Application of Gut Cell Models for Toxicological and Bioactivity Studies of Functional and Novel Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Current Approaches in In Vitro Toxicology
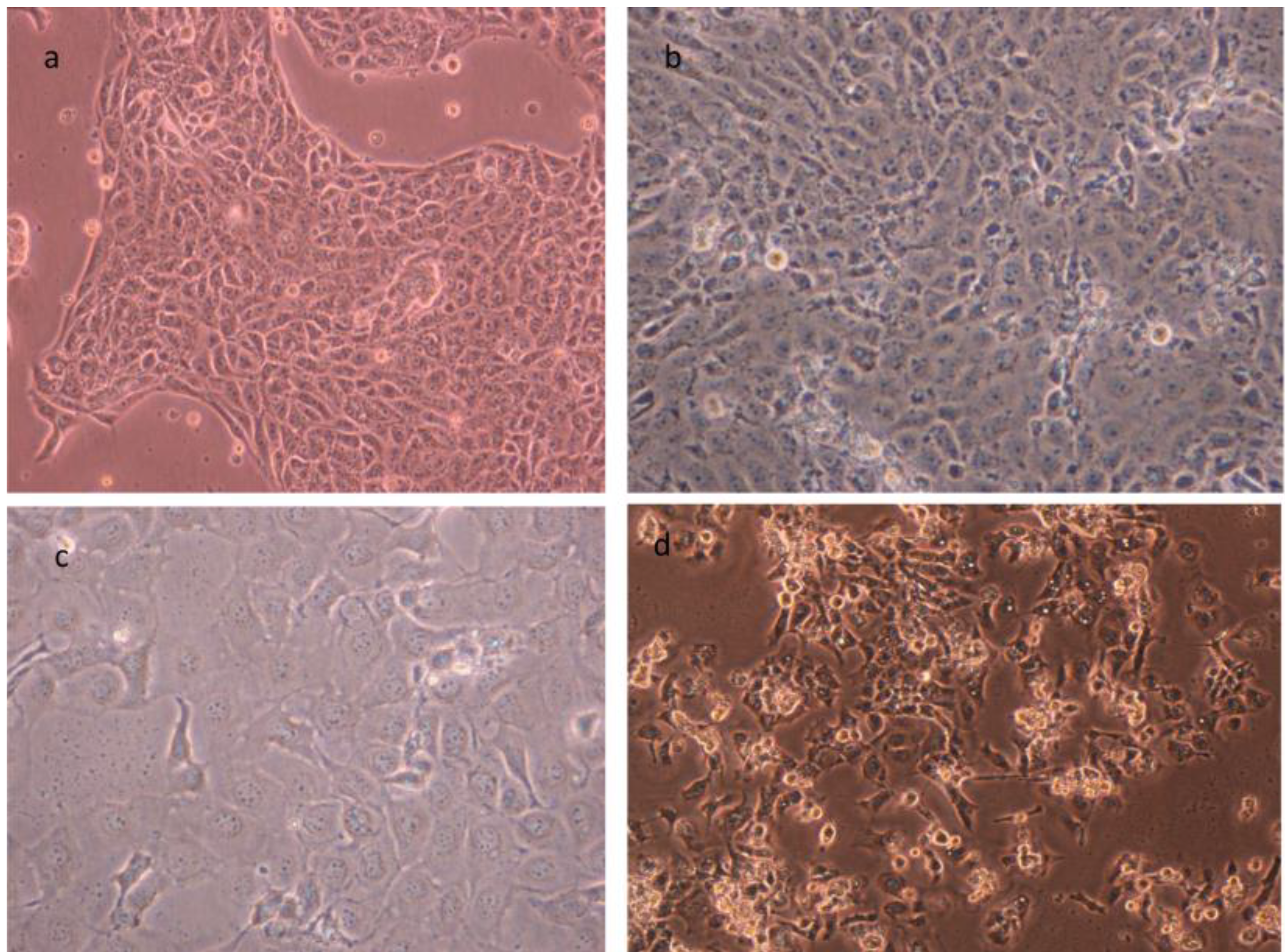
3. Cell Cultures
| Cell Line/Model | Origin | Type | Status | Species | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIEC-6 | Small intestine | Epithelia | Normal | Human | University ofSherbrooke a |
| H4 | Small intestinal foetal tissue | Epithelia | Normal | Human | MassachusettsGeneral Hospital b |
| H4-1 | Small intestinal foetal tissue | Epithelia | Normal | Human | BioNutriTech c |
| PSI-1 | Mature small intestine | Epithelia | Normal | Pig | BioNutriTech c |
| CLAB | Enterocytes | Epithelia | Normal | Pig | BioNutriTech c |
| Pom 2 | Blood | Monocytes | Normal | Pig | BioNutriTech c |
| TLT | Blood | Monocytes | Normal | Human | BioNutriTech c |
| Gut 3D model | Functional | Normal | Human | BioNutriTech c | |
| Gut 3D model | Functional | Normal | Pig | BioNutriTech c |
4. Available In Vitro Cell Models for Risk Assessment and Toxicology Studies of Functional Foods

- Which cell line has the most relevant phenotype for a designed study?
