Metal Contents in Fish from the Bay of Bengal and Potential Consumer Exposure—The EAF-Nansen Programme
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Data Management and Presentation of Analytical Data
2.4. Consumer Exposure
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
2.5.1. Noncarcinogenic Exposure
2.5.2. Carcinogenic Exposure
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Metal Contents in Fish Species from Sri Lanka
3.3. Metal Contents in Fish Species from Bangladesh
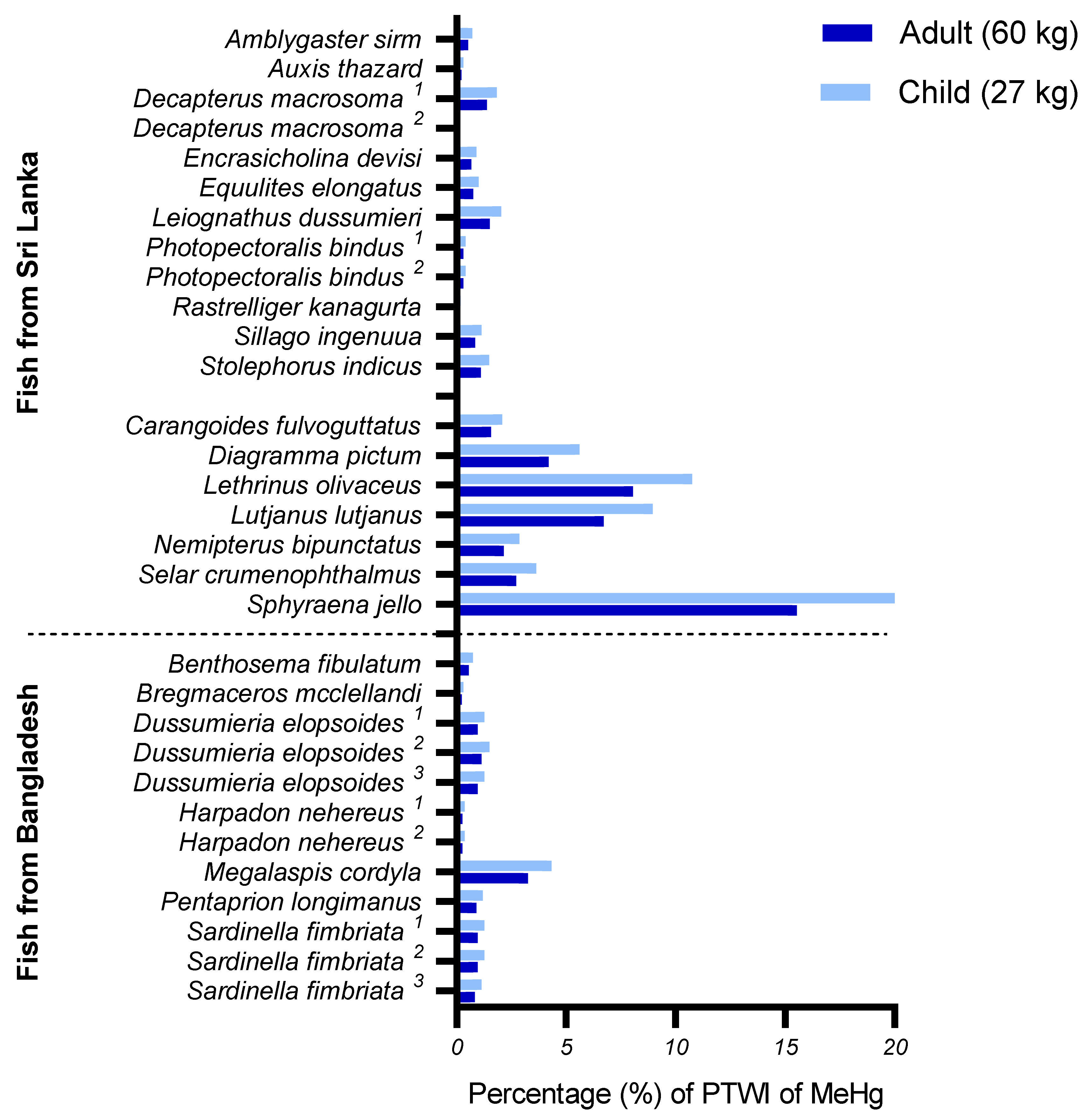
3.4. Potential Consumer Exposure
3.5. Health Risk Assessment in Edible Tissues of Different Fish Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hicks, C.C.; Cohen, P.J.; Graham, N.A.J.; Nash, K.L.; Allison, E.H.; D’Lima, C.; Mills, D.J.; Roscher, M.; Thilsted, S.H.; Thorne-Lyman, A.L.; et al. Harnessing global fisheries to tackle micronutrient deficiencies. Nature 2019, 574, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reksten, A.M.; Somasundaram, T.; Kjellevold, M.; Nordhagen, A.; Bøkevoll, A.; Pincus, L.M.; Rizwan, A.A.M.; Manun, A.; Thilsted, S.H.; Htut, T.; et al. Nutrient composition of 19 fish species from Sri Lanka and potential contribution to food and nutrition security. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2020, 91, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhagen, A.; Rizwan, A.A.M.; Aakre, I.; Moxness Reksten, A.; Pincus, L.M.; Bøkevoll, A. Nutrient Composition of Demersal, Pelagic, and Mesopelagic Fish Species Sampled Off the Coast of Bangladesh and Their Potential Contribution to Food and Nutrition Security—The EAF-Nansen Programme. Foods 2020, 9, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; Available online: http://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/I9540EN/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Fiedler, J.L.; Lividini, K.; Drummond, E.; Thilsted, S.H. Strengthening the contribution of aquaculture to food and nutrition security: The potential of a vitamin A-rich, small fish in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources Development. Annual Performance Report Colombo, Sri Lanka. 2016. Available online: https://www.parliament.lk/uploads/documents/paperspresented/performance-report-ministry-of-fisheries-aquatic-2016.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Stoffella, P.J. Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. GMS 2005, 19, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, H.B. (Ed.) Heavy Metals in the Environment: Origin, Interaction and Remediation; Academic Press: London, England, 2005; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Jarup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.K.; Islam, S.; Rahman, M.; Haque, M.; Islam, M. Heavy Metals in Water, Sediment and Some Fishes of Buriganga River, Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2010, 4, 321–332. [Google Scholar]
