Comparison of Intraoral and Extraoral Digital Scanners: Evaluation of Surface Topography and Precision
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Digital Scanners
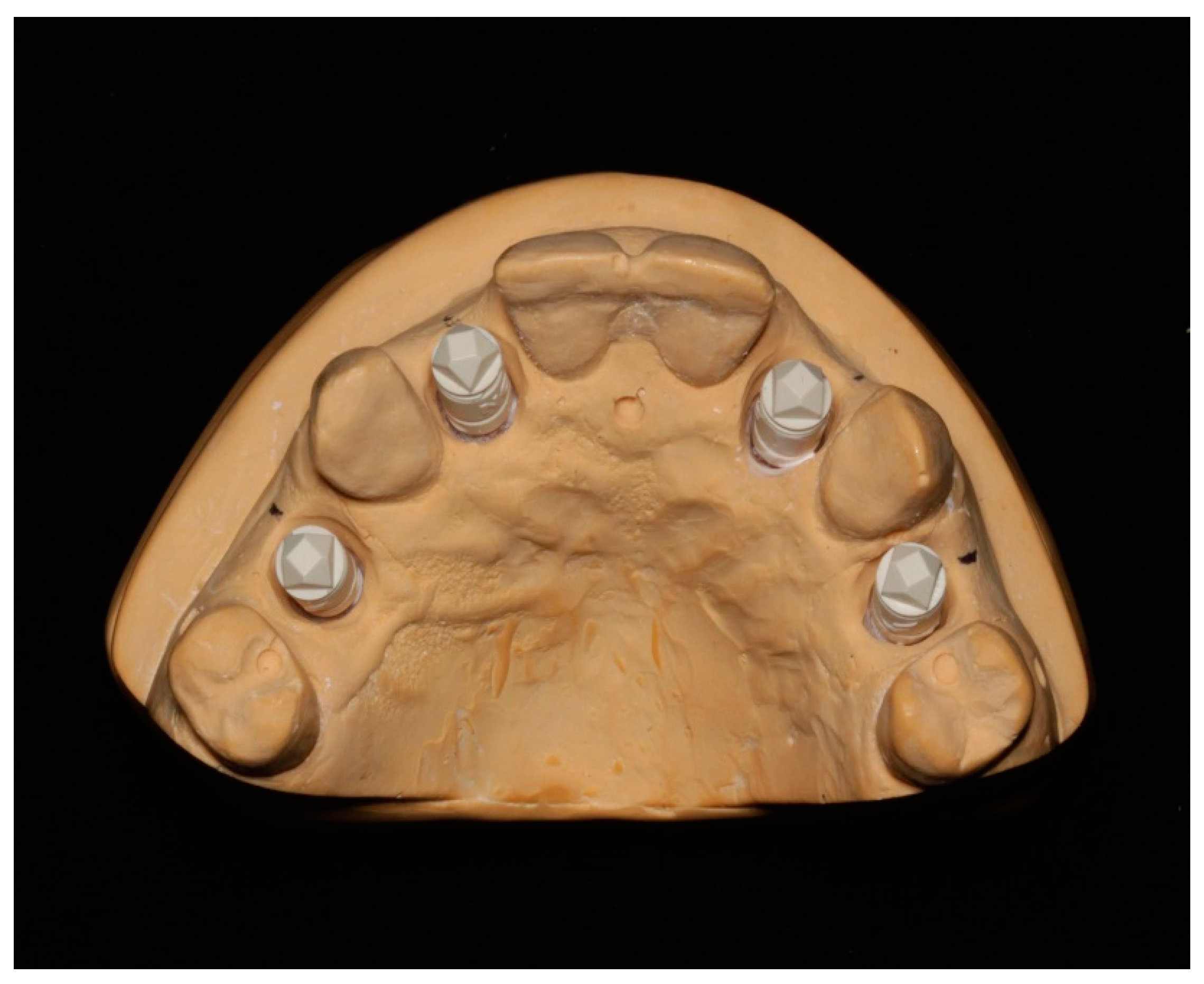
2.2. Data Collection
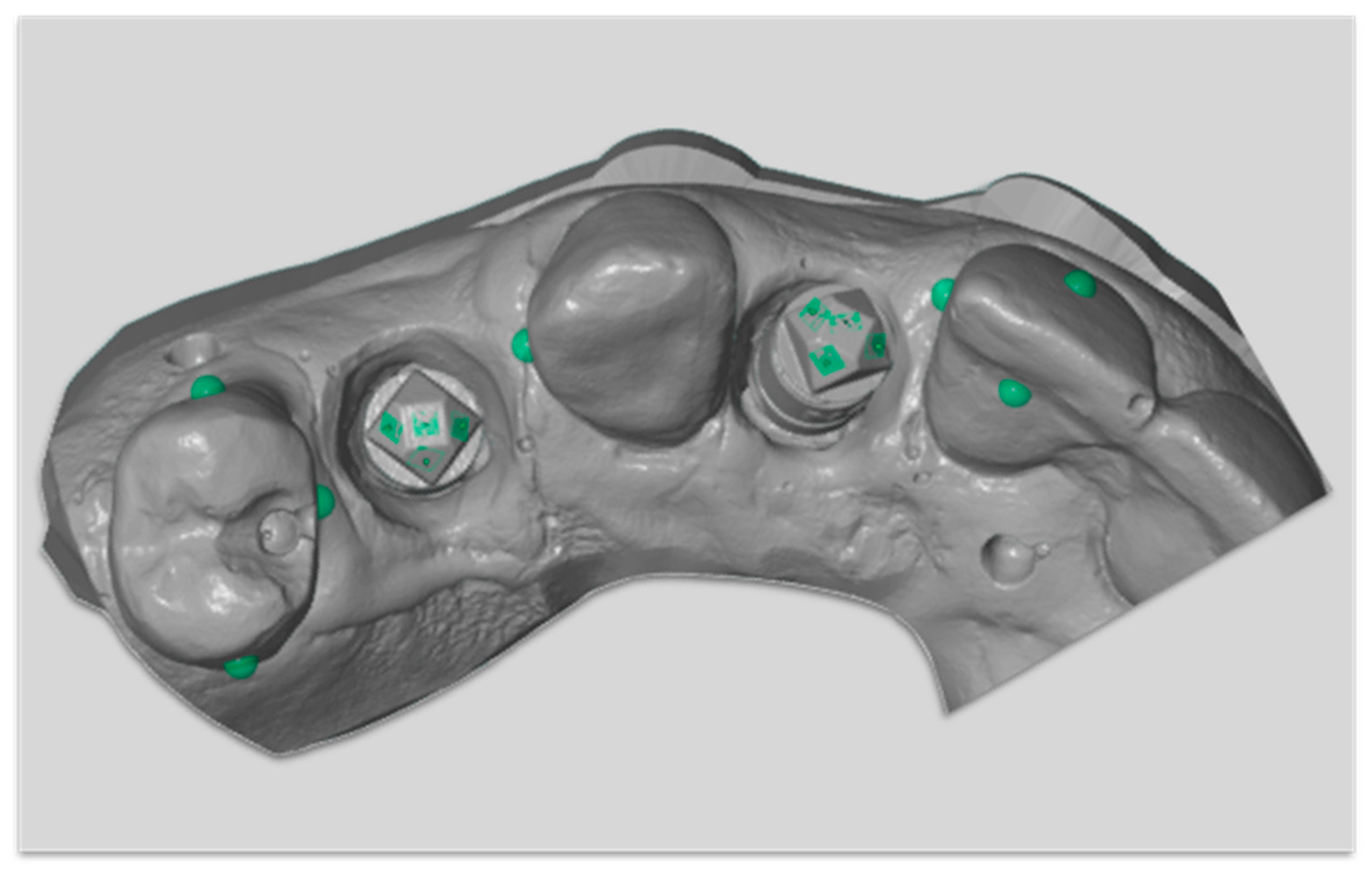
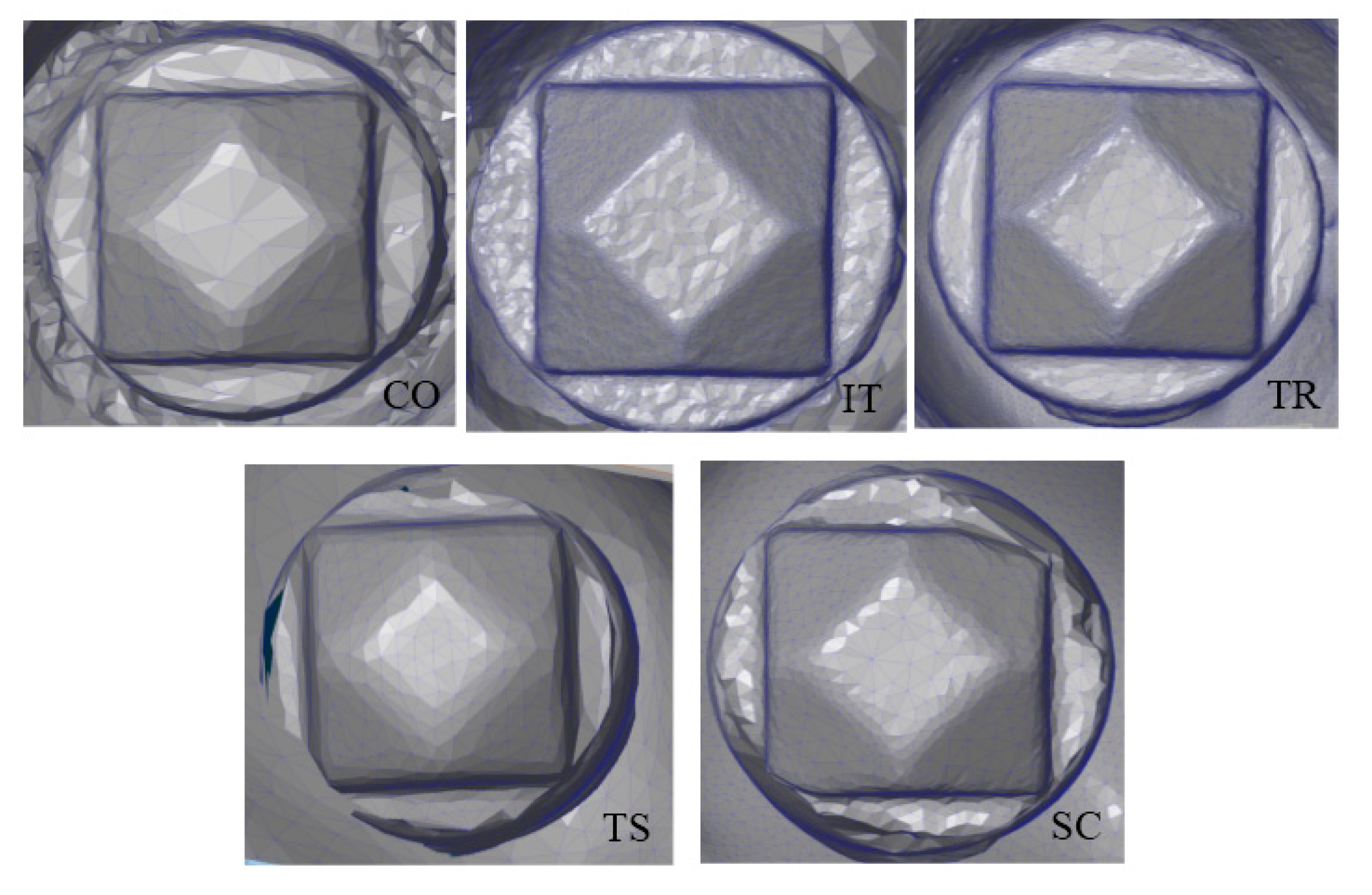
2.3. Surface Topography Measurement on Implant Scanbody
2.4. Surface Topography Measurements on Tooth Surfaces
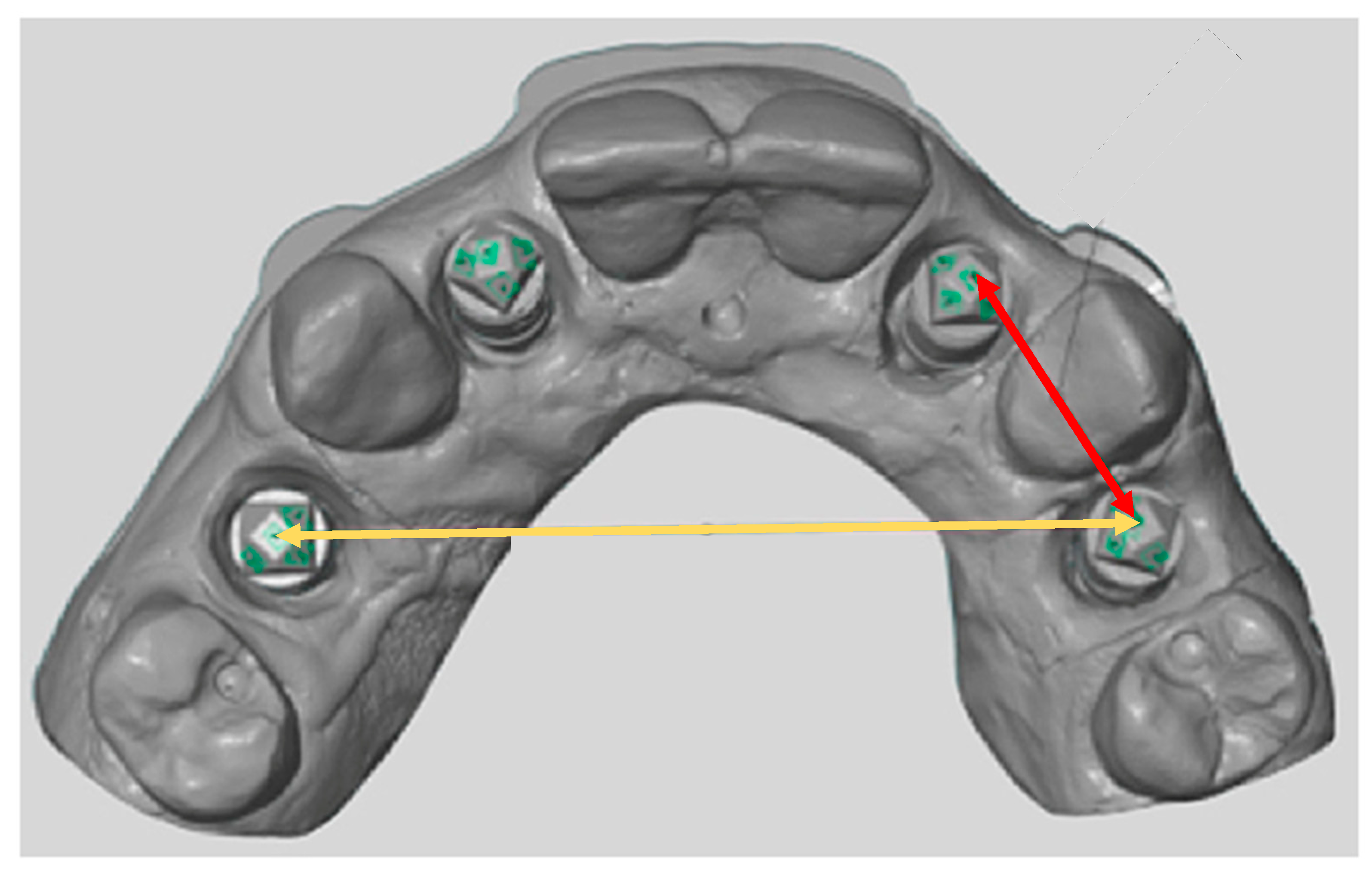
2.5. Precision Measurement between Implant Scanbodies
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
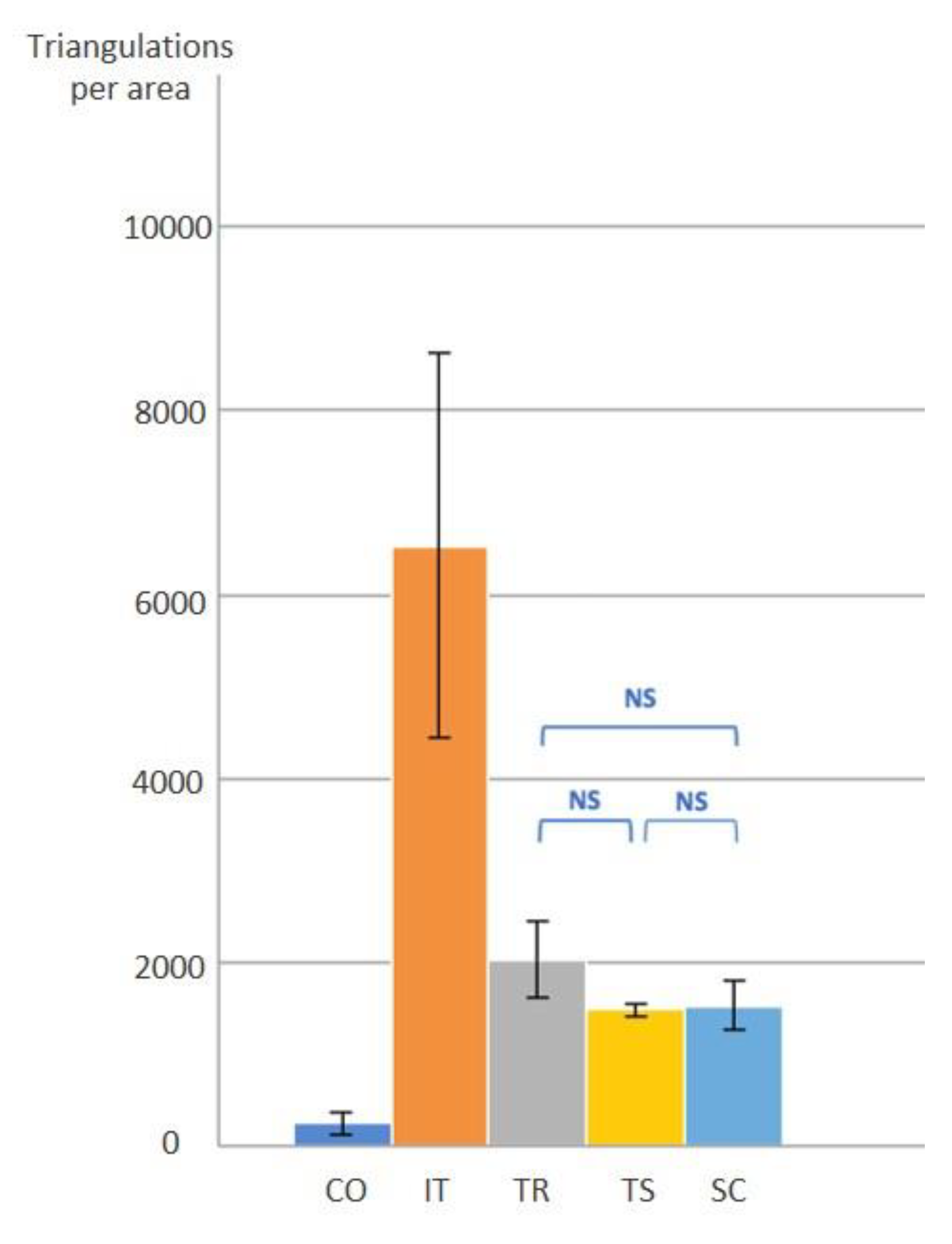
- Scanning resolution, in terms of the number of triangulation points, does not correlate to the precision. Rather, precision correlates with scanning mechanism.
- Reproducing the surface topography did not depend on the anatomical tooth structure and position.
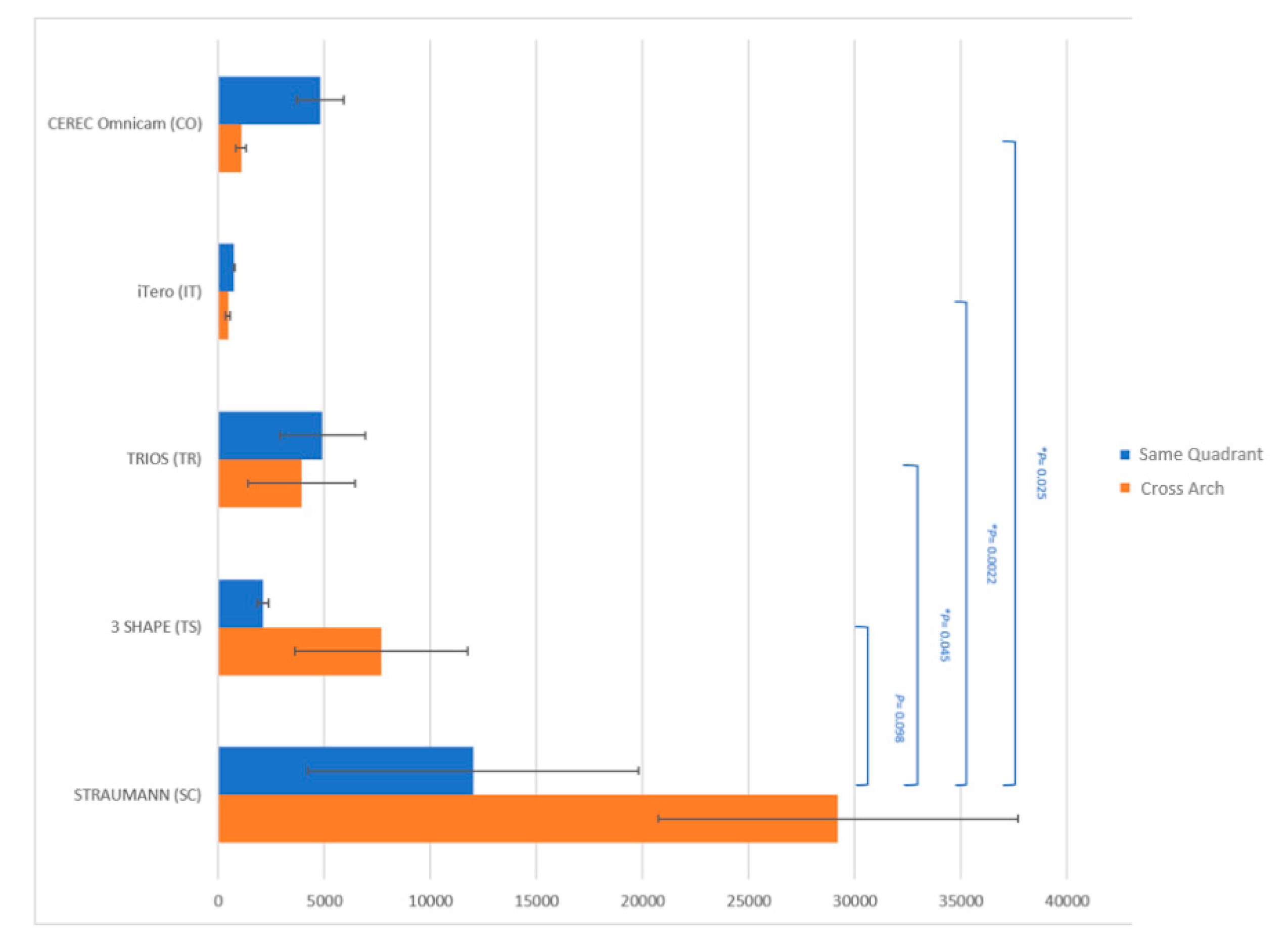
- In the same quadrant, the precision in the linear measurements had no statistical difference amongst the extraoral and intraoral scanners, though the SC extraoral scanner demonstrated the highest precision.