Malaria Publications before and during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Management and Data Analysis
3. Results
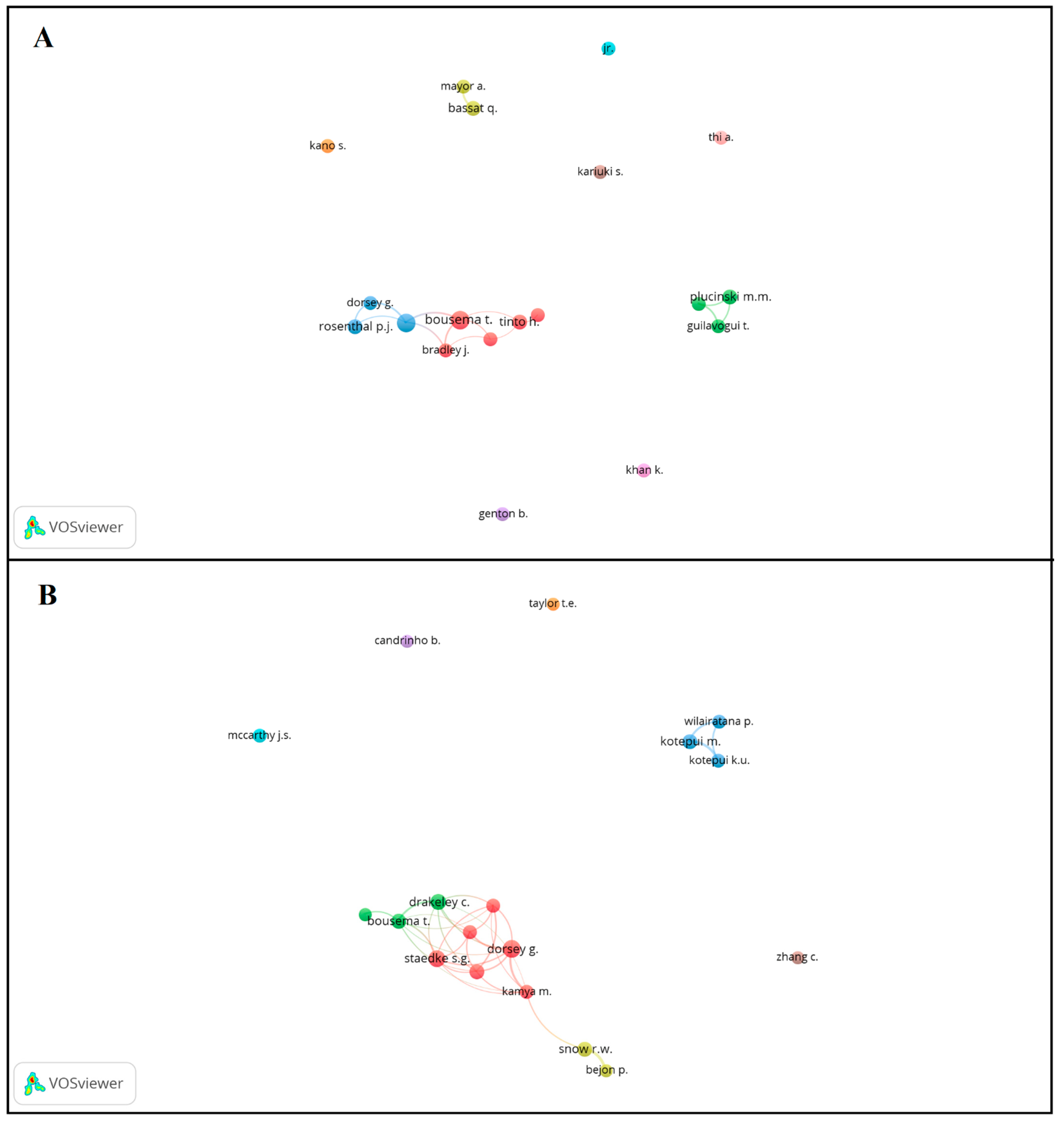
3.1. Authors
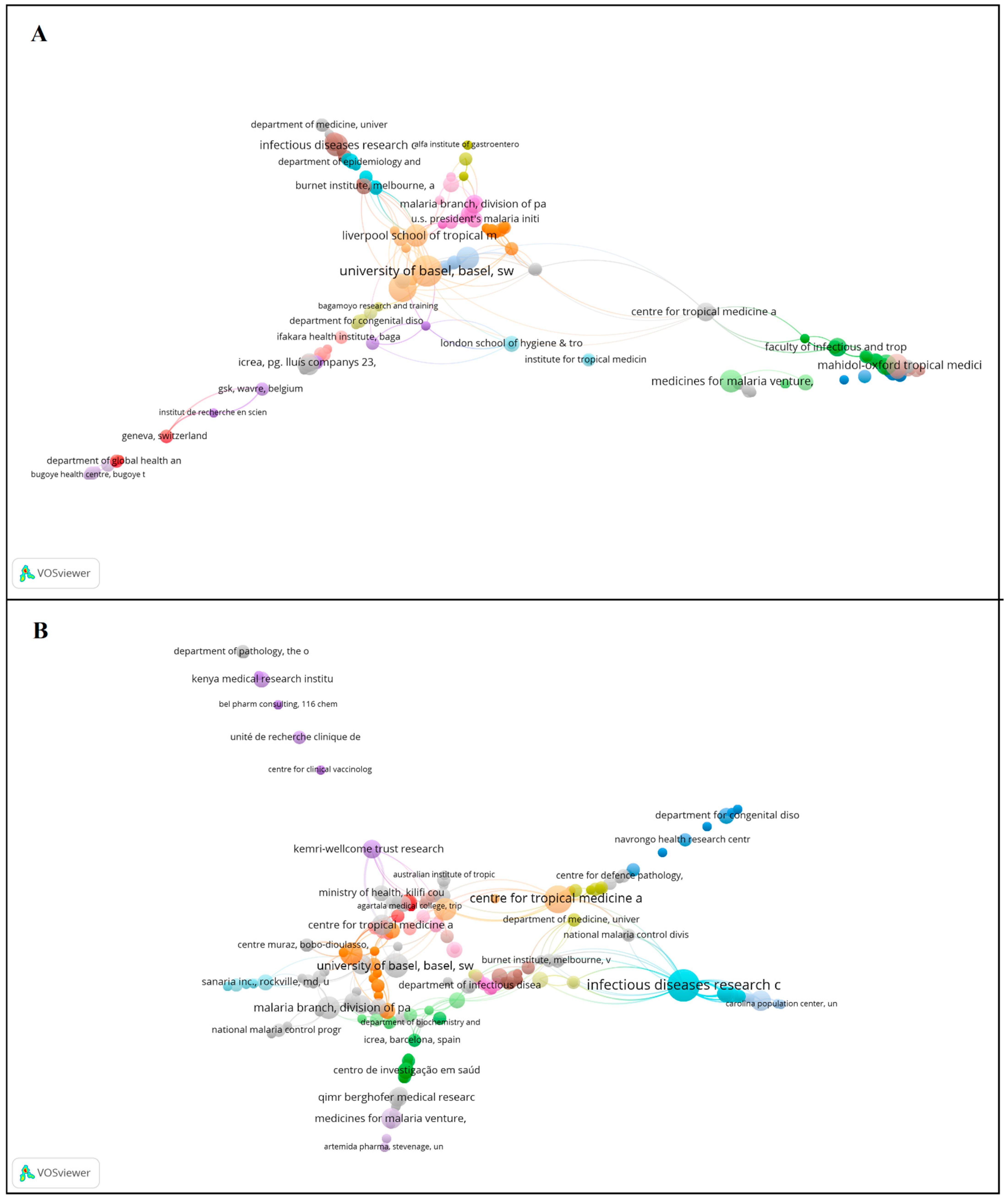
3.2. Affiliations
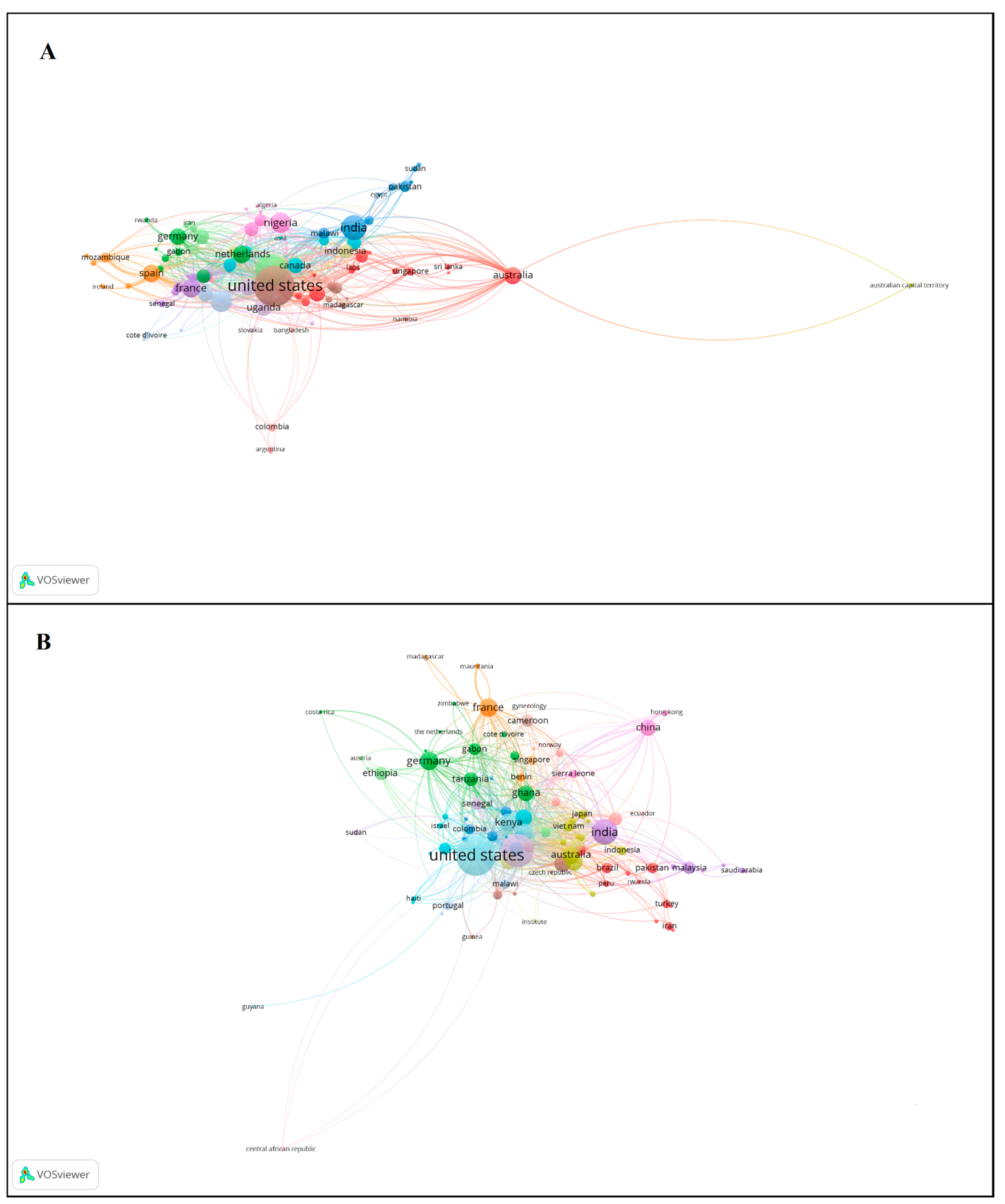
3.3. Countries
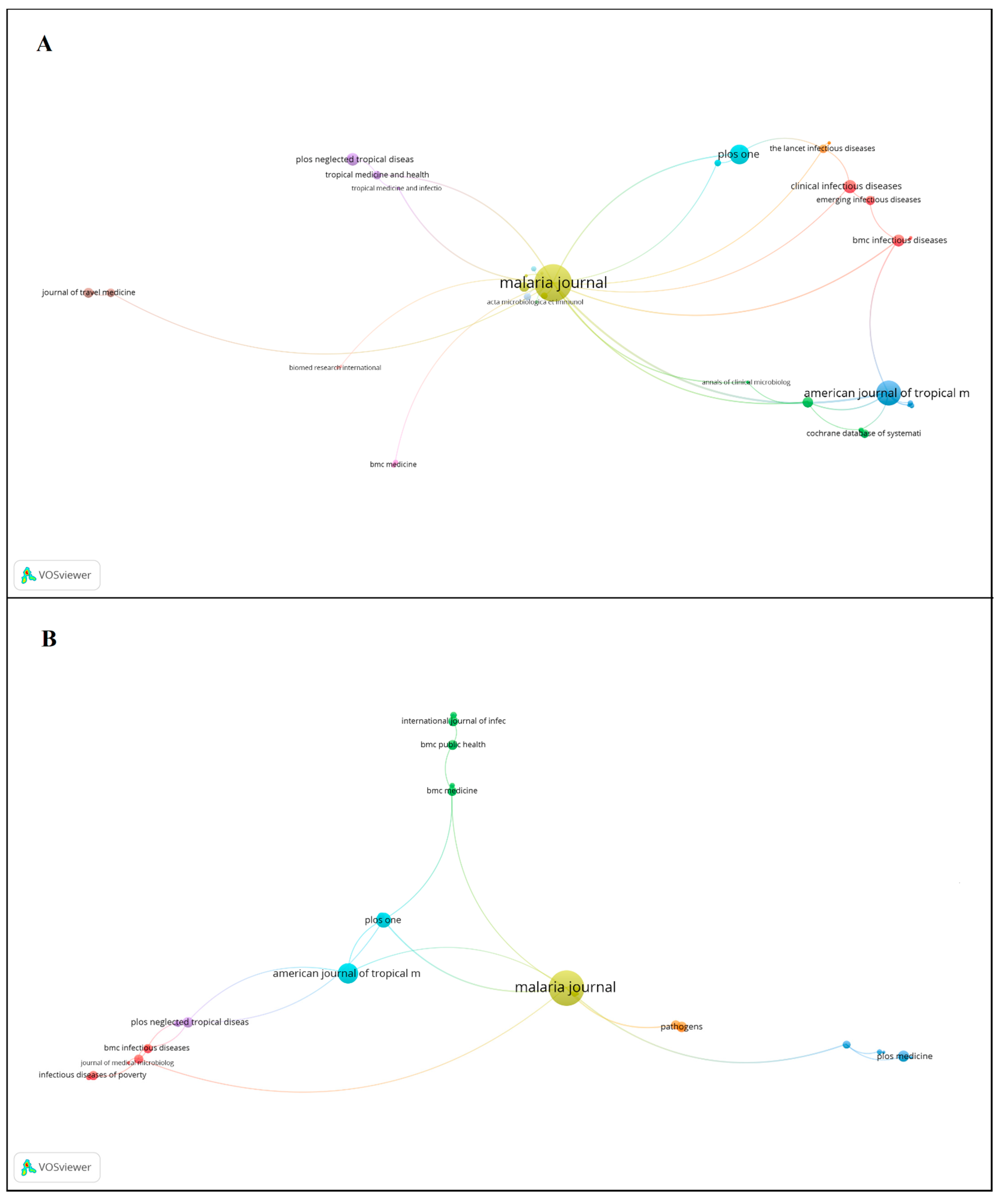
3.4. Source Titles
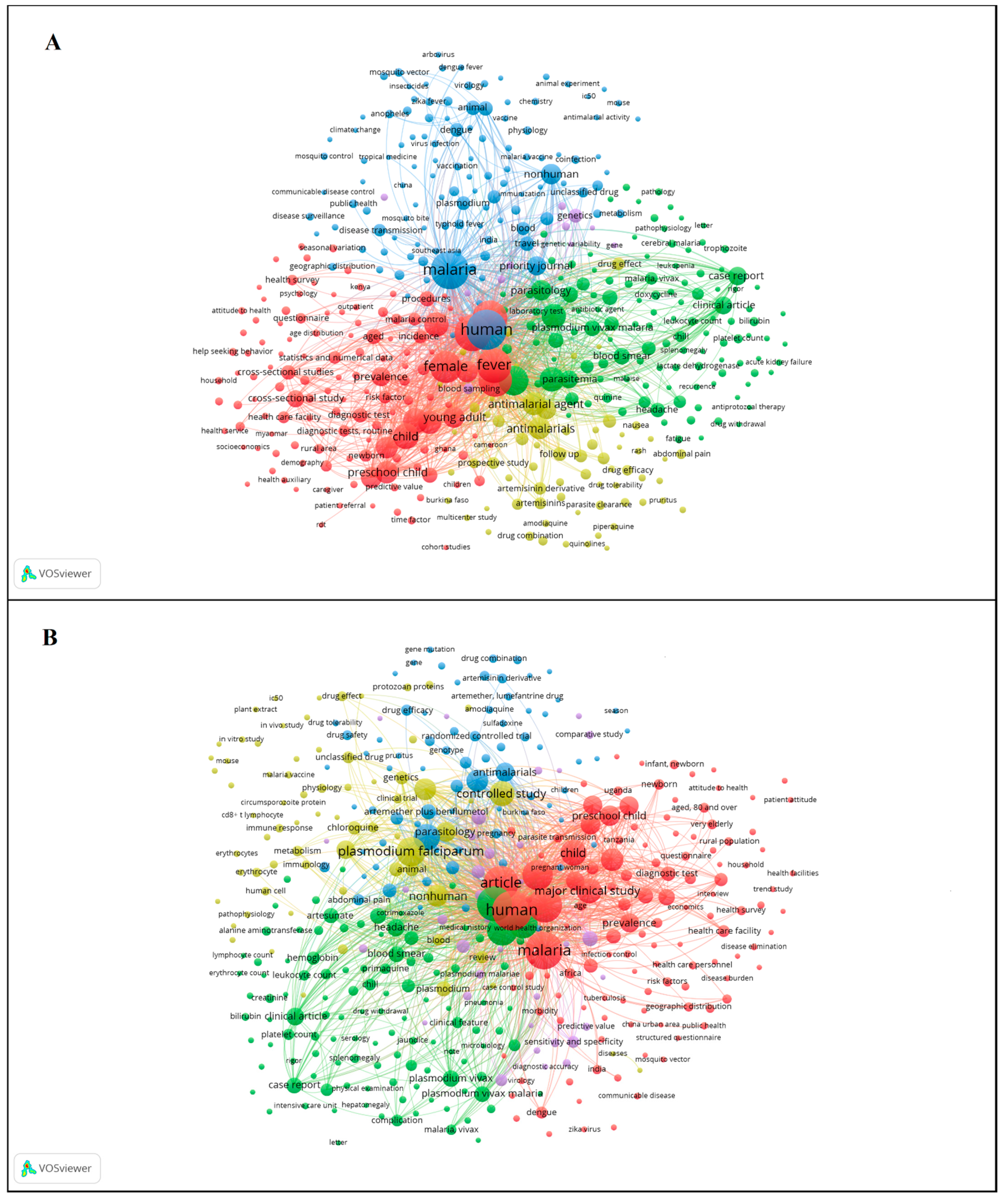
3.5. Keywords
3.6. Funding Sponsors
3.7. Languages, Publication Types, and Subject Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Burm, S.W.; Hong, S.H.; Ghayda, R.A.; Kronbichler, A.; Smith, L.; Koyanagi, A.; Jacob, L.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, J.I. A comprehensive review of Coronavirus Disease 2019: Epidemiology, transmission, risk factors, and international responses. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, B.; Duan, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, C.; et al. Global analysis of the COVID-19 research landscape and scientific impact. Am. J. Infect. Control 2022, 50, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, H. Global research trends in pediatric COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 798005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, L.; Kalfa, N.; Beckers, G.M.A.; Kaefer, M.; Nieuwhof-Leppink, A.J.; Fossum, M.; Herbst, K.W.; Bagli, D.; ESPU Research Committee. The impact of COVID-19 on research. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2020, 16, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omary, M.B.; Eswaraka, J.; Kimball, S.D.; Moghe, P.V.