Evaluating the Clinical Success of Clear Aligners for Rotational Tooth Movements in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
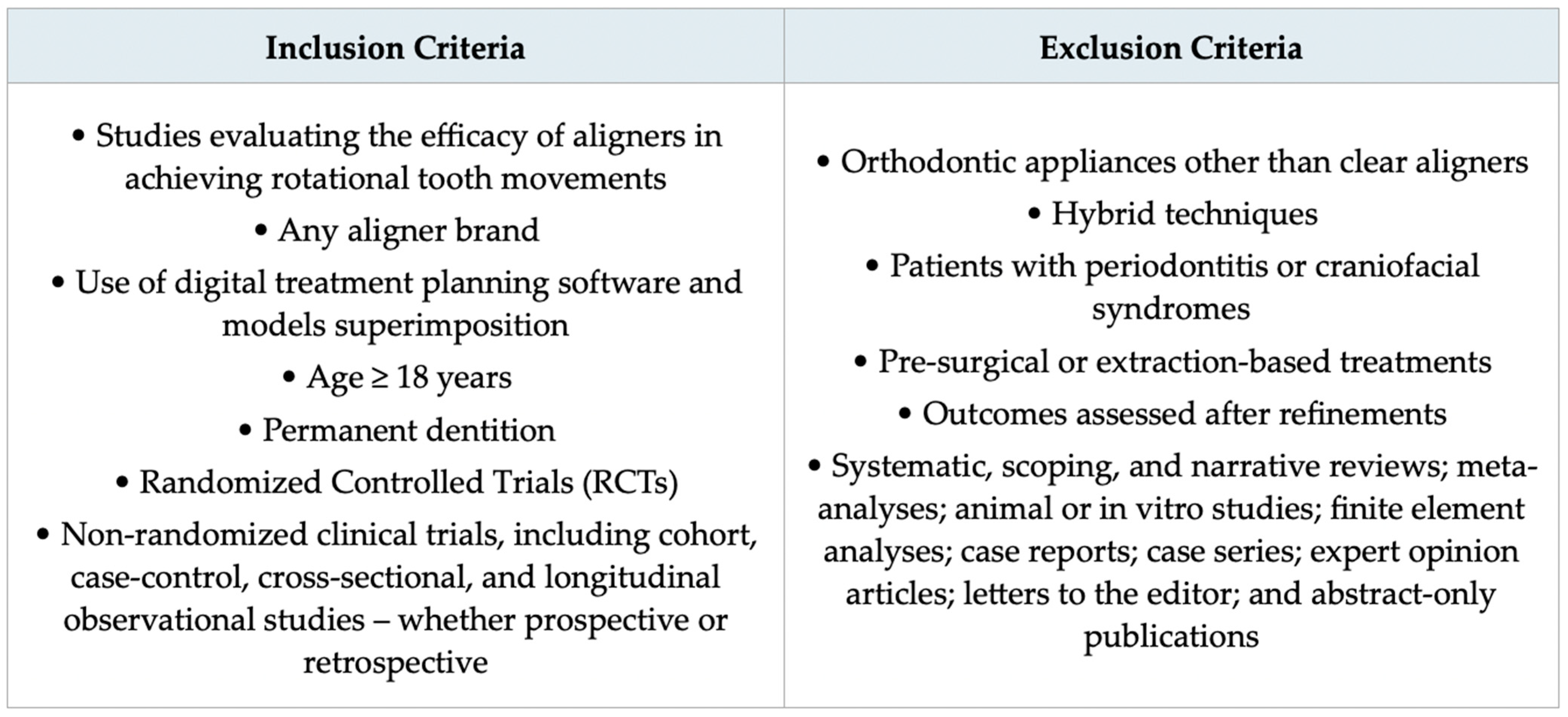
- Population: orthodontic patients undergoing CAT;
- Intervention: predicted rotational tooth movement on the virtual treatment plan;
- Comparison: achieved rotational tooth movement;
- Outcome: accuracy of the rotation.
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Selection of Sources of Evidence
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Charting Process
- First author and year of publication, country, study design, sample size, average age, and participant gender;
- Aligner system, teeth assessed, superimposition software, mean planned and achieved rotation, and accuracy of movement;
- Use and type of attachments, presence of IPR, mean number of aligners, staging protocol, wear schedule (days), and mean treatment duration.
