In Vitro Comparison of Trueness and Precision of an AI-Driven Real-Time Library Matching Protocol with Irregular Geometry Scan Bodies for Full-Arch Implant Scanning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Preparation
2.2. Master STL Creation
2.3. Scanning Procedure
Scanners in the Study
2.4. Design of the Study
2.4.1. Overview
2.4.2. Hypothesis
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
2.5.1. Evaluating Trueness
2.5.2. Evaluating Precision
2.5.3. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Trueness
3.2. Precision
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of Trueness and Precision in Digital Intraoral Scanners
4.2. Contribution to Existing Scientific Literature
4.3. Enhancement in Accuracy Through Scan-Body Geometry
4.4. Comparison with Peer-Reviewed Literature
4.5. Implications for Clinical Practice
4.6. Challenges and Limitations of the Present Study
4.7. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zafiropoulos, G.-G.; Galil, A.A.; Deli, G. An Interocclusal Recording Method for the Fabrication of Full-Arch Implant-Retained Restorations. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M. Impression Techniques for the Resorbed Mandibular Arch: A Guide to Increased Stability. J. Sci. Soc. 2015, 42, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, M.P.; Pinto, C.P.; Sponchiado, A.P.; Ornaghi, B.P. Dimensional Stability of a Novel Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Technique. Braz. J. Oral Sci. 2014, 13, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkūnas, V.; Gečiauskaitė, A.; Jegelevičius, D.; Vaitiekūnas, M. Accuracy of Digital Implant Impressions with Intraoral Scanners: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Fiore, A.; Meneghello, R.; Graiff, L.; Savio, G.; Vigolo, P.; Monaco, C.; Stellini, E. Full-Arch Digital Scanning Systems Performances for Implant-Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses: A Comparative Study of Eight Intraoral Scanners. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Mehl, A. Influence of Scanning Strategies on the Accuracy of Digital Intraoral Scanning Systems. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2013, 16, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drancourt, N.; Auroy, P.; Veyrune, J.-L.; Osta, N.E.; Nicolas, E. Accuracy of Conventional and Digital Impressions for Full-Arch Implant-Supported Prostheses: An In Vitro Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, N.E.H.; Abofadle, A.; Bahig, D. Accuracy of Different Digital Data Acquisition Workflows for Full-Arch Maxillary Implant Prostheses: An In-Vitro Study. Egypt. Dent. J. 2024, 70, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkūnas, V.; Gedrimiene, A.; Adaškevičius, R.; Al-Haj Husain, N.; Özcan, M. Comparison of the Clinical Accuracy of Digital and Conventional Dental Implant Impressions. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2020, 28, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Vazouras, K.; Chen, Y.-W.; Kotina, E.; Natto, Z.S.; Kang, K.; Chochlidakis, K. Digital vs. Conventional Implant Impressions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.N.; Lee, A.; Lavasani, S.; Boehm, T. An Overview of Digital Workflows for Precision Implant Dentistry. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2022, 50, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Sanda, M.; Baba, K. Effects of Different Types of Intraoral Scanners and Scanning Ranges on the Precision of Digital Implant Impressions in the Edentulous Maxilla: An In-Vitro Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.; Veronesi, G.; Hauschild, U.; Mijiritsky, E.; Mangano, C. Trueness