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Scotto, K.W. The COVID-19 pandemic and research shutdown: Staying safe and productive. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2745–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoobane, P.; Masinde, M.; Mabhaudhi, T. Predicting infectious diseases: A bibliometric review on Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Espinoza Oyarce, D.A.; Donner, E. Transmission of COVID-19 and other infectious diseases in public washrooms: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawakami, T.; Karako, K.; Song, P.; Sugiura, W.; Kokudo, N. Infectious disease activity during the COVID-19 epidemic in Japan: Lessons learned from prevention and control measures. Biosci. Trends 2021, 15, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.G. Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 65, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aborode, A.T.; David, K.B.; Uwishema, O.; Nathaniel, A.L.; Imisioluwa, J.O.; Onigbinde, S.B.; Farooq, F. Fighting COVID-19 at the expense of malaria in Africa: The consequences and policy options. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogerson, S.J.; Beeson, J.G.; Laman, M.; Poespoprodjo, J.R.; William, T.; Simpson, J.A.; Price, R.N. Identifying and combating the impacts of COVID-19 on malaria. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haakenstad, A.; Harle, A.C.; Tsakalos, G.; Micah, A.E.; Tao, T.; Anjomshoa, M.; Cohen, J.; Fullman, N.; Hay, S.I.; Mestrovic, T.; et al. Tracking spending on malaria by source in 106 countries, 2000–2016: An economic modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaves, E.J.; Valle, R.; Chandrasekera, R.M.; Soto, G.; Burke, R.L.; Cummings, J.F.; Bausch, D.G.; Kasper, M.R. Use of bibliometric analysis to assess the scientific productivity and impact of the global emerging infections surveillance and response system program, 2006–2012. Mil. Med. 2017, 182, e1749–e1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Dai, R.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Shi, G.; Tian, J.; Chen, C.; Hambly, B.D.; et al. Bibliometric analysis on COVID-19: A comparison of research between english and chinese studies. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawuki, J.; Yu, X.; Musa, T.H. Bibliometric analysis of ebola research indexed in Web of Science and Scopus (2010–2020). BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5476567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Q.; Zhu, G.D.; Cao, J.; Huang, J.Y. Research supporting malaria control and elimination in China over four decades: A bibliometric analysis of academic articles published in chinese from 1980 to 2019. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Archived: WHO Timeline—COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-04-2020-who-timeline---covid-19 (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Perianes-Rodriguez, A.; Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. J. Informetr. 