[AuHg(o-C6H4PPh2)2I]: A Dinuclear Heterometallic Blue Emitter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
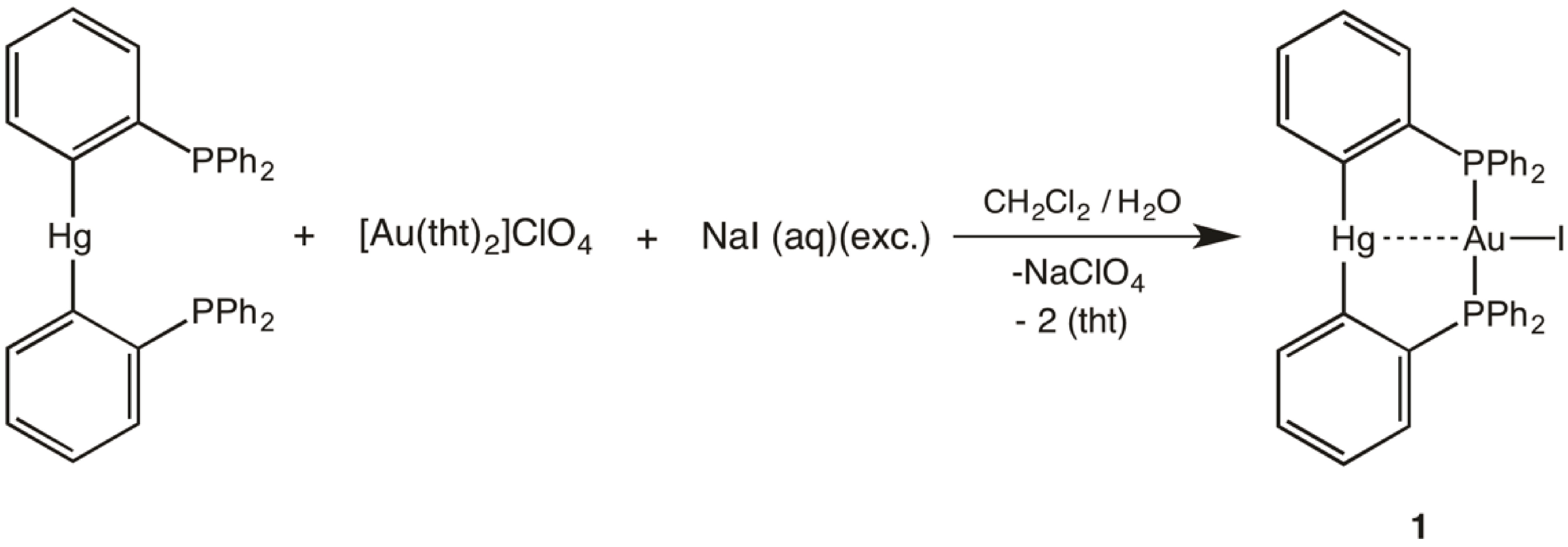
2.2. Crystal Structure
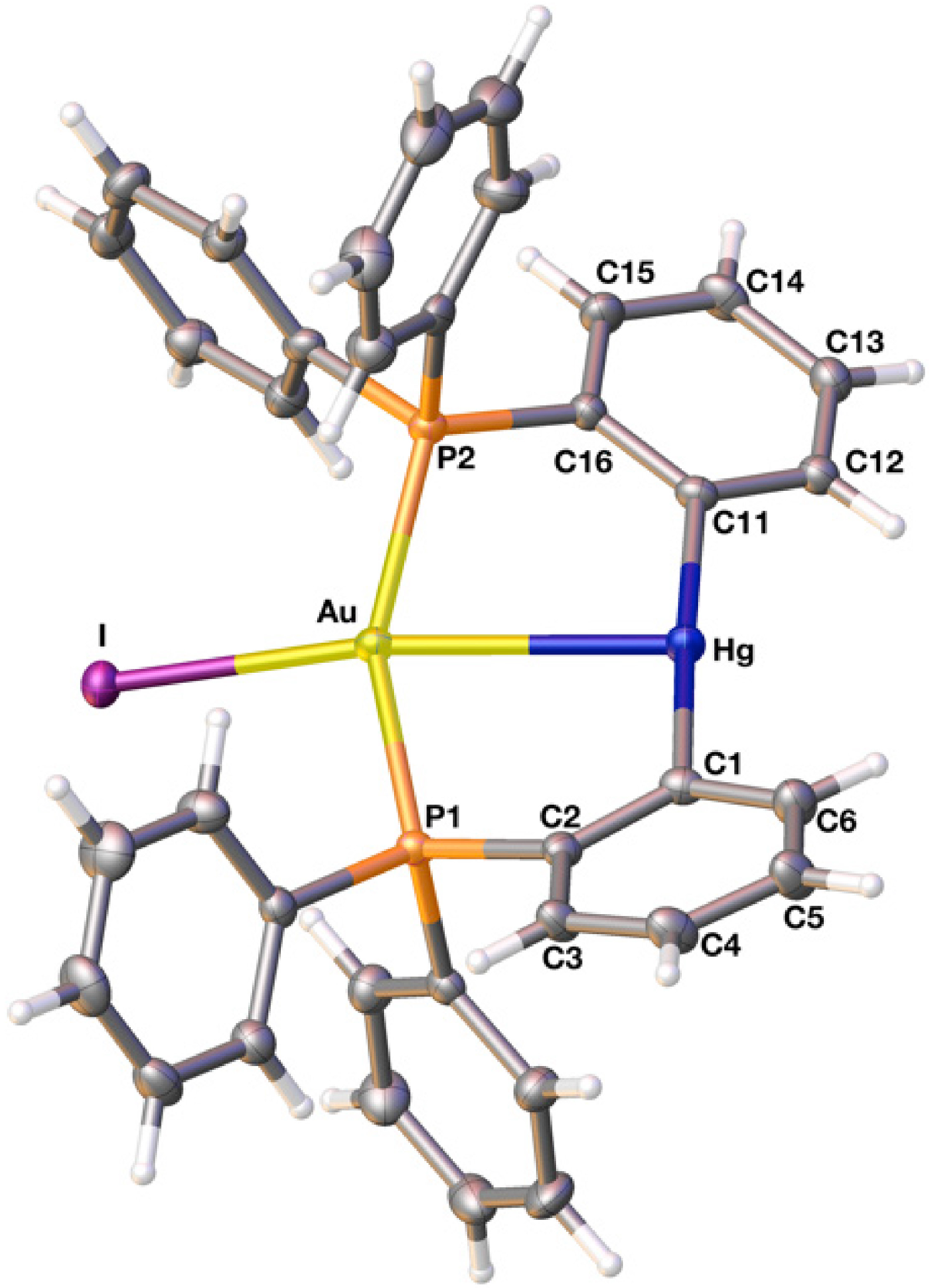
| Bond Distance (Å)/Angle(º) | 1 |
|---|---|
| Au-Hg | 3.0944(2) |
| Au-P(1) | 2.3298(11) |
| Au-P(2) | 2.3323(11) |
| Au-I | 2.8997(3) |
| Hg-C(1) | 2.097(4) |
| Hg-C(11) | 2.090(4) |
| P(1)-Au-P(2) | 154.25(4) |
| I-Au-Hg | 163.150(9) |
| C(1)-Hg-C(11) | 175.47(16) |
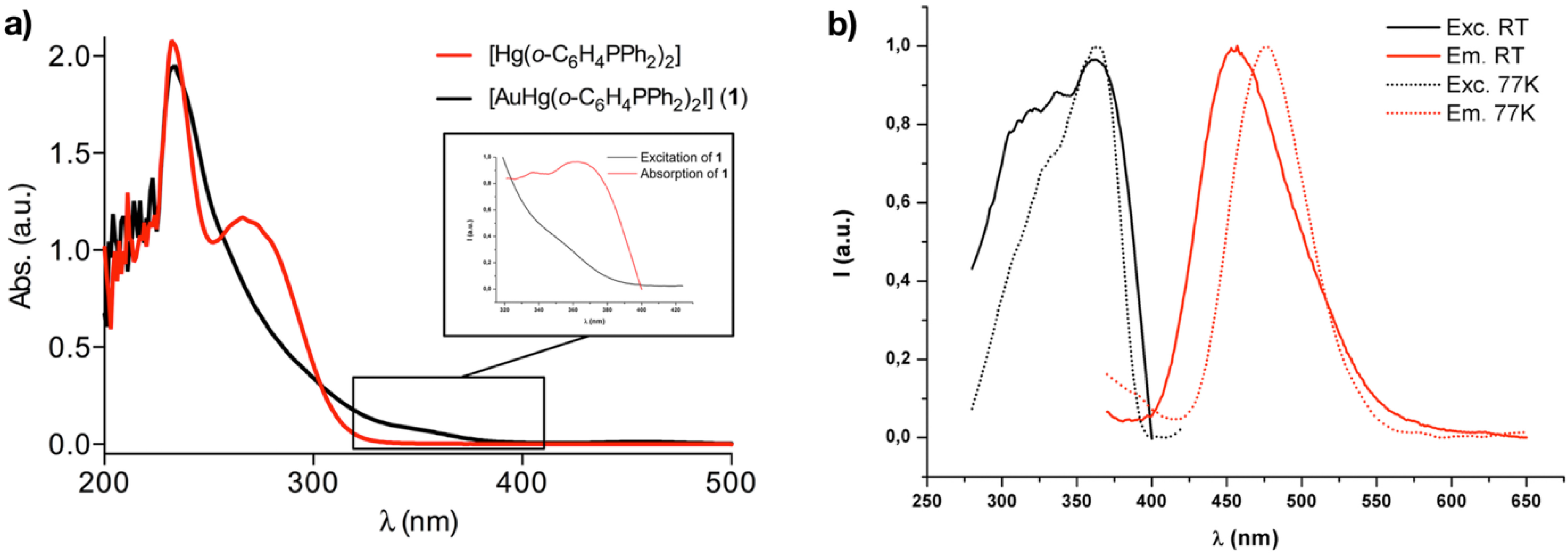
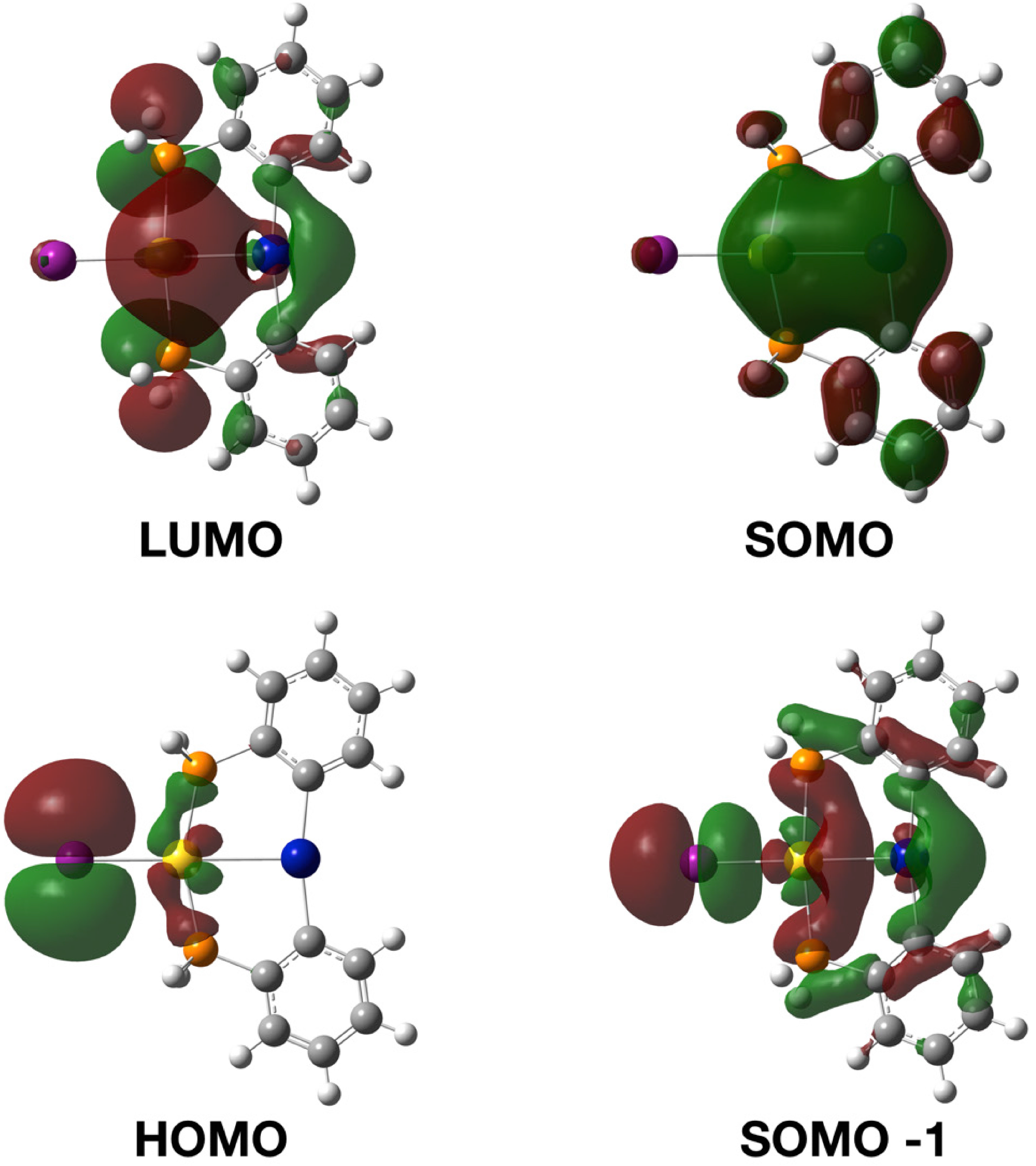
2.3. Photophysical Properties and Theoretical Calculations
| Complex | Medium (T [K]) | λabs [nm] (ε [M−1 cm−1]) | λem (λexc)[nm]/τ [μs]/]/Ф (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CH2Cl2 (RT) | 236(32920), 357(1246) | - |
| Solid (RT) | 456 (367)/1.57/27.6 | ||
| Solid (77K) | 475 (363) |
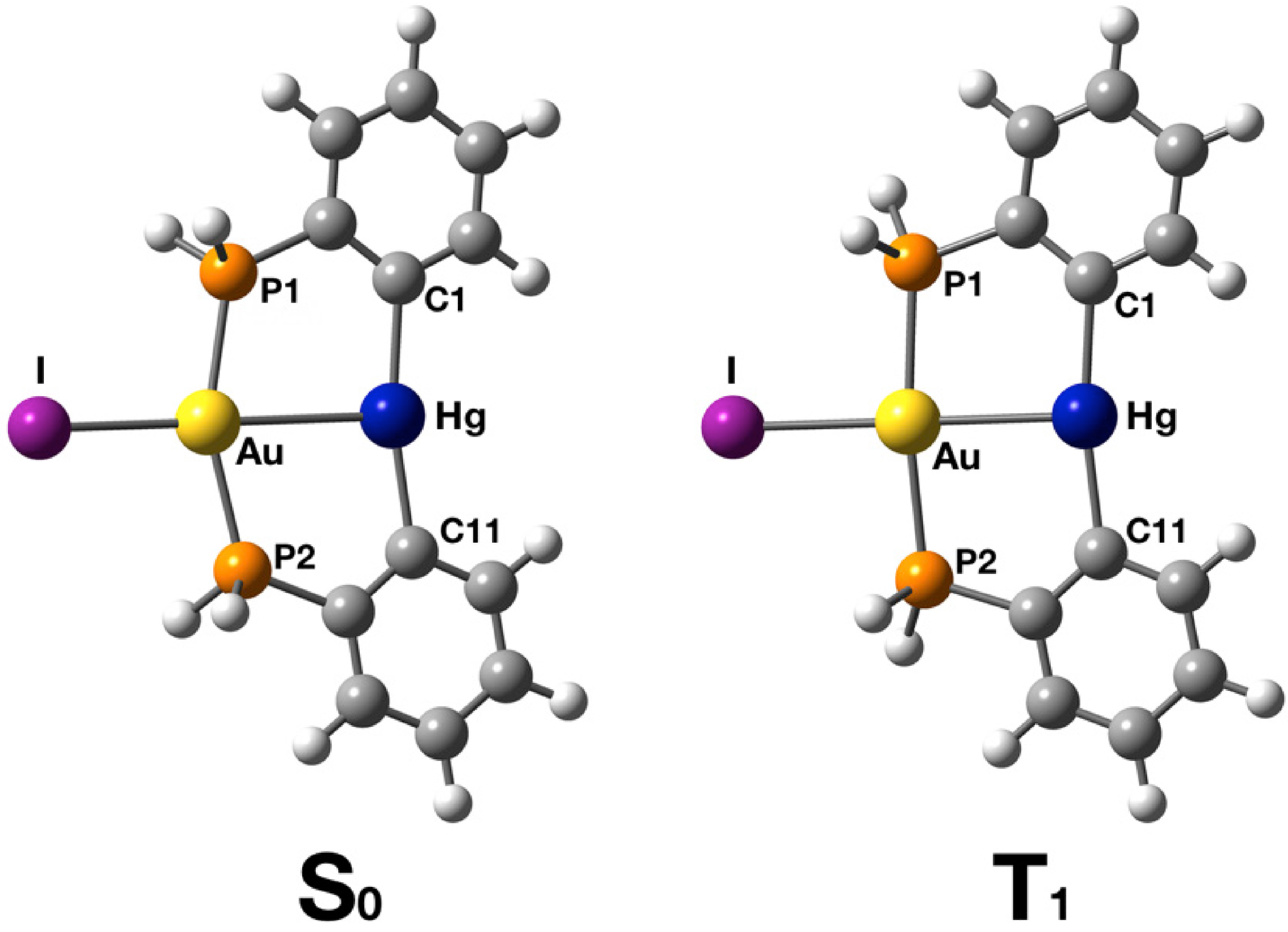
| Distances/Angles | Exp. in 1 | S0 in 1a | T1 in 1a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au-Hg | 3.09 | 3.05 | 2.79 |
| Au-P1 | 2.33 | 2.35 | 2.46 |
| Au-P2 | 2.33 | 2.35 | 2.46 |
| Au-I | 2.90 | 2.78 | 2.76 |
| Hg-C1 | 2.10 | 2.13 | 2.13 |
| Hg-C11 | 2.09 | 2.13 | 2.13 |
| Hg-Au-I | 163.2 | 180.0 | 179.0 |
| P1-Au-P2 | 154.3 | 157.4 | 168.3 |
| C1-Hg-C11 | 175.5 | 168.4 | 170.5 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Considerations
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Synthesis of [AuHg(o-C6H4PPh2)2I], 1
3.4. X-ray Crystallography Details
| Parameter | Compound 1 |
|---|---|
| Formula | C37 H30 Au Cl2 Hg I P2 |
| Formula weight | 1131.91 |
