The Connection Between Canine Fossa Topography and Facial Morphology
Abstract
1. Introduction
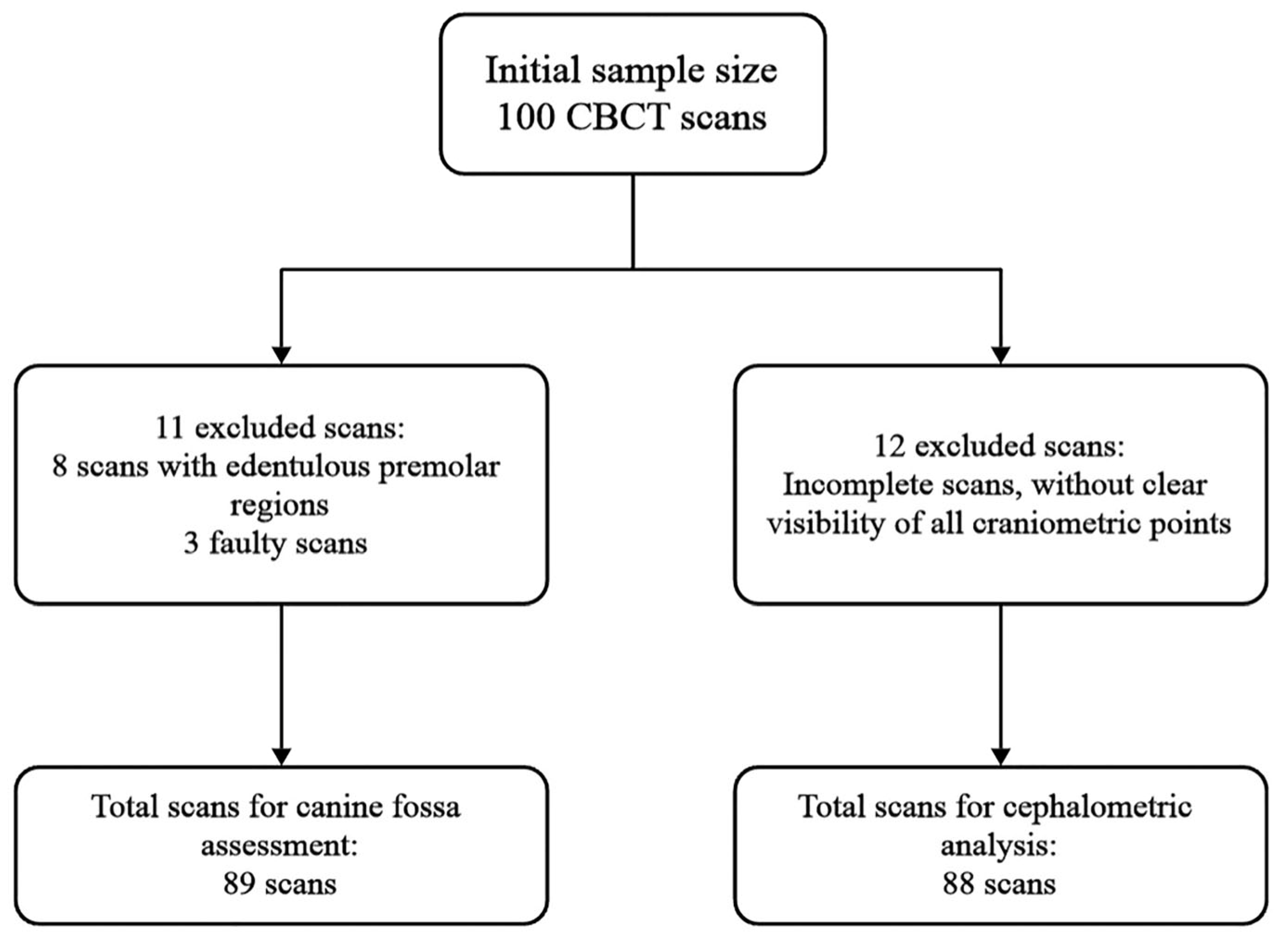
2. Materials and Methods
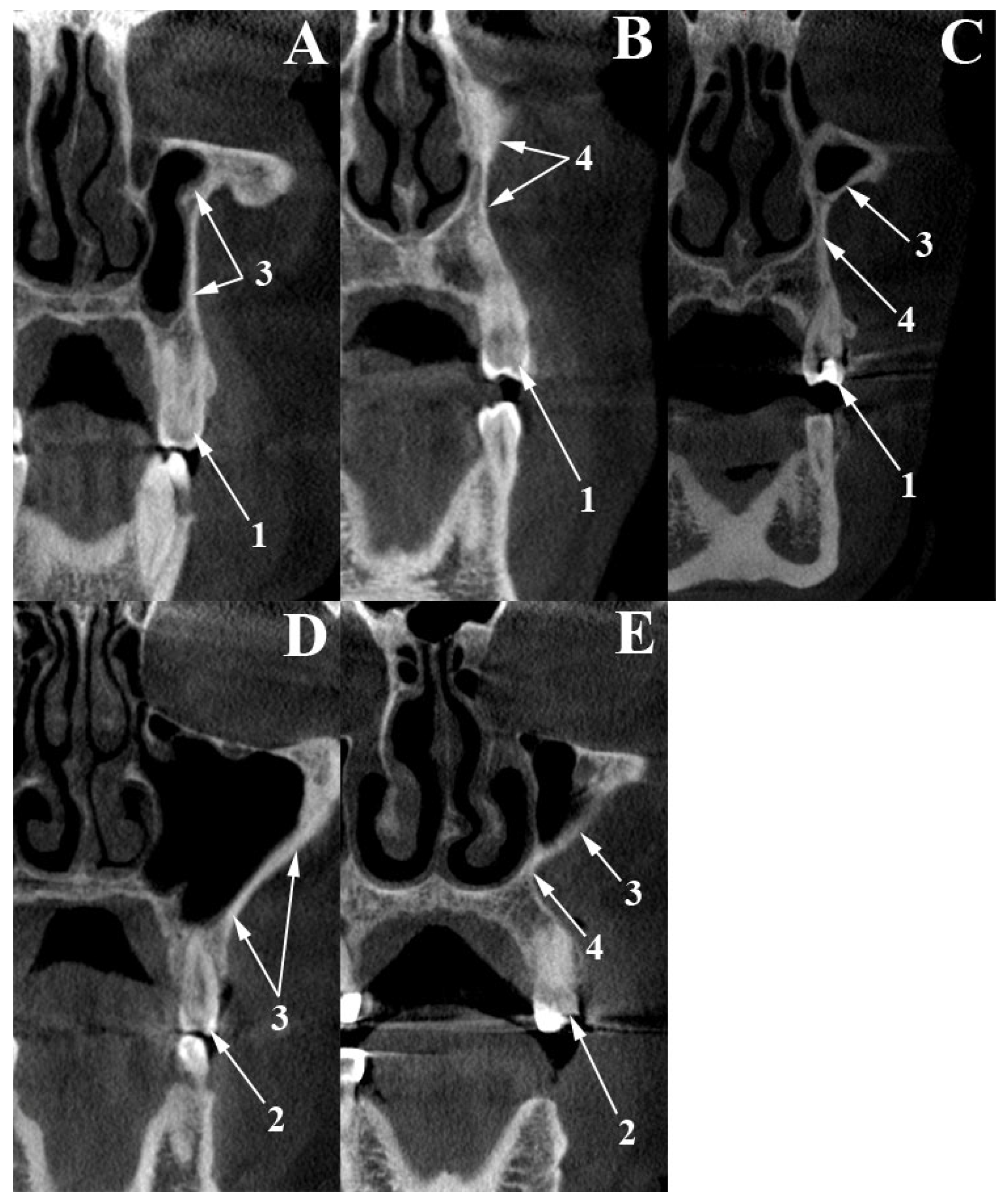
2.1. Canine Fossa Assessment
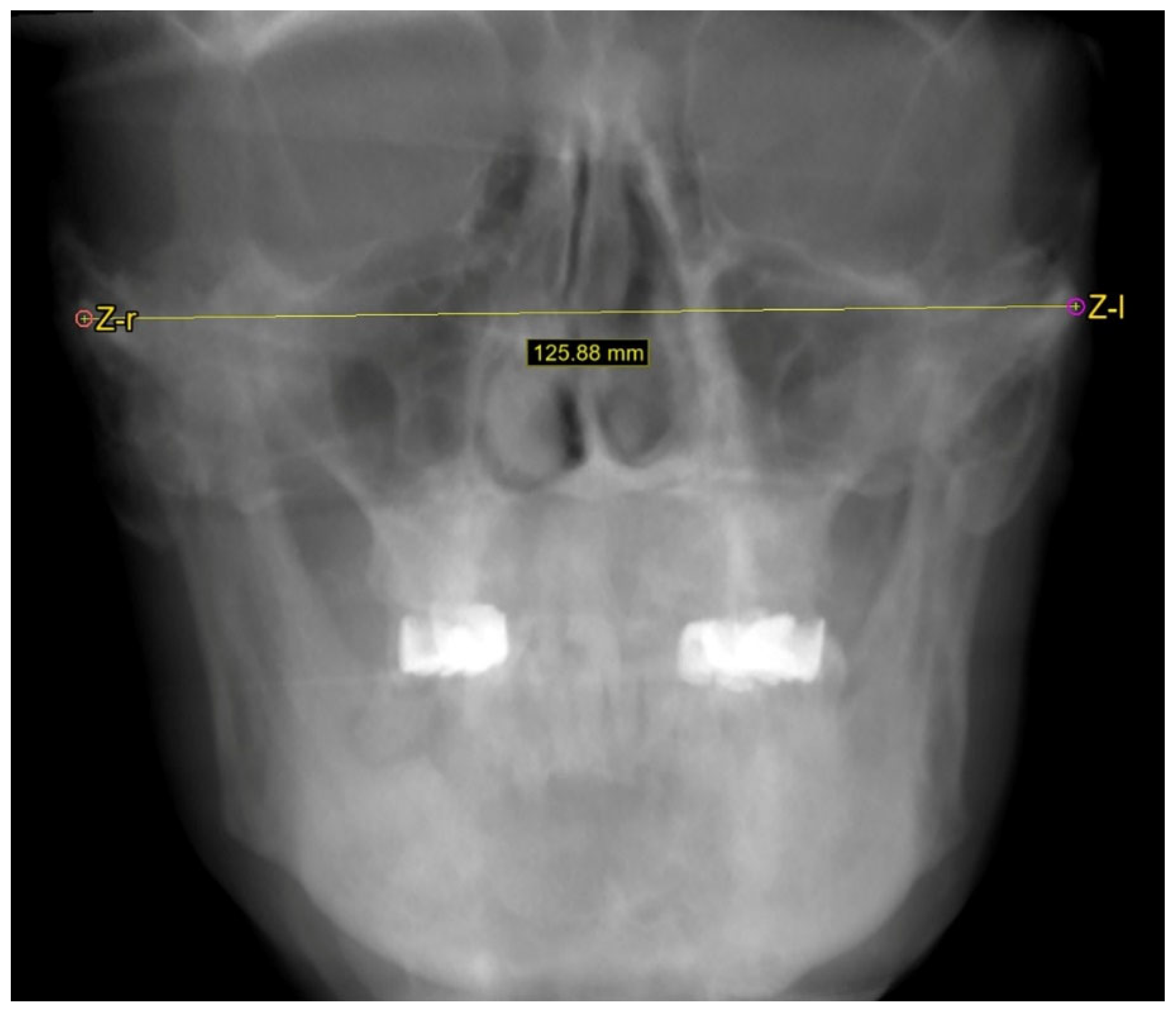
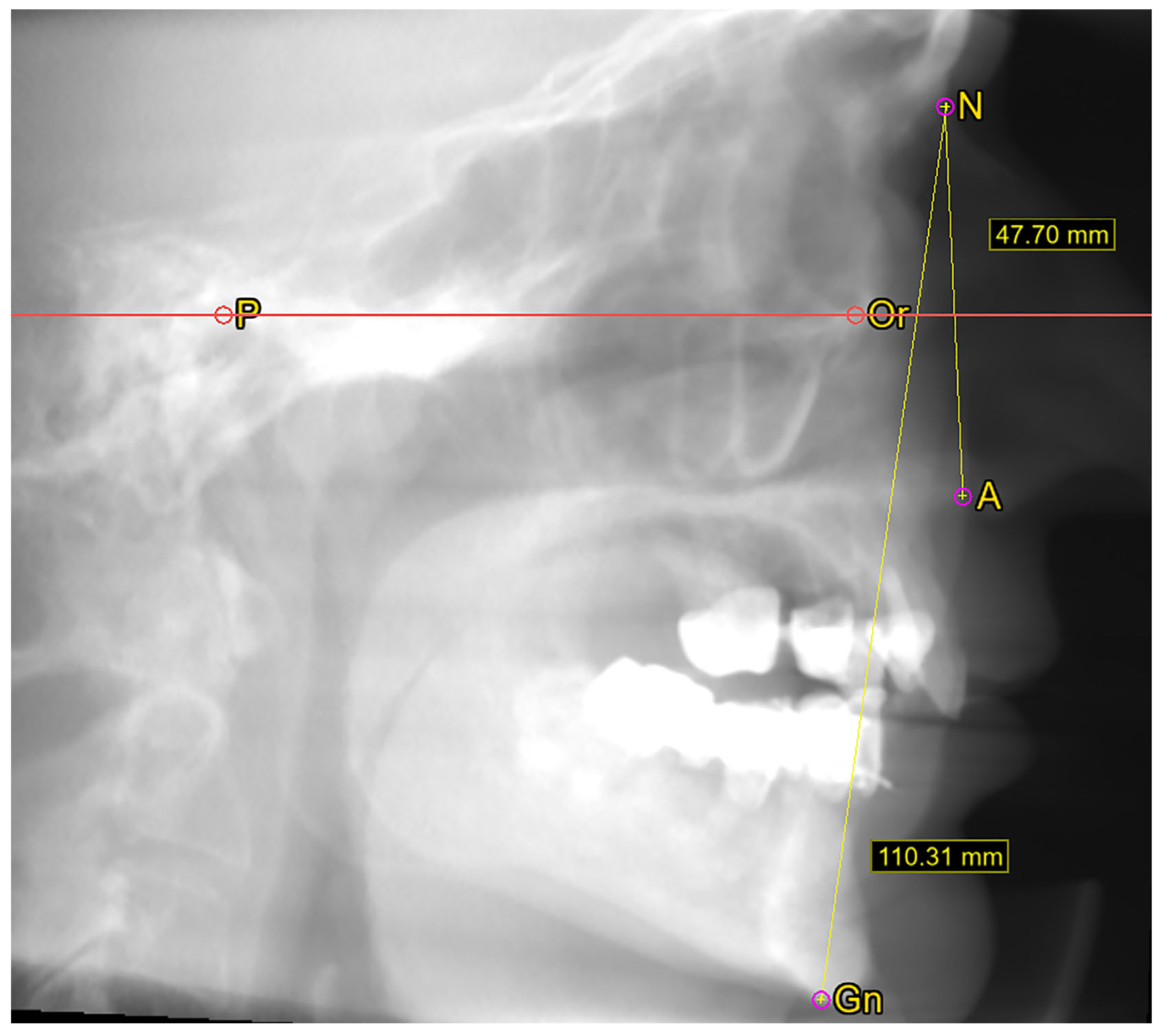
2.2. Cephalometric Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Canine Fossa
3.2. Cephalometric Analysis
3.2.1. Facial Width
3.2.2. Midface Height
3.2.3. Facial Height
3.2.4. Facial Index
3.3. Correlation Between the Canine Fossa and Facial Type
4. Discussion
4.1. Canine Fossa Type
4.2. Cephalometric Analysis
4.3. Clinical Significance
4.4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mellinger, W.J. The Canine Fossa. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1940, 31, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.D.; Black, M.T.; Folkens, P.A. Human Osteology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–662. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, D.E. The Evolution of the Human Head; The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; p. 768. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, A.; Sung, K.H.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, U.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Han, S.H.; Sui, H.J. Anatomical changes in the East Asian midface skeleton with aging. Folia Morphol. 2017, 76, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribot, F.; Bartual, M.; Enciso, A.J.; Wang, Q. The canine fossa and the evolution of the midface in humans. Acta Anthropol. Sin. 2020, 39, 191–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathananthar, S.; Nagaonkar, S.; Paleri, V.; Le, T.; Robinson, S.; Wormald, P.J. Canine fossa puncture and clearance of the maxillary sinus for the severely diseased maxillary sinus. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheny, K.E.; Duncavage, J.A. Contemporary indications for the Caldwell-Luc procedure. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 11, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFreitas, J.; Lucente, F.E. The Caldwell-Luc procedure: Institutional review of 670 cases: 1975–1985. Laryngoscope 1988, 98, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Yoo, F.; Wang, M.; Vengerovich, G.; Suh, J.D. Modified endoscopic Denker approach in management of inverted papilloma of the anterior maxillary sinus. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muresan, A.N.; Dandoczi, C.A.; Tudose, R.C.; Hostiuc, S.; Rusu, M.C. Anatomical Possibilities of the Alveolar Bone at the Upper Second Premolar Level. Medicina 2024, 60, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudose, R.C.; Rusu, M.C. A novel perspective on geniculate ganglion fossa: Cone beam computed tomography analysis of pneumatization and dehiscence. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2025, 260, 152402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, M.C.; Sandulescu, M.; Ilie, O.C. Infraorbital canal bilaterally replaced by a lateroantral canal. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2015, 37, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosman, S.D. Anthropometric method of facial analysis in orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. 1950, 36, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standring, S.; Anand, N.; Birch, R.; Collins, P.; Crossman, A.; Gleeson, M.; Jawaheer, G.; Smith, A.L.; Spratt, J.D.; Stringer, M.D.; et al. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 41st ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J. The subnasion. A new cranial point. Its significance in modern and fossil man, the anthropoids, and lower mammals. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1930, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Shrestha, N.; Upadhyay, H.P. Prevalence of Leptoprosopic type of Face among Dental Students. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2019, 57, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, K.O.; Wong, S.P. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol. Methods 1996, 1, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosau, M.; Rink, D.; Driemel, O.; Draenert, F.G. Maxillary sinus anatomy: A cadaveric study with clinical implications. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez Sayans, M.; Suarez Quintanilla, J.A.; Chamorro Petronacci, C.M.; Suarez Penaranda, J.M.; Lopez Jornet, P.; Gomez Garcia, F.; Guerrero Sanchez, Y. Volumetric study of the maxillary sinus in patients with sinus pathology. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, F.; da Silva Fernandes, C.M.; Kuhnen, B.; Scarso Filho, J.; Gonçalves, M.; da Costa Serra, M. Maxillary sinuses’ height/width/depth of Brazilian subjects and influence of sex, age, skin color, and nutritional status: A CBCT study. Forensic Imaging 2022, 31, 200522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.H.; Park, H.D.; Yoon, H.R.; Kang, M.K.; Koh, K.S.; Kim, H.J. Topographic anatomy of the inferior wall of the maxillary sinus in Koreans. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krennmair, G.; Ulm, C.; Lugmayr, H. Maxillary sinus septa: Incidence, morphology and clinical implications. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 25, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kian Ang, K.; Ahamad, A.; Garden, A.S. Chapter 9—The Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses. In Radiation Oncology, 9th ed.; Cox, J.D., Ang, K.K., Eds.; Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Przystanska, A.; Kulczyk, T.; Rewekant, A.; Sroka, A.; Jonczyk-Potoczna, K.; Gawriolek, K.; Czajka-Jakubowska, A. The Association between Maxillary Sinus Dimensions and Midface Parameters during Human Postnatal Growth. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6391465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.T. Three-Dimensional CBCT Based Evaluation of the Maxillary Sinus by Facial Index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evteev, A.A.; Grosheva, A.N. Nasal cavity and maxillary sinuses form variation among modern humans of Asian descent. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2019, 169, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yoon, H.R.; Kim, K.D.; Kang, M.K.; Kwak, H.H.; Park, H.D.; Han, S.H.; Park, C.S. Personal-computer-based three-dimensional reconstruction and simulation of maxillary sinus. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2003, 24, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.; Suarez, F.; Monje, A.; Benavides, E.; Wang, H.L. Evaluation of maxillary sinus width on cone-beam computed tomography for sinus augmentation and new sinus classification based on sinus width. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlstrand-Johnson, P.; Jannert, M.; Strombeck, A.; Abul-Kasim, K. Computed tomography measurements of different dimensions of maxillary and frontal sinuses. BMC Med. Imaging 2011, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquib Abullais, S.; AlQahtani, S.M.; Alqahtani, S.; Alaamri, A.; Azhar Dawasaz, A.; Alqahtani, A.; Dhadse, P.V. Radiographic assessment of maxillary sinus membrane and lateral wall thickness using cone-beam CT in different facial types in southwestern Saudi Arabia. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustian, W.F. The floor of the maxillary sinus and its dental, oral and nasal relations. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1933, 20, 2175–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz-Timme, S.; Gabriel, P.; Tutkuviene, J.; Poppa, P.; Obertova, Z.; Gibelli, D.; De Angelis, D.; Ratnayake, M.; Rizgeliene, R.; Barkus, A.; et al. Metric and morphological assessment of facial features: A study on three European populations. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 207, 239.e1–239.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogodescu, E.; Popa, M.; Luca, M.; Igna, A.; Miron, M.; Martha, K.; Tudor, A.; Todea, C. Updating Standards of Facial Growth in Romanian Children and Adolescents Using the Anthropometric Method-A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetti, V.R.; Pai, S.R.; Sneha, G.; Gupta, C.; Chethan, P. Study of Prosopic (Facial) Index of Indian and Malaysian Students. Int. J. Morphol. 