2016, 10, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantengco, O.A.G. Investigating the evolution of COVID-19 research trends and collaborations in Southeast Asia: A bibliometric analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 102325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IMF. IMF Country Information 2022. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Countries#T (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- The World Bank. Country and Economies 2022. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/country (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Raynaud, M.; Goutaudier, V.; Louis, K.; Al-Awadhi, S.; Dubourg, Q.; Truchot, A.; Brousse, R.; Saleh, N.; Giarraputo, A.; Debiais, C.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on publication dynamics and non-COVID-19 research production. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, M.; Zhang, H.; Louis, K.; Goutaudier, V.; Wang, J.; Dubourg, Q.; Wei, Y.; Demir, Z.; Debiais, C.; Aubert, O.; et al. COVID-19-related medical research: A meta-research and critical appraisal. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustini, A.J.; Schroeder, A.R.; Axelrod, D.M. Trends in views of articles published in 3 leading medical journals during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e216459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviv-Reuven, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Publication patterns’ changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal and short-term scientometric analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 6761–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, A.A. Perspectives on repositioning chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19. Sudan. J. Paediatr. 2020, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Hou, Z.; Cui, C.; Zhang, M.; Tu, S.; Li, H.; Liu, D. Updates on the pharmacology of chloroquine against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A perspective on its use in the general and geriatric population. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 21, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, P.; Venkatesan, N.; Venkatesan, S.; Gurunthalingam, M.P.; Thangaraju, E. Can HCQ be considered a “Safe Weapon” for COVID-19 in the indian population? SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendic, S.; Guengerich, F.P. Metabolism and interactions of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine with human cytochrome P450 enzymes and drug transporters. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 21, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.Y.; Frieman, M.; Wolfram, J. Insights from nanomedicine into chloroquine efficacy against COVID-19. Nat Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Tiwari, A.; Dash, M.; Sinha, A. ACE2 mutation might explain lower COVID-19 burden in malaria endemic areas. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Dash, M.; Tiwari, A.; Sinha, A. Malaria, COVID-19 and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: What does the available population data say? Open Biol. 2021, 11, 210213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Xue, X. The impact of ACE2 polymorphisms on COVID-19 disease: Susceptibility, severity, and therapy. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 753721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Wong, Y.K.; He, Y.; Adegnika, A.A.; Kremsner, P.G.; Agnandji, S.T.; Sall, A.A.; Liang, Z.; Qiu, C.; et al. Preparedness is essential for malaria-endemic regions during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, J. COVID-19 and the impact on malaria. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 35, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Mvalo, T.; Akech, S.; Agweyu, A.; Baker, K.; Bar-Zeev, N.; Campbell, H.; Checkley, W.; Chisti, M.J.; Colbourn, T.; et al. Protecting children in low-income and middle-income countries from COVID-19. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e002844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda-Kapata, P.; Kapata, N.; Zumla, A. COVID-19 and malaria: A symptom screening challenge for malaria endemic countries. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.J.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Rumisha, S.F.; Amratia, P.; Arambepola, R.; Battle, K.E.; Cameron, E.; Chestnutt, E.; Gibson, H.S.; Harris, J.; et al. Indirect effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on malaria intervention coverage, morbidity, and mortality in Africa: A geospatial modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.G.; Goss, S.; Gelister, Y.; Alegana, V.; Brown, R.J.; Clarke, S.C.; Fitchett, J.R.; Atun, R.; Scott, J.A.G.; Newell, M.L.; et al. Global funding trends for malaria research in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e772–e781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, T.; Rottingen, J.A.; Kieny, M.P. Informing the establishment of the WHO global observatory on health research and development: A call for papers. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2015, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mala, W.; Wilairatana, P.; Wattanapisit, A.; Kotepui, K.U.; Kotepui, M. Malaria Publications before and during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Bibliometric Analysis. Publications 2022, 10, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications10030028
Mala W, Wilairatana P, Wattanapisit A, Kotepui KU, Kotepui M. Malaria Publications before and during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Bibliometric Analysis. Publications. 2022; 10(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications10030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleMala, Wanida, Polrat Wilairatana, Apichai Wattanapisit, Kwuntida Uthaisar Kotepui, and Manas Kotepui. 2022. "Malaria Publications before and during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Bibliometric Analysis" Publications 10, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications10030028
APA StyleMala, W., Wilairatana, P., Wattanapisit, A., Kotepui, K. U., & Kotepui, M. (2022). Malaria Publications before and during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Bibliometric Analysis. Publications, 10(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications10030028






