Evaluating the Success of Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review with Case Illustration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
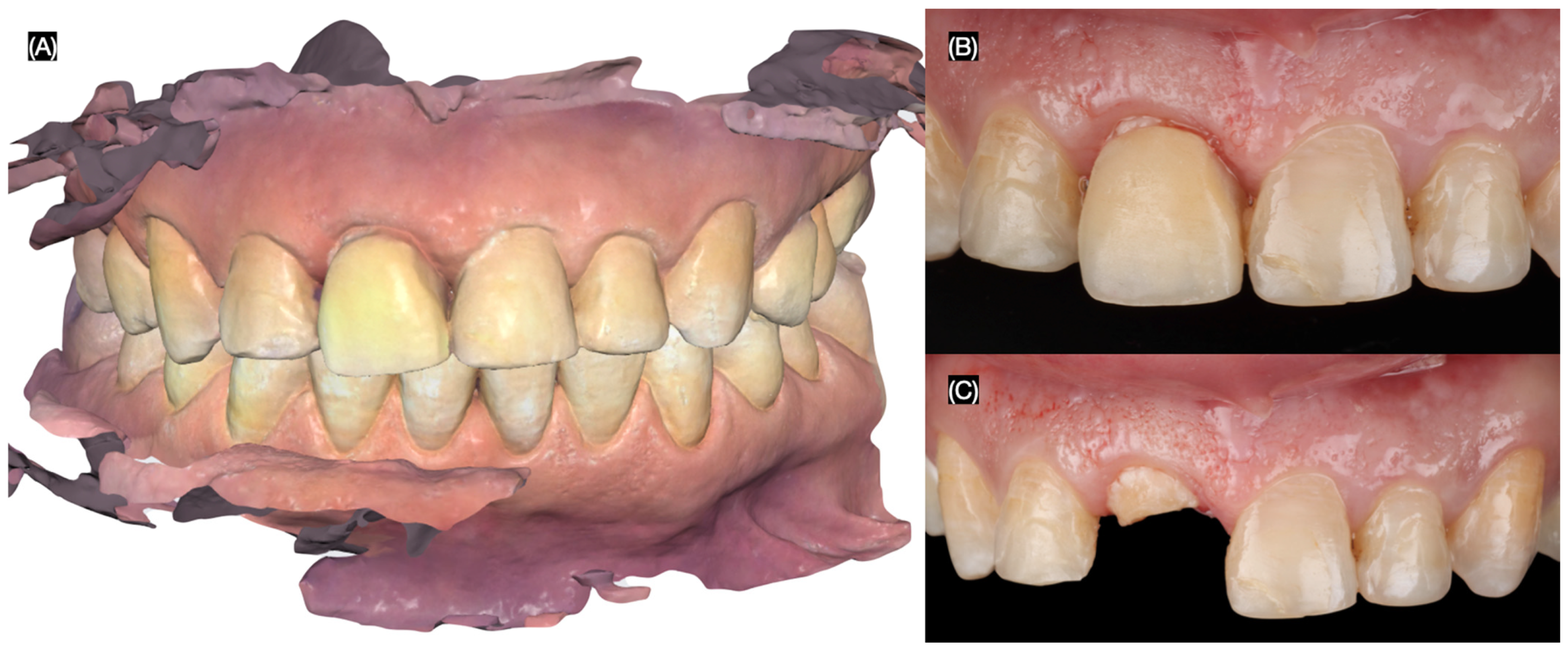
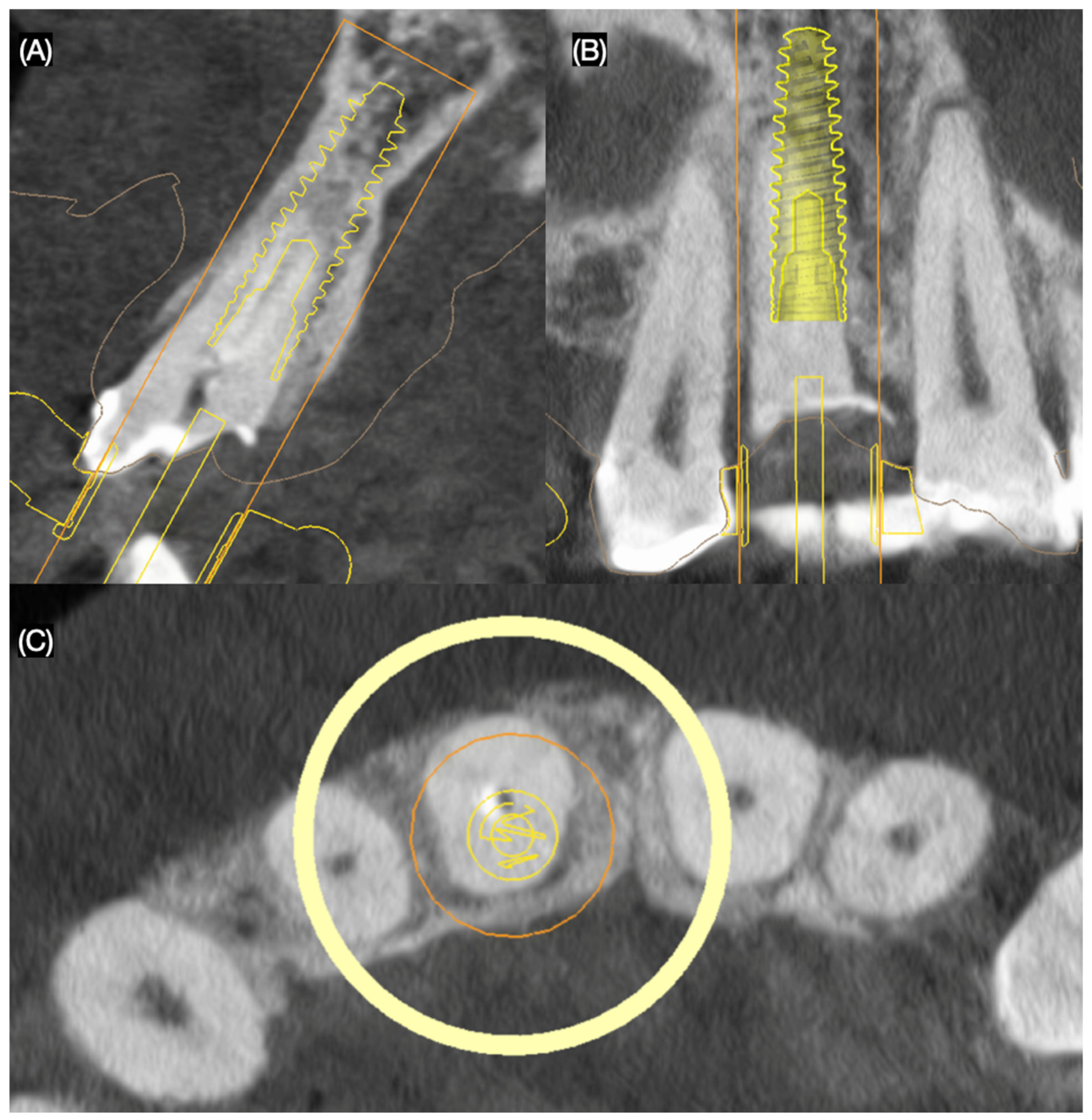
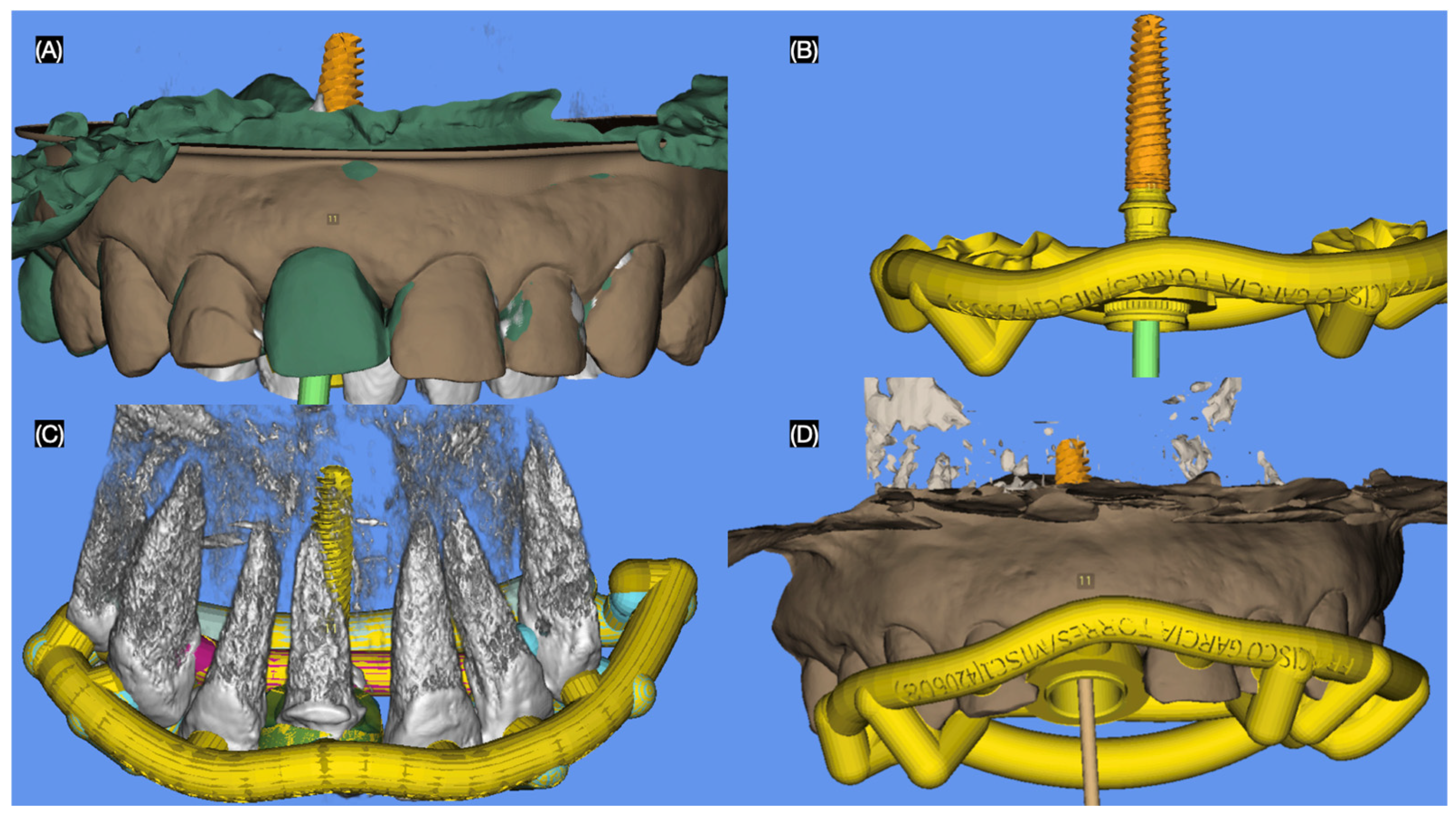
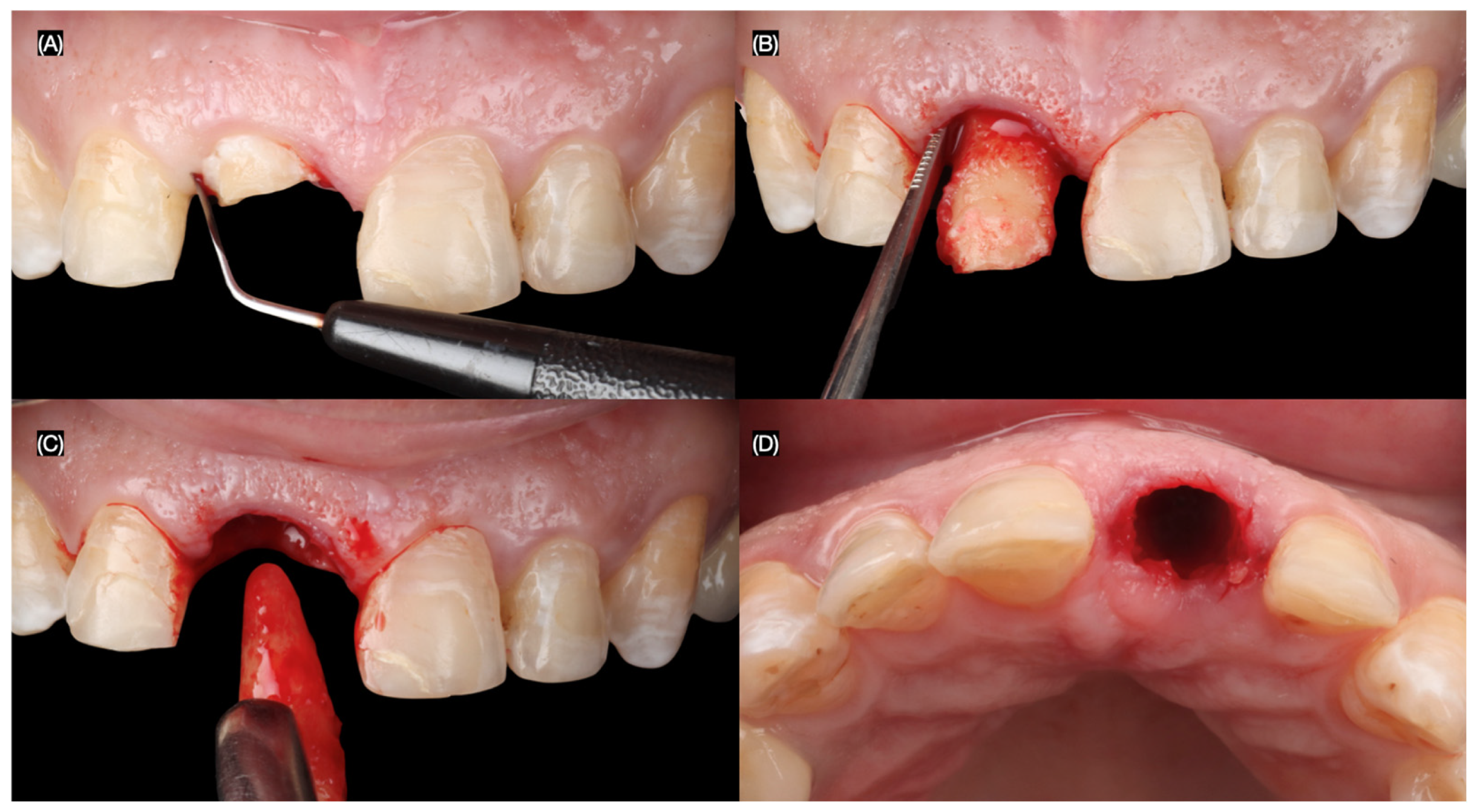
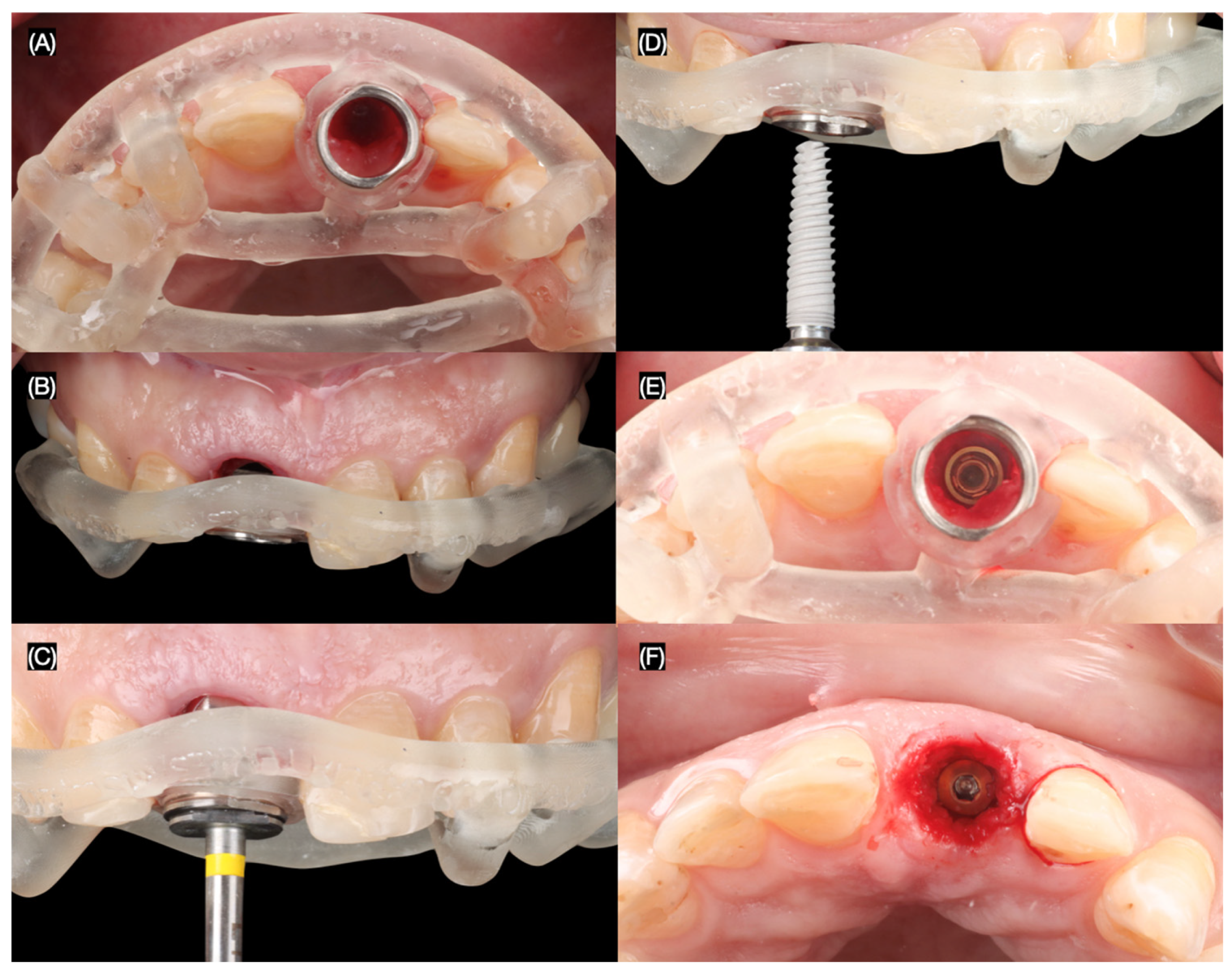
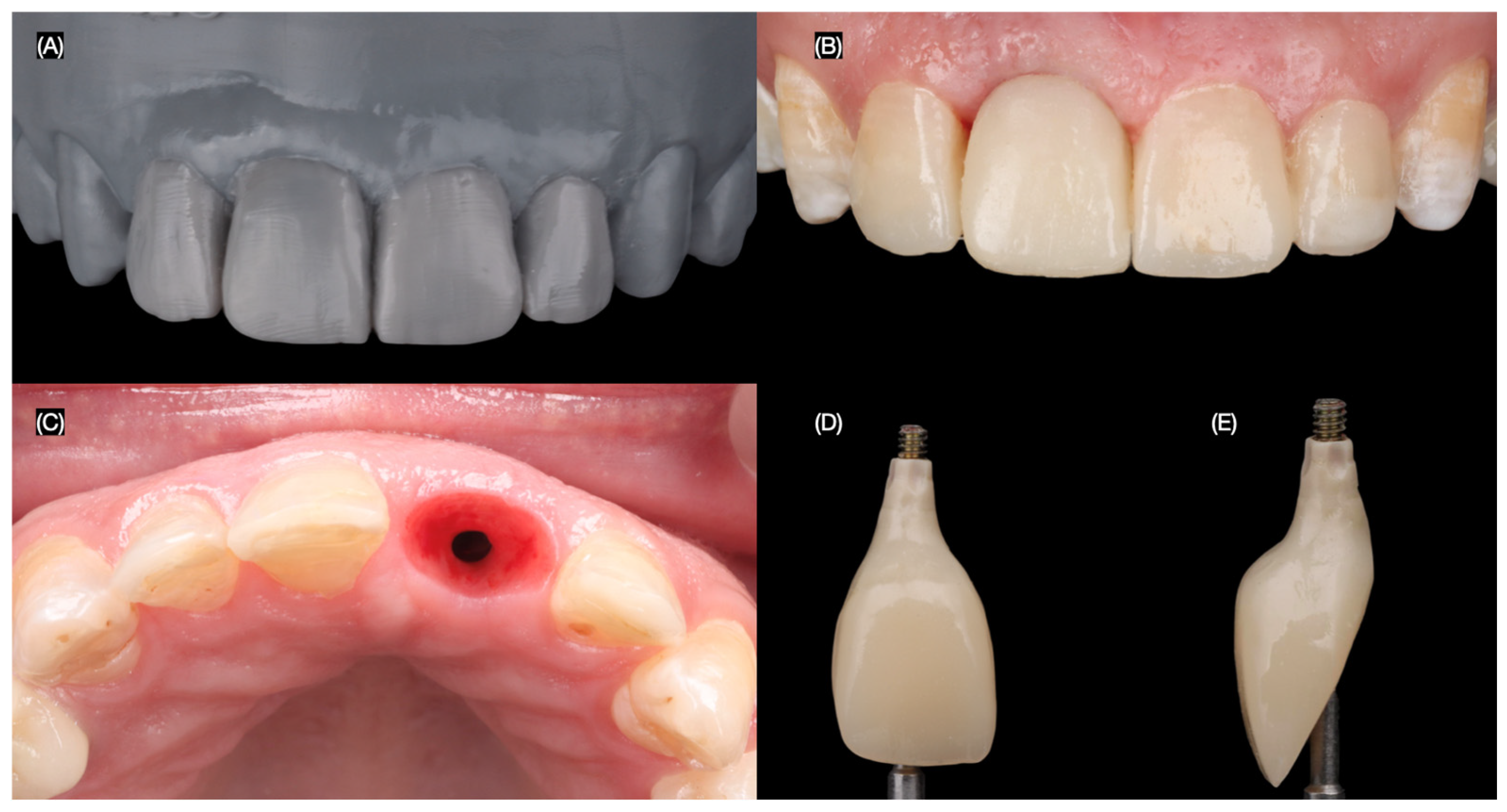
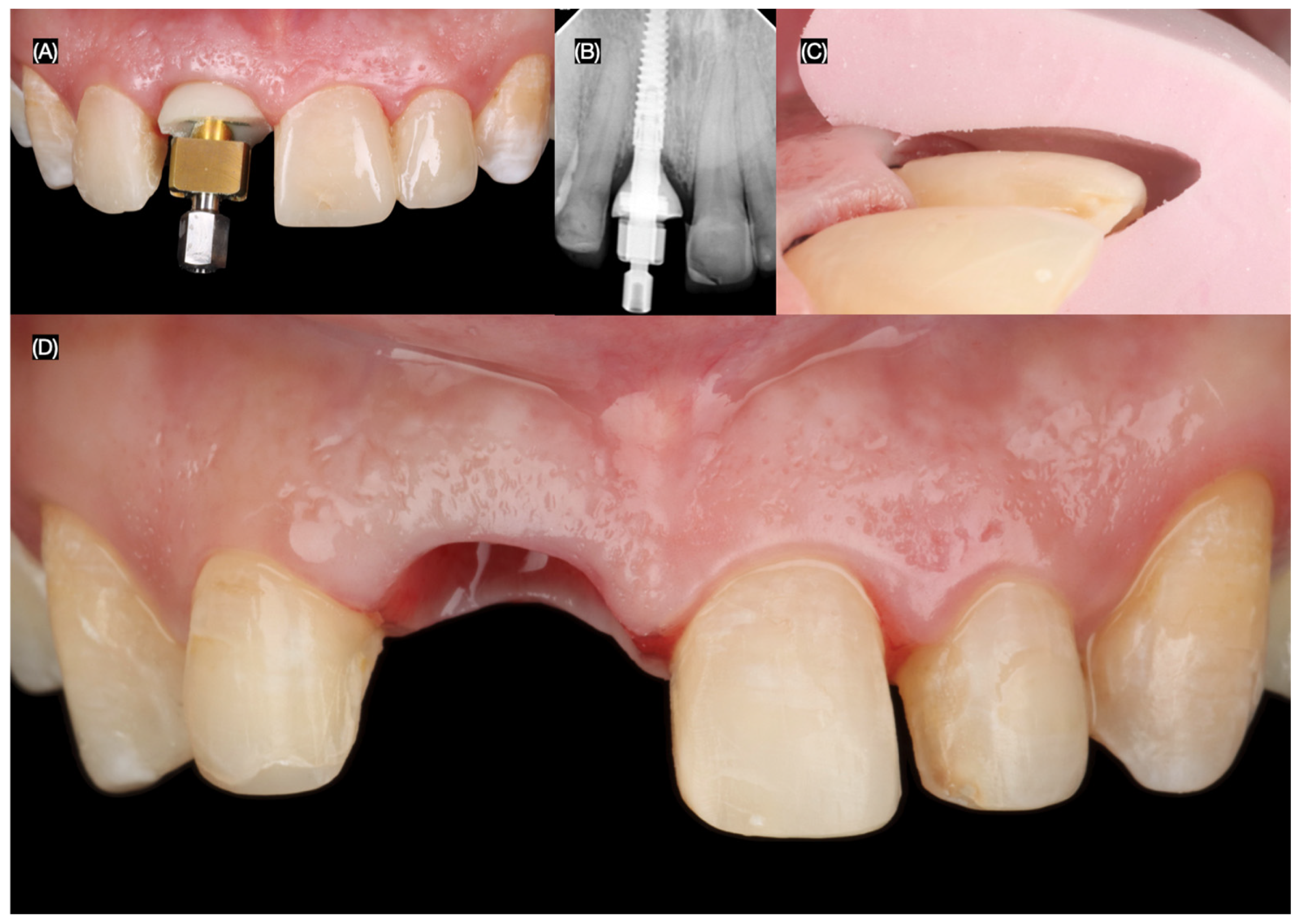
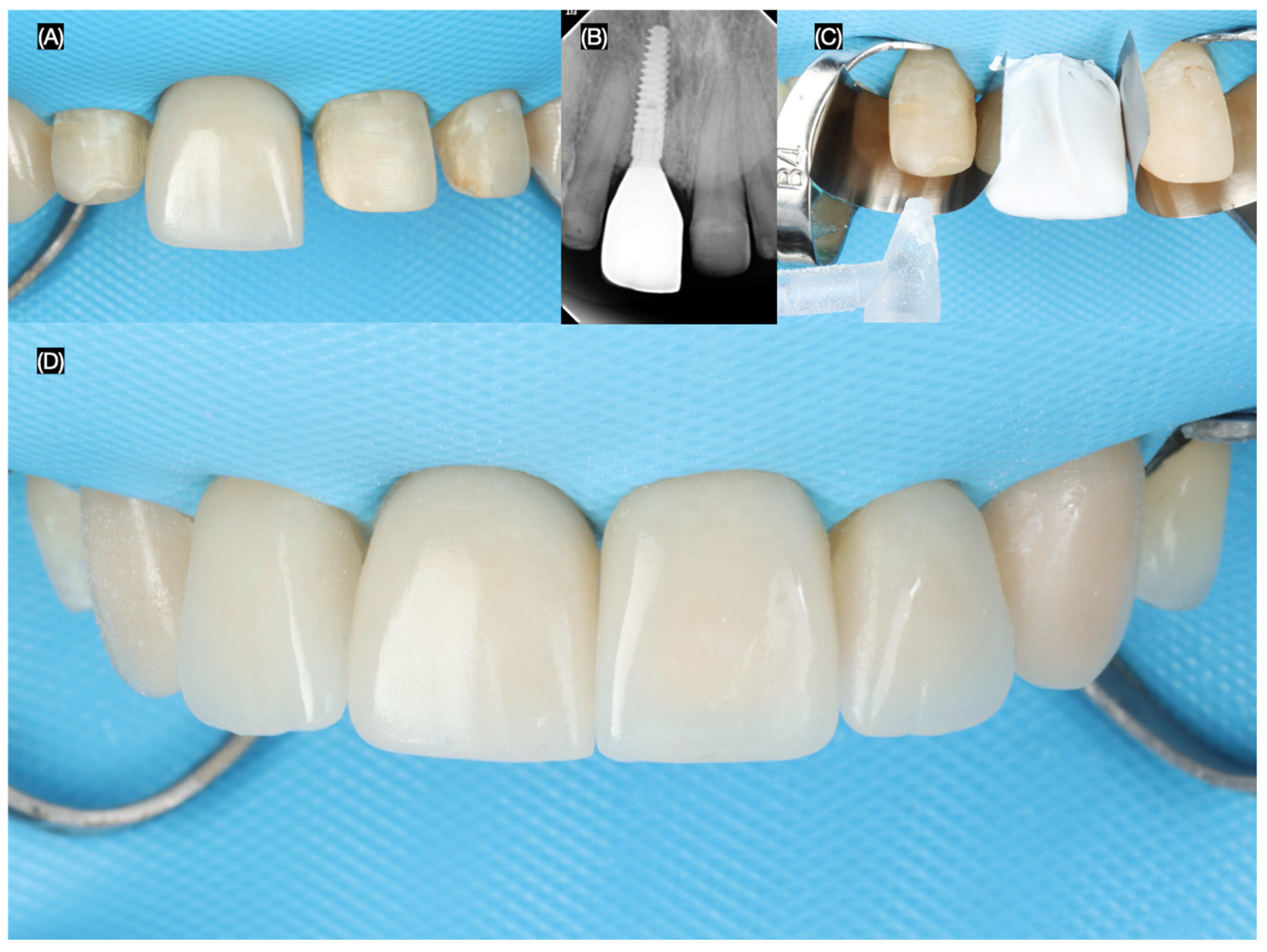
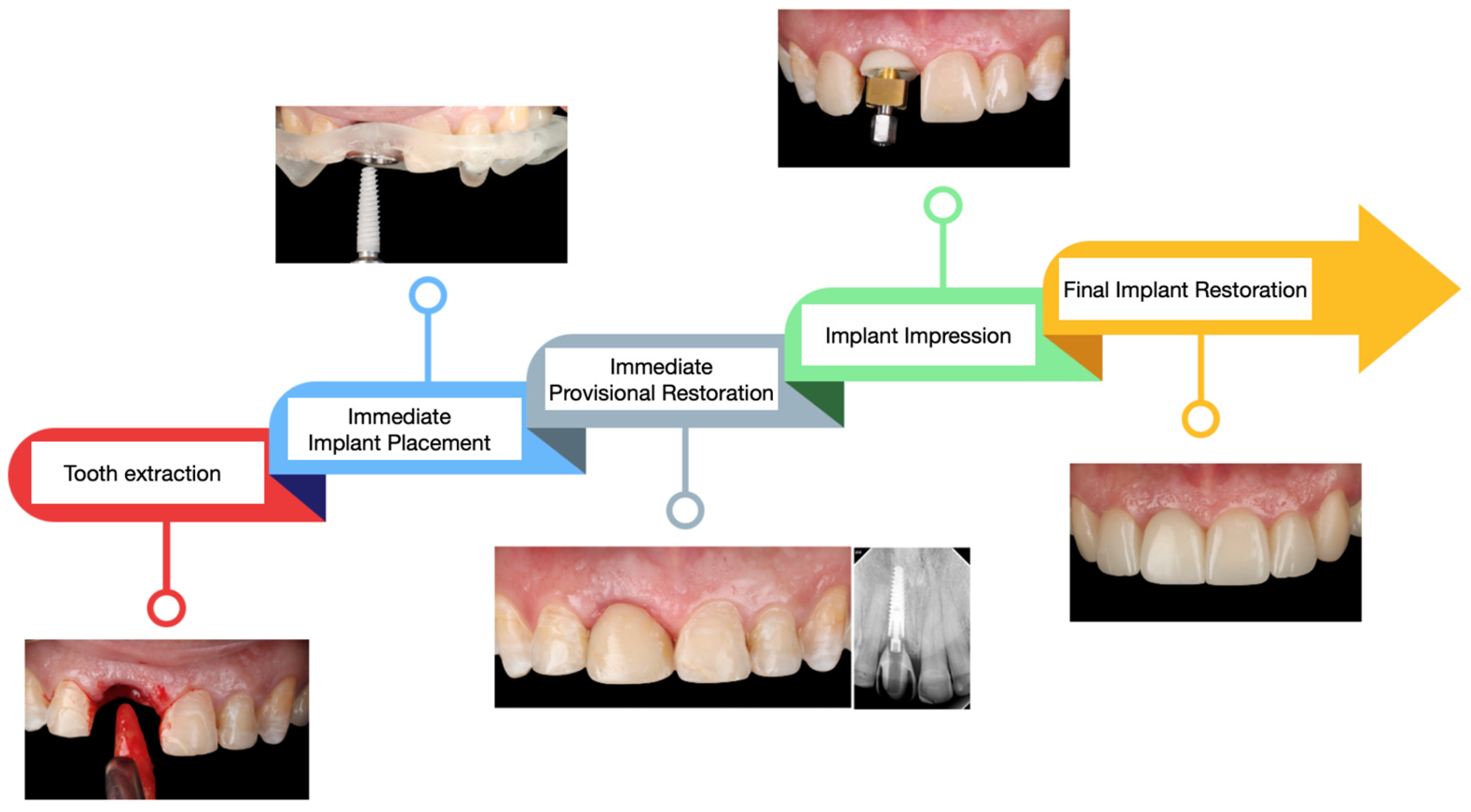
2.2. Case Report
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Literature Review
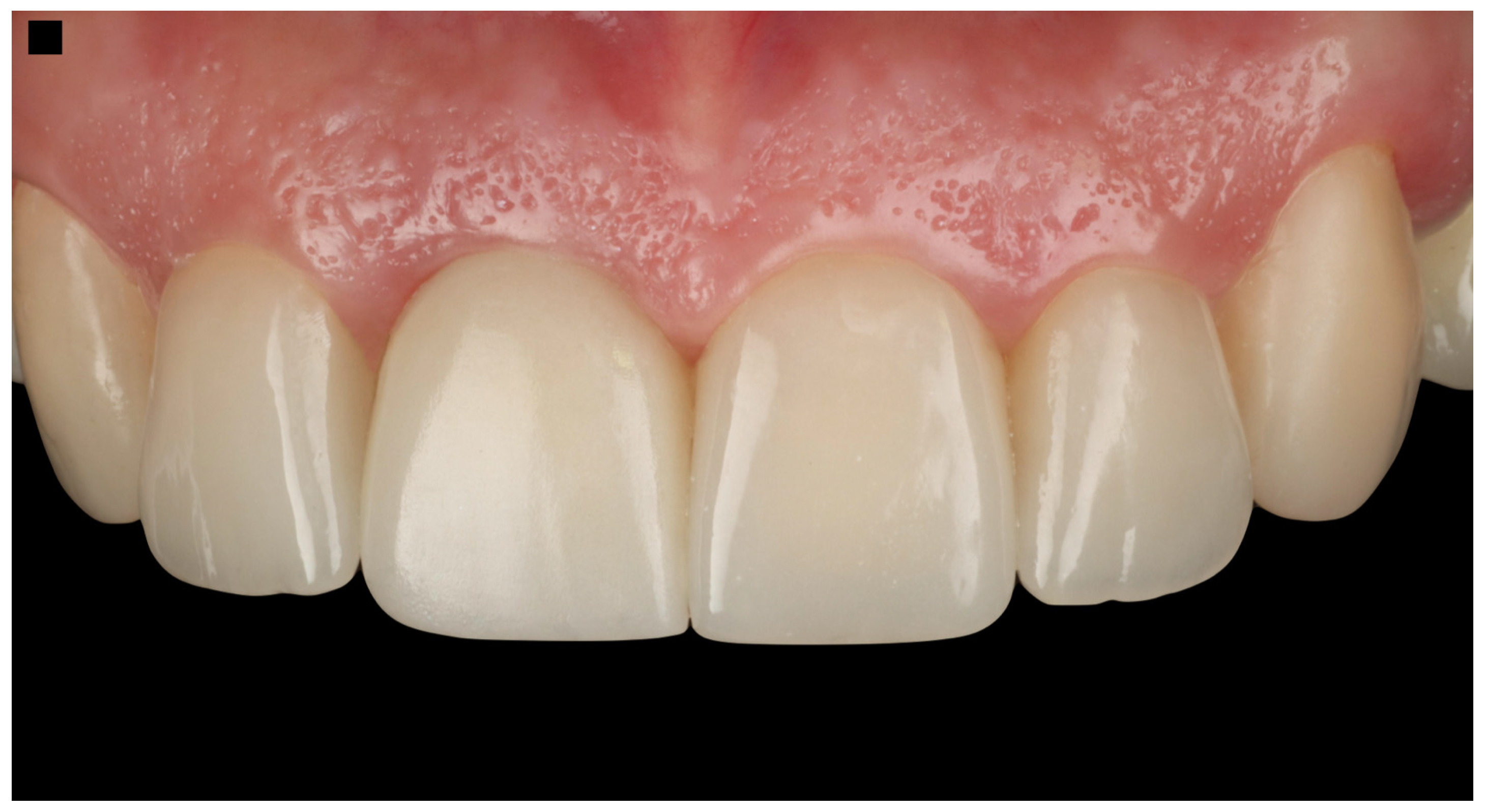
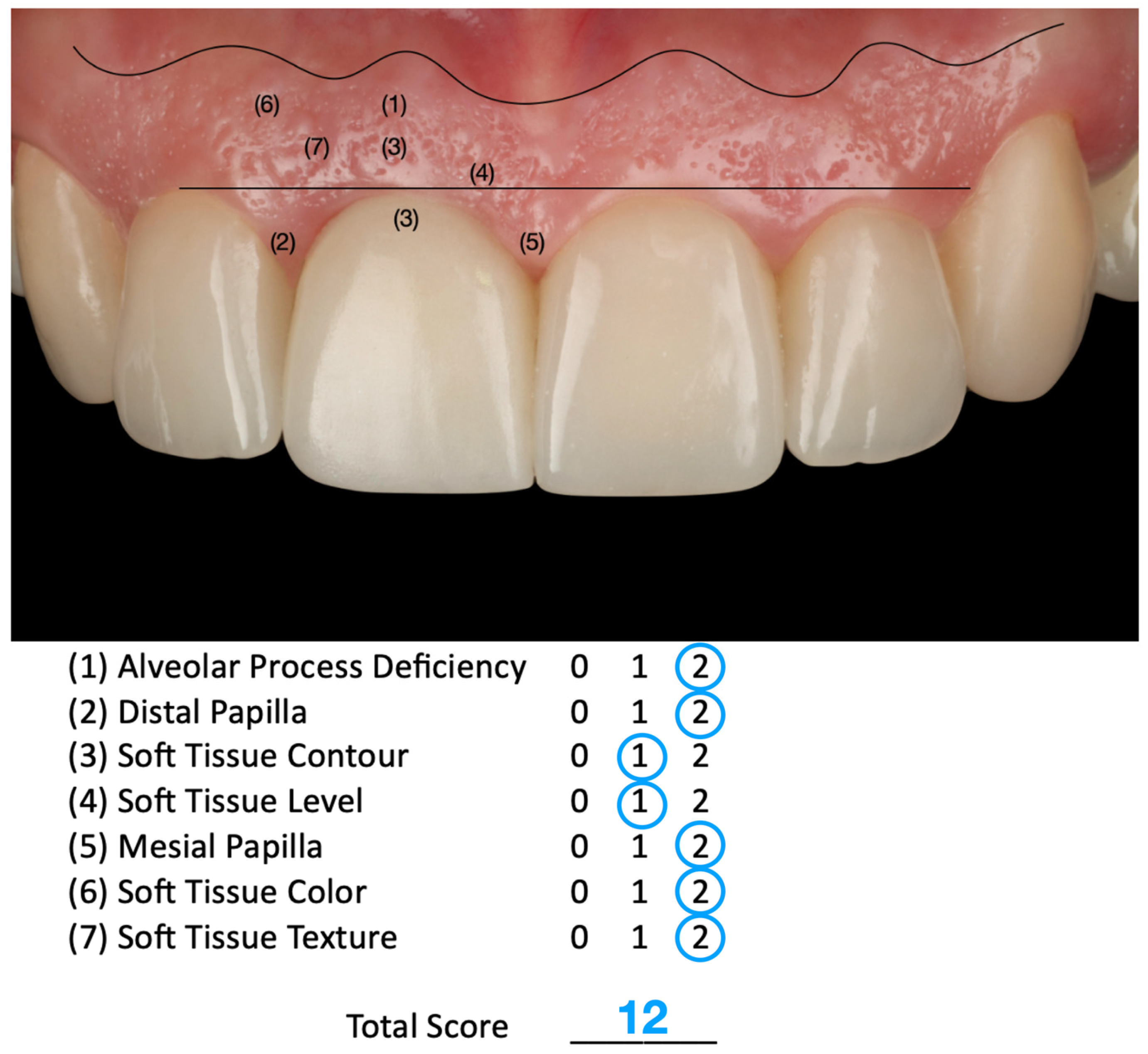
3.2. Results of the Case Report
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges of Dental Care in the Smile Zone
4.2. Long-Term Success
4.3. Three-Dimensional Planning
4.4. Surgical Guide
4.5. Immediate Implant Combined with Bone Grafting
4.6. Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration
4.7. Patients’ Comfort with Immediate Implant Therapy
4.8. Managing Complications
4.9. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AlTarawneh, S.; Hamdan, A.A.S.; Alhadidi, A.; Hattar, S.; Al-Rabab’ah, M.; Baqain, Z. Esthetic outcome of immediately placed and nonfunctionally loaded implants in the anterior maxilla utilizing a definitive abutment: A pilot clinical trial. Dent. Res. J. 2020, 17, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Awawdeh, M.; Alotaibi, M.B.; Alharbi, A.H.; Alnafisah, S.A.; Alasiri, T.S.; Alrashidi, N.I. A Systematic Review of Patient Satisfaction With Removable Partial Dentures (RPDs). Cureus 2024, 16, e51793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jensen-Louwerse, C.; Sikma, H.; Cune, M.S.; Guljé, F.L.; Meijer, H.J.A. Single implant-supported two-unit cantilever fixed partial dentures in the posterior region: A retrospective case series with a mean follow-up of 6.5 years. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2021, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Nimwegen, W.G.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Tymstra, N.; Vissink, A.; Meijer, H.J.A. How to treat two adjacent missing teeth with dental implants. A systematic review on single implant-supported two-unit cantilever FDP’s and results of a 5-year prospective comparative study in the aesthetic zone. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.M. A brief historical perspective on dental implants, their surface coatings and treatments. Open Dent. J. 2014, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Metz, F.C. History of implantology. J. Colo. Dent. Assoc. 1987, 66, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, E.J. Implantation of artificial crown and bridge abutments. 1913. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2008, 29, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawat, P.; Saxena, D.; Sharma, A. Dr. Per-Ingvar Branemark: The Father of Modern Dental Implantology. Cureus 2024, 16, e73950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dajjuka, B.J.; Kambala, S.R.; Dhamande, M.M.; Minase, D.A.; Agrawal, P. Clinical Outcomes of Single Tooth Implant Placement in the Mandibular Region: A Case Report. Cureus 2024, 16, e66379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Titus, L.A.P.; Balaji, S.; Jothi, P.A. Knowledge and Awareness of Dental Implant Treatment versus Fixed Partial Dentures. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implant. 2020, 30, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, T.M.; Campos, C.H.; Gonçalves, G.M.; de Moraes, M.; Rodrigues Garcia, R.C. Mastication improvement after partial implant-supported prosthesis use. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92 (Suppl. 12), 189S–194S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setzer, F.C.; Kim, S. Comparison of long-term survival of implants and endodontically treated teeth. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cochran, D.L. The scientific basis for and clinical experiences with Straumann implants including the ITI Dental Implant System: A consensus report. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11 (Suppl. 1), 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, M.S.; Keys, W.; Richards, D. Long-term (10-year) dental implant survival: A systematic review and sensitivity meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2019, 84, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettamanti, L.; Andrisani, C.; Bassi, M.A.; Vinci, R.; Silvestre-Rangil, J.; Tagliabue, A. Immediate loading implants: Review of the critical aspects. ORAL Implantol. 2017, 10, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, L.; Anwar, M.; Chand, P. Immediate dental implant placement with immediate loading following extraction of natural teeth. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 6, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Wojtovicz, E.; España-Lopez, A.; Jimenez-Guerra, A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Ortiz-Garcia, I.; Serrera-Figallo, M.A. Survival rates and bone loss after immediate loading of implants in fresh extraction sockets (single gaps). A clinical prospective study with 4 year follow-up. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Buccal 2018, 23, e230–e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wipawin, R.; Amornsettachai, P.; Panyayong, W.; Rokaya, D.; Thiradilok, S.; Pujarern, P.; Suphangul, S. Clinical outcomes of 3-5 years follow-up of immediate implant placement in posterior teeth: A prospective study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Magrin, G.L.; Rafael, S.N.F.; Passoni, B.B.; Magini, R.S.; Benfatti, C.A.M.; Gruber, R.; Peruzzo, D.C. Clinical and tomographic comparison of dental implants placed by guided virtual surgery versus conventional technique: A split-mouth randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Pareek, R.; Rajawat, G.S.; Kadam, A.; Al Abdulsalam, M.; Al Abdulathim, A. Comparison of Bone Healing in Immediate Implant Placement versus Delayed Implant Placement. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2021, 13 (Suppl. 2), S1309–S1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Javaid, M.A.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S. Immediate Implants: Clinical Guidelines for Esthetic Outcomes. Dent. J. 2016, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bungthong, W.; Amornsettachai, P.; Luangchana, P.; Chuenjitkuntaworn, B.; Suphangul, S. Bone Dimensional Change Following Immediate Implant Placement in Posterior Teeth with CBCT: A 6-Month Prospective Clinical Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Evans, C.D.; Chen, S.T. Esthetic outcomes of immediate implant placements. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, G.; Chamieh, F.; Fromentin, O. One-by-one immediate dental implants: A papillae preservation concept for adjacent implants in a compromised periodontal case. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ebenezer, V.; Balakrishnan, K.; Asir, R.V.; Sragunar, B. Immediate placement of endosseous implants into the extraction sockets. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7 (Suppl. 1), S234–S237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Angelis, P.; Manicone, P.F.; Gasparini, G.; De Angelis, S.; Liguori, M.G.; De Filippis, I.; D’Addona, A. Influence of Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization with or without Soft Tissue Augmentation on Hard and Soft Tissues in the Esthetic Zone: A One-Year Retrospective Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8822804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rathi, M.; Manohar, B. Management of Single Tooth Replacement in the Esthetic Region Using Immediate Implant Placement: A Case Report. Clin. Case Rep. 2025, 13, e70089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, Q.V.; Park, S.C.; Ketabi, M.; Deporter, D.A. Anatomically Driven Immediate Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone: Two Case Reports as Proof of Principle. J. Oral Implantol. 2023, 49, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Azzouz, K.; Almasri, R.; Emadi, T. Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization in the Esthetic Zone Using Flapless Technique. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2021, 42, g1–g4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarnow, D.P.; Chu, S.J. Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2017, 38, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandra Sekar, A.; Praveen, M.; Saxena, A.; Gautam, A. Immediate implant placement: A case report. J. Indian. Prosthodont. Soc. 2012, 12, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fang, J.; Xin, X.R.; Li, W.; Wang, H.C.; Lv, H.X.; Zhou, Y.M. Immediate implant placement in combination with platelet rich-fibrin into extraction sites with periapical infection in the esthetic zone: A case report and review of literature. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Takvani, R.; Takvani, A.; Pethapur, A.; Kaushik, S. Immediate Loading and Implant Placement With Bone Grafting in Severely Proclined Anterior Mobile Teeth in the Esthetic Zone: A Report of an Intriguing Case. Cureus 2024, 16, e71541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fernandes, G.; Mysore, A.; Shetye, O.; Aras, M.; Chitre, V. Customizing the Emergence Profile Around an Immediately Loaded Single Implant in the Esthetic Zone: A Case Report. Cureus 2024, 16, e58279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Furtado Araújo, M.V.; Sommerville, D.; Dhingra, A.; Schincaglia, G.P. Immediate Placement and Restoration of an Implant in an Infected Socket in the Esthetic Zone. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2015, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jundaeng, J.; Chamchong, R.; Nithikathkul, C. Dental implant in esthetic zone: A case report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2025, 13, 2050313X241311702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, R.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Duan, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y. Effectiveness of immediate implant placement into defective sockets in the esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025, 133, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, A.; Gonzaga, L.; Amorim, K.; Wittneben, J.G.; Martig, L.; Morton, D.; Martin, W.; Gallucci, G.O.; Wismeijer, D. Selection criteria for immediate implant placement and immediate loading for single tooth replacement in the maxillary esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2023, 34 (Suppl. 26), 304–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Chen, Y.; Han, C.; Wu, D.; Yu, F.; He, D. Immediate Implant Placement With or Without Immediate Provisionalization in the Maxillary Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2023, 38, 422–434c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyssens, L.; de Lat, L.; Cosyn, J. Immediate implant placement with or without connective tissue graft: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 284–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittneben, J.G.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; Hamilton, A.; Alnasser, M.; Obermaier, B.; Morton, D.; Gallucci, G.O.; Wismeijer, D. Clinical performance of immediately placed and immediately loaded single implants in the esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2023, 34 (Suppl. 26), 266–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco Bohórquez, P.; Rucco, R.; Zubizarreta-Macho, Á.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; de la Vega Buró, S.; Madroño, E.C.; Marín, L.S.H.; Hernández Montero, S. Failure Rate, Marginal Bone Loss, and Pink Esthetic with Socket-Shield Technique for Immediate Dental Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone. A Systematic Review and Me-ta-Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Slagter, K.W.; den Hartog, L.; Bakker, N.A.; Vissink, A.; Meijer, H.J.; Raghoebar, G.M. Immediate placement of dental implants in the esthetic zone: A systematic review and pooled analysis. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, e241–e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Lee, C.T.; He, S.M.; Zhang, S.; Bao, J.; Xie, Z.G. Buccal bone dimensional changes at immediate implant sites in the maxillary esthetic zone within a 4-12-month follow-up period: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Weigl, P.; Gu, X. Immediate placement of dental implants into infected versus noninfected sites in the esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Su, Y.Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Clinical Outcomes Following Immediate Loading of Single-Tooth Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürhauser, R.; Florescu, D.; Benesch, T.; Haas, R.; Mailath, G.; Watzek, G. Evaluation of soft tissue around single-tooth implant crowns: The pink esthetic score. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, H.; Vohra, F.; Lillywhite, G.R. Restorative rehabilitation in a patient with sports trauma. Eur. J. Dent. 2016, 10, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Cosyn, J.; Blanco, J. EAO Position Paper: Immediate Implant Placement: Managing Hard and Soft Tissue Stability from Diagnosis to Prosthetic Treatment. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2023, 36, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.; Goldstein, M. Immediate implant placement: Treatment planning and surgical steps for successful outcome. Periodontol. 2000 2008, 47, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evian, C.I.; Al-Momani, A.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Sanavi, F. Therapeutic management for immediate implant placement in sites with periapical deficiencies where coronal bone is present: Technique and case report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2006, 21, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Aichelmann-Reidy, M.B.; Oates, T.W. Advances in implant therapy in North America: Improved outcomes and application in the compromised dentition. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 82, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- István, V.; Katalin, N. Az azonnali implantációról a Denti implantátumok azonnali beültetésével szerzett 10 eves tapasztalataink alapján [Long term (10 years) experience of immediate implant placement]. Fog Orv Sz. 2009, 102, 217–222. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liñares, A.; Dopico, J.; Magrin, G.; Blanco, J. Critical review on bone grafting during immediate implant placement. Periodontol. 2000 2023, 93, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswambaran, M.; Arora, V.; Tripathi, R.C.; Dhiman, R.K. Clinical evaluation of immediate implants using different types of bone augmentation materials. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2014, 70, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garcia-Sanchez, R.; Dopico, J.; Kalemaj, Z.; Buti, J.; Pardo Zamora, G.; Mardas, N. Comparison of clinical outcomes of immediate versus delayed placement of dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 231–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanissorn, C.; Guo, J.; Jing Ying Chan, D.; Koyi, B.; Kujan, O.; Khzam, N.; Miranda, L.A. Success Rates and Complications Associated with Single Immediate Implants: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Riachi, E.; Juodzbalys, G.; Maciuliene, D. Clinical Outcomes of Immediate, Early, and Delayed Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2024, 39, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernaerts, A.; Barbier, L.; Abeloos, J.; De Backer, T.; Bosmans, F.; Vanhoenacker, F.M.; Casselman, J. Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging in Dental Implants: A Primer for Clinical Radiologists. Thieme Med. Publ. 2020, 24, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, R.; Salmon, B.; Codari, M.; Hassan, B.; Bornstein, M.M. Cone beam computed tomography in implant dentistry: Recommendations for clinical use. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ritter, L.; Reiz, S.D.; Rothamel, D.; Dreiseidler, T.; Karapetian, V.; Scheer, M.; Zöller, J.E. Registration accuracy of three-dimensional surface and cone beam computed tomography data for virtual implant planning. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwindling, F.S.; Boehm, S.; Herpel, C.; Kronsteiner, D.; Vogel, L.; Juerchott, A.