and Precision of Four Intraoral Scanners in Oral Implantology: A Comparative In-Vitro Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallarico, M.; Lumbau, A.I.; Scrascia, R.; Demelas, G.; Sanseverino, F.; Amarena, R.; Meloni, S.M. Feasibility of Using a Prosthetic-Based Impression Template to Improve the Trueness and Precision of a Complete-Arch Digital Impression on Four and Six Implants: An In-Vitro Study. Materials 2020, 13, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultanoğlu, E.G.; Keleş, B. Comparison of the Accuracy and Precision of Digital Scans for Implant-Supported Maxillary Hybrid Prostheses: An In-Vitro Study. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2024, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.; Özcan, M.; Martínez-Rus, F.; Pradíes, G. Accuracy of a Digital Impression System Based on Active Wavefront Sampling Technology for Implants Considering Operator Experience, Implant Angulation, and Depth. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e54–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, H.-L.; Tao, X. Accuracy of Edentulous Full-Arch Implant Impression: An In-Vitro Comparison between Conventional Impression, Intraoral Scan with and without Splinting, and Photogrammetry. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2024, 35, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, G.; Yilmaz, H.; Treviño, A.; Kökat, A.M.; Yilmaz, B. The Effect of Scanner Type and Scan Body Position on the Accuracy of Complete-Arch Digital Implant Scans. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, L.; Pozzi, A.; Lio, F.; Rompen, E.; Zechner, W.; Nardi, A. Influence of Implant Scan-Body Material, Position and Operator on the Accuracy of Digital Impressions for Complete-Arch Restorations: A Randomised In-Vitro Trial. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örtorp, A.; Jemt, T.; Bäck, T. Photogrammetry and Conventional Impressions for Recording Implant Positions: A Comparative Laboratory Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2005, 7, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivara, F.; Lumetti, S.; Calciolari, E.; Toffoli, A.; Forlani, G.; Manfredi, E. Photogrammetric Method to Measure the Discrepancy between Clinical and Software-Designed Positions of Implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, R.; Goujat, A.; Venet, L.; Viguie, G.; Viennot, S.; Robinson, P.; Farges, J.-C.; Fages, M.; Ducret, M. Intraoral Scanner Technologies: A Review to Make a Successful Impression. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8427595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafaee, F.; Firouz, F.; Mohajeri, M.; Hashemi, R.; Ghorbani Gholiabad, S. In-Vitro Comparison of the Accuracy (Precision and Trueness) of Seven Dental Scanners. J. Dent. 2021, 22, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5725-1:1994; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 1: General Principles and Definitions. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- ISO 12836:2015; Dentistry—Digitizing Devices for CAD/CAM Systems for Indirect Dental Restorations—Test Methods for Assessing Accuracy. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Nulty, A.B. An In-Vivo Comparison of Trueness and Precision of Two Novel Methods for Improving Edentulous Full-Arch Implant Scanning Accuracy: A Pilot Study. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menditto, A.; Patriarca, M.; Magnusson, B. Understanding the Meaning of Accuracy, Trueness and Precision. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2007, 12, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnick, S.L.; Lewis, L.A. The Importance of Precision. In Positioning Techniques in Clinical Dentistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenesti, E.; Gosmaro, F. Trueness, Precision and Accuracy: A Critical Overview of the Concepts as Well as Proposals for Revision. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2015, 20, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratos, M.; Bergin, J.M.; Rubenstein, J.E.; Sorensen, J.A. Effect of Simulated Intraoral Variables on the Accuracy of a Photogrammetric Imaging Technique for Complete-Arch Implant Prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, J.M.; Rubenstein, J.E.; Mancl, L.; Brudvik, J.S.; Raigrodski, A.J. An In-Vitro Comparison of Photogrammetric and Conventional Complete-Arch Implant Impression Techniques. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 110, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; Antonaya-Martín, J.L.; del Río-Highsmith, J.; Correia, A.; Gómez-Polo, M. Photogrammetry Technique for the 3D Digital Impression of Multiple Dental Implants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuani, V.T.; Ferreira, R.; Manfredi, G.G.P.; Cardoso, M.V.; Sant’Ana, A.C.P. Photogrammetry as an Alternative for Acquiring Digital Dental Models: A Proof of Concept. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 127, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, F.; Pranno, N.; Franchina, A.; Di Carlo, V.; Brauner, E.; Ferri, A.; Pellegrino, G.; Grecchi, E.; Goker, F.; Stefanelli, L.V. Artificial Intelligence: A New Diagnostic Software in Dentistry—A Preliminary Performance Diagnostic Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z. Improved Scanning Accuracy with Newly Designed Scan Bodies: An In-Vitro Study Comparing Digital versus Conventional Impression Techniques for Complete-Arch Implant Rehabilitation. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Polo, M.; Sallorenzo, A.; Ortega, R.; Gomez-Polo, C.; Barmak, A.B.; Att, W.; Revilla-León, M. Influence of Implant Angulation and Clinical Implant Scan Body Height on the Accuracy of Complete-Arch Intraoral Digital Scans. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntovas, P.; Spanopoulou, M.; Martin, W.; Sykaras, N. Superimposition of Intraoral Scans of an Edentulous Arch with Implants and Implant-Supported Provisional Restoration Implementing a Novel Implant Prosthetic Scan Body. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2022, 66, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasrisuebwong, P.; Kulchotirat, T.; Anunmana, C. Effects of Inter-Implant Distance on the Accuracy of Intraoral Scanners: An In-Vitro Study. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2021, 13, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemt, T.; Bäck, T.; Petersson, A. Photogrammetry—An Alternative to Conventional Impressions in Implant Dentistry? A Clinical Pilot Study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1999, 12, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
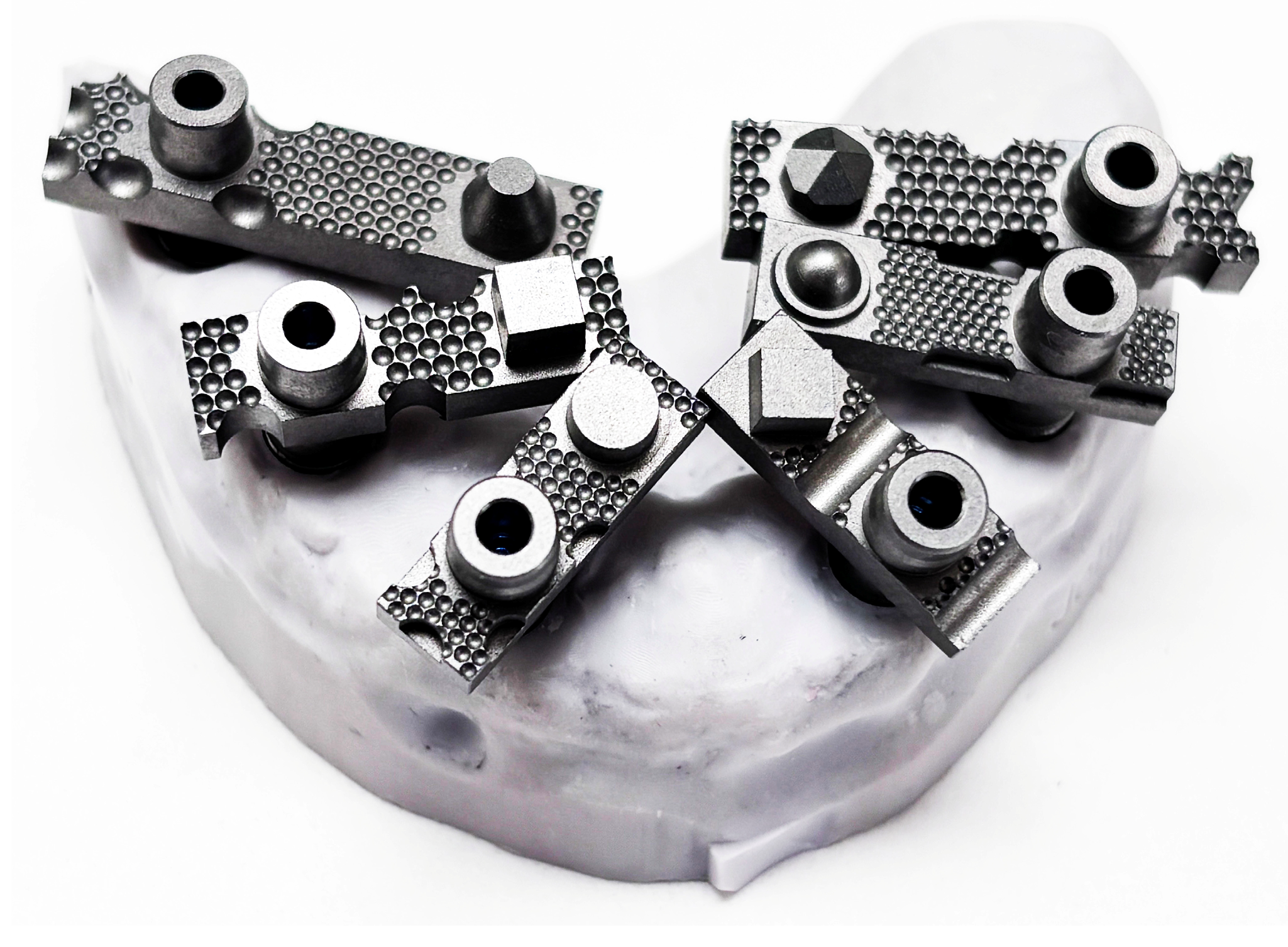

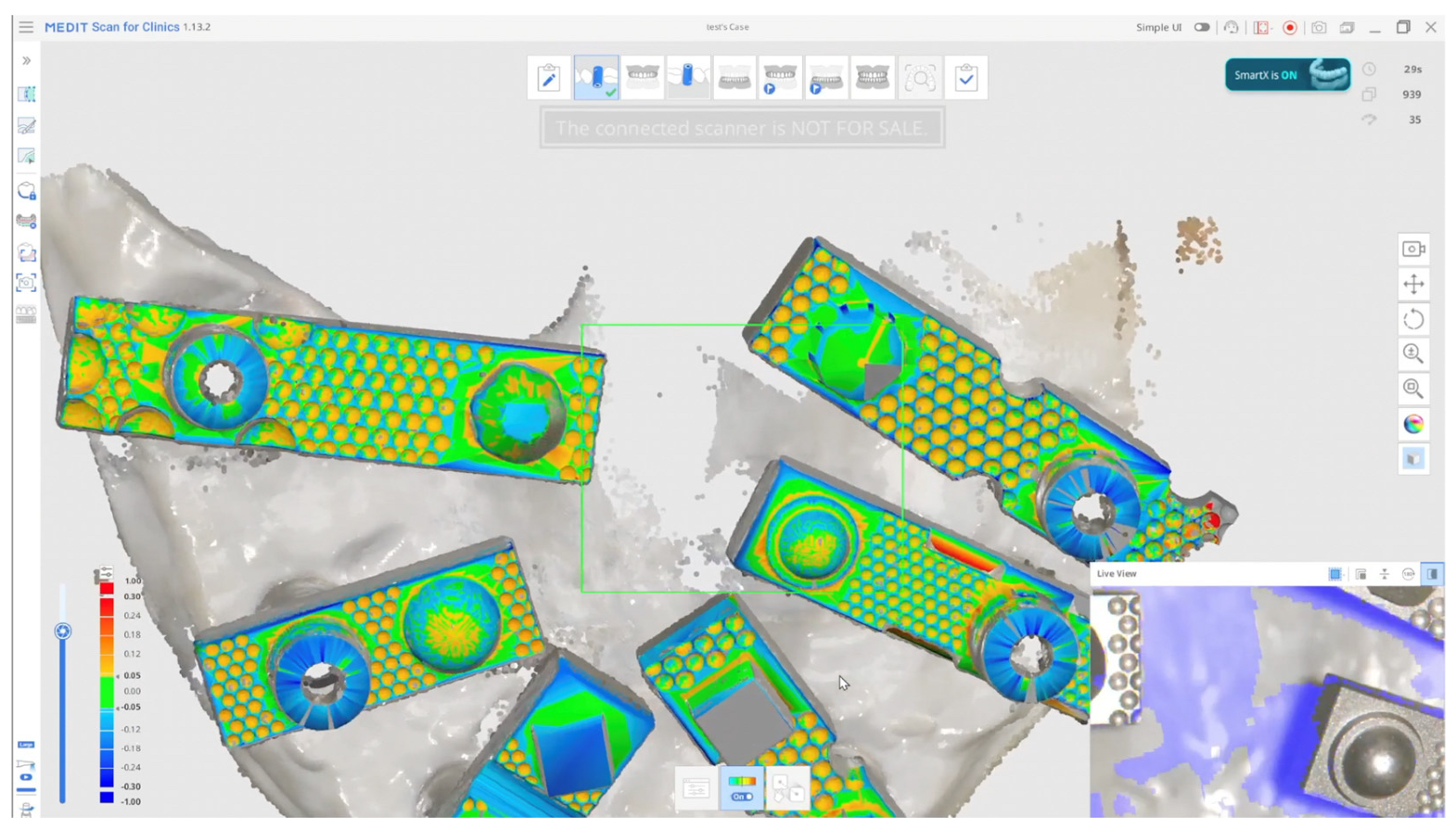
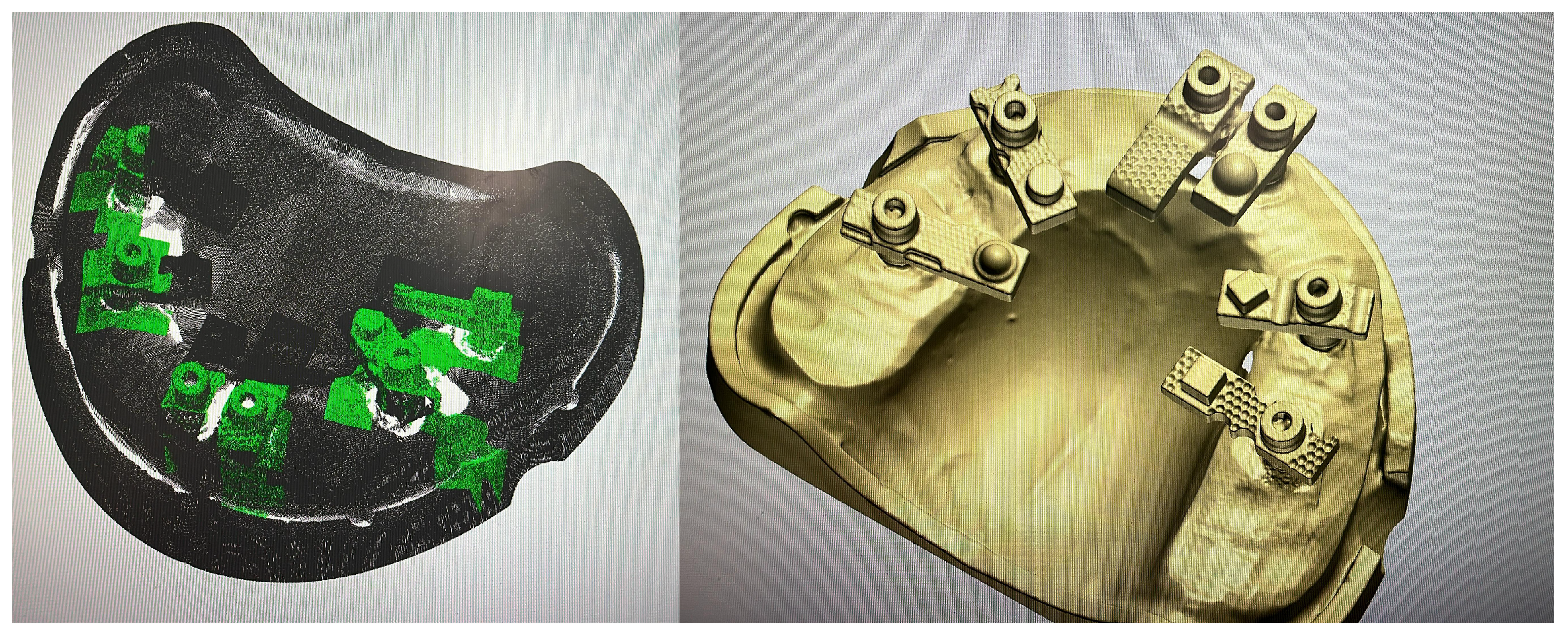
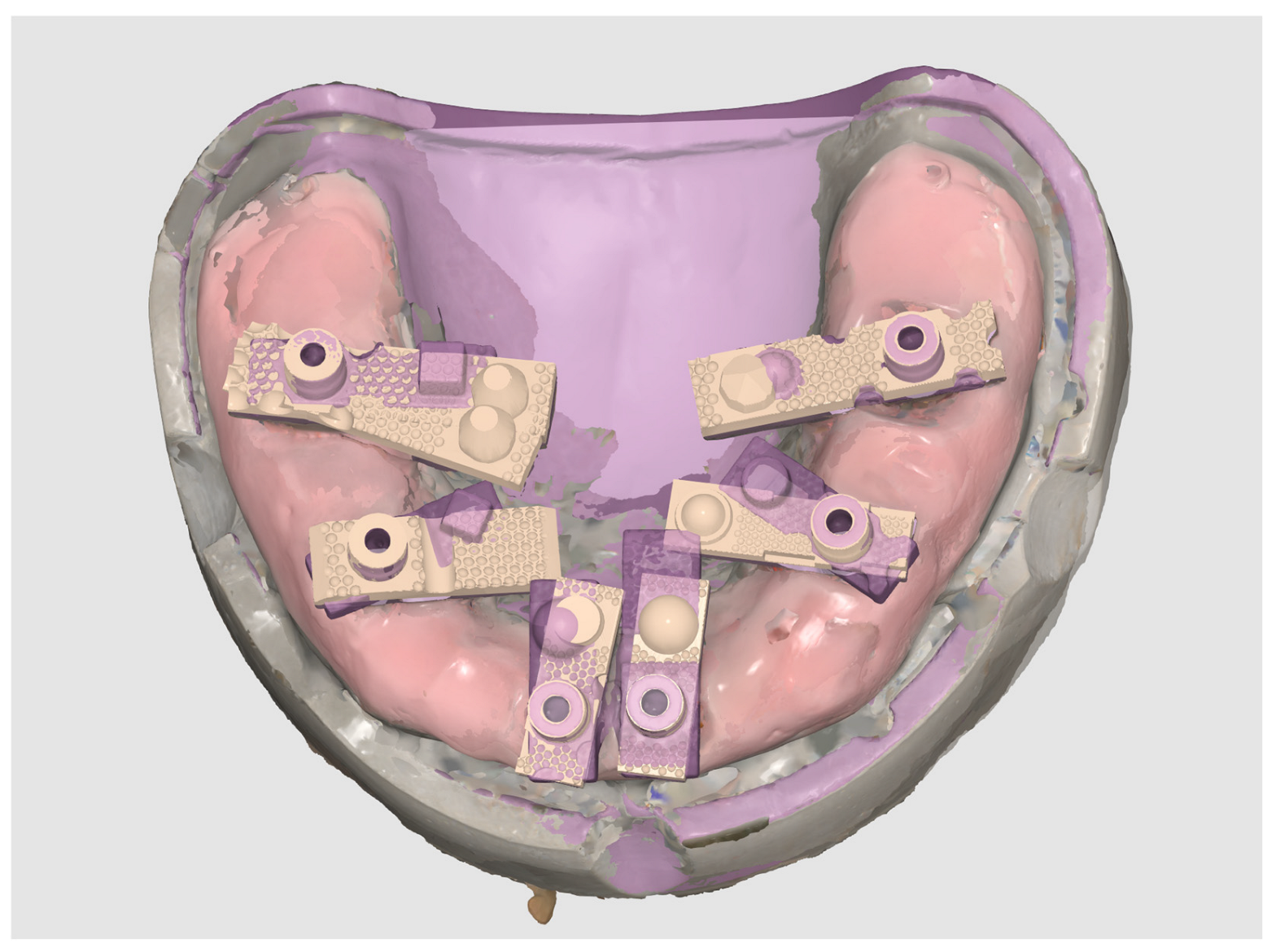
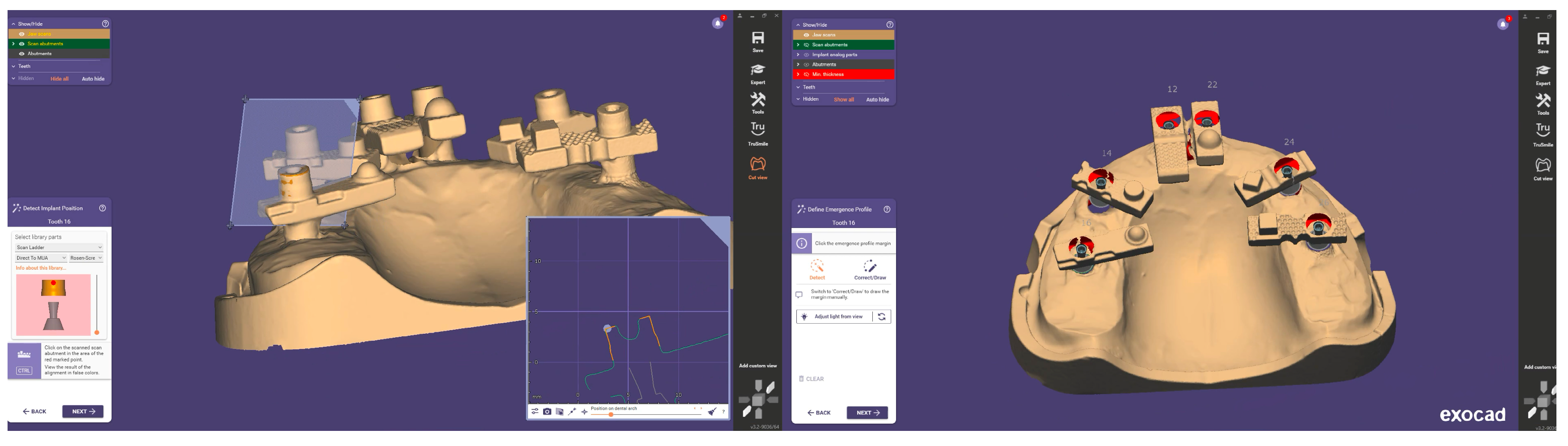
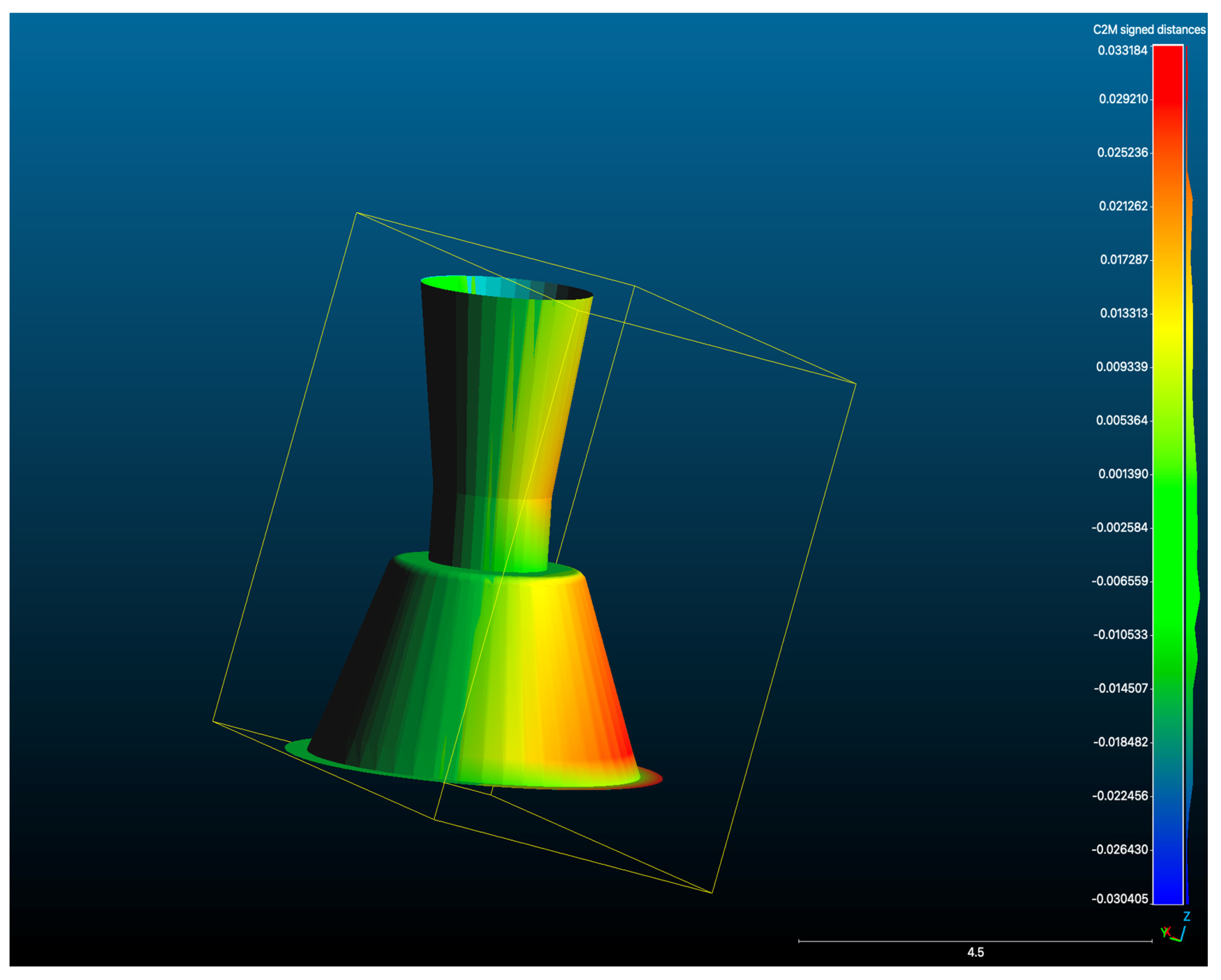
| Name | Manufacturer | Technology | STL Export | PLY/OBJ Colour Export | Photogrammetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | 3Shape, Copenhagen, Denmark | Structured white light desktop scanner. | YES | NO | NO |
| i900 | Medit, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea | Structured light-Active Speed 3D Video™ | YES | YES | NO |
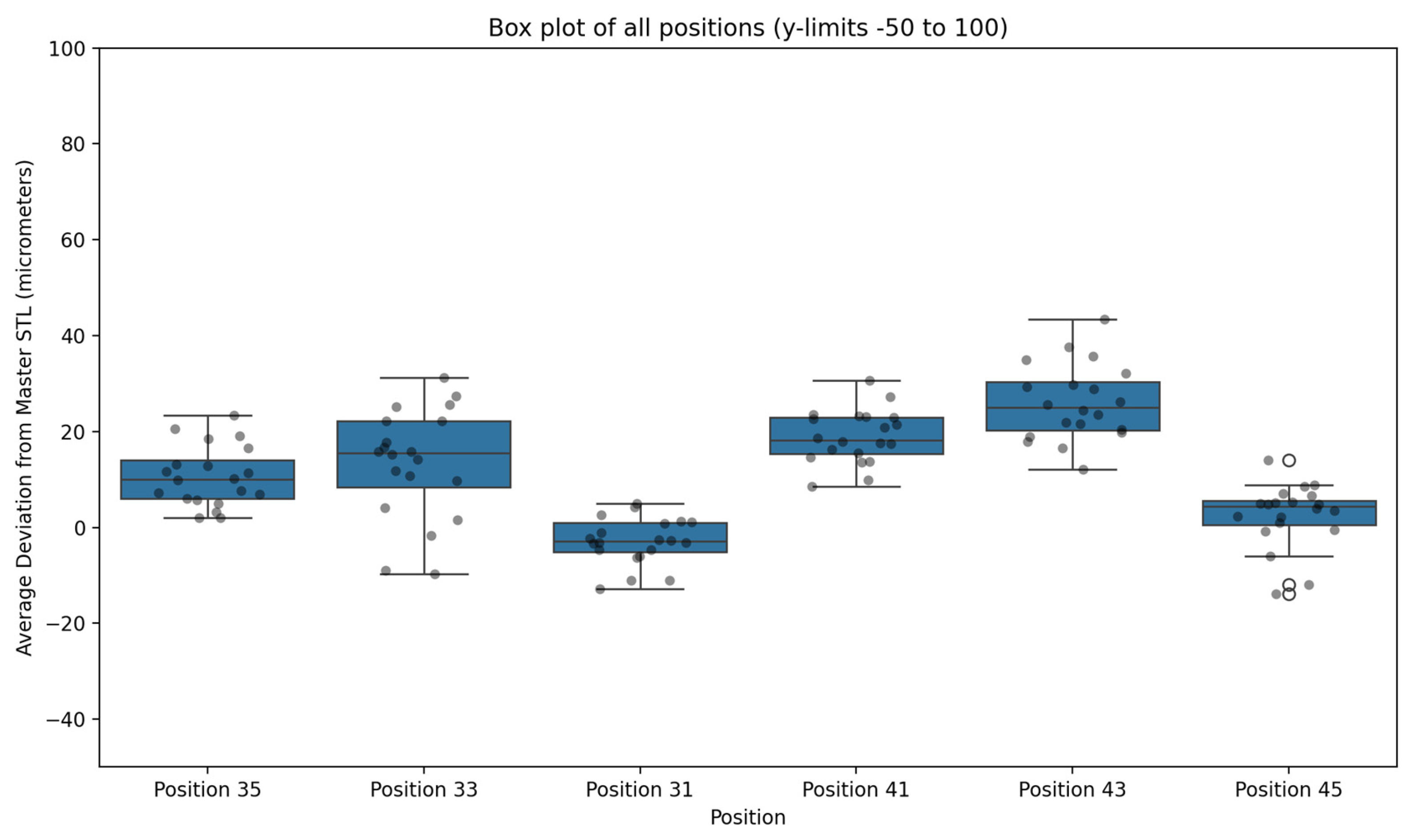