- Jinadasa, B.; Fowler, S.W. Critical review of mercury contamination in Sri Lankan fish and aquatic products. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.S.; Rahman, M.; Sultana, S.; Babu, S.M.O.F.; Sarker, M.S.I. Bioaccumulation and heavy metal concentration in tissues of some commercial fishes from the Meghna River Estuary in Bangladesh and human health implications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Gautam, N.; Mishra, A.; Gupta, R. Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). Fishery Exports and the Economic Development of Least Developed Countries: Bangladesh, Cambodia, The Comoros, Mozambique, Myanmar and Uganda; United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, N.; Mollah, M.Z.I.; Alam, M.F.; Safiur Rahman, M. Seasonal investigation of heavy metals in marine fishes captured from the Bay of Bengal and the implications for human health risk assessment. Food Control. 2016, 70, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E. (Ed.) Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Evaluation of the Safety of Fishery Products: Chapter 5; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Gonzalez, M.I.; Mendez-Armenta, M. Heavy metals: Implications associated to fish consumption. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A. Arsenic species in seafood: Origin and human health implications. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.E.; Hoffman, K.; Wing, S.; Lowman, A. Fish Consumption Patterns and Mercury Advisory Knowledge among Fishers in the Haw River Basin. N. C. Med. J. 2016, 77, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC), No 1881/2006 of setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Comm. L 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed (Codex Stan 193-1995); FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneve, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EU). No 488/2014 of 12 May 2014 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regard maximum levels of cadmium in foodstuffs, Text with EEA relevance. Off. J. Eur. Comm. L 2014, 138, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on the risk for public health related to the presence of mercury and methylmercury in food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2985. [Google Scholar]
- Herrman, J.L.; Younes, M. Background to the ADI/TDI/PTWI. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1999, 30, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Proceedings of the 73rd Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) Meeting—Food Additives and Contaminants, Geneva, Switzerland, 8–17 June 2010.
