Role of Myokines on the Bone Metabolism of Craniofacial Region: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
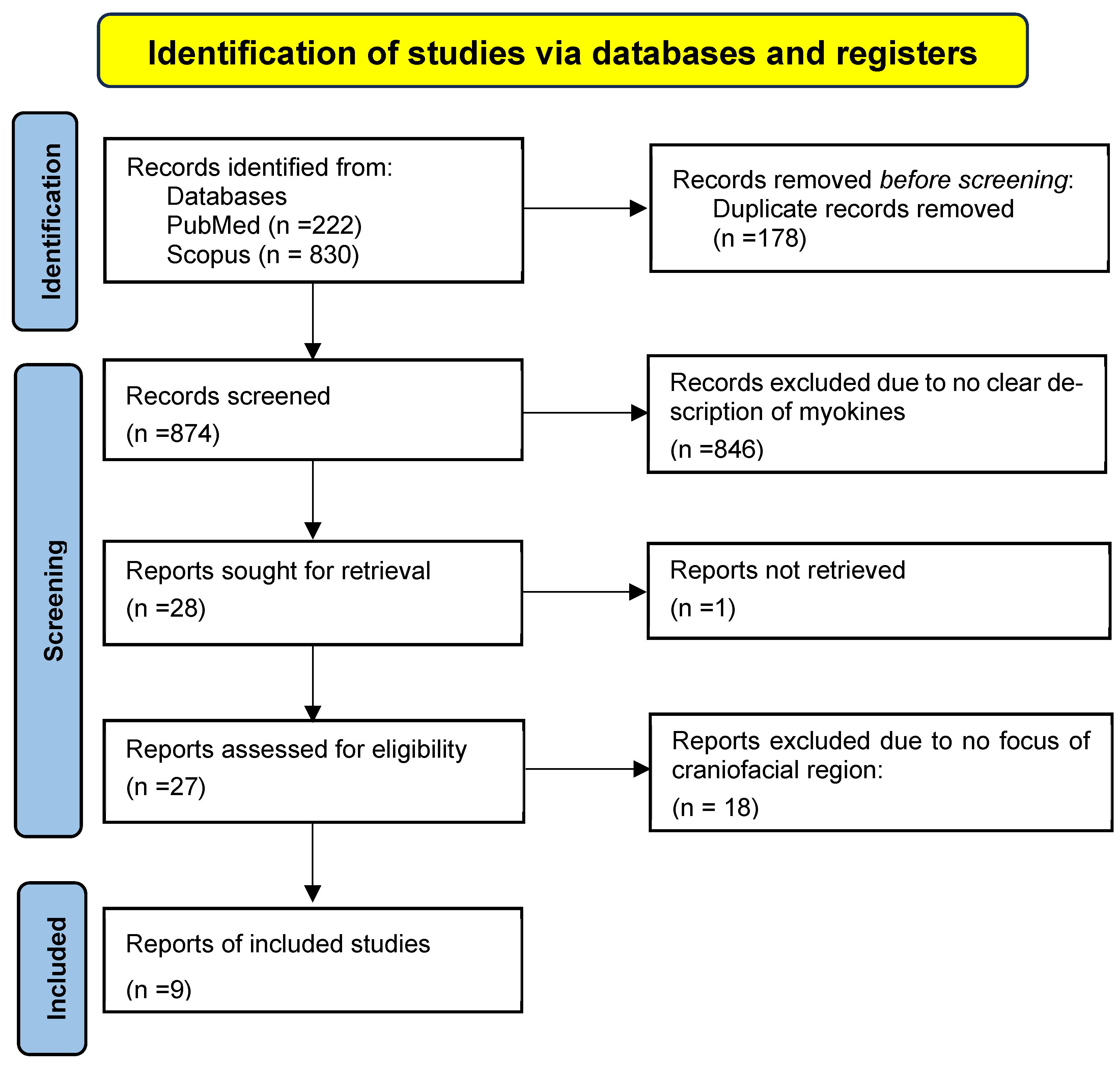
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Role of Myokines in Craniofacial Region
3.2.1. IL-6
3.2.2. Myostatin
3.2.3. Irisin
3.2.4. IGF-1
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Key Findings
4.2. Comparison with Myokine Research in Other Skeletal Regions
4.3. Functional and Developmental Uniqueness of Craniofacial Muscles and Bones
4.4. Potential Mechanisms of Myokine Action in the Craniofacial Region
4.5. Clinical Implications
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPa | Mega Pascal |
| Hz | Hertz |
| RANKL | Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand |
| OPG | Osteopontegrin |
| TMD | Temporomandibular disorders |
| TMJ | Temporomandibular joint |
| IGF-1 | Insukin-like growth factor-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| BMD | Bone mineral density |
| BV | Bone volume |
| TV | Trabecular Volume |
| PDL | Periodontal ligament |
| BNDF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BAIBA | β-aminoisobutyric acid |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| PRISMA-ScR | The Extension for Scoping Reviews of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta analyses statement |
| FNDC5 | Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 |
| PICO | Population Intervention Control Outcome |
| MAPK | Mitogen activated protein kinase pathway |
References
- Conith, A.J.; Lam, D.T.; Albertson, R.C. Muscle-induced loading as an important source of variation in craniofacial skeletal shape. Genesis 2019, 57, e23263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintoye, S. The distinctive jaw and alveolar bone regeneration. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.G. Importance of Muscle Movement for Normal Craniofacial Development. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2010, 21, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliaridis, S. Masticatory muscle influence on craniofacial growth. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1995, 53, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolstra, J.H.; Van Eijden, T.M.G.J. Prediction of volumetric strain in the human temporomandibular joint cartilage during jaw movement. J. Anat. 2006, 209, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buvinic, S.; Balanta-Melo, J.; Kupczik, K.; Vásquez, W.; Beato, C.; Toro-Ibacache, V. Muscle-Bone Crosstalk in the Masticatory System: From Biomechanical to Molecular Interactions. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 606947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotto, M.; Bonewald, L. Bone and muscle: Interactions beyond mechanical. Bone 2015, 80, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L.; Mihai, T.A.; Schenker, R.A.; Marin, M.I.; Schenker, M.; Streba, C.T.; Gheonea, D.I.; Piele, D. The effect of physical exercises on TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 cytokines expression and NK cells in cancer. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2025, 66, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, K.; Hiasa, M.; Tenshin, H.; Teramachi, J.; Oda, A.; Harada, T.; Higa, Y.; Sogabe, K.; Oura, M.; Sumitani, R.; et al. Mechanical unloading aggravates bone destruction and tumor expansion in myeloma. Haematologica 2021, 107, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Ghay, R.; Goyal, G.; Saini, R.V. Exploring the Role of Acute Exercise-Induced Myokine Release in Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity in Healthy and Diabetic Individuals. Cureus 2025, 17, e78991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, D.; Jähn, K.; Lara-Castillo, N. Muscle–Bone Crosstalk: Emerging Opportunities for Novel Therapeutic Approaches to Treat Musculoskeletal Pathologies. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonewald, L. Use it or lose it to age: A review of bone and muscle communication. Bone 2019, 120, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Ichioka, H.; Akamatsu, Y.; Oseko, F.; Mazda, O.; Imanishi, J.; Kanamura, N.; Kita, M. Effects of mechanical stress on cytokine production in mandible-derived osteoblasts. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, S.; Ogura, N.; Sakamaki, H.; Abiko, Y.; Nagura, H. Interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in the synovial fluid of the temporomandibular joint with respect to cartilage destruction. Oral Dis. 2000, 6, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.J.; Macari, S.; Coimbra, C.C.; Pereira, T.D.S.F.; Barrioni, B.R.; Gomez, R.S.; Silva, T.A.; Paiva, S.M. Aerobic and resistance training improve alveolar bone quality and interferes with bone-remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in mice. Bone 2020, 138, 115496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravosa, M.J.; Lopez, E.K.; Menegaz, R.A.; Stock, S.R.; Stack, M.S.; Hamrick, M.W. Using “Mighty Mouse” to understand masticatory plasticity: Myostatin-deficient mice and musculoskeletal function. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, E.K.; Stock, S.R.; Hamrick, M.W.; Ravosa, M.J. Biomineralization and adaptive plasticity of the temporomandibular joint in myostatin knockout mice. Arch. Oral Biol. 2006, 51, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byron, C.D.; Borke, J.; Yu, J.; Pashley, D.; Wingard, C.J.; Hamrick, M. Effects of increased muscle mass on mouse sagittal suture morphology and mechanics. Anat. Rec. 2004, 279, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Pullisaar, H.; Landin, M.A.; Heyward, C.A.; Schröder, M.; Geng, T.; Grano, M.; Reseland, J.E. FNDC5/irisin is expressed and regulated differently in human periodontal ligament cells, dental pulp stem cells and osteoblasts. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 124, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pullisaar, H.; Stunes, A.K.; Nogueira, L.P.; Syversen, U.; Reseland, J.E. Irisin reduces orthodontic tooth movement in rats by promoting the osteogenic potential in the periodontal ligament. Eur. J. Orthod. 2023, 45, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, W. Changes of the condylar cartilage and subchondral bone in the temporomandibular joints of rats under unilateral mastication and expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, D.E. The Evolution of the Human Head [Internet]; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.2307/j.ctvjnrtmh (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Herring, S.W. Functional Morphology of Mammalian Mastication. Am. Zool. 1993, 33, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.M. Skeletal structural adaptations to mechanical usage (SATMU): 2. Redefining Wolff’s Law: The remodeling problem. Anat. Rec. 1990, 226, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscle as an Endocrine Organ: Focus on Muscle-Derived Interleukin-6. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1379–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.G.; Lopes, M.A.; Batista, M.L. Physical Exercise-Induced Myokines and Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk: A Review of Current Knowledge and the Implications for Health and Metabolic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonewald, L.F. The Role of the Osteocyte in Bone and Nonbone Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaianni, G.; Cuscito, C.; Mongelli, T.; Oranger, A.; Mori, G.; Brunetti, G.; Colucci, S.; Cinti, S.; Grano, M. Irisin Enhances Osteoblast Differentiation In Vitro. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 902186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecka-Czernik, B. Marrow fat metabolism is linked to the systemic energy metabolism. Bone 2012, 50, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygili, E.; Pekassa, M.; Saygili, E.; Rackauskas, G.; Hommes, D.; Noor-Ebad, F.; Gemein, C.; Zink, M.D.; Schwinger, R.H.; Weis, J.; et al. Mechanical stretch of sympathetic neurons induces VEGF expression via a NGF and CNTF signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 410, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.J.; Andrade, E.F.; Barroso, L.C.; Lima, R.R.D.; Macari, S.; Paiva, S.M.; Silva, T.A. Irisin effects on bone: Systematic review with meta-analysis of preclinical studies and prospects for oral health. Braz. Oral Res. 2022, 36, e055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, M.W.; Samaddar, T.; Pennington, C.; McCormick, J. Increased Muscle Mass with Myostatin Deficiency Improves Gains in Bone Strength with Exercise. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherron, A.C.; Lawler, A.M.; Lee, S.J. Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-p superfamily member. Nature 1997, 387, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnieu, A.; Carnac, G.; Vernus, B. Myostatin in the Pathophysiology of Skeletal Muscle. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehring, B.; Binkley, N. Myostatin—The Holy Grail for Muscle, Bone, and Fat? Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2013, 11, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.E.; Maerz, M.D.; Buckner, J.H. IL-6: A cytokine at the crossroads of autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantini, M.; Massimino, M.L.; Rapizzi, E.; Rossini, K.; Catani, C.; Dallalibera, L.; Carraro, U. Human Satellite Cell-Proliferation in Vitro Is Regulated by Autocrine Secretion of IL-6 Stimulated by a Soluble Factor(s) Released by Activated Monocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.L.; Baeza-Raja, B.; Perdiguero, E.; Jardí, M.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Interleukin-6 Is an Essential Regulator of Satellite Cell-Mediated Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendal, L.; Søgaard, K.; Kjær, M.; Sjøgaard, G.; Langberg, H.; Kristiansen, J. Increase in interstitial interleukin-6 of human skeletal muscle with repetitive low-force exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.D.; Boström, P.; O’Sullivan, J.F.; Schinzel, R.T.; Lewis, G.D.; Dejam, A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Palma, M.J.; Calhoun, S.; Georgiadi, A.; et al. β-Aminoisobutyric Acid Induces Browning of White Fat and Hepatic β-Oxidation and Is Inversely Correlated with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldspink, G. Mechanical Signals, IGF-I Gene Splicing, and Muscle Adaptation. Physiology 2005, 20, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijnders, C.M.A.; Bravenboer, N.; Tromp, A.M.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Lips, P. Effect of mechanical loading on insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression in rat tibia. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 192, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D.; Tahimic, C.; Chang, W.; Wang, Y.; Philippou, A.; Barton, E.R. Role of IGF-I signaling in muscle bone interactions. Bone 2015, 80, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noden, D.M.; Francis-West, P. The differentiation and morphogenesis of craniofacial muscles. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 1194–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquharson, C. Bones and Cartilage: Developmental and Evolutionary Skeletal Biology. Second Edition. Br. Poult. Sci. 2015, 56, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Concept 1: Myokines | Concept 2: Bone Metabolism | Concept 3: Craniofacial/Masticatory |
|---|---|---|
| myokine * | “bone remodeling” | craniofacial |
| “muscle-derived cytokine *” | “bone metabolism” | mandible OR mandibular |
| irisin | osteogenesis | maxilla OR maxillary |
| myostatin | osteoblast * | “temporomandibular joint” OR TMJ |
| interleukin-6 OR IL-6 | osteoclast * | “facial bone *” |
| Cytokines [Mesh] | “bone mineral density” | “jaw bone *” |
