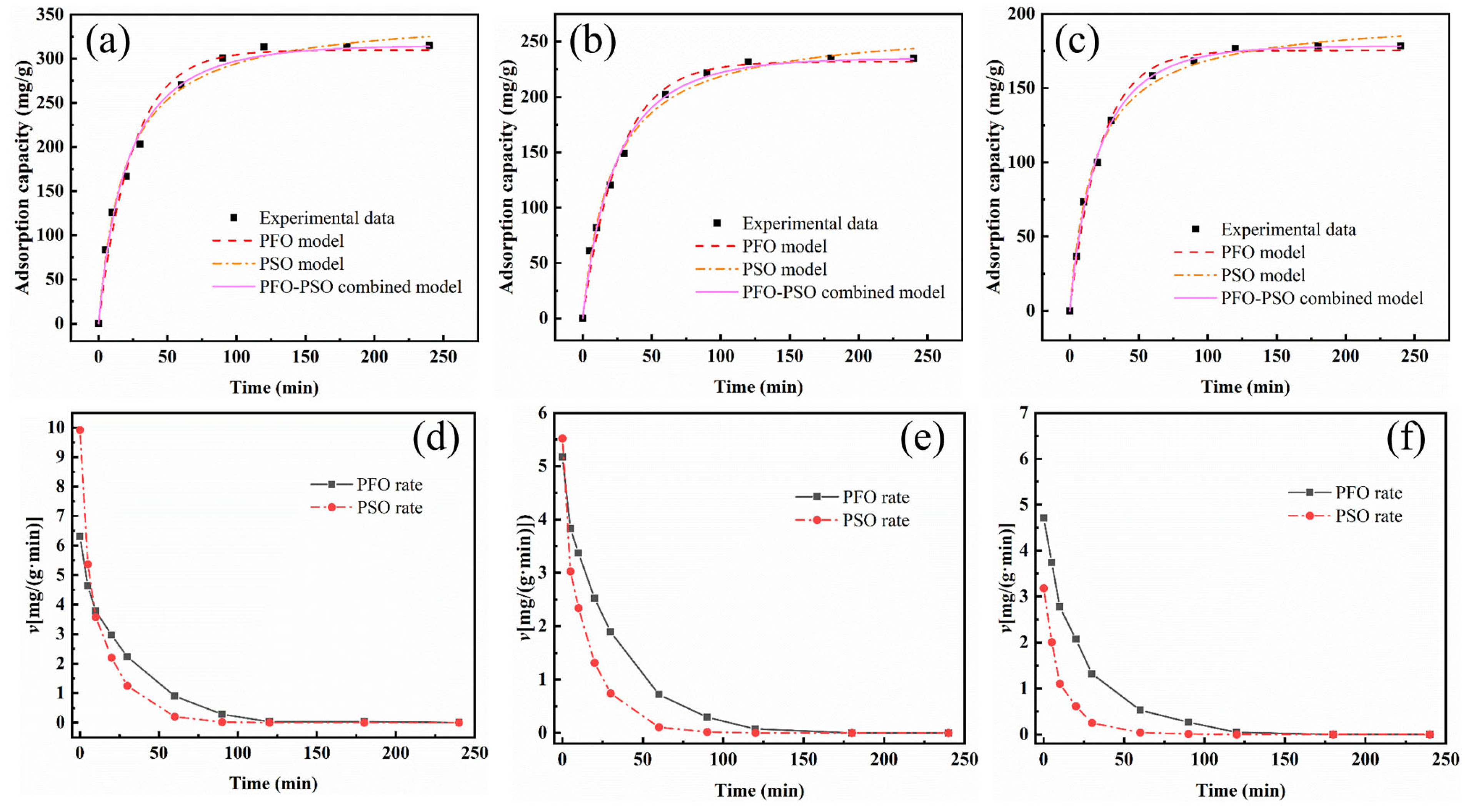
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
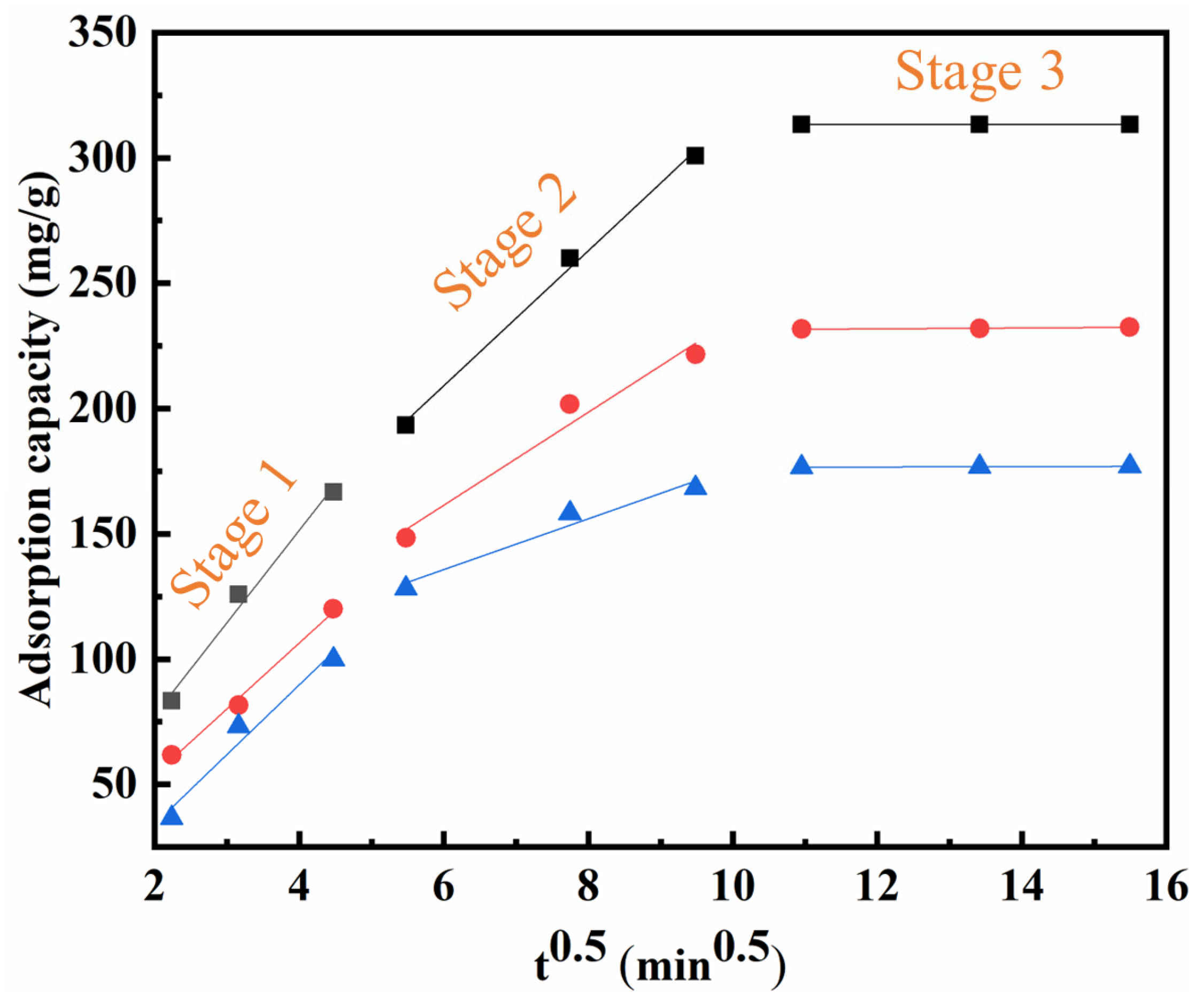
3.6. Mass Transfer Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, T.; Yu, S.; Chen, J. Optimization design of cane sugar evaporative crystallizer based on orthogonal test and computational fluid dynamics. J. Food Process. Eng. 2020, 43, 313355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindl, R.J. The clarification of cane juice. Int. Sugar J. 1999, 101, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Chai, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, X. Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan-modified diatomite for the removal of gallic acid and caffeic acid from sugar solution. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 219, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coca, M.; García, M.T.; Mato, S.; Cartón, Á.; González, G. Evolution of colorants in sugarbeet juices during decolorization using styrenic resins. J. Food Eng. 2008, 89, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Rackemann, D.W.; Moghaddam, L.; Wei, B.; Li, K.; Lu, H.; Xie, C.; Hang, F.; Doherty, W.O.S. Ceramic membrane filtration of factory sugarcane juice: Effect of pretreatment on permeate flux, juice quality and fouling. J. Food Eng. 2019, 243, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fechter, W.L.; Kitching, S.M.; Rajh, M.; Reimann, R.H.; Ahmed, F.E.; Jensen, C.; Schorn, P.M.; Walthew, D.C. Direct production of white sugar and whitestrap molasses by applying membrane and ion exchange technology in a cane sugar mill. Proc. Int. Soc. Sugar Cane Technol. 2001, 24, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Zheng, Y.M.; Zhang, B.G.; Dai, Y.R. A critical review on the electrospun nanofibrous membranes for the adsorption of heavy metals in water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 401, 123608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, F.; Selmi, T.; Kesraoui, A.; Seffen, M. Low-cost activated carbon preparation from Corn stigmata fibers chemically activated using H3PO4, ZnCl2 and KOH: Study of methhylene blue adsorption, stochastic isotherm and fractal kinetic. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 178, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S. N-doped porous carbon from different nitrogen sources for high-performance supercapacitors and CO2 adsorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 786, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Dong, Y.; Liu, F.; Huang, H. Design of O2/SO2 dual-doped porous carbon as superior sorbent for elemental mercury removal from flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liang, Y.; Dong, H.; Hu, H.; Liu, S.; Peng, L.; Zheng, M.