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Proceedings of the Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Sixty-Seventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, Rome, Italy, 20–29 June 2006.
- World Health Organization (WHO); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Seventy-Second [72nd] Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.R.; Khan, M.Z.H.; Khan, M.; Aktar, S.; Rahman, M.; Hossain, F.; Hasan, A.S.M.M. Heavy metals distribution and contamination in surface water of the Bay of Bengal coast. Cogent. Environ. Sci. 2016, 2, 1140001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.S.; Sultana, S.; Habib, A.; Ullah, H.; Musa, N.; Hossain, M.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Sarker, M.S.I. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some commercially important fishes from a tropical river estuary suggests higher potential health risk in children than adults. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naigaga, I.; Kaiser, H.; Muller, W.; Ojok, L.; Dismas, M.; Magezi, G.; Muhumuza, E. Fish as bioindicators in aquatic environmental pollution assessment: A case study in Lake Victoria wetlands, Uganda. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mohsein, H.; Mahmoud, M. Accumulation of Some Heavy Metals in Oreochromis niloticus from the Nile in Egypt: Potential Hazards to Fish and Consumers. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moxness Reksten, A.; Bøkevoll, A.; Frantzen, S.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Kögel, T.; Kolås, K.; Aakre, I.; Kjellevold, M. Sampling protocol for the determination of nutrients and contaminants in fish and other seafood—The EAF-Nansen Programme. MethodsX 2020, 7, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaza, S.; de Balogh, K.; Palmery, M.; Pastorelli, A.A.; Stacchini, P. Human exposure in Italy to lead, cadmium and mercury through fish and seafood product consumption from Eastern Central Atlantic Fishing Area. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 40, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellatte, E.; Brambilla, G.; Miniero, R.; Abete, M.C.; Orletti, R.; Chessa, G.; Ubaldi, A.; Chiaravalle, E.; Tiso, M.; Ferrari, A. Individual methylmercury intake estimates from local seafood of the Mediterranean Sea, in Italy. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, G.; Bravo, J.C.; Fernández, C.; Tarazona, J.V. A New Method for Total Mercury and Methyl Mercury Analysis in Muscle of Seawater Fish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, A.; Bono, G.; Bonsignore, M.; Falco, F.; Giuga, M.; Quinci, E.M. Heavy metals concentrations in some commercially key species from Sicilian coasts (Mediterranean Sea): Potential human health risk estimation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsignore, M.; Salvagio Manta, D.; Oliveri, E.; Sprovieri, M.; Basilone, G.; Bonanno, A. Mercury in fishes from Augusta Bay (southern Italy): Risk assessment and health implication. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramanayake, T.W. The Growth Chart. Sri Lanka J. Child Health 2009, 29, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangladesh Institute of Research and Rehabilitation in Diabetes; Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders (BIRDEM). Dietary Guidelines for Bangladesh. Dhaka: Bangladesh Institute of Research and Rehabilitation in Diabetes; Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Walpole, S.C.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Edwards, P.; Cleland, J.; Stevens, G.; Roberts, I. The weight of nations: An estimation of adult human biomass. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Census and Statistics, Ministry of National Policies and Economic Affairs Sri Lanka. Household Income and Expenditure Survey 2016; Department of Census and Statistics: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2016. Available online: http://www.statistics.gov.lk/HIES/HIES2016/HIES2016_FinalReport.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2019).