2011, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Kataria, K.R. Comparative study of proposic (facial) index of Sindhi community of Jodhpur district of Rajasthan and other communities and races. Int. J. Anat. Res. 2013, 3, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Nicoli, G.; Piva, S.; Ferraris, P.; Nicoli, F.; Jensen, O.T. Extra-Long Nasal Wall-Directed Dental Implants for Maxillary Complete Arch Immediate Function: A Pilot Study. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 31, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouya, F.; Vaghefi, S.; Raygan, S.; Nejad, F. Cephalometry and Determination of Facial (Prosopic) Index of Persian Adolescents. Life Sci. J. 2021, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ozsahin, E.; Kizilkanat, E.; Boyan, N.; Soames, R.; Oğuz, Ö. Evaluation of Face Shape in Turkish Individuals. Int. J. Morphol. 2016, 34, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Perales, P.; Rangert, B. Tilted implants as an alternative to maxillary sinus grafting: A clinical, radiologic, and periotest study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2001, 3, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vico, G.; Bonino, M.; Spinelli, D.; Schiavetti, R.; Sannino, G.; Pozzi, A.; Ottria, L. Rationale for tilted implants: FEA considerations and clinical reports. Oral Implantol. 2012, 4, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, O.T.; Perkins, S.; Van de Water, F.W. Nasal fossa and maxillary sinus grafting of implants from a palatal approach: Report of a case. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 50, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.B.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, K.L.; Lim, H.C.; Han, J.Y. Long-term outcomes of the implants accidentally protruding into nasal cavity extended to posterior maxilla due to inferior meatus pneumatization. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, U.S.; Sharma, N.K.; Singh, R.K.; Mahammad, S.; Mehrotra, D.; Singh, N.; Mandhyan, D. Direct vs. indirect sinus lift procedure: A comparison. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 3, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albu, S.; Baciut, M.; Opincariu, I.; Rotaru, H.; Dinu, C. The canine fossa puncture technique in chronic odontogenic maxillary sinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2011, 25, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, V.; Santosh, S.; Aishwarya, A. Canine fossa approaches in endoscopic sinus surgery—our experience. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 60, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Listl, S.; Faggion, C.M., Jr. An economic evaluation of different sinus lift techniques. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Tan, W.C.; Zwahlen, M.; Lang, N.P. A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of implants inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 216–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, S.S.; Tarnow, D.P.; Froum, S.J.; Cho, S.C.; Zadeh, H.H.; Stoupel, J.; Del Fabbro, M.; Testori, T. Maxillary sinus elevation by lateral window approach: Evolution of technology and technique. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gender | Position | Side | Type | No. of Cases | Prevalence (%) | 95% CI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | PM1 | Left | 1 | 17 | 39.53 | 26.37–54.42 |
| 2 | 6 | 13.95 | 6.56–27.26 | |||
| 3 | 20 | 46.51 | 32.51–61.08 | |||
| Right | 1 | 17 | 39.53 | 26.37–54.42 | ||
| 2 | 4 | 9.30 | 3.68–21.60 | |||
| 3 | 22 | 51.16 | 36.75–65.38 | |||
| PM2 | Left | 1 | 35 | 81.40 | 67.38–90.26 | |
| 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–8.20 | |||
| 3 | 8 | 18.60 | 9.74–32.62 | |||
| Right | 1 | 34 | 79.07 | 64.79–88.58 | ||
| 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–8.20 | |||
| 3 | 9 | 20.93 | 11.42–35.21 | |||
| Male | PM1 | Left | 1 | 16 | 34.78 | 22.68–49.23 |
| 2 | 7 | 15.21 | 7.57–28.22 | |||
| 3 | 23 | 50.00 | 36.12–63.88 | |||
| Right | 1 | 18 | 39.13 | 26.39–53.54 | ||
