The Impact of Centrifugation Devices and Collection Tubes on Fibrin Characteristics and Growth Factor Release Under High- and Low-Speed Protocols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects and Sample Collection
2.3. Study Part 1: Centrifugation Analysis
2.3.1. Preparation of Platelet Concentrates
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.3. Growth Factor Quantification
2.4. Study Part 2: Centrifugation Tube Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
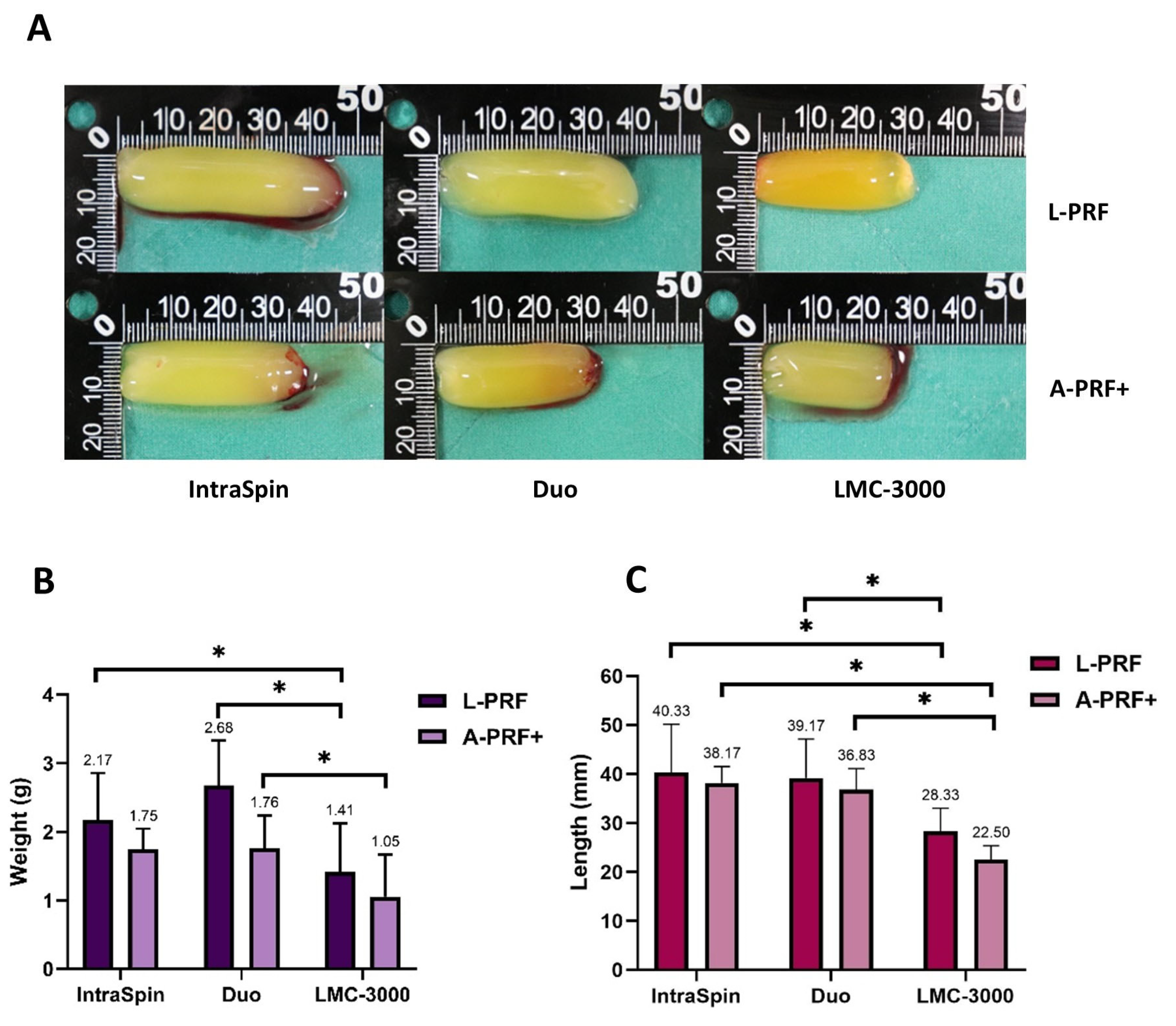
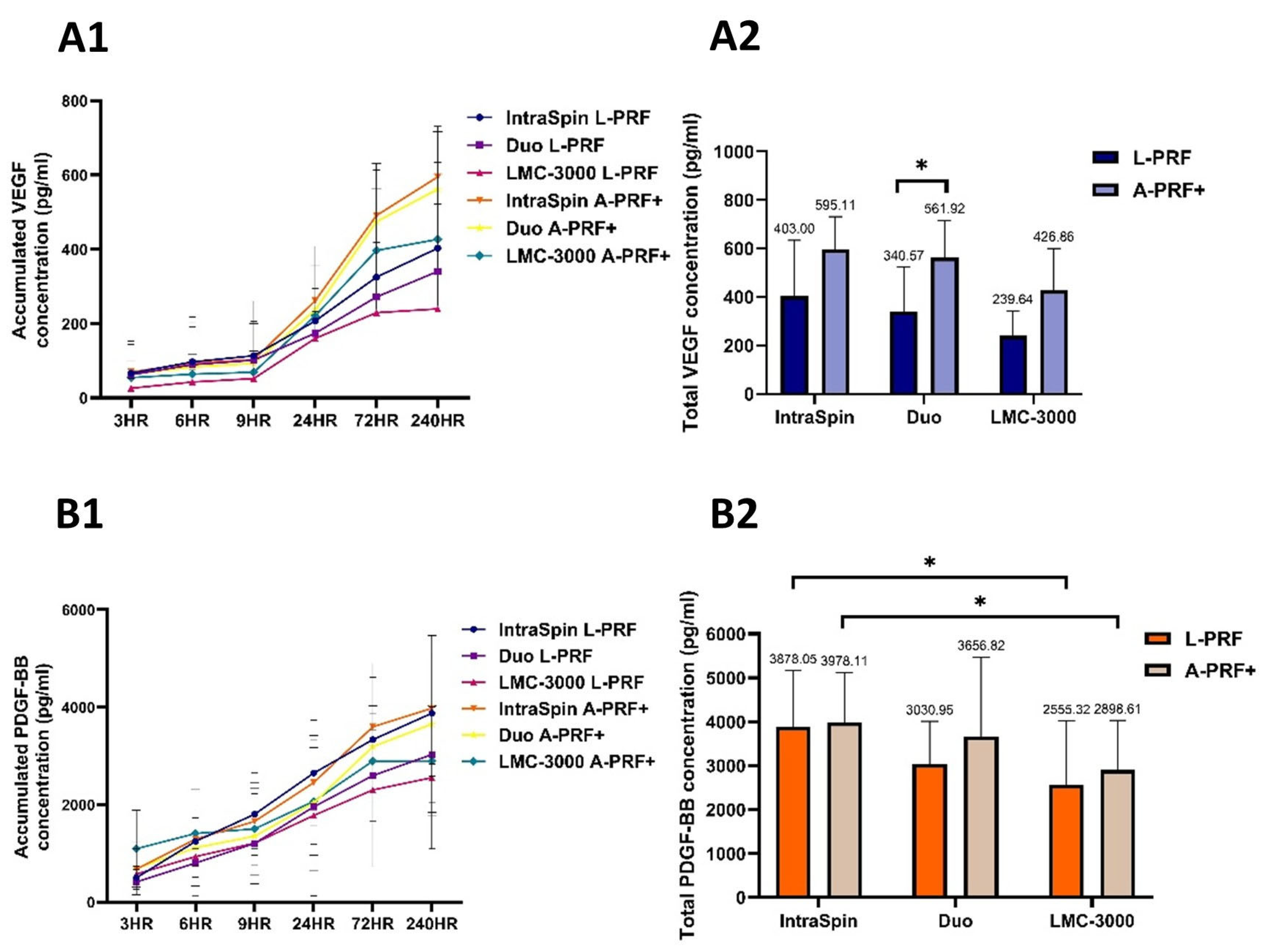
3.1. Study Part 1: Centrifugation Analysis
3.1.1. Macroscopic Analysis
3.1.2. SEM Analysis
3.1.3. Release of Growth Factors
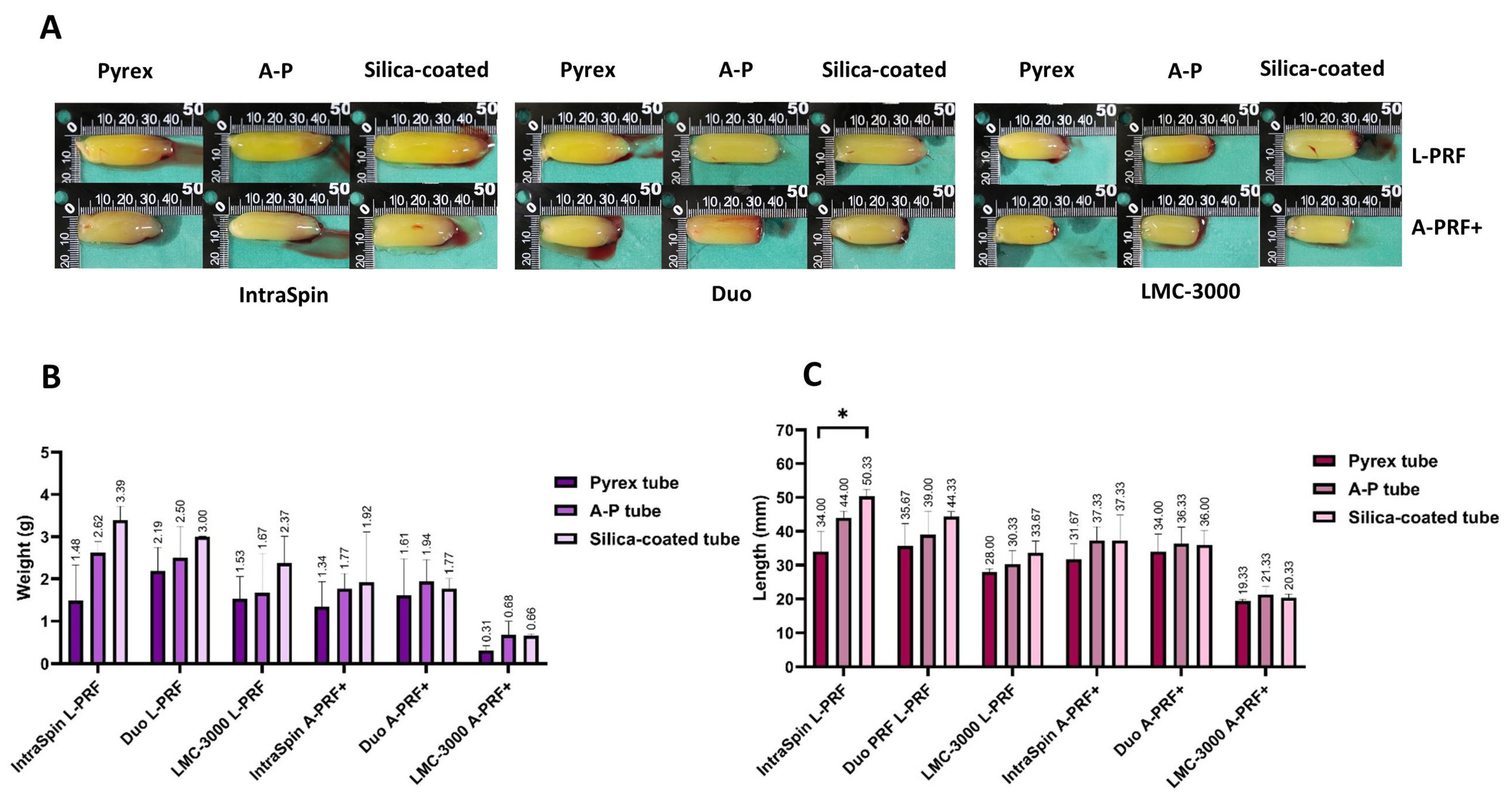
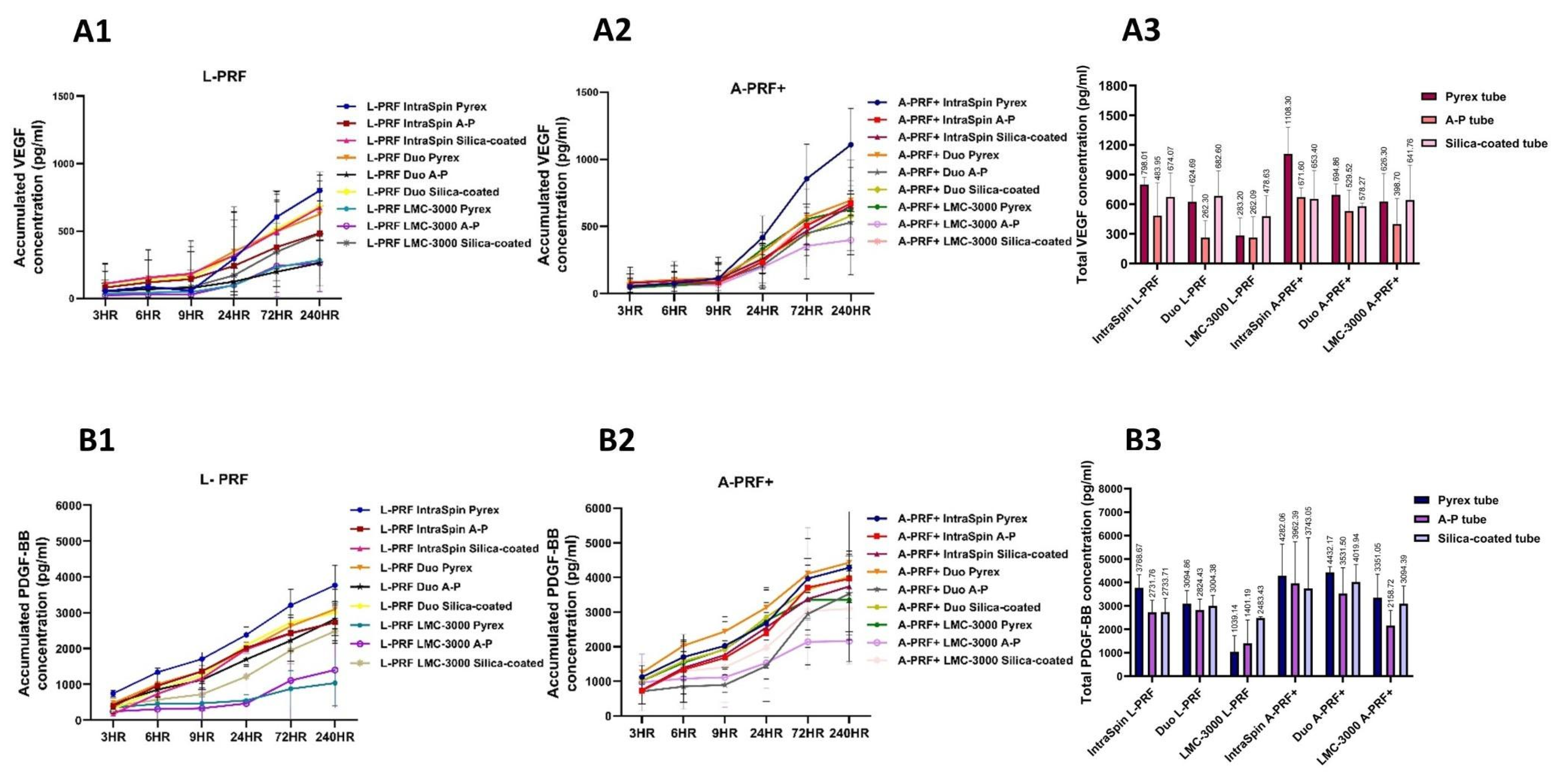
3.2. Study Part 2: Centrifugation Tube Analysis
3.2.1. Macroscopic Analysis
3.2.2. Release of Growth Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartold, M.; Ivanovski, S. Biological Processes and Factors Involved in Soft and Hard Tissue Healing. Periodontol. 2000 2025, 97, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E.; Carlson, E.R.; Eichstaedt, R.M.; Schimmele, S.R.; Strauss, J.E.; Georgeff, K.R. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Growth Factor Enhancement for Bone Grafts. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshidfar, N.; Amiri, M.A.; Estrin, N.E.; Ahmad, P.; Sculean, A.; Zhang, Y.; Miron, R.J. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) versus Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (i-PRF): A Systematic Review across All Fields of Medicine. Periodontol. 2000 2025, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acerra, A.; Caggiano, M.; Chiacchio, A.; Scognamiglio, B.; D’Ambrosio, F. PRF and PRP in Dentistry: An Umbrella Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.C.; Lana, G.L.; Santos, G.S.; Visoni, S.B.C.; Brigagão, R.J.; Santos, N.; Sobreiro, R.; da Cruz Silva Reis, A.