Exploring Peri-Implantitis Risk-Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Eligibility Requirements
2.3. Case Definitions
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Data Acquisition
2.5.1. Medical Files
2.5.2. Clinical Examination
2.6. Microbiological Samples Collection and Examination
2.7. Reproducibility and Repeatability
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
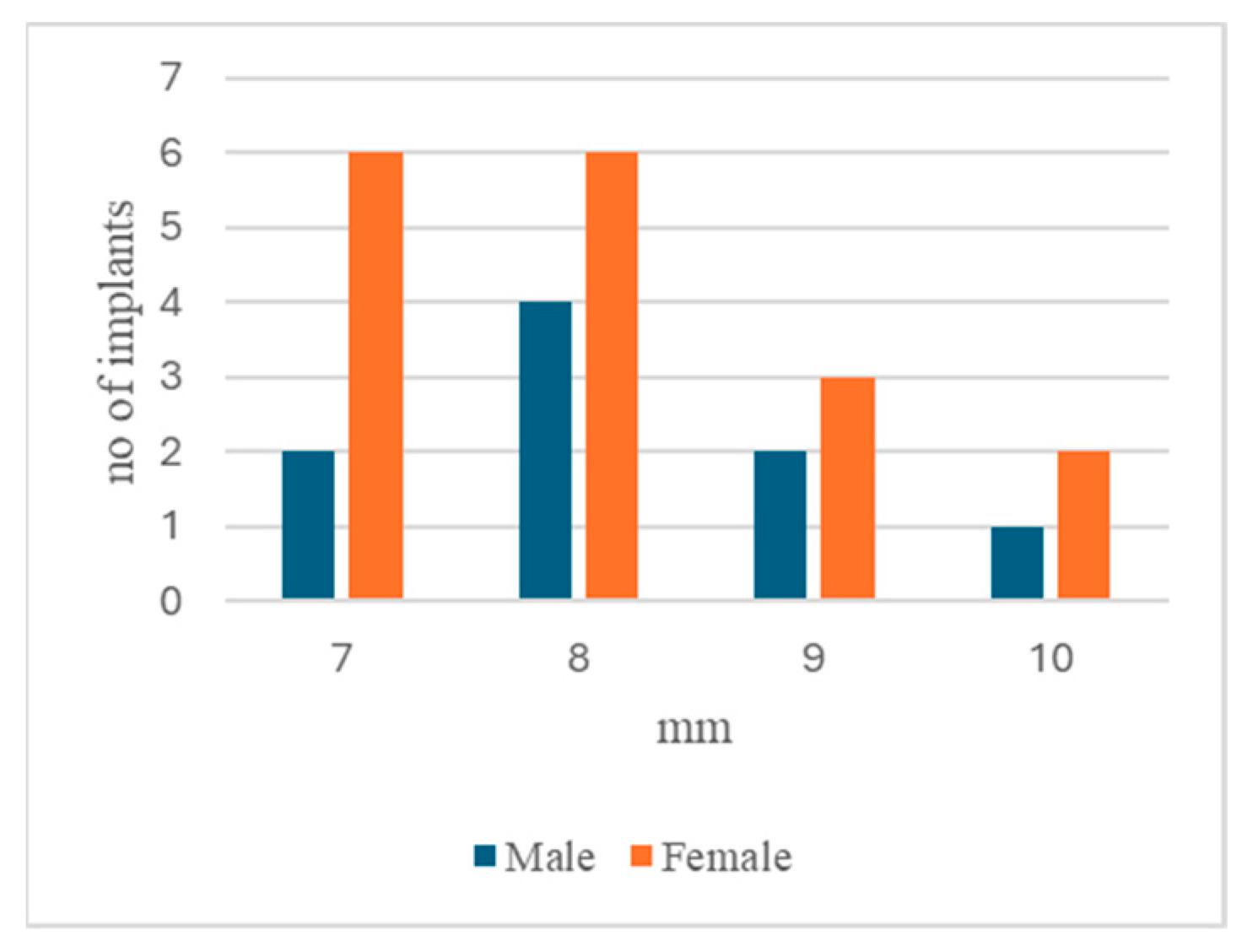
3.2.1. Gender Distribution
3.2.2. Age Groups
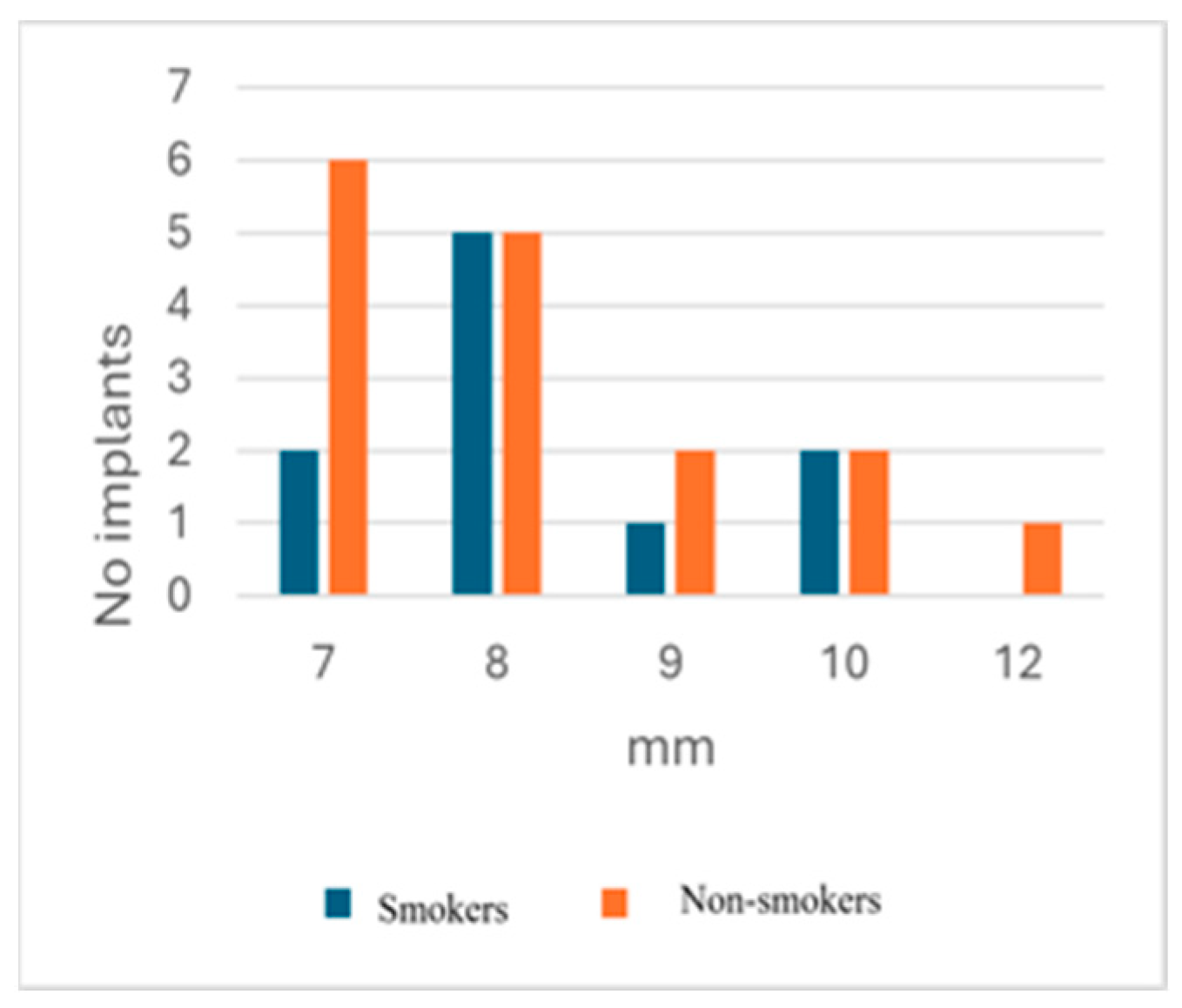
3.2.3. Smoker/Non-Smoker Distribution
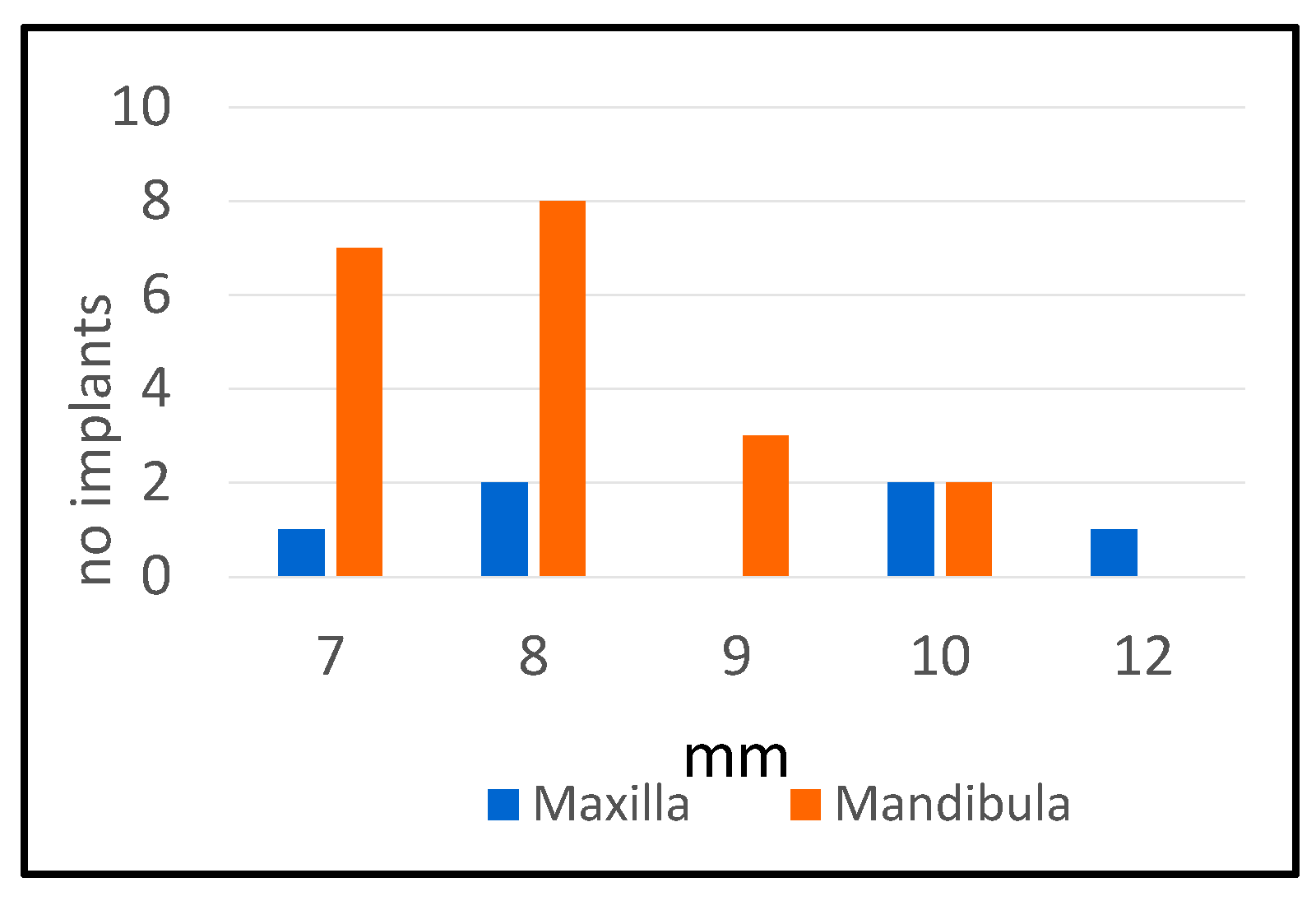
3.2.4. Maxilla/Mandibula Distribution
3.2.5. Stage and Type of Prothesis
3.3. Microbiological Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Findings—Consistency and Discrepancies with Previous Findings
4.2. Limitations of the Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| BoP | Bleeding on probing |
| FC | Fixed cemented |
| FS | Fixed screwed |
| RO | Removable overdenture |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Standard error |
References
- Oral Health WHO.INT. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/oral-health (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- The National Study on the Oral Health Status of Romanians CMSR.RO. Available online: https://cmsr.ro/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Rezumat-Studiu-national-privind-starea-de-sanatate-orala-a-romanilor-1.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Oral Health Country Profile CDN.WHO.INT. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/country-profiles/oral-health/oral-health-rou-2022-country-profile.pdf?sfvrsn=6b74cbdc_9 (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- The Number of Dental Implants Has Tripled in Romania in the Last 5 Years. DENTALMANAGERS.RO. Available online: https://www.dentalmanagers.ro/studiu-numarul-implanturilor-dentare-s-a-triplat-in-romania-in-ultimii-5-ani/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Romania Dental Implants Market Size and Forecast (2021–2031), Country Share, Trend, and Growth Opportunity Analysis Report Coverage: By Product (Dental Bridges, Dental Crowns, Dentures, Abutments, and Others), Material (Titanium Implants, Zirconium Implants, and Others), End User (Hospitals and Clinics, Dental Laboratories, and Others), and Country MARKETRESEARCH.COM. Available online: https://www.marketresearch.com/TIP-Knowledge-Services-v4095/Romania-Dental-Implants-Size-Forecast-37948337/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Herrera, D.; Berglundh, T.; Schwarz, F.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Sculean, A.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N.; Tonetti, M.S.; Sanz, M.; et al. Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases-The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50 (Suppl. 26), 4–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Consensus Report of Workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. 