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Rammelsberg, P.; Hilgenfeld, T. Geometric Reproducibility of Three-Dimensional Oral Implant Planning Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schropp, L.; Kostopoulos, L.; Wenzel, A. Bone healing following immediate versus delayed placement of titanium implants into extraction sockets: A prospective clinical study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, C.; Andersson, L.; Linde, A. Bone augmentation at fenestrated implants by an osteopromotive membrane technique. A controlled clinical study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1991, 2, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz-Arad, D.; Chaushu, G. The ways and wherefores of immediate placement of implants into fresh extraction sites: A literature review. J. Periodontol. 1997, 68, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabbagh, M.; Kutkut, A. Immediate implant placement: Surgical techniques for prevention and management of complications. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 59, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Antibiotics at dental implant placement to prevent complications. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD004152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Sabbagh, M. Implants in the esthetic zone. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 50, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Nart, J. Management and sequelae of dental implant removal. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 88, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Criterion | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Time period | Publications available between January 2010 and March 2025 | All publications published before January 2010 |
| Language | English | Non-English. |
| Type of articles | All research types, including case studies (e.g., case reports, case series, clinical techniques) and literature reviews (e.g., systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Full text available. | Letters, books, book chapters, and full text not available |
| Authors/Year | Title | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rathi M et al. 2025 [27] | Management of Single Tooth Replacement in the Esthetic Region Using Immediate Implant Placement: A Case Report | An implant (4.0 mm diameter) replacing a fractured maxillary right central incisor. The implant was placed in conjunction with a mixture of autologous and xenograft with collagen membrane. | Understanding hard and soft tissue anatomy, microesthetics, and patient expectations is imperative for evidence-based treatment planning and successful implant therapy. |
| Nguyen QV et al. 2023 [28]. | Anatomically Driven Immediate Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone: Two Case Reports as Proof of Principle | An implant (3.5 × 11.5 mm) replacing a fractured maxillary lateral incisor. Osteotomy guided by reinserted extracted root; implant placed flapless with sticky bone graft (PRF + cortical allograft). | Anatomical guidance via reinsertion of the root optimizes implant positioning along the palatal wall, enabling ideal 3D orientation and preserving soft tissue. The technique is effective, but the stability of the reinserted root may be challenging. |
| Yang C et al. 2021 [29]. | Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization in the Esthetic Zone Using Flapless Technique | An implant (4.3 mm × 18 mm) replaced the maxillary right central incisor due to trauma. | Analyzing the CBCT for bone thickness and bone levels, as well as classifying the predicted extraction socket type, is important in choosing the correct surgical technique, graft materials, and membranes if needed; the type and size of dental implant; and making the decision to immediately load a provisional prosthesis. |
