Mandibular Endochondral Growth Is Specifically Augmented by Nutritional Supplementation with Myo-Inositol Even in Rabbits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment with Rabbits
2.2. Micro Computed Tomography Analysis
2.3. Preparation of Histological Sections
2.4. Histological Analysis for the Thickness of the Mandibular Condylar Cartilage
2.5. Immunohistochemical Staining for Pik3cd
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
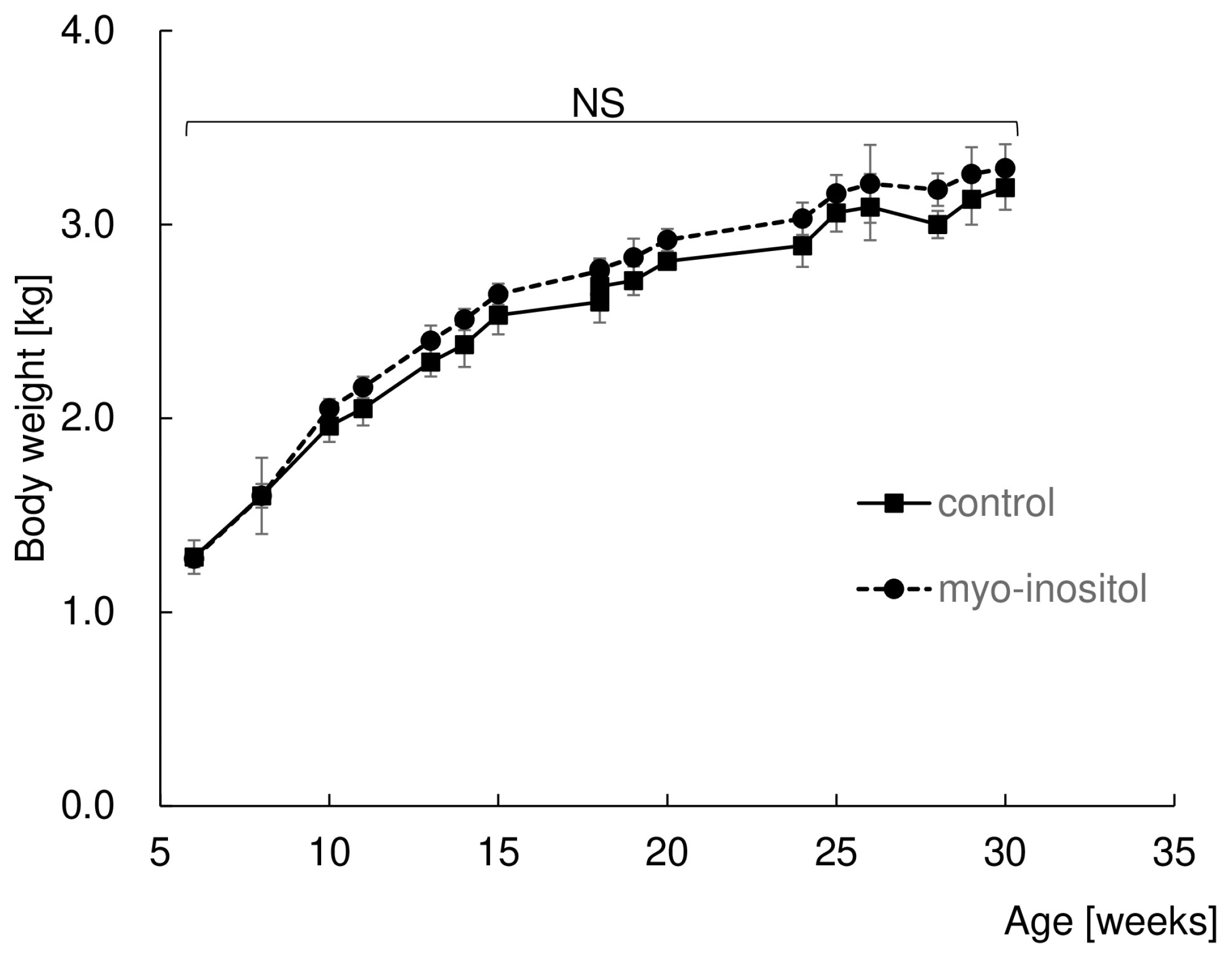
3.1. Myo-Inositol Had No Effect on Body Weight
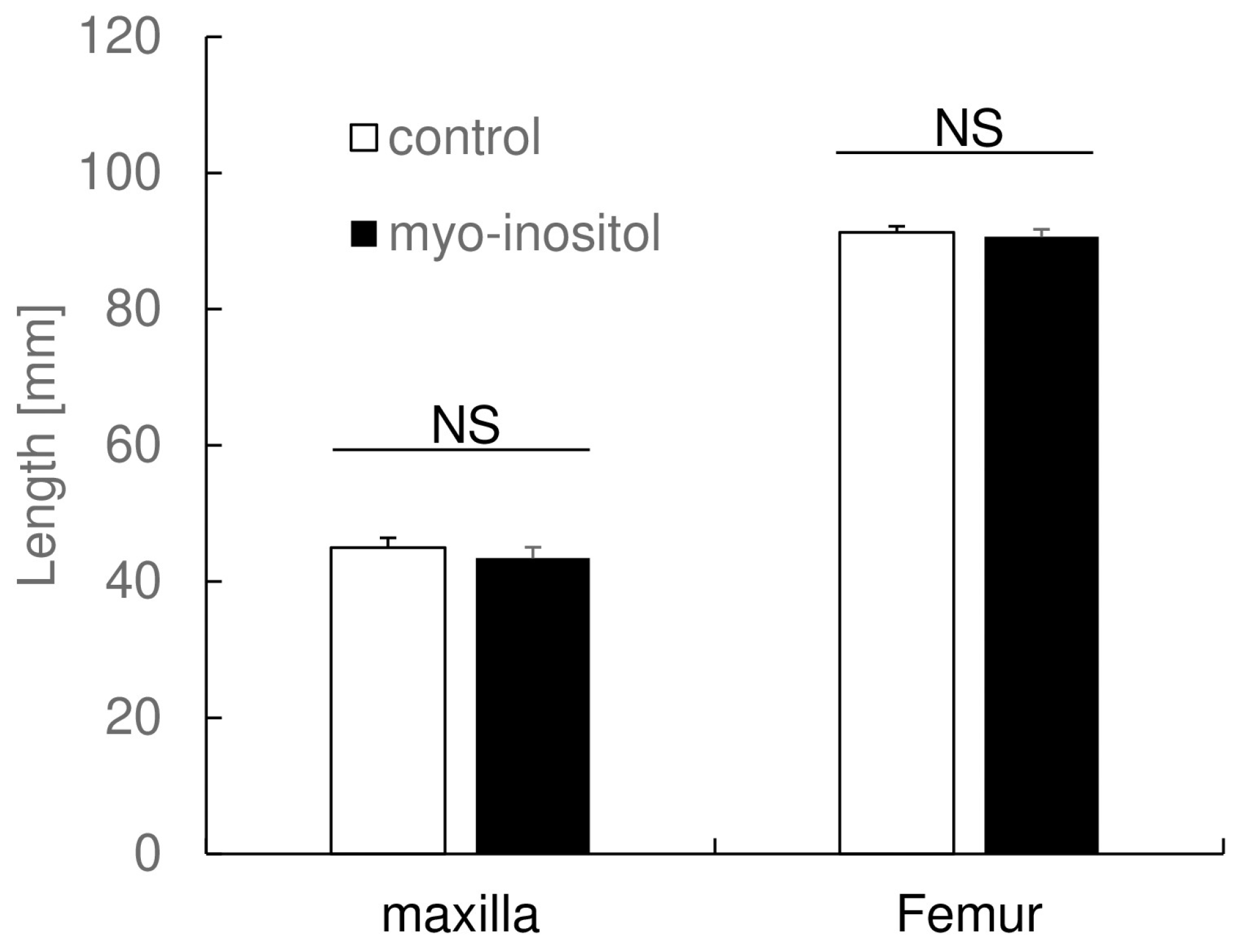
3.2. Myo-Inositol Had No Effect on Maxillary Length and Femur Length
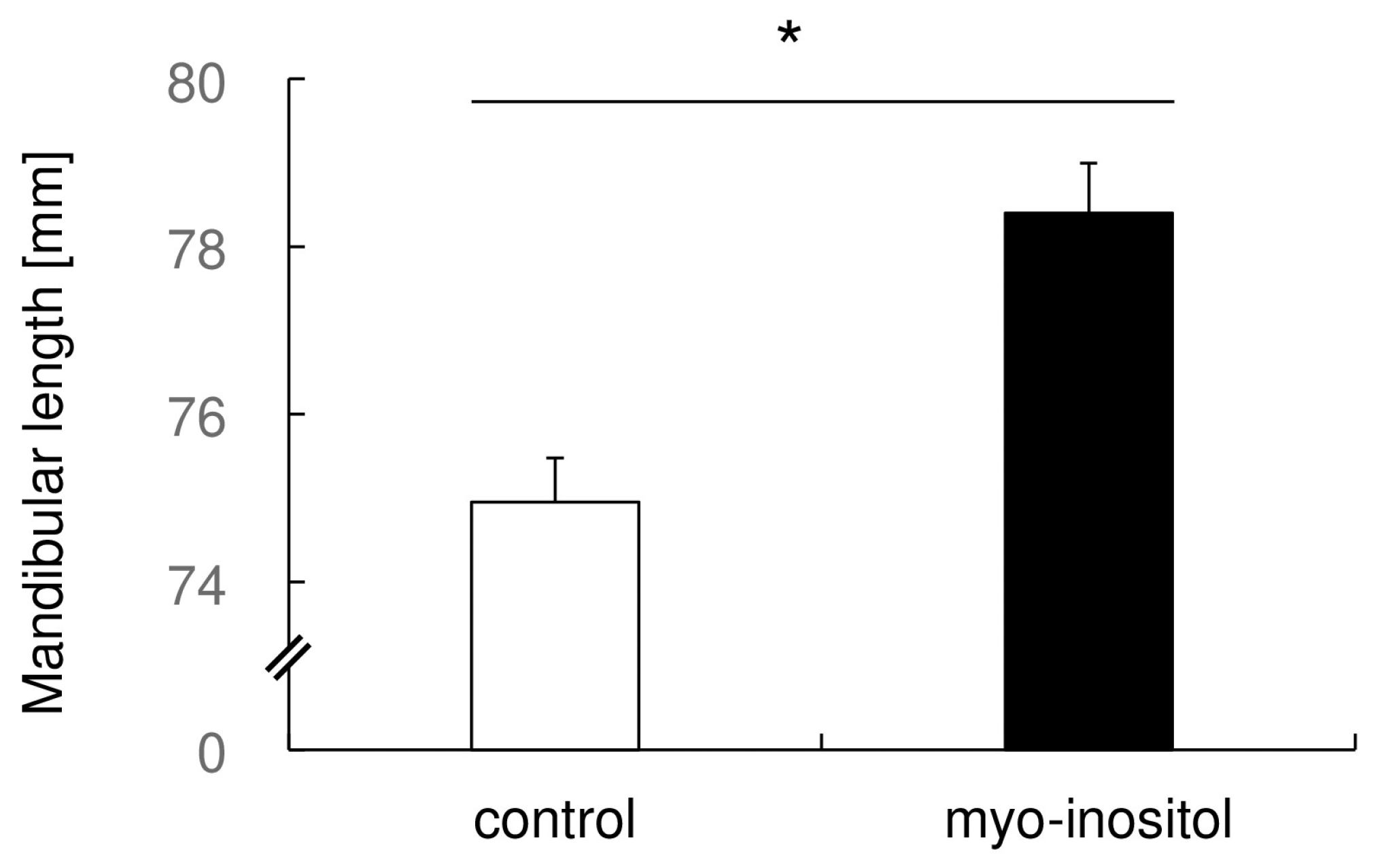
3.3. Myo-Inositol Specifically Augmented the Mandibular Growth
3.4. Pik3cd Is Strongly Expressed in Mandibular Condylar Cartilage
3.5. Myo-Inositol Increased the Thickness of Mandibular Condylar Cartilage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsasser, W.A.; Wylie, W.L. The craniofacial morphology of mandibular retrusion. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1948, 6, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egermark-Eriksson, I.; Ingervall, B.; Carlsson, G.E. The dependence of mandibular dysfunction in children on functional and morphologic malocclusion. Am. J. Orthod. 1983, 83, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, T.; Ono, T.; Otsuka, R.; Honda, E.; Harada, K.; Kurabayashi, T.; Ohyama, K. Mandibular distraction osteogenesis in a skeletal class ii patient with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2007, 131, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrikson, T.; Ekberg, E.C.; Nilner, M. Symptoms and signs of temporomandibular disorders in girls with normal occlusion and class ii malocclusion. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1997, 55, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellberg, H. Juvenile chronic arthritis. Dentofacial morphology, growth, mandibular function and orthodontic treatment. Swed. Dent. J. Suppl. 1995, 109, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Raposo, R.; Peleteiro, B.; Paço, M.; Pinho, T. Orthodontic camouflage versus orthodontic-orthognathic surgical treatment in class ii malocclusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.M.; Zedalis, D.; Howard, C.W.; Boyle, R.P.; Prussin, A.J. Surgical alternatives for treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea: Review and case series. Ann. R. Australas. Coll. Dent. Surg. 2000, 15, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Behrents, R.G.; Shelgikar, A.V.; Conley, R.S.; Flores-Mir, C.; Hans, M.; Levine, M.; McNamara, J.A.; Palomo, J.M.; Pliska, B.; Stockstill, J.W.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and orthodontics: An american association of orthodontists white paper. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 13–28.