Mg-Doped Li2FeTiO4 as a High-Performance Cathode Material Enabling Fast and Stable Li-ion Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
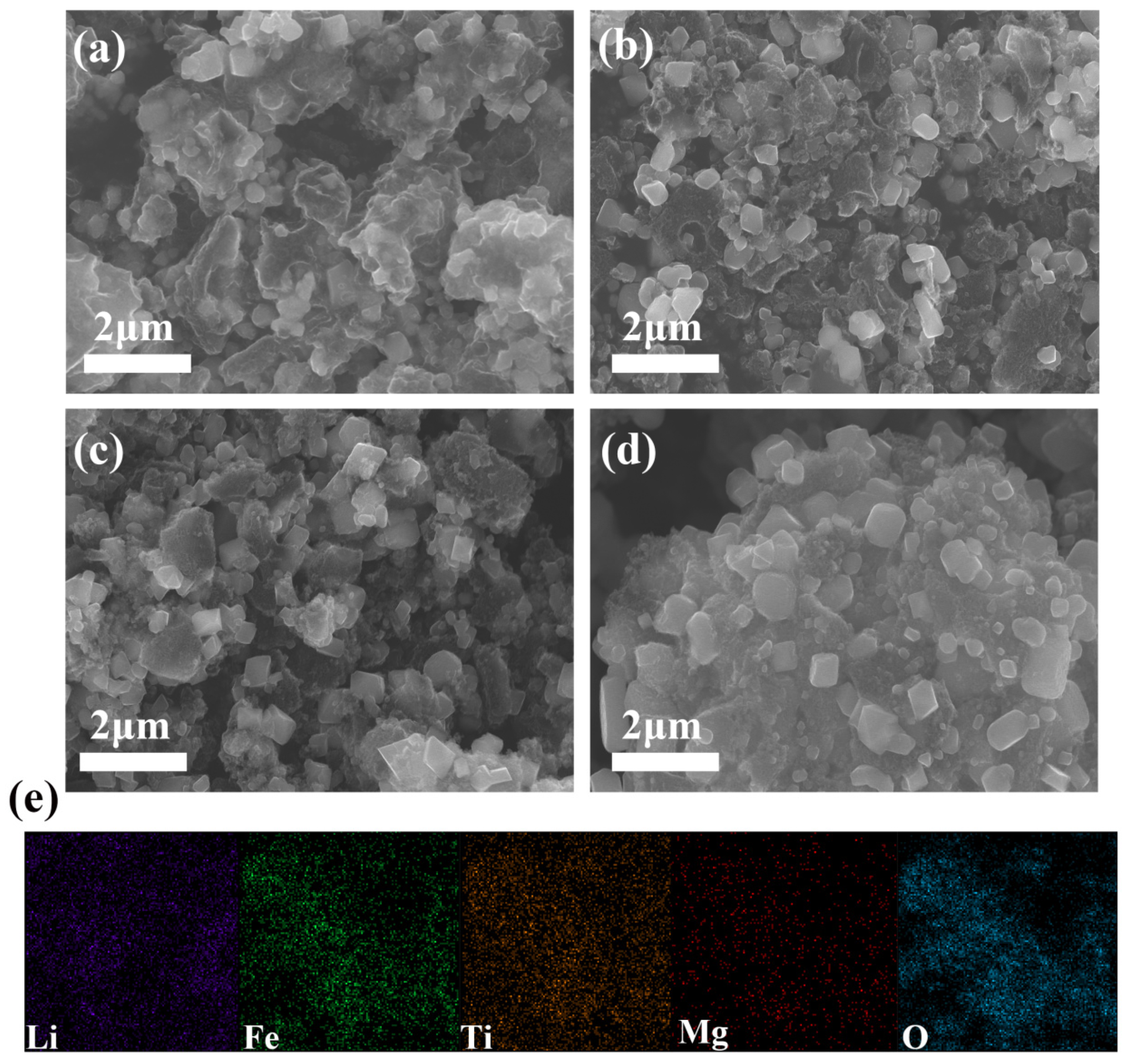