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y. Rational Synthesis of Highly Porous Carbon from Waste Bagasse for Advanced Supercapacitor Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5325–15332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Fu, X.; Peng, H.; Lv, S. Enhanced adsorption capacity of MgO/N-doped active carbon derived from sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Ma, W.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, X.; Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Li, L. Experimental and DFT study on the adsorption of VOCs on activated carbon/metal oxides composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.W.L.; Yilmaz, G.; Ong, W.L.; Ho, G.W. One-step activation towards spontaneous etching of hollow and hierarchical porous carbon nanospheres for enhanced pollutant adsorption and energy storage. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 220, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ge, W.; Liu, L.; Qiu, G. Preparation, adsorption performance and mechanism of MgO-loaded biochar in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, S.; Castellano, C.; Gervasini, A. Tailoring the structural and morphological properties of hydroxyapatite materials to enhance the capture efficiency towards copper(II) and lead(II) ions. N. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 4520–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhong, W.; Jing, C.; Wei, W. Modifying hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with humic acid for highly efficient removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 490, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Han, R.; Wei, W. Reed biochar supported hydroxyapatite nanocomposite: Characterization and reactivity for methylene blue removal from aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, H.; Ding, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J. Preparation of a porous hydroxyapatite-carbon composite with the bio-template of sugarcane top stems and its use for the Pb(II) removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-Fuentes, J.A.; Galán-Méndez, F.; Hernández-Medel, M.D.R.; García-Gómez, R.S.; Bernal-González, M.; Mendoza-Pérez, S.; Durán-Domínguez-de-Bazúa, M.D.C. Effectiveness of bagasse activated carbon in raw cane juice clarification. Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.J. A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/biochar nanocomposites: Adsorption behavior and mechanisms for the removal of copper(II) from aqueous media. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu-Yu, E.; Cheng, L.Y.; Ding, M.; Jiang, J.X. Rosin-based polymer@silica core–shell adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and application to melanoidin adsorption. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 132, 109937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.; Li, S.; Tan, D.; Pan, M.; Sang, S.; Ho, C. Trapping reactions of reactive carbonyl species with tea polyphenols in simulated physiological conditions. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budryn, G.; Nebesny, E.; Podsędek, A.; Żyżelewicz, D.; Materska, M.; Jankowski, S.; Janda, B. Effect of different extraction methods on the recovery of chlorogenic acids, caffeine and Maillard reaction products in coffee beans. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, P.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M. Reactions of d-glucose with phenolic amino acids: Further insights into the competition between Maillard and Pictet–Spengler condensation pathways. Carbohyd. Res. 2005, 340, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, G.F.; Schmitt, F.; Kanzler, C.; Dirk Epping, J.; Flemig, S.; Hornemann, A. Structural characterization of melanoidin formed from d-glucose and l-alanine at different temperatures applying FTIR, NMR, EPR, and MALDI-ToF-MS. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lu, H.; Rackemann, D.; Shi, C.; Li, W.; Li, K.; Doherty, W.O.S. Quaternary ammonium-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres as an effective green adsorbent to remove high-molecular-weight invert sugar alkaline degradation products (HISADPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniechwitz, D.; Reichardt, N.; Ralph, J.; Blaut, M.; Steinhart, H.; Bunzel, M. Isolation and characterisation of a coffee melanoidin fraction. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2008, 88, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payet, B.; Sing, A.S.C.; Smadja, J. Comparison of the concentrations of phenolic constituents in cane sugar manufacturing products with their antioxidant activities. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7270–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Almeida, J.M.; Salatino, A.; Genovese, M.I.; Lajolo, F.M. Phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of culms and sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) products. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, A.