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, A.K.; Duggal, R.; Parkash, H. Skeletal and dentoalveolar effects of twin-block and bionator appliances in the treatment of class ii malocclusion: A comparative study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 130, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, L.H.; Franco, A.A.; Gerig, G.; Proffit, W.R.; Slice, D.E.; Enlow, D.H.; Yamashita, H.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Scanavini, M.A.; Vigorito, J.W. Assessment of mandibular growth and response to orthopedic treatment with 3-dimensional magnetic resonance images. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 128, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, L.H.; Franco, A.A.; Gerig, G.; Proffit, W.R.; Slice, D.E.; Enlow, D.H.; Lederman, H.M.; Amorim, L.; Scanavini, M.A.; Vigorito, J.W. Comparison of relative mandibular growth vectors with high-resolution 3-dimensional imaging. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 128, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zymperdikas, V.F.; Koretsi, V.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Papadopoulos, M.A. Treatment effects of fixed functional appliances in patients with class ii malocclusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2016, 38, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciatore, G.; Ugolini, A.; Sforza, C.; Gbinigie, O.; Plüddemann, A. Long-term effects of functional appliances in treated versus untreated patients with class ii malocclusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A. The “wits” appraisal of jaw disharmony. Am. J. Orthod. 1975, 67, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavoni, C.; Lombardo, E.C.; Lione, R.; Faltin, K., Jr.; McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Cozza, P.; Franchi, L. Treatment timing for functional jaw orthopaedics followed by fixed appliances: A controlled long-term study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2018, 40, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, P.M.; Fiorillo, L.; Cervino, G.; Cardarelli, F.; Cicciù, M.; Laino, L. Elastodontic treatment with oral bio-activators in young children. Minerva Dent. Oral Sci. 2022, 71, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSherry, P.F.; Bradley, H. Class ii correction-reducing patient compliance: A review of the available techniques. J. Orthod. 2000, 27, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dboush, R.; Soltan, R.; Rao, J.; El-Bialy, T. Skeletal and dental effects of herbst appliance anchored with temporary anchorage devices: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2022, 25, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, P.; Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; De Toffol, L.; McNamara, J.A., Jr. Mandibular changes produced by functional appliances in class ii malocclusion: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 599.e1–599.e12, discussion 599.e1–599.