Abstract
The internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) is a topic of constant research interest due to the impact these have on economic growth and employment in developed, emerging and developing countries. A desire to understand and a growing interest in the study of the internationalization process of SMEs has provoked a significant increase in the production of manuscripts in this field in the last decade. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out periodic reviews on the state-of-the-art of this phenomenon in order to highlight advances and limitations, to motivate reflections and stimulate progress in future research. Thus, the main objective of this study is to describe the state-of-the-art of the research into SME Internationalization based on a bibliometric analysis of 1152 manuscripts published from 1990 to 2018. The results enable the identification of the main agents that are constantly developing this field through an analysis of scientific production and collaboration indicators. Furthermore, through a co-word analysis, this research establishes hot-spot research trends that need to be developed in future research. The main contribution of this research is the configuration of a knowledge map on SME Internationalization research.
1. Introduction
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) are thought to be the cornerstone of the economy of most countries. According to the World Trade Report [1], the majority of firms in every single country are classified as small and medium enterprises. Although a common definition of SMEs does not exist, a consensus of the variables used to classify a business as an SME can be attained, based on thresholds for the number of employees and/or turnover. SMEs are considered to be the engine of economic growth [2,3,4,5] due their large number. Besides, they account for a relevant share of employment [3].
In this regard, not only are they relevant in developing and emerging countries [6,7], but they are also the backbone of the private sector in developed countries. In developing countries, they may act as a vehicle for social inclusion, by enabling certain population sectors, such as women, to participate in economic activities. Moreover, with regard to job creation, SMEs account for two-thirds of total employment in both developing and developed countries. Furthermore, they contribute to the GDP at around 35 percent and 50 percent in developing and developed countries, respectively. Notwithstanding the impact of SMEs on the economy, employment in SMEs is less well qualified than in large firms. Also, the productivity of SMEs and their contribution to GDP is lower than larger companies [1].
Despite the abovementioned role of SMEs in the economy, the accelerated globalization of world markets has spurred SMEs on to compete in international markets, thereby becoming key players in ecosystems that support large enterprises [8]. In this vein, the understanding of the particular process of internationalization in SMEs has gained relevance due to the fact that foreign market entry is regarded as an enabler of competitive advantage [9,10], making their internationalization process a vitally relevant study field [11]. In particular, the idiosyncrasies of SMEs such as their dynamism and capacity to exploit new opportunities and knowledge pave new ways for innovation [3]. Moreover, the internationalization process seems to be different from the process experienced by large companies, not being linear, controlled, or timely [12,13].
Research on the process of SME internationalization has flourished over the last decades [12,14,15,16]. An increasing number of theoretical articles have been published since the 80s, trying to analyze the procedures and approaches towards SME internationalization, focusing especially on the resource constraints they face. It is fair to say that the internationalization of SMEs has drawn the attention of the research community; however, there is a lack of quantitative and bibliometrically based surveys, especially of those focused on the internationalization of SMEs. Existing papers are subject to bias on the part of researchers and often lack many fundamental aspects of a bibliometric study.
Bibliometric analyses are relevant to elucidate the principal agents and the most studied thematic areas of a field of study. In the field of SME Internationalization, it is presumed that a bibliometric study could contribute to facilitate understanding by analyzing its evolution and its intellectual core. Bibliometric analyses are appropriate, bearing in mind that every discipline needs to look in the mirror occasionally to analyze the past and to establish future research lines for both practical as well as theoretical investigations [17]. Furthermore, Prévot et al. [18] argue that bibliometrics is important both for those who are familiar as well as those who are not familiar with a topic.
The aim of this study is to offer a state-of-the-art of the research on SME Internationalization, based on research published from 1990 to 2018 retrieved from the Scopus database in order to show information regarding scientific production, scientific collaboration and a co-word analysis to detect hotspot trends.
Therefore, through a bibliometric analysis of 1152 articles, this manuscript provides several contributions to the literature on SME Internationalization. As a first contribution, it affords an exhaustive overview of this research area from 1990 to 2018, by stating some performance indicators, such as publications per year, most cited articles, most eminent authors, most productive journals, institutions and countries. As a second contribution, this paper graphically illustrates networks of co-authorship and collaboration between countries. Finally, as a third contribution, this study by means of strategic diagram illustrations based on co-occurrence analysis reveals the most researched themes and enables the identification of the most prominent topics. Thus, this literature review presents a unique comprehensive study that extend existing reviews on this topic, by expanding the period under analysis and bringing a new focus to this field.
The outcomes may be valuable for educators, researchers, managers and policymakers. Educators may find a synopsis of themes for inclusion in their teaching resources. Likewise, it provides researchers with a complete picture of the global research on SME Internationalization that will help them to broaden their insights on this topic and act as a guide for future research trends. Managers would gain up-to-date knowledge on mechanisms of SME internationalization. Finally, policymakers, based on such insights, could develop effective incentives for the internationalization of SMEs.
The paper is structured as follows. The next section is a brief review of SME Internationalization literature, followed by a description of the study method. Next, results and discussion are presented. The paper ends with the conclusions, limitations, and main implications of this research.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. SME Internationalization
There is not a global consensus of how a small and medium-sized enterprise should be defined. Certain thresholds based on turnover, size or number of employees are commonly accepted. According to the European Commission [19], the category of micro, small and medium-sized enterprises consists of enterprises that employ fewer than 250 persons or, have either an annual turnover not exceeding €50 million or an annual balance sheet total not exceeding €43 million. Regardless of these thresholds, SMEs have undoubtedly undergone vast international growth in foreign markets through exports, contractual agreements, joint ventures, foreign direct investment (FDI) or a mix of these entry modes and are thus being increasingly recognized for their globalization strategies [20]. Consequently, the analysis of SME internationalization is vital with a view to achieving a better understanding of internationalization patterns in small businesses [21]. The interest of academic researchers does not come as a surprise given the importance of SMEs in the worldwide economy. According to Braunerhjelm and Halldin [21] (p. 60), “the evidence to support a general shift towards a different mode of entry for small and young firms is by and large non-existent”. Thus, the theoretical background is still far from conclusive.
Internationalization may be defined as a process in which firms are increasingly involved in an international market [22,23], with the foreign nature of the operations [23,24] or the actors involved, being the core of the concept [4,25,26]. Accordingly, there is an increase in the awareness of the direct and indirect influences of international transactions on the future of the firm.
SME internationalization has been studied to increase productivity through sales overseas. In this way, research encompasses theories of international business. First, Hymer [27] tried to explain international production through the market power theory, which considers that two conditions should be met to obtain foreign direct investment (FDI), namely competitive advantage and the existence of an imperfection in the target market. In this regard, the Eclectic paradigm (OLI) [28] highlighted three different advantages: Ownership (O), location (L) and internationalization (I). The link between the three dimensions is considered to be an organizational capability that enables competitive advantage.
In this vein, the resource-based view (RBV) states that obtaining resources or capabilities regarded as unique and difficult to imitate endows firms with a competitive advantage [29] in the home country which could also be applied to overseas markets in order to increase economic performance [30]. What is more, internationalization is deemed to be an enabler to discover untapped resources and detect opportunities with the consequent creation of new resources. The process of internationalization could be understood as “the process of mobilizing, accumulating, and developing resource stocks for international activities” [31] (p. 479). Thus, acquisitions or strategic alliances are deemed to be enablers with which to gain new resources [32]. Thus growth, in the sense of international growth, has been tied to internationalization [33].
In addition to resources, the internationalization process has been studied under the institutional-based view, which established that the institutional environment has an important impact on the strategy of the firm and its performance, with the internationalization strategy being influenced by the institution. The adoption of norms and behaviours of the host country may lead the firm to gain legitimacy and maintain its competitive advantage [34]. In a similar way, Chandler [35] proposed the organizational theory of corporate internationalization, which focuses on the link between corporate strategy and organizational structure. This theory analyses the evolution of the organization structure when a firm internationalizes. In this vein, the strategic management view [36] claims the existence of a relationship between corporate strategy, organizational structure and controlling options. Internationalization provokes a regular phase change in the organizational structure of the firm.
Additionally, the network approach focuses on the relevance of the environment and surrounding elements as enablers with regard to the decision to undertake internationalization, with the interaction way being a key driver of the internationalization process [37,38]. Therefore, collaboration with other institutions becomes vital to avoid access barriers [39].
The abovementioned theories have been applied to firms, regardless of size. Whereas SMEs are characterized by their lack of resources and their difficulty to access them, globalization, technology and the information revolution have enabled SMEs to commit to international business. Thus, literature on SME internationalization has spawned areas of research mainly focused on drivers or enablers that help SMEs [20], specific barriers that SMEs have to face [40] and different patterns or pathways to gain access to international markets [41].
2.2. Main Topics in Research
2.2.1. Enablers
The growing interest in the research community to analyse the drivers or enablers to the internationalization process in SMEs is justified by the impact that this process has on competitiveness and growth performance for SMEs. Thus, as far as this process is understood, public regulations could foster the internationalization process. With regards to the factors affecting the internationalization process in SMEs, these can be classified as internal or firm-specific or external factors.
Regarding internal factors, many SMEs are endowed with unique intangible resources and capabilities [42,43,44,45] that make them adept at allocating scarce resources [46]. One of these firm-specific factors is the learning ability [47]. Not only are information and knowledge considered enablers of internationalization, also the entrepreneurial prowess of founders or managers [44] who could have previous managerial experience in international markets, is deemed to be a determining factor [48]. Moreover, the level of innovation could act as an enabler of the process [3,49] in order to help SMEs to gain access to international markets [42,50,51,52]. Moreover, the ability to build networks and clusters [53] or the collaboration strategy have been highlighted as important facilitators of overseas expansion [11].
Research has focused on the study of the external factors, which are those related to the home-country and host-country. Regarding home-country factors, export promotion programs (EPP) or governmental support [53,54], cost and time involved in exporting, transport cost indicators in the home country, market dynamics, industry [53] and background variables from the local business environment [55] are thought to be vital. Although the reduced size of the home market may be an enabler, some studies have shown that internationalization strategy is taken into consideration in SMEs, regardless of the size of their internal markets [44,56,57]. Additionally, in the host country, tariffs, laws, political risk factors, and geographical and psychological distance [58,59] are outlined as the main factors. Overall, one external factor facilitated by globalization that has diminished the cost of internationalization for SMEs is communication innovation [42,57], which has enabled the foreign expansion of smaller firms [57,60,61].
2.2.2. Barriers
Removing barriers is a way to encourage SMEs to consolidate their presence in international markets. Thus, factors that restrict their growth and innovation capacity have been studied in order to propitiate the internationalization process of SMEs.
Regarding the barriers or constraints for SMEs, these have been studied in order to direct policymakers in providing assistance to SMEs to overcome the main difficulties. Although smallness is considered a factor that hampers the internationalization process [62], these studies are grounded on the resource-based view that considered that the lack of capabilities and skills needed to enter in a foreign market was the main restriction to capturing business opportunities [60,61]. In this vein, the dearth of human resources has been analysed [60,63], with the lack of knowledge of international business, inexperience and risk perception, management and organization being characteristics that prevent any kind of internationalization [64].
Additionally, environmental barriers or external impediments are considered even more important when the target market is dissimilar to the domestic market. In such a way, political and operational risks could arise from the foreignness of the new environment, cost issues or access to financial resources [60,63].
2.2.3. Patterns or Pathways
The abovementioned barriers exist at any stage in the international process and differ in intensity depending on the level of internationalization and the way or path a firm chooses to access a foreign market. Selecting the entry mode is considered to be the most important strategic decision that a company has to make in the internationalization process [9,26,65]. It is thought to be a mix of environmental and individual factors [66].
Regarding mode of entries, exporting has been considered the cheapest, simplest and quickest mode of entry [67,68] and consequently, export performance has been largely researched. Other modes of entries are partnership, licensing, franchising and owned subsidiaries.
Additionally, the study of the patterns or pathways in internationalization has gained prominence in the internationalization academic world in recent years. Patterns or pathways encompass different models, from the traditional Uppsala model to born global or international new ventures (INVs) [42,61,69] the born-again global firms [70].
On the one hand, the traditional incremental model, Uppsala model [22] states that the process of internationalization is slow and gradual or by stages. In this vein, the knowledge acquired in the initial stages is used in subsequent stages, with the cumulative processes featuring in the central role of the model [64]. On the other hand, the accelerated internationalization of SMEs is not explained by the Uppsala model [71,72]. In this case, born-global firms/business/ventures or INVs are thought to be those that, on average, generate at least 25 percent of total sales from foreign markets within three years from their inception [42]. Given the number of SMEs that internationalize soon after they are founded, there is an overwhelming majority of born global literature, motivated by the interest from the academic world and political circles [21]. This phenomenon has challenged the traditional views of gradual internationalization and has drawn attention to the new paradigm born-global represents in the world economy with the logic of young and resource-constrained firms [73].
In a similar vein, the concept of born-again global also features in research. According to Schueffel, Baldegger and Amann [41], a born-again global concept conveys the fact that a firm focused on the domestic market decided to make a strategic decision and transform into a globally focused company. Some authors state that the incident that triggers the internationalization process is a change in ownership and/or management, a management buyout, and a takeover by another firm or an administrator, which then triggers the internationalization process [70].
The abovementioned characteristics highlight the increasingly flourishing literature regarding the topic of SME internationalization, which requires a quantitative and qualitative analysis to order previous studies and map future research. To the best of our knowledge, there is only one study regarding this topic.
