Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y42 in Biofilm and Planktonic States Improves Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Modulates Gut Microbiota of Balb/c Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Stains and Culture Conditions
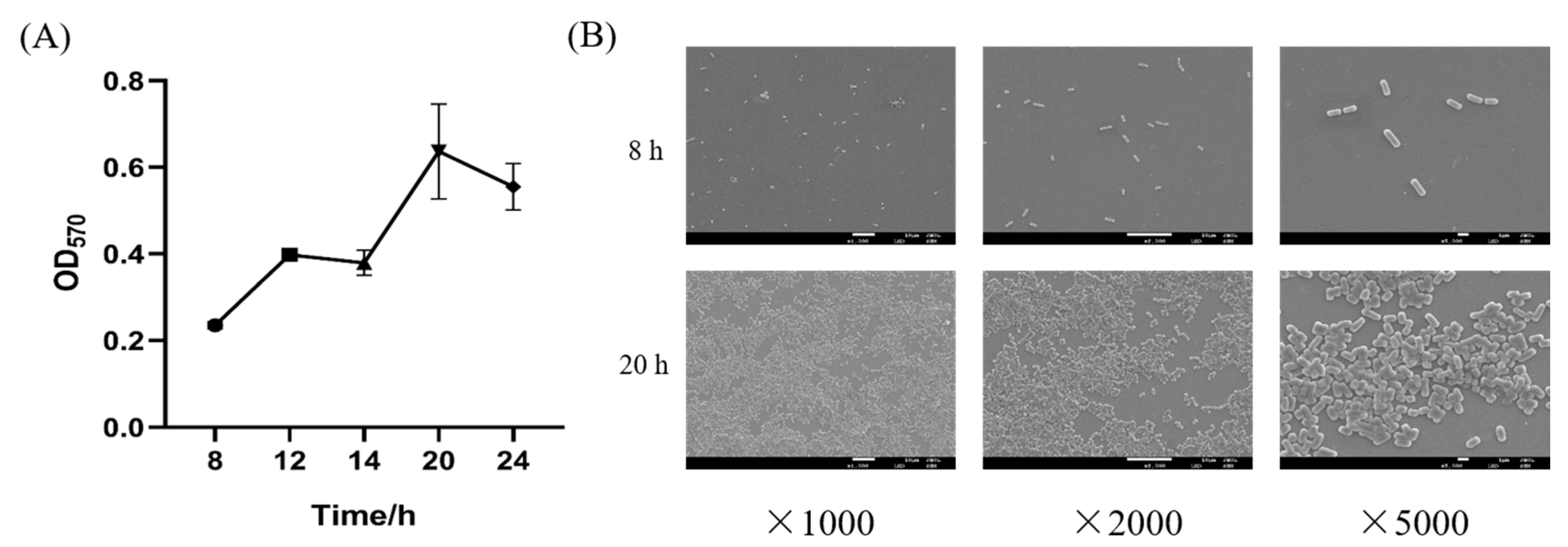
2.2. Biofilm Formation of L. plantarum Y42
2.3. Biofilm Growth Curve and Observation by SEM
2.4. Preparation of Planktonic and Biofilm Cells
2.5. Tolerance to Artificial Gastrointestinal Conditions
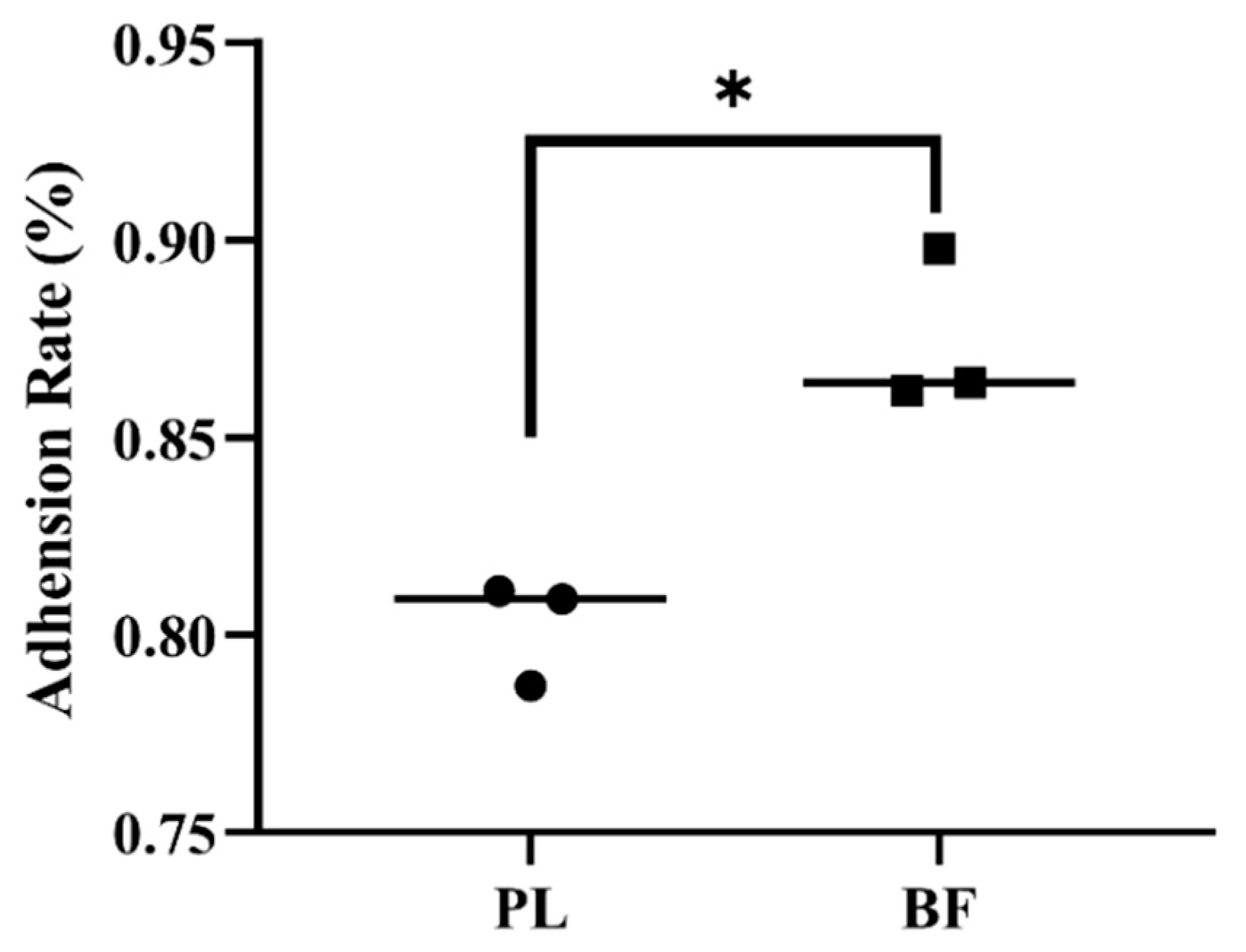
2.6. HT-29 Cell Culture and Adhesion Assay on HT-29 Cells of Biofilm and Planktonic Bacteria
2.6.1. HT-29 Cell Culture
2.6.2. Adhesion Assay on HT-29 Cells of Biofilm and Planktonic Bacteria
2.7. Animal and Experimental Design
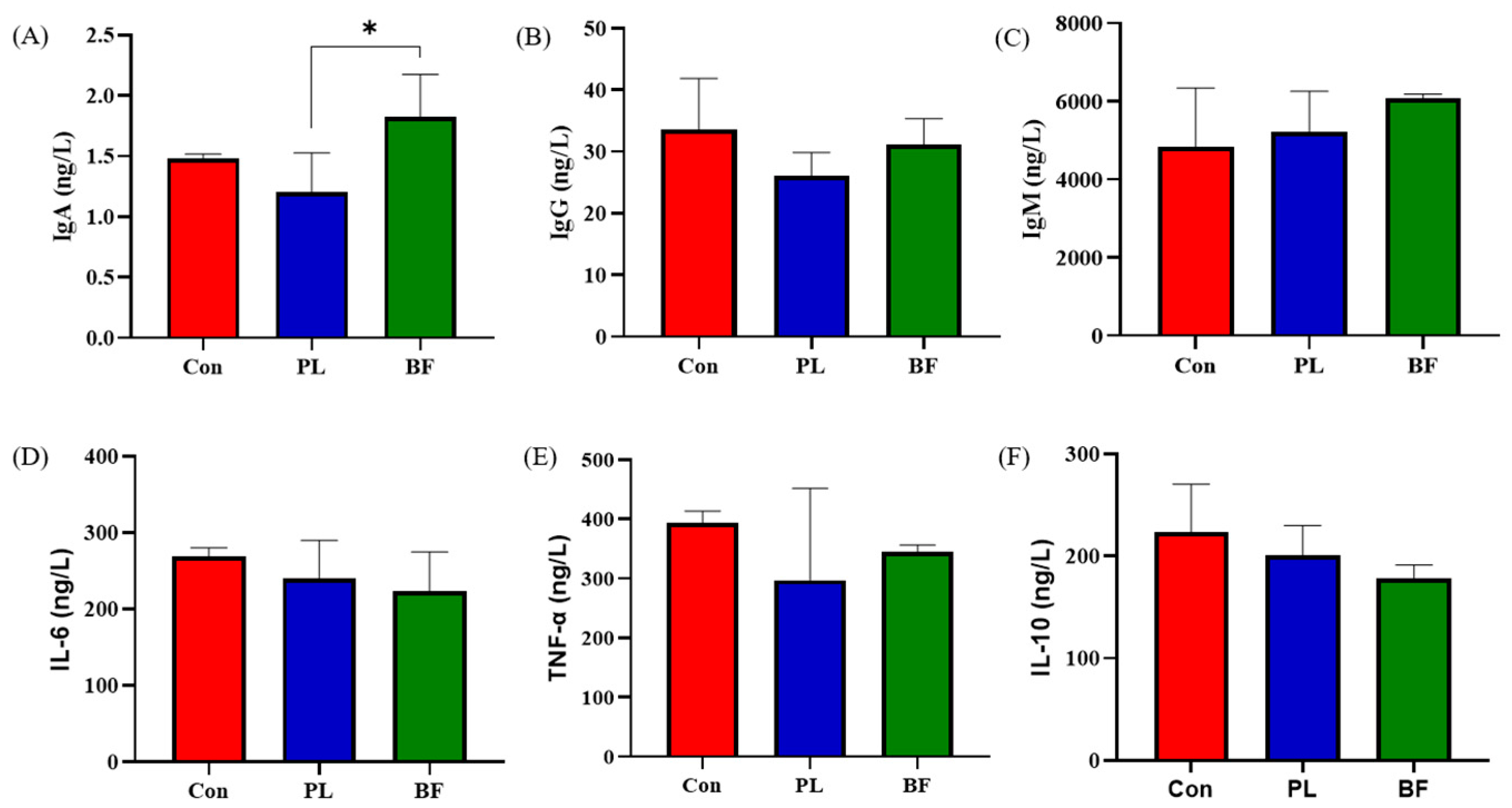
2.8. IgA, IgG, IgM, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 Analysis
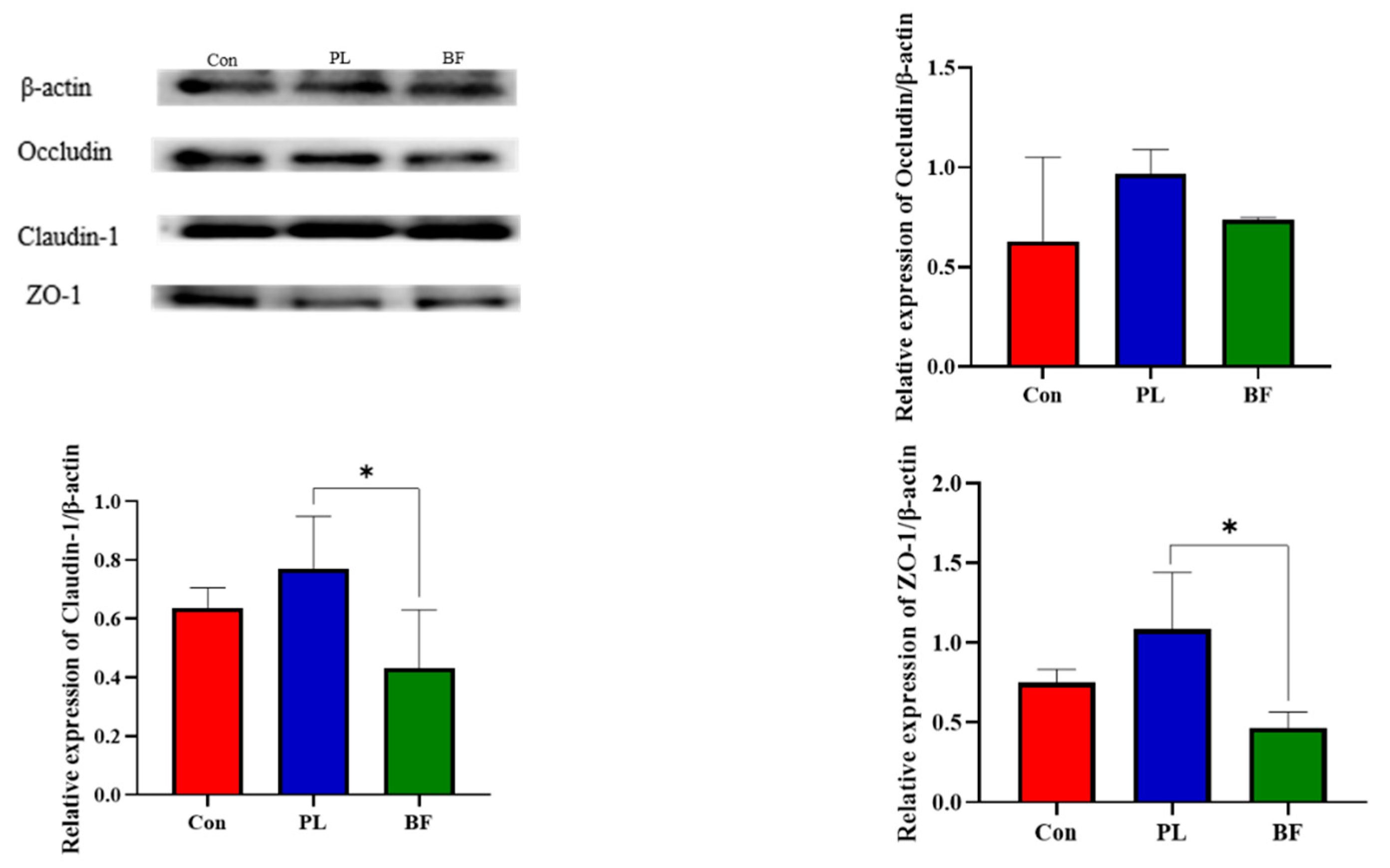
2.9. Western Blotting Analysis
2.10. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biofilm Formation of L. plantarum Y42
3.2. Tolerance of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 to Artificial Gastrointestinal Conditions
3.3. Adhesion Rates of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 on HT-29 Cell Monolayers
3.4. Effects of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 on the TJ Proteins Expression of HT-29 Cell Monolayers
3.5. Animal Experiments
3.5.1. Effects of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 Administration on Body Weight of Balb/c Mice
3.5.2. Effects of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 Administration on Immunity of Balb/c Mice
3.5.3. Effects of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 Administration on the TJ Proteins Expression of Balb/c Mice
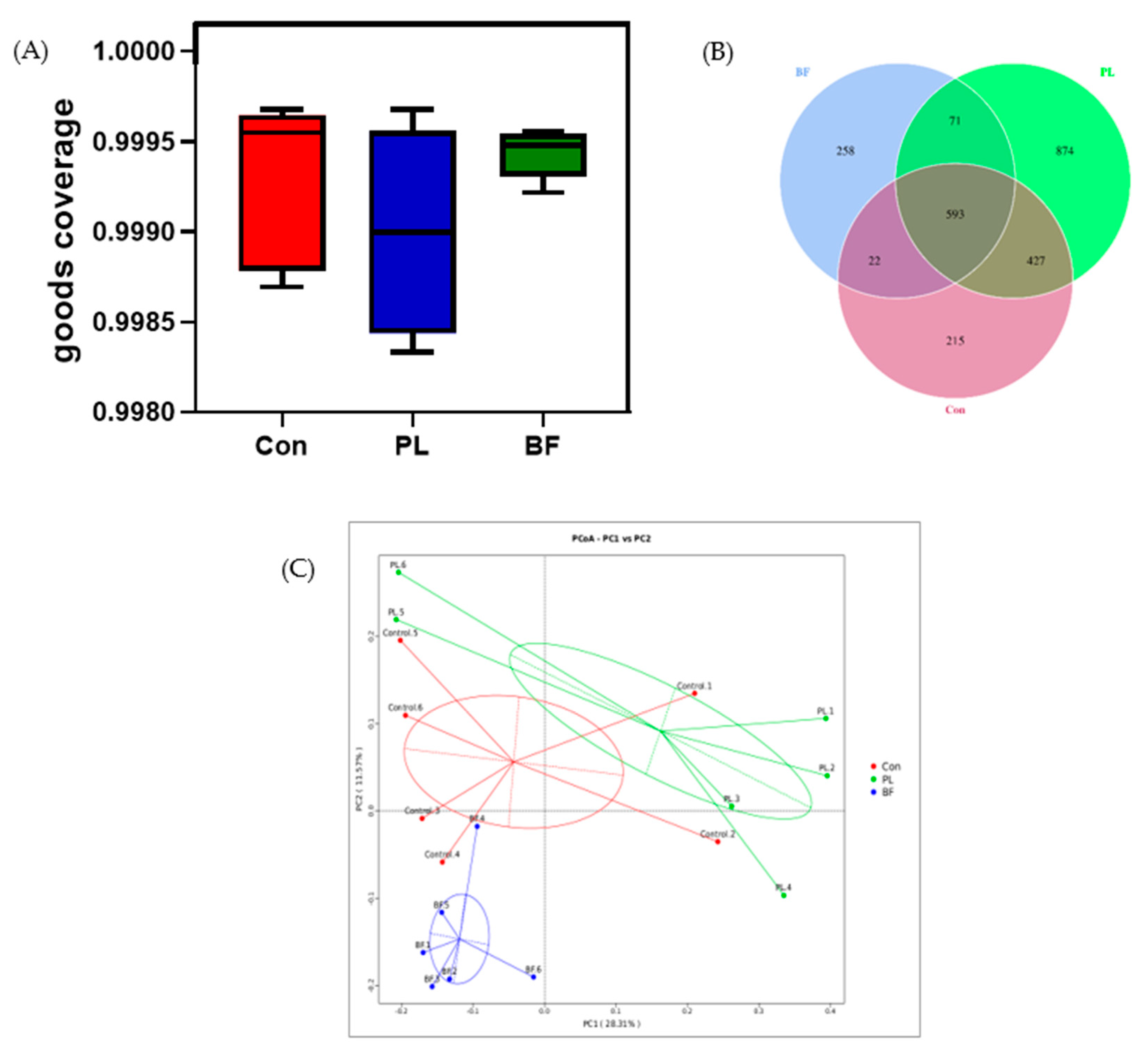