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orliaguet, T.; Dechelotte, P.; Scheye, T.; Vanneuville, G. The relationship between meckel’s cartilage and the development of the human fetal mandible. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1993, 15, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doraczynska-Kowalik, A.; Nelke, K.H.; Pawlak, W.; Sasiadek, M.M.; Gerber, H. Genetic factors involved in mandibular prognathism. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, e422–e431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koffi, K.A.; Doublier, S.; Ricort, J.M.; Babajko, S.; Nassif, A.; Isaac, J. The role of gh/igf axis in dento-alveolar complex from development to aging and therapeutics: A narrative review. Cells 2021, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yi, J.; Li, Y. Effects of nutrition and hormones on functional appliance treatment outcome in patients with skeletal class ii malocclusion. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2020, 9, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.S.; Hatch, N.E.; Hayami, T.; Jheon, A.; Kapila, S. Igf-1 tmj injections enhance mandibular growth and bone quality in juvenile rats. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2022, 25, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Itoh, K.; Ohyama, K. Local administration of igf-i stimulates the growth of mandibular condyle in mature rats. J. Orthod. 2004, 31, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Suzuki, S.; Kuroda, T. Effects of local administration of insulin-like growth factor-i on mandibular condylar growth in rats. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2003, 50, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; El-Kadi, A.O.; El-Bialy, T. Effects of growth hormone and ultrasound on mandibular growth in rats: Microct and toxicity analyses. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, S.; Kanzaki, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nakamura, Y. Possible alternative treatment for mandibular asymmetry by local unilateral igf-1 injection into the mandibular condylar cavity: Experimental study in mice. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 152, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.S.; Tu, M. Role of fat-soluble vitamins in osteoarthritis management. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, O.D.; Vidal Wilman, M.; Vidal Neira, L.F. Nutrition, osteoarthritis and cartilage metabolism. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A.; Vannucci, S.J.; Bondy, C.A.; Carter, S.D.; Innes, J.F.; Arteaga, M.F.; Trujillo, E.; Ferraz, I.; Shakibaei, M.; Martín-Vasallo, P. Glucose transport and metabolism in chondrocytes: A key to understanding chondrogenesis, skeletal development and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis. Histol. Histopathol. 