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Designing a novel targeted-release nano-container based on the silanized graphene oxide decorated with cerium acetylacetonate loaded beta-cyclodextrin (β-CD-CeA-MGO) for epoxy anti-corrosion coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Men, X.; Xue, Q. Colorful superhydrophobic pigments with superior anti-fouling performance and environmental durability. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolphen, R.; Thiravetyan, P. Adsorption of melanoidins by chitin nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaratanamongkol, A.; Thiravetyan, P. Decolorization of melanoidin by activated carbon obtained from bagasse bottom ash. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Mehmood, S.; Ali, S.; Qaswar, M.; Shakoor, A.; Chen, D. Highly efficient uranium (VI) capture from aqueous solution by means of a hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daware, G.B.; Gogate, P.R. Adsorption of 3-Aminopyridine (3AP) from aqueous solution using sugarcane bagasse activated carbon (SBAC). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rfw, A.; Lgd, A.; Kai, L.A.; Xjf, A.; Wen, L.B.; Hql, A. Fabrication and characterization of sugarcane bagasse–calcium carbonate composite for the efficient removal of crystal violet dye from wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 27484–27492. [Google Scholar]
- Yca, B.; Zza, B.; Yl, C.; Yla, B.; Yca, B.; Ywa, B.; Jz, D.; Hui, L.E.; Ran, X.; Sha, W. Glucose enhanced the oxidation performance of iron-manganese binary oxides: Structure and mechanism of removing tetracycline. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2020, 573, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, C.; Lei, F.; Rackemann, D.; Li, K.; Li, W.; Doherty, W.O.S. High-performance quaternary ammonium-functionalized chitosan/graphene oxide composite aerogel for remelt syrup decolorization in sugar refining. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, S. The sorption and short-term immobilization of lead and cadmium by nano-hydroxyapatite/biochar in aqueous solution and soil. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.F.; Khan, S.A.; Hussain, D.; Tabrez, U.; Ahamad, I.; Fatma, T.; Khan, T.A. A sugarcane bagasse carbon-based composite material to decolor and reduce bacterial loads in waste water from textile industry. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 176, 114301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, B.; Li, T.; Wu, G. Preparation of phosphoric acid activated carbon from sugarcane bagasse by mechanochemical processing. Bioresources 2012, 7, 5109–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ordonez-Loza, J.; Chejne, F.; Jameel, A.G.A.; Telalovic, S.; Arrieta, A.A.; Sarathy, S.M. An investigation into the pyrolysis and oxidation of bio-oil from sugarcane bagasse: Kinetics and evolved gases using TGA-FTIR. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, D.; Kong, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Su, M. Rapid and effective removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by facile synthesized hierarchical hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.; Ghafar, N.A.; Ngadi, N.; Razmi, F.A.; Inuwa, I.M.; Mat, R.; Amin, N.A.S. Effective removal of anionic textile dyes using adsorbent synthesized from coffee waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Guo, J.; Bai, L.; Chen, X.; Li, B. High effective adsorption of Pb(II) from solution by biochar derived from torrefaction of ammonium persulphate pretreated bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Covalent organic frameworks as efficient adsorbent for sulfamerazine removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 383, 121126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Cheng, R.; Wang, J. Adsorption of diclofenac from aqueous solution using UiO-66-type metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Cheng, R.; Kang, M.; Wang, J. Kinetic and equilibrium of U(VI) adsorption onto magnetic amidoxime-functionalized chitosan beads. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tan, C.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C. Porous activated carbons derived from waste sugarcane bagasse for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cai, L.; Yue, T.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, X. Kinetics and thermodynamics analysis of apple polyphenols adsorption by aminated magnetic chitosan microspheres. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. A general kinetic model for adsorption: Theoretical analysis and modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhu, N.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Lang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiao, W. Enhanced adsorption of Pb(II) onto modified hydrochar: Modeling and mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Pu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, D.; Chen, H.; Wen, T.; Hu, B.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; et al. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4/CFA composites for the efficient removal of U(VI) from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
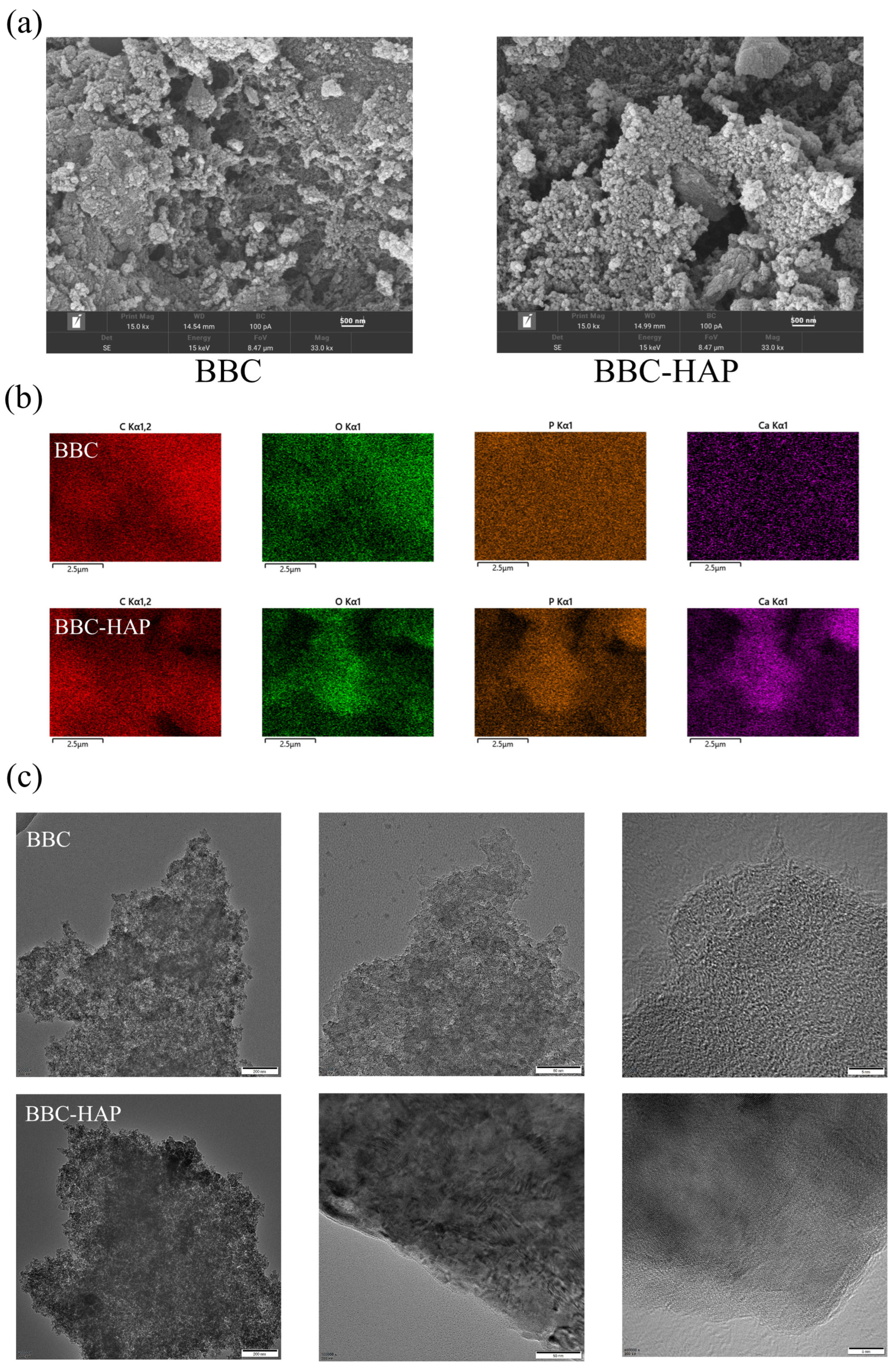
| Element | C (%) | O (%) | P (%) | Ca (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBC | 77.95 ± 0.15 | 16.24 ± 0.15 | 5.81 ± 0.06 | 0.00 ± 0.03 |
