Effect of Water Content on Properties of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures and Their Application in Oxidative Absorption of H2S
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
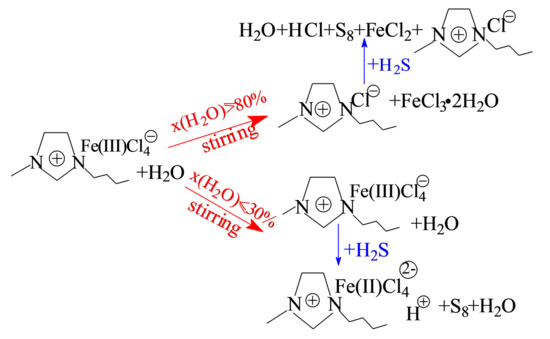
2.1. Effect of Water Concentration on the Formation of [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures
2.2. Acidity of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures
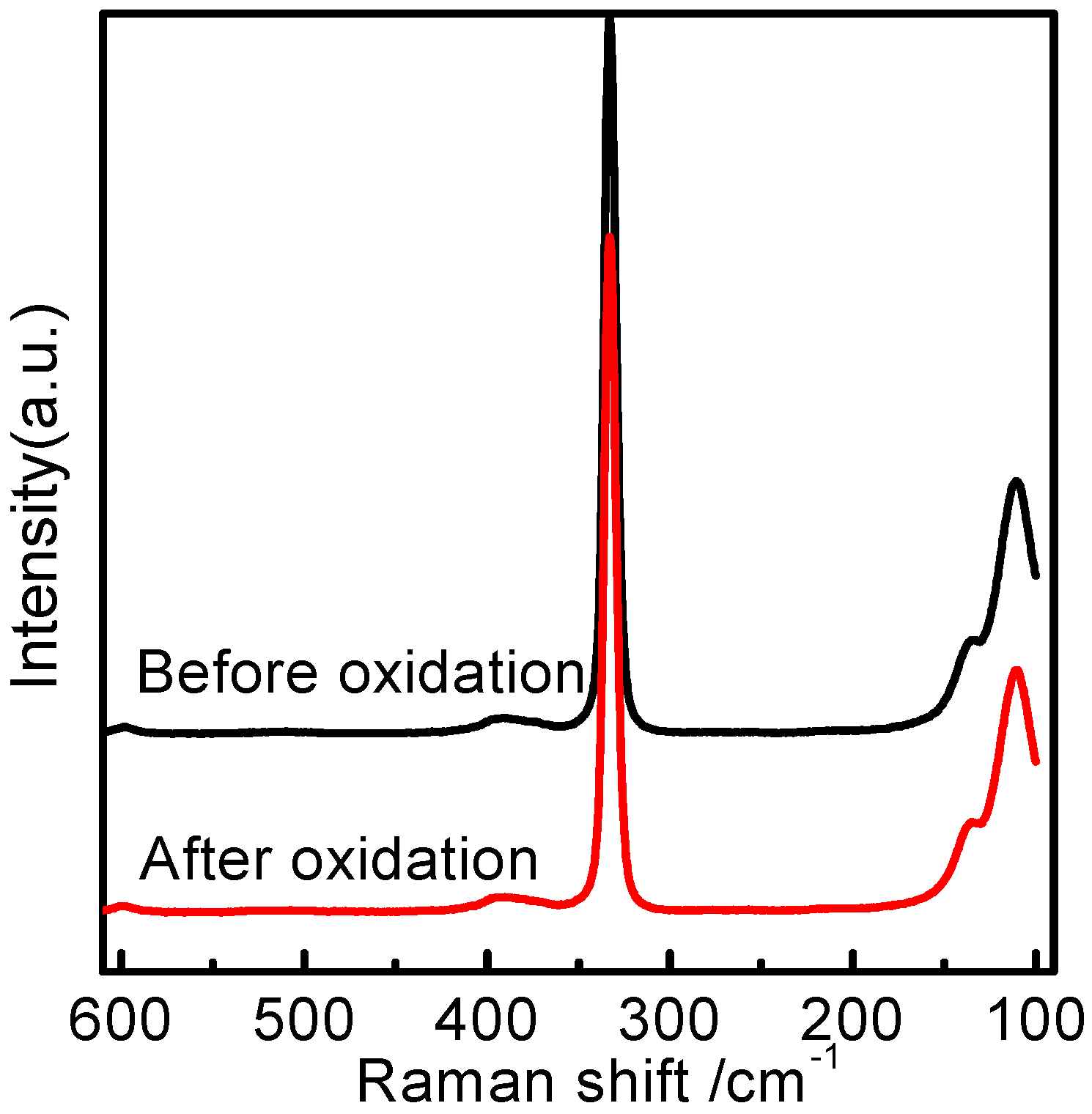
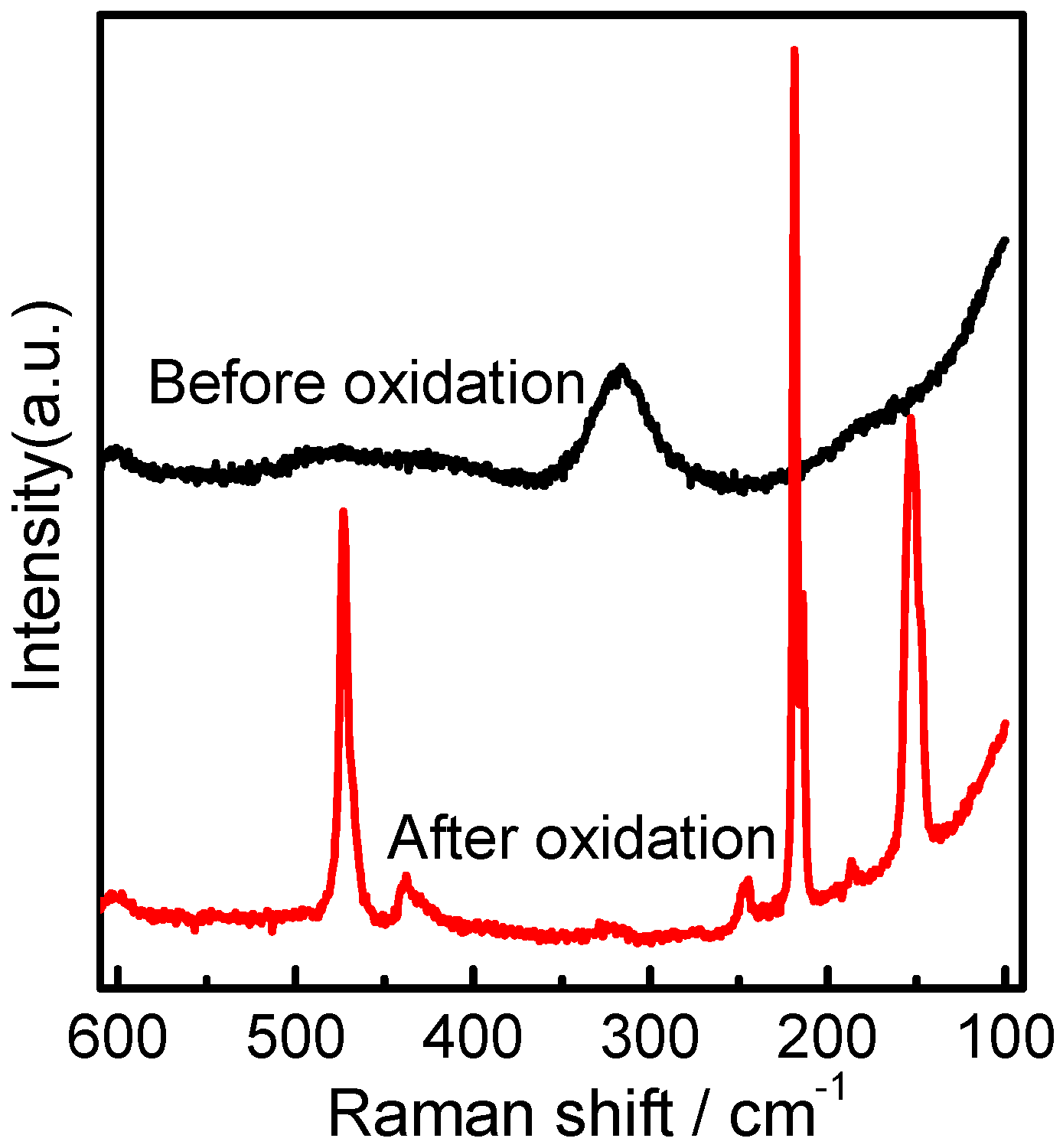
2.3. Raman Spectral Analysis of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures

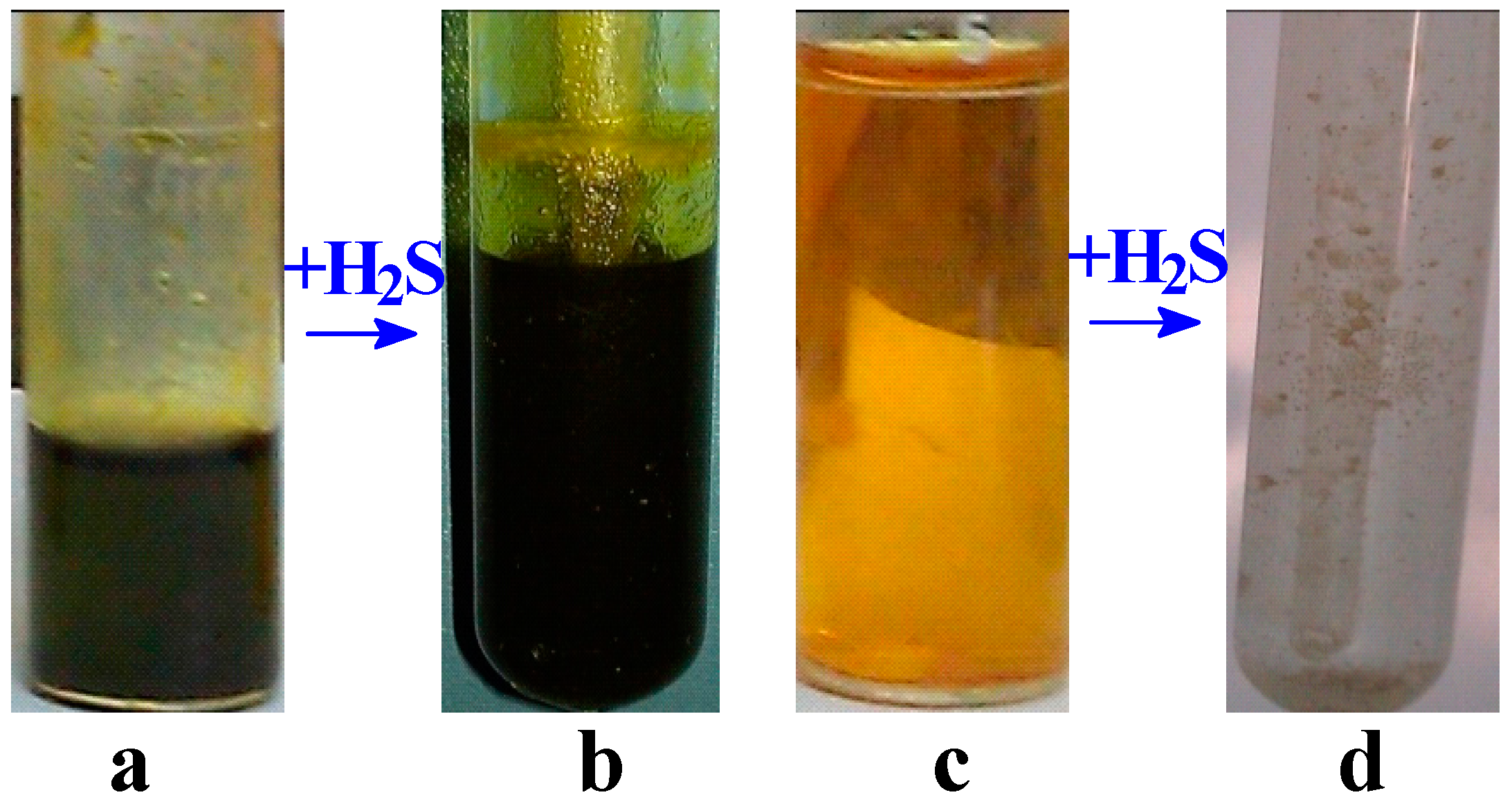
2.4. Oxidative Absorption of H2S by Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures

3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Absorption Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, H. Discovery of a magnetic ionic liquid [bmim]FeCl4. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1590–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Saito, G. Influence of structural variations in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cation and tetrahalogenoferrate(III) anion on the physical properties of the paramagnetic ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-G.; Yang, J.-Z.; Lu, X.-M.; Gui, J.