| FNDC5 protein, human [Mesh] | “bone resorption” | “masticatory muscle *” |
| Myostatin [Mesh] | Bone Remodeling [Mesh] | masseter OR temporalis |
| Interleukin-6 [Mesh] | Osteogenesis [Mesh] | Mandible [Mesh] |
| Osteoblasts [Mesh] | Maxilla [Mesh] | |
| Bone Resorption [Mesh] | Temporomandibular Joint [Mesh] |
| Population |
|
| Intervention/exposure |
|
| Control |
|
| Outcome |
|
| Author and Year | Population | Intervention | Control | Myokine Considered | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yamamoto et al. [16] | Mandiblederived osteoblast cells from 4–6-weeks old male mice. | Intermittent hydrostatic pressure (magnitude: 0.1, 1, and 6 MPa; time: 10, 30, and 60 min; frequency: 1 Hz) | Varying level of hydrostatic pressure. | IL-6 | The hydrostatic pressure simulating the occlusal force influenced the RANKL/OPG ratio in maintaining the bone homeostasis through osteoclastogenesis. |
| Shinoda et al. [17] | 48 patients with TMD | Synovial fluids from TMD patients with osseous changes. | 18 healthy individuals | IL-6 | IL-6 was increased in the patients with osseous changes due to chronic TMD and absent in healthy controls, suggesting its role in TMD pathogenesis. |
| Periera et al. [18] | Mice | Aerobic or resistant physical training combined with orthodontic tooth movement | Sedentary mice | IL-6, IGF-1 | Increased BMD, BV, BV/TV, and IGF-1 production was noted in the maxilla in the physical training group. |
| Ravosa et al. [19] | Myostatin deficient and wild mice | Masticatory overloading through diet. | New Zealand white rabbit. | Myostatin | Tissue mineral density was lowest at the TMJ and highest at the symphysis. |
| Nicholson et al. [20] | Myostatin-knockout mice. | Increased jaw adductor activity due to masticatory overload | Wild-type mice | Myostatin | There was altered mineralization of condylar subchondral bone due to increased masticatory stress in myostatin-deficient mice. |
| Byron et al. [21] | Myostatin-deficient mice | Increased bite force due to hard diet and temporalis muscle mass | Wild-type mice | Myostatin | The sagittal suture connective tissue was less stiff due to hyper muscular temporalis and dissipated bite force better. |
| Yang et al. [22] | Sprague -Dawley rats | Presence of irisin in PDL, dental pulp, and osteoblasts through cell culture | Cultured human PDL, dental pulp, and osteoblasts | Irisin | Irisin presence in the rat and human PDL was confirmed. The irisin production was affected during osteoblast like differentiation. |
| Yang et al., 2023 [23] | Wistar rats; right side of the maxilla | Irisin injected submucosally along with mesial movement of molar | Wistar rats; left side of maxilla | Irisin | Osteogenic potential of periodontal ligament was enhanced, and it reduced the orthodontic tooth movement on the compression side. |
| Liu et al. [24] | Wistar rats | Unilateral loading with dental splints | Control-group rats | IGF-1 | IGF-1 was increased in the non-chewing side, and condylar degeneration was seen on the chewing side. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajan, A.S.; Tanaka, E. Role of Myokines on the Bone Metabolism of Craniofacial Region: A Scoping Review. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090400
Rajan AS, Tanaka E. Role of Myokines on the Bone Metabolism of Craniofacial Region: A Scoping Review. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(9):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090400
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajan, Ahana S., and Eiji Tanaka. 2025. "Role of Myokines on the Bone Metabolism of Craniofacial Region: A Scoping Review" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 9: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090400
APA StyleRajan, A. S., & Tanaka, E. (2025). Role of Myokines on the Bone Metabolism of Craniofacial Region: A Scoping Review. Dentistry Journal, 13(9), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13090400