| 2 | 5 | 10.87 | 4.73–23.04 | |||
| 3 | 23 | 50.00 | 36.12–63.88 | |||
| PM2 | Left | 1 | 36 | 78.26 | 64.43–87.74 | |
| 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–7.71 | |||
| 3 | 10 | 21.74 | 12.26–35.57 | |||
| Right | 1 | 35 | 76.09 | 62.06–86.09 | ||
| 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–7.71 | |||
| 3 | 11 | 23.91 | 13.91–37.94 |
| Gender | Male | Female | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | Facial Width | Midface Height | Facial Height | Facial Index | Facial Width | Midface Height | Facial Height | Facial Index |
| Mean | 130.02 | 52.44 | 116.96 | 90.14 | 122.04 | 51.74 | 112.42 | 92.21 |
| Standard Error | 0.95 | 0.44 | 0.61 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 0.68 |
| Median | 130.08 | 52.68 | 116.71 | 88.48 | 121.56 | 51.58 | 112.16 | 92.09 |
| Standard Deviation | 6.07 | 2.81 | 3.90 | 5.15 | 4.72 | 2.57 | 5.01 | 4.63 |
| Sample Variance | 36.83 | 7.87 | 15.20 | 26.48 | 22.26 | 6.59 | 25.15 | 21.47 |
| Kurtosis | −1.12 | 2.37 | 0.74 | −0.33 | −0.74 | −0.07 | 1.45 | 0.52 |
| Skewness | −0.16 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.69 | −0.13 | 0.57 | −0.73 | 0.02 |
| Range | 20.38 | 15.73 | 18.06 | 21.19 | 19.66 | 10.93 | 25.63 | 24.13 |
| Minimum | 119.56 | 46.08 | 108.22 | 80.30 | 111.50 | 47.58 | 95.76 | 80.30 |
| Maximum | 139.94 | 61.81 | 126.27 | 101.49 | 131.15 | 58.51 | 121.38 | 104.43 |
| Confidence Level (95%) | 1.92 | 0.89 | 1.23 | 1.62 | 1.39 | 0.75 | 1.47 | 1.36 |
| Facial Type | Occurrences in Type-1 Canine Fossa | Occurrences in Type-3 Canine Fossa | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europrosopic | 3 | 0 | 0 | NA | 1 |
| Mesoprosopic | 21 | 4 | 0.86 | 0.31–4.35 | 1 |
| Leptoprosopic | 17 | 8 | 4.71 | 1.18–18.72 | 0.022 |
| Hyperleptoprosopic | 16 | 0 | 0 | NA | 0.055 |
| Population Sample | Mean (SD) | Observations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Our study | Romania | 91.24 (4.96) | - |
| Ritz-Timme et al. [34] | Germany | 86.4 (5.2) | - |
| Italy | 97.9 (7.7) | - | |
| Lithuania | 80.4 (5.0) | - | |