3. Methodology
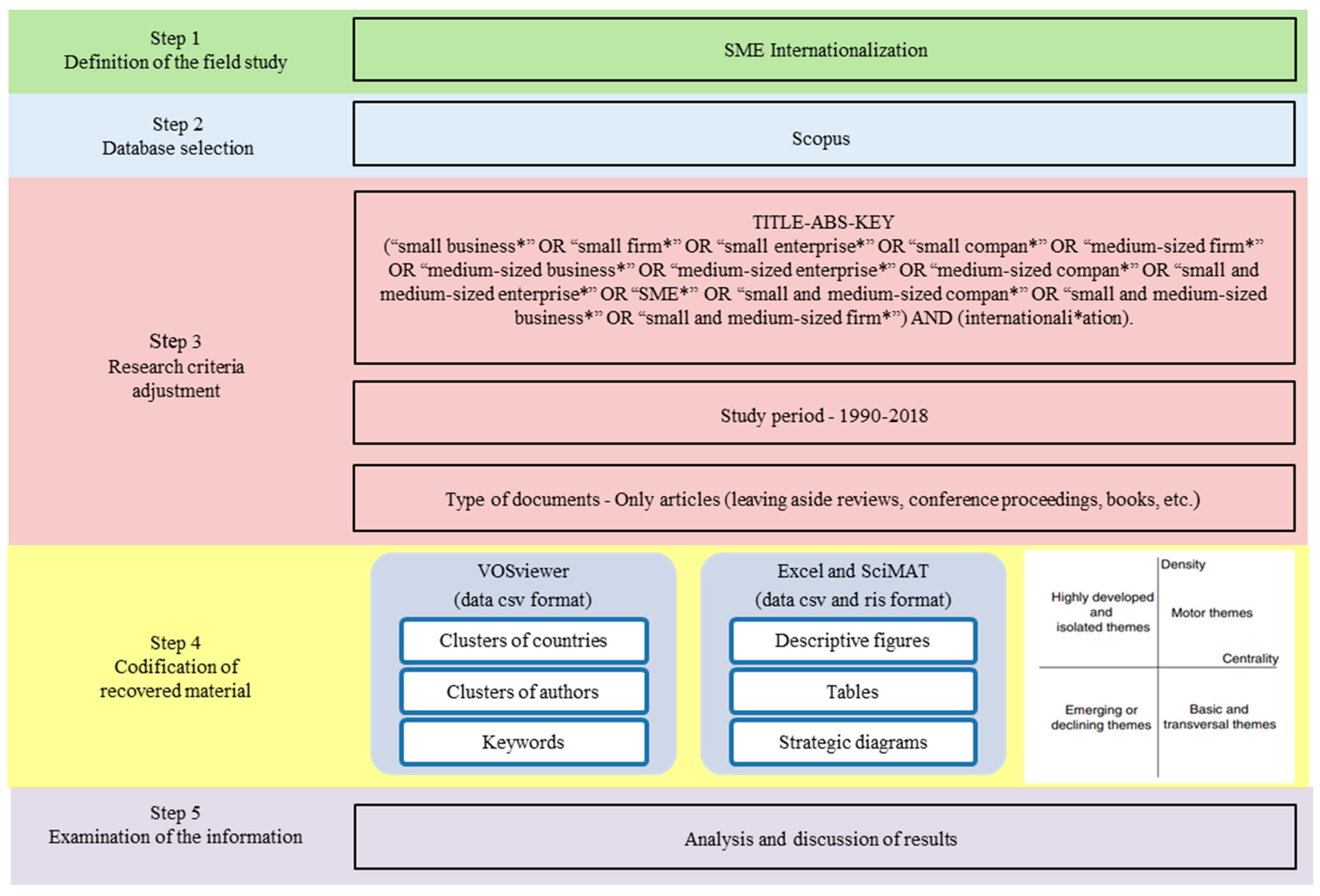
Previous articles [74,75] suggest that bibliometric analyses need to follow five clear steps: (1) definition of the field of study, (2) database selection, (3) research criteria adjustment, (4) codification of recovered material and (5) examination of the information. In this vein, this research follows these steps to carry out a transparent, reproducible and iterative review process. See Scheme 1 for a complete overview of the process.
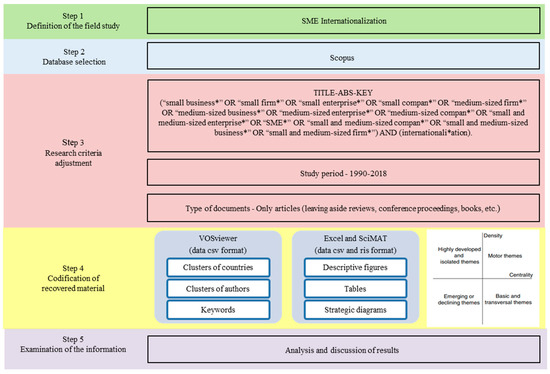
Scheme 1.
Steps of the bibliometric analysis. Source: Own elaboration.
3.1. Definition of the Field of Study
As specified in the introduction section, there is a need to carry out an exhaustive bibliometric analysis on SME Internationalization research. Therefore the core focus of this manuscript is to show information regarding scientific production, collaboration networks and, in particular, a keywords co-occurrence analysis of this field of study.
3.2. Database Selection
Traditionally, bibliometric studies were carried out based on the Web of Science (WoS) database [76,77]. However, the emergence of the Scopus database in 2004 set up a valid alternative to compete with the WoS database [77]. Thus, there are currently two major databases to conduct bibliometric analyses, Scopus and Web of Science (WoS). Based on the study of [78], who argue that 84% of the manuscripts of WoS are also indexed in Scopus and that Scopus contains more journals than WoS, this study was developed with the information from the Scopus database. This reduces the risk of omitting relevant manuscripts during the search.
3.3. Research Criteria Adjustment
Bibliometric analyses need the establishment of very precise research criteria with regard to obtaining the adequate information [17,74]. Thus, in order to address a broad array of word combinations, the parameters used to retrieve the search were: “TITLE-ABSTRACT-KEYWORD” (“small business*” OR “small firm*” OR “small enterprise*” OR “small compan*” OR “medium-sized firm*” OR “medium-sized business*” OR “medium-sized enterprise*” OR “medium-sized compan*” OR “small and medium-sized enterprise*” OR “SME*” OR “small and medium-sized compan*” OR “small and medium-sized business*” OR “small and medium-sized firm*”) AND (internationali*ation). The search was limited to the period between 1990 and 2018, since the first paper on this topic in the Scopus database was located in 1990. In terms of inclusion and exclusion criteria regarding document types, we have included only articles, avoiding review articles (to reduce duplicities), book chapters, books and conferences papers. After the exclusion process, the final sample consisted of 1152 manuscripts.
3.4. Codification of Recovered Material
Data was downloaded from the Scopus database in ris and csv formats and codified using Excel (version 2013), SciMAT (v1.1.04) and VOSviewer (v1.6.9). The permutation of these tools permitted the coding of data for the identification of production indicators (e.g., published articles), the calculation of performance indicators (e.g., h-index), the elaboration of tables, the illustration of descriptive graphs, as well as the debugging and processing of data prior to the use of bibliometric software.
3.5. Examination of the Information
As stated in the codification of the recovered material step, the examination of some information (e.g., calculation of performance indicators or the identification of productivity indicators) was accomplished with Excel (e.g., calculation of formulas) and SciMAT (e.g., detection procedures). Nevertheless, given the core focus and principal aim of this study, it was decided to use two complementary bibliometric tools, i.e., VOSviewer and SciMAT, to illustrate, visualize and identify scientific maps [79,80,81]. On the one hand, VOSviewer is one of the most widely used bibliometric software programs for graphically representing maps that helps to detect collaboration networks between countries and authors [74,82]. On the other hand, SciMAT is a very helpful software that enables the detection of previously researched themes and emerging research trends of a specific field of research though co-word analysis [83].
The results obtained by the co-word analysis, are presented by SciMAT through strategic diagrams that are divided in four quadrants (see step 4 of Scheme 1) [84]. The topics located in the upper right quadrant are known as motor topics, since they possess a strong centrality and a high density. These themes are well developed and are important for the intellectual core of a field. The lower right quadrant includes basic, general and cross-cutting topics. These topics are relevant; nevertheless they still need to be developed. Themes that appear in the lower left quadrant are considered as either emerging or disappearing topics, as they possess low centrality and low density. Finally, themes in the upper left quadrant are peripheral for the field, i.e., they have well-developed internal links but irrelevant external links. Besides, the strategic diagrams comprise a third dimension; within the quadrants appear some spheres (representing the themes) and the volume of each sphere represents the number of documents in which each keyword appears [83].
4. Results and Discussion
Table 1 shows a summary of the coded data used to develop this bibliometric study. This constituted a total of 1152 articles by 1921 authors affiliated with institutions in 78 countries and published in 378 journals, citing 11,022 references.

Table 1.
Summary of used data.
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
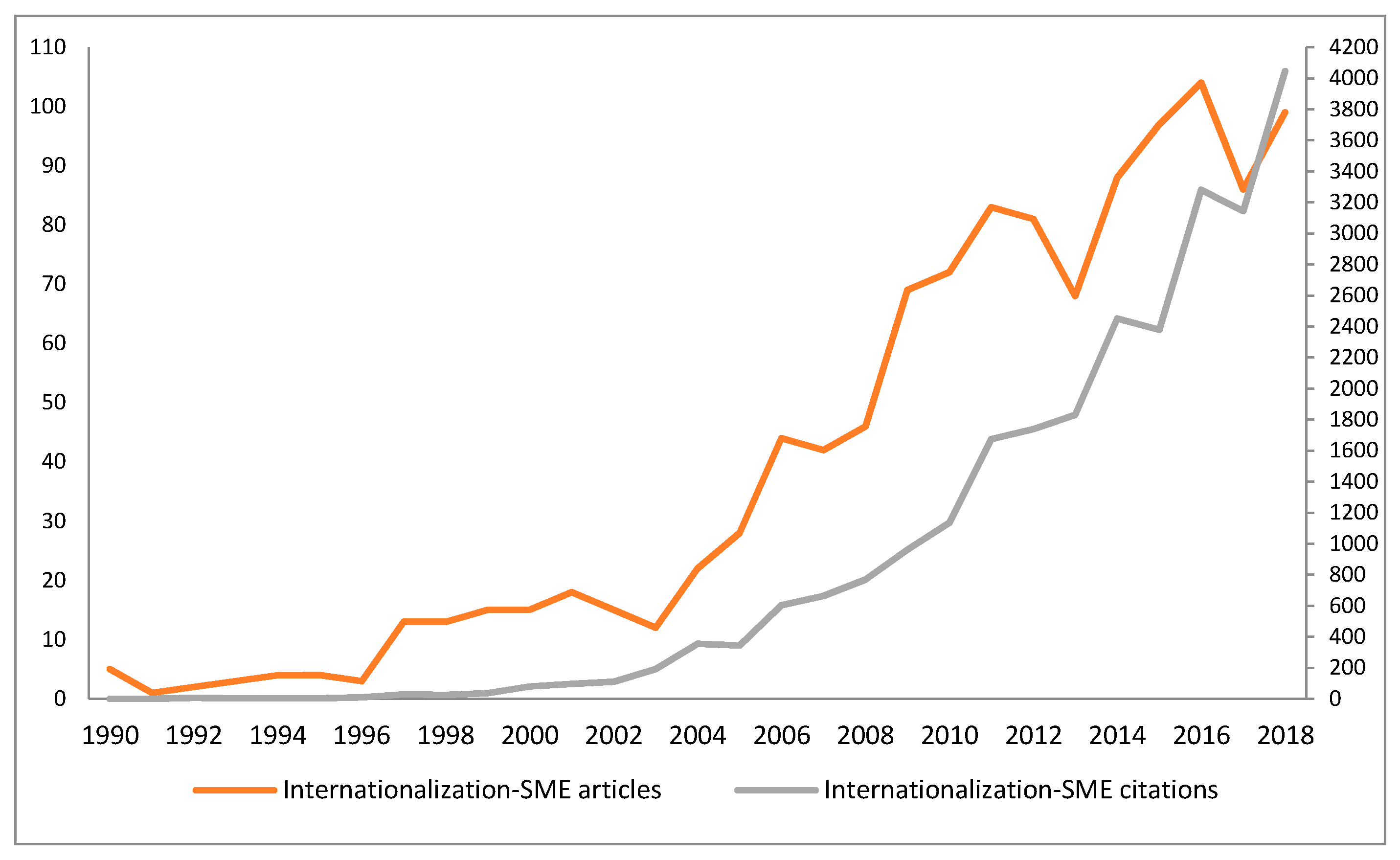
Figure 1 shows that the number of published articles on this subject has increased gradually since 1990. The chronological distribution reveals three stages in the publication trend. The early days comprise the period from 1990 to 1996 in which publications were scarce. In subsequent years—1997-2008—the number of publications increased and the average number of articles published per year was 23.8. From 2009 onwards, research in SME Internationalization received great attention. Despite decreases in research output in some years, the average number of published articles per year was 84.7. This suggests that 74% of the studies on this subject have been published in the last nine years and the trend is upwards. Figure 1 also illustrates that quotes and published articles have grown similarly. These results are consistent with previous studies [85] that established that the first years suffered from low productivity.
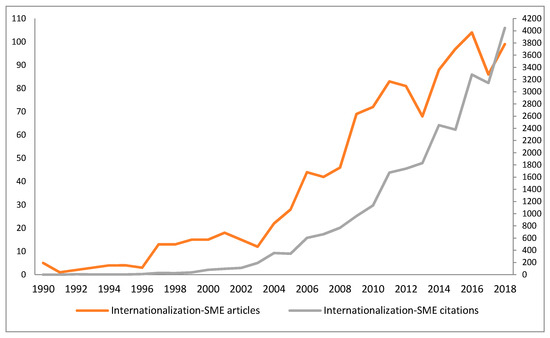
Figure 1.
Evolution of published articles and citations from 1990 to 2018. Source: Own elaboration based on Scopus 2018.
Table 2 shows some of the main characteristics of published papers such as average citations per year, number of authors per year, average number of authors per articles, number of journals and countries that published at least one article in a specific year. As can be seen, 2016 and 2018 are the most productive years with 104 and 99 published articles respectively. Furthermore 2018 stands out as the year with the highest number of citations (4,045) and the highest average citations per article (38.89). This table indicates that the average number of citations per article has also increased exponentially, it could be said that each year more authors are interested in the research on SME Internationalization. Regarding the average number of authors per year, it suggests that there are an increasing number of collaborations among researchers to address this research topic. In addition, there has been constant growth in the number of journals and countries that publish on this subject. In 2018, there were 70 different journals and 42 different countries that published at least one article related to this research topic.