| Crystal habit | Colorless prism |
| Crystal size | 0.40 × 0.15 × 0.15 mm3 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/a |
| a/Å | 17.1928(4) |
| b/Å | 11.2469(3) |
| c/Å | 18.0925(4) |
| β/deg | β 96.1080(10) |
| V/Å3 | 3478.61(15) |
| Z | 4 |
| Dc/Mg·m−3 | 2.161 |
| Mr | 9.780 |
| F(000) | 2112 |
| T/K | 173 |
| θ range/deg | 3.90–27.60 |
| No. rflns measd | 52126 |
| No. unique rflns | 8039 |
| Rint | 0.0585 |
| Ra (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0278 |
| Rwb (F2, all rflns) | 0.0377 |
| Sc | 1.027 |
3.5. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laguna, A. Modern Supramolecular Gold Chemistry: Gold-Metal Interactions and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pyykkö, P. Strong Closed-Shell Interactions in Inorganic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 597–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyykkö, P. Theoretical chemistry of gold. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4412–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykkö, P. Theoretical chemistry of gold. III. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1967–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.J.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pérez, J.; Laguna, A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Fackler, J.P., Jr. {Tl[Au(C6Cl5)2]}n: A vapochromic complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2022–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roundhill, D.M.; Fackler, J.P., Jr. Optoelectronic Properties of Inorganic Compounds; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Koshevoy, I.O.; Chang, Y.