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Ferrari, S.; et al. The Biological Role of Platelet Derivatives in Regenerative Aesthetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oneto, P.; Etulain, J. PRP in Wound Healing Applications. Platelets 2021, 32, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukroun, J.; Adda, F.; Schoeffler, C.; Vervelle, A. Une Opportunité en Paro-Implantologie: Le PRF. Implantodontie 2001, 42, 55–62. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Dohan, D.M.; Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Gogly, B. Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): A Second-Generation Platelet Concentrate. Part I: Technological Concepts and Evolution. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, e37–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calciolari, E.; Dourou, M.; Akcali, A.; Donos, N. Differences between First- and Second-Generation Autologous Platelet Concentrates. Periodontol. 2000 2025, 97, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Barahona, M.; Castillo, J.; Freire-Meza, E.; Vásquez-Palacios, A.C.; Morales-Navarro, D.; Avecillas-Rodas, R. Radiographic Evaluation in Alveolar Preservation Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Chen, W.; Fang, M.; Peters, O.A.; Hosseinpour, S. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Autologous Platelet-Rich Products in Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walch, B.; Kolk, A.; Scheibl, D.; Guarda, M.; Maier, S.C.; Denk, L. The Effect of Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Plus (A-PRF+) on Graft Stability in Dental Implants and Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Procedures: A New Low-Speed Standardized Centrifugation Protocol. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanaati, S.; Booms, P.; Orlowska, A.; Kubesch, A.; Lorenz, J.; Rutkowski, J.; Landes, C.; Sader, R.; Kirkpatrick, C.; Choukroun, J. Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A New Concept for Cell-Based Tissue Engineering by Means of Inflammatory Cells. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.; Flückiger, L.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Sawada, K.; Sculean, A.; Schaller, B.; Miron, R.J. Comparative Release of Growth Factors from PRP, PRF, and Advanced-PRF. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Miron, R.J.; Hernandez, M.; Kandalam, U.; Zhang, Y.; Choukroun, J. Optimized Platelet-Rich Fibrin with the Low-Speed Concept: Growth Factor Release, Biocompatibility, and Cellular Response. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bagdadi, K.; Kubesch, A.; Yu, X.; Al-Maawi, S.; Orlowska, A.; Dias, A.; Booms, P.; Dohle, E.; Sader, R.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; et al. Reduction of Relative Centrifugal Forces Increases Growth Factor Release within Solid Platelet-Rich-Fibrin (PRF)- Based Matrices: A Proof of Concept of LSCC (Low Speed Centrifugation Concept). Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2019, 45, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukroun, J.; Ghanaati, S. Introducing the Low-Speed Centrifugation Concept. In Platelet Rich Fibrin in Regenerative Dentistry: Biological Background and Clinical Indications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 33–46. ISBN 978-1-119-40679-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Pinto, N.R.; Pereda, A.; Jiménez, P.; Corso, M.D.; Kang, B.-S.; Nally, M.; Lanata, N.; Wang, H.