Can the Concentration of Citric Acid Affect Its Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assessment of Antimicrobial Activity
Macrodiluition Test
2.2. Sample Selection for Intratubular Decontamination
2.3. Sample Preparation and Infection
2.4. Antimicrobial Test
2.5. Antimicrobial Evaluation of the Solutions by CLSM
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
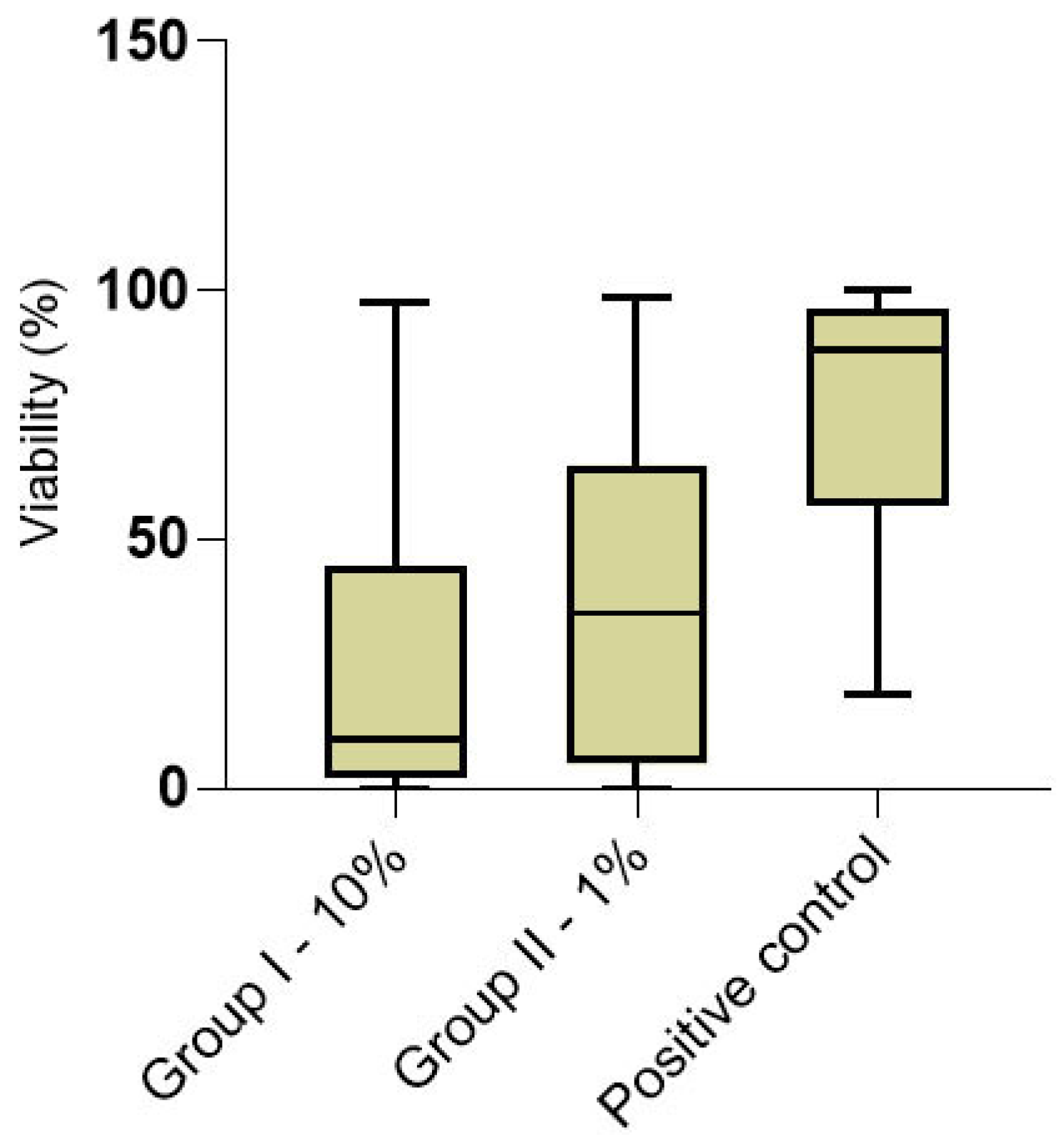
3.1. Cytotoxicity
3.2. Antimicrobial Analysis
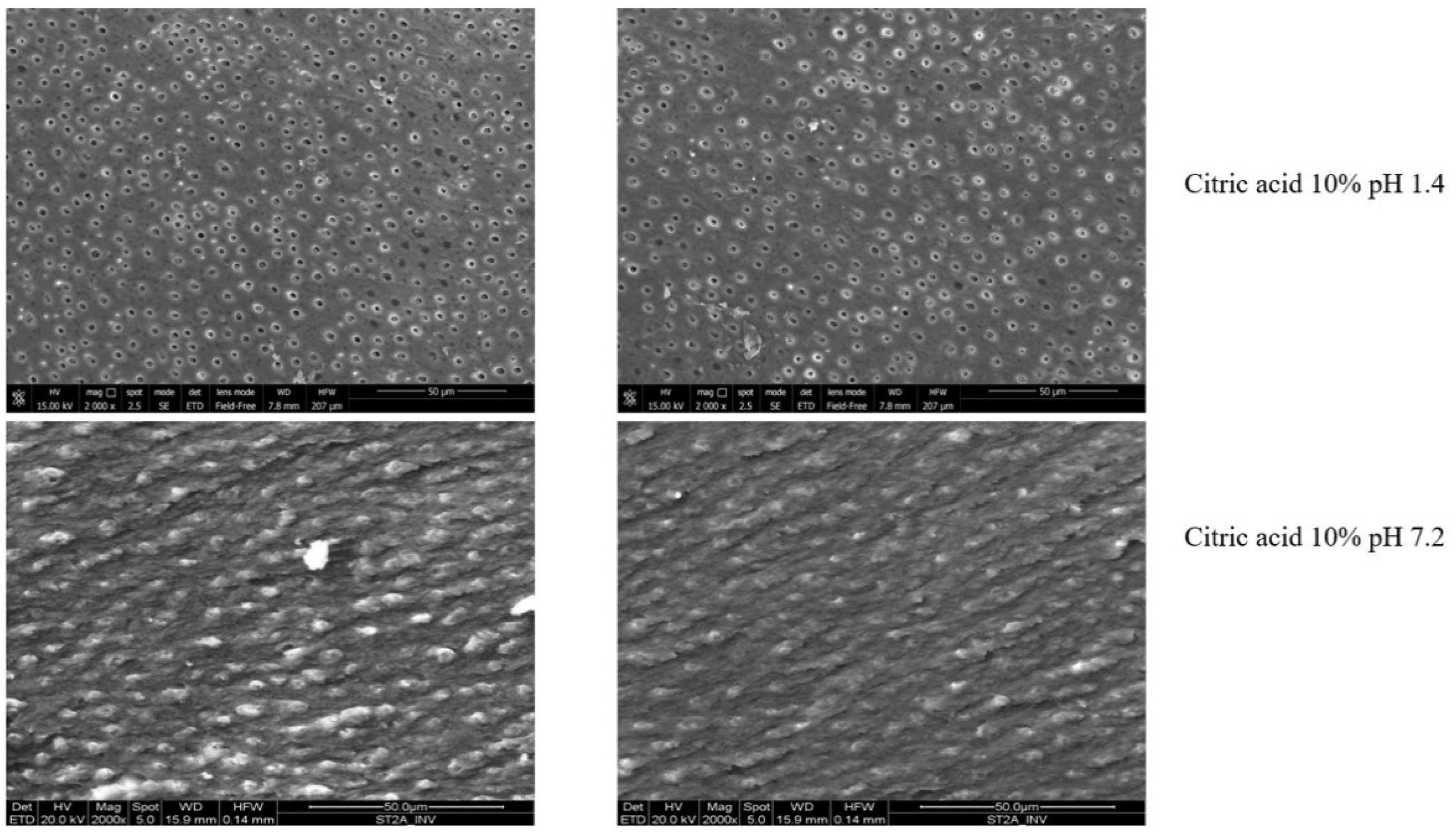
3.3. Intratubular Decontamination Analysis (CLSM)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abedi-Amin, A.; Luzi, A.; Giovarruscio, M.; Paolone, G.; Darvizeh, A.; Agulló, V.V.; Sauro, S. Innovative Root-End Filling Materials Based on Calcium-Silicates and Calcium-Phosphates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N. Clinical Implications and Microbiology of Bacterial Persistence after Treatment Procedures. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1291–1301.E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, N.A.; Eleazer, P.D.; Averbach, R.E.; Seltzer, S. Scanning Electron Microscopic Study of the Efficacy of Various Irrigating Solutions. J. Endod. 1975, 1, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutner, J.; Mines, P.; Anderson, A. Irrigation Trends Among American Association of Endodontists Members: A Web-Based Survey. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Moliz, M.T.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M.; Espigares-Rodríguez, E.; Liébana-Ureña, J.; Espigares-García, M. Bactericidal Activity of Phosphoric Acid, Citric Acid, And EDTA Solutions Against Enterococcus Faecalis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2008, 106, e84–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardino, L.; Ambu, E.; Becce, C.; Rimondini, L.; Morra, M. Surface Tension Comparison of Four Common Root Canal Irrigants and Two New Irrigants Containing Antibiotic. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanza, A.; D’Angelo, M.; Reda, R.; Gambarini, G.; Testarelli, L.; Di Nardo, D. An Update on Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Endodontics: Mechanical Characteristics, Testing and Fu-ture Perspective—An Overview. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayman, B.E.; Kopp, W.M.; Pinero, G.J.; Lazzari, E.P. Citric and Lactic Acids as Root Canal Irri-Gants In Vitro. J. Endod. 1979, 5, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelza, M.F.Z.; Antoniazzi, J.H.; Scelza, P. Efficacy of Final Irrigation: A Scanning Electron Mi-Croscopic Evaluation. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banode, A.M.; Gade, V.; Patil, S.; Chandhok, D.; Sinkar, R. Comparative Scanning Electron Microscopy Evaluation of Smear Layer Removal with 17% Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, 10% Citric Acid and Newer Irrigant QMix: In Vitro Study. Indian J. Oral Heal. Res. 2015, 1, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, C.; Dagna, A.; Vinci, A.; Beltrami, R.; Cucca, L.; Giardino, L. Decalcifying capability of Irrigating Solutions on Root Canal Dentin Mineral Content. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2015, 6, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Patil, V.; Kumar, K.S.; Ratnakar, P.; Rairam, S.; Tripathi, S. Comparative Analysis of Smear Layer Removal by Conventional Endodontic Irrigants with a Newly Experimented Irrigant-Fumaric Acid: A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2018, 21, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennequin, M.; Pajot, J.; Avignant, D. Effects of different pH values of citric acid solutions on the calcium and phosphorus contents of human root dentin. J. Endod. 1994, 20, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haznedaroğlu, F. Efficacy of various concentrations of citric acid at different pH values for smear layer removal. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2003, 96, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.; De-Deus, G.; Leal, F.; Azevedo, É.; Coutinho-Filho, T.; Paciornik, S. Strong Effect on Dentin After the Use of High Concentrations of Citric Acid: An Assessment with Co-Site Optical Microscopy And ESEM. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, G.D.R.; Cunha, C.B.C.S.; Primo, L.S.D.S.G.; Maia, L. Effect of the Sodium Hypochlorite and Citric Acid Association on Smear Layer Removal of Primary Molars. Braz. Oral Res. 2005, 19, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, A.; Yüksel, B.N.; Ziya, M.; Gümüş, H.; Doğan, S.; Sari, Ş. The Effect of Different Irrigation Protocols on Smear Layer Removal in Root Canals of Primary Teeth: A SEM Study. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2019, 77, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, M.; Kontakiotis, E.; Nakou, M. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effectiveness of Citric Acid and Sodium Hypochlorite on The Anaerobic Flora of The Infected Root Canal. Int. Endod. J. 1994, 27, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Suzuki, R.; Nakamura, H. Root Canal Irrigation with Citric Acid Solution. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.G.