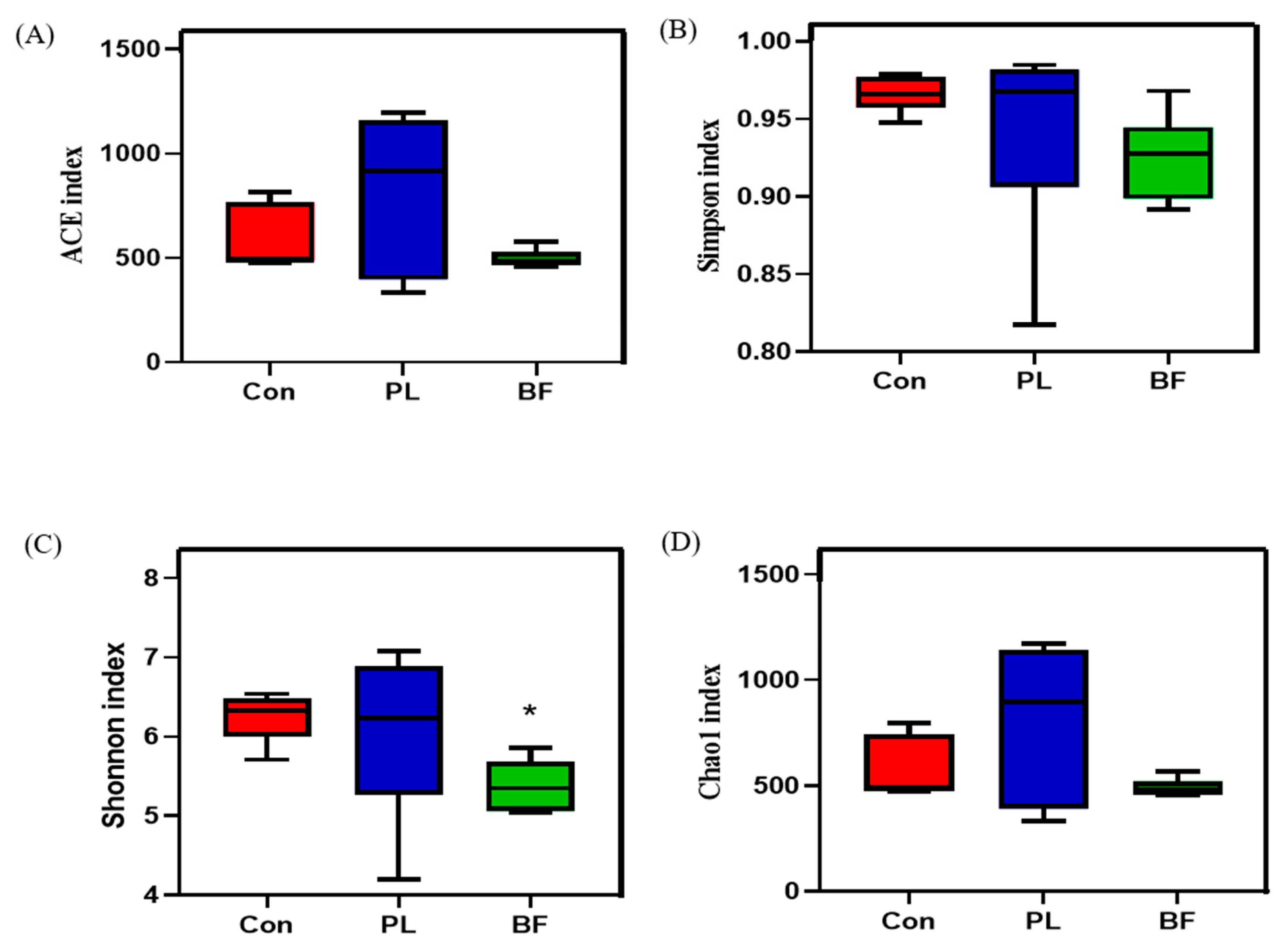
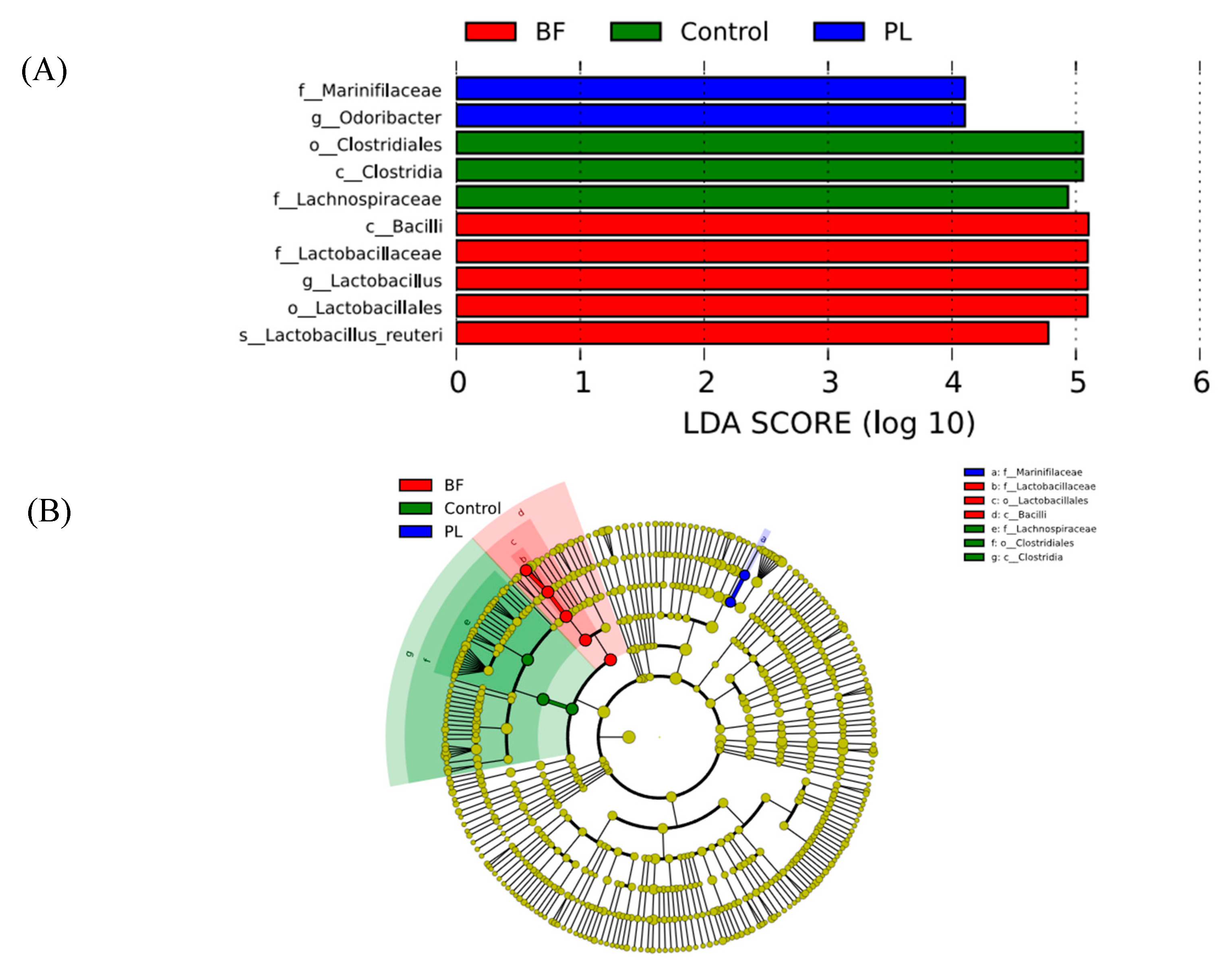
3.5.4. Effects of Biofilm and Planktonic L. plantarum Y42 Administration on the Gut Microbiota of Balb/c Mice
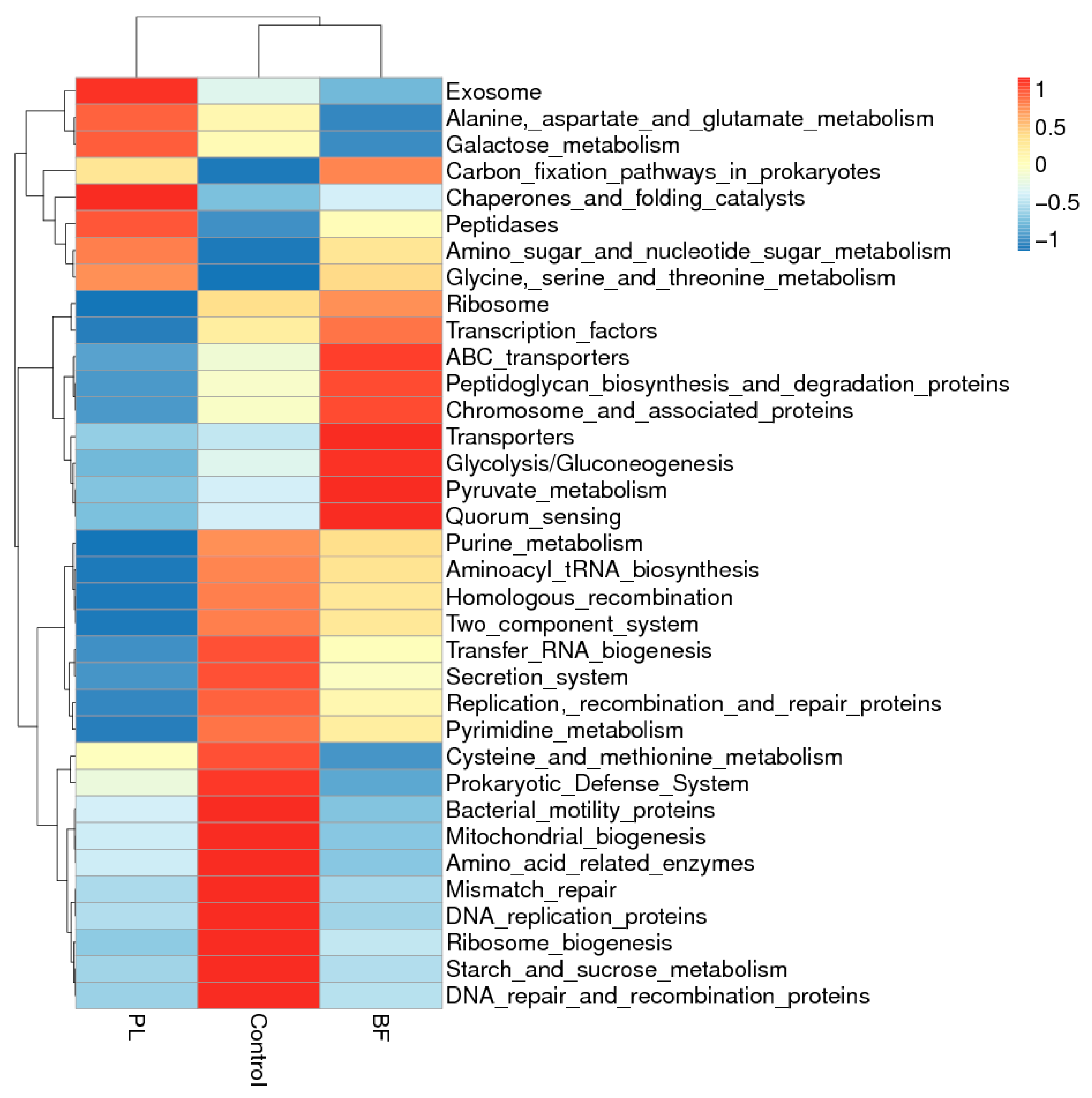
3.5.5. Predicted Functional Genes in the Gut Microbiota of the Balb/c Mice
3.5.6. Correlation Analysis between Occludin, Claudin-1, ZO-1, and Intestinal Microbiome Diversity of the Balb/c Mice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morelli, L.; Capurso, L. FAO/WHO Guidelines on Probiotics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Gueimonde, M.; Hernández, M.; Sanz, Y.; Salminen, S. Adhesion of Selected Bifidobacterium Strains to Human Intestinal Mucus and the Role of Adhesion in Enteropathogen Exclusion. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2672–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdeano, C.M.; Perdigon, G. Role of viability of probiotic strains in their persistence in the gut and in mucosal immune stimulation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 97, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Zong, X. Clostridium Butyricum ZJU-F1 Benefits the Intestinal Barrier Function and Immune Response Associated with Its Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Weaned Piglets. Cells 2021, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongrattanapipat, S.; Chiracharoenchitta, A.; Choowongwitthaya, B.; Komsathorn, P.; La-Ongkham, O.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Tunsagool, P.; Nakphaichit, M. Selection of potential probiotics with cholesterol-lowering properties for probiotic yoghurt production. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2021, 1, 108201322110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, J.K.; Kumar, A.; Duary, R.K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Grover, S.; Batish, V.K. Functional and Probiotic Attributes of an Indigenous Isolate of Lactobacillus plantarum. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoudia, N.; Rieu, A.; Briandet, R.; Deschamps, J.; Chluba, J.; Jego, G.; Garrido, C.; Guzzo, J. Biofilms of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus fermentum: Effect on stress responses, antagonistic effects on pathogen growth and immunomodulatory properties. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, S.A.; Benson, A.K.; Tannock, G.W.; Loach, D.M.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M.; Oh, P.L.; Heng, N.C.K.; Patil, P.B.; Juge, N.; et al. The Evolution of Host Specialization in the Vertebrate Gut Symbiont Lactobacillus reuteri. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vries, M.C.; Vaughan, E.E.; Kleerebezem, M.; de Vos, W.M. Lactobacillus plantarum—Survival, functional and potential probiotic properties in the human intestinal tract. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, M.; Doi, Y.; Hellwich, K.-H.; Hess, M.; Hodge, P.; Kubisa, P.; Rinaudo, M.; Schué, F. Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 377–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannella, G.; Lombardi, S.J.; Coppola, F.; Vergalito, F.; Iorizzo, M.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Iannini, C.; Sorrentino, E.; Coppola, R. Effect of Biofilm Formation by Lactobacillus plantarum on the Malolactic Fermentation in Model Wine. Foods 2020, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, H.; Senda, S.; Tokuda, H.; Uchiyama, H.; Nomura, N. Stress resistance of biofilm and planktonic Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum JCM 1149. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, P.; Kong, F.; Zhu, C.; Lu, C.; Lin, H. Evaluation of the differences between biofilm and planktonic Brucella abortus via metabolomics and proteomics. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2021, 21, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, M.; Siragusa, S.; Campanella, D.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Comparative proteomic analysis of biofilm and planktonic cells of Lactobacillus plantarum DB200. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. Characterization and transcriptomic basis of biofilm formation by Lactobacillus plantarum J26 isolated from traditional fermented dairy products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 125, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, F.A.; Yan, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Untargeted metabolomics reveals metabolic state of Bifidobacterium bifidum in the biofilm and planktonic states. LWT 2020, 118, 108772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Dakić, I.; Savić, B.; Švabić-Vlahović, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Man, C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Ren, H.; Cheng, W.; Jiang, Y. Preparation of elemental selenium-enriched fermented milk by newly isolated Lactobacillus brevis from kefir grains. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 44, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Hu, C.-H.; Ren, L.-Q.; Wang, D.-C.; Ye, B.-C. Enhancement of bile resistance by maltodextrin supplementation in Lactobacillus plantarum Lp-115. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.; Maillart, G.; Garénaux, A.; Jugiau, F.; Federighi, M.; Cappelier, J.-M. Adhesion Ability of Campylobacter jejuni to Ht-29 Cells Increases with the Augmentation of Oxidant Agent Concentration. Curr. Microbiol. 