- Which other organ systems have an influence in vivo on our employed system and how can we integrate them in our study?
- Is the model validated and if not, which validated model will be used as comparative control?
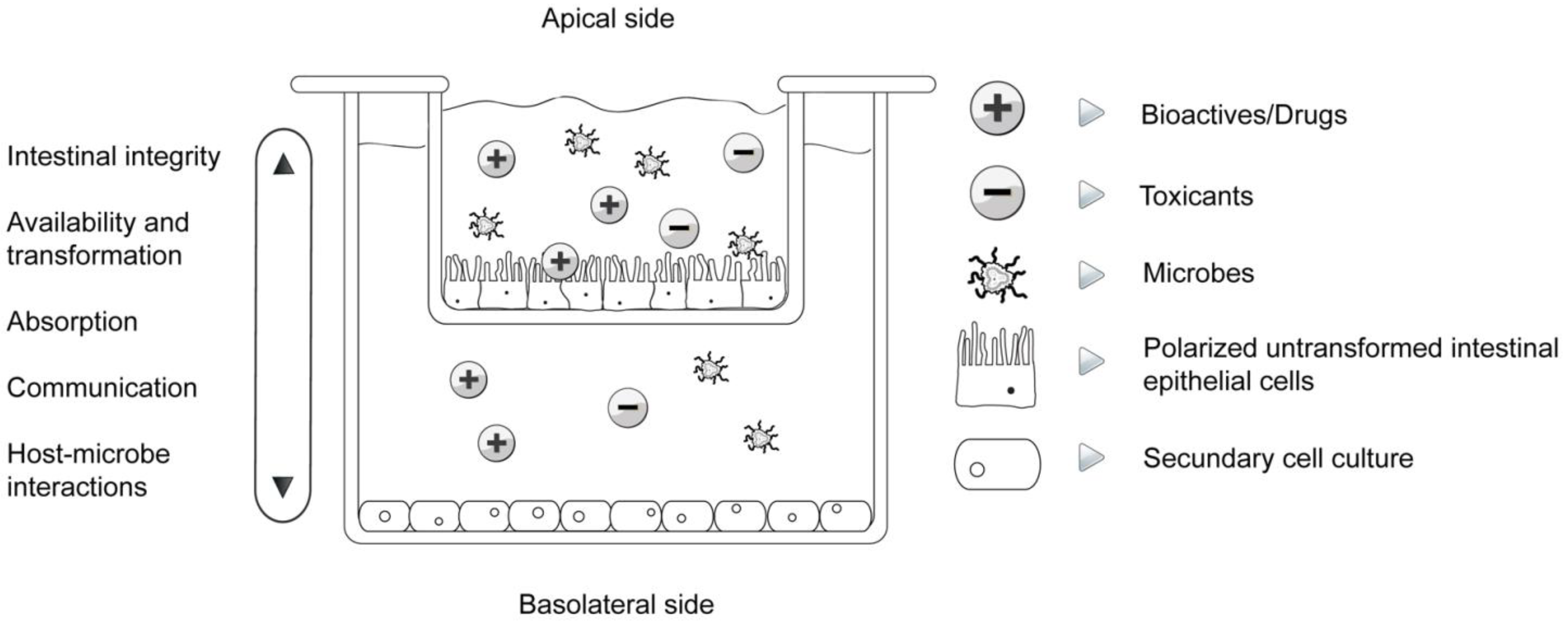
| Study | Parameter/Implications | References |
|---|---|---|
| Trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) | Cell differentiation, connectedness, polarization, intestinal integrity | [8,18,32,35] |
| Bioaccessibility, absorption and biotransformation | Transition from the apical to the basal compartment and vice versa, cellular absorption, transformation | [8,18,24,25,36,37] |
| Host-microbe interactions | Attachment, communication, migration, influence on epithelial function, simulation of normal gut microflora, their influence on biotransformation as well as absorption of bioactives | [26,31,37,38,39] |
| Communication | Cell-cell, cell cross-talk, expression of cytokines, chemokines, nuclear factors, connexins... | [1,8,32,38,40,41] |
| Immunomodulation | Expression of cytokines and nuclear factors in separated apical and basal compartments, immunoprofiling, pro- and anti-inflammatory orientation | [8,32,37,38,40] |
| Custom bioassays | Combination of different strategies, combination of different cell lines, HTS integration | [13,30] |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrari, C.K.; Torres, E.A. Biochemical pharmacology of functional foods and prevention of chronic diseases of aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, P.; de Silva, M.F.; Pettman, S. European regulations on nutraceuticals, dietary supplements and functional foods: A framework based on safety. Toxicology 2006, 221, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugas, M.; Tsigarida, E.; Robinson, T.; Calistri, P. Risk assessment of biological hazards in the European Union. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 120, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, Codex Alimentarius: Foods Derived from Biotechnology; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004.