-C.; Karttunen, A.J.; Haukka, M.; Pakkanen, T.; Chou, P.-T. Modulation of Metallophilic Bonds: Solvent-Induced Isomerization and Luminescence Vapochromism of a Polymorphic Au–Cu Cluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6564–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, V.J.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D. Copper(I)-assisted red-shifted phosphorescence in Au(I)···Cu(I) heteropolynuclear complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 16486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.J.; Laguna, A.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Montiel, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Rodríguez-Castillo, M. Photophysical and Theoretical Studies on Luminescent Tetranuclear Coinage Metal Building Blocks. Organometallics 2006, 25, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D.; Rodríguez-Castillo, M. Influence of the Electronic Characteristics of N-Donor Ligands in the Excited State of Heteronuclear Gold(I)–Copper(I) Systems. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6910–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D.; Rodríguez-Castillo, M. Very Short Metallophilic Interactions Induced by Three-Center–Two-Electron Perhalophenyl Ligands in Phosphorescent Au–Cu Complexes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 3720–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.J.; Laguna, A.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Montiel, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pérez, J.; Puelles, R.C. Mesitylgold(I) and Silver(I) Perfluorocarboxylates as Precursors of Supramolecular Au/Ag Systems. Organometallics 2006, 25, 4307–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.J.; Hardacre, C.; Laguna, A.; Lagunas, M.C.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Montiel, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Puelles, R.C.; Sanchez-Forcada, E. Multiple Evidence for Gold(I)···Silver(I) Interactions in Solution. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6222–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D. Experimental and Theoretical Comparison of the Metallophilicity between d10–d10 AuI–HgII and d8-d10 AuIII–HgII Interactions. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, O.; Laguna, A.; Fernández, E.J.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Jones, P.G.; Teichert, M.; Monge, M.; Pyykkö, P.; Runeberg, N.; Schütz, M.; Werner, H.J. Experimental and theoretical studies of the d8-d10 interaction between Pd(II) and Au(I): bis(chloro[(phenylthiomethyl)diphenylphosphine]gold(I))-dichloropalladium(II) and related systems. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 4786–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.J.; Laguna, A.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Nema, M.M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pérez, J.; Silvestru, C. Experimental and theoretical evidence of the first Au(I)···Bi(III) interaction. Chem. Commun. 2007, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilma Bojan, R.