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Lima, C.V.; Barão, V.A. Citric Acid Reduces Oral Biofilm and Influences the Electrochemical Behavior of Titanium: An in Situ And In Vitro Study. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundukad, B.; Udayakumar, G.; Grela, E.; Kaur, D.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Doyle, P.S. Weak Acids as an Alternative Anti-Microbial Therapy. Biofilm 2020, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, K.F.; Rogero, M.M.; Fock, R.A.; Borelli, P.; Gavini, G. Cytotoxicity analysis of EDTA and Citric Acid Applied on Murine Resident Macrophages Culture. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-P.; Jeng, J.-H.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Lei, D.; Chang, M.-C. Morphological alterations associated with the cytotoxic and cytostatic effects of citric acid on cultured human dental pulp cells. J. Endod. 1999, 25, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, O.A. Research that matters-biocompatibility and cytotoxicity screening. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 46, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices–Part 5: Tests for In Vitro CytotoxIcity. 2009. Available online: http://nhiso.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/ISO-10993-5-2009.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Generali, L.; Bertoldi, C.; Bidossi, A.; Cassinelli, C.; Morra, M.; Del Fabbro, M.; Savadori, P.; Ballal, N.V.; Giardino, L. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Activity of a New Class of Silver Citrate-Based Compounds as Endodontic Irrigants. Materials 2020, 13, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha Neto, M.; Coêlho, J.A.; Pinto, K.P.; Cuellar, M.; Marcucci, M.C.; Silva, E.; Andrade, F.B.; Sassone, L.M. Antibacterial Efficacy of Triple Antibiotic Medication with Macrogol (3Mix-MP), Traditional Triple Antibiotic Paste, Calcium Hydroxide, and Ethanol Extract of Propolis: An In-tratubular Dentin Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, F.B.; Arias, M.P.C.; Maliza, A.G.A.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Graeff, M.S.Z.; Silva, P.A.A.; Midena, R.Z.; De Moraes, I.G. A New Improved Protocol for In Vitro Intratubular Dentinal Bacterial Contamination for Antimicrobial Endodontic Tests: Standardization and Validation by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2015, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Haapasalo, M. A New Noninvasive Model to Study the Effectiveness of Dentin Disinfection by Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, L.; Del Fabbro, M.; Morra, M.; Pereira, T.; de Andrade, F.B.; Savadori, P.; Generali, L. Dual Rinse® HEDP increases the surface tension of NaOCl but may increase its dentin disinfection efficacy. Odontology 2019, 107, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, L.; Del Fabbro, M.; Cesario, F.; Fernandes, F.S.; Andrade, F.B. Antimicrobial Effec-Tiveness of Oxidant and Chelating Agents Combination in Infected Dentine: An Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Study. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez de Paz, L.E. Image Analysis Software Based on Color Segmentation for Characterization of Viability and Physiological Activity of Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2017/745 of 5 April 2017 on Medical Devices, Amending Directive 2001/83/EC, Regulation (EC) No. 178/2002 and Regulation (EC) 1223/2009 and Repealing Council Directives 90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Union L 2017, 117, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, J.C.; Brown, C.M.; Mader, C.L.; Peters, D.D.; Shulman, J.D. A Scanning Electron Microscopic Evaluation of Root Canal Debridement Using Saline, Sodium Hypochlorite, and Citric Acid. J. Endod. 1984, 10, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapasalo, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Irrigation in Endodontics. Br. Dent. J. 2014, 216, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malheiros, C.; Marques, M.; Gavini, G. In Vitro Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Effects of Acid Solutions Used as Canal Irrigants. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelza, M.F.; Daniel, R.L.; Santos, E.M.; Jaeger, M.M. Cytotoxic Effects Of 10% Citric Acid And EDTA-T Used as Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Analysis. J. Endod. 2001, 27, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.C.; Chan, C.P.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chang, M.C.; Jeng, J.-H. The effects of extracellular citric acid acidosis on the viability, cellular adhesion capacity and protein synthesis of cultured human gingival fibroblasts. Aust. Dent. J. 1999, 44, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Escobar, E.; González-Rodríguez, M.P.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M. Cytotoxic Effects of Two Acid Solutions And 2.5% Sodium Hypochlorite Used in Endodontic Therapy. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal. 2010, 15, e90–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bajrami, D.; Hoxha, V.; Gorduysus, O.; Muftuoglu, S.; Zeybek, N.D.; Küçükkaya, S. Cytotoxic 611 Effect of Endodontic Irrigants In Vitro. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2014, 10, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Giardino, L.; Bidossi, A.; Del Fabbro, M.; Savadori, P.; Maddalone, M.; Ferrari, L.; Ballal, N.V.; Das, S.; Rao, B.S.S. Antimicrobial Activity, Toxicity and Accumulated Hard-Tissue Debris (AHTD) Removal Efficacy of Several Chelating Agents. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.; Rehani, U.; Agarwal, A.; Kaushik, M.; Adlakha, V. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Endodontic Irrigants Against Enterococcus Faecalis and Escherichia Coli: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2013, 6, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.; Silva, E.J.; Duque, T.M.; Zaia, A.A.; Ferraz, C.C.; Almeida, J.F.; Gomes, B.P. Anti-Microbial and Cytotoxic Effects of Phosphoric Acid Solution Compared to Other Root Canal Irrigants. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2015, 23, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Haapasalo, M. Effect of Smear Layer against Disinfection Protocols on Enterococcus faecalis–infected Dentin. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morago, A.; Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M.; Baca, P.; Ruiz-Linares, M.; Arias-Moliz, M.T. Influence of Smear Layer on the Antimicrobial Activity of a Sodium Hypochlorite/Etidronic Acid Irrigating Solution in Infected Dentin. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1647–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loel, D.A. Use of acid cleanser in endodontic therapy. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1975, 90, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterrett, J.D.; Delaney, B.; Rizkalla, A.; Hawkins, C.H. Optimal Citric Acid Concentration for Dentinal Demineralization. Quintessence Int. 1991, 22, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
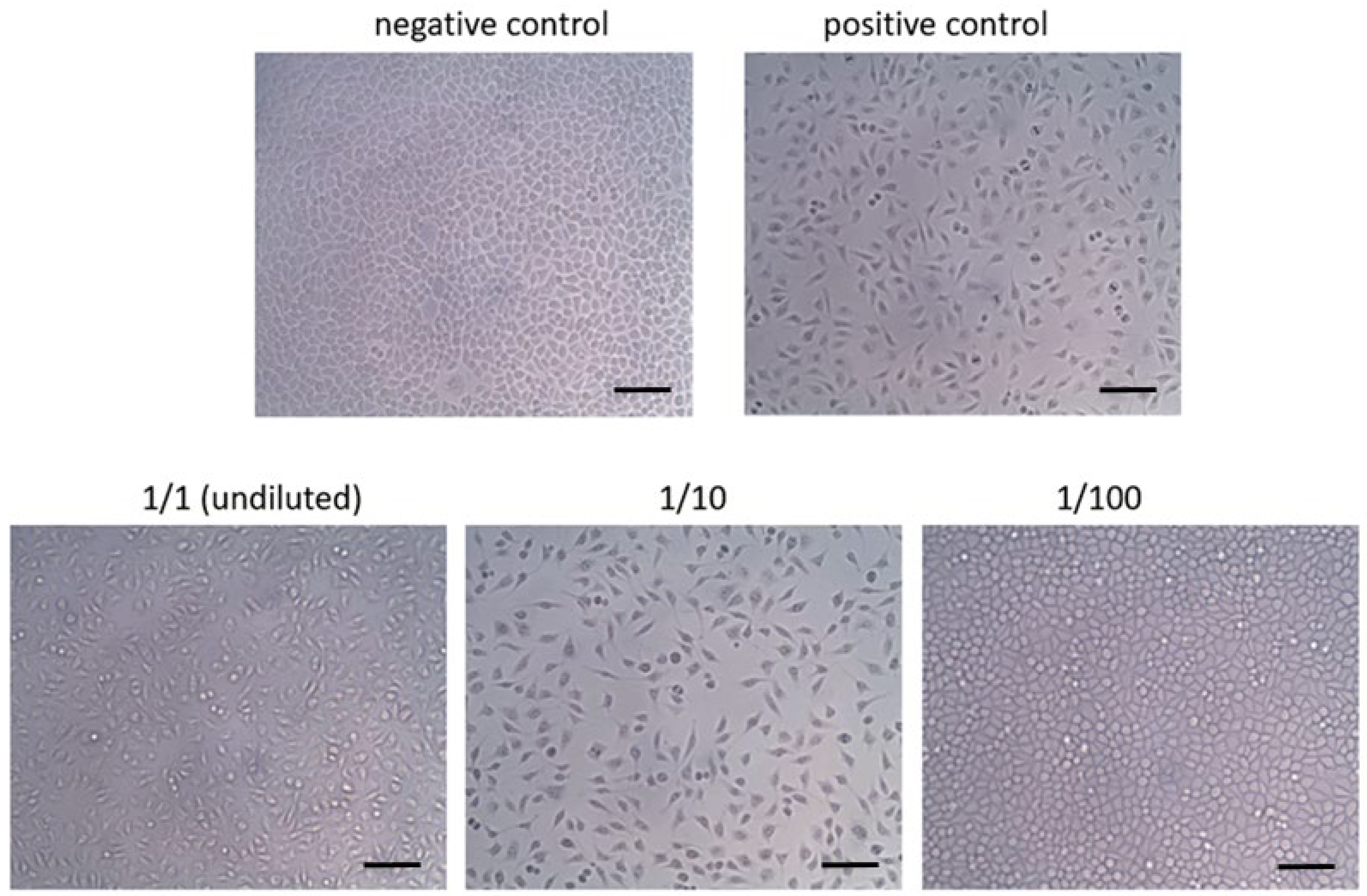

| Grade | Reactivity | Reactivity Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | Discrete intracytoplasmic granules; no cell lysis |
| 1 | Slight | Not more than 20% of the cells are round, loosely attached and without intracytoplasmic granules; occasional lysed cells are present |
| 2 | Mild | Not more than 50% of the cells are round and devoid of intracytoplasmic granules; no extensive cell lysis and empty areas between cells |
| 3 | Moderate | Not more than 70% of the cell layers contain rounded cells or are lysed |