- The Ministry of Fisheries and Aquaculture Resources. Fisheries Statistics; Ministry of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bogard, J.R.; Farook, S.; Marks, G.C.; Waid, J.; Belton, B.; Ali, M.; Thilsted, S.H. Higher fish but lower micronutrient intakes: Temporal changes in fish consumption from capture fisheries and aquaculture in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175098. [Google Scholar]
- United States Envonmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment: Guidance for Superfund; Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A), Interim Final (EPA/540/1-89/002); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 1.
- Varol, M.; Kaya, G.K.; Alp, A. Heavy metal and arsenic concentrations in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farmed in a dam reservoir on the Firat (Euphrates) River: Risk-based consumption advisories. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Envonmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table (TR=1E-06, HQ=1), Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories; Office of Water, United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/regshwmd/risk/human/Index.htm (accessed on 10 February 2002).
- Chiocchetti, G.; Jadán-Piedra, C.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V. Metal(loid) contamination in seafood products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3715–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on Arsenic in Food. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinadasa, K.; Fowler, S. A Critical Review of Arsenic Contamination in Sri Lankan Foods. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control. 2019, 6, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julshamn, K.; Nilsen, B.; Frantzen, S.; Valdersnes, S.; Maage, A.; Nedreaas, K.; Sloth, J.J. Total and inorganic arsenic in fish samples from Norwegian waters. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2012, 5, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruttens, A.; Blanpain, A.C.; De Temmerman, L.; Waegeneers, N. Arsenic speciation in food in Belgium: Part 1: Fish, molluscs and crustaceans. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 121, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raknuzzaman, M.; Islam, M.; Al Mamun, M.H.; Tokumura, M.; Sekine, M.; Masunaga, S. Trace metal contamination in commercial fish and crustaceans collected from coastal area of Bangladesh and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17298–17310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mania, M.; Rebeniak, M.; Szynal, T.; Wojciechowska-Mazurek, M.; Starska, K.; Ledzion, E.; Postupolski, J. Total and inorganic arsenic in fish, seafood and seaweeds—Exposure assessment. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2015, 66, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, H.K.; Mitra, A.K.; Sengupta, P.K.; Hossain, A.; Islam, F.; Rabbani, G.H. Arsenic concentrations in rice, vegetables, and fish in Bangladesh: A preliminary study. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Cadmium in food—Scientific opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 980. [Google Scholar]