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Echeverría, R.; Lehtonen, O.; Sundholm, D. Double Photoinduced Jahn-Teller Distortion of Tetrahedral AuI-SnII Complexes. ChemPlusChem 2013, 79, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.J.; Laguna, A.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Mendizabal, F.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pérez, J. Theoretical and photoluminescence studies on the d10-s2 AuI-TlI interaction in extended unsupported chains. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D. Analysis of fluorescence quenching of naphthalene by two mercury containing organometallic complexes. J. Lumin. 2014, 154, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D. Experimental and Theoretical Evidence of the Existence of Gold (I)···Mercury (II) Interactions in Solution through Fluorescence-Quenching Measurements. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4754–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.J.; Laguna, A.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pérez, J. [{AuTl(C6Cl5)2(toluene)}2(dioxane)]: A striking structure that leads to a blue luminescence. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1760–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.J.; Laguna, A.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Montiel, M.; Olmos, M.E. Photophysical Studies and Excited-State Structure of a Blue Phosphorescent Gold−Thallium Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2953–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, A.J.; Donamaría, R.; Lippolis, V.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Manso, E.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E. Influence of Crown Thioether Ligands in the Structures and of Perhalophenyl Groups in the Optical Properties of Complexes with Argentoaurophilic Interactions. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 10471–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Olmstead, M.M.; Balch, A.L. Inorganic topochemistry. Vapor-induced solid state transformations of luminescent, three-coordinate gold(I) complexes. Chem. Sci. 2012, 4, 311. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.H.; Schmitt, J.C.; Shearer, J.; Jia, J.; Olmstead, M.M.; Fettinger, J.C.; Balch, A.L. Crystallographic and Computational Studies of Luminescent, Binuclear Gold(I) Complexes, AuI2(Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2)2I2 (n = 3–6). Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Chan, K.; Miskowski, V.; Che, C.-M. The intrinsic 3[dσ*pσ] emission of binuclear Gold(I) complexes with two bridging diphosphane ligands lies in the near UV; Emissions in the visible region are due to exciplexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2783–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.F.; Chan, K.C.; Cheung, K.K.; Che, C.M. Substrate-Binding reactions of the 3[dσ*pσ] excited state of binuclear gold(I) complexes with bridging bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)methane ligands: emission and time-resolved absorption spectroscopic studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 4656–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WebElements Periodic Table. Available online: http://www.webelements.com/ (accessed on 30 November 2014).