| 4 | Severe | Nearly complete destruction of the cell layers |
| Group I | N | Group II | N | Positive Control | N | GI vs. GII p-Value | GI vs. C + p-Value | GII vs. C + p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 9.70 (2.18–44.60) | 10 | 35.2 (4.87–64.90) | 10 | 88.17 (56.81–95.13) | 4 | 0.019 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cervical portion | 12.86 (2.03–61.92) | 10 | 34.80 (9.42–71.50) | 10 | 88.17 (55.94–96.13) | 4 | 0.051 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Apical portion | 8.0 (2.92–44.6) | 10 | 38.46 (1.95–62.57) | 10 | 88.29 (56.81–94.66) | 4 | 0.213 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| C vs. A p-value | 0.527 | 10 | 0.644 | 10 | 0.782 | 4 | |||
| Superficial layer | 9.10 (2.03–38.98) | 10 | 39.40 (4.95–64.53) | 10 | 89.58 (71.38–95.06) | 4 | 0.048 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Deep layer | 11.4 (2.22–47.67) | 10 | 34.44 (4.87–69.11) | 10 | 85.39 (50.79–96.13) | 4 | 0.220 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| S vs. D p-value | 0.237 | 10 | 0.762 | 10 | 0.561 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giardino, L.; Generali, L.; Savadori, P.; Barros, M.C.; de Melo Simas, L.L.; Pytko-Polończyk, J.; Wilkoński, W.; Ballal, V.; Andrade, F.B.d. Can the Concentration of Citric Acid Affect Its Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity? Dent. J. 2022, 10, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10080148
Giardino L, Generali L, Savadori P, Barros MC, de Melo Simas LL, Pytko-Polończyk J, Wilkoński W, Ballal V, Andrade FBd. Can the Concentration of Citric Acid Affect Its Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity? Dentistry Journal. 2022; 10(8):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10080148
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiardino, Luciano, Luigi Generali, Paolo Savadori, Mirela Cesar Barros, Leticia Lobo de Melo Simas, Jolanta Pytko-Polończyk, Wojciech Wilkoński, Vasudev Ballal, and Flaviana Bombarda de Andrade. 2022. "Can the Concentration of Citric Acid Affect Its Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity?" Dentistry Journal 10, no. 8: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10080148
APA StyleGiardino, L., Generali, L., Savadori, P., Barros, M. C., de Melo Simas, L. L., Pytko-Polończyk, J., Wilkoński, W., Ballal, V., & Andrade, F. B. d. (2022). Can the Concentration of Citric Acid Affect Its Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity? Dentistry Journal, 10(8), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10080148