Table 2.
The main characteristics of the articles on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises from 1990 to 2018.
4.1.1. Distribution of Scientific Production
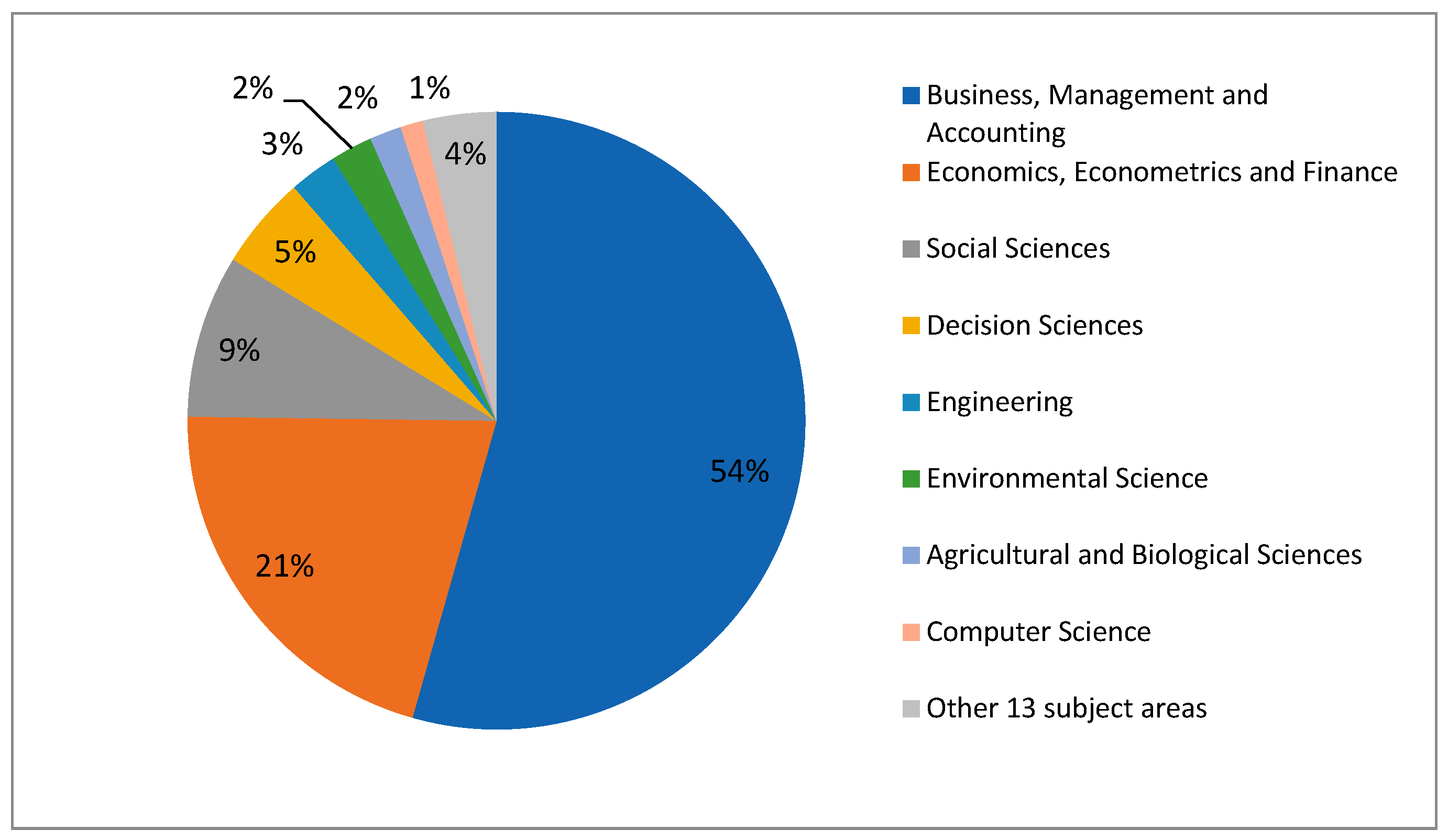
Figure 2 identifies the principal subject areas under which the Scopus database classifies the scientific production on SME Internationalization. As can be seen the most relevant subject area is Business, Management and Accounting with 54% followed by Economics, Econometrics and Finance with 21%. Another two subject areas worth mentioning are Social Science with 9% and Decision Sciences with 5%. These four disciplines encompass 89% of the total published papers; while a further 17 areas together complete the remaining 11% of published articles. As stated by previous studies [85], SME Internationalization research receives attention from academics from many different disciplines. These previous statements are supported by our results.
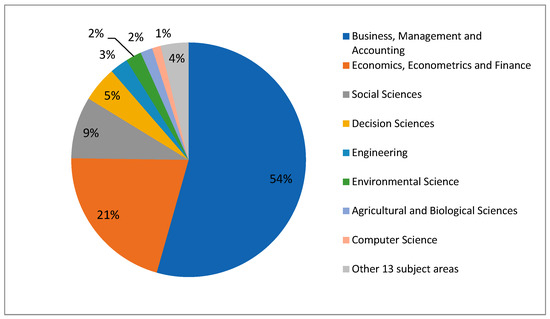
Figure 2.
Subject areas that stand out on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises research. Source: Own elaboration based on Scopus 2018.
As stated in Table 1, SME Internationalization research was published in 378 different Scopus journals from 1990 to 2018. Table 3 notes the ten most productive journals on SME Internationalization during the period under study. In first place is the Journal of International Entrepreneurship with 57 articles followed by the International Business Review and the Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development with 52 and 36 articles, respectively. Further, data reveal that 82.81% of other journals have published between one and three articles.

Table 3.
The top 10 most productive journals on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises research from 1990 to 2018.
Table 3 also presents additional bibliometric indicators, such as citations, average citations per article, year of first publication, year of last publication and the h-Index. The journal with most citations (C) is the International Business Review with 1873 followed by the International Marketing Review with 1112 and the Journal of Small Business Management with 1074. Taking into consideration the average citations per article (C/A) the International Small Business Journal appears at the top with 48.81 citations per article, followed by the Journal of Small Business Management with 42.96 and the International Marketing Review with 38.34 citations per article. In order to try to mitigate the effect of the year of publication, the indicator representing the average number of citations per articles since the year of the first published article (C/Y) is presented. According to this indicator, the International Business Review leads with 89.19 citations per year while the Journal of World Business with 85.64 reaches second place. With regard to the h-Index there are three major journals, these are the International Business Review, the Journal of International Entrepreneurship and the Journal of Small Business Management; all with an h-Index greater than 19. Finally, there is another noteworthy aspect: the top ten journals belong to Europe and the United States. Specifically, eight are from the United Kingdom, one from the Netherlands and one from the United States, demonstrating that journals from these regions are at the forefront of SME Internationalization research.
4.1.2. Countries, Institutions, Authors and Papers
As shown in Table 1, 78 different countries have published articles about SME Internationalization research. The number of documents published by each country and the number of citations each country holds describe the impact of the most influential countries in the research area. Table 4 shows that the most productive country is the United Kingdom with 171 articles, followed by the United States with 128 and Italy with 98. The next place is occupied by Spain with 94 documents. As far as these results are concerned it should be noted that a paper could represent more than one country, as countries are determined by the affiliated institutions of the academics concerned. Considering the number of articles per 1 million inhabitants (AH), Finland reaches first place with 11.34, Sweden appears in second place with 7.75 and the United Kingdom holds third place with 0.39. Analyzing the total number of citations (C) the United Kingdom has the highest number with 3659 followed by the United States and Canada with 3,173 and 3,059, respectively. Also, it is worth mentioning that Canada comes first with 41.34 citations per article, followed by Australia with 30.59 and the United States with 24.79.

Table 4.
The top 10 most productive countries on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises research from 1990 to 2018.
Regarding the h-Index, the United Kingdom reappears in first place with an h-index of 40, followed by the United States with 32 and Australia, Finland and Sweden with 24 each. Another aspect to be highlighted in the results is that Spain began to investigate SME Internationalization in 2005, from which time there has been a great and growing interest in the subject.
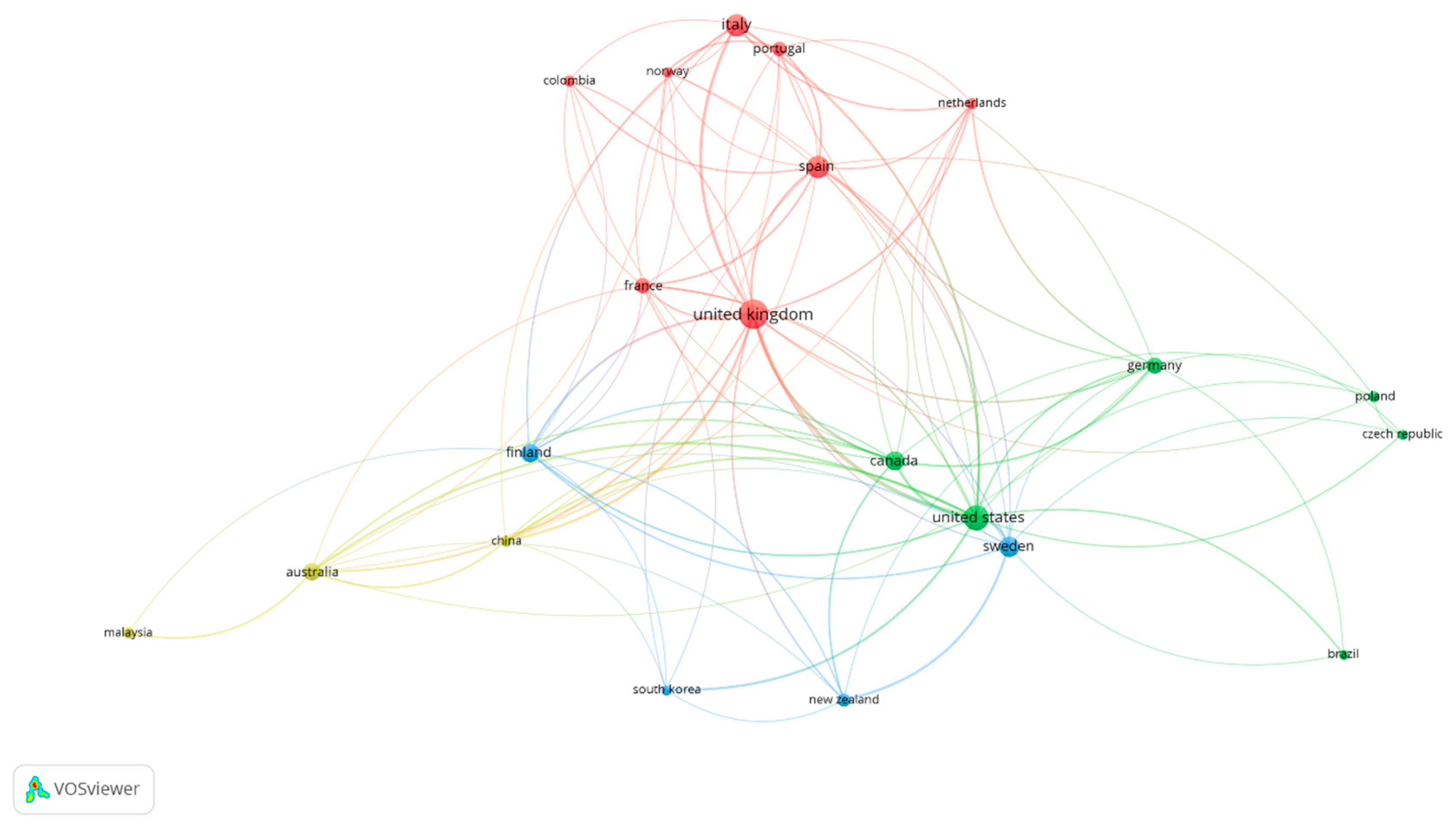
Figure 3 illustrates a network that shows the international collaboration between the principal countries that published articles related to SME Internationalization. The size of circles varies, as it shows the number of published articles per country, while their colour corresponds to the cluster that encompasses each of the different country groups. Four different clusters can be observed. The first one (red) is led by the United Kingdom which presents a strong collaborative link with European countries such as Spain, Italy, France and Portugal. The second group (green) is led by the United States whose main collaborative countries are Canada, Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic and Brazil. The third cluster (blue) is led by Sweden which has close collaborations with countries such as Finland, New Zealand and South Korea. The yellow cluster has Australia as its leader and the main collaborative countries are Malaysia and China.
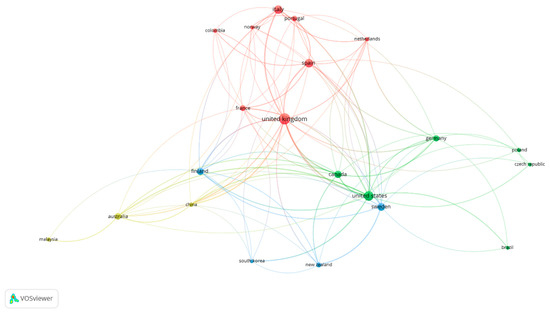
Figure 3.
Network of the co-authorship-based cooperation between countries from 1990 to 2018. Source: Data from Scopus (2018), generated using VOSviewer.