| Tarnow DP et al. 2017 [30]. | Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report | Replacement of a maxillary right central incisor with internal root resorption and type 3 recession defect with an immediate implant combined with bone and soft tissue graft. | The use of immediate implant and provisional restoration therapy in type 3 (recession) clinical situations can result in predictable esthetic outcomes. The diagnostic keys for success are (1) pre-existing labial tooth malposition; (2) flapless tooth removal with the palatal tissues at the proper height; (3) palatal implant placement; (4) dual-zone bone grafting; (5) provisional restoration placement in non-occlusal function; and (6) proper tissue healing for 4 to 6 months. |
| Chandra Sekar A et al. 2012 [31] | Immediate Implant Placement: A Case Report | Replacement of maxillary lateral incisor due to trauma with an implant (3.7 mm × 13 mm) in conjunction with bone graft. | Aiming to reduce the process of alveolar bone resorption and treatment time, the immediate placement of endosseous implants into extraction sockets is known to achieve a high success rate of between 94 and 100%, compared to the delayed placement. |
| Fang J et al. 2021 [32] | Immediate implant placement in combination with platelet-rich fibrin into extraction sites with periapical infection in the esthetic zone: A case report and review of literature | An implant (3.3 × 12 mm) replacing a fractured maxillary central incisor with periapical infection. PRF mixed with xenograft (Bio-Oss) and layered with PRF-collagen-PRF membrane barrier. | PRF promoted soft/hard tissue healing and managed infection effectively, resulting in stable bone and esthetic outcomes at 1-year follow-up despite initial infection and bone defects. |
| Takvani R et al. 2024 [33] | Immediate Loading and Implant Placement with Bone Grafting in Severely Proclined Anterior Mobile Teeth in the Esthetic Zone: A Report of an Intriguing Case | Three implants (3.8 × 13 mm and 3.75 × 10 mm) replaced four upper anterior teeth. Implants were placed using a surgical guide and flapless extraction. Bone graft included autograft and xenograft (Bio-Oss). | Immediate implant placement with grafting and provisional bridge achieved primary stability (35–40 Ncm). At 1-year follow-up, stable soft tissue contour and healthy marginal bone levels were observed. |
| Fernandes G et al. 2024 [34] | Customizing the Emergence Profile Around an Immediately Loaded Single Implant in the Esthetic Zone: A Case Report | An implant (4 × 11.5 mm) was placed in the maxillary central incisor region after ridge augmentation with autogenous block graft and xenograft. A customized emergence profile was developed using composite interim restoration. | The emergence profile was shaped incrementally over 2 months. Final restoration transferred tissue contours accurately using a custom impression coping. Esthetic results were harmonious with adjacent teeth. |
| Furtado Araújo MV et al. 2015 [35] | Immediate Placement and Restoration of an Implant in an Infected Socket in the Esthetic Zone | An implant (4.1 × 12 mm) replacing a fractured maxillary central incisor with periapical lesion. Atraumatic extraction, xenograft in buccal gap, and immediate screw-retained provisional crown. | At 12-month follow-up, facial soft tissue and hard tissue contours were symmetrical and stable. Highlights the importance of biotype, implant depth, and prosthetic emergence profile. |
| Jundaeng J et al. 2025 [36] | Dental implant in esthetic zone: A case report | An implant (3.5 × 10 mm) was placed in the upper left central incisor region with labial thread exposure. Papilla preservation flap and xenograft bone graft were used to manage concavity. Healing abutment placed for non-submerged healing. | Four-month osseointegration followed by E-max CAD crown on anodized abutment. At the 3-month follow-up, the esthetic outcome was natural, with stable gingiva and no bone loss. |
