Effects of Different Crystallization Protocols on Marginal Gap of Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns: SEM Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
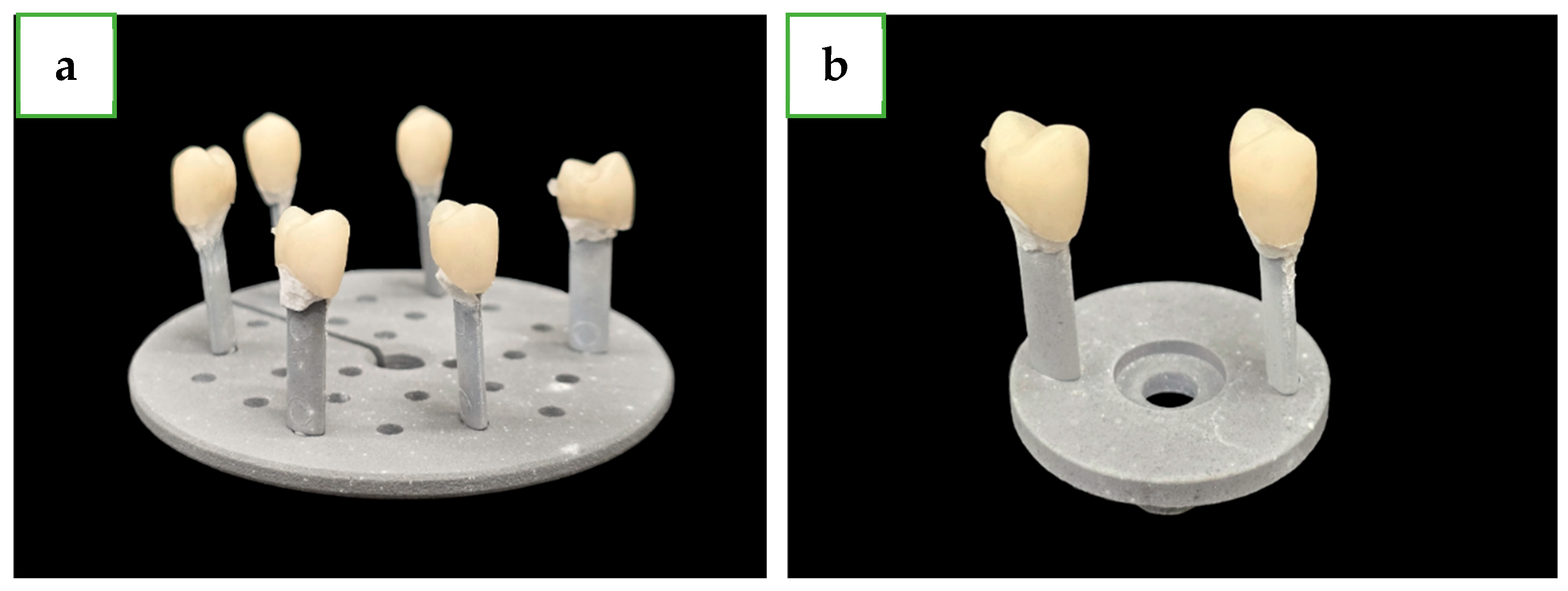
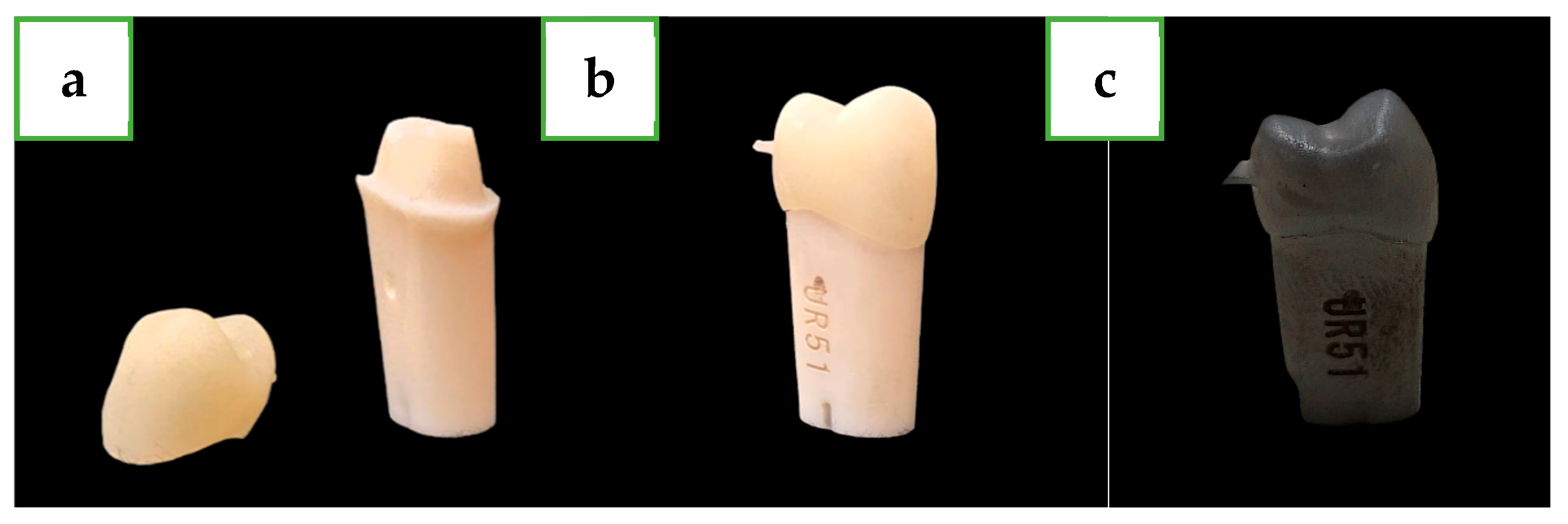
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. Groups and Experimental Protocols
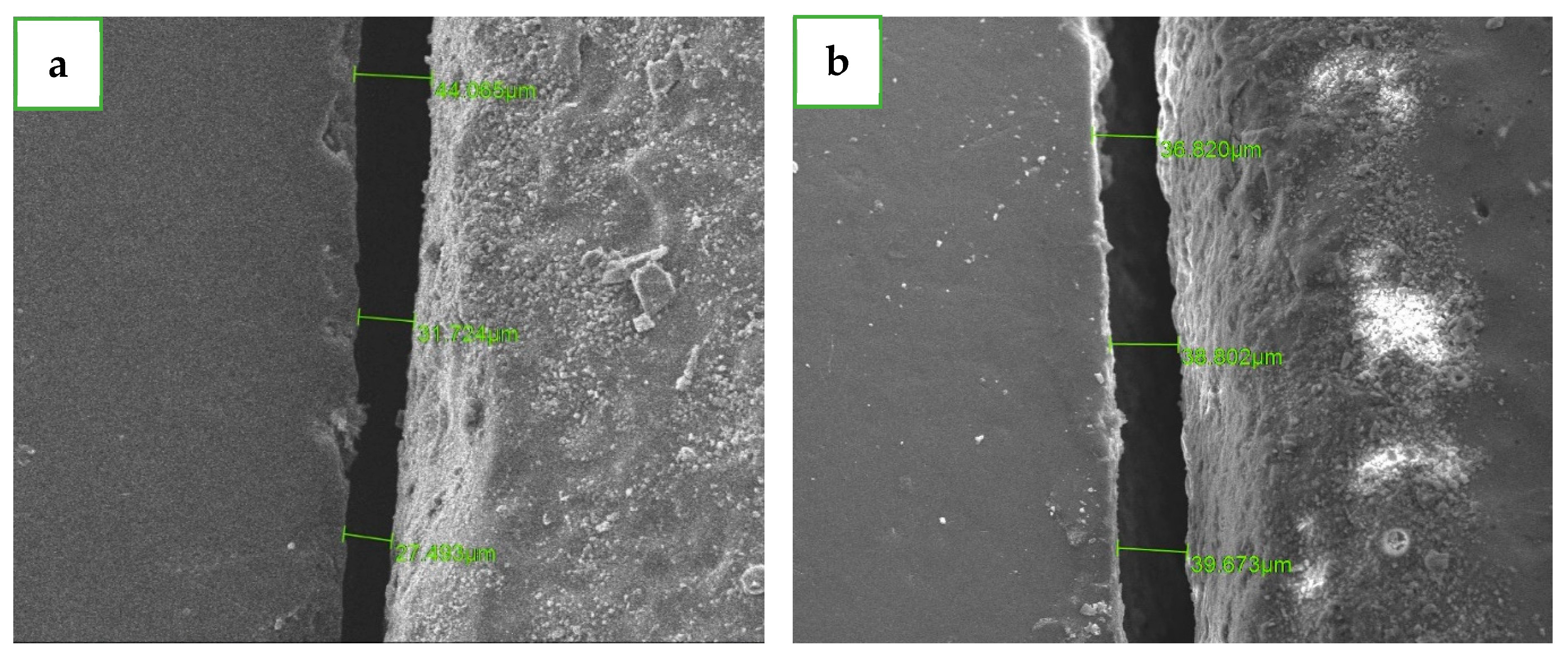
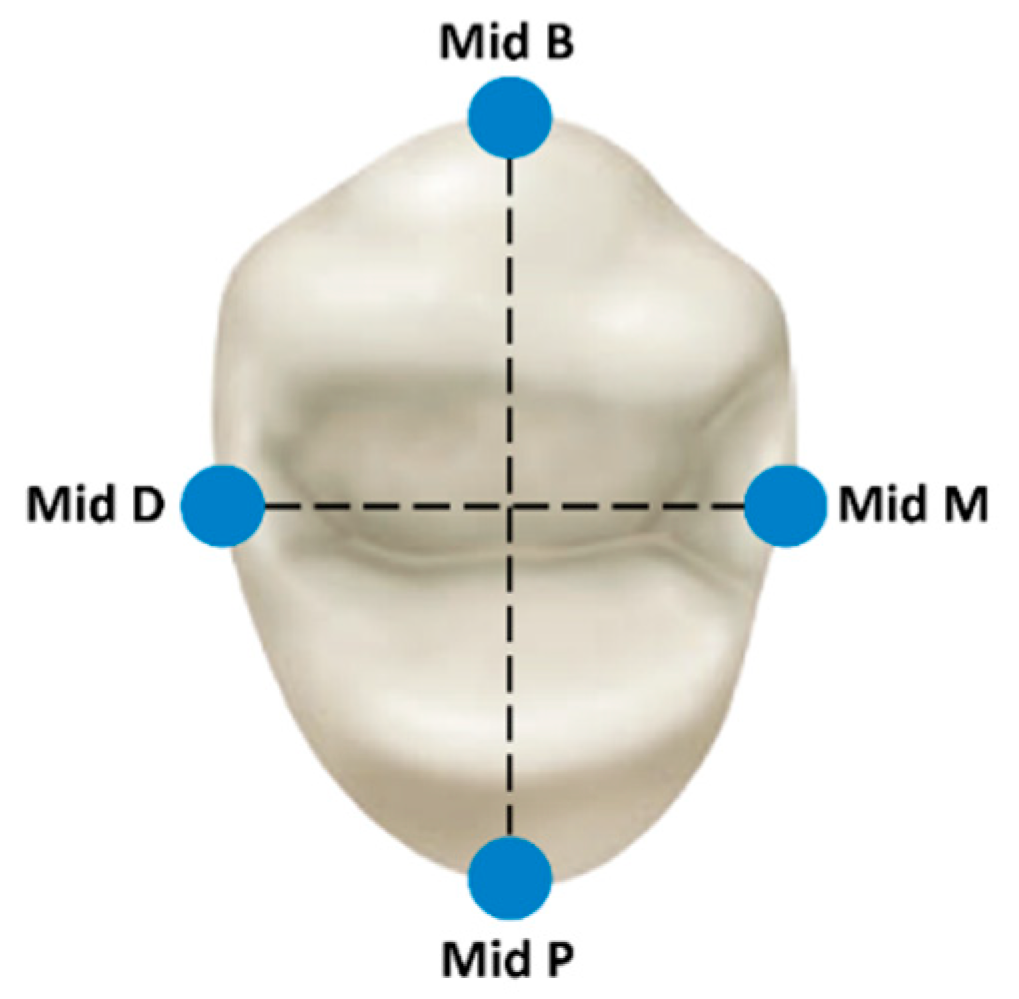
2.4. Main Variables and Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spitznagel, F.A.; Boldt, J.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C. CAD/CAM Ceramic Restorative Materials for Natural Teeth. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosentritt, M.; Hahnel, S.; Engelhardt, F.; Behr, M.; Preis, V. In vitro performance and fracture resistance of CAD/CAM-fabricated implant supported molar crowns. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M.; Mangano, F.G.; Leone, R.; Sorrentino, R. “Digitally Oriented Materials”: Focus on Lithium Disilicate Ceramics. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 9840594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.; Wange, P.; Hartmann, P. Phosphate glasses and glass-ceramics for medical applications. Glass Sci. Technol. 1997, 70, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.; Uhm, S.H. Effect of the Crystallization Process on the Marginal and Internal Gaps of Lithium Disilicate CAD/CAM Crowns. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8635483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, S.A.; Ferracane, J.L.; da Costa, J. Effect of Crystallization Firing on Marginal Gap of CAD/CAM Fabricated Lithium Disilicate Crowns. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, A.; Gabriel Chu, T.M. The science and application of IPS e.Max dental ceramic. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Coronel, C.; Ordoñez Balladares, A.; Fajardo, J.I.; Martín Biedma, B.J. Resistance to Fracture of Lithium Disilicate Feldspathic Restorations Manufactured Using a CAD/CAM System and Crystallized with Different Thermal Units and Programs. Materials 2021, 14, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörmann, W.H.; Brandestini, M.; Lutz, F. The Cerec system: Computer-assisted preparation of direct ceramic inlays in 1 setting. Quintessenz 1987, 38, 457–470. [Google Scholar]
- Mormann, W.H.; Brandestini, M.; Lutz, F.; Barbakow, F.; Gotsch, T. CAD-CAM ceramic inlays and onlays: A case report after 3 years in place. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1990, 120, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivoclar Vivadent AG. IPS Ivocolor Stains and Glazes-Instuctions for Use; Ivoclar Vivadent: Schaan, Liechtenstein, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo-Gómez, F.; Murillo-Alvarado, F.; Vásquez-Sancho, F.; Avendaño, E.; Urcuyo, R. Effect of “fast”-crystallization and simultaneous glazing on physicochemical properties of lithium-disilicate CAD/CAM ceramic. J. Dent. 2024, 148, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Gómez, F.; Murillo-Alvarado, F. Effect of “fast”-crystallization-simultaneous-glazing on mechanical/morphological properties of lithium-disilicate CAD/CAM ceramic. Dent. Mater. 