2002, 17, 1239–1267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernigou, P.; Sitbon, J.; Dubory, A.; Auregan, J.C. Vitamin d history part iii: The “modern times”—New questions for orthopaedic practice: Deficiency, cell therapy, osteomalacia, fractures, supplementation, infections. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1755–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, T.; Murata, T.; Watanabe, A.; Hida, A.; Ohba, H.; Iwayama, Y.; Mishima, K.; Gondo, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Defective craniofacial development and brain function in a mouse model for depletion of intracellular inositol synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10785–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Itohiya, K.; Fukaya, S.; Katsumata, Y.; Nakamura, Y. Nutritional supplementation with myo-inositol in growing mice specifically augments mandibular endochondral growth. Bone 2019, 121, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Eichberg, J. A myo-inositol pool utilized for phosphatidylinositol synthesis is depleted in sciatic nerve from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9818–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, E.; McAdam, S.; Coadwell, J.; Chantry, D.; Turner, M. Structural organization of the mouse phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p110d gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohyama, S.; Kanzaki, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Katsumata, Y.; Arai, C.; Ida, T.; Wada, S.; Shimoyama, M.; Shugo, M.; et al. Myo-inositol augments chondrocytic differentiation. Dent. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2023, 9, 1000399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, A.; Watahiki, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Irie, T.; Tachikawa, T.; Maki, K. Effects of mastication on mandibular growth evaluated by microcomputed tomography. Eur. J. Orthod. 2010, 32, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hichijo, N.; Kawai, N.; Mori, H.; Sano, R.; Ohnuki, Y.; Okumura, S.; Langenbach, G.E.; Tanaka, E. Effects of the masticatory demand on the rat mandibular development. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014, 41, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, I.; Nakamura, M.; Takahashi, I.; Kagayama, M.; Mitani, H. An immunohistochemical study of localization of type i and type ii collagens in mandibular condylar cartilage compared with tibial growth plate. Histochemistry 1990, 93, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croze, M.L.; Soulage, C.O. Potential role and therapeutic interests of myo-inositol in metabolic diseases. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1811–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, R.S., Jr.; Darnell, B. Myo-inositol content of common foods: Development of a high-myo-inositol diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1980, 33, 1954–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Verdugo, E.; López-Tolsa, G.E.; Pascual, R.; Pellón, R. Environmental enrichment accelerates the acquisition of schedule-induced drinking in rats. Behav. Process. 2023, 212, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaría-Villegas, A.; Manrique-Hernandez, R.; Alvarez-Varela, E.; Restrepo-Serna, C. Effect of removable functional appliances on mandibular length in patients with class ii with retrognathism: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthaios, S.; Tsolakis, A.I.; Haidich, A.B.; Galanis, I.; Tsolakis, I.A. Dental and skeletal effects of herbst appliance, forsus fatigue resistance device, and class ii elastics-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med 2022, 11, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, K.; McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Kimura, T.; Murata, S.; Iizuka, T. Craniofacial structure of japanese and european-american adults with normal occlusions and well-balanced faces. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1996, 110, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi, S.; Seifi, M.; Soleymani, A.A.; Mohamadian, F.; Alam, M. Comparative study of changes in the airway dimensions following the treatment of class ii malocclusion patients with the twin-block and seifi appliances. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijs, W.A. The functional significance of morphological variation of the human mandible and masticatory muscles. Acta Morphol. Neerl. Scand. 1989, 27, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Simoes, W.A. Insights into maxillary and mandibular growth for a better practice. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 1996, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pepicelli, A.; Woods, M.; Briggs, C. The mandibular muscles and their importance in orthodontics: A contemporary review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 128, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, G.; Danzi, G.; Cimino, R.; Paduano, S.; Michelotti, A. Association between posterior crossbite, skeletal, and muscle asymmetry: A systematic review. Eur. J. Orthod. 2016, 38, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirttiniemi, P.; Peltomäki, T.; Müller, L.; Luder, H.U. Abnormal mandibular growth and the condylar cartilage. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibbets, J.M.; Carlson, D.S. Implications of temporomandibular disorders for facial growth and orthodontic treatment. Semin. Orthod. 