Manganese-Substituted Myoglobin: Characterization and Reactivity of an Oxidizing Intermediate towards a Weak C-H Bond
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
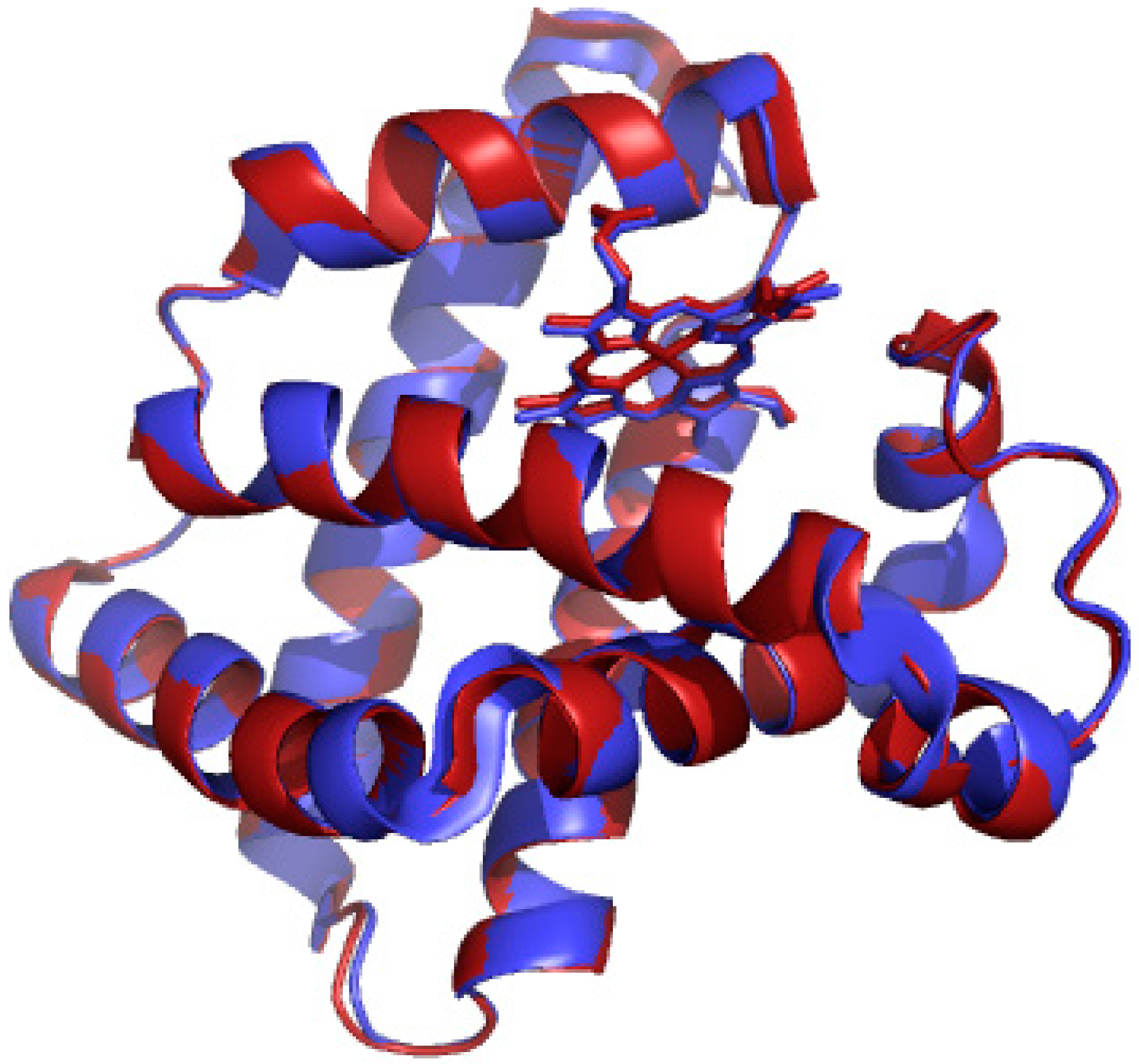
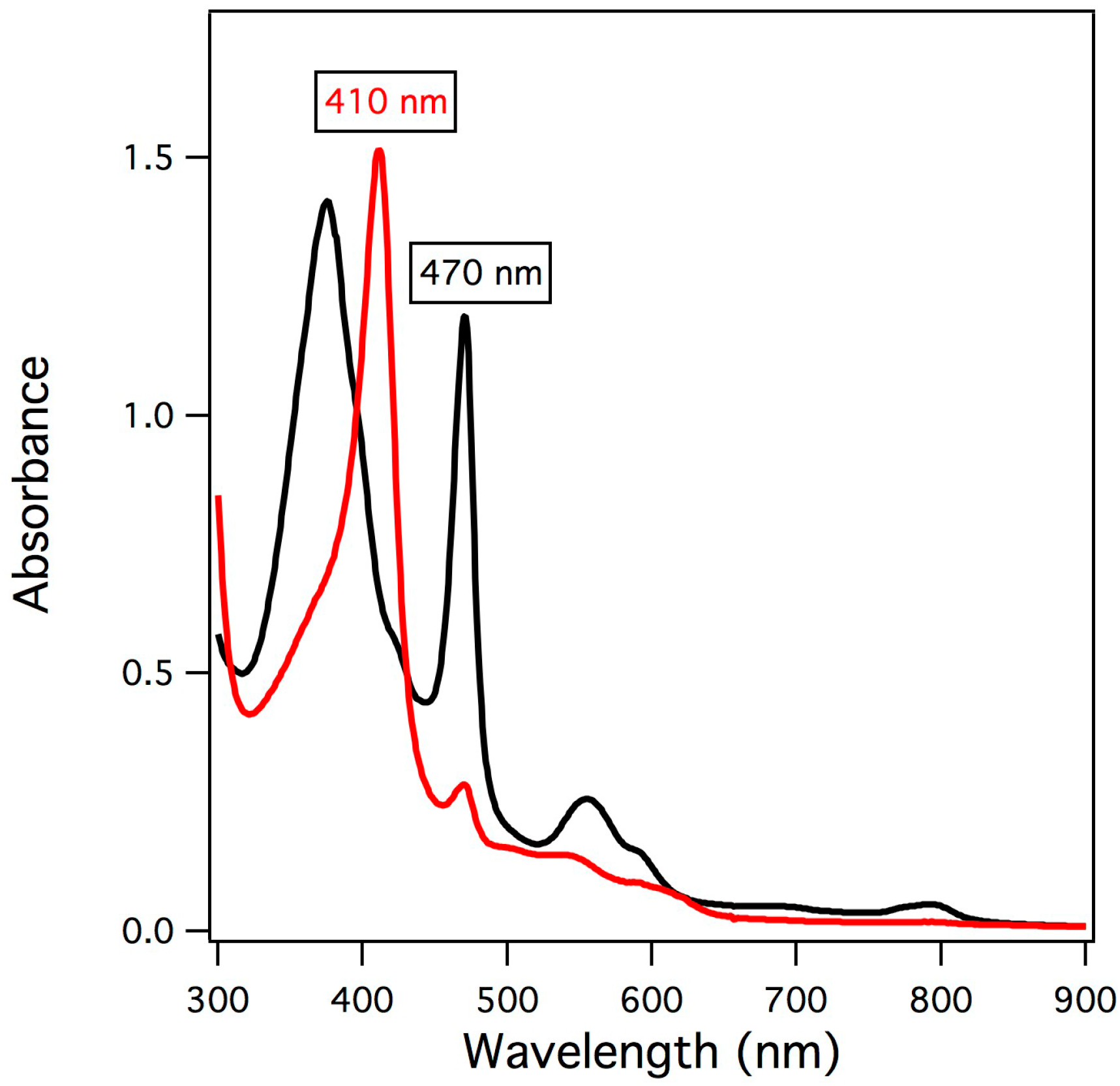
2.1. UV/vis Spectroscopy of Manganese-Substituted Myoglobin
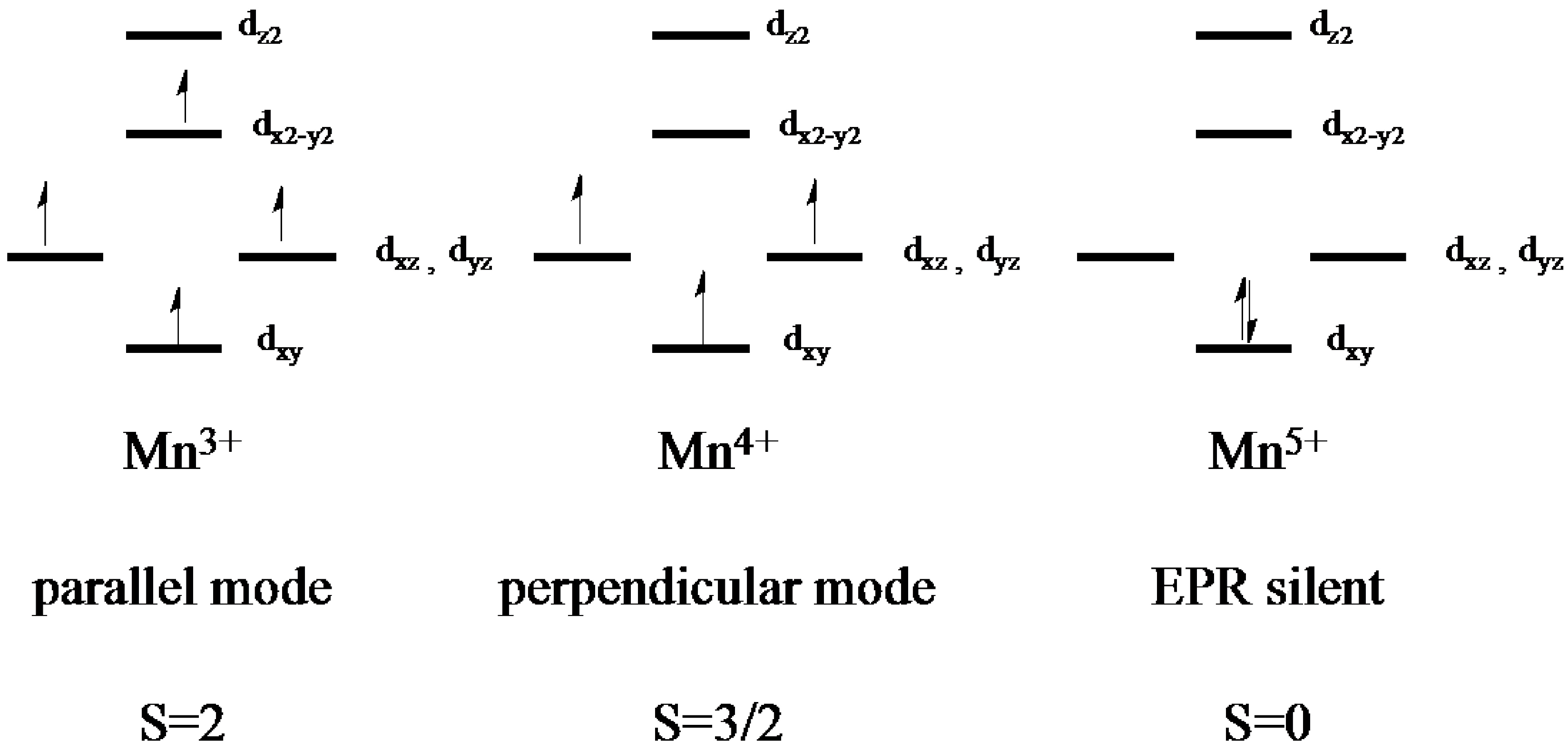
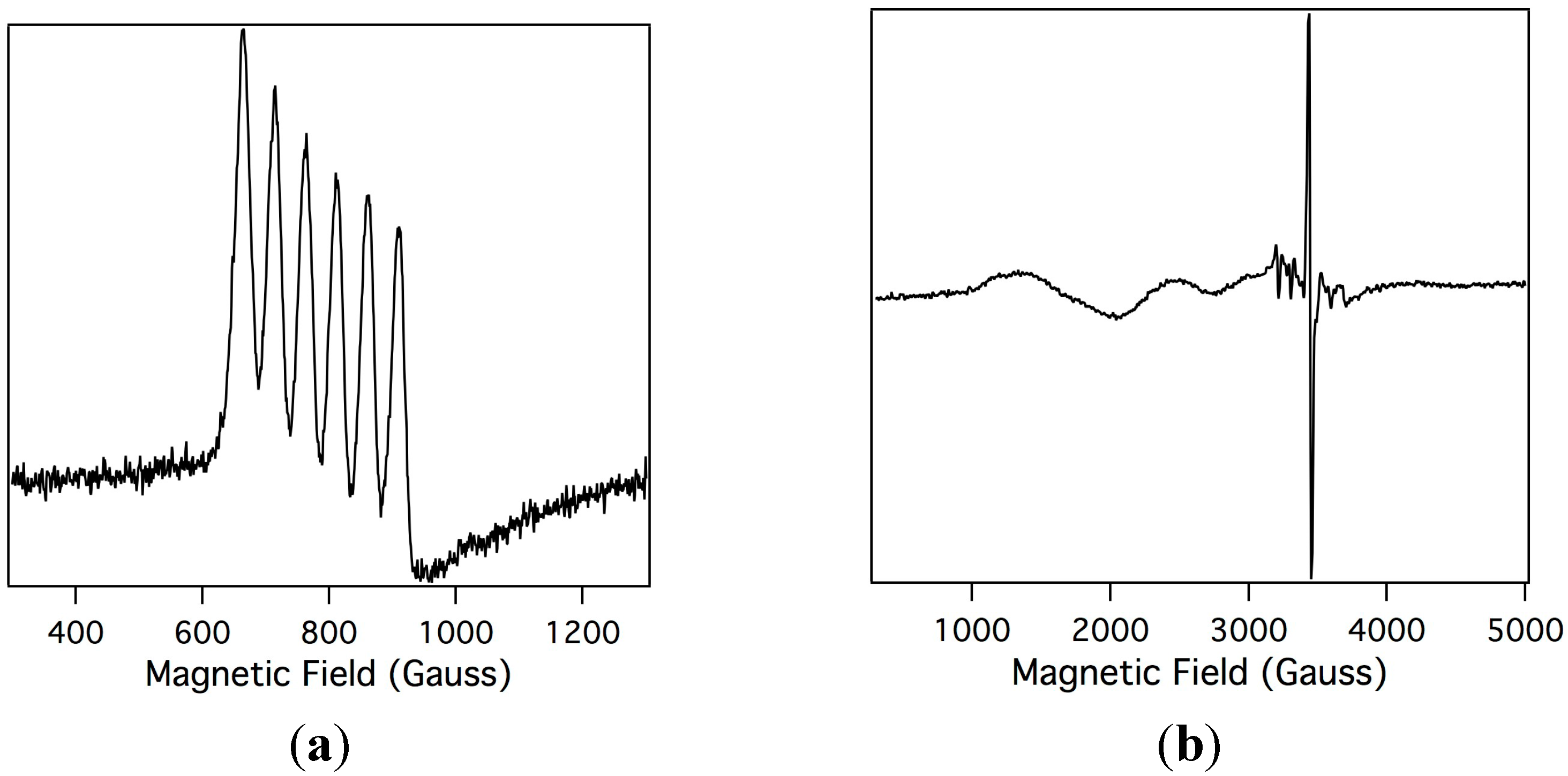
2.2. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance of the Mn-Myoglobin Intermediate

2.3. Reaction of the Mn-Myoglobin Intermediate with 1,4 Cyclohexadiene
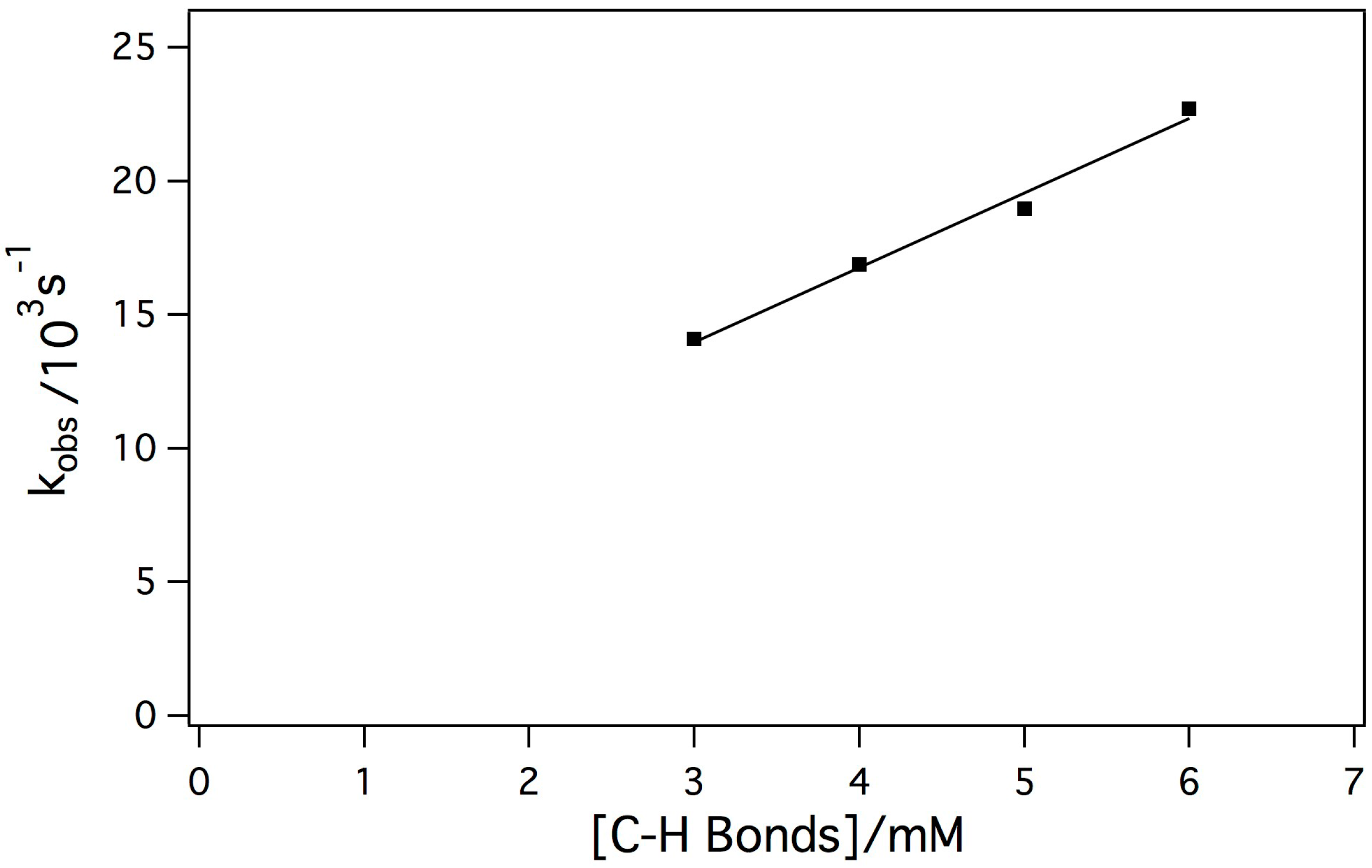
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Methods
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Preparation of Mn-Myoglobin
3.4. Preparation of EPR Samples
3.5. Kinetic analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, C.M.; Ward, T.R. Design of artificial metalloenzymes. Appl. Organometallic Chem. 2005, 19, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, S.-I.; Matsui, T.; Watanabe, Y. Conversion of Myoglobin into a Highly Stereo-specific Peroxygenase by the L29H/H64L Mutation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 9784–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Ohashi, M.; Kono, M.; Kondo, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yamane, T.; Watanabe, Y. Crystal Structures of Artificial Metalloproteins: Tight Binding of FeIII(Schiff-Base) by Mutation of Ala71 to Gly in Apo-Myoglobin. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 2852–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, N.; Ueno, T.; Unno, M.; Matsui, T.; Ikeda-Saito, M.; Watanabe, Y. Ligand design for the improvement of stability of metal complex: Protein hybrids. Chem. Comm. 2008, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, C.; Lebioda, L.; Dawson, J.H. Amphitrite ornata Dehaloperoxidase (DHP): Investigations of Structural Factors that Influence the Mechanism of Halophenol Dehalogenation Using “Peroxidase-like” Myoglobin Mutants and “Myoglobin-like” DHP Mutants. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8172–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, D.K.; Liang, L.; Barrios, D.A.; Zhang, J.-L.; Lu, Y. The Important Role of Covalent Anchor Positions in Tuning Catalytic Properties of a Rationally Designed MnSalen-Containing Metalloenzyme. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-W.; Yeung, N.; Gao, Y.-G.; Miner, K.D.; Lei, L.; Robinson, H.; Lu, Y. Introducing a 2-His-1-Glu Non-heme Iron Center into Myoglobin Confers Nitric Oxide Reductase Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9970–9972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yeung, N.; Sieracki, N.; Marshall, N.M. Design of Functional Metalloproteins. Nature 2009, 460, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yeung, N.; Russell, B.S.; Garner, D.K.; Lu, Y. Catalytic Reduction of NO to N2O by a Designed Heme-Copper Center in Myoglobin: Implications for the Role of Metal Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6766–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, B.A.; Sligar, S.G.; Olson, J.S.; Phillips, G.M., Jr. Mechansims of Ligand Recognition in Myoglobin. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, J.K.S.; Skibsted, L. Nitric Oxide and Myoglobins. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Dejima, H.; Matsuo, T.; Sato, H.; Murata, D.; Hisaeda, Y. Blue Myoglobin Reconstituted with an Iron Porphycene Shows Extremely High Oxygen Affinity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11226–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, T.; Hayashi, A.; Abe, M.; Matsuda, T.; Hisaeda, Y.; Hayashi, T. Meso-Unsubstituted