2.1. SEM Analysis of Li2MgxFe1−xTiO4 Samples
2.2. XRD Analysis of Li2MgxFe1−xTiO4 Samples
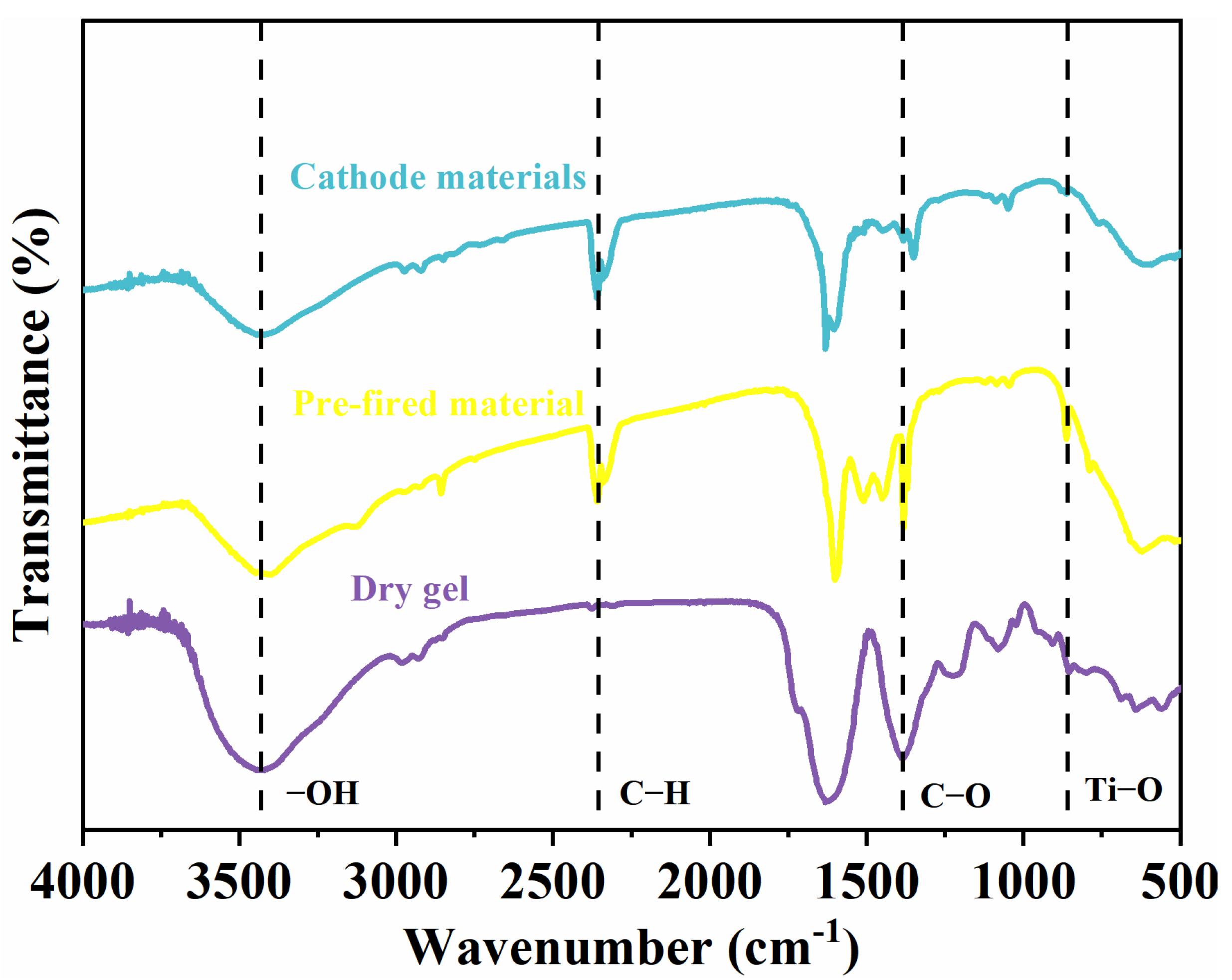