Table 5 presents the main features of the ten most productive institutions on SME Internationalization research from 1990 to 2018. These institutions are located in eight countries. The Lappeenrannan Teknillinen Yliopisto (Finland) takes first place with 23 articles. This is followed by the University of Glasgow (United Kingdom) and Handelshögskolan i Stockholm (Sweden) with 19 papers each, while the other seven centers have between 12 and 17 articles. If we consider the total number of citations (C), the works of the University of Nottingham (United Kingdom) are more cited and it takes first position with 795 citations, followed by Ulster University (Ireland) with 778 and Handelshögskolan i Stockholm (Sweden) with 544. The University of Nottingham is also the institution with the highest average citations per article (C/A) with 66.25 and other two relevant institutions with high number of citations per articles are Ulster University with 45.76 and the Università degli Studi di Pavia (Italy) with 31.13. The University of Glasgow and the University of Seville (Spain) stand out as the institutions with the highest h-Index. Finally, it should be noted that eight of these ten institutions have continued to publish articles related to SME Internationalization in the last two years, which shows that the research fields have been and continue to be very prolific in this area.

Table 5.
The top 10 most productive institutions on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises research from 1990 to 2018.
This study identifies the top 10 ranking influential authors. The main characteristics of the ten most productive authors on SME Internationalization research are shown in Table 6. These ten authors are affiliated with seven institutions, all of which belong to European countries. In particular, three of these authors are linked with Lappeenranta University of Technology (Finland). The author with the most published articles is Crick, D. with 16 followed by Kuivalainen, O. and Saarenketo, S. with 14 articles each. Crick, D. is also the author with most citations (C) and citations per article (C/A) followed by Loane, S., both authors affiliated with universities from the United Kingdom. Other relevant authors are Zucchella, A. with 10 articles and 435 citations and Saarenketo, S. with 14 articles and 412 citations. Finally, it is important to mention that most of these authors have a publishing record of longer than ten years on this topic. This indicates that today, it continues to be a central research topic with opportunities for exploration.

Table 6.
The top 10 most productive authors on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises research from 1990 to 2018.
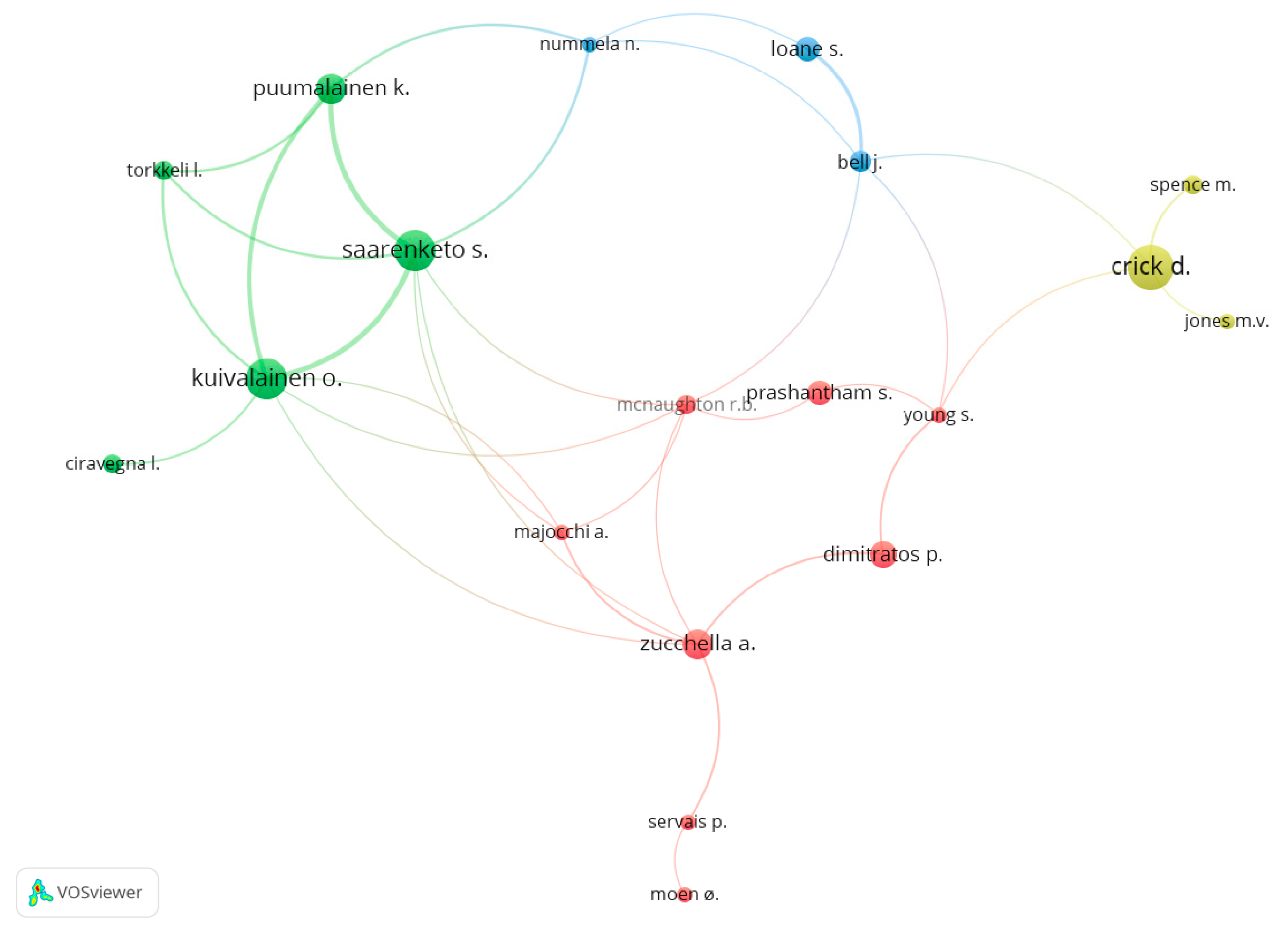
Figure 4 shows a network of relationships between authors who have a minimum of five documents in common. Four different clusters can be observed. The first one (yellow) is led by Crick, D. As already mentioned, he is one of the main authors of the research on the internationalization of SMEs and a relevant author in international entrepreneurship. He works mainly with Spence, M (School of Management in University of Ottawa, Canada) and Jones, M.V. (University of Sheffield, United Kingdom). The second cluster (green) is led by Kuivalainen, O. and Saarenketo, S. respectively. They are the second and the third most productive authors in this area of knowledge and they are affiliated with Lappeenranta University of Technology (Finland). Puumalainen, K. and Torkkeli, L., who also are affiliated with Lappeenranta University of Technology, participate in this cluster jointly with Ciravegna, L. who is affiliated with King’s College London. Zucchella, A. from the University of Pavia (Italy) leads the third cluster (red). Her research area is international business and international entrepreneurship and she also has collaborated with Kuivalainen, O. and Saarenketo, S. Prashantham, S. Dimitrattos, P., Young, S., Majocchi, A. and Prashantham, S. are relevant authors in this cluster. Finally, there is a four cluster (blue) led by Loane, S. She is affiliated with the University of Ulster (United Kingdom). She has worked with Nummela, N. (University of Turku, Finland) and Bell, J. (University of Ulster, United Kingdom).
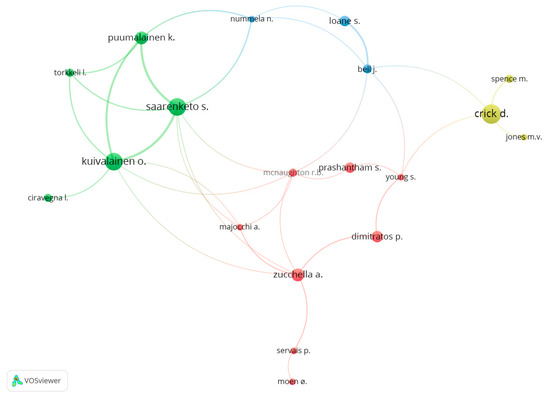
Figure 4.
Network of relationships between authors (minimum five documents in common). Source: Data from Scopus (2018), generated using VOSviewer.
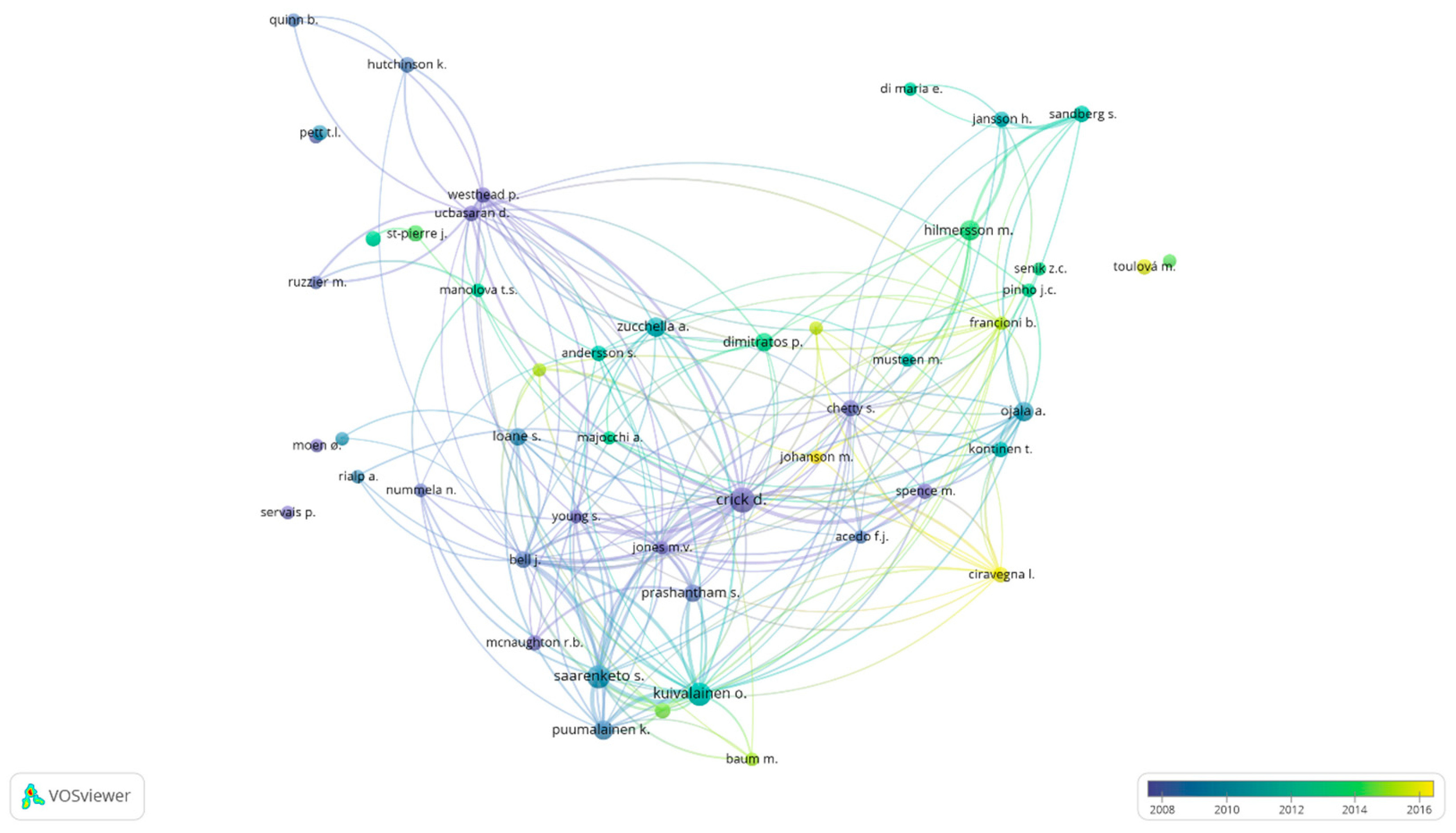
Figure 5 illustrates an overlay visualization map based on the citations received by the authors from 1990 to 2018. This figure shows citation development over time; i.e., it helps to identify which authors had received more citations in the past to detect the authors that were “founders” and relevant for the emergence of a topic. Also, it enables the authors who have been receiving more citations in recent years to be recognized. As can be seen, Crick, D. is the leader of an atomized collaboration network. Similarly, Kuivalainen, O., Saarenketo, S., Ojala, A, and Hilmersson, M. are presented as leaders in this area of study, confirming the results shown in Table 6. However, it should also be noted that in recent years other authors have been receiving considerable attention, such as Ciravegna, I., Johanson, M., Francioni, B., Toulová, M. who are becoming a hotspot trend.
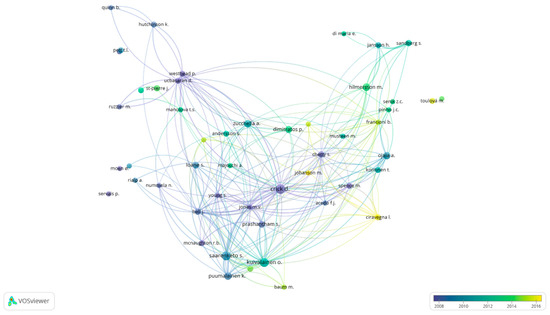
Figure 5.
Overlay visualization based on citations from 1990 to 2018. Source: Data from Scopus (2018), generated using VOSviewer.
Table 7 displays the top five most cited articles from 1990 to 2018. All of them represent papers with the greatest impact in the field of SME Internationalization research. The article, “The internationalization and performance of SMEs”, from Lu and Beanmish [86] is the most cited article with 919 citations. This empirical study examined the effect of two internationalization strategies, exporting and foreign direct investment (FDI), on SME performance (ROA). Coviello and Munro [38] are the authors of the second most-cited article, “Network relationships and the internationalisation process of small software firms”, accounting for 737 citations. This paper offers a conceptual framework of the small firm internationalization process which integrates the “stage” and “network” perspectives. The third most-cited article is “The influence of the management team’s international experience on the internationalization behaviors of SMES” from Reuber and Fischer [87] with 595 citations. This empirical work shows that internationally experienced management teams have a greater propensity to develop foreign strategic partners than to obtain foreign sales, and these behaviours exert subsequent influence in firm performance. Trying to avoid the effect of publication years, the variable C/Y is calculated. As can be seen, the most influential paper is again from Lu and Beanmish [86] with 54.1 citations per year but the second article in order of the variable C/Y is “Internationalization and the performance of born-global SMEs: The mediating role of social network” from Zhou, Wu y Luo [88]. This empirical paper examines the extent to which social networks mediate the influence of internationalization orientations of born-global SMEs on performance measures.