- Jinadasa, B.K.; Edirisinghe, E.M.; Wickramasinghe, I. Total mercury, cadmium and lead levels in main export fish of Sri Lanka. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2014, 7, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Ning, J.-J.; Ke, C.-L.; Huang, H.-H. Bioaccessibility and human health implications of heavy metals in different trophic level marine organisms: A case study of the South China Sea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, D.; Lazaro-Llanos, N. Omega-3 Fatty Acids versus Heavy Metals: A Quantitative Estimation of the Benefit-Risk Ratio for the Consumption of Commonly-Consumed Fish and Products in Metro Manila. KIMIKA 2015, 26, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdthep, P.; Tongyonk, L.; Rojanapantip, L. Concentrations of cadmium and arsenic in seafood from Muang District, Rayong Province. J. Health Res. 2009, 23, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Li, X. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species from the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has-Schön, E.; Bogut, I.; Strelec, I. Heavy Metal Profile in Five Fish Species Included in Human Diet, Domiciled in the End Flow of River Neretva (Croatia). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). RASFF Portal Brussels, Belgium. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/portal/?event=searchForm&cleanSearch=1 (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Larsen, T.; Thilsted, S.H.; Kongsbak, K.; Hansen, M. Whole small fish as a rich calcium source. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 83, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, N.; Wahab, M.A.; Chamnan, C.; Thilsted, S.H. The role of fish in food-based strategies to combat vitamin A and mineral deficiencies in developing countries. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on Lead in Food. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1570. [Google Scholar]
- Canli, M.; Atli, G. The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C. The Use of Household Expenditure Surveys for the Assessment of Food Insecurity. In Measurement and Assessment of Food Deprivation and Undernutrition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on health benefits of seafood (fish and shellfish) consumption in relation to health risks associated with exposure to methylmercury. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the World (FAO)/Worhld Health Organization (WHO). Report of the Joint Expert Consultation on the Risks and Benefits of Fish Consumption. FAO Fish. Aquac. Rep. 2010, 978, 50. [Google Scholar]

| Metal | Maximum Limit (mg/kg w.w.) | Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake (PTWI) |
|---|---|---|
| Arsenic (As) | - a | - b |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.050 c | PTMI: 25 µg/kg b.w. d |
| Mercury (Hg) | 0.50 c,e,f | 1.6 µg/kg b.w. g |
| Lead (Pb) | 0.30 c,e | - b |
| Scientific Name | Tissue Sampled | Number of Composite Samples | Number of Fish in Each Composite Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish from Sri Lanka | |||
| Small fish | |||
| Amblygaster sirm | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Auxis thazard | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Decapterus macrosoma1 | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Decapterus macrosoma2 | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Encrasicholina devisi | Whole fish | 3 | 50 |
| Equulites elongates | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Leiognathus dussumieri | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Photopectoralis bindus1 | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Photopectoralis bindus2 | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Rastrelliger kanagurta | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Sillago ingenuua | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Stolephorus indicus | Whole fish | 3 | 25 |
| Large fish | |||
