Comparison of Narrow (<3.75 mm) and Standard (≥3.75 mm) Diameter Implants Supporting the Same Multiple Fixed Prostheses and Mirroring Real-World Clinical Scenarios: Non-Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Participants
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Patients of legal age (>18 years) of both sexes.
- Clinical need for multiple fixed alveolar ridge rehabilitations.
- Clinical suitability to insert, at least, one narrow dental implant splinted to a standard diameter dental implant.
- Signed informed consent.
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Presence of an active infection.
- Being under active treatment with, or having received in the last 30 days, treatment with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunosuppressants, systemic corticosteroids, and/or anticoagulants.
- Presence of severe hematologic disorders.
- Chronic treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Previous diagnosis of chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis.
- Presence of Diabetes mellitus with improper metabolic control (glycosylated hemoglobin higher than 9%).
- Patients subjected to dialysis.
- Presence of malignant tumors, hemangioma, or angioma in the surgical area.
- History of ischemic cardiopathy in the last year.
- Pregnancy or plan to become pregnant during the study.
- Metabolic bone disease
- Patient receiving treatment with oral or intravenous bisphosphonates.
- Any other condition incompatible with participation in the study.
2.4. Randomization and Blinding
2.5. Study Groups
2.6. Study Variables
2.6.1. Principal Variable
2.6.2. Secondary Variables
2.7. Interventions
2.8. Sample Size Calculation
2.9. Statistical Methods
2.10. Report/Publication Guidelines
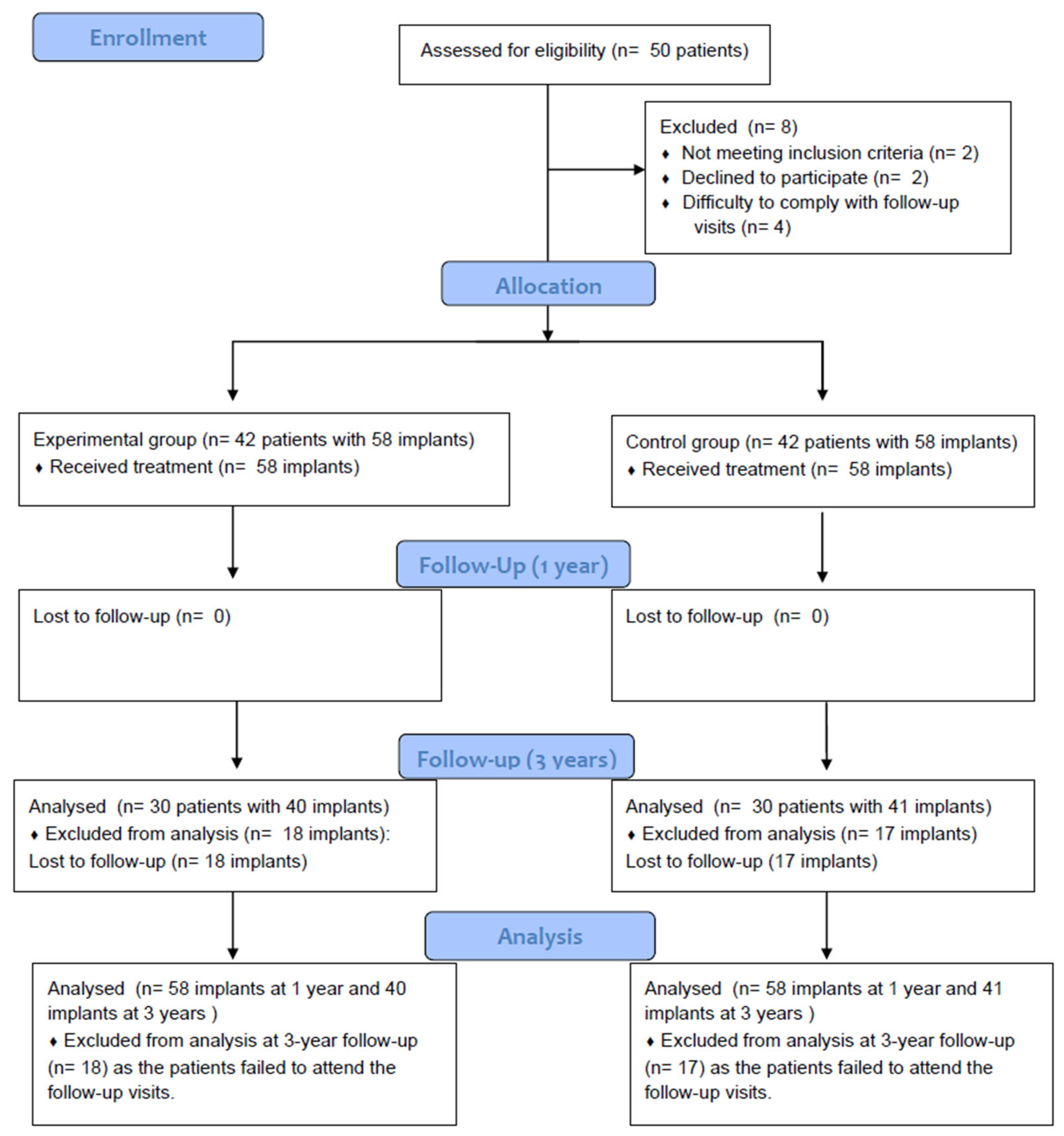
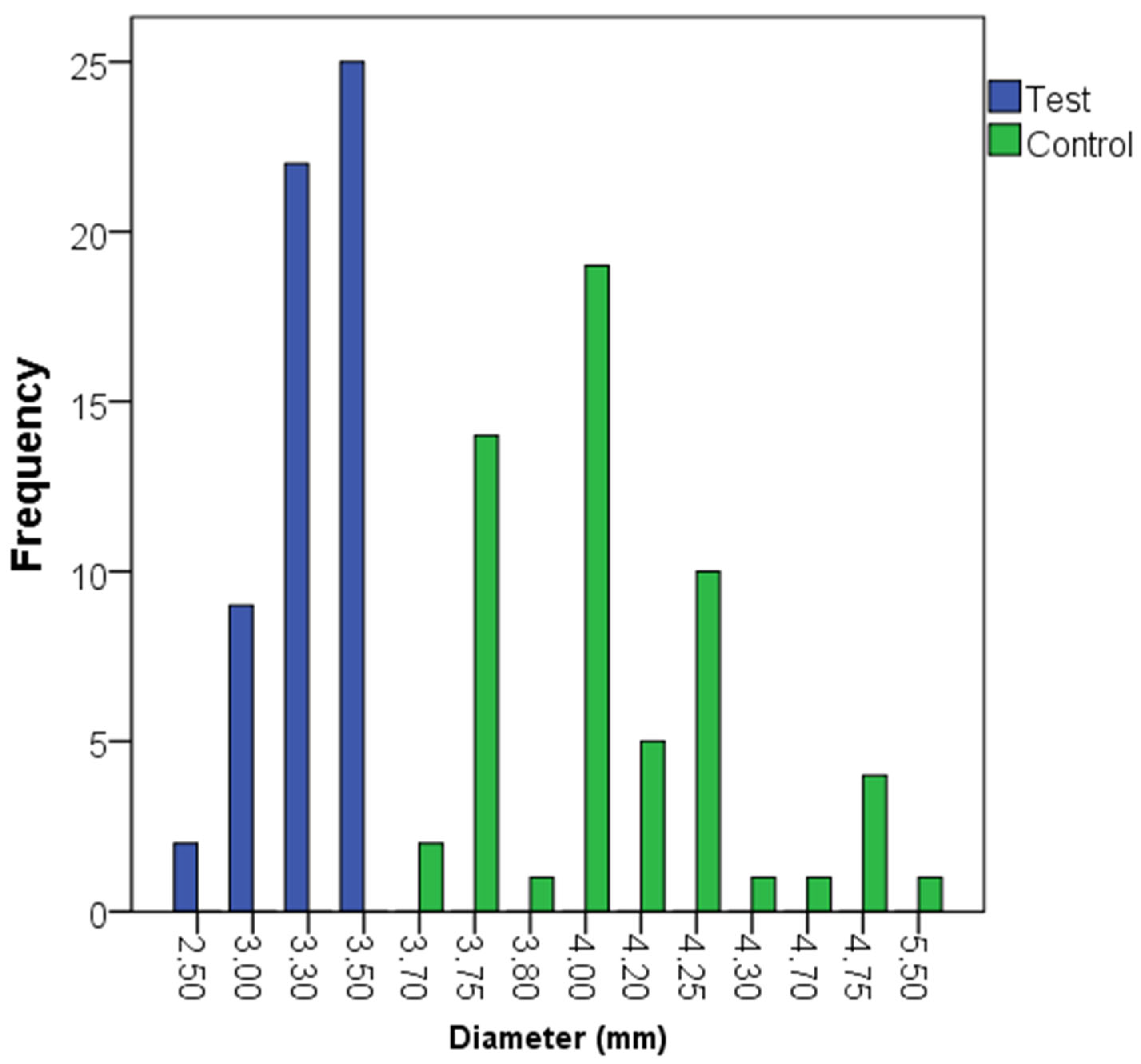
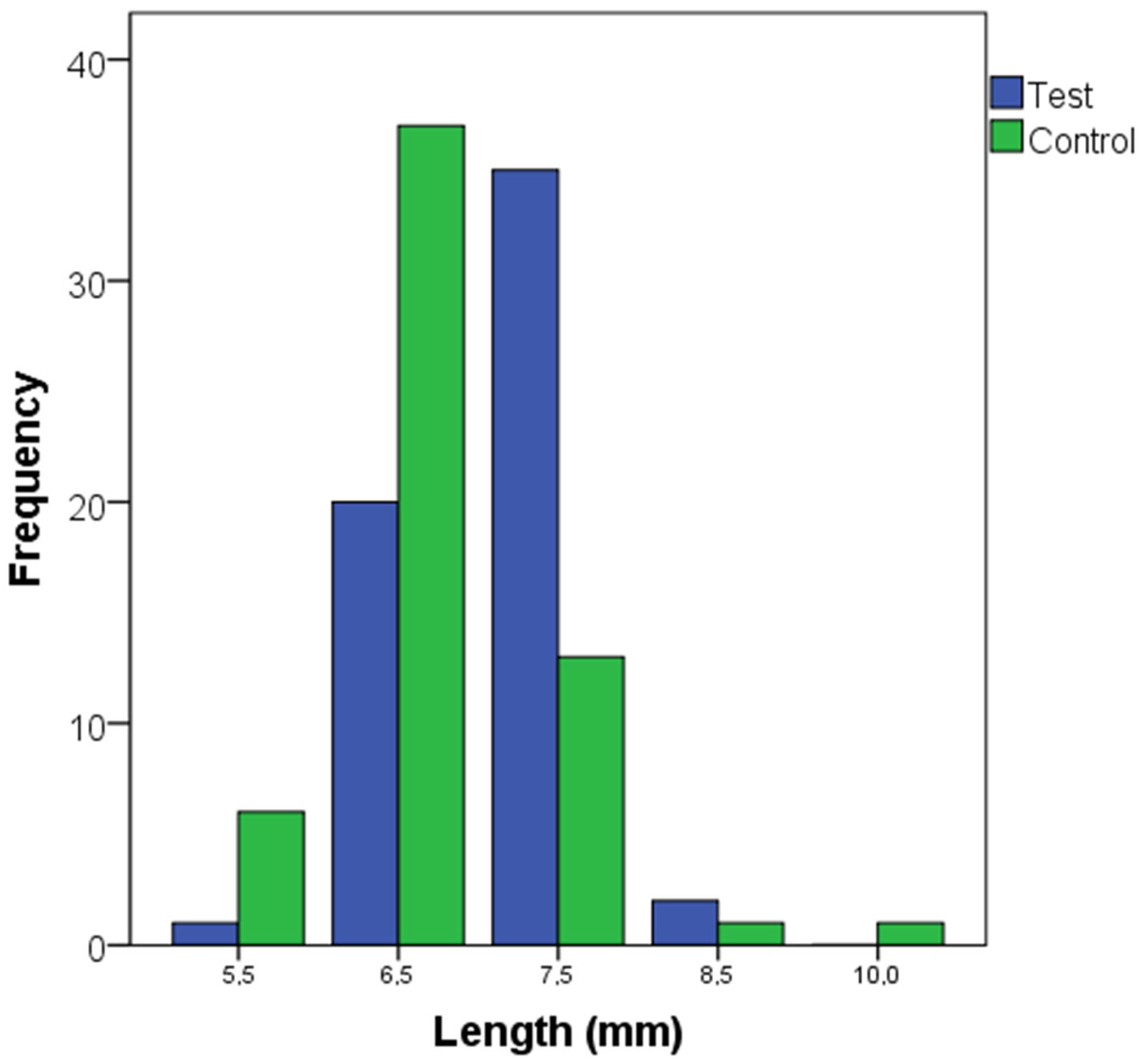
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atwood, D.A. Reduction of residual ridges: A major oral disease entity. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1971, 26, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, K.M.; Huber, C.D.; Lippnig, W.R.; Ulm, C.; Watzek, G.; Tangl, S. Atrophy of the residual alveolar ridge following tooth loss in an historical population. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsmill, V.J. Post-extraction remodeling of the adult mandible. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1999, 10, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adell, R.; Lekholm, U.; Grondahl, K.; Branemark, P.I.; Lindstrom, J.; Jacobsson, M. Reconstruction of severely resorbed edentulous maxillae using osseointegrated fixtures in immediate autogenous bone grafts. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1990, 5, 233–246. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.T.; Buser, D.; Sculean, A.; Belser, U.C. Complications and treatment errors in implant positioning in the aesthetic zone: Diagnosis and possible solutions. Periodontology 2000 2023, 92, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Martin, W.; Belser, U.C. Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: Anatomic and surgical considerations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.-Y.; Fu, J.-H.; Wang, H.-L. The Role of Implant Position on Long-Term Success. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2014, 4, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.; Saxegaard, E.; Knutsen, B.M.; Haanaes, H.R. A prospective clinical study evaluating the safety and effectiveness of narrow-diameter threaded implants in the anterior region of the maxilla. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 16, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Parize, H.N.; Bohner, L.O.L.; Gama, L.T.; Porporatti, A.L.; Mezzomo, L.A.M.; Martin, W.C.; Goncalves, T. Narrow-diameter implants in the anterior region: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Is Alveolar Ridge Split a Risk Factor for Implant Survival? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Saracho, J.; Begona, L.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Long-Term Follow-Up of 2.5-mm Narrow-Diameter Implants Supporting a Fixed Prostheses. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Haydar, B.; Kang, P.; Momen-Heravi, F. Efficacy of Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Expansion Through the Alveolar Ridge Split Procedure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2023, 38, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, S.; Du, Z.; Yang, R.; Shi, B.; Ji, W. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes and Risk Indicator Analyses of Narrow-Diameter Implants in the Posterior Jaw: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 10 to 27 Years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2025, 36, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, G.; Zaccheroni, Z.; Tayeb, S.; Oliverio, A.; Mancuso, E.; Bonifazi, L.; Giudice, A.; Barausse, C.; Felice, P. Flapless Mini Implants Immediately Loaded for Full-Arch Overdenture Rehabilitation: An Up-To-15-Year Retrospective Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanoff, C.J.; Sennerby, L.; Johansson, C.; Rangert, B.; Lekholm, U. Influence of implant diameters on the integration of screw implants. An experimental study in rabbits. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 26, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemtov-Yona, K.; Rittel, D.; Machtei, E.E.; Levin, L. Effect of dental implant diameter on fatigue performance. Part II: Failure analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, M.; Poli, P.P.; Giboli, L.; Beretta, M.; Maiorana, C.; Pellegrini, M. Clinical Factors on Dental Implant Fractures: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-W.; Kim, N.