-L.; Quirynen, M. The Impact of the Centrifuge Characteristics and Centrifugation Protocols on the Cells, Growth Factors, and Fibrin Architecture of a Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) Clot and Membrane. Platelets 2018, 29, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.; Choukroun, J.; Ghanaati, S. Controversies Related to Scientific Report Describing G-Forces from Studies on Platelet-Rich Fibrin: Necessity for Standardization of Relative Centrifugal Force Values. Int. J. Growth Factors Stem Cells Dent. 2018, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Xu, H.; Chai, J.; Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Feng, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; de Almeida Barros Mourão, C.F.; et al. Comparison of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Produced Using 3 Commercially Available Centrifuges at Both High (~700 g) and Low (~200 g) Relative Centrifugation Forces. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Vizcaino, C. Systematic Review of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Centrifugation Protocols in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and the Introduction of AR2T3: An Easy to Remember Acronym to Correctly Report Vertical and Horizontal PRF Centrifugation. Front. Oral Maxillofac. Med. 2023, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Del Corso, M.; Diss, A.; Mouhyi, J.; Charrier, J.-B. Three-Dimensional Architecture and Cell Composition of a Choukroun’s Platelet-Rich Fibrin Clot and Membrane. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Dham, A.; Dham, U.; Zhang, Y.; Pikos, M.A.; Sculean, A. The Effect of Age, Gender, and Time between Blood Draw and Start of Centrifugation on the Size Outcomes of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Membranes. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.B.; Andrade, C.; Li, X.; Pinto, N.