| Carangoides fulvoguttatus | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Diagramma pictum | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Lethrinus olivaceus | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Lutjanus lutjanus | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Nemipterus bipunctatus | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Selar crumenophthalmus | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Sphyraena jello | Fillet | 3 | 5 |
| Fish from Bangladesh a | |||
| Benthosema fibulatum Bregmaceros mcclellandi | Whole fish Whole fish | 3 3 | 250 280 |
| Dussumieria elopsoides1 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 25 |
| Dussumieria elopsoides2 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 25 |
| Dussumieria elopsoides3 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 23 b |
| Harpadon nehereus1 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 25 |
| Harpadon nehereus2 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 20 |
| Megalaspis cordyla | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 5 |
| Pentaprion longimanus | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 25 |
| Sardinella fimbriata1 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 23 b |
| Sardinella fimbriata2 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 25 |
| Sardinella fimbriata3 | Fillet with skin and bones | 3 | 25 |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Local Name | Habitat | Average Weight (g) b | Average Length (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish from Sri Lanka | Sinhalese Name c | Tamil Name c | ||||
| Small fish | ||||||
| Amblygaster sirm | Trenched sardinella | Hurulla | Keerimeen saalai | Pelagic | 278 ± 20 | 10.5 |
| Auxis thazard | Frigate tuna | Alagoduwa | Urulan soorai | Pelagic | 1180 ± 27 | 16.2 |
| Decapterus macrosoma1 | Shortfin scad | Linna | Mundakan kilichchi | Pelagic | 763 ± 23 | 13.5 |
| Decapterus macrosoma2 | Shortfin scad | Linna | Mundakan kilichchi | Pelagic | 273 ± 22 | 9.2 |
| Encrasicholina devisi | Devis’ anchovy | Halmessa | Neththili | Pelagic | 219 ± 1 | 10.5 |
| Equulites elongatus | Slender ponyfish | Karalla | Karal | Demersal | 183 ± 8 | 7.7 |
| Leiognathus dussumieri | Dussumier’s ponyfish | Karalla | Vari karai | Demersal | 637 ± 56 | 10.6 |
| Photopectoralis bindus1 | Orangefin ponyfish | Karalla | Tatnam-kare | Demersal | 245 ± 20 | 7.4 |
| Photopectoralis bindus2 | Orangefin ponyfish | Karalla | Tatnam-kare | Demersal | 228 ± 10 | 7.5 |
| Rastrelliger kanagurta | Indian mackerel | Kumbalava | Kanang keluththi | Pelagic | 610 ± 6 | 12.5 |
| Sillago ingenuua | Bay whiting | - d | Kelangan | Demersal | 1099 ± 24 | 16.3 |
| Stolephorus indicus | Indian anchovy | Halmassa | Neththili | Pelagic | 676 ± 10 | 13.2 |
| Large fish | ||||||
| Carangoides fulvoguttatuse | Yellowspotted trevally | Thumba parawa | Manjal parai | Reef-associated | 168 ± 31 | 20.5 ± 1.5 |
| Diagramma pictum | Painted sweetlips | Gobaya | Kallu kallewa | Reef-associated | 1694 ± 906 | 47.9 ± 7.5 |
| Lethrinus olivaceus | Long-face emperor | Uru hota | Thinan | Reef-associated | 1886 ± 2275 | 46.4 ± 17.4 |
| Lutjanus lutjanus | Bigeye snapper | Hunu ranna | Nooleni | Demersal | 317 ± 58 | 27.5 ± 1.8 |
| Nemipterus bipunctatuse | Delagoa threadfin bream | - d | Cundil | Demersal | 78 ± 45 | 16.3 ± 3.2 |
| Selar crumenophthalmuse | Bigeye scad | Bolla | Chooparai | Reef-associated | 174 ± 45 | 21.3 ± 1.7 |
| Sphyraena jello | Pickhandle barracuda | Silava | Jeela | Reef-associated | 2885 ± 557 | 88.5 ± 5.6 |
| Fish from Bangladesh | ||||||
| Benthosema fibulatum | Spinycheek lanternfish | Puiya | Mesopelagic | 0.6 | <5 | |
| Bregmaceros mcclellandi | Unicorn cod | - d | Mesopelagic | 0.5 | <6 | |