-H.; Lee, Y.; Oh, Y.-A.; Lee, J.-H.; You, H.-K. Implant fracture failure rate and potential associated risk indicators: An up to 12-year retrospective study of implants in 5,124 patients. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Jeong, S.-N.; Kim, N.-H.; Lee, D.-W. Incidence and pattern of implant fractures: A long-term follow-up multicenter study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Liu, B.L.; Qian, S.J.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Lai, H.C. Clinical evaluation of narrow-diameter implants versus standard-diameter implants with lateral bone augmentation in posterior jaws: Three-year results of a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kympouropoulos, S. Real World Evidence: Methodological issues and opportunities from the European Health Data Space. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2023, 23, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Alkhraisat, M.H.; Pinas, L.; Orive, G. Efficacy of biologically guided implant site preparation to obtain adequate primary implant stability. Ann. Anat. 2015, 199, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E. Plasma rich in growth factors: Preliminary results of use in the preparation of future sites for implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1999, 14, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Anitua, E.; Andia, I.; Ardanza, B.; Nurden, P.; Nurden, A.T. Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiegnitz, E.; Al-Nawas, B. Narrow-diameter implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, C.; Saliba-Serre, B.; Ruquet, M.; Raskin, A.; Hüe, O.; Silvestri, F.; Mense, C. Assessment of bone density in edentulous maxillae using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 125, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemtov-Yona, K. Quantitative assessment of the jawbone quality classification: A meta-analysis study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, C.S.; Choi, S.H.; Chai, J.K.; Jung, U.W. Long-term retrospective study of narrow implants for fixed dental prostheses. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok-Jo, C.; June -Kye, L.; Chae-Heon, C. Finite element stress analysis of implant supported prosthesis with or without abutment. J. Dent. Implant. Res. 1997, 16, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothberg, C.; Andre, U.; Grondahl, K.; Ljungquist, B.; Thomsen, P.; Slotte, C. Immediately loaded implants with or without abutments supporting fixed partial dentures: 1-year results from a prospective, randomized, clinical trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinato, S.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Bernardello, F.; Zaffe, D. Minimum Abutment Height to Eliminate Bone Loss: Influence of Implant Neck Design and Platform Switching. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, P.; Solyom, E.; Vancsa, S.; Matrai, P.; Hegyi, P.; Varga, G.; Hermann, P.; Borbely, J.; Sculean, A.; Mikulas, K. Less marginal bone loss around bone-level implants restored with long abutments: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Periodontology 2000 2024, 94, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Perez, R.; Bartolome, J.F.; Pradies, G. Original vs compatible stock abutment- implant connection: An in vitro analysis of the internal accuracy and mechanical fatigue behaviour. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2022, 66, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrisnard, L.; Renouard, F.; Renault, P.; Barquins, M. Influence of implant length and bicortical anchorage on implant stress distribution. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2003, 5, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofre, J.; Cendoya, P.; Munoz, P. Effect of splinting mini-implants on marginal bone loss: A biomechanical model and clinical randomized study with mandibular overdentures. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncelli, B.; Poyrazoglu, E.; Koyluoglu, A.M.; Tezcan, S. Comparison of load transfer by implant abutments of various diameters. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 1997, 5, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Toti, P.; Marconcini, S.; Enrica, G.; Pedretti, G.; Barone, A.; Covani, U. The Influence of Prosthesis Design on the Outcomes of Tooth Implants Immediately Placed and Loaded by Means of One-Piece Titanium Machined Restoration. J. Oral Implant. 2018, 44, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.T.; Chiou, L.L.; Chen, H.H.; Lin, G.H.; Kao, R.T.; Curtis, D.A. Influence of Dental Implant Diameters on Prosthesis Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2025, 0, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraschini, V.; Porto Barboza, E. Immediate versus conventional loaded single implants in the posterior mandible: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskunses, F.M.; Tak, O. Clinical performance of narrow-diameter titanium-zirconium implants in immediately loaded fixed full-arch prostheses: A 2-year clinical study. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2021, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, F.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xia, H.; Xia, D.; Bai, Y. Immediate Versus Non-immediate Loading Protocols for Reduced-Diameter Implants Supporting Overdentures: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2024, 39, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachiou, A.; Tsirogiannis, P.; Ioannidis, A.; Joda, T.; Sykaras, N.; Naka, O. Narrow-diameter implants for treatment with fixed restorations in the posterior region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2025, 34, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P.; Zaniboni, M. Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 237–259. [Google Scholar]