2.3. FTIR Analysis of Li2MgxFe1−xTiO4 Samples
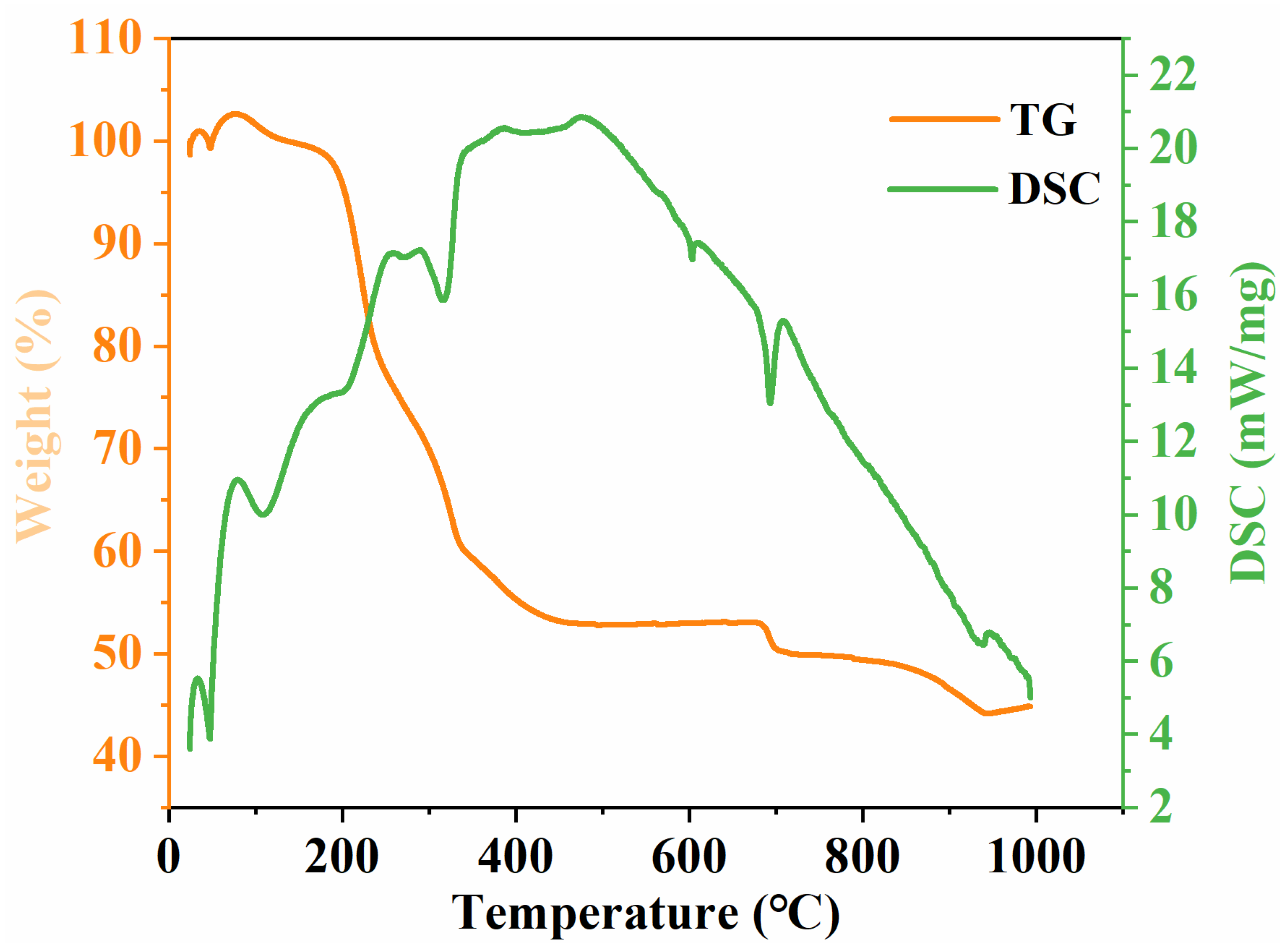
2.4. TG-DSC Analysis of Li2MgxFe1−xTiO4 Samples
2.5. Valence Analysis of Li2MgxFe1−xTiO4 Samples