| Dussumieria elopsoides1 | Slender rainbow sardine | Maricha | Pelagic | 49.7 | 17.0 | |
| Dussumieria elopsoides2 | Slender rainbow sardine | Maricha | Pelagic | 72.6 | 20.3 | |
| Dussumieria elopsoides3 | Slender rainbow sardine | Maricha | Pelagic | 67.8 | 19.3 | |
| Harpadon nehereus1 | Bombay duck | Loittya | Demersal | 110.3 | 25.5 | |
| Harpadon nehereus2 | Bombay duck | Loittya | Demersal | 117.7 | 24.2 | |
| Megalaspis cordyla | Torpedo scad | Kuawa | Pelagic | 114.6 | 25.2 | |
| Pentaprion longimanus | Longfin mojarra | Dom Mach | Demersal | 20.8 | 11.4 | |
| Sardinella fimbriata1 | Fringescale sardinella | Chapila | Pelagic | 35.2 | 16.1 | |
| Sardinella fimbriata2 | Fringescale sardinella | Chapila | Pelagic | 40.3 | 16.4 | |
| Sardinella fimbriata3 | Fringescale sardinella | Chapila | Pelagic | 43.5 | 16.4 | |
| Species a | As (mg/kg w.w.) | Cd (mg/kg w.w.) | Hg (mg/kg w.w.) | Pb (mg/kg w.w.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish from Sri Lanka | ||||
| Small fish | ||||
| Amblygaster sirm | 1.13 ± 0.06 | 0.300 ± 0.026 b | 0.012 ± 0.002 | 0.011 ± 0.001 |
| Auxis thazard | 1.10 ± 0.00 | 0.177 ± 0.021 c | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.006 ± 0.000 |
| Decapterus macrosoma1 | 9.27 ± 1.02 | 1.043 ± 0.100 b | 0.031 ± 0.005 | 0.018 ± 0.001 |
| Decapterus macrosoma2 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 0.467 ± 0.035 b | 0.002 ± 0.000 | 0.006 ± 0.001 |
| Encrasicholina devisi | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.303 ± 0.023 b | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.001 |
| Equulites elongatus | 1.80 ± 0.10 | 0.103 ± 0.006 b | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.002 |
| Leiognathus dussumieri | 3.77 ± 0.38 | 0.049 ± 0.002 | 0.034 ± 0.003 | 0.081 ± 0.017 |
| Photopectoralis bindus1 | 1.57 ± 0.06 | 0.072 ± 0.040 b | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.031 ± 0.001 |
| Photopectoralis bindus2 | 1.90 ± 0.17 | 0.055 ± 0.005 b | 0.007 ± 0.007 | 0.020 ± 0.003 |
| Rastrelliger kanagurta | 0.69 ± 0.03 | 0.273 ± 0.006 b | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.001 |
| Sillago ingenuua | 1.33 ± 0.12 | 0.147 ± 0.006 b | 0.019 ± 0.004 | 0.021 ± 0.007 |
| Stolephorus indicus | 1.80 ± 0.10 | 0.507 ± 0.020 b | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.008 ± 0.001 |
| Mean for small fish | 2.18 ± 2.32 | 0.291 ± 0.275 | 0.015 ± 0.011 | 0.019 ± 0.021 |
| Large fish | ||||
| Carangoides fulvoguttatus | 1.50 ± 0.30 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.035 ± 0.004 | 0.005 ± 0.001 |
| Diagramma pictum | 5.47 ± 0.06 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.094 ± 0.016 | 0.005 ± 0.000 |
| Lethrinus olivaceus | 1.00 ± 0.36 | 0.001 ± 0.000 | 0.180 ± 0.156 | 0.005 ± 0.000 |
| Lutjanus lutjanus | 0.69 ± 0.15 | 0.019 ± 0.004 | 0.150 ± 0.026 | 0.005 ± 0.001 |
| Nemipterus bipunctatus | 0.58 ± 0.09 | 0.012 ± 0.006 | 0.048 ± 0.015 | 0.005 ± 0.001 |
| Selar crumenophthalmus | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 0.027 ± 0.018 | 0.061 ± 0.022 | 0.006 ± 0.000 |
| Sphyraena jello | 0.64 ± 0.28 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.347 ± 0.032 | 0.005 ± 0.000 |
| Mean for large fish | 1.53 ± 1.69 * | 0.010 ± 0.011 *** | 0.131 ± 0.116 ** | 0.005 ± 0.001 *** |
| Fish from Bangladesh | ||||
| Benthosema fibulatum | 2.33 ± 0.06 | 0.183 ± 0.001 b | 0.010 ± 0.001 | 0.032 ± 0.001 |
| Bregmaceros mcclellandi | 1.23 ± 0.21 | 0.033 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.000 | 0.025 ± 0.015 |
| Dussumieria elopsoides1 | 1.77 ± 0.15 | 0.133 ± 0.032 b | 0.017 ± 0.003 | 0.007 ± 0.002 |
| Dussumieria elopsoides2 | 1.04 ± 0.14 | 0.193 ± 0.021 b | 0.020 ± 0.000 | 0.006 ± 0.001 |