2023, 39 (Suppl. S1), e48–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.O.; Özcan, M.; Pavanelli, C.A.; Buso, L.; Lombardo, G.H.; Michida, S.M.; Mesquita, A.M.; Bottino, M.A. Marginal and internal discrepancies related to margin design of ceramic crowns fabricated by a CAD/CAM system. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 21, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoernschild, K.L.; Campbell, S.D. Periodontal tissue responses after insertion of artificial crowns and fixed partial dentures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 84, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailer, I.; Fehér, A.; Filser, F.; Gauckler, L.J.; Lüthy, H.; Hämmerle, C.H. Five-year clinical results of zirconia frameworks for posterior fixed partial dentures. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 20, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McLean, J.W.; von Fraunhofer, J.A. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br. Dent. J. 1971, 131, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, E.; Suárez, M.J.; Serrano, B.; Lozano, J.F. A comparison of the marginal vertical discrepancies of zirconium and metal ceramic posterior fixed dental prostheses before and after cementation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 102, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.H. Effect of cement space settings on the marginal and internal fit of 3D-printed definitive resin crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Euán, R.; Figueras-Álvarez, O.; Cabratosa-Termes, J.; Brufau-de Barberà, M.; Gomes-Azevedo, S. Comparison of the marginal adaptation of zirconium dioxide crowns in preparations with two different finish lines. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 21, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, C.J.; Campagni, W.V.; Aquilino, S.A. Tooth preparations for complete crowns: An art form based on scientific principles. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Izhack, G.; Shely, A.; Naishlos, S.; Glikman, A.; Frishman, L.; Meirowitz, A.; Dolev, E. The Influence of Three Different Digital Cement Spacers on the Marginal Gap Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Crowns Fabricated by CAD-CAM System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolev, E.; Bitterman, Y.; Meirowitz, A. Comparison of marginal fit between CAD-CAM and hot-press lithium disilicate crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.J. Wheeler’s Dental Anatomy, Physiology, and Occlusion, 9th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2021; pp. 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Shely, A.; Nissan, J.; Lugassy, D.; Rosner, O.; Zenziper, E.; Egbaria, T.; Ben-Izhack, G. Three Self-Adhesive Resin Cements and Their Influence on the Marginal Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Single Crowns: An In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscope Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shely, A.; Lugassy, D.; Anufriev, M.; Nissan, J.; Rauchwerger, O.; Ben-Izhack, G. SEM Evaluation of the Marginal Gap of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Full Crowns and the Effect of Post Crystallization: An In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, W.G.; Souza, L.F.B.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Valandro, L.F.; Kapczinski, M.P.; Mengatto, C.M.; Fraga, S. Fit and fatigue behavior of CAD-CAM lithium disilicate crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 130, e1–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashkar, A.; Taymour, M.; El-Tannir, A. Evaluation of the marginal and internal gaps of partially crystallized versus fully crystallized zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate CAD-CAM crowns: An in vitro comparison of the silicone replica technique, direct view, and 3-dimensional superimposition analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 129, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizonaki, M.; Jacquet, W.; Bottenberg, P.; Depla, L.; Boone, M.; De Coster, P.J. Evaluation of marginal and internal fit of lithium disilicate CAD-CAM crowns with different finish lines by using a micro-CT technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 127, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Niizuma, Y.; Sugai, R.; Manabe, A. Influence of the Crystallization Firing Process on Marginal and Internal Adaptation of Silicate-based Glass-ceramic Inlays Fabricated With a CAD/CAM Chairside System. Oper Dent. 2023, 48, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, B.; Eckert, S.; Kunkela, J.; Ingr, T.; Mounajjed, R. The marginal fit of lithium disilicate crowns: Press vs. CAD/CAM. Braz. Oral Res. 2018, 32, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarbal, A.; Azarbal, M.; Engelmeier, R.L.; Kunkel, T.C. Marginal Fit Comparison of CAD/CAM Crowns Milled from Two Different Materials. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, B.; Dudley, J. A comparison of the marginal gaps of lithium disilicate crowns fabricated by two different intraoral scanners. Aust. Dent. J. 2020, 65, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Internal Relief | Contact Strength Parameters | Material Thickness Parameters | Marginal Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radial spacer: 90 μm | Proximal contacts: 25 μm | Radial minimal thickness: 1000 μm | Margin ramp width: 50 μm |
| Occlusal spacer: 120 μm | Dynamic contacts: 25 μm | Occlusal minimal thickness: 1500 μm | Margin thickness: 50 μm |
| Occlusal contacts: 25 μm | Margin ramp angle: 60° |
| Features or Protocol | Long P1 (Approx. 24 min) | Short P3 (Approx. 15 min) |
|---|---|---|
| Standby temperature | 403 °C | 403 °C |
| Closing time | 6:00 min:s | 1:30 min:s |
| Heating rate | 90 °C/min | 90 °C/min |
| Firing temp 1 | 820 °C | 820 °C |
| Holding time | 0:10 min:s | 0:10 min:s |
| Heating rate to temp 2 | 30 °C/min | 30 °C/min |
| Firing temp 2 | 840 °C | 840 °C |
| Holding time 2 | 7:00 min:s | 7:00 min:s |
| Vacuum 1 | 550–820 °C | 550–820 °C |
| Vacuum 2 | 820–840 °C | 820–840 °C |
| Long-term cooling | 700 °C | 700 °C |
| Cooling rate | 0 °C/min | 0 °C/min |
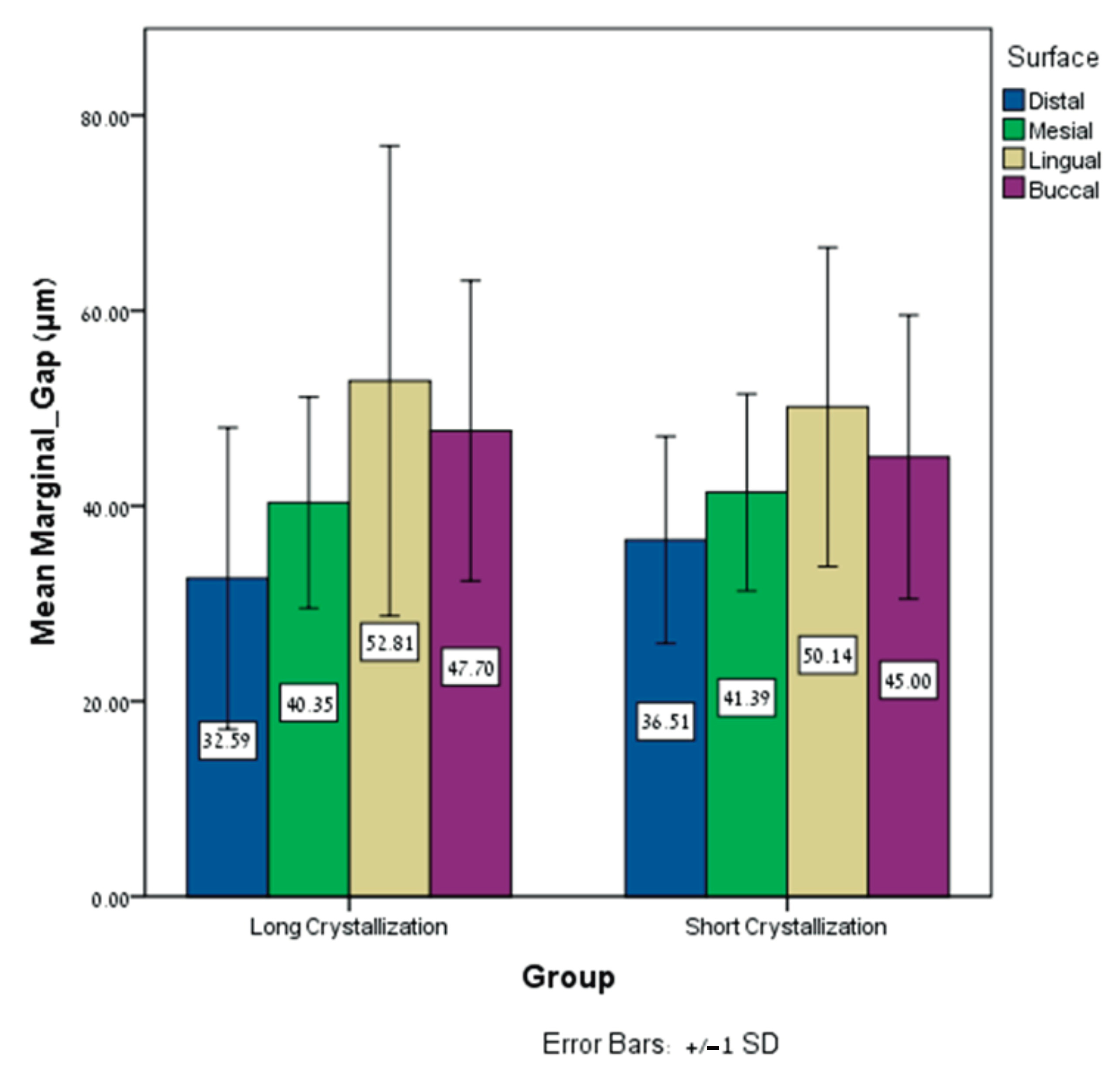
| Distal Surface | Mesial Surface | Palatal Surface | Buccal Surface | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Marginal Gap (MMG) (μm) | Mean ± SD | Range | Min Max | Mean ± SD | Range | Min Max | Mean ± SD | Range | Min Max | Mean ± SD | Range | Min Max |
| Long crystallization | 32.58 ± 15.43 | 64.12 | 6.74 70.86 | 40.34 ± 10.8 | 41.60 | 20.67 62.27 | 52.80 ± 24.07 | 124.95 | 25.65 150.60 | 47.70 ± 15.39 | 55.36 | 20.40 75.76 |