Iron Corrole in Hemoproteins: Remarkable Differences in Effects on Peroxidase Activities between Myoglobin and Horseradish Peroxidase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15124–15125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oohora, K.; Kihira, Y.; Mizohata, E.; Inoue, T.; Hayashi, T. C(sp3)-H hydroxylation catalyzed by Myoglobin reconstituted with manganese porphycene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17282–17285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Ikeda-Saito, M.; Yonetani, T. Electron paramagnetic resonance and spectrophotometric studies of the peroxide compounds of manganese-substituted horseradish peroxidase, cytochrome-c peroxidase, and manganese-porphyrin model complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 912, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterman, M.R.; Yonetani, T. Studies on Modified Hemoglobins I. Properties of Hybrid Hemoglobins Containing Manganese Protoporphyrin IX. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 5847–5852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yonetani, T.; Asakura, T. Studies on Cytochrome c Peroxidase: IV. Comparison of Manganese Porphyrin-Containing Cytochrome c Peroxidase, Horseradish Peroxidase, and Myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, L.C. Metal Replaced Hemoproteins. J. Chem. Educ. 1976, 53, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-Z.; Taniguchi, I.; Mulchandani, A. Redox properties of engineered ruthenium myoglobin. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 75, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, M.S.; Mazumdar, S.; Mitra, S. Binding of Cyanide and Thiocyanate to Manganese Reconstituted Myoglobin and Formation of Peroxide Compound: Optical Spectral, Multinuclear NMR, and Kinetic Studies. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 5362–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.S.; Mitra, S. Kinetic studies of the two-step reactions of H2O2 with manganese-reconstituted myoglobin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1296, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, D.R.; Addison, A.W.; Dolphin, D.; James, B.R. Preparation of Ruthenium(II) and Ruthenum(III) Myoglobin and the Reaction of Dioxygen, and Carbon Monoxide, with Ruthenium (II) Myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 7002–7006. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zahran, Z.N.; Chooback, L.; Copeland, D.M.; West, A.H.; Richter-Addo, G.B. Crystal structures of manganese- and cobalt-substituted myoglobin in complex with NO and nitrite reveal unusal ligand conformations. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nick, R.J.; Ray, G.B.; Fish, K.M.; Spiro, T.G.; Groves, J.T. Evidence for a Weak Mn=O Bond and a Non-Porphyrin Radical in Manganese-Substituted Horseradish Peroxidase Compound I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 1838–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinecke, J.L.; Yi, J.; Pereira, J.C.M.; Richter-Addo, G.B.; Ford, P.C. Nitrite reduction by CoII and MnII substituted myoglobins. Towards understanding necessary components of Mb nitrite reductase activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 107, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Borovik, A.S. Monomeric Mn and Fe Complexes with Terminal Hydroxo and Oxo Ligands: Probing Reactivity via O-H Bond Dissociation Energies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13234–13242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.P. Corrolazines: New Frontiers in High-Valent Metalloporphyrinoid Stability and Reactivity. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdilla, M.J.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Manganese(III) Corrole-Oxidant Adduct as the Active Intermediate in Catalytic Hydrogen Atom Transfer. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 47, 10718–10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, J.T.; Gross, Z.; Stern, M.T. Preparation and Reactivity of Oxoiron(IV) Porphyrins. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 5065–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsell, T.H.; Behan, R.K.; Green, M.T.; Hendrich, M.P.; Borovik, A.S. Preparation and Properties of a Monomeric MnIV-Oxo complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8728–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsell, T.H.; Yang, M.-Y.; Borovik, A.S. C-H Bond Cleavage with Reductants: Re-Investigating the Reactivity of Monomeric MnIII/IV-Oxo Complexes and the Role of Oxo Ligand Basicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2762–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokop, K.A.; Neu, H.M.; de Visser, S.P.; Goldberg, D.P. A Manganese(V)-Oxo pi-Cation Radical Complex: Influence of One-Electron Oxidation on Oxygen-Atom Transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15874–15877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGown, A.J.; Kerber, W.D.; Fujii, H.; Goldberg, D.P. Catalytic Reactivity of a Mesa-N-Substituted Corrole and Evidence for a High-Valent Iron-Oxo Species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8040–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeladee, P.; Goldberg, D.P. Epoxidation Catalyzed by Manganese(V) Oxo and Imido Complexes: Role of the Oxidant-Mn-Oxo (Imido) Intermediates. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 3083–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Leeladee, P.; McGown, A.J.; DeBeer, S.; Goldberg, D.P. A high-valent Iron-oxo Corrolazine Activates C-H Bonds via Hydrogen-atom Transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7392–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Goldberg, I.; Botoshansky, M.; Buchman, Y.; Gross, Z. Oxygen Atom Transfer Reactions from Isolated (Oxo)manganese(V) Corroles to Sulfides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15233–15245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teale, F.W. Cleavage of the haem-protein link by acid methylethylketone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1959, 35, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.V.; Brayer, G.D. High-resolution study of the three-dimensional structure of horse heart metmyoglobin. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 213, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, H.B. Heme Peroxidases; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Drago, R.S. Physical Methods for Chemists, 2nd ed.; Saunders College Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.A.; Lashley, M.R.; Wyatt, J.K.; Nantz, M.H.; Britt, R.D. Dual-Mode EPR Study of Mn(III) Salen and the Mn(III) Salen-Catalyzed Epoxidation of cis-β-Methylstyrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5710–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shook, R.L.; Gunderson, W.A.; Greaves, J.; Ziller, J.W.; Hendrich, M.P.; Borovik, A.S. A Monomeric MnIII-Peroxo Complex Derived Directly from Dioxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8888–8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, S.C.; Wu, X.; Cho, J.; Cho, K.