2.7. Dealing with Missing Data
2.8. Synthesis of Results
3. Results
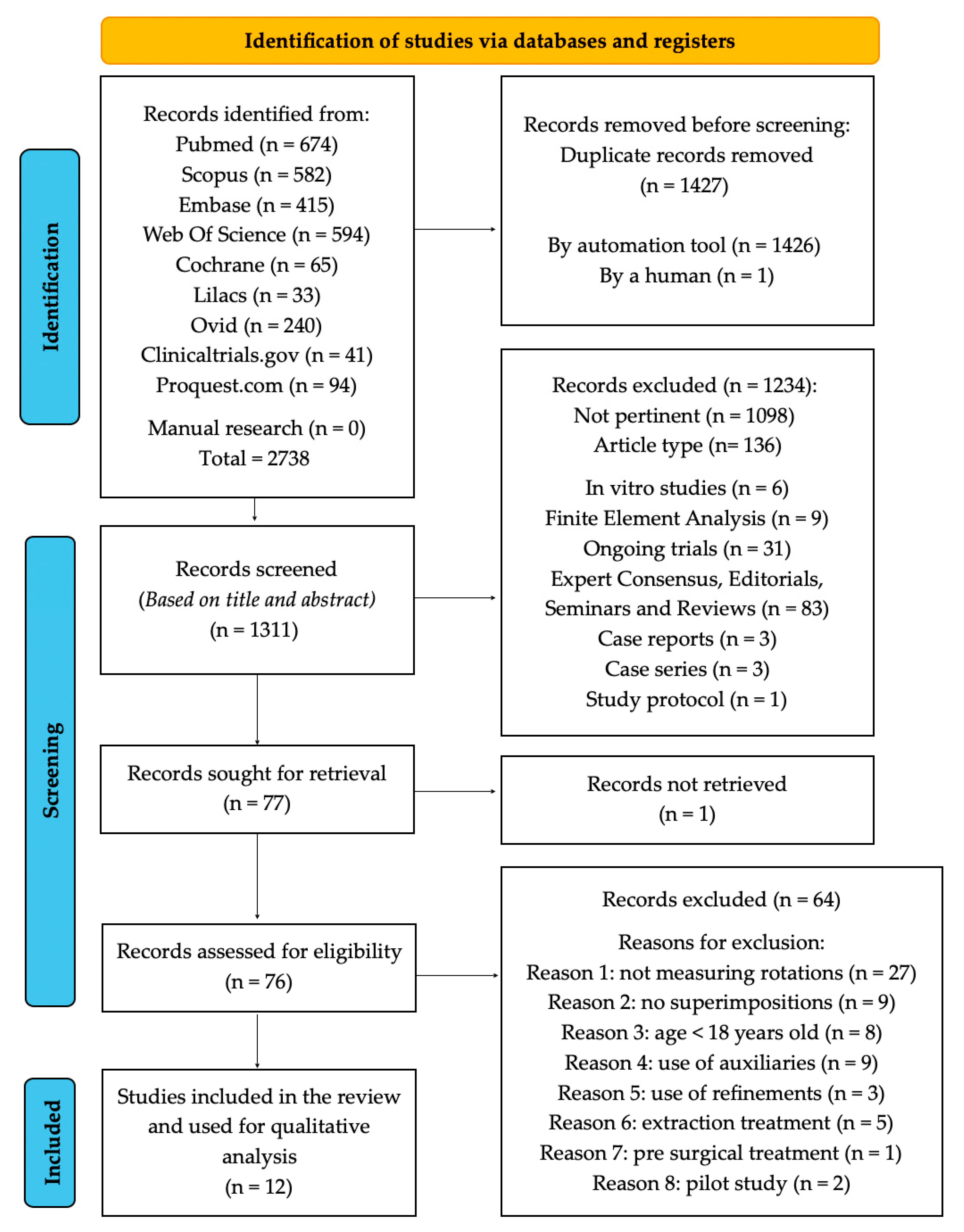
3.1. Selection of Sources of Evidence
3.2. Characteristics of Sources of Evidence
| First Author, Year (Reference) | Country | Study Design | Sample Size (n° of Patients) | Average Age (Years) | Gender of Participants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Nadawi 2021 [38] | USA | RCT | 89 | 35.4 | 30 M, 45 F |
| Castroflorio 2023 [39] | Italy | Prospective | 79 | 30.8 ± 12 | 23 M, 56 F |
| D’Antò 2024 [40] | Italy | Prospective | 45 | 29.2 ± 6.6 | 21 M, 24 F |
| Ghislanzoni 2024 [41] | Italy | Prospective | 21 | 20.1 ± 1.9 | 9 M, 12 F |
| Kravitz 2008 [42] | USA | Prospective | 31 | 29.4 | 13 M, 18 F |
| Lombardo 2017 [43] | Italy | Retrospective | 16 | 28.7 | 6 M, 10 F |
| Maree 2022 [44] | Australia | Retrospective | 30 | N/R | N/R |
| Medeiros 2024 [45] | Brazil | Retrospective | 56 | 33 | 17 M, 39 F |
| Mario 2024 [46] | Italy | Retrospective | 120 | 35.2 ± 7.4 | 64 M, 56 F |
| Sachdev 2021 [47] | Thailand | Prospective | 30 | 31.8 | 10 M, 20 F |
| Sorour 2022 [48] | India | Retrospective | 62 | 33 | 19 M, 43 F |
| Taebi-Harandy 2023 [49] | USA | Retrospective | 32 | 34.52 ± 11.3 | 3 M, 29 F |
3.3. Results of Individual Sources of Evidence
- Primary outcome
3.3.1. Aligner System Used
3.3.2. Teeth Assessed
3.3.3. Superimposition Software
3.3.4. Mean Planned Rotation and Mean Achieved Rotation
3.3.5. Percent Accuracy
3.3.6. Lack of Correction (LC)
3.3.7. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
3.3.8. Rotational Accuracy by Tooth Type
- Secondary outcomes
3.3.9. Attachments
3.3.10. Interproximal Reduction (IPR)
3.3.11. Rotation Rate and Mean Number of Aligners