| BBC-HAP | 55.08 ± 0.23 | 21.05 ± 0.23 | 4.67 ± 0.11 | 19.21 ± 0.13 |
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm2/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAP | 103.81 | 0.48 | 18.58 |
| BBC | 832.55 | 0.96 | 4.63 |
| BBC-HAP | 1067.67 | 1.22 | 4.56 |
| Model | Parameters | Adj.R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir model | qm = 560.41 ± 19.72 mg/g; kL = 0.05 L/mg | 0.993 |
| Freundlich model | kF = 68.99 ± 7.58 mg/g; n = 2.21 ± 0.03 | 0.984 |
| Concentration (mg/L) | 150 | 200 | 250 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe, exp (mg/g) | 178.33 ± 1.18 | 240.00 ± 7.07 | 313.33 ± 2.36 | |
| PFO | qe,cal (mg/g) | 178.06 | 243.94 | 309.75 |
| k1 (1/min) | 0.04 | 0.042 | 0.041 | |
| Adj.R2 | 0.994 | 0.984 | 0.983 | |
| PSO | qe,cal (mg/g) | 203.44 | 276.84 | 351.14 |
| k2 [g/(mg·min)] | 0.00024 | 0.00019 | 0.00015 | |
| Adj.R2 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.992 | |
| PFO-PSO | kPFO (1/min) | 0.0264 | 0.022 | 0.02 |
| kPSO [g/(mg·min)] | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| Adj.R2 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.993 | |
| Concentration mg/L | k1-Int | Adj.R2 | k2-Int | Adj.R2 | k3-Int | Adj.R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 36.8633 | 0.976 | 26.9377 | 0.992 | 0.0044 | 0.995 |
| 200 | 26.2982 | 0.987 | 18.5470 | 0.935 | 0.1709 | 0.970 |
| 150 | 27.7951 | 0.929 | 10.1364 | 0.917 | 0.0635 | 0.956 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Luo, M.; Xie, C.; Li, K.; Hang, F.; Shi, C.; Doherty, W.O.S. Effective Adsorption of Colorants from Sugarcane Juice by Bagasse-Based Biochar-Hydroxyapatite Composite. Foods 2022, 11, 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142171
Wang C, Luo M, Xie C, Li K, Hang F, Shi C, Doherty WOS. Effective Adsorption of Colorants from Sugarcane Juice by Bagasse-Based Biochar-Hydroxyapatite Composite. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142171
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng, Mengying Luo, Caifeng Xie, Kai Li, Fangxue Hang, Changrong Shi, and William O. S. Doherty. 2022. "Effective Adsorption of Colorants from Sugarcane Juice by Bagasse-Based Biochar-Hydroxyapatite Composite" Foods 11, no. 14: 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142171
APA StyleWang, C., Luo, M., Xie, C., Li, K., Hang, F., Shi, C., & Doherty, W. O. S. (2022). Effective Adsorption of Colorants from Sugarcane Juice by Bagasse-Based Biochar-Hydroxyapatite Composite. Foods, 11(14), 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142171