-S.; Huang, M. Studies on an ionic liquid based on FeCl3 and its properties. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 226, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Gaertner, P. An iron-containing ionic liquid as recyclable catalyst for aryl grignard cross-coupling of alkyl halides. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yan, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Fe-containing magnetic ionic liquid as an effective catalyst for the glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Nguyen, L.; Jeon, E.; Kim, J.; Cheong, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Fe-containing ionic liquids as catalysts for the dimerization of bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-diene. J. Catal. 2008, 258, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, S.J.; Motekaitis, R.J.; Martell, A.E. Degradation of coordinated β-diketonates as iron chelate catalysts during the oxidation of H2S to S8 by molecular oxygen. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2000, 299, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, D.; Martell, A.E. The evolution, chemistry and applications of chelated iron hydrogen sulfide removal and oxidation processes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 117, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, A.; Bellussi, G.; Pollesel, P.; Romano, U.; Perego, C. Process for the Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide, by Means of its Oxidation in the Presence of Hetero Polyacids. U.S. Patent 7,553,473 B2, 30 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, L. Wet oxidation desulfurization of hydrogen sulfide with application of Fe-based ionic liquid. CIESC J. 2010, 61, 963–968. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Ha, S.H.; You, C.-Y.; Koo, Y.-M. Recovery of magnetic ionic liquid [bmim]FeCl4 using electromagnet. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 436–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, B.; Zhao, C.; Qian, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, G. Recovery of [bmim]FeCl4 from homogeneous mixture using a simple chemical method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, U.; Pobudkowska, A.; Rogalski, M. Surface tension of binary mixtures of imidazolium and ammonium based ionic liquids with alcohols, or water: Cation, anion effect. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishina, E.P.; Ramenskaya, L.M.; Gruzdev, M.S.; Kraeva, O.V. Water effect on physicochemical properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids with inorganic anions. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 177, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Kumar, A. Cation-anion-water interactions in aqueous mixtures of imidazolium based ionic liquids. Vib. Spectrosc 2011, 55, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, P.; Stepinski, D.; Rausch, D.; Bergeron, R.; Jakab, S.; Dietz, M. Solute-induced dissolution of hydrophobic ionic liquids in water. Talanta 2007, 72, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, G.A.; Heller, W.T. Small-angle neutron scattering studies of model protein denaturation in aqueous solutions of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Yue, S.; Cokoja, M.; Zhou, M.-D.; Zang, S.-L.; Kühn, F.E. Imidazolium perrhenate ionic liquids as efficient catalysts for the selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfones. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 744, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashin, A.S.; Galkin, K.I.; Khokhlova, E.A.; Ananikov, V.P. Direct observation of self-organized water-containing structures in the liquid phase and their influence on 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural formation in ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piché, S.; Larachi, F. Dynamics of pH on the oxidation of with iron(III) chelates in anoxic conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 7673–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Oxidative absorption of hydrogen sulfide by iron-containing ionic liquids. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 5930–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Kou, Y. Determination of the Lewis acidity of ionic liquids by means of an IR spectroscopic probe. Chem. Commun. 2004, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Li, C.; Tao, L.; Yu, N.; Hu, S.; Yin, D. Synthesis of diphenylmethane derivatives in Lewis acidic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 245, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Li, P.; Sun, L.; He, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Mu, R.; Yu, J. Physicochemical properties of iron-based chloride imidazole ionic liquid and wet desulfurization mechanism of hydrogen sulfide. J. China Coal Soc. 2011, 36, 135–139. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, M. Characterization of [bmim]Cl/FeCl3 ionic liquid with spectra. Pet. Sci. 2005, 2, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Marston, A.; Bush, S. Raman spectral investigation of the complex species of ferric chloride in concentrated aqueous solution. Appl. Spectrosc. 