| Block Number | Position 35 | Position 33 | Position 31 | Position 41 | Position 43 | Position 45 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.18 | 25.12 | 3.19 | 23.06 | 26.17 | 0.98 |
| 2 | 18.43 | 15.23 | 4.7 | 8.58 | 19.86 | 4.79 |
| 3 | 10.10 | 31.28 | 6.33 | 17.42 | 43.46 | 7.05 |
| 4 | 12.87 | 4.05 | 2.61 | 13.70 | 18.93 | 3.54 |
| 5 | 9.92 | 15.77 | 2.75 | 30.69 | 23.54 | 5.96 |
| 6 | 7.25 | 9.75 | 0.85 | 9.84 | 32.06 | 4.93 |
| 7 | 4.91 | 22.25 | 4.25 | 13.59 | 34.90 | 5.26 |
| 8 | 7.71 | 22.24 | 1.27 | 21.42 | 12.10 | 0.77 |
| 9 | 11.36 | 1.70 | 1.17 | 23.19 | 25.56 | 14.07 |
| 10 | 16.52 | 10.81 | 6.07 | 18.65 | 24.36 | 4.78 |
| 11 | 20.62 | 16.73 | 3.36 | 16.20 | 21.85 | 8.47 |
| 12 | 6.08 | 8.94 | 4.71 | 22.88 | 21.64 | 3.87 |
| 13 | 19.00 | 14.21 | 10.99 | 23.50 | 16.48 | 5.15 |
| 14 | 6.92 | 15.82 | 1.14 | 14.63 | 37.62 | 6.59 |
| 15 | 2.04 | 17.68 | 12.77 | 15.54 | 17.84 | 13.88 |
| 16 | 5.67 | 27.43 | 2.26 | 20.90 | 35.72 | 2.10 |
| 17 | 2.04 | 25.55 | 5.00 | 17.62 | 29.29 | 11.88 |
| 18 | 11.68 | 11.77 | 3.16 | 22.60 | 29.70 | 0.56 |
| 19 | 23.44 | 1.53 | 11.08 | 27.17 | 28.85 | 8.81 |
| 20 | 13.16 | 9.78 | 2.62 | 17.86 | 20.41 | 2.32 |
| Name | Mean (μm) | Std. Deviation (μm) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position 35 | 10.65 | 6.32 | <000.1 |
| Position 33 | 15.38 | 8.41 | <000.1 |
| Position 31 | 4.54 | 3.54 | <000.1 |
| Position 41 | 18.95 | 5.57 | <000.1 |
| Position 43 | 26.02 | 7.94 | <000.1 |
| Position 45 | 5.79 | 3.99 | <000.1 |
| Position | N Complete | Mean Corr to Others | Max Corr to Other | Max Corr Partner | Mean Abs Diff to Others | Best Linear R2 | Best Linea Partner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position 45 | 20 | −0.08 | 0.26 | Position 35 | 10.21 | 0.26 | Position 35 |