20), S286–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Social Science Statistics socscistatistics.com. Available online: https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Kabir, L.; Stiesch, M.; Grischke, J. The effect of keratinized mucosa on the severity of peri-implant mucositis differs between periodontally healthy subjects and the general population: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldsland, O.C.; Scheie, A.A.; Aass, A.M. The association between selected risk indicators and severity of peri-implantitis using mixed model analyses. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarazzo, F.; Sabóia-Gomes, R.; Alves, B.E.S.; de Oliveira, R.P.; Araújo, M.G. Prevalence, extent and severity of peri-implant diseases. A cross-sectional study based on a university setting in Brazil. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A.; Müller, N.; Cionca, N. The epidemiology of peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 6), 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Aghazadeh, A.; Hallström, H.; Persson, G.R. Factors related to peri-implantitis—A retrospective study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Becker, K.; Sahm, N.; Horstkemper, T.; Rousi, K.; Becker, J. The prevalence of peri-implant diseases for two-piece implants with an internal tube-in-tube connection: A cross-sectional analysis of 512 implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Covani, U.; Botticelli, D.; Serino, G.; Penarrocha, M. Clinical and microbiological findings in patients with peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalayer Naderi, N.; Semyari, H.; Elahinia, Z. The Impact of Smoking on Gingiva: A Histopathological Study. Iran. J. Pathol. 2015, 10, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Amerio, E.; Blasi, G.; Valles, C.; Blanc, V.; Àlvarez, G.; Arredondo, A.; Nart, J.; Monje, A. Impact of smoking on peri-implant bleeding on probing. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinidis, I.K.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Gerdes, S.; Walter, M.H. Cross-sectional study on the prevalence and risk indicators of peri-implant diseases. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kordbacheh Changi, K.; Finkelstein, J.; Papapanou, P.N. Peri-implantitis prevalence, incidence rate, and risk factors: A study of electronic health records at a U.S. dental school. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Anjum, F. Staphylococcus epidermidis Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563240/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Pereira, E.M.; de Mattos, C.S.; Dos Santos, O.C.; Ferreira, D.C.; de Oliveira, T.L.R.; Laport, M.S.; de Oliveira Ferreira, E.; Dos Santos, K.R.N. Staphylococcus hominis subspecies can be identified by SDS-PAGE or MALDI-TOF MS profiles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, E.; Salloum, T.; Tokajian, S. From Normal Flora to Brain Abscesses: A Review of Streptococcus intermedius. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Gilbert, S.C.; Clark, D.; Wade, W.G.; Beighton, D. Population structure of Streptococcus oralis. Microbiology 2009, 155 Pt 8, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daca, A.; Jarzembowski, T. From the Friend to the Foe—Enterococcus faecalis Diverse Impact on the Human Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.; Butt, A.A.; Adley, C.C. Sphingomonas paucimobilis. In Antimicrobial Therapy and Vaccines, 3rd ed.; Yu, V.L., Ed.; ESun Technologies, LLC: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2016; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273339770_Sphingomonas_paucimobilis (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Flanagan, D. Enterococcus faecalis and Dental Implants. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 43, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, A.M.; Mendes, J.M.; Silva, A.S.; Gonçalves, M.d.P.; Cardoso, M.; Coelho, C. Opportunistic Pathogens Isolated from Peri-Implant and Periodontal Subgingival Plaque from Adjacent Teeth. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekal, S.; Gaudreau, C.; Laurence, R.A.; Simoneau, E.; Raynal, L. Streptococcus pseudoporcinus sp. nov., a novel species isolated from the genitourinary tract of women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2584–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wong, T.T.; Prasad, N.; Lee, B.; Urban, C.; Segal-Maurer, S.; Truett, G. Streptococcus pseudoporcinus: Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2020, 2020, 4135246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamura, S.; Niimori, D.; Ihn, H. A case of leg cellulitis caused by multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pseudoporcinus. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2018, 7, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabdoub, S.M.; Tsigarida, A.A.; Kumar, P.S. Patient-specific analysis of periodontal and peri-implant microbiomes. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 168S–175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.-J.; Kwon, Y.; Park, C.; So, Y.J.; Park, T.H.; Jeong, S.; Im, J.; Yun, C.-H.; Han, S.H. Streptococcus gordonii: Pathogenesis and Host Response to Its Cell Wall Components. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolenbrander, P.E.; Palmer, R.J., Jr.; Periasamy, S.; Jakubovics, N.S. Oral multispecies biofilm development and the key role of cell-cell distance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, H.F.; Lamont, R.J. Oral microbial communities in sickness and in health. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iușan, S.A.L.; Lucaciu, O.P.; Petrescu, N.B.; Mirică, I.C.; Toc, D.-A.; Albu, S.; Costache, C. The Main Bacterial Communities Identified in the Sites Affected by Periimplantitis: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilands, J.; Wickström, C.; Kinnby, B.; Davies, J.R.; Hall, J.; Friberg, B.; Svensäter, G. Bacterial profiles and proteolytic activity in peri-implantitis versus healthy sites. Anaerobe 2015, 35 Pt A, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, R.; Henningsen, A.; Jung, O.; Heiland, M.; Hammächer, C.; Stein, J.M. Definition, etiology, prevention and treatment of peri-implantitis—A review. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, R.A.; Fraser, H.; Hardie, J.M.; Beighton, D. Phenotypic differentiation of Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus strains within the “Streptococcus milleri group”. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.; Hoshino, T.; Kilian, M. Taxonomy of the Anginosus group of the genus Streptococcus and description of Streptococcus anginosus subsp. whileyi subsp. nov. and Streptococcus constellatus subsp. viborgensis subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63 Pt 7, 2506–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, T.A.; Unakal, C.G. Staphylococcus aureus Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441868/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Lang, N.P.; Mult, H.C.; Tonetti, M.S. Peri-implantitis: Etiology, pathogenesis, prevention, and therapy. In Dental Implant Complications; Froum, S.J., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Diversity analysis of subgingival microbial bacteria in peri-implantitis in Uygur population. Medicine 2018, 97, e9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, G.R.; Renvert, S. Cluster of bacteria associated with peri-implantitis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Manoil, D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faveri, M.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Shibli, J.A.; Pérez-Chaparro, P.J.; Feres, M. Microbiological diversity of peri-implantitis biofilms. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 830, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Sabogal, M.A.; Castillo, D.M.; Rincón, M.V.; Gómez, L.A.; Lesmes, Y.A.; Chambrone, L. Microbiome and Microbial Biofilm Profiles of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1066–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziogou, A.; Giannakodimos, I.; Giannakodimos, A.; Baliou, S.; Ioannou, P. Kocuria Species Infections in Humans—A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuntas, F.; Yildiz, O.; Eser, B.; Gündogan, K.; Sumerkan, B.; Cetin, M. Catheter-related bacteremia due to Kocuria rosea in a patient undergoing peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. BMC Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenemann, N.A.; Sauerwald, F.; Thimel, D.; Mayr, E. A rare case of periprosthetic joint infection of the hip due to Kocuria spp. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, E.; Selvi, S.S.; Nikerel, E.; Teusink, B.; Toksoy Öner, E.; Çakır, T. A genome-scale metabolic network of the aroma bacterium Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. cremoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou, G.; Luis Saleta, J.; Sáez Nieto, J.A.; Tomás, M.; Valdezate, S.; Sousa, D.; Lueiro, F.; Villanueva, R.; Jose Pereira, M.; Llinares, P. Nosocomial Outbreaks Caused by Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegueti, M.G.; Gaspar, G.G.; Laus, A.M.; Basile-Filho, A.; Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Auxiliadora-Martins, M. Bacteremia by Leuconostoc mesenteroides in an immunocompetent patient with chronic Chagas disease: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenocur, H.S.; Smith, M.A.; Vellozzi, E.M.; Shapiro, J.; Isenberg, H.D. Odontogenic infection secondary to Leuconostoc species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1893–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, A.T.; Jeronymo-Ceneviva, A.B.; Todorov, S.D.; Penna, A.L.B. The Two Faces of Leuconostoc mesenteroides in Food Systems. Food Rev. Int. 2015, 31, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosako, Y.; Sakazaki, R.; Yoshizaki, E. Yokenella regensburgei gen. nov., sp. nov.: A new genus and species in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1984, 37, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, G.; Song, J.E.; Chang, J. First report of Yokenella regensburgei isolated from external auditory canal after diving in valley. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e05177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- V, A.S.; Suji, T.; Jayanth, S.T.; Sahni, R.D. Yokenella regensburgei urinary tract infection in an immunocompetent patient: A case report. Access Microbiol. 2023, 5, 000571.v4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kang, Y.J.; Huh, H.J.; Ki, C.; Lee, N.Y. First Report of Yokenella regensburgei Isolated from the Wound Exudate after Disarticulation Due to Diabetic Foot Infection in Korea. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk-Zurek, M.; Sitkiewicz, I.; Koziel, J. The Clinical View on Streptococcus anginosus Group—Opportunistic Pathogens Coming Out of Hiding. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 956677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis--the ‘accidental’ pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Rossetti, P.H.; Penarrocha, D. Identification of Enterococcus Faecalis and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa on and in Implants in Individuals with Peri-implant Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van de Velde, T.; Thevissen, E.; Persson, G.R.; Johansson, C.; De Bruyn, H. Two-year outcome with Nobel Direct implants: A retrospective radiographic and microbiologic study in 10 patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakkers, J.; Liu, L.; Hentenaar, D.F.M.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Vissink, A.; Meijer, H.J.A.; Walters, L.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; de Waal, Y.C.M. The Peri-Implant Microbiome-A Possible Factor Determining the Success of Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment? Dent. J. 2024, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săndulescu, M.; Sîrbu, V.D.; Popovici, I.A. Bacterial species associated with peri-implant disease—A literature review. Germs 2023, 13, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial-Molina, M.; López-Martínez, J.; O’Valle, F.; Galindo-Moreno, P. Microbial Profiles and Detection Techniques in Peri-Implant Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2016, 7, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pérez-Chaparro, P.J.; Duarte, P.M.; Shibli, J.A.; Montenegro, S.; Lacerda Heluy, S.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M. The Current Weight of Evidence of the Microbiologic Profile Associated with Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, M.; Grusovin, M.; Canullo, L. The Microbiologic Profile Associated with Peri-Implantitis in Humans: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Mandal, M. Microbial Biofilm: Formation, Architecture, Antibiotic Resistance, and Control Strategies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șchiopu, P.; Toc, D.A.; Colosi, I.A.; Costache, C.; Ruospo, G.; Berar, G.; Gălbău, Ș.-G.; Ghilea, A.C.; Botan, A.; Pană, A.-G.; et al. An Overview of the Factors Involved in Biofilm Production by the Enterococcus Genus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Tay, J.R.H.; Mattheos, N.; Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Seneviratne, C.J. A Mapping Review of the Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis: The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis. Cells 2024, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; Chopo-Escuin, G.; Tommassen, J.