Table 7.
The top five most cited articles from 1990 to 2018.
Finally, it should be noted that two of the top five articles have been published by the same journal, the Journal of International Business Studies. According to the data, this journal occupies the twelfth position with regard to the number of articles published on the research subject.
4.2. Content Analysis
The analysis of the research trends is divided in three sub-periods, selected by the criteria of other previous studies [81,83] that suggest the inclusion of a reasonable number of articles in each period, albeit being for different number of years. In this way, the first sub-period encompasses years from 1990 to 2008 with a total of 305 articles. The second sub-period is from 2009 to 2013, including 373 papers. And finally, the third sub-period is from 2014 to 2018 with a total of 474 articles.
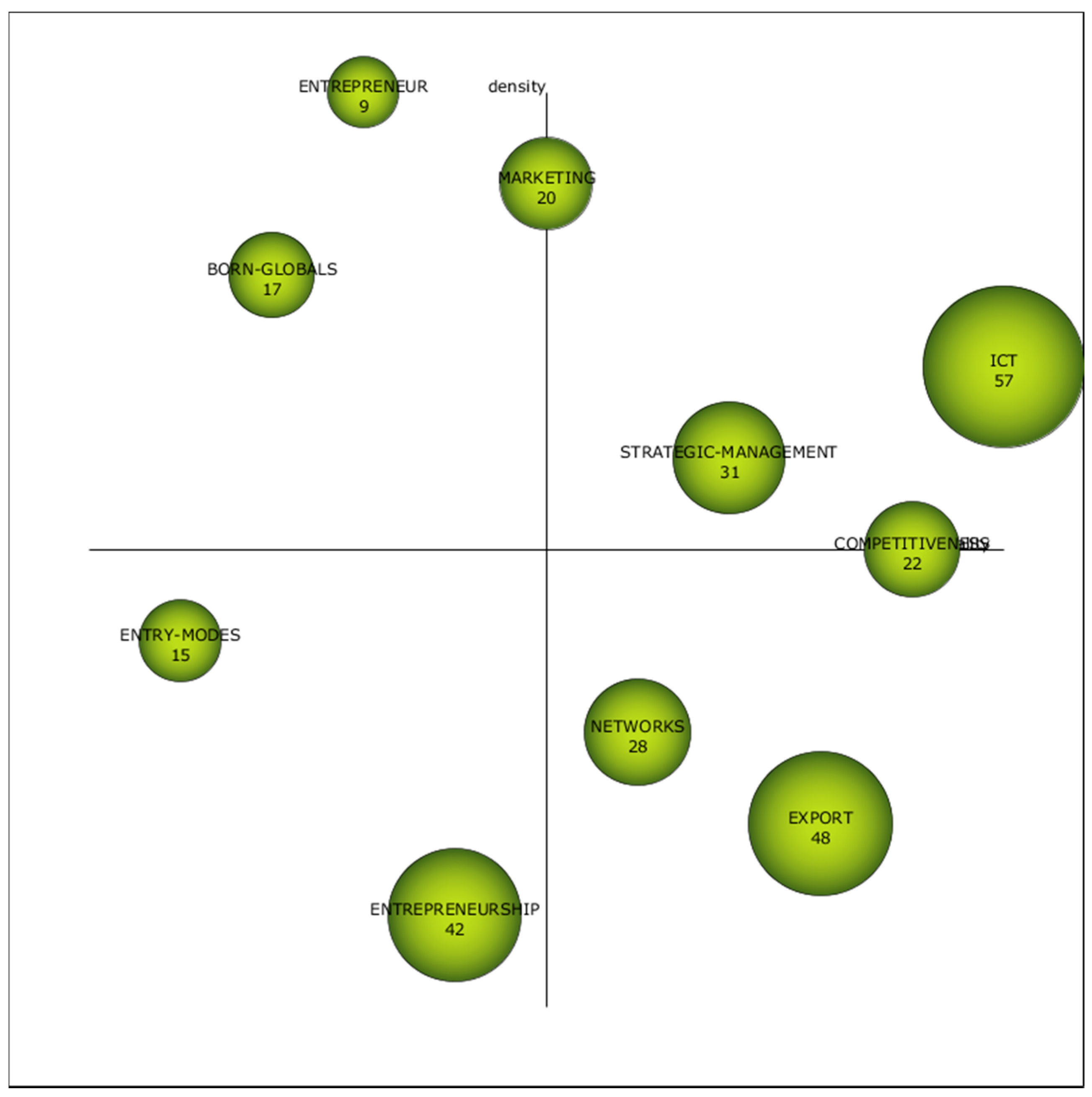
The study of the first sub-period (1990-2008) is shown in the strategic diagram of Figure 6 and in Table 8. The four quadrants present the topics in the literature according to their density and centrality. Regarding the upper right quadrant, this presents three motor themes, which are those that have been thoroughly studied and are crucial in the field due to their high density and strong centrality. Accordingly, in this first sub-period the motor themes are ICT (Information, Communication Technology), Strategic-Management and Competitiveness. The position of ICT does not come as a surprise since advances in ICT fostered new ways to extend businesses [89]. Thus, the capacity of the firm to adapt to new ICTs was considered a key driver for internationalization. Not only does ICT capacity contribute to better export performance by reducing the cost of exporting, the ICT intensity makes rapid, more extensive internationalization possible [90,91]. Moreover, the ICT topic is studied under the knowledge-based view, considering new ICTs as a way to obtain information regarding competitors, specific markets, and customers [91].
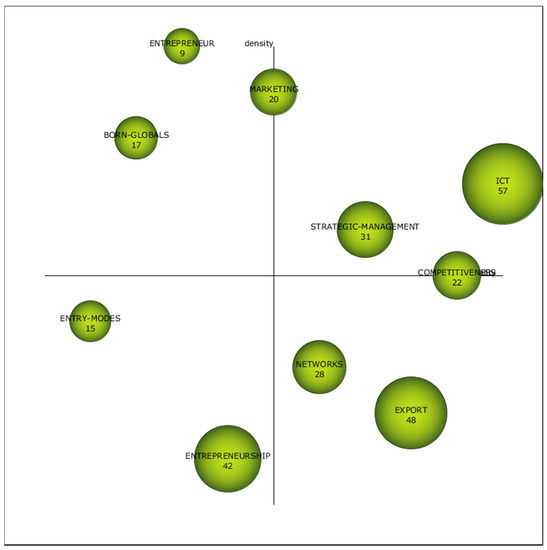
Figure 6.
Strategic diagram from 1990 to 2008. Source: Data from Scopus (2018), generated using SciMAT.

Table 8.
The characteristics of the strategic diagram topics from 1990 to 2008.
Strategic-Management is a motor topic in this sub-period because the importance the design of the organization plays in gaining a competitive advantage in global markets [92]. In this vein, deploying an effective international strategy in accordance with firms’ managerial capabilities is thought to be relevant [93]. Thus, the decision-making process regarding the way a firm could open up to overseas markets could be influenced by management limitations. Accordingly, this was studied as a possible barrier to internationalization. That is, the weaker orientation towards international markets of small enterprises [94,95,96,97]. Moreover, Competitiveness is a motor theme because, as borderless businesses increase, firms have greater pressure to internationalize in order to maintain their competitiveness [98], becoming crucial in developing economies [99].
In regard to the basic themes, those in the lower right quadrant, which are considered the general and cross-cutting themes, two topics seem to dominate this quadrant: Export and Network. Exports is thought to be the most basic and the least risky path to internationalization. For that reason, it appears as a basic theme and there has been an interest in the export performance, showing a positive effect on performance and productivity, [100,101,102,103,104,105] and the role of governmental policies in spurring SMEs on in international business [106]. Regarding the Network view, this is considered as one school of thought for internationalization. This view claims that building relationships with other enterprises, governments, suppliers or customers could play an important role in entering new markets, facilitating entry into foreign markets and fostering export discovery [107,108]. Indeed, networks may make the learning process possible by repeated interaction with foreign agents [109,110]. This concept is related to social capital or social networks, cost and economic-growth.
The lower left quadrant shows emerging or disappearing topics. Figure 6 highlights Entrepreneurship and Entry modes as topics with low density and centrality, with the analysis of their evolution being important in the subsequent sub-periods. Entrepreneurship and Entry-modes appear as themes. Entrepreneurship theory with the keywords international-business, family firms and international marketing and the study of the different entry-modes related with psychic-distance. The first place to start is in the markets that are in closer proximity to the domestic market in terms of physical distance [111].
The upper left quadrant shows themes that are marginal to the field due to irrelevant, albeit well-developed, internal links. These are Born-Global and Entrepreneur.
The second sub-period (Figure 7 and Table 9) encompasses the years from 2009 to 2013 and shows two motor themes: Corporate-strategy and Firm-size. Again, in this sub-period, the term Corporate-strategy is highlighted as a motor theme. Accordingly, the decision of a firm to enter into international markets conveys the corporate strategy of the company. The literature has paid attention to the internationalization decision because it is regarded as the most complex decision a firm could undertake [40]. According to the eclectic theory [28] and the resource-based view, the firm may make the internationalization decision if it has the competitive resources and knowledge to obtain a competitive advantage [40].
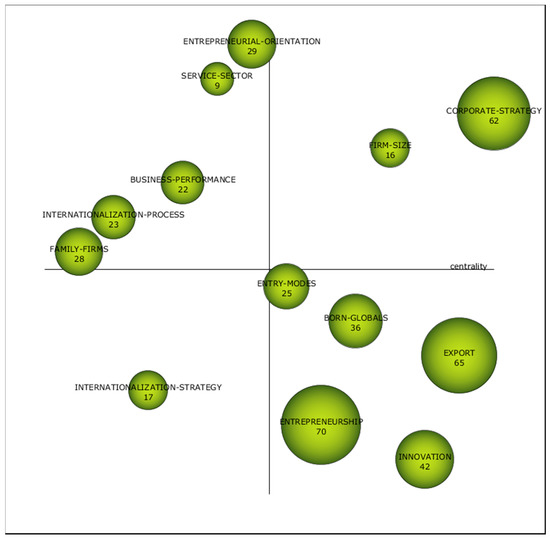
Figure 7.
Strategic diagram from 2009 to 2013. Source: Data from Scopus (2018) generated using SciMAT.

Table 9.
The characteristics of the strategic diagram topics from 2009 to 2013.
The second motor theme is Firm-size, which is not surprising due to its connection with SMEs. Firm-size is considered an internal factor, together with human resources, managerial knowledge, technological innovation and ICT capacity that have all been studied by the research community as internal barriers. Namely, Firm-size is related to lower resource capacities in terms of financing, knowledge, and managerial experience. While some authors have revealed empirically that larger firms are more likely to engage in international businesses and show better export performance [112,113], others have seen Firm-size as enabling rather than restraining the international process, especially with born-global firms [114]. In such a context, Firm-size has been considered a key determinant of the entry mode. For instance, Abel Koch [115] revealed that the propensity of indirect exporting decreases with firm size.
The five basic themes convey topics that are relevant and ones which should be well-developed. It is worth noting that Entrepreneurship was in the first sub-period as an emergent topic and in this second sub-period appears as a basic theme due to its connection with International Entrepreneurship. An extant literature exists regarding the importance of entrepreneurship [116] and attempts to describe the entrepreneur. According to the entrepreneurship process perspective, emphasis is put on opportunism as the ability to recognize international opportunity [117]. In this context, it is important to recognize an opportunity, in particular in emerging economies [118]. The strategic orientation in emerging economies is a topic of interest that deserves more attention since SMEs in emerging markets have different access to resources, capabilities and networks [119] and government is committed to providing support [120] as the promotion of entrepreneurship could help economic growth. In this vein, economic growth and competitiveness have been fostered through entrepreneurship and innovations [121,122]. Successful regional economies are thought to be efficient in terms of innovative systems and to have higher levels of entrepreneurship [123].
Exports remains among the basic themes in the second sub-period, as it was in the first sub-period. The theme Born-Global changes from an isolated theme to a basic theme, showing the growing interest in the research community, however it has not grown enough to be considered a well-developed topic.
Furthermore, Entry-modes becomes basic in the second sub-period. Innovation appears as a basic theme. Inasmuch as it is regarded as an enabler to internationalization, the interest in the research community has grown. The lack of innovation in SMEs has led to governments promoting innovation as a way to gain competitive advantage in international markets [3].
Emergent or decadent topics can also be observed such as internationalization-strategy which is connected with global mindset. Furthermore, there are other isolated topics such as Entrepreneurial-Orientation, Family-Firms, Business-performance, Internationalization-process and Service-Sector.