| Position 43 | 20 | −0.09 | 0.36 | Position 33 | 10.90 | 0.26 | Position 33 |
| Position 33 | 20 | 0.12 | 0.40 | Position 43 | 11.63 | 0.16 | Position 43 |
| Position 35 | 20 | 0.00 | 0.16 | Position 45 | 11.10 | 0.02 | Position 45 |
| Position 31 | 20 | −0.03 | 0.36 | Position 35 | 15.71 | 0.13 | Position 35 |
| Position 41 | 20 | 0.05 | 0.40 | Position 31 | 11.03 | 0.16 | Position 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nulty, A.B.; Kelly, C.; Ambridge, O.; Ambridge, M.; Ferguson, R.; Hoffer, A. In Vitro Comparison of Trueness and Precision of an AI-Driven Real-Time Library Matching Protocol with Irregular Geometry Scan Bodies for Full-Arch Implant Scanning. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13110533
Nulty AB, Kelly C, Ambridge O, Ambridge M, Ferguson R, Hoffer A. In Vitro Comparison of Trueness and Precision of an AI-Driven Real-Time Library Matching Protocol with Irregular Geometry Scan Bodies for Full-Arch Implant Scanning. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(11):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13110533
Chicago/Turabian StyleNulty, Adam Brian, Cameron Kelly, Oliver Ambridge, Mark Ambridge, Rick Ferguson, and Ashtyn Hoffer. 2025. "In Vitro Comparison of Trueness and Precision of an AI-Driven Real-Time Library Matching Protocol with Irregular Geometry Scan Bodies for Full-Arch Implant Scanning" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 11: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13110533
APA StyleNulty, A. B., Kelly, C., Ambridge, O., Ambridge, M., Ferguson, R., & Hoffer, A. (2025). In Vitro Comparison of Trueness and Precision of an AI-Driven Real-Time Library Matching Protocol with Irregular Geometry Scan Bodies for Full-Arch Implant Scanning. Dentistry Journal, 13(11), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13110533