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Arenas, J. Biofilms as Promoters of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance and Tolerance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R. Biofilms and Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 437, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, E.; Grischke, J.; Winkel, A.; Eberhard, J.; Kommerein, N.; Doll, K.; Yang, I.; Stiesch, M. Evaluation of Biofilm Colonization on Multi-Part Dental Implants in a Rat Model. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.; Giordano, F.; Sangiovanni, G.; Capuano, N.; Acerra, A.; D’Ambrosio, F. The Interaction between the Oral Microbiome and Systemic Diseases: A Narrative Review. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1862–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, L.; Cavalcanti, R.; Rupe, C.; Scartabelli, D.; Serni, L.; Chambrone, L.; Cairo, F. Clinical efficacy of adjunctive methods for the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Wisitrasameewon, W.; Humagain, M.; Thunyakitpisal, P. Peri-implantitis Update: Risk Indicators, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gianfilippo, R.; Sirinirund, B.; Rodriguez, M.V.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.-L. Long-Term Prognosis of Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review of Prospective Trials with More Than 3 Years of Follow-Up. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Mirra, D.; Roccuzzo, A. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. Br. Dent. J. 2024, 236, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient No. | Implant No. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 22 | 50 | |
| Implants with Peri-Implantitis | Healthy Implants | ||
| Patients with peri-implantitis | 16 | 26 | 11 |
| Patients with healthy implants | 6 | 0 | 13 |
| Condition | No. of Implants | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| Peri-implantitis | 26 | 24 | |
| Bone loss | 26 | 0 | 100% |
| Edema | 15 | 0 | 58% |
| Redness | 15 | 0 | 58% |
| Bleeding | 23 | 0 | 88.46% |
| Suppuration | 22 | 0 | 84.62% |
| Pus | 8 | 0 | 30.77% |
| Male | % | Female | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 11 | 11 | ||
| No. of patients with peri-implantitis | 8 | 72.7% | 8 | 72.7% |
| Vertical bone loss | 8 | 100% | 8 | 100% |
| Edema | 5 | 62.5% | 5 | 62.5% |
| Redness | 6 | 75% | 4 | 50% |
| Bleeding | 7 | 87.5% | 7 | 87.5% |
| Suppuration | 6 | 75% | 6 | 75% |
| Pus | 4 | 50% | 2 | 25% |
| Bacteria occurrence | 7 | 87.5% | 4 | 50% |
| Average Probing Depths mm ± SD | Peri-Implantitis Occurrence Interval Years ± SD | No. of Implants with Peri-Implantitis/Pus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 8.67 ± 1.65 | 11.87 ± 3.6 | 5 out of 9 |
| t = 2.8953, p = 0.0055 | χ2 = 3.9699, p = 0.046322 | ||
| Female | 8.06 ± 1.03 | 6.11 ± 4. 48 | 3 out of 17 |
| Age Group | <40 Years | % | 40–59 Years | % | ≥60 Years | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 6 | 14 | 2 | |||
| No. of patients with peri-implantitis | 3 | 50% | 9 | 64.3% | 2 | 100% |