- Milinkovic, I.; Cordaro, L. Are there specific indications for the different alveolar bone augmentation procedures for implant placement? A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipioni, A.; Bruschi, G.B.; Calesini, G. The edentulous ridge expansion technique: A five-year study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1994, 14, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Alkhraisat, M.H.; Miguel-Sanchez, A.; Orive, G. Surgical correction of horizontal bone defect using the lateral maxillary wall: Outcomes of a retrospective study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnayef, B.; Monje, A.; Lin, G.H.; Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Chan, H.L.; Wang, H.L.; Hernandez-Alfaro, F. Alveolar ridge split on horizontal bone augmentation: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Bellini, P.; Buti, J.; Felice, P. Immediate loading of 3 mm-diameter implants as an alternative to horizontal bone augmentation for placing 4 mm-diameter implants: One-year post-loading results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Clin. Trials Dent. 2020, 2, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Bortolin, M.; Taschieri, S.; Weinstein, R.L. Effect of autologous growth factors in maxillary sinus augmentation: A systematic review. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca-Gonzalez, L.; Serrano Zamora, R.; Rancan, L.; Gonzalez Fernandez-Tresguerres, F.; Fernandez-Tresguerres, I.; Lopez-Pintor, R.M.; Lopez-Quiles, J.; Leco, I.; Torres, J. Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) and leukocyte-platelet rich fibrin (L-PRF): Comparative release of growth factors and biological effect on osteoblasts. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2022, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caponio, V.C.A.; Baca-Gonzalez, L.; Gonzalez-Serrano, J.; Torres, J.; Lopez-Pintor, R.M. Effect of the use of platelet concentrates on new bone formation in alveolar ridge preservation: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 4131–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-Garcia, M.P.; Prados-Sanchez, E.; Olmedo-Gaya, M.V.; Munoz-Soto, E.; Vallecillo-Capilla, M.; Bravo, M. Dental implant stability is influenced by implant diameter and localization and by the use of plasma rich in growth factors. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Group | Location | Jaw | Total | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla | Mandible | ||||
| Narrow implants | Anterior teeth | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.000 a |