3.3.12. Days of Aligner Wear and Average Treatment Duration
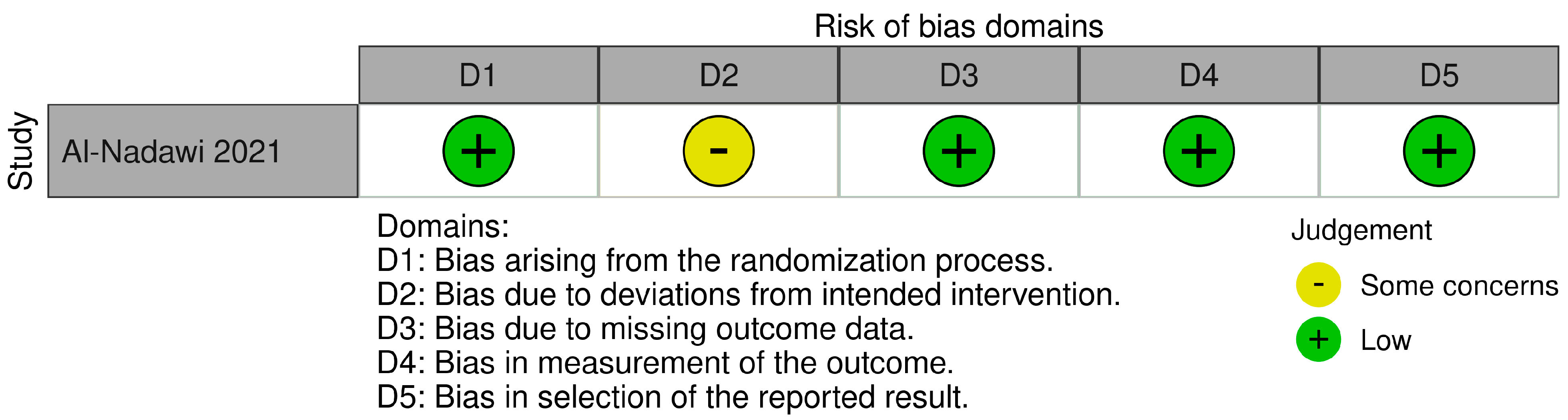
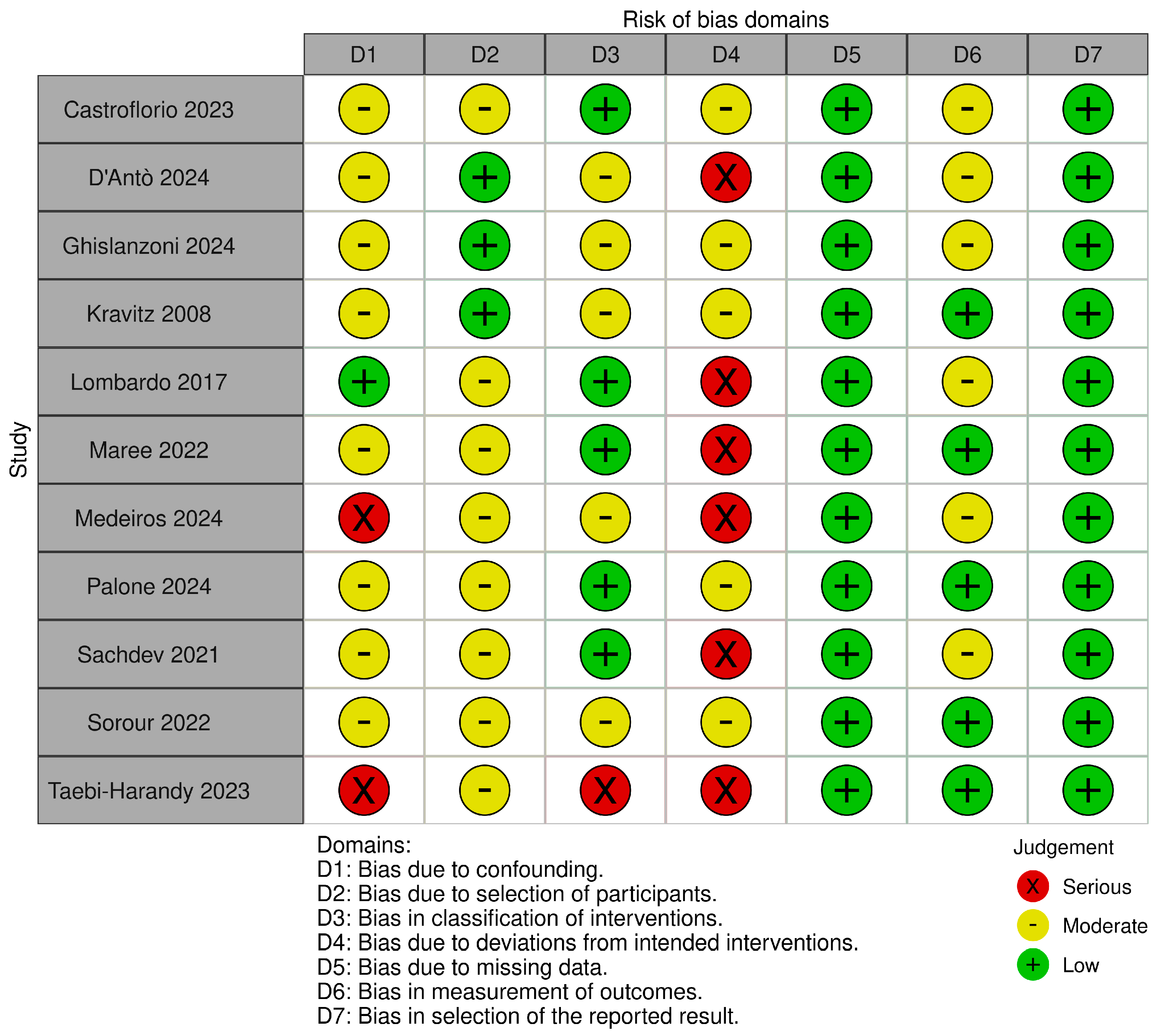
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.4.1. RoB 2
3.4.2. ROBINS-I
3.4.3. GRADE
3.5. Synthesis of the Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence and Comparison with Existing Literature
4.1.1. Tooth Type
4.1.2. Attachments
4.1.3. Interproximal Reduction (IPR)
4.1.4. Staging
4.1.5. Materials and Aligner System Used
4.1.6. Aligner Wear Protocols
4.1.7. Additional Strategies to Enhance Rotational Predictability with CAT
4.2. Study Limitations
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
- Overall, rotational accuracy was suboptimal across studies, with considerable variability across studies and no investigation reporting complete correspondence between planned and achieved rotation. However, a progressive improvement in performance was observed in more recent studies, likely related to advances in materials, digital planning, and clinical protocols.
- Tooth-specific performance varies significantly, with incisors and molars showing generally higher accuracy compared to “round-shaped teeth”, especially maxillary canines and premolars.
- The role of attachments and interproximal enamel reduction (IPR) is potentially relevant, but current evidence remains inconclusive. Considerable heterogeneity in study protocols and insufficient standardization prevent reliable comparisons and preclude definitive conclusions on the isolated contribution of each factor.
- Staging emerges as a critical factor in improving rotational control: values below 1.5° per aligner are associated with enhanced accuracy, although most studies employed a staging of approximately 2° per stage.