| Vertical bone loss | 3 | 100% | 9 | 100% | 2 | 100% |
| Edema | 3 | 100% | 4 | 44.5% | 1 | 50% |
| Redness | 2 | 66.7% | 5 | 55.5% | 1 | 50% |
| Bleeding | 3 | 50% | 7 | 77.7% | 2 | 100% |
| Suppuration | 2 | 66.7% | 6 | 66.7% | 2 | 100% |
| Pus | 1 | 33.4% | 1 | 11.1% | 1 | 50% |
| Bacteria occurrence | 2 | 66.7% | 7 | 77.7% | 1 | 50% |
| Average Probing Depths mm ± SD | Peri-Implantitis Occurrence Interval Years ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| <40 years | 8.33 ± 0.577 | 7± 2.04 |
| 40–59 years | 8.11 ± 1,31 | 9.25 ± 4.78 |
| ≥60 years | 8.8 ± 2.05 | 6 ± 4.42 |
| Smokers | % | Non-Smokers | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 9 | 13 | ||
| No. of patients with peri-implantitis | 6 | 66.7% | 9 | 69.2% |
| Vertical bone loss | 6 | 100% | 9 | 100% |
| Edema | 2 | 33.4% | 8 | 88.8% |
| Redness | 2 | 33.4% | 8 | 88.8% |
| Bleeding | 5 | 83.4% | 9 | 100% |
| Suppuration | 4 | 66.6% | 7 | 77.8% |
| Pus | 1 | 16.7% | 5 | 55.6% |
| Bacteria occurrence | 5 | 83.3% | 8 | 88.9% |
| Average Probing Depths mm ± SD | Peri-Implantitis Occurrence Interval Years ± SD | No. of Implants with Peri-Implantitis Edema and Redness | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smokers | 8.30 ± 1.06 | 4.94 ± 3.92 | 2 out of 10 |
| χ2 = 7.1155, p = 0.007642 | |||
| Non-smokers | 8.25 ± 1.43 | 6.13 ± 5.03 | 13 out of 16 |
| No. of Implants Which Have Peri-Implantitis | Average Probing Depths mm ± SD | Peri-Implantitis Occurrence Interval Years ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla No. of implants 20 | 6 (30%) | 9.17 ± 1.83 | 11.84 ± 2.56 |
| χ2 = 6.46, | t = 2.08046 | t = 1.993 | |
| p = 0.01101 | p = 0.024164 | p = 0.0324 | |
| Mandibula No. of implants 30 | 20 (66.67%) | 8 ± 0.97 | 7.24 ± 4.84 |
| Maxilla | % | Mandibula | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of implants | 20 | 30 | ||
| No. of implants with peri-implantitis | 6 | 30% | 20 | 66.67% |
| Vertical bone loss | 6 | 100% | 20 | 100% |
| Edema | 3 | 50% | 12 | 60% |
| Redness | 3 | 50% | 12 | 60% |
| Bleeding | 4 | 66.67% | 18 | 90% |
| Suppuration | 4 | 66.67% | 17 | 85% |
| Pus | 2 | 33.34% | 6 | 30% |
| Bacteria occurrence | 6 | 100% | 15 | 75% |
| Type of Prosthesis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Implants | Fixed Cemented FC | Fixed Screw FS | Removable Overdenture RO | FC and FS | ||||
| with PI | with PI | with PI | ||||||
| Stage | 16 | 27 | 4 | |||||
| Type | ||||||||
| Prosthesis | 32 | 16 | 11 68.7% | 12 | 3 25% | 4 | 4 100% | χ2 = 5.25 p = 0.022 |
| PMMA Prosthesis | 15 | 15 | 7 46.7% | |||||
| Healing screw | 3 | |||||||
| Average Probing Depths (mm) | Peri-Implantitis Occurrence Interval (years) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prosthesis | PMMA Prosthesis | Prosthesis | PMMA Prosthesis | ||||
| Fixed Cemented FC | Fixed Screw FS | Removable Overdenture | Fixed Screw FS | Fixed Cemented FC | Fixed Screw FS | Removable Overdenture | Fixed Screw FS |
| 9.09 ± 1.44 | 7.33 ± 0.57 | 8 ± 1.54 | 7.57± 0.54 | 10.63 ± 4.12 | 8 ± 5.29 | 4 (1 patient) | 2 (1 patient) |
| FC and FS t = 2.0124, p = 0.03359 | FC and PMMA FS t = 2.643, p = 0.008861 | FC and RO t = 3.13, p = 0.003925 | FC and PMMA FS t = 5.046, p = 0.00072 | ||||