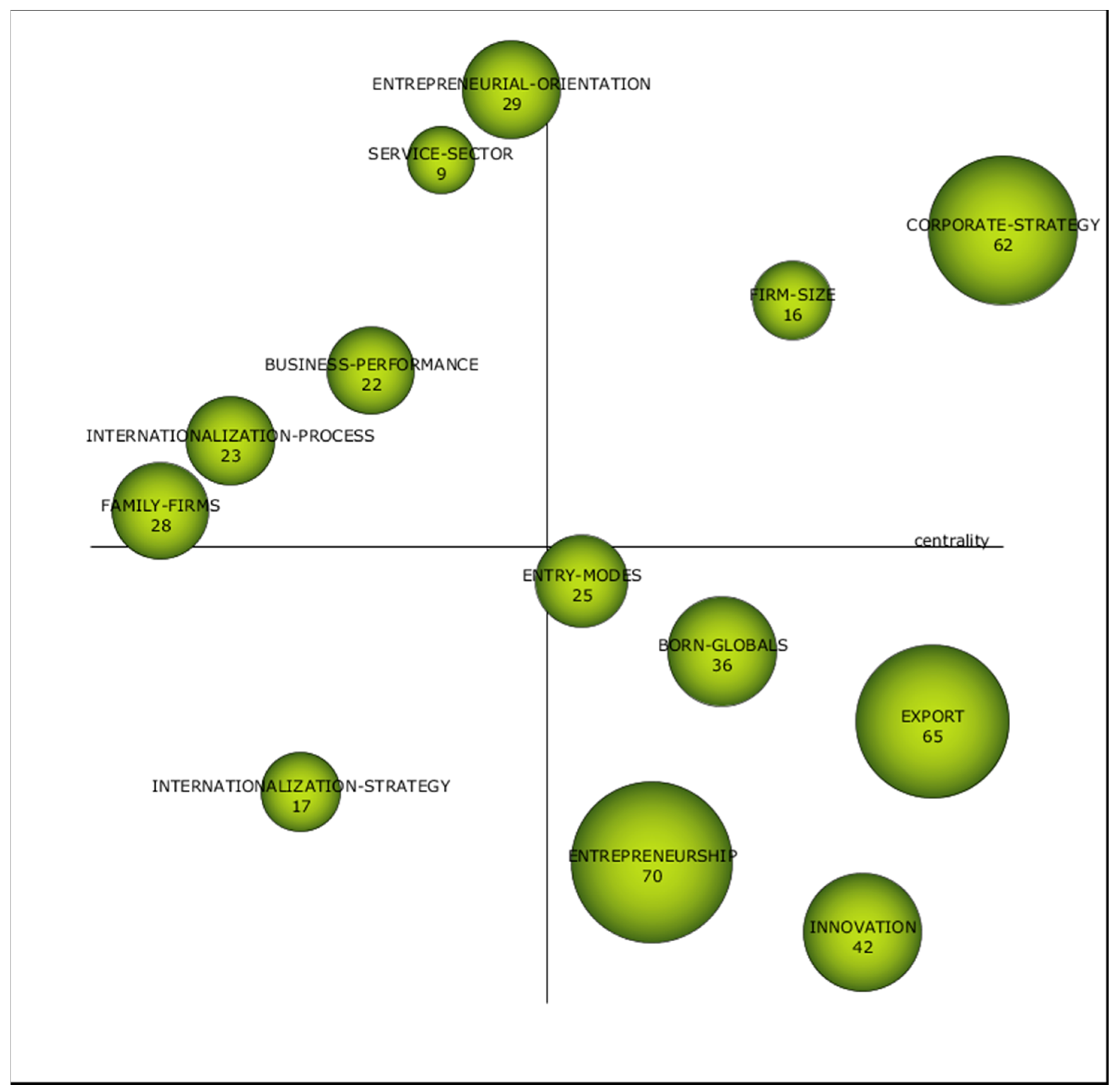
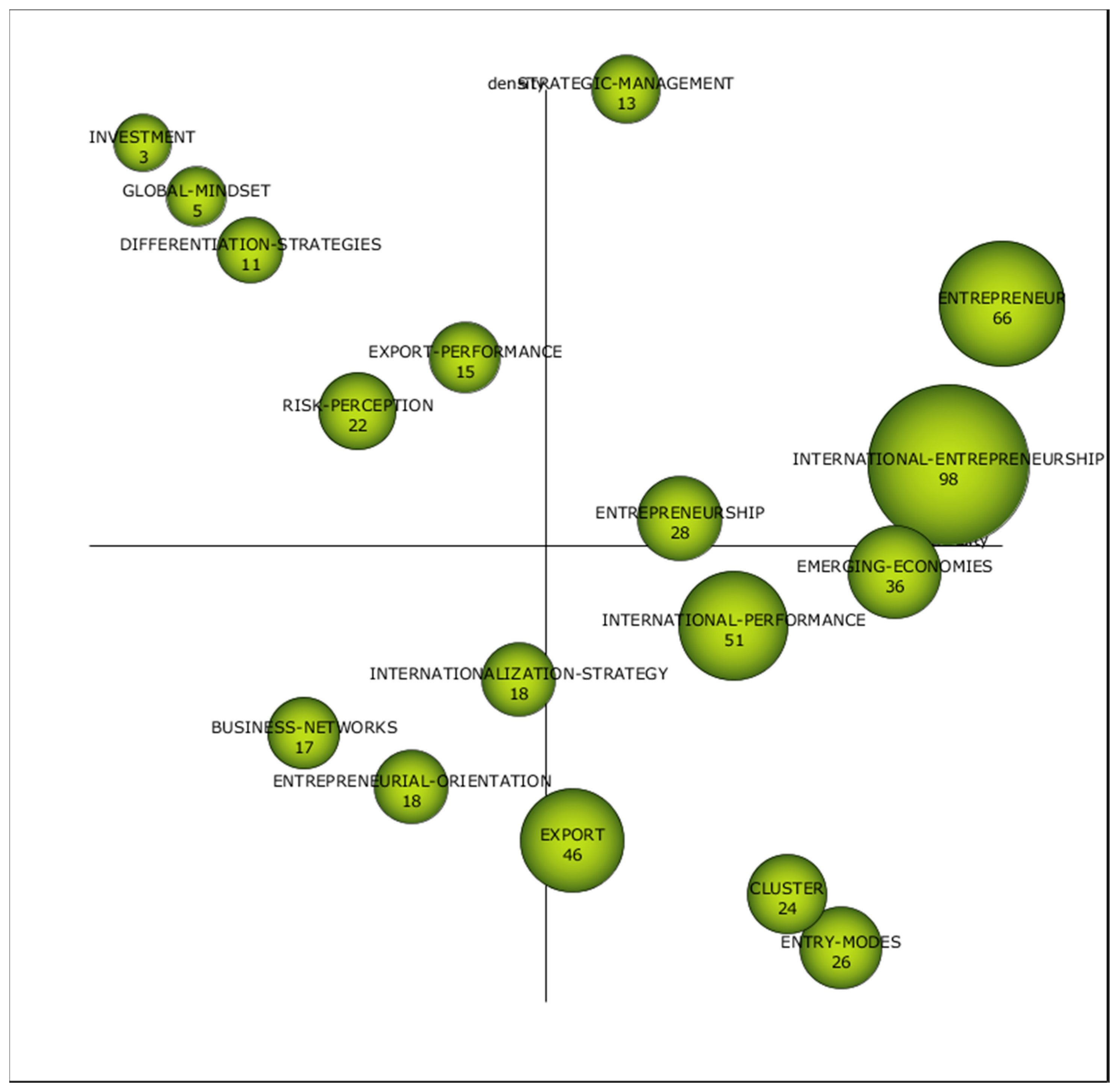
The analysis of the third sub-period (Figure 8 and Table 10) presents four motor themes: International-entrepreneurship, Entrepreneurship, Entrepreneur and Strategic-management. It is worth mentioning that Entrepreneurship was an emergent topic in the first sub-period, a basic one in the second sup-period and a motor theme in the last. Moreover, International-entrepreneurship appears as a topic on its own. International-entrepreneurship is grounded in theories of international business and entrepreneurship [124]. It was McDougall [125] who first used the term, “development of international new ventures or start-ups that, from their inception, engage in international business”. Others highlight that technological progress has brought about the opening of new markets internationally, giving rise to International-entrepreneurship as a new phenomenon [126]. For whatever the reason, it has become a well-developed field of research and the concept has evolved in the last years, being the internationalization of small businesses a particular part of the domain of International-entrepreneurship [127]. In this vein, Networks, opportunity-recognition and born-globals are related topics.
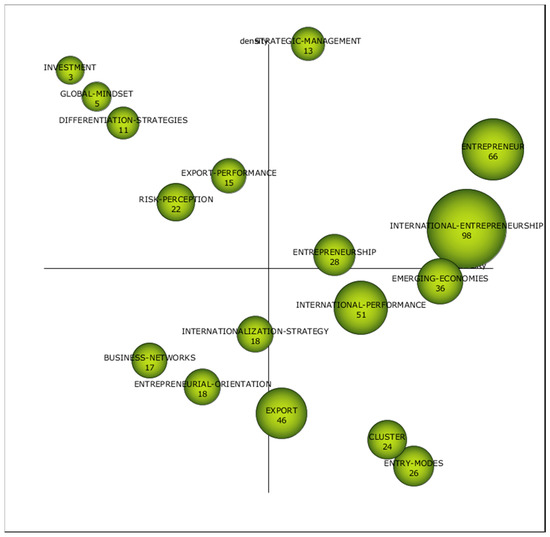
Figure 8.
Strategic diagram from 2014 to 2018. Source: Data from Scopus (2018), generated using SciMAT.

Table 10.
The characteristics of the strategic diagram topics from 2014 to 2018.
The role of the Entrepreneur is studied in order to find out the personal characteristics of the founder that leads to an international commitment in the framework of the entrepreneurship theory [128]. In this regard, the word is connected to innovation and technological innovation. Thus, Entrepreneurship becomes a motor theme. Strategic-management remains as a motor theme in the three sub-periods. This shows that the strategy of globalization has gained prominence and become increasingly relevant. According to Yang [129], internationalization conveys that strategic management is an all-round international standard.
As far as the basic themes are concerned, these are International-performance, Export, Emerging-economies, Entry modes and Clusters. In this sub-period, international performance is analyzed together with business performance and, in particular, family firms, showing a widespread field of research. Exports and entry modes remain as basic themes. Emerging economies appears as a basic topic, related to internationalization-knowledge, internationalization processes and marketing capabilities. Cluster is also one of the basic themes, due to the fact that SMEs that are immersed in an industrial cluster are more likely to achieve international performance.
In the lower left quadrant, Internationalization strategy, Business network, Entrepreneurial orientation appear as emergent or decadent topics. In this vein, research has emphasized the importance of deploying an effective international strategy with a focus on human resources due to the fact that the Internationalization strategy depends on the market selection, mode of entry, pathway or adaption of the product, and this strategy goes hand in hand with human capital [130]. Thus, previous experience or knowledge from managers could have an impact on the decision to opt for internationalization. Similarly, Entrepreneurial orientation is thought to be a dynamic capability that has been studied under the resource-based theory [131] and could be fostered through entrepreneurial orientation since it could enhance the external business environment [132]. Finally, Business network is highly influenced by social capital, which is said to be a crucial element in supporting the decision to opt for internationalization and in enabling the process [133].
4.3. Interpretation of the Analysis
The results obtained through the bibliometric analysis show the state-of-the-art of SME Internationalization research, based on 1152 articles indexed in the Scopus database from 1990 to 2018. Table 11 highlights the most relevant results and the primary conclusions of this research. Alongside this, Figure 9 illustrates a comprehensive knowledge map of the intellectual structure of this field in a simple and interactive way.

Table 11.
Most relevant results and primary conclusions of the manuscripts that address the Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises.
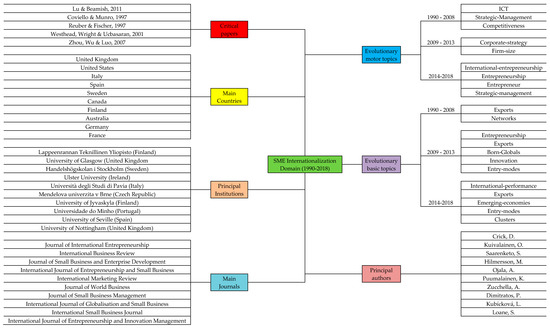
Figure 9.
A comprehensive knowledge map on Internationalization of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises research.
Table 11 shows that SME Internationalization is a consolidated theme in the literature. As displayed in Figure 1 and Table 2 it has been a topic of growing interest since 2004, reaching its highest productive year in 2016 with 104 publications. Looking at the distribution of the scientific production, of the total of 1152 articles retrieved for this study, 54% correspond to the subject area of Business, Management and Accounting followed by that of Economics, Econometrics and Finance with 21% and then Social Sciences with 9%. This demonstrates that research on this subject is concentrated in these three subject areas (83% of total publications). Furthermore, even if SME Internationalization research is published in a widespread number of journals, the majority of those correspond to journals devoted to research on international entrepreneurship, international business, international marketing, small businesses and entrepreneurship.
The analysis of the number of articles published by country illustrates that European and North-American countries are the most productive ones, with the three most important being the United Kingdom, the United States and Italy. However, the most productive institution, Lappeenrannan Teknillinen Yliopisto, does not belong to any of these countries but is located in Finland. Looking at the most prominent authors, those who have the highest number of published manuscripts are Crick, D., Kuivalainen, O. and Saarenketo, S. It should also be noted that the ten most productive authors belong to European institutions, strengthening the dominance of this continent in research on the internationalization of SMEs. In general, these results reinforce the case that SME Internationalization research is published by a large number of countries, institutions and authors in a widespread number of journals.
Regarding some collaboration indicators, country co-authorship studies shows that the United Kingdom, the United States, Sweden and Australia are the leaders of the four collaboration clusters for researching this topic. Similarly, the majority of countries that belong to these clusters correspond to European countries. Furthermore, analyzing author co-authorship, it was found that there are five authors who are the most important when it comes to establishing collaborative links between authors; these are Crick, D., Loane, S., Kuivalainen, O., Saarenketo, S. and Zuchella, A. The collaborative network between countries and authors, demonstrate that there is only a moderate level of collaboration for the research on SME Internationalization.
Focusing on impact indicators, it can be established that the most representative (cited) papers in this field correspond to Lu and Beamish [86] with 919 citations, Coviello and Munro [38] with 737 citations, and Reuber and Fischer [87] with 595 citations. Regarding the most cited country, the United Kingdom appears again at the top with 3659 citations. Furthermore, the most cited institution also corresponds to the United Kingdom; this is the University of Nottingham with 795 citations. Moreover, the most cited journal also belongs to the United Kingdom; i.e., the International Business Review with 1873 citations. These results reflect that the United Kingdom is the country that leads the way in research in this field.