- Other strategies, such as planned overcorrections and refinements, may enhance rotational control but require further validation.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kesling, H.D. The Philosophy of the Tooth Positioning Appliance. Am. J. Orthod. Oral Surg. 1945, 31, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Efficacy of Clear Aligners in Controlling Orthodontic Tooth Movement: A Systematic Review. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroflorio, T.; Parrini, S.; Rossini, G. Aligner Biomechanics: Where We Are Now and Where We Are Heading For. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2024, 13, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Sun, X.; Lu, J.; Teng, L.; Bai, Y.; Xie, X. Twenty Years of Clear Aligner Therapy: A Bibliometric Analysis (2002–2022). Australas. Orthod. J. 2023, 39, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.; Derakhshan, M.; Kaza, S.; Li, C. Design of the Invisalign System Performance. Semin. Orthod. 2017, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, S.; De Felice, M.E.; Valenti, C.; Pagano, S.; Caruso, S.; Gatto, R.; Lombardo, G. An Evaluation of the Invisalign® Aligner Technique and Consideration of the Force System: A Systematic Review. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Arqub, S.A. Biomechanics of Clear Aligners: Hidden Truths & First Principles. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2022, 11, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan-Lopez, L.; Barcia-Gonzalez, J.; Plasencia, E. A Systematic Review of the Accuracy and Efficiency of Dental Movements with Invisalign®. Korean J. Orthod. 2019, 49, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassir, Y.A.; Nabbat, S.A.; McIntyre, G.T.; Bearn, D.R. Clinical Effectiveness of Clear Aligner Treatment Compared to Fixed Appliance Treatment: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 2353–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneshi, M.; O’Malley, L.; El-Angbawi, A.; Thiruvenkatachari, B. Effectiveness of Clear Orthodontic Aligners in Correcting Malocclusions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Evid.-Based Dent. Pract. 2025, 25, 102081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, S.; Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, H. Risk Factors for Midcourse Correction during Treatment of First Series of Aligners with Invisalign. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 162, e96–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S. Improving the Predictability of Clear Aligners. Semin. Orthod. 2017, 23, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Machado, V.; Botelho, J.; Proença, L.; Mendes, J.J.; Delgado, A.S. Comparison of Pain Perception between Clear Aligners and Fixed Appliances: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, A.; Suárez-Fernández, C.; Miquel, A.; Bardini, G.; Spinas, E. Biological Effects of Orthodontic Tooth Movement on the Periodontium in Regenerated Bone Defects: A Scoping Review. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Periodontal Health during Clear Aligners Treatment: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Orthod. 2015, 37, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, J.; Mei, L.; Du, J.; Levrini, L.; Abbate, G.M.; Li, H. Periodontal Health during Orthodontic Treatment with Clear Aligners and Fixed Appliances: A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2018, 149, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.; Koletsi, D.; Iliadi, A.; Peltomaki, T.; Eliades, T. Treatment Outcome with Orthodontic Aligners and Fixed Appliances: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses. Eur. J. Orthod. 2020, 42, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, R.; Ni, Z.; Yu, Z. Efficiency, Effectiveness and Treatment Stability of Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2017, 20, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; Awawdeh, M.; Alhazmi, N.; Alamoud, K.A.; Iyer, K.; Abutayyem, H.; Alswairki, H.J.; Hajeer, M.Y. A Systematic Review of Interventions-Does Invisalign Move Teeth as Effectively as Orthodontic Fixed Appliances? Scientifica 2024, 2024, 4268902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipani, E.; Pisani, E.; Verrone, M.; Bitonto, F.; Verdecchia, A.; Spinas, E. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Corticotomy and Piezocision on Canine Retraction: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminian, A.; Garino, F.; Castroflorio, T.; Younessian, F. Biomechanics of Tooth Rotation in Clear Aligner Therapy. In Seminars in Orthodontics; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwafi, A.; Bichu, Y.M.; Avanessian, A.; Zou, B. Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Assessing the Predictability and Clinical Effectiveness of Clear Aligner Therapy. Dent. Rev. 2023, 3, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichu, Y.M.; Weir, T.; Zou, B.; Adel, S.; Vaid, N.R. Clear Aligner Therapy Concerns: Addressing Discrepancies Between Digitally Anticipated Outcomes and Clinical Ground Realities. Turk. J. Orthod. 2024, 37, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletsi, D.; Iliadi, A.; Eliades, T. Predictability of Rotational Tooth Movement with Orthodontic Aligners Comparing Software-Based and Achieved Data: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Orthod. 2021, 48, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, S.; Lee, R. The Predictability of Tooth Movement with Clear Aligner Systems. In Seminars in Orthodontics; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamenis, S.C.; Deshmukh, S.; Bhosale, V.; Rodrigues, L.; Agrawal, J.; Agrawal, M.S.; Umalkar, D. An Umbrella Review for Assessment of Treatment Effectiveness of Clear Aligners Compared to Conventional Fixed Appliances in Orthodontic Patients. J. Indian Orthod. Soc. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, D.; Farella, M. Methodological Issues in Current Clear Aligner Research. In Seminars in Orthodontics; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMogbel, A.; Alshawy, E.S.; Alhusainy, A. Efficacy of Clear Aligner Therapy over Conventional Fixed Appliances in Controlling Orthodontic Movement: A Systematic Review. J. Orthod. Sci. 2024, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassia, V.; Fiori, A.; Diodati, F.; Sayahpour, B.; Jamilian, A.; Armogida, N.; d’Apuzzo, F.; Nucci, L. Clear Aligners: A Network and Bibliometric Analysis of 50 Pivotal Articles. Dent. Med. Probl. 