1972, 26, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Etschmann, B.; Brugger, J.; Spiccia, L.; Foran, G.; McInnes, B. UV–Vis spectrophotometric and XAFS studies of ferric chloride complexes in hyper-saline LiCl solutions at 25–90 °C. Chem. Geol. 2006, 231, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, I.; Fletcher, J.; Bates, C.; Lockwood, D.; Mischler, G. Temperature dependent electron-phonon coupling in FeCl2 observed by raman scattering. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1978, 11, 4425–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černošek, Z.; Holubova, J.; Černošková, E.; Růžička, A. Sulfur—A new information on this seemingly well-known element. J. Non Oxide Glasses 2009, 1, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gendel, Y.; Levi, N.; Lahav, O. H2S(g) removal using a modified, low-pH liquid redox sulfur recovery (LRSR) process with electrochemical regeneration of the Fe catalyst couple. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8315–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deberry, D.W.; Trofe, T.W. Composition and Process for the Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide from Gaseous Streams. U.S. Patent 5,705,135 A, 6 January 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Kleerebezem, R.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Kinetics of the reactive absorption of hydrogen sulfide into aqueous ferric sulfate solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, F.-Y.; Mather, A.E. Solubility of hydrogen sulfide in [bmim][PF6]. Int. J. Thermophys. 2007, 28, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, A.H.; Rahmati-Rostami, M.; Ghotbi, C.; Hosseini-Jenab, M.; Ahmadi, A.N. Solubility of H2S in ionic liquids [bmim][PF6], [bmim][BF4], and [bmim][TF2N]. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomelli, C.S.; Chiappe, C.; Vidis, A.; Laurenczy, G.; Dyson, P.J. Influence of the interaction between hydrogen sulfide and ionic liquids on solubility: Experimental and theoretical investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13014–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Tavassoli, A.; Nassernejad, B. Kinetic studies and reactor modeling of single step H2S removal using chelated iron solution. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2010, 88, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
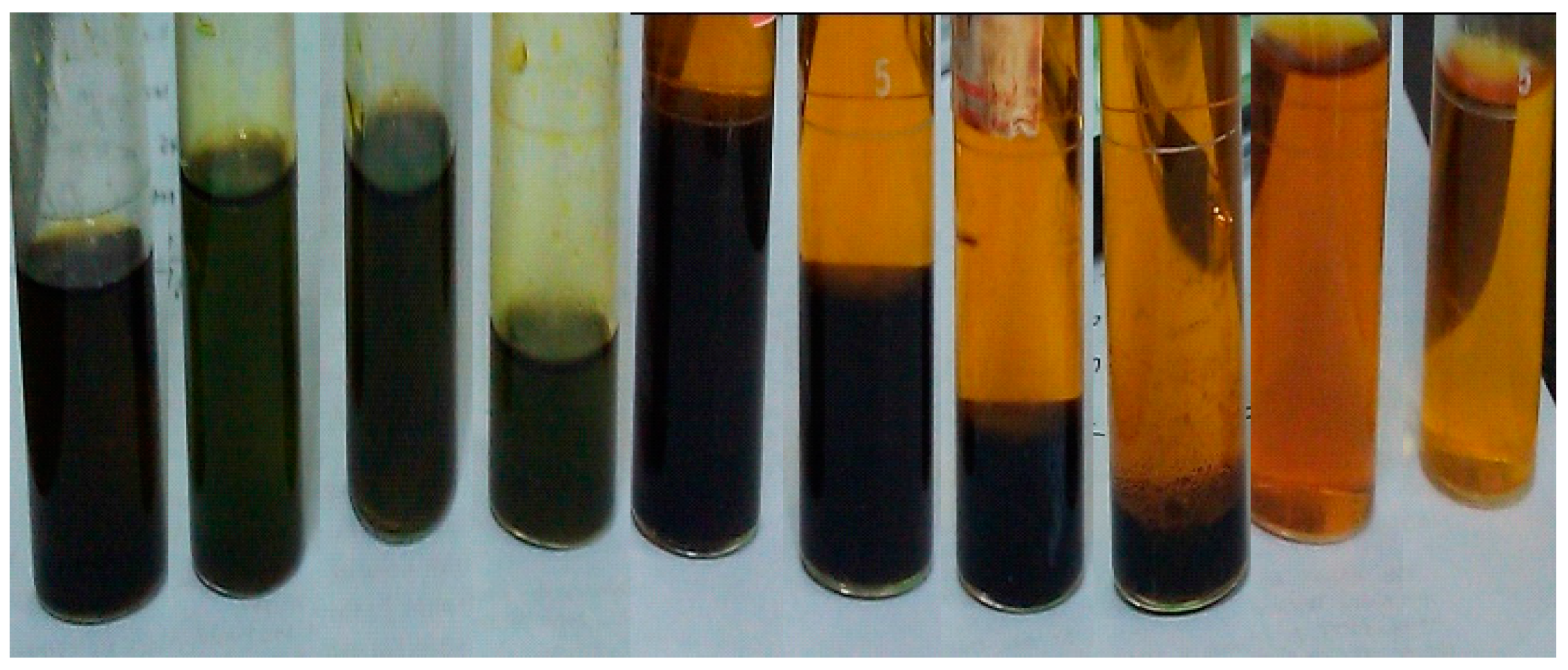


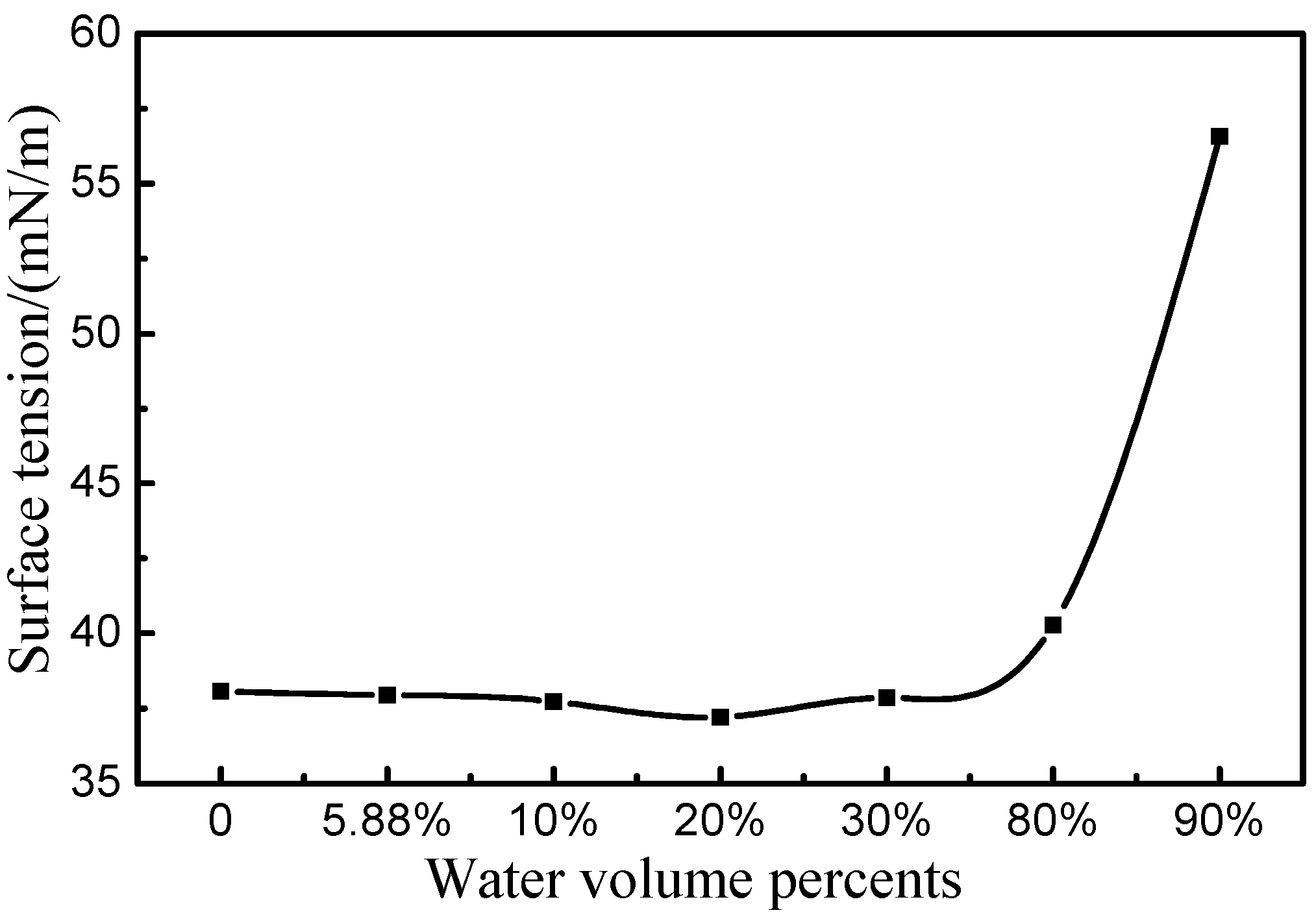
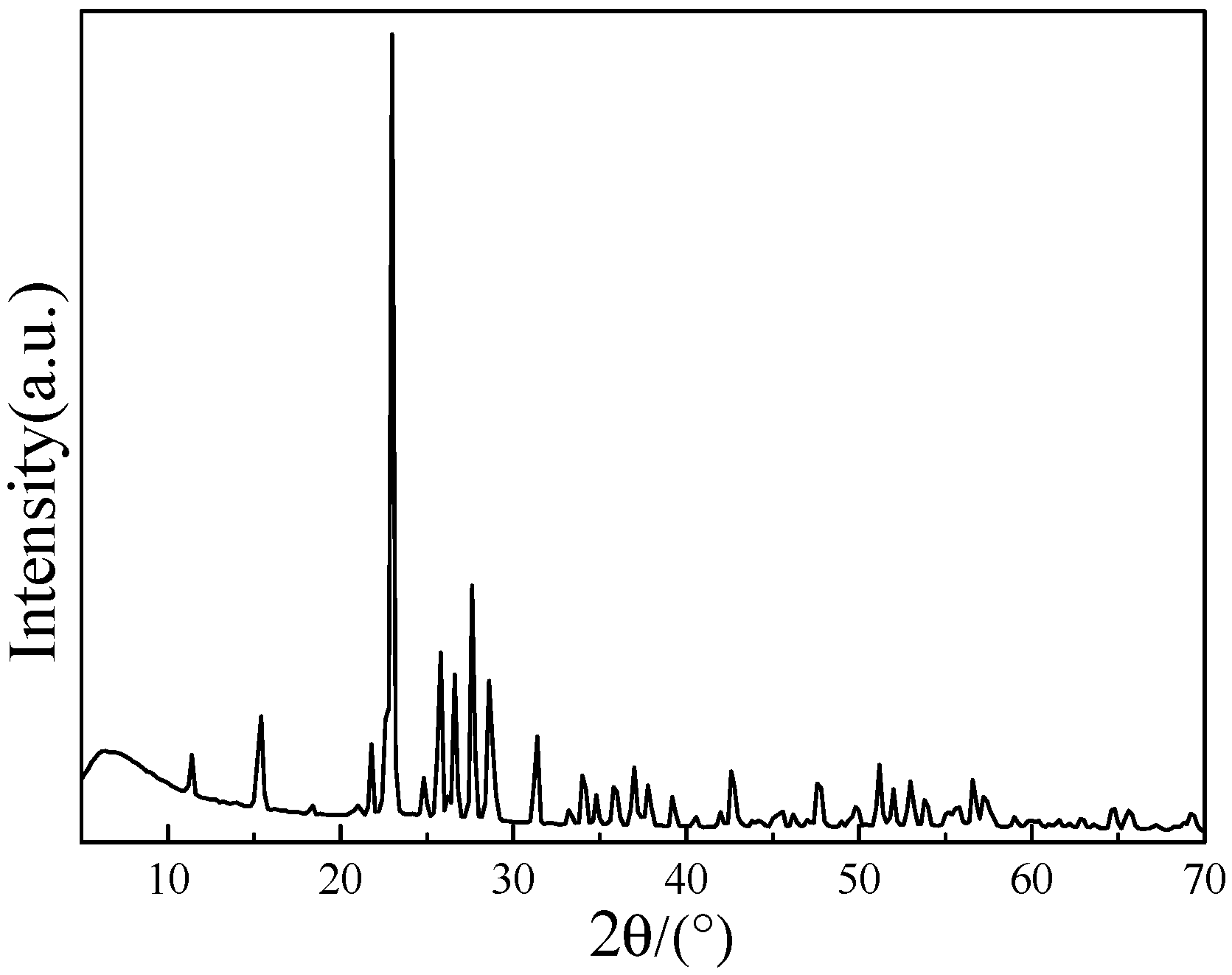
| Water Concentration in Homogeneous Mixtures (v/v) % | 0 | 5.88 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight percent of iron(III) in homogeneous mixtures (%) | 16.6 | 15.87 | 4.19 |
| Weight percent of absorbed H2S in mixtures (%) | 0.78 | 0.82 | 1.15 |
| Concentration of volatile HCl in mixtures (×10−6) | 841.11 | 326.86 | 52.16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Ding, R. Effect of Water Content on Properties of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures and Their Application in Oxidative Absorption of H2S. Inorganics 2018, 6, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6010011
Wang J, Ding R. Effect of Water Content on Properties of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures and Their Application in Oxidative Absorption of H2S. Inorganics. 2018; 6(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianhong, and Renren Ding. 2018. "Effect of Water Content on Properties of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures and Their Application in Oxidative Absorption of H2S" Inorganics 6, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6010011
APA StyleWang, J., & Ding, R. (2018). Effect of Water Content on Properties of Homogeneous [bmim]Fe(III)Cl4–H2O Mixtures and Their Application in Oxidative Absorption of H2S. Inorganics, 6(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6010011