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Impact of g Force and Timing on the Characteristics of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maawi, S.; Dohle, E.; Kretschmer, W.; Rutkowski, J.; Sader, R.; Ghanaati, S. A Standardized g-Force Allows the Preparation of Similar Platelet-Rich Fibrin Qualities Regardless of Rotor Angle. Tissue Eng. Part A 2022, 28, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, S.; Shen, K.; Miron, R.J.; Zhang, Y. Antibacterial Effects of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Produced by Horizontal Centrifugation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubesch, A.; Barbeck, M.; Al-Maawi, S.; Orlowska, A.; Booms, P.F.; Sader, R.A.; Miron, R.J.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Choukroun, J.; Ghanaati, S. A Low-Speed Centrifugation Concept Leads to Cell Accumulation and Vascularization of Solid Platelet-Rich Fibrin: An Experimental Study in Vivo. Platelets 2019, 30, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, E.S.; Alves, G.G.; Barbosa, R.; Spiegel, C.N.; Mello-Machado, R.C.; Al-Maawi, S.; Ghanaati, S.; de Almeida Barros Mourão, C.F. Effects of Rotor Angle and Time after Centrifugation on the Biological in Vitro Properties of Platelet Rich Fibrin Membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheno, E.; de Almeida Barros Mourão, C.F.; Mello-Machado, R.C.; Lourenço, E.S.; Miron, R.J.; Catarino, K.F.F.; Calasans-Maia, M.D. In Vivo Evaluation of the Biocompatibility and Biodegradation of a New Denatured Plasma Membrane Combined with Liquid PRF (Alb-PRF). Platelets 2020, 32, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Kono, M.; Katagiri, H.; Schaller, B.; Zhang, Y.; Sculean, A.; Miron, R.J. Histological Comparison of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Clots Prepared by Fixed-Angle Versus Horizontal Centrifugation. Platelets 2021, 32, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan, D.M.; Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Gogly, B. Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): A Second-Generation Platelet Concentrate. Part III: Leucocyte Activation: A New Feature for Platelet Concentrates? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, e51–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Chai, J.; Zheng, S.; Feng, M.; Sculean, A.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Method for Evaluating and Quantifying Cell Types in Platelet Rich Fibrin and an Introduction to Horizontal Centrifugation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 2257–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujino, T.; Takahashi, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Isobe, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nakata, K.; Kawase, T. Evidence for Contamination of Silica Microparticles in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices Prepared Using Silica-Coated Plastic Tubes. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujino, T.; Masuki, H.; Nakamura, M.; Isobe, K.; Kawabata, H.; Aizawa, H.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, H.; Okuda, K.; et al. Striking Differences in Platelet Distribution between Advanced-Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Concentrated Growth Factors: Effects of Silica-Containing Plastic Tubes. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; de Peppo, G.M.; Doglioli, P.; Sammartino, G. Slow Release of Growth Factors and Thrombospondin-1 in Choukroun’s Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): A Gold Standard to Achieve for All Surgical Platelet Concentrates Technologies. Growth Factors 2009, 27, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuki, H.; Isobe, K.; Kawabata, H.; Tsujino, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Sato, A.; Aizawa, H.; Mourão, C.F.; Kawase, T. Acute Cytotoxic Effects of Silica Microparticles Used for Coating of Plastic Blood-Collection Tubes on Human Periosteal Cells. Odontology 2020, 108, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Kawase, T.; Dham, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Sculean, A. A Technical Note on Contamination from PRF Tubes Containing Silica and Silicone. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Centrifuge | IntraSpin | Duo | LMC-3000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Fixed Angle) | (Fixed Angle) | (Swing-Out Horizontal) | |
| Radius at RCF-max | 85 mm | 110 mm | 160 mm |
| High RCF (L-PRF) Low RCF (A-PRF+) | 2700 RPM = 693× g 1450 RPM = 200× g (used in study 1500 RPM) | 2385 RPM = 700× g (used in study 2400 RPM) 1300 RPM = 207× g | 1978 RPM = 700× g (used in study 2000 RPM) 1057 RPM = 200× g (used in study 1100 RPM) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bunyatratchata, O.; Nimlamool, W.; Sangin, S. The Impact of Centrifugation Devices and Collection Tubes on Fibrin Characteristics and Growth Factor Release Under High- and Low-Speed Protocols. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100476
Bunyatratchata O, Nimlamool W, Sangin S. The Impact of Centrifugation Devices and Collection Tubes on Fibrin Characteristics and Growth Factor Release Under High- and Low-Speed Protocols. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(10):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100476
Chicago/Turabian StyleBunyatratchata, Oranit, Wutigri Nimlamool, and Supatra Sangin. 2025. "The Impact of Centrifugation Devices and Collection Tubes on Fibrin Characteristics and Growth Factor Release Under High- and Low-Speed Protocols" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 10: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100476
APA StyleBunyatratchata, O., Nimlamool, W., & Sangin, S. (2025). The Impact of Centrifugation Devices and Collection Tubes on Fibrin Characteristics and Growth Factor Release Under High- and Low-Speed Protocols. Dentistry Journal, 13(10), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100476