2025, 62, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, A.; Serra, F.G.; Gallo, V.; Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T. The 50 Most-Cited Articles on Clear Aligner Treatment: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, e343–e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J.; GRADE Working Group. GRADE: An Emerging Consensus on Rating Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Atkins, D.; Brozek, J.; Vist, G.; Alderson, P.; Glasziou, P.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE Guidelines: 2. Framing the Question and Deciding on Important Outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balshem, H.; Helfand, M.; Schünemann, H.J.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Meerpohl, J.; Norris, S.; et al. GRADE Guidelines: 3. Rating the Quality of Evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nadawi, M.; Kravitz, N.; Hansa, I.; Makki, L.; Ferguson, D.; Vaid, N. Effect of Clear Aligner Wear Protocol on the Efficacy of Tooth Movement. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroflorio, T.; Sedran, A.; Parrini, S.; Garino, F.; Reverdito, M.; Capuozzo, R.; Mutinelli, S.; Grybauskas, S.; Vaitiekūnas, M.; Deregibus, A. Predictability of Orthodontic Tooth Movement with Aligners: Effect of Treatment Design. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antò, V.; Rongo, R.; Casaburo, S.D.; Martina, S.; Petrucci, P.; Keraj, K.; Valletta, R. Predictability of Tooth Rotations in Patients Treated with Clear Aligners. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislanzoni, L.H.; Kalemaj, Z.; Manuelli, M.; Magni, C.; Polimeni, A.; Lucchese, A. How Well Does Invisalign ClinCheck Predict Actual Results: A Prospective Study. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2024, 27, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, N.; Kusnoto, B.; Agran, B.; Viana, G. Influence of Attachments and Interproximal Reduction on the Accuracy of Canine Rotation with Invisalign. A Prospective Clinical Study. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Arreghini, A.; Ramina, F.; Huanca Ghislanzoni, L.T.; Siciliani, G. Predictability of Orthodontic Movement with Orthodontic Aligners: A Retrospective Study. Prog. Orthod. 2017, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maree, A.; Kerr, B.; Weir, T.; Freer, E. Clinical Expression of Programmed Rotation and Uprighting of Bilateral Winged Maxillary Central Incisors with the Invisalign Appliance: A Retrospective Study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 161, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, R.B.; Santos, R.F.; Mendes-Miguel, J.A.; Rothier, E.K.C.; Mendes, F.M.; Dominguez, G.C. Accuracy of Invisalign® Aligners in Adult Patients: A Retrospective Study of Angular Tooth Movements. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2024, 29, e2423237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mario, P.; de Villagomez, S.S.; Federica, P.; Cremonini, F.; Salvatore, R.; Lombardo, L. Evaluation of Tooth Movement Accuracy with the F22 Aligner System: A Retrospective Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, S.; Tantidhnazet, S.; Saengfai, N.N. Accuracy of Tooth Movement with In-House Clear Aligners. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2021, 10, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorour, H.; Fadia, D.; Ferguson, D.J.; Makki, L.; Adel, S.; Hansa, I.; Vaid, N.R. Efficacy of Anterior Tooth Simulations with Clear Aligner Therapy—A Retrospective Cohort study of Invisalign and Flash Aligner Systems. Open Dent. J. 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taebi-Harandy, M.; Mehta, S.; Warren, E.; Feldman, J.; Yadav, S. Outcomes Associated with 3M Clarity Aligners. J. Clin. Orthod. 2023, 57, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Grünheid, T.; Loh, C.; Larson, B.E. How Accurate Is Invisalign in Nonextraction Cases? Are Predicted Tooth Positions Achieved? Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lione, R.; Paoloni, V.; De Razza, F.C.; Pavoni, C.; Cozza, P. Analysis of Maxillary First Molar Derotation with Invisalign Clear Aligners in Permanent Dentition. Life 2022, 12, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Singh, M.; Karkazis, E.; Liu, D.; Nimeri, G.; Ahuja, B. Efficacy of Invisalign Attachments: A Retrospective Study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 160, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Kaur, H.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Romanyk, D.; Major, P.; Flores Mir, C. Effectiveness of Clear Aligner Therapy for Orthodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorati, M.; Drago, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Pesce, P.; Battista, G.; Campobasso, A.; Gastaldi, G.; Valvecchi, F.F.; Mari, A.D. Accuracy of Orthodontic Movements with 3D Printed Aligners: A Prospective Observational Pilot Study. Korean J. Orthod. 2024, 54, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Lee, S.; Scharm, J.; Kim, S.; Amin, A.; Wu, T.; Lu, W.; Ni, A.; Ko, C.; Fields, H.; et al. Comparison of Maxillary Anterior Tooth Movement between Invisalign and Fixed Appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 164, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, G.; Campobasso, A.; Croce, S.; Hussain, U.; Battista, G.; Lo Muzio, E.; Mandelli, G.; Ambrosi, A.; Gastaldi, G. Accuracy of Clear Aligners in the Orthodontic Rotational Movement Using Different Attachment Configurations. Orthod. Craniofac. Res 2024, 27, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilello, G.; Fazio, M.; Amato, E.; Crivello, L.; Galvano, A.; Currò, G. Accuracy Evaluation of Orthodontic Movements with Aligners: A Prospective Observational Study. Prog. Orthod. 2022, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedliński, M.; Mazur, M.; Greco, M.; Belfus, J.; Grocholewicz, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. Attachments for the Orthodontic Aligner Treatment-State of the Art-A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khursheed Alam, M.; Hajeer, M.Y.; Shqaidef, A.; Alswairki, H.J.; Alfawzan, A.A.; Shrivastava, D.; Chandan Srivastava, K.; Cicciù, M.; Minervini, G. Impact of Various Aligner Auxiliaries on Orthodontic Activity: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Saudi Dent. J. 2024, 36, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, L.; Albertini, P.; Siciliani, V. The Hybrid Approach: A Solution to Overcome Unpredictable Movements in Clear Aligner Therapy. APOS Trends Orthod. 