| Kataria et al. [37] | Sindhi | 92.89 | - |
| Ogodescu et al. [35] | Romania | 81.33 (3.55) | Age group 13–14.5 years |
| Shetti et al. [36] | Malaysian | 85.72 (5.4) | Male group |
| Malaysian | 87.71 (5.1) | Female group | |
| Indian | 87.19 (5.2) | Male group | |
| Indian | 86.75 (6.3) | Female group |
| Hypereuroprosopic | Europrosopic | Mesoprosopic | Leptoprosopic | Hyperleptoprosopic | Observations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our study | 0 | 7 (8%) | 29 (33%) | 32 (36%) | 20 (23%) | - |
| Nicoli et al. (2019) [38] | 190 (19%) | 532 (53.2%) | 216 (21.6%) | 56 (5.6%) | 6 (0.6%) | Using a different scale of facial index |
| Kataria et al. (2013) [37] | 0 | 2 (2%) | 7 (7%) | 46 (46%) | 45 (45%) | Study conducted on male group |
| Ozsahin et al. (2016) [40] | 85 (18.1%) | 166 (35.3%) | 156 (33.2%) | 41 (8.7%) | 22 (4.7%) | Male group |
| 83 (15.6%) | 183 (34.33%) | 183 (34.33%) | 63 (11.8%) | 21 (3.94%) | Female group | |
| Pouya et al. (2021) [39] | 7.1% | 21.8% | 36% | 25.3% | 9.8% | Male group |
| 4.46% | 34.23% | 44.35% | 13.34% | 3.62% | Female group |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dandoczi, C.A.; Rusu, M.C.; Tudose, R.C. The Connection Between Canine Fossa Topography and Facial Morphology. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060229
Dandoczi CA, Rusu MC, Tudose RC. The Connection Between Canine Fossa Topography and Facial Morphology. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(6):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060229
Chicago/Turabian StyleDandoczi, Carol Antonio, Mugurel Constantin Rusu, and Răzvan Costin Tudose. 2025. "The Connection Between Canine Fossa Topography and Facial Morphology" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 6: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060229
APA StyleDandoczi, C. A., Rusu, M. C., & Tudose, R. C. (2025). The Connection Between Canine Fossa Topography and Facial Morphology. Dentistry Journal, 13(6), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060229