1995, 1, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, M. Overbite correction and sagittal changes: Late mixed-dentition treatment effects. Aust. Orthod. J. 2001, 17, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, S.; Vivek Reddy, G.; Perala, J.; Thejasri, K.; Singaraju, G.S.; Mandava, P. Sagittal positional changes of the mandible following alignment and levelling of class ii division 2 cases: An observational study in decelerating stages of adolescent growth spurt. Cureus 2022, 14, e32653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, R.J.; Jing, J.; Feng, J.Q. Genetic influences on temporomandibular joint development and growth. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 115, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinton, R.J. Genes that regulate morphogenesis and growth of the temporomandibular joint: A review. Dev. Dyn. 2014, 243, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocum, D.L.; Roberts, W.E. Part i: Development and physiology of the temporomandibular joint. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouno, K.; Kuroe, K.; Ito, G. Effects of the biting type activator on class ii subjects in the mixed dentition. Orthod. Waves Jpn. Ed. 2005, 64, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Siriwat, P.P.; Jarabak, J.R. Malocclusion and facial morphology is there a relationship?: An epidemiologic study. Angle Orthod. 1985, 55, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kanclerska, J.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Nowacki, D.; Szymanska-Chabowska, A.; Poreba, R.; Mazur, G.; Martynowicz, H. Sleep architecture and vitamin d in hypertensives with obstructive sleep apnea: A polysomnographic study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2024, 61, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizbakhsh, M.; Razavi, M.; Minaian, M.; Teimoori, F.; Dadgar, S.; Maghsoodi, S. The effect of local injection of the human growth hormone on the mandibular condyle growth in rabbit. Dent. Res. J. 2014, 11, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Uludağ, H.; El-Bialy, T. Effect of nonviral plasmid delivered basic fibroblast growth factor and low intensity pulsed ultrasound on mandibular condylar growth: A preliminary study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 426710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciampolillo, A.; De Tullio, C.; Giorgino, F. The igf-i/igf-i receptor pathway: Implications in the pathophysiology of thyroid cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luder, H.U.; Leblond, C.P.; von der Mark, K. Cellular stages in cartilage formation as revealed by morphometry, radioautography and type ii collagen immunostaining of the mandibular condyle from weanling rats. Am. J. Anat. 1988, 182, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basudan, A.M.; Aziz, M.A.; Yang, Y. Implications of zonal architecture on differential gene expression profiling and altered pathway expressions in mandibular condylar cartilage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, A.K.; Donato, K.; Dhuli, K.; Stuppia, L.; Bertelli, M. Dietary supplements for polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2022, 63, E206–E213. [Google Scholar]