2020, 10, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, F.; Mikhaiel, B.; Schmidt, F.; Lapatki, B.G. Mechanical Load Exerted by PET-G Aligners during Mesial and Distal Derotation of a Mandibular Canine: An in Vitro Study. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2017, 78, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, F.; Sang, T.; Wu, J. Factors Affecting the Efficacy of Invisalign in Anterior Tooth Rotation. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 163, 540–552.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mohimd, H.; Oualalou, Y.; Zaoui, F.; Houb-Dine, A.; Benyahia, H. Attachment Geometry and Clinical Predictability in Aligner Treatment: A Systematic Review. APOS Trends Orthod. 2025, 15, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlias, N.; Dalstra, M.; Cornelis, M.; Cattaneo, P. In Vitro Comparison of Different Invisalign® and 3Shape® Attachment Shapes to Control Premolar Rotation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 840622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, W.; Engelke, B.; Jung, K.; Dathe, H.; Fialka-Fricke, J.; Kubein-Meesenburg, D.; Sadat-Khonsari, R. Initial Forces and Moments Delivered by Removable Thermoplastic Appliances during Rotation of an Upper Central Incisor. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandis, N.; Polychronopoulou, A.; Eliades, T. Sample Size Estimation: An Overview with Applications to Orthodontic Clinical Trial Designs. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 140, e141–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haouili, N.; Kravitz, N.D.; Vaid, N.R.; Ferguson, D.J.; Makki, L. Has Invisalign Improved? A Prospective Follow-up Study on the Efficacy of Tooth Movement with Invisalign. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 158, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Burruezo, I.; Gandía-Franco, J.-L.; Cobo, J.; Vela-Hernández, A.; Bellot-Arcís, C. Arch Expansion with the Invisalign System: Efficacy and Predictability. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lozano, D.; Castellanos-Andrés, D.; López-Jiménez, A. Staging of Orthodontic Tooth Movement in Clear Aligner Treatment: Macro-Staging and Micro-Staging-A Narrative Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwafi, A.A.; Panther, S.; Lo, A.; Yen, E.H.; Zou, B. Measuring Maxillary Posterior Tooth Movement: A Model Assessment Using Palatal and Dental Superimposition. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 2024, e65531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antò, V.; Valletta, R.; Ferretti, R.; Bucci, R.; Kirlis, R.; Rongo, R. Predictability of Maxillary Molar Distalization and Derotation with Clear Aligners: A Prospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.T. Orthodontic Clear Aligner Treatment. Semin. Orthod. 2017, 23, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracchia, D.E.; Bignotti, D.; Lai, S.; Battista, E.; Verdecchia, A.; Spinas, E. Predictability of Lower Incisor Intrusion with Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Influencing Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Keilig, L.; Schwarze, J.; Jung, B.A.; Bourauel, C. Treatment Outcome and Efficacy of an Aligner Technique—Regarding Incisor Torque, Premolar Derotation and Molar Distalization. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, S.; Errica, M.F.; Cubeddu, S.; Curreli, F.; Salman, N.; Cobo, T.; Verdecchia, A.; Spinas, E. The Efficacy of Clear Aligners in Leveling the Curve of Spee: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.; Weir, T.; Llewellyn, S.; Freer, E.; Kerr, B. Clinical Expression of Programmed Mandibular Canine Rotation Using Various Attachment Protocols and 1- vs. 2-Week Wear Protocols with Invisalign SmartTrack Aligners: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 162, e103–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, J.J. The Readers’ Corner. Invisalign. J. Clin. Orthod. 2014, 48, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Sultanoglu, E.; Gürel, H.; Gülyurt, M. The Effects of Different Attachment Types and Positions on Rotation Movement in Clear Aligner Treatments: A Finite Element Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e66273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucera, R.; Dolci, C.; Bellocchio, A.; Costa, S.; Barbera, S.; Rustico, L.; Farronato, M.; Militi, A.; Portelli, M. Effects of Composite Attachments on Orthodontic Clear Aligners Therapy: A Systematic Review. Materials 2022, 15, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.-F.; Xu, T.-M.; Shu, G. Comparison of Achieved and Predicted Tooth Movement of Maxillary First Molars and Central Incisors: First Premolar Extraction Treatment with Invisalign. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Hua, X.; Yang, L.; Aoki, K.; Shang, S.; Lin, D. A Systematic Review of Biomechanics of Clear Aligners by Finite Element Analysis. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Patel, D.; Yadav, S. Staging Orthodontic Aligners for Complex Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Turk. J. Orthod. 2021, 34, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lai, W.; Long, H. Determination of Optimal Incisor Overtreatment and Molar Anchorage Preparation for First-Premolar Extraction Patients Treated with Clear Aligners. Eur. J. Orthod. 2025, 47, cjaf049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Align Technology Introduces One-Week Aligner Wear for Invisalign(R) Teen and Full Products | Align Technology. Available online: https://investor.aligntech.com/news-releases/news-release-details/align-technology-introduces-one-week-aligner-wear-invisalignr/ (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Johal, A.; Bondemark, L. Clear Aligner Orthodontic Treatment: Angle Society of Europe Consensus Viewpoint. J. Orthod. 2021, 48, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortona, A.; Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T. Clear Aligner Orthodontic Therapy of Rotated Mandibular Round-Shaped Teeth: A Finite Element Study. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Si, J.; Xue, C.; Xu, H. Seeking Orderness out of the Orderless Movements: An up-to-Date Review of the Biomechanics in Clear Aligners. Prog. Orthod. 2024, 25, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, R.B.; Santos, R.F.; Mendes-Miguel, J.A.; Rothier, E.K.C.; Mendes, F.M.; Dominguez, G.C. Accuracy of Arch Expansion with Two Thermoplastic Materials in Invisalign® Patients: EX30® and SmartTrack®. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2024, 29, e2423212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.-S.; Park, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.-I. Force and Moment Analysis of Clear Aligners: Impact of Material Properties and Design on Premolar Rotation. Korean J. Orthod. 2025, 55, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, P.; Mazzanti, V.; Mollica, F.; Pellitteri, F.; Palone, M.; Lombardo, L. Stress Relaxation Properties of Five Orthodontic Aligner Materials: A 14-Day In-Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbauer, R.; Sabbagh, H.; Janjic Rankovic, M.; Becker, K. 3D Printed Orthodontic Aligners—A Scoping Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, J.R.; McGorray, S.P.; Nair, M.; Wheeler, T.T. Variables Affecting Orthodontic Tooth Movement with Clear Aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 145, S82–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, C.T.; McGorray, S.P.; Dolce, C.; Nair, M.; Wheeler, T.T. Orthodontic Tooth Movement with Clear Aligners. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 657973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M. A Comparison of Treatment Effectiveness between Clear Aligner and Fixed Appliance Therapies. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, J.; Peter, E. Efficacy of Clear Aligner Wear Protocols in Orthodontic Tooth Movement-a Systematic Review. Eur. J. Orthod. 2024, 46, cjae020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Mei, L.; Long, H.; Jian, F.; Lai, W. Changing Clear Aligners Every 10 Days or 14 Days? A Randomised Controlled Trial. Australas. Orthod. J. 2023, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, M. Conceptual Overcorrection in Orthodontics: A Strategy to Enhance Invisalign’s Effectiveness. AJO-DO Clin. Companion 2024, 4, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palone, M.; Pignotti, A.; Morin, E.; Pancari, C.; Spedicato, G.; Cremonini, F.; Lombardo, L. Analysis of Overcorrection to Be Included for Planning Clear Aligner Therapy: A Retrospective Study. Angle Orthod. 2023, 93, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Lin, D.; Yuan, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Hu, G.; Lai, W.; Long, H. Predictability of Tooth Derotation with Clear Aligners and Its Influencing Factors: A Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2025, 47, cjaf036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Arqub, S.; Banankhah, S.; Sharma, R.; Godoy, L.; Kuo, C.; Ahmed, M.; Alfardan, M.; Uribe, F. Association between Initial Complexity, Frequency of Refinements, Treatment Duration, and Outcome in Invisalign Orthodontic Treatment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 162, E141–E155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, G.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Ferrante, L.; Avantario, P.; Campanelli, M.; Palermo, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Dipalma, G. Temporary Anchorage Devices in Clear Aligner Therapy: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, N.R.; Sabouni, W.; Wilmes, B.; Bichu, Y.M.; Thakkar, D.P.; Adel, S.M. Customized Adjuncts with Clear Aligner Therapy: “The Golden Circle Model” Explained! J. World Fed. Orthod. 2022, 11, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Long, H.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, D.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Fang, B.; Jin, Z.; He, H.; Bai, Y.; et al. Expert Consensus on the Clinical Strategies for Orthodontic Treatment with Clear Aligners. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2025, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Kim, H.; Park, H. Micro-Implant Uprighting Cantilever for the Correction of a Severely Rotated and Angulated Mandibular Canine during Clear Aligner Treatment. Australas. Orthod. J. 2025, 41, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda Ladewig, V.; Miron Stefani, C.; De Luca Canto, G.; Pandis, N.; Flores-Mir, C. A Mapping Review of Systematic Reviews in Orthodontics: A Five-Year Analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2025, 47, cjaf040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, T. The Application of 3d Metrology Software in the Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Aligner Treatment Outcomes. Australas. Orthod. J. 2021, 37, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkow, K.Y. Efficacy of Invisalign: A Retrospective Case Series of Intrusion, Extrusion, and Rotation with Trend Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Marquette University, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chaluparambil, M.; Abu Arqub, S.; Kuo, C.-L.; Godoy, L.D.C.; Upadhyay, M.; Yadav, S. Age-Stratified Assessment of Orthodontic Tooth Movement Outcomes with Clear Aligners. Prog. Orthod. 2024, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy | Results |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (((((aligner*) OR (invisalign)) OR (spark)) OR (clearcorrect)) AND ((tooth movement[MeSH Terms]) OR (rotation[MeSH Terms]) OR (rotation*) OR (“tooth movement*”))) AND (((((((((treatment outcome[MeSH Terms]) OR (accuracy)) OR (predictability)) OR (predict*)) OR (efficacy)) OR (“planned movement*”)) OR (outcome*)) OR (discrepancy)) OR (efficacy)) Sort by: Most Recent | 674 |
| Scopus | (TITLE-ABS-KEY ((aligner* OR invisalign OR spark OR clearcorrect))) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“tooth movement*” OR rotation* OR “orthodontic movement*”)) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY (accuracy OR predictability OR predict* OR efficacy OR “planned movement*” OR outcome* OR discrepancy)) | 582 |
| Embase | (‘clear aligner*’ OR aligner* OR ‘invisalign’ OR ‘invisalign’/exp OR invisalign OR ‘spark’ OR ‘spark’/exp OR spark OR clearcorrect) AND (rotation* OR ‘tooth movement’/exp OR ‘tooth rotation’ OR ‘tooth rotation*’ OR ‘tooth movement*’ OR ‘orthodontic movement*’) AND (‘treatment outcome’/exp OR accuracy OR predictability OR predict* OR efficacy OR ‘planned movement*’ OR outcome* OR discrepancy) | 415 |
| Web Of Science | #1 ALL = (aligner* OR “clear aligner*” OR invisalign OR spark OR “clearcorrect”) #2 ALL = (rotation* OR “tooth rotation*” OR “tooth movement*” OR “orthodontic movement*”) #3 ALL = (“treatment outcome*” OR accuracy OR predictability OR predict* OR efficacy OR “planned movement*” OR outcome* OR discrepancy) #1 AND #2 AND #3 | 594 |