Finally, the content analysis (just the third period, i.e., 2014-2018) developed through a co-word analysis, illustrates that there exist four motor topics that attract the most research in this field. These are: International-entrepreneurship, Entrepreneurship, Entrepreneur and Strategic-management. Similarly, the analysis allows five basic and transversal topics to be identified that need to be developed and that emerge as future lines of research, these being International-performance, Exports, Emerging-economies, Entry-modes and Clusters.
Based on our results and in an attempt to compare with previous research on the topic [85,134], some similarities and differences have been found. First, with regard to the period of time analyzed, database selection and search parameter, they are different. While in Ribau et al. [134] the period is from 1977 to 2014, the databases used are EBSCO, Emerald, Web of Science and ScienceDirect and the sample encompasses 554 articles; Dabić et al. [85] analyzed the period 1992-2017, the database used is Web of Science and the sample consists of 762 articles. It is worth mentioning that the search parameter used in the present study is broader than the one applied in [85,134]. Second, both studies [85,134] agree with the present research, by stating that Europe is the most productive geographic area, highlighting the importance of SMEs across Europe. The most productive countries are coincident, being United Kingdom, United States and Italy. Moreover, emerging economies is deemed as a research gap in [85], although in [134] developing economies is said to require further research. Third, with regard to the core or motor topics, our results show similar conclusions with [134]. In this vein, the three studies coincide in the topic of international performance as a topic that deserves more future research. As the authors in [134] state, despite the variety of research on internationalization, there is a need to understand the impact of internationalization on financial performance. Also, entry modes is a topic that is thought to require further research. Finally, entrepreneurship topic is highlighted as a motor stream in [85] as well as in the present study.
5. Conclusions
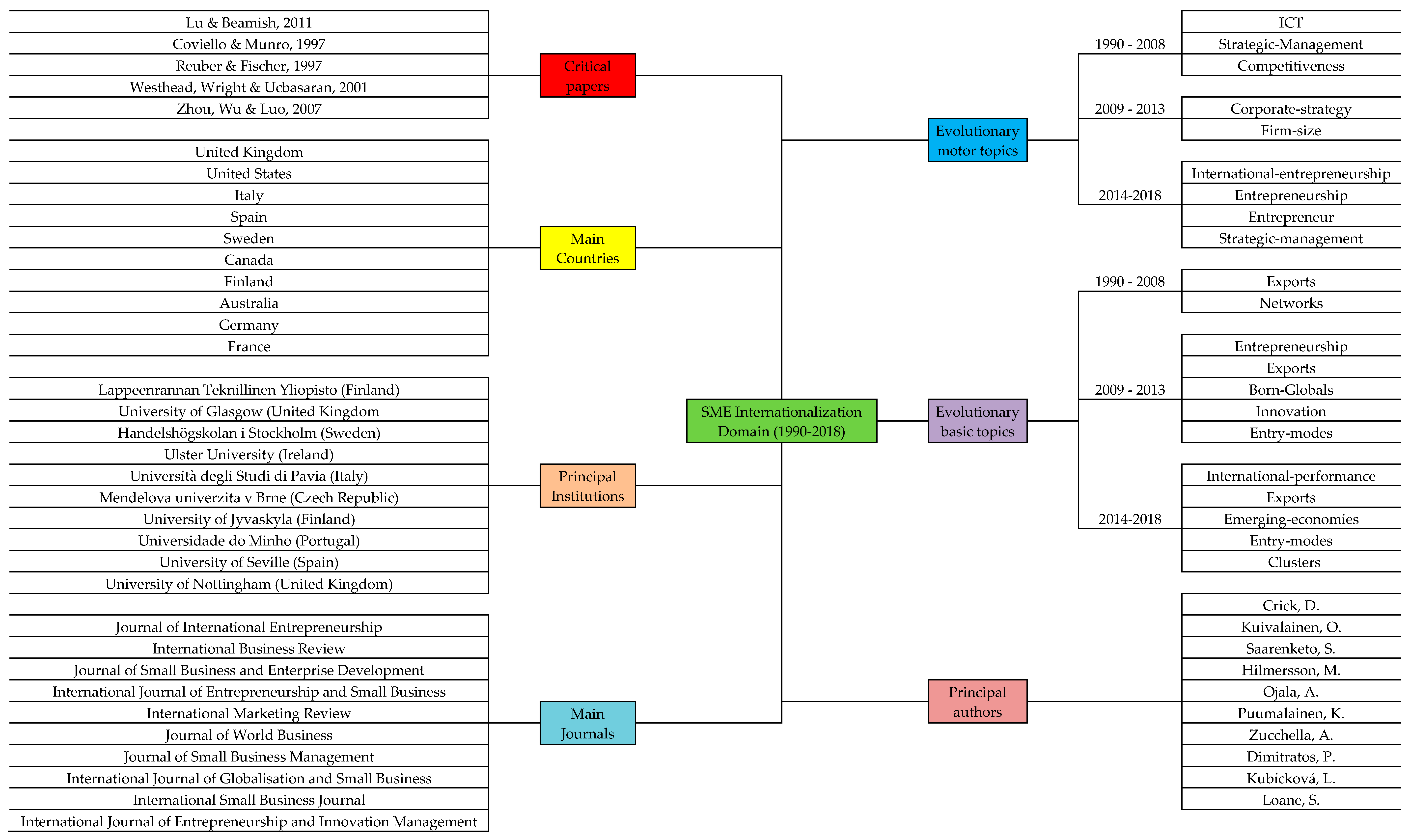
The aim of this study is to analyze the state-of-the-art of SME internationalization research and to detect research gaps through bibliometric techniques. Therefore, the principal contribution of this manuscript is the use of bibliometrics for the study of this field. This research, based on a great number of peer-reviewed articles (1152 in total between 1990-2018) elucidates productivity indicators, collaboration indicators and impact indicators, which help scholars to detect the main agents (authors, institutions, countries and journals) that are developing this field (see Figure 9).
Besides this, based on the analysis of the keywords used by authors to characterize their studies and by a co-occurrence analysis, it was possible to suggest some topics that need to be developed in the future. First, internationalization is associated with the term international entrepreneurship inasmuch as the process, based on the creation, discovery, evaluation and exploitation of opportunities, focuses on markets other than the domestic one. In this vein, the competitive advantage is pursued by the figure of the international entrepreneur who seeks to foster innovation and technological innovation as a way to open new international markets. Furthermore, the concept of born-global is highlighted inasmuch as it conveys a new logic for young and resource-constrained firms. Accordingly, the role of the entrepreneur is crucial in the internationalization process since certain personal characteristics could encourage the seeking out and detection of international opportunities. This is particularly true in emerging economies where entrepreneurship education could become an enabler for the discovery of international opportunities and to increase the competitiveness of SMEs with the consequent economic growth. Finally, internationalization strategy may be analysed not only with regard to individual firms, but also from the point of view of industrial clusters, thereby revealing a different mode of entry or pathway.
The implications of this study are twofold. First, international organizations have claimed that the relevance of SMEs to economies deserves special attention in an endeavor to bring clarity to SME internationalization.
Second, the presentation of a well-established and comprehensive bibliometric analysis may help young and senior researchers to broaden their knowledge regarding SME internationalization and most importantly, to detect literature gaps. The origin, evolution and current status of SME Internationalization is set out as well as the distribution of the research between subject areas, journals, countries, institutions and authors. Finally, academics researching on this topic may find this study relevant since it provides information regarding the status of current research, helping to identify future research opportunities.
This work is not exempt from certain limitations. First, the characteristic of a bibliometric analysis is that it is based mainly on quantitative analysis and it is true that some authors may publish few papers but nevertheless have a significant influence on their research area [135]. Second, the selection of one database, Scopus, over another, for instance the WoS database could also be a limitation. However, Scopus was chosen due to the fact that almost 84% of the articles in WoS can be found in Scopus [78]. Moreover, there are fewer indexed journals in WoS than in Scopus. Thus, the selection of the Scopus database reduces the risk of overlooking documents. Third, not all relevant research regarding born global and international new ventures is taken into account. Only literature about these patterns or pathways has been uncovered if the articles used SME internationalization as a term specifically [134]. Fourth, the selection of the periods is based on the decision of the researchers albeit being based on previous studies that used SciMAT for similar studies [81,84]. Finally, it should be taken into consideration that this study covers only studies published up until 2018.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.d.P.C.-B. and G.M.M.-C.; Formal analysis, M.d.P.C.-B. and G.M.M.-C.; Methodology, E.T.-Y. and M.d.l.M.C.-U.; Software, M.d.l.M.C.-U.; Validation, E.T.-Y.; Writing—original draft, M.d.P.C.-B., G.M.M.-C., E.T.-Y. and M.d.l.M.C.-U.; Writing— review & editing, M.d.P.C.-B., G.M.M.-C., E.T.-Y. and M.d.l.M.C.-U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Trade Organization. World Trade Report 2016: Levelling the Trading Field for SMEs; WTO, Ed.: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bruque, S.; Moyano, J. Organisational determinants of information technology adoption and implementation in SMEs: The case of family and cooperative firms. Technovation 2007, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, E.; Dayan, M.; Genc, O.F. The impact of SME internationalization on innovation: The mediating role of market and entrepreneurial orientation. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2019, 82, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghzaoui, S. SMEs’ internationalization: An analysis with the concept of resources and competencies. J. Innov. Econ. Manag. 2011, 7, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, W.; Stumpo, G. Small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises in Latin America and the Caribbean under the new economic model. World Dev. 2000, 28, 1643–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agndal, H.; Chetty, S. The impact of relationships on changes in internationalisation strategies of SMEs. Eur. J. Mark. 2007, 41, 1449–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, P.R.; Javalgi, R.R.G. Internationalization of SMEs in India: Fostering entrepreneurship by leveraging information technology. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2007, 2, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikowski, P. A bibliometric analysis of born global firms. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 85, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.M.; Richardson, C. The internationalisation of service-sector SMEs in an emerging market. Rev. Int. Bus. Strateg. 2019, 29, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Baum, M. Internationalization strategy, firm resources and the survival of SMEs in the export market. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2014, 45, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Soares, A.L.; De Sousa, J.P. Information, knowledge and collaboration management in the internationalisation of SMEs: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rod, M.; El Banna, A.; Munim, A. SME Internationalization: An Critical Review of Non-Traditional Approaches. In Proceedings of the 32nd Industrial Marketing and Purchasing Group Conference, Poznan, Poland, September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Etemad, H.; Wright, R.W. Internationalization of SMEs: Toward a New Paradigm. Small Bus. Econ. 2003, 20, 1–4. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40229246 (accessed on 18 September 2019). [CrossRef]
- Bratkovic, T.; Antoncic, B.; Ruzzier, M. Strategic utilization of entrepreneur’s resource-based social capital and small firm growth. J. Manag. Organ. 2009, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keupp, M.M.; Gassmann, O. The past and the future of international entrepreneurship: A review and suggestions for developing the field. J. Manag. 2009, 35, 600–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.V.; Coviello, N.; Tang, Y.K. International Entrepreneurship research (1989–2009): A domain ontology and thematic analysis. J. Bus. Ventur. 2011, 26, 632–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi Silva, V.V.; Ribeiro, J.L.D.; Alvarez, G.R.; Caregnato, S.E. Competence-Based Management Research in the Web of Science and Scopus Databases: Scientific Production, Collaboration, and Impact. Publications 2019, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévot, F.; Branchet, B.; Boissin, J.P.; Castagnos, J.C.; Guieu, G. The intellectual structure of the competence-based management field: A bibliometric analysis. Res. Compet. Based Manag. 2010, 5, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. User Guide to the SME Definition; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015.