- Wang, S.; Fackler, J.P., Jr. Synthesis and characterization of [HgAu(CH2SPPh2CH2)2]PF6, the first example of structurally characterized carbene double insertions into metal-sulfur bonds. Organometallics 1989, 8, 1578–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Bhargava, S.K.; Griffiths, K.D.; Robertson, G.B.; Wickramasinghe, W.A.; Willis, A.C. Dinuclear Complexes of Gold(I) Containing Bridging Cyclometalated Arylphosphane or Arylarsane Ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1987, 26, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fackler, J.P., Jr. Heterobimetallic complexes of Gold and Mercury. Syntheses and characterizations of HgII(CH2P(S)Ph2)2(AuICl)2 and HgIIAuI(CH2P(S)Ph2)2AuIIICl4. Organometallics 1990, 9, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Usón, R.; Laguna, A.; Laguna, M.; Jiménez, J.; Gómez, M.P.; Sainz, A.; Jones, P.G. Gold complexes with heterocyclic thiones as ligands. X-ray structure determination of [Au(C5H5NS)2]ClO4. Dalton Trans. 1990, 3457–3463. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, M.A.; Contel, M.; Hockless, D.C.R.; Welling, L.L. Bis{(2-diphenylphosphino)phenyl} mercury: a novel bidentate ligand and transfer reagent for the o-C6H4PPh2 group. Chem. Commun. 1998, 21, 2401–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELX-97, Program for Crystal Structure Refinement; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, C.; Plesset, M.S. Note on an Approximation Treatment for Many-Electron Systems. Phys. Rev. 1934, 46, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Radom, L.; Schleyer, P.V.R.; Pople, J.A. Ab initio Molecular Orbital Theory; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Andrae, D.; Häußermann, U.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Energy-adjusted ab initio pseudopotentials for the second and third row transition elements. Theor. Chim. Acta 1990, 77, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykkö, P.; Runeberg, N.; Mendizabal, F. Theory of the d10–d10 Closed-Shell Attraction: 1. Dimers Near Equilibrium. Chem. Eur. J. 1997, 3, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.M.L.; Sundermann, A. Correlation consistent valence basis sets for use with the Stuttgart-Dresden-Bonn relativistic effective core potentials: The atoms Ga-Kr and In-Xe. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 3408–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergner, A.; Dolg, M.; Küchle, W.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Ab initio energy-adjusted pseudopotentials for elements of groups 13–17. Mol. Phys. 1993, 80, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzinaga, S.; Andzelm, J. Gaussian Basis Sets for Molecular Orbital Calculations; Huzinaga, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Huzinaga, S. Gaussian-type functions for polyatomic systems. I. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 42, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E.; Pascual, D. [AuHg(o-C6H4PPh2)2I]: A Dinuclear Heterometallic Blue Emitter. Inorganics 2015, 3, 27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010027
López-de-Luzuriaga JM, Monge M, Olmos ME, Pascual D. [AuHg(o-C6H4PPh2)2I]: A Dinuclear Heterometallic Blue Emitter. Inorganics. 2015; 3(1):27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-de-Luzuriaga, José M., Miguel Monge, M. Elena Olmos, and David Pascual. 2015. "[AuHg(o-C6H4PPh2)2I]: A Dinuclear Heterometallic Blue Emitter" Inorganics 3, no. 1: 27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010027
APA StyleLópez-de-Luzuriaga, J. M., Monge, M., Olmos, M. E., & Pascual, D. (2015). [AuHg(o-C6H4PPh2)2I]: A Dinuclear Heterometallic Blue Emitter. Inorganics, 3(1), 27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010027