| Authors/Year | Title | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen R et al. (2025) [37] | Effectiveness of Immediate Implant Placement into Defective Sockets in the Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | A systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis of 23 clinical studies from 2000 to 2022 evaluating 630 implants placed in sockets with defects in the anterior esthetic region. Outcomes assessed included survival rate, marginal bone loss (MBL), gingival recession, and pink esthetic score (PES). | Immediate implant placement (IIP) into defective sockets showed a 98.1% survival rate. MBL was 1.03 mm at 6 months, 0.72 mm at 12 months, and 1.15 mm at ≥24 months. Gingival recession at 12 months averaged 0.25 mm. PES at 12 and ≥24 months were 12.34 and 12.58, respectively. IIP in socket defects is feasible with favorable outcomes. |
| Hamilton A et al. (2023) [38] | Selection criteria for immediate implant placement and immediate loading for single tooth replacement in the maxillary esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 68 studies evaluating Type 1A protocols (immediate implant placement and immediate loading). Inclusion: single implants (15–25 FDI) with a minimum 12-month follow-up. Risk assessments conducted per site-specific factors. | Type 1A protocol shows high survival (97.7%) and early survival (98.3%) rates. Facial bone gap > 2 mm and presence of chronic endodontic infection were associated with higher success. Strict selection criteria are crucial for predictable outcomes. |
| Qin R el al (2023) [39] | Immediate Implant Placement with or Without Immediate Provisionalization in the Maxillary Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | Systematic review of 8 RCTs comparing immediate implant placement with immediate loading (IPIL) vs. delayed loading (IPDL) in the maxillary esthetic zone. Outcomes included midfacial mucosal level, papilla height, marginal bone loss, survival, and peri-implant soft tissue health. | IPIL showed significantly less midfacial mucosal recession (0.48 mm difference), better papilla preservation (SMD –0.16), and improved ridge dimension (SMD 0.94). No significant differences were found in implant survival, bone loss, probing depth, or plaque score. |
| Seyssens L. et al. (2020) [40] | Immediate implant placement with or without connective tissue graft: A systematic review and meta-analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 5 RCTs and 3 non-RCTs (409 implants). Compared immediate implant placement (IIP) with vs. without buccal connective tissue graft (CTG). Primary outcome: vertical mid-facial soft tissue changes. Minimum 12-month follow-up. | CTG significantly improved vertical mid-facial tissue stability (mean gain: 0.41 mm; p < 0.001) and reduced risk of ≥1 mm soft tissue asymmetry 12-fold. No significant differences in pink esthetic score, marginal bone level, or probing depth. CTG recommended when high risk of recession exists. |
| Wittneben JG et al. (2023) [41] | Clinical performance of immediately placed and immediately loaded single implants in the esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 63 studies (10 RCTs, 28 prospective, 25 retrospective) on Type 1A implant placement (immediate placement and loading) in the maxillary esthetic zone. Primary outcomes: implant and prosthetic survival. Secondary: PES, WES, midfacial recession, papilla height. | Implant survival: 99.2% at 1 year, 97.5% at 3 years, 95.8% at 5 years. Restoration survival: 98.9% at 1 year, 96.8% at 2 years, 94.8% at 5 years. Mean PES gain: +0.82. Papilla height showed a decrease (–0.71 mm), and midfacial recession was minimal (–0.15 mm). |
| Velasco Bohórquez P el al (2021) [42] | Failure Rate, Marginal Bone Loss, and Pink Esthetic with Socket-Shield Technique for Immediate Dental Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies (RCTs, prospective, retrospective, case series). Compared socket-shield technique (SST) to conventional immediate implant placement (CIIP) for failure rate, marginal bone loss, and pink esthetic score (PES). | SST showed a 1.37% implant failure rate (CI: 0.21–2.54%)—no difference vs. CIIP. SST had significantly less marginal bone loss (–0.5 mm, p < 0.01) and higher PES (mean difference: 1.15 points). PES improved with time (0.02 points/month, p = 0.049). Recommended for preserving esthetics. |