- De Massis, A.; Frattini, F.; Majocchi, A.; Piscitello, L. Family firms in the global economy: Toward a deeper understanding of internationalization determinants, processes, and outcomes. Glob. Strateg. J. 2018, 8, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunerhjelm, P.; Halldin, T. Born globals—Presence, performance and prospects. Int. Bus. Rev. 2019, 28, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.; Vahlne, J.-E. The internationalization process of the firm-a model of knowledge development and increasing foreign market commitment. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1977, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, L.S.; Luostarinen, R. Internationalization: Evolution of a Concept. J. Gen. Manag. 1988, 14, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calof, J.L.; Beamish, P.W. Adapting to foreign markets: Explaining internationalization. Int. Bus. Rev. 1995, 4, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, P.W. The internationalization process for smaller ontario firms: A research agenda. In Research in Global Strategic Management; Rusman, A., Ed.; JAI Press: Greenwich, Conn, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert, L. Stratégies internationales et développement d’un leadership mondial. Gestion 2002, 27, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymer, S.H. The International Operations of National Firms. In A Study of Direct Foreign Investment; MIT Monographs in Economics: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, J.H. The Eclectic Paradigm of International Production: A Restatement and Some Possible Extensions. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1988, 19, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, C.A.; Ghoshal, S. Managing Across Borders—The Transnational Solution; Harvard Business School Press: Brighton, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzzier, M.; Hisrich, R.D.; Antoncic, B. SME internationalization research: Past, present, and future. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2006, 13, 476–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Teng, B.-S. Between Trust and Control: Developing Confidence in Partner Cooperation in Alliances. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1998, 23, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsakienė, R.; Tvaronavičienė, M. The Internationalization of Smes: An Integrative Approach. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2012, 13, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMaggio, P.; Powell, W. The Iron Cage Revisited: Institutional Isomorphism in Organizational Fields. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1983, 48, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, A.D. Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of the American Industrial Enterprise; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Stopford, J.; Wells, L. Managing the Multinational Enterprise; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Blomstermo, A.; Eriksson, K.; Lindstrand, A.; Sharma, D.D. The perceived usefulness of network experiential knowledge in the internationalizing firm. J. Int. Manag. 2004, 10, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, N.; Munro, H. Network Relationships and internationalisation process of the Small Software Firms. Int. Bus. Rev. 1997, 6, 361–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinz, H.J.; Van Rijnsoever, F.J.; Nauta, F. How to Green the red Dragon: A Start-ups’ Little Helper for Sustainable Development in China. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2016, 25, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, Z.; Nieto, M.J. Internationalization strategy of small and medium-sized family businesses: Some influential factors. Fam. Bus. Rev. 2005, 18, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueffel, P.; Baldegger, R.; Amann, W. Behavioral patterns in born-again global firms: Towards a conceptual framework of the internationalization activities of mature SMEs. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2014, 22, 418–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.A.; Cavusgil, S.T. Innovation, organizational capabilities, and the born-global firm. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantunen, A.; Nummela, N.; Puumalainen, K.; Saarenketo, S. Strategic orientations of born globals-Do they really matter? J. World Bus. 2008, 43, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rialp, A.; Rialp, J.; Knight, G.A. The phenomenon of early internationalizing firms: What do we know after a decade (1993–2003) of scientific inquiry? Int. Bus. Rev. 2005, 14, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.; Matherne, B.; Carleton, J. Technological Resource Leveraging and the Internationalisation of New Ventures. J. Int. Entrep. 2003, 1, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavusgil, S.T.; Knight, G. The born global firm: An entrepreneurial and capabilities perspective on early and rapid internationalization. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2015, 46, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Ocampo, J.; Govindan, K.; Gonzalez-Perez, M.A. Internationalization of Mexican family firms: The cases of Xignux and Grupo Alfa. Rev. Int. Bus. Strateg. 2017, 27, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewerdine, L.; Welch, C. Are international new ventures really new? A process study of organizational emergence and internationalization. J. World Bus. 2013, 48, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervan, S.; Al-Ansaari, Y.; Xu, J. Environmental determinants of open innovation in Dubai SMEs. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 50, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivalainen, O.; Sundqvist, S.; Saarenketo, S.; McNaughton, R.B. Internationalization patterns of small and medium-sized enterprises. Int. Mark. Rev. 2012, 29, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiman, B.; Golovko, E. Innovation and internationalization through exports. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2011, 42, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, J.; García-Rodríguez, R.M. Technology and export behaviour: A resource-based view approach. Int. Bus. Rev. 2005, 14, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratten, V.; Dana, L.P.; Han, M.; Welpe, I. Internationalisation of SMEs: European comparative studies. Int. J. Entrep. Small Bus. 2007, 4, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonidou, L.C.; Palihawadana, D.; Theodosiou, M. National Export-Promotion Programs as Drivers of Organizational Resources and Capabilities: Effects on Strategy, Competitive Advantage, and Performance. J. Int. Mark. 2011, 19, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stottinger, B.; Holzmuller, H. Cross-National Stability of an Export Performance Model—A Comparative Study of Austria and the US. Manag. Int. Rev. 2001, 41, 7. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40658177 (accessed on 25 September 2019).
- Shimbun Nikkei Sangyoo. Benchaa Shin Sedai (New Generation Ventures); Nihon Keizai Shimbun: Tokyo, Japan, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Eurofound Mandl, I.; Celikel-Esser, F.; Širok, K. Born Global: The Potential of Job Creation in New International Businesses; European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions: Dublin, Ireland, 2012.
- D’Angelo, A.; Majocchi, A.; Zucchella, A.; Buck, T. Geographical pathways for SME internationalization: Insights from an Italian sample. Int. Mark. Rev. 2013, 30, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugman, A.M.; Verbeke, A. A perspective on regional and global strategies of multinational enterprises. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavusgil, S.T.; Knight, G. Born Global Firms: A New International Enterprise; Business e.: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Oviatt, B.M.; McDougall, P.P. Toward a Theory of International New ventures. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1994, 25, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, C.; Werner, A. Fostering International Entrepreneurship: Are SMEs Targeted Adequately by Official Foreign Trade Promotion Schemes? SSRN Electron. J. 2008, 41, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.; Edwards, R.; Schroder, B. How smaller born-global firms use networks and alliances to overcome constraints to rapid internationalization. J. Int. Mark. 2006, 14, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Rosado-Serrano, A. Gradual Internationalization vs. Born-Global/International new venture models. Int. Mark. Rev. 2019, 36, 830–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, H.S. Foreign entry mode and performance: The moderating effects of environment. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2005, 43, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannone, G.; Ughetto, E. Born globals: A cross-country survey on high-tech start-ups. Int. Bus. Rev. 2014, 23, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonidou, L.C.; Katsikeas, C.S.; Coudounaris, D.N. Five decades of business research into exporting: A bibliographic analysis. J. Int. Manag. 2010, 16, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majocchi, A.; Bacchiocchi, E.; Mayrhofer, U. Firm size, business experience and export intensity in SMEs: A longitudinal approach to complex relationships. Int. Bus. Rev. 2005, 14, 719–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, Ø. The Born Globals A new generation of small European exporters. Int. Mark. Rev. 2002, 19, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; McNaughton, R.; Young, S. “Born-again global” firms: An extension to the “born global” phenomenon. J. Int. Manag. 2001, 7, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.E.; Kundu, S.K.; Ciravegna, L. Born global or born regional Evidence from an exploratory study in the Costa Rican software industry. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2009, 40, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.; Hutchings, K.; Lazaris, M.; Zyngier, S. A model of rapid knowledge development: The smaller born-global firm. Int. Bus. Rev. 2010, 19, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, I.; McDougall-Covin, P.; L Rose, E. Born globals and international business: Evolution of a field of research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2015, 46, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Vergara, M.; Alvarez-Marin, A.; Placencio-Hidalgo, D. A bibliometric analysis of creativity in the field of business economics. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco-Uriarte, M.D.L.M.; Casado-Belmonte, M.D.P.; Marín-Carrillo, G.M.; Terán-Yépez, E. A bibliometric analysis of international competitiveness (1983–2017). Sustainability 2019, 11, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, É.; Campbell, D.; Gingras, Y.; Larivière, V. Comparing Bibliometric Statistics Obtained From theWeb of Science and Scopus. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Salinas, D.; Lopez-Cózar, E.D.; Jiménez-Contreras, E. Ranking of departments and researchers within a university using two different databases: Web of science versus scopus. Scientometrics 2009, 80, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J. A New Methodology for Constructing a Publication-Level Classification System of Science Ludo. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2013, 63, 2378–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L.; Dekker, R.; van den Berg, J. A Comparison of Two Techniques for Bibliometric Mapping: Multidimensional Scaling and VOS. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; Martínez, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Fujita, H.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Knowledge-Based Systems 25 years at Knowledge-Based Systems: A bibliometric analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgado-Armenteros, E.M.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Torres-Ruiz, F.J.; Cobo, M.J. Analysing the conceptual evolution of qualitative marketing research through science mapping analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 102, 519–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. SciMAT: A new science mapping analysis software tool. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 1609–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabić, M.; Maley, J.; Dana, L.-P.; Novak, I.; Pellegrini, M.M.; Caputo, A. Pathways of SME Internationalization: A bibliometric and systematic review. Small Bus. Econ. 2019, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.W.; Beamish, P.W. The internationalization and performance of SMEs. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuber, A.R.; Fischer, E. The Influence of the Management Team’s International Experience on the Internationalization Behaviors of SMES. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1997, 28, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, W.; Luo, X. Internationalization and the performance of born-global SMEs: The mediating role of social networks. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2007, 38, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovics, R.R.; Kurt, Y.; Sinkovics, N. The effect of matching on perceived export barriers and performance in an era of globalization discontents: Empirical evidence from UK SMEs. Int. Bus. Rev. 2018, 27, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspelund, A.; Moen, Ø. Internationalization of Small High-Tech Firms: The Role of Information Technology. J. Euromarketing 2004, 13, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.; Hoppen, N.; Luce, F.B. Information technology impact on market orientation in e-business. J. Bus. Res. 2009, 62, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, C.A.; Ghoshal, S. Transnational Management: Text, Cases, and Readings in Cross-Border Management, 2nd ed.; Irwin: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, A. Impact of Internationalization on Firm Performance: A Literature Review. IOSR J. Bus. Manag. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Preece, S.B.; Baetz, M.C. Explaining the international intensity and global diversity of early-stage technology-based firms. J. Bus. Ventur. 1999, 14, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwaal, E.; Donkers, B. Firm Size and Export Intensity: Solving an Empirical Puzzle. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2002, 33, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.A. Entrepreneurship and strategy in the international SME. J. Int. Manag. 2001, 7, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahti, A.; Madupu, V.; Yavas, U.; Babakus, E. Cooperative strategy, knowledge intensity and export performance of small and medium sized enterprises. J. World Bus. 2005, 40, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaglia, F.; Goldstein, A.; Mathews, J.A. Accelerated internationalization by emerging markets’ multinationals: The case of the white goods sector. J. World Bus. 2007, 42, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorós, J.E.; Etchebarne, M.S.; Zapata, I.T.; Felzensztein, C. International entrepreneurial firms in Chile: An exploratory profile. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, B.; Hwang, A.R. Productivity and the export market: A firm-level analysis. J. Dev. Econ. 1995, 47, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.B.; Jensen, J.B.; Lawrence, R.Z. Exporters, Jobs, and Wages in U. S. Manufacturing:1976–1987. Brook. Pap. Econ. Act. Microecon. 1995, 1995, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.B.; Jensen, J.B. Exceptional exporter performance: Cause, effect, or both? J. Int. Econ. 1999, 47, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.B.; Wagner, J. Exports and Success in German Manufacturing. Weltwirtsch. Arch. 1996, 133, 134–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, B.Y.; Chung, S.; Roberts, M.J. Productivity and Turnover in the Export Market: Micro-level Evidence from the Republic of Korea and Taiwan (China). World Bank Econ. Rev. 2000, 14, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.A.; Farinas, J.C.; Ruano, S. Firm productivity and export markets: A non-parametric approach. J. Int. Econ. 2002, 57, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, S.; Blankenburg Holm, D. Internationalisation of small to medium-sized manufacturing firms: A network approach. Int. Bus. Rev. 2000, 9, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, N.Ε.; Mcauley, A. Internationalisation and the Smaller Firm: A Review of Contemporary Empirical Research. MIR Manag. Int. Rev. 2013, 39, 223–256. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40835788 (accessed on 13 October 2019).
- Ghauri, P.N.; Tarnovskaya, V.; Elg, U. Market driving multinationals and their global sourcing network. Int. Mark. Rev. 2008, 25, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafley, A.G.; Charan, R. The Game-Changer: How you Can Drive Revenue and Profit Growth with Innovation, 1st ed.; Crown Publications: New York, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0307381736. [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrand, A.; Eriksson, K.; Sharma, D.D. The perceived usefulness of knowledge supplied by foreign client networks. Int. Bus. Rev. 2009, 18, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Gupta, P. Process and intensity of internationalization of IT firms—Evidence from India. Int. Bus. Rev. 2014, 23, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J. A Note on the Firm Size—Export Relationship. Small Bus. Econ. 2001, 17, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Li, Q.C. Exporting, R & D, and absorptive capacity in UK establishments. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 2009, 61, 74–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.A.; Liesch, P.W. Internationalization: From incremental to born global. J. World Bus. 2016, 51, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel-koch, J. Who Uses Intermediaries in International Trade? Evidence from Firm-level Survey Data. World Econ. 2013, 36, 1014–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, P. Innovation and Entrepreneurship; Routledge: Abingdon upon Thames, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mainela, T.; Puhakka, V.; Servais, P. The Concept of International Opportunity in International Entrepreneurship: A Review and a Research Agenda. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2014, 16, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmersson, M.; Jansson, H. Reducing Uncertainty in the Emerging Market Entry Process: On the Distance, and Uncertainty. J. Int. Mark. 2012, 20, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, L.P.; Hamilton, R.T.; Wick, K. Deciding to export: An exploratory study of Singaporean entrepreneurs. J. Int. Entrep. 2009, 7, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callen, M.T.; Cherif, R.; Hasanov, F.; Hegazy, M.A.; Khandelwal, P. Economic Diversification in the GCC: Past, Present, and Future; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, P.; Asheim, B.; Boschma, R.; Schwartz, D.; Tödtling, F. Handbook of Regional Innovation and Growth; Edward Elgar Publishing: Troutham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Audretsch, D.; Keilbach, M.; Lehmann, E. Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huggins, R.; Morgan, B.; Williams, N. Regions as enterprising places: Governance, policy and development. In Enterprising Places: Leadership and Governance Networks; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Perényi, Á.; Losoncz, M. A systematic review of international entrepreneurship special issue articles. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, P.P. International versus domestic entrepreneurship: New venture strategic behavior and industry structure. J. Bus. Ventur. 1989, 4, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.F. International entrepreneurship: A new growth opportunity. New Manag. 1988, 3, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, R.W.; Ricks, D.A. Trends in International Business Research: Twenty-Five Years Later. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1994, 25, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Cohen, B. Sustainable Entrepreneurship Research: Taking Stock and looking ahead. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2018, 27, 300–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. Research on Enterprise Internationalization Strategy Based on Path Dependence Theory: Literature Review and Future Prospect. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2017, 07, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Lehmann, E.E.; Schenkenhofer, J. Internationalization strategies of hidden champions: Lessons from Germany. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2018, 26, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pett, T.; Wolff, J.A. Entrepreneurial Orientation and Learning in High and Low Performing SMEs. J. Small Bus. Strateg. 2016, 26, 71–86. Available online: https://libjournals.mtsu.edu/index.php/jsbs/article/view/615 (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Berko Obeng Damoah, O. A critical incident analysis of the export behaviour of SMEs: Evidence from an emerging market. Crit. Perspect. Int. Bus. 2018, 14, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrand, A.; Hånell, S.M. International and market-specific social capital effects on international opportunity exploitation in the internationalization process. J. World Bus. 2017, 52, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribau, C.P.; Moreira, A.C.; Raposo, M. SME internationalization research: Mapping the state of the art. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 2016, 35, 280–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terán-Yépez, E.; Marín-Carrillo, G.M.; Casado-Belmonte, M.P.; Capobianco-Uriarte, M.M. Sustainable entrepreneurship: Review of its evolution and new trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).