| Dussumieria elopsoides3 | 1.37 ± 0.06 | 0.163 ± 0.006 b | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.006 ± 0.000 |
| Harpadon nehereus1 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.007 ± 0.000 | 0.005 ± 0.000 | 0.020 ± 0.000 |
| Harpadon nehereus2 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.013 ± 0.013 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.020 ± 0.000 |
| Megalaspis cordyla | 2.23 ± 0.23 | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.058 ± 0.009 | 0.008 ± 0.004 |
| Pentaprion longimanus | 3.13 ± 0.35 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.003 |
| Sardinella fimbriata1 | 3.07 ± 0.06 | 0.067 ± 0.008 b | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.048 ± 0.003 |
| Sardinella fimbriata2 | 2.87 ± 0.06 | 0.069 ± 0.005 b | 0.017 ± 0.000 | 0.035 ± 0.005 |
| Sardinella fimbriata3 | 2.23 ± 0.06 | 0.091 ± 0.006 b | 0.015 ± 0.002 | 0.062 ± 0.008 |
| Mean for all fish | 1.80 ± 1.01 | 0.082 ± 0.069 *** | 0.017 ± 0.014 *** | 0.023 ± 0.018 *** |
| Metal | Mean Metal Content (mg/kg w.w.) | THQ | HI | TR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish from Sri Lanka | |||||||
| Small Fish | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | |
| As | 2.18 | 0.5208 | 0.6997 | 0.5984 | 0.8040 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 3.1 × 10−3 |
| Cd | 0.291 | 0.0695 | 0.0934 | 7.9 × 10−5 | 1.1 × 10−4 | ||
| Hg | 0.015 | 0.0036 | 0.0048 | NA a | NA a | ||
| Pb | 0.019 | 0.0045 | 0.0060 | 1.2 × 10−7 | 1.6 × 10−7 | ||
| Large fish | |||||||
| As | 1.530 | 0.3655 | 0.4911 | 0.4004 | 0.5379 | 1.6 × 10−3 | 3.1 × 10−3 |
| Cd | 0.010 | 0.0024 | 0.0032 | 2.7 × 10−6 | 3.7 × 10−6 | ||
| Hg | 0.131 | 0.0313 | 0.0420 | NA a | NA a | ||
| Pb | 0.005 | 0.0012 | 0.0016 | 3.0 × 10−8 | 4.1 × 10−8 | ||
| Fish from Bangladesh | |||||||
| As | 1.800 | 0.5400 | 0.7333 | 0.5766 | 0.7830 | 2.4 × 10−3 | 3.3 × 10−3 |
| Cd | 0.082 | 0.0246 | 0.0334 | 2.8 × 10−5 | 2.8 × 10−5 | ||
| Hg | 0.017 | 0.0051 | 0.0069 | NA a | NA a | ||
| Pb | 0.023 | 0.0069 | 0.0093 | 1.8 × 10−7 | 2.3 × 10−7 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© FAO 2021, CC BY NC SA IGO 3.0. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moxness Reksten, A.; Rahman, Z.; Kjellevold, M.; Garrido Gamarro, E.; Thilsted, S.H.; Pincus, L.M.; Aakre, I.; Ryder, J.; Ariyawansa, S.; Nordhagen, A.; et al. Metal Contents in Fish from the Bay of Bengal and Potential Consumer Exposure—The EAF-Nansen Programme. Foods 2021, 10, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051147
Moxness Reksten A, Rahman Z, Kjellevold M, Garrido Gamarro E, Thilsted SH, Pincus LM, Aakre I, Ryder J, Ariyawansa S, Nordhagen A, et al. Metal Contents in Fish from the Bay of Bengal and Potential Consumer Exposure—The EAF-Nansen Programme. Foods. 2021; 10(5):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051147
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoxness Reksten, Amalie, Zillur Rahman, Marian Kjellevold, Esther Garrido Gamarro, Shakuntala H. Thilsted, Lauren M. Pincus, Inger Aakre, John Ryder, Sujeewa Ariyawansa, Anna Nordhagen, and et al. 2021. "Metal Contents in Fish from the Bay of Bengal and Potential Consumer Exposure—The EAF-Nansen Programme" Foods 10, no. 5: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051147
APA StyleMoxness Reksten, A., Rahman, Z., Kjellevold, M., Garrido Gamarro, E., Thilsted, S. H., Pincus, L. M., Aakre, I., Ryder, J., Ariyawansa, S., Nordhagen, A., & Lundebye, A.-K. (2021). Metal Contents in Fish from the Bay of Bengal and Potential Consumer Exposure—The EAF-Nansen Programme. Foods, 10(5), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051147