- World Health Organization, Application of Risk Analysis to Food Standards Issues. Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- World Health Organization, Risk Management and Food Safety—FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 65; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1997.
- Verkerk, R.H.; Hickey, S. A critique of prevailing approaches to nutrient risk analysis pertaining to food supplements with specific reference to the European Union. Toxicology 2010, 278, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencic, A.; Langerholc, T. Functional cell models of the gut and their applications in food microbiology—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S4–S14. [Google Scholar]
- Hartung, T. Comparative analysis of the revised Directive 2010/63/EU for the protection of laboratory animals with its predecessor 86/609/EEC—A t4 report. ALTEX 2010, 27, 285–303. [Google Scholar]
- Snodin, D.J. An EU perspective on the use of in vitro methods in regulatory pharmaceutical toxicology. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 127, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidle, T.; Stephens, M.L. Bringing toxicology into the 21st century: A global call to action. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshian, M.; Akbarsha, M.A.; Blaauboer, B.; Caloni, F.; Cosson, P.; Curren, R.; Goldberg, A.; Gruber, F.; Ohl, F.; Pfaller, W.; et al. A framework program for the teaching of alternative methods (replacement, reduction, refinement) to animal experimentation. ALTEX 2011, 28, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet, E. Current standing and future prospects for the technologies proposed to transform toxicity testing in the 21st century. ALTEX 2011, 28, 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Natsch, A.; Gfeller, H.; Emter, R.; Ellis, G. Use of in vitro testing to identify an unexpected skin sensitizing impurity in a commercial product: A case study. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.; Bremm, K.D.; Alépée, N.; Bessems, J.G.; Blaauboer, B.; Boehn, S.N.; Burek, C.; Coecke, S.; Gombau, L.; Hewit, N.J.; et al. Report from the EPAA workshop: In vitro ADME in safety testing used by EPAA industry sectors. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenfreund, E.; Puerner, J.A. Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicol. Lett. 1985, 24, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North-Root, H.; Yackovitch, F.; Demetrulias, J.; Gacula, M., Jr.; Heinze, J.E. Evaluation of an in vitro cell toxicity using rabbit corneal cells to predict the eye irritation potential of surfactants. Toxicol. Lett. 1982, 14, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapecar, M.; Leouffre, T.; Faure, M.; Jensen, H.E.; Granum, P.E.; Cencic, A.; Hardy, S.P. The use of a porcine intestinal cell model system for evaluating the food safety risk of Bacillus cereus probiotics and the implications for assessing enterotoxigenicity. APMIS 2011, 119, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.; Basketter, D.; Creton, S.; Pelkonen, O.; van Benthem, J.; Zuang, J.; Andersen, K.E.; Angers-Loustau, A.; Aptula, A.; Bal-Price, A.; et al. Alternative (non-animal) methods for cosmetics testing: Current status and future prospects—2010. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 367–485. [Google Scholar]
- Burczynski, M.E.; Rocket, J.C. Surrogate Tissue Analysis: Genomic, Proteomic and Metabolomic Approaches; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nuwaysir, E.F.; Bittner, M.; Trent, J.; Barrett, J.C.; Afshari, C.A.; Trent, J. Microarrays and toxicology: The advent of toxicogenomics. Mol. Carcinog. 1999, 24, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, S.C. Drug Safety Evaluation, 1st ed; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, M.E. Physiologically modelling of organic compounds. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1991, 35, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, E.; Carvajal-Lerida, I.; Perez-Galvez, A. In vitro bioaccessibility assessment as a prediction tool of nutritional efficiency. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Lourenço, H.M.; Nunes, M.L.; Roseiro, C.; Santos, C.; Barranco, A.; Rainien, S.; Langerholc, T.; Cencic, A. New tools to assess toxicity, bioaccessibility and uptake of chemical contaminants in meat and seafood. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 510–522. [Google Scholar]
- Nissen, L.; Chingwaru, W.; Sgorbati, B.; Biavati, B.; Cencic, A. Gut health promoting activity of new putative probiotic/protective Lactobacillus spp. strains: A functional study in the small intestinal cell model. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Blaauboer, B.J. The contribution of in vitro toxicity data in hazard and risk assessment: Current limitations and future perspectives. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 180, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A. Non-animal methodologies within biomedical research and toxicity testing. ALTEX 2008, 25, 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ootani, A.; Li, X.; Sangiorgi, E.; Ho, Q.T.; Ueno, H.; Toda, S.; Sugihara, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Weissman, I.L.; Capecchi, M.R.; Kuo, C.J. Sustained in vitro intestinal epithelial culture within a Wnt-dependent stem cell niche. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbrand, G.; Pool-Zobel, B.; Baker, V.; Balls, M.; Blaauboer, B.J.; Boobies, A.; Carere, A.; Kevekordes, S.; Lhuguenot, J.C.; Pieters, R.; Kleiner, J. Methods of in vitro toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 193–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peracaula, R.; Barrabes, S.; Sarrats, A.; Rudd, P.M.; de Llorens, R. Altered glycosylation in tumours focused to cancer diagnosis. Dis. Markers 2008, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Langerholc, T.; Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Wollgast, J.; Gradisnik, L.; Cencic, A. Novel and established intestinal cell line models—An indispensable tool in food science and nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, S11–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivec, M.; Botic, T.; Koren, S.; Jakobsen, M.; Weingartl, H.; Cencic, A. Interactions of macrophages with probiotic bacteria lead to increased antiviral response against vesicular stomatitis virus. Antiviral Res. 2007, 75, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipenbaher, N.; Moeller, P.L.; Dolinsek, J.; Jakobsen, M.; Weingartl, H.; Cencic, A. Nitric oxide (NO) production in mammalian non-tumorigenic epithelial cells of the small intestine and macrophages induced by individual strains of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breemen, R.B.; Li, Y. Caco-2 cell permeability assays to measure drug absorption. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2005, 1, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Madgula, V.L.; Avula, B.; Choi, Y.W.; Pullela, S.V.; Khan, I.A.; Walker, L.A.; Khan, S.I. Transport of Schisandra chinensis extract and its biologically-active constituents across Caco-2 cell monolayers—An in-vitro model of intestinal transport. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Sergent, T.; Ribonnet, L.; Kolosova, A.; Garsou, S.; Schaut, A.; de Saeger, S.; van Peteghem, C.; Larondelle, Y.; Pussemier, L.; Schneider, Y.J. Molecular and cellular effects of food contaminants and secondary plant components and their plausible interactions at the intestinal level. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 813–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Perna, F.; Carnevali, P.; Vitali, B.; Ciati, R.; Gionchetti, P.; Rizzello, F.; Campieri, M.; Brigidi, P. Interaction of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains with human intestinal epithelial cells: Adhesion properties, competition against enteropathogens and modulation of IL-8 production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeer, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; de Keersmaecker, S.C. Host interactions of probiotic bacterial surface molecules: Comparison with commensals and pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, F.; Mascia, C.; Astegiano, M.; Chiarpotto, E.; Nano, M.; Vizio, B.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Poli, G. Pro-oxidant and proapoptotic effects of cholesterol oxidation products on human colonic epithelial cells: A potential mechanism of inflammatory bowel disease progression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergent, T.; Piront, N.; Meurice, J.; Toussaint, O.; Schneider, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of dietary phenolic compounds in an in vitro model of inflamed human intestinal epithelium. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvault, A.L.; Machado, R.; Afonso, C.; Lourenco, H.M.; Nunes, M.L.; Coelho, I.; Langerholc, T.; Marques, A. Bioaccessibility of Hg, Cd and As in cooked black scabbard fish and edible crab. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, E.; Jonkers, D.; Juuti-Uusitalo, K.; van Ijzendoorn, S.; Troost, F.; Duimel, H.; Broers, J.; Verheyen, F.; Dekker, J.; Masclee, A. Effects of ethanol and acetaldehyde on tight junction integrity: In vitro study in a three dimensional intestinal epithelial cell culture model. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35008. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, D.; Hamilton, G.A.; Ingber, D.E. From 3D cell culture to organs-on-chips. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Trapecar, M.; Cencic, A. Application of Gut Cell Models for Toxicological and Bioactivity Studies of Functional and Novel Foods. Foods 2012, 1, 40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods1010040
Trapecar M, Cencic A. Application of Gut Cell Models for Toxicological and Bioactivity Studies of Functional and Novel Foods. Foods. 2012; 1(1):40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods1010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrapecar, Martin, and Avrelija Cencic. 2012. "Application of Gut Cell Models for Toxicological and Bioactivity Studies of Functional and Novel Foods" Foods 1, no. 1: 40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods1010040
APA StyleTrapecar, M., & Cencic, A. (2012). Application of Gut Cell Models for Toxicological and Bioactivity Studies of Functional and Novel Foods. Foods, 1(1), 40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods1010040