-B.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, M.S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kubo, M.; Ogura, T.; Shaik, S.; Nam, W. Water as an Oxygen Source: Synthesis, Characterization, and Reactivity Studies of a Mononuclear Nonheme Manganese(IV) Oxo Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8190–9194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, J.M. Hydrogen Atom Abstraction by Metal-Oxo Complexes: Understanding the Analogy with Organic Radical Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordwell, F.G.; Cheng, J.P.; Harrelson, J.A. Homolytic bond dissociation energies in solution from equilibrium acidity and electrochemical data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stone, K.L.; Hua, J.; Choudhry, H. Manganese-Substituted Myoglobin: Characterization and Reactivity of an Oxidizing Intermediate towards a Weak C-H Bond. Inorganics 2015, 3, 219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3020219
Stone KL, Hua J, Choudhry H. Manganese-Substituted Myoglobin: Characterization and Reactivity of an Oxidizing Intermediate towards a Weak C-H Bond. Inorganics. 2015; 3(2):219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3020219
Chicago/Turabian StyleStone, Kari L., Joey Hua, and Humdoon Choudhry. 2015. "Manganese-Substituted Myoglobin: Characterization and Reactivity of an Oxidizing Intermediate towards a Weak C-H Bond" Inorganics 3, no. 2: 219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3020219
APA StyleStone, K. L., Hua, J., & Choudhry, H. (2015). Manganese-Substituted Myoglobin: Characterization and Reactivity of an Oxidizing Intermediate towards a Weak C-H Bond. Inorganics, 3(2), 219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3020219