2010, 61, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greppi, A.; Saubade, F.; Botta, C.; Humblot, C.; Guyot, J.P.; Cocolin, L. Potential probiotic Pichia kudriavzevii strains and their ability to enhance folate content of traditional cereal-based African fermented food—ScienceDirect. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Zhu, X.; Tuo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Mu, G.; Jiang, S. Reducing antigenicity of β-lactoglobulin, probiotic properties and safety evaluation of Lactobacillus plantarum AHQ-14 and Lactobacillus bulgaricus BD0390. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.X.; Li, J.N.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Niu, H.M. Probiotics biofilm-Integrated electrospun eanofiber membranes: A new starter culture for fermented milk production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3198–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Deng, X.; Tu, M.; Tao, Y.; Xiang, W.; Rao, Y. Metabolic profiles of Lactobacillus paraplantarum in biofilm and planktonic states and investigation of its intestinal modulation and immunoregulation in dogs. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5317–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.N.; Wakita, D.; Franklin, M.; de Carvalho, T.T.; Abolhesn, A.; Gomez, A.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chen, S.; Lehman, T.J.; Sato, K.; et al. Intestinal Permeability and IgA Provoke Immune Vasculitis Linked to Cardiovascular Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 51, 508–521.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min-Hyun, K.; Hyeyoung, K. The roles of glutamine in the intestine and its implication in intestinal diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1051. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, W. Glutamine deficiency links clindamycin-induced dysbiosis and intestinal barrier dysfunction in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 126, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olerud, J.E.; Philip, F.; James, G.A.; Secor, P.R.; Kate, M.I.; Stewart, P.S. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm and planktonic cultures differentially impact gene expression, mapk phosphorylation, and cytokine production in human keratinocytes. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski, J.; Troost, F.J.; Konings, I.; Dekker, J.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.-J.M.; Wells, J.M. Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by Lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G851–G859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, R.; McBain, A.J.; O’Neill, C.A. Strain-Dependent Augmentation of Tight-Junction Barrier Function in Human Primary Epidermal Keratinocytes by Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Lysates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4887–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santarmaki, V.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Mavrogonatou, E.; Kiourtzidis, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Tassou, C.; Tsakalidou, E.; Simopoulos, C.; Ypsilantis, P. Survival, Intestinal Mucosa Adhesion, and Immunomodulatory Potential of Lactobacillus plantarum Strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xia, J.; Lv, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Bian, X.; Ye, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Effects of Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05 on immunity and metabolism in germ-free rats. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5077–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Min, G.K.; Hong, J.L.; Kim, G.B. Lactobacillus plantarum CAU1055 ameliorates inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells and a dextran sulfate sodium–induced colitis animal model. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6718–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, K.; Nejad, M.R.; Asadzadeh, H.; Zali, M.R. PTU-199 Proinflammatory cytokine (Il-8) in Microscopic Enteritis. Gut 2013, 62, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, H.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, J.; Sa, R.; Chen, W.; Wan, X. Matrine protects against DSS-induced murine colitis by improving gut barrier integrity, inhibiting the PPAR-α signaling pathway, and modulating gut microbiota. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Luo, X.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Quorum Sensing, Biofilm, and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier: Involvement the Role of Probiotic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. QUORUM SENSING: Cell-to-Cell communication in bacteria—Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuwahara, T.; Yamashita, A.; Hirakawa, H.; Nakayama, H.; Toh, H.; Okada, N.; Kuhara, S.; Hattori, M.; Hayashi, T.; Ohnishi, Y. Genomic analysis of Bacteroides fragilis reveals extensive DNA inversions regulating cell surface adaptation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14919–14924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Ross, R.P.; Jin, Y.; Chen, W. Orally Administered CLA ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice via intestinal barrier improvement, oxidative stress reduction, inflammatory cytokine and gut microbiota modulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13282–13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, F. Severe burn injury alters intestinal microbiota composition and impairs intestinal barrier in mice. Burn. Trauma 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Time/h | Initial Cell Number (Log CFU/mL) | Gastric Juice | Intestinal Juice | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Number (Log CFU/mL) | Survival Rate/% | Cell Number (Log CFU/mL) | Survival Rate/% | ||
| PL | 9.19 ± 0.34 | 7.63 ± 0.13 | 83.05 ± 1.59 | 4.67 ± 0.38 | 61.20 ± 3.94 a |
| BF | 9.64 ± 0.26 | 7.65 ± 0.32 | 79.32 ± 1.22 | 6.70 ± 0.08 | 87.65 ± 2.73 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y42 in Biofilm and Planktonic States Improves Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Modulates Gut Microbiota of Balb/c Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101451
Zhang L, Meng Y, Li J, Yu J, Mu G, Tuo Y. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y42 in Biofilm and Planktonic States Improves Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Modulates Gut Microbiota of Balb/c Mice. Foods. 2022; 11(10):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101451
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lijuan, Yuan Meng, Jiayi Li, Jiang Yu, Guangqing Mu, and Yanfeng Tuo. 2022. "Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y42 in Biofilm and Planktonic States Improves Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Modulates Gut Microbiota of Balb/c Mice" Foods 11, no. 10: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101451
APA StyleZhang, L., Meng, Y., Li, J., Yu, J., Mu, G., & Tuo, Y. (2022). Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y42 in Biofilm and Planktonic States Improves Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Modulates Gut Microbiota of Balb/c Mice. Foods, 11(10), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101451