| Cochrane Library | #1 aligner* OR (clear NEXT aligner*) OR invisalign OR spark OR “clearcorrect” #2 rotation* OR (tooth NEXT rotation*) OR (tooth NEXT movement*) OR (orthodontic NEXT movement*) #3 (treatment NEXT outcome*) OR accuracy OR predictability OR predict* OR efficacy OR (planned NEXT movement*) OR outcome* OR discrepancy #1 AND #2 AND #3 | 65 |
| LILACs | (aligner* OR “clear aligner*” OR invisalign OR spark OR “clearcorrect”) AND (rotation* OR “tooth movement*” OR “tooth rotation*” OR “orthodontic movement*”) AND (“treatment outcome*” OR accuracy OR predictability OR predict* OR efficacy OR “planned movement*” OR outcome* OR discrepancy) | 33 |
| Ovid | #1 (aligner* or “clear aligner*” or Invisalign or Spark or “ClearCorrect”).mp. #2 Tooth Movement/or Rotation/or “tooth movement*”.tw. or rotation*.tw. or “orthodontic movement*”.tw. #3 Treatment Outcome/or “treatment outcome*”.tw. or accuracy.tw. or efficacy.tw. or predict*.tw. or “planned movement*”.tw. or outcome*.tw. or discrepancy.tw. #4 #1 AND #2 AND #3 | 240 |
| Clinicaltrials.gov | (clear aligner OR Invisalign OR aligner OR “clear aligners” OR Spark OR ClearCorrect) AND (tooth movement OR rotation OR orthodontic movement OR dental rotation) AND (accuracy OR efficacy OR predictability OR treatment outcome) | 41 |
| Proquest.com | abstract(clear aligner OR Invisalign OR aligner OR “clear aligners” OR Spark OR ClearCorrect) AND abstract(tooth movement OR rotation OR orthodontic movement OR dental rotation) AND abstract(accuracy OR efficacy OR predictability OR treatment outcome) | 94 |
| First Author, Year (Reference) | Aligner System Used | Teeth Assessed | Superimposition Software | Mean Planned Rotation (°) | Mean Achieved Rotation (°) | Percent Accuracy | LC | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Nadawi 2021 [38] | Invisalign (SmartTrack) | From central incisors to second molars, Mx and Mb | eModel Compare 9.0 | N/R | N/R | N/R | Group A: 2.88° Group B: 2.86° Group C: 2.54° | N/R |
| Castroflorio 2023 [39] | Invisalign | From central incisors to second molars, Mx and Mb | Geomagic Qualify | 7.24° | N/R | N/R | 2.93° | N/R |
| D’Antò 2024 [40] | Ordoline aligners | From central incisors to second molars, Mx and Mb | Geomagic Control X | 8.9° | 6.5° | 76.8% | N/R | 2.34° |
| Ghislanzoni 2024 [41] | Invisalign | From central incisors to first molars, Mx and Mb | VAM Software | 2.54° | 1.56° | N/R | N/R | 2.3° |
| Kravitz 2008 [42] | Invisalign | Canines, Mx and Mb | ToothMeasure | 11.8° | N/R | Group AO: 33.3 ± 28.6% Group IO: 43.1 ± 22.6% Group N: 30.8 ± 27.3% | N/R | N/R |
| Lombardo 2017 [43] | F22 aligners | From central incisors to second molars, Mx and Mb | VAM Software | 8° | 3.77° | 68.1% | 4.42° | N/R |
| Maree 2022 [44] | Invisalign (SmartTrack) | Central incisors, Mx | Geomagic Control X | 18.75° | 13.37° | 71.3% | N/R | N/R |
| Medeiros 2024 [45] | Group A: Invisalign EX30 Group B: Invisalign (SmartTrack) | From incisors to molars | Geomagic Control | Total: 7.8° Group A: 8.09° Group B: 7.7° | Total: 3.3° Group A: 3.75° Group B: 3.22° | N/R | Total: 4.45° Group A: 4.34° Group B: 4.48° | N/R |
| Mario 2024 [46] | F22 aligners | From central incisors to first molars, Mx and Mb | Onyxceph 3TM | 8.3° | 4.81° | 61.6% | 4.18° | N/R |
| Sachdev 2021 [47] | In-office 3D direct-printed aligners | From central incisors to canines, Mx and Mb | OrthoAnalyzer TM | 6.34° | 3.13° | 50.1% | 3.21° | N/R |
| Sorour 2022 [48] | Group A: Invisalign Group B: Flash | From central incisors to canines, Mx and Mb | eModel Compare 8.1 | N/R | N/R | N/R | Group A: 3.2° Group B: 3.1° Total: 3.2° | N/R |
| Taebi-Harandy 2023 [49] | 3M Clarity | From central incisors to second bicuspid, Mx and Mb | 3D Slicer Version 4.11 | 4.84° | 2.72° | N/R | 0.74° | N/R |
| First Author, Year (Reference) | Attachments | IPR | Rotation Rate (°/Aligner) | Mean n° of Aligners | Days of Aligner Wear | Average Treatment Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Nadawi 2021 [38] | Individualized per patient Average of 6 attachments/arch | Yes, <1 mm/arch on average | N/R | Group A: 20 Group B: 21 Group C: 20 | Group A: 7 days Group B: 10 days Group C: 14 days | Group A: 5 months Group B: 8 months Group C: 9 months |
| Castroflorio 2023 [39] | 3 configurations:
| Individualized per patient | 2°/aligner | Mx: 27 ± 15 Mb: 25 ± 11 | 7 to 14 days | 9.8 ± 3.8 months |
| D’Antò 2024 [40] | Conventional attachments
| Yes, allowed | N/R | N/R | 10 days | N/R |
| Ghislanzoni 2024 [41] |
| Yes, if needed, only on anterior teeth | N/R | 14 | 14 days | 7 months |
| Kravitz 2008 [42] |
|
| N/R | 10 Mx, 11 Mb | 14 to 21 days | 7.2 months |
| Lombardo 2017 [43] | F22 system Grip Points | Yes, allowed | 2°/aligner | N/R | 14 days | N/R |
| Maree 2022 [44] | Different geometries:
| No | 2°/aligner | N/R | 14 days | N/R |
| Medeiros 2024 [45] | Yes, but not specified | N/R | N/R | 24 | 14 days | 11.2 months |
| Palone 2024 [46] | F22 system Grip Points, triangular shaped. Used for derotation ≥ 10° of rounded teeth and >20° for Mb incisors and Mx lateral incisors | Yes, allowed | 2°/aligner | 15 | 14 days | N/R |
| Sachdev 2021 [47] | Only for derotations ≥5°, according to the attachments protocol | Yes, allowed | 2°/aligner | 7 | 14 days | N/R |
| Sorour 2022 [48] | Yes
| N/R | N/R | Group A: 21 Mx, 20 Mb Group B: 21 Mx, 21 Mb | 10 days | Group A: 8.4 months Group B: 6.9 months |
| Taebi-Harandy 2023 [49] | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benedetti, G.; Sicca, N.; Lopponi, G.; Dettori, C.; Verdecchia, A.; Spinas, E. Evaluating the Clinical Success of Clear Aligners for Rotational Tooth Movements in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100440
Benedetti G, Sicca N, Lopponi G, Dettori C, Verdecchia A, Spinas E. Evaluating the Clinical Success of Clear Aligners for Rotational Tooth Movements in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(10):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100440
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenedetti, Giulia, Nicolò Sicca, Gaia Lopponi, Claudia Dettori, Alessio Verdecchia, and Enrico Spinas. 2025. "Evaluating the Clinical Success of Clear Aligners for Rotational Tooth Movements in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 10: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100440
APA StyleBenedetti, G., Sicca, N., Lopponi, G., Dettori, C., Verdecchia, A., & Spinas, E. (2025). Evaluating the Clinical Success of Clear Aligners for Rotational Tooth Movements in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review. Dentistry Journal, 13(10), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13100440