| Slagter KW et al.(2014) [43] | Immediate placement of dental implants in the esthetic zone: a systematic review and pooled analysis | Systematic review of 34 studies (RCTs, prospective, and retrospective) evaluating immediately placed single implants in the esthetic zone. Pooled analysis examined implant survival, marginal bone loss (MBL), and interproximal and midfacial tissue levels. | Implant survival was 97.1% (95% CI: 95.8–98.0). Mean MBL: 0.81 ± 0.48 mm. Interproximal mucosal loss: 0.38 ± 0.23 mm; midfacial mucosal loss: 0.54 ± 0.39 mm. Delayed provisionalization, flap use, and CT grafts were associated with >0.5 mm MBL. Immediate provisionalization may favor stability. |
| Mao Z el al (2021) [44] | Buccal bone dimensional changes at immediate implant sites in the maxillary esthetic zone within a 4-12-month follow-up period: A systematic review and meta-analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies (4 RCTs, 12 NRCTs; 568 implants) evaluating horizontal (CHBD) and vertical (CVBD) buccal bone changes 4–12 months after immediate implant placement in the maxillary esthetic zone. Meta-regression analyzed the effect of grafting, flap design, and restoration protocol. | CHBD: 0.71 mm, CVBD: 0.58 mm. Bone grafting significantly reduced CHBD (mean reduction 0.46 mm, p = 0.015). Flapless approach and immediate provisionalization were associated with less resorption, though not statistically significant. Immediate placement does not prevent buccal bone loss. |
| Chen H et al.(2018) [45] | Immediate placement of dental implants into infected versus noninfected sites in the esthetic zone: A systematic review and meta-analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 9 clinical studies (n = 1735 implants) comparing immediate implant placement into infected vs. noninfected extraction sockets in the esthetic zone. Outcomes included implant survival, bone level, and gingival level changes. | Similar implant survival rates in infected (97.6%) and noninfected (98.4%) sites (RR = 0.99; p = 0.138). No significant differences in bone level change (MD = 0.03 mm) or gingival level change (MD = –0.06 mm). Thorough debridement remains essential for success. |
| Cheng Q et al.(2020) [46] | Clinical Outcomes Following Immediate Loading of Single-Tooth Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 7 RCTs (n = 386) evaluating single-tooth immediate implants. Most studies used a parallel design; one multicenter study included both parallel and split-mouth designs. Immediate loading (within 24 h) was compared to conventional loading, assessing implant survival, marginal bone loss, soft tissue changes, esthetic outcomes, and patient satisfaction. | No significant difference in 1-year implant survival (RR = 0.99; 95% CI: 0.95–1.02). MBL and soft tissue changes were comparable. Esthetic outcomes and patient satisfaction were similar between immediate and conventional loading protocols. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurado, C.A.; Garcia-Torres, F.; Rojas-Rueda, S.; Karimi, K.; Antal, M.A. Evaluating the Success of Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review with Case Illustration. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080365
Jurado CA, Garcia-Torres F, Rojas-Rueda S, Karimi K, Antal MA. Evaluating the Success of Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review with Case Illustration. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(8):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080365
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurado, Carlos A., Francisco Garcia-Torres, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Kiarash Karimi, and Mark Adam Antal. 2025. "Evaluating the Success of Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review with Case Illustration" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 8: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080365
APA StyleJurado, C. A., Garcia-Torres, F., Rojas-Rueda, S., Karimi, K., & Antal, M. A. (2025). Evaluating the Success of Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review with Case Illustration. Dentistry Journal, 13(8), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080365