| Short crystallization | 36.50 ± 10.60 | 37.26 | 18.42 55.68 | 41.38 ± 10.09 | 36.93 | 25.04 61.97 | 50.13 ± 16.33 | 53.55 | 23.26 76.81 | 45.00 ± 14.53 | 49.19 | 24.71 73.89 |
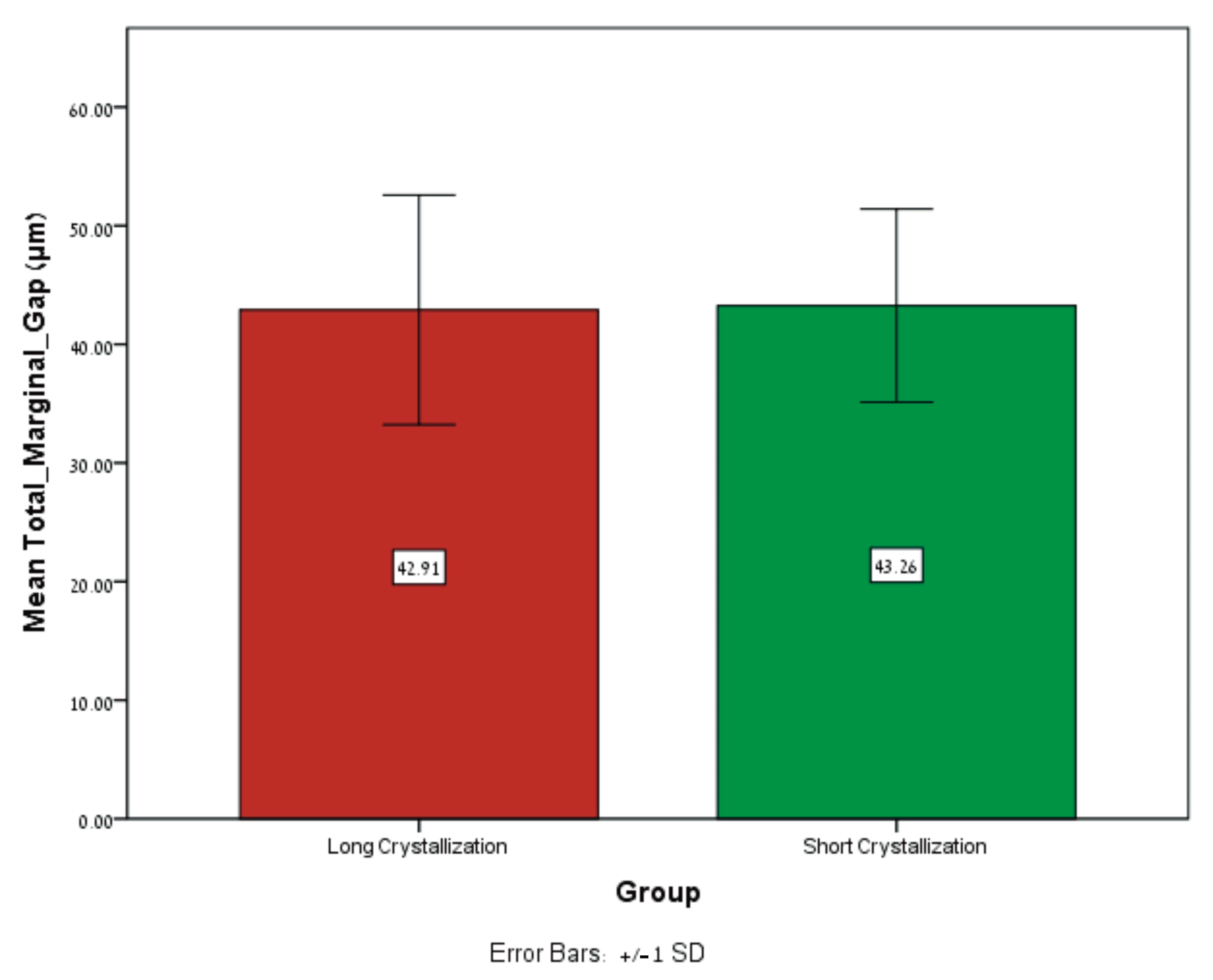
| Mean Total Marginal Gap (MTMG) (μm) | Mean ± SD | Range | Min Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long Crystallization | 42.91 ± 9.67 | 43.74 | 27.04 70.78 |
| Short Crystallization | 43.25 ± 8.14 | 28.20 | 29.42 57.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shadur, A.; Nissan, J.; Lugassy, D.; Umansky, A.; Zenziper, E.; Ben-Izhack, G. Effects of Different Crystallization Protocols on Marginal Gap of Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns: SEM Analysis. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12120416
Shadur A, Nissan J, Lugassy D, Umansky A, Zenziper E, Ben-Izhack G. Effects of Different Crystallization Protocols on Marginal Gap of Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns: SEM Analysis. Dentistry Journal. 2024; 12(12):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12120416
Chicago/Turabian StyleShadur, Alon, Joseph Nissan, Diva Lugassy, Ariana Umansky, Eran Zenziper, and Gil Ben-Izhack. 2024. "Effects of Different Crystallization Protocols on Marginal Gap of Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns: SEM Analysis" Dentistry Journal 12, no. 12: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12120416
APA StyleShadur, A., Nissan, J., Lugassy, D., Umansky, A., Zenziper, E., & Ben-Izhack, G. (2024). Effects of Different Crystallization Protocols on Marginal Gap of Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns: SEM Analysis. Dentistry Journal, 12(12), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj12120416