- Kotlyar, A.M.; Seifer, D.B. Women with pcos who undergo ivf: A comprehensive review of therapeutic strategies for successful outcomes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2023, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiri, L.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Di Lorenzo, C. Combined treatment of myo-inositol and d-chiro-inositol (80:1) as a therapeutic approach to restore inositol eumetabolism in patients with bipolar disorder taking lithium and valproic acid. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 5483–5489. [Google Scholar]
- Motuhifonua, S.K.; Lin, L.; Alsweiler, J.; Crawford, T.J.; Crowther, C.A. Antenatal dietary supplementation with myo-inositol for preventing gestational diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2, Cd011507. [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno, G.; Unfer, V. Inositol safety: Clinical evidences. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coban, G.; Buyuk, S.K. Sleep disordered breathing and oral health-related quality of life in children with different skeletal malocclusions. Cranio 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, P.; King, T.; Lee, M.; Erasmus, J. Retrospective study of eligibility for orthognathic surgery using the index of orthognathic functional treatment need (ioftn). Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimoyama, M.; Kanzaki, H.; Tohyama, S.; Ida, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Katsumata, Y.; Arai, C.; Wada, S.; Manase, S.; Tomonari, H. Mandibular Endochondral Growth Is Specifically Augmented by Nutritional Supplementation with Myo-Inositol Even in Rabbits. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12030049
Shimoyama M, Kanzaki H, Tohyama S, Ida T, Ishikawa M, Katsumata Y, Arai C, Wada S, Manase S, Tomonari H. Mandibular Endochondral Growth Is Specifically Augmented by Nutritional Supplementation with Myo-Inositol Even in Rabbits. Dentistry Journal. 2024; 12(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimoyama, Miho, Hiroyuki Kanzaki, Syunnosuke Tohyama, Tomomi Ida, Misao Ishikawa, Yuta Katsumata, Chihiro Arai, Satoshi Wada, Shugo Manase, and Hiroshi Tomonari. 2024. "Mandibular Endochondral Growth Is Specifically Augmented by Nutritional Supplementation with Myo-Inositol Even in Rabbits" Dentistry Journal 12, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12030049
APA StyleShimoyama, M., Kanzaki, H., Tohyama, S., Ida, T., Ishikawa, M., Katsumata, Y., Arai, C., Wada, S., Manase, S., & Tomonari, H. (2024). Mandibular Endochondral Growth Is Specifically Augmented by Nutritional Supplementation with Myo-Inositol Even in Rabbits. Dentistry Journal, 12(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12030049