| Premolars | 10 | 21 | 31 | ||
| Molars | 5 | 19 | 24 | ||
| Total | 17 | 41 | 58 | ||
| Regular implants | Anterior teeth | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Premolars | 3 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Molars | 14 | 39 | 53 | ||
| Total | 18 | 40 | 58 | ||
| p-value | 0.840 a | ||||
| Variable | Test | Control | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone type | I | 6 | 1 | 0.033 a |
| II | 37 | 31 | ||
| III | 14 | 20 | ||
| IV | 1 | 6 | ||
| Insertion torque (Ncm) (median; range) | 60; 10 to 70 | 60; 10 to 65 | 0.888 b | |
| Loading protocol | Immediate | 32 | 32 | 1.000 a |
| Delayed | 26 | 26 | ||
| Variable | Test | Control | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antagonist type | Implant | 30 | 34 | 0.752 a |
| Tooth | 27 | 23 | ||
| Removable denture | 1 | 1 | ||
| Prosthesis type | Complete | 1 | 1 | 1.000 a |
| Partial | 57 | 57 | ||
| Failed prosthesis | 12 months | 0 | 0 | NA |
| 36 months | 0 | 0 | NA | |
| Change in mean MBL-12 months (mm) | Median; range | 0.0; −2.2 to 0.7 | 0.0; −1.0 to 1.1 | 0.029 b |
| Change in mean MBL-36 months (mm) | Median; range | −0.2; −1.5 to 0.8 | 0.0; −1.3 to 0.8 | 0.079 c |
| Implant Failure-36 months | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Bleeding on probing-36 months | 0 | 0 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anitua, E.; Alcaine, A.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Comparison of Narrow (<3.75 mm) and Standard (≥3.75 mm) Diameter Implants Supporting the Same Multiple Fixed Prostheses and Mirroring Real-World Clinical Scenarios: Non-Randomized Clinical Trial. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090420
Anitua E, Alcaine A, Alkhraisat MH. Comparison of Narrow (<3.75 mm) and Standard (≥3.75 mm) Diameter Implants Supporting the Same Multiple Fixed Prostheses and Mirroring Real-World Clinical Scenarios: Non-Randomized Clinical Trial. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(9):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090420
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnitua, Eduardo, Ander Alcaine, and Mohammad Hamdan Alkhraisat. 2025. "Comparison of Narrow (<3.75 mm) and Standard (≥3.75 mm) Diameter Implants Supporting the Same Multiple Fixed Prostheses and Mirroring Real-World Clinical Scenarios: Non-Randomized Clinical Trial" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 9: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090420
APA StyleAnitua, E., Alcaine, A., & Alkhraisat, M. H. (2025). Comparison of Narrow (<3.75 mm) and Standard (≥3.75 mm) Diameter Implants Supporting the Same Multiple Fixed Prostheses and Mirroring Real-World Clinical Scenarios: Non-Randomized Clinical Trial. Dentistry Journal, 13(9), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090420