| Average Probing Depths mm ± SD | Peri-Implantitis Occurrence Interval Years ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Megagen AnyOne | Megagen AnyRidge | Megagen AnyOne | Megagen AnyRidge |
| 8.11± 0.78 | 7.63 ± 0.91 | 5.66 ± 4.31 | 3.25 ± 1.03 |
| Implants without Detection of Bacteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| With peri-implantitis | 26 | 5 (19.23%) | χ2 = 5.2653 |
| Without peri-implantitis | 24 | 12 (50%) | p = 0.021754 |
| Bacterial Identification | No. Implants | No. Implants | No. Implants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >105 | 104–105 | 103–104 | |||
| Kocuria rosea | 2 | Staphylococcus hominis ssp. Hominis | 2 | Kocuria rosea | 1 |
| Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. Cremoris | 1 | Enterococcus faecalis | 3 | Streptococcus oralis | 1 |
| Streptococcus gordonii | 1 | Streptococcus anginosus | 1 | Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. Cremoris | 2 |
| Streptococcus constelatus | 3 | Streptococcus intermedius | 1 | Streptococcus sanguinis | 1 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 2 | Sphingomonas paucimobilis | 1 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 2 |
| Staphylococcus hominis ssp. Hominis | 1 | Streptococcus gordonii | 2 | Staphylococcus hominis ssp. Hominis | 1 |
| Streptococcus pseudoporcinus | 2 | Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. Cremoris | 1 | Streptococcus intermedius | 1 |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 3 | Kocuria rosea | 1 | Enterococcus faecalis | 1 |
| Yokenella regensburgei | 1 | Staphylococcus aureus | 1 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1 |
| >105 | 104–105 | 103–104 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptococcus | 6 | 4 | 3 | 13 |
| Staphylococcus | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Enterococcus | 3 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| Kocuria | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Leuconostoc | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Yokenella | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sphingomonas | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Pseudomonas | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iușan, S.A.L.; Lucaciu, O.P.; Petrescu, N.B.; Mirică, I.C.; Toc, D.-A.; Albu, S.; Costache, C. Exploring Peri-Implantitis Risk-Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13040148
Iușan SAL, Lucaciu OP, Petrescu NB, Mirică IC, Toc D-A, Albu S, Costache C. Exploring Peri-Implantitis Risk-Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(4):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13040148
Chicago/Turabian StyleIușan, Simina Angela Lăcrimioara, Ondine Patricia Lucaciu, Nausica Bianca Petrescu, Ioana Codruța Mirică, Dan-Alexandru Toc, Silviu Albu, and Carmen Costache. 2025. "Exploring Peri-Implantitis Risk-Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 4: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13040148
APA StyleIușan, S. A. L., Lucaciu, O. P., Petrescu, N. B., Mirică, I. C., Toc, D.-A., Albu, S., & Costache, C. (2025). Exploring Peri-Implantitis Risk-Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Dentistry Journal, 13(4), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13040148