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joda, T.; Katsoulis, J.; Bragger, U. Clinical Fitting and Adjustment Time for Implant-Supported Crowns Comparing Digital and Conventional Workflows. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapos, T.; Ashy, L.M.; Gallucci, G.O.; Weber, H.P.; Wismeijer, D. Computer-aided design and computer-assisted manufacturing in prosthetic implant dentistry. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mormann, W.H.; Brandestini, M.; Lutz, F. The Cerec system: Computer-assisted preparation of direct ceramic inlays in 1 setting. Quintessenz 1987, 38, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Betensky, R.A.; Gianneschi, G.E.; Gallucci, G.O. Accuracy of digital versus conventional implant impressions. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Gallucci, G.O. Digital vs. conventional implant impressions: Efficiency outcomes. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Macarthur, R.X.T.; Gallucci, G.O. An evaluation of student and clinician perception of digital and conventional implant impressions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 110, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mortadi, N.; Eggbeer, D.; Lewis, J.; Williams, R.J. CAD/CAM/AM applications in the manufacture of dental appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2012, 142, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuer, F.; Schweiger, J.; Edelhoff, D. Digital dentistry: An overview of recent developments for CAD/CAM generated restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2008, 204, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flugge, T.V.; Schlager, S.; Nelson, K.; Nahles, S.; Metzger, M.C. Precision of intraoral digital dental impressions with iTero and extraoral digitization with the iTero and a model scanner. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.R.; Flores-Mir, C.; Nebbe, B.; Raboud, D.W.; Heo, G.; Major, P.W. Validity, reliability, and reproducibility of plaster vs digital study models: Comparison of peer assessment rating and Bolton analysis and their constituent measurements. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.K.; Gallucci, G.O.; Lee, S.J. Accuracy in the digital workflow: From data acquisition to the digitally milled cast. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaar, S.T.; van der Zel, J.M. Accuracy of dental digitizers. Int. Dent. J. 2006, 56, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braian, M.; Wennerberg, A. Trueness and precision of 5 intraoral scanners for scanning edentulous and dentate complete-arch mandibular casts: A comparative in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 129–136.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, J.; Ludlow, M.; Mennito, A.; Kelly, A.; Evans, Z.; Renne, W. Effect of scan pattern on complete-arch scans with 4 digital scanners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Linghu, C.; Yu, K.; Zhu, J.; Luo, H.; Qian, C.; Chen, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, J. Fast Digital Patterning of Surface Topography toward Three-Dimensional Shape-Changing Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 48412–48418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, H.B.; Wyatt, G.D.; Buschang, P.H. Reliability and validity of intraoral and extraoral scanners. Prog. Orthod. 2015, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, A.; Andersson, M.; Oden, A.; Sandborgh-Englund, G. A three-dimensional evaluation of a laser scanner and a touch-probe scanner. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 95, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, O.; Kuepper, H.; Sigusch, B.W.; Thompson, G.A.; Hefti, A.F.; Guentsch, A. Three-dimensional fit of lithium disilicate partial crowns in vitro. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.F. Optical triangulation-based microtopographic inspection of surfaces. Sensors 2012, 12, 4399–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renne, W.; Ludlow, M.; Fryml, J.; Schurch, Z.; Mennito, A.; Kessler, R.; Lauer, A. Evaluation of the accuracy of 7 digital scanners: An in vitro analysis based on 3-dimensional comparisons. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohner, L.O.L.; De Luca Canto, G.; Marcio, B.S.; Lagana, D.C.; Sesma, N.; Tortamano Neto, P. Computer-aided analysis of digital dental impressions obtained from intraoral and extraoral scanners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flugge, T.V.; Att, W.; Metzger, M.C.; Nelson, K. Precision of Dental Implant Digitization Using Intraoral Scanners. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muallah, J.; Wesemann, C.; Nowak, R.; Robben, J.; Mah, J.; Pospiech, P.; Bumann, A. Accuracy of full-arch scans using intraoral and extraoral scanners: An in vitro study using a new method of evaluation. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2017, 20, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Shinya, A.; Kuroda, S.; Gomi, H. The accuracy of the CAD system using intraoral and extraoral scanners for designing of fixed dental prostheses. Dent. Mater. J. 2017, 36, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammoun, R.; Suprono, M.S.; Goodacre, C.J.; Oyoyo, U.; Carrico, C.K.; Kattadiyil, M.T. Influence of Tooth Preparation Design and Scan Angulations on the Accuracy of Two Intraoral Digital Scanners: An in Vitro Study Based on 3-Dimensional Comparisons. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. Accuracy of complete-arch dental impressions: A new method of measuring trueness and precision. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 109, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. In-vitro evaluation of the accuracy of conventional and digital methods of obtaining full-arch dental impressions. Quintessence Int. 2015, 46, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, J.F.; Keul, C.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Beuer, F.; Edelhoff, D. Accuracy of digital models obtained by direct and indirect data capturing. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, J.F.; Wallbach, J.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Gernet, W.; Beuer, F.; Edelhoff, D. Computer-aided evaluation of preparations for CAD/CAM-fabricated all-ceramic crowns. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
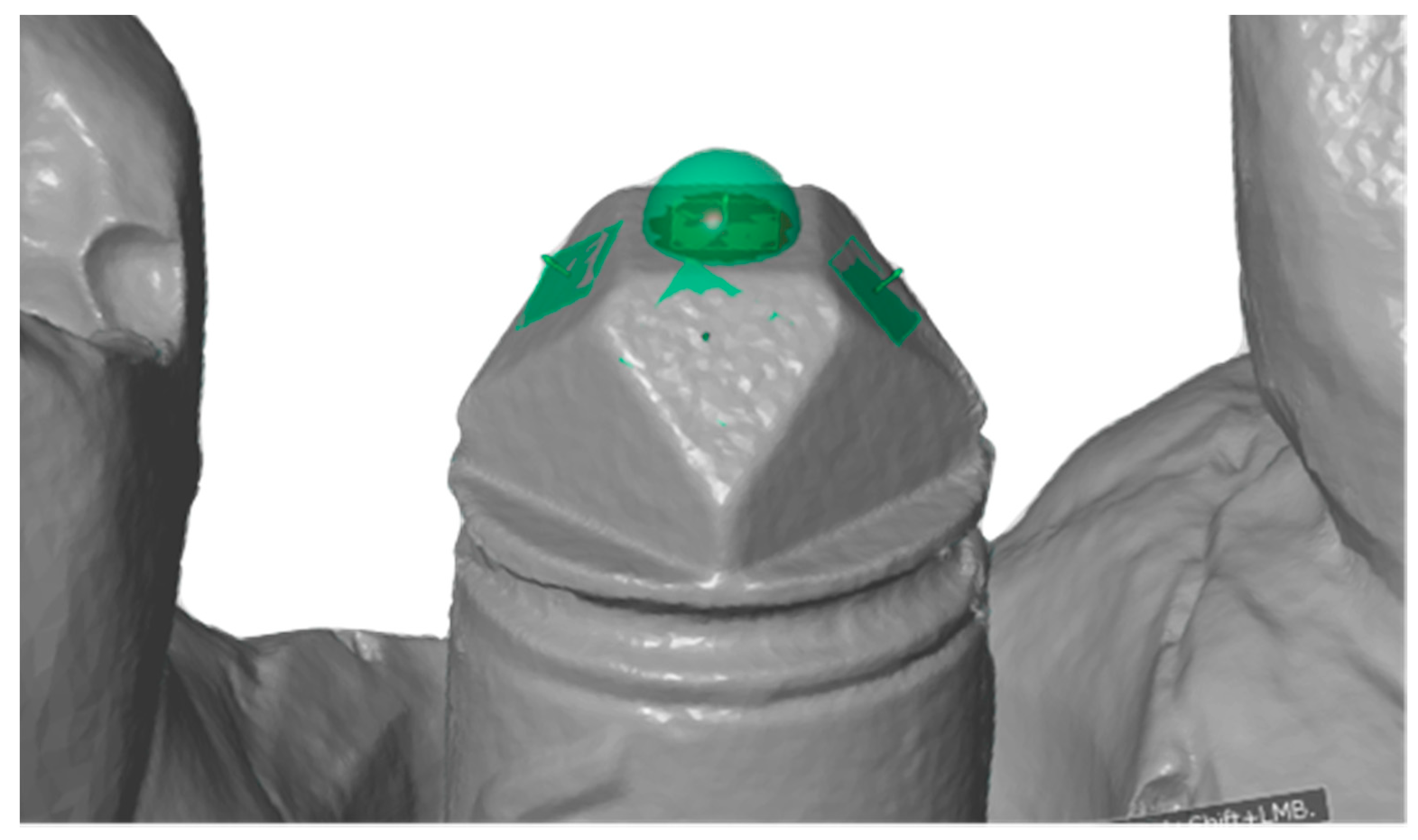

| Scanner | Cerec Omnica (CO) | Itero Hd2.9 (IT) | Trios 3 Basic(TR) | 3Shape D700 (TS) | Straumann Cares 3 Series (SC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Intraoral | Intraoral | Intraoral | Extraoral | Extraoral |
| Manufacturer | Sirona | Align Tech | 3Shape | 3Shape | Straumann |
| Light Source | White LED | Red Laser | Laser | Red Laser | Laser |
| Characteristics | Video capturing | Still image capturing | Video capturing | 2 cameras, adaptive scanning tech | Model on a movable plate |
| Scanner | CEREC OMNICAM (CO) | ITERO (IT) | TRIOS (TR) | 3SHAPE D700 (TS) | STRAUMANN CARES 3 Series (SC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Triangulation on the scanbody (DPA) | 2395 ± 1163.5 | 65,355 ± 20,920.4 | 20,251 ± 4103.6 | 14,794 ± 705.4 | 15,288 ± 2717.5 |
| Comparison | B Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Ant. vs. Post | −0.001 (p = 0.985) |
| Flat vs. Contour | −0.066 (p = 0.256) |
| Interproximal vs. non-interproximal | 0.023 (p = 0.713) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.J.; Cheong, C.W. Comparison of Intraoral and Extraoral Digital Scanners: Evaluation of Surface Topography and Precision. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8020052
Lee SJ, Kim S-W, Lee JJ, Cheong CW. Comparison of Intraoral and Extraoral Digital Scanners: Evaluation of Surface Topography and Precision. Dentistry Journal. 2020; 8(2):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang J., Soo-Woo Kim, Joshua J. Lee, and Chan W. Cheong. 2020. "Comparison of Intraoral and Extraoral Digital Scanners: Evaluation of Surface Topography and Precision" Dentistry Journal 8, no. 2: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8020052
APA StyleLee, S. J., Kim, S.-W., Lee, J. J., & Cheong, C. W. (2020). Comparison of Intraoral and Extraoral Digital Scanners: Evaluation of Surface Topography and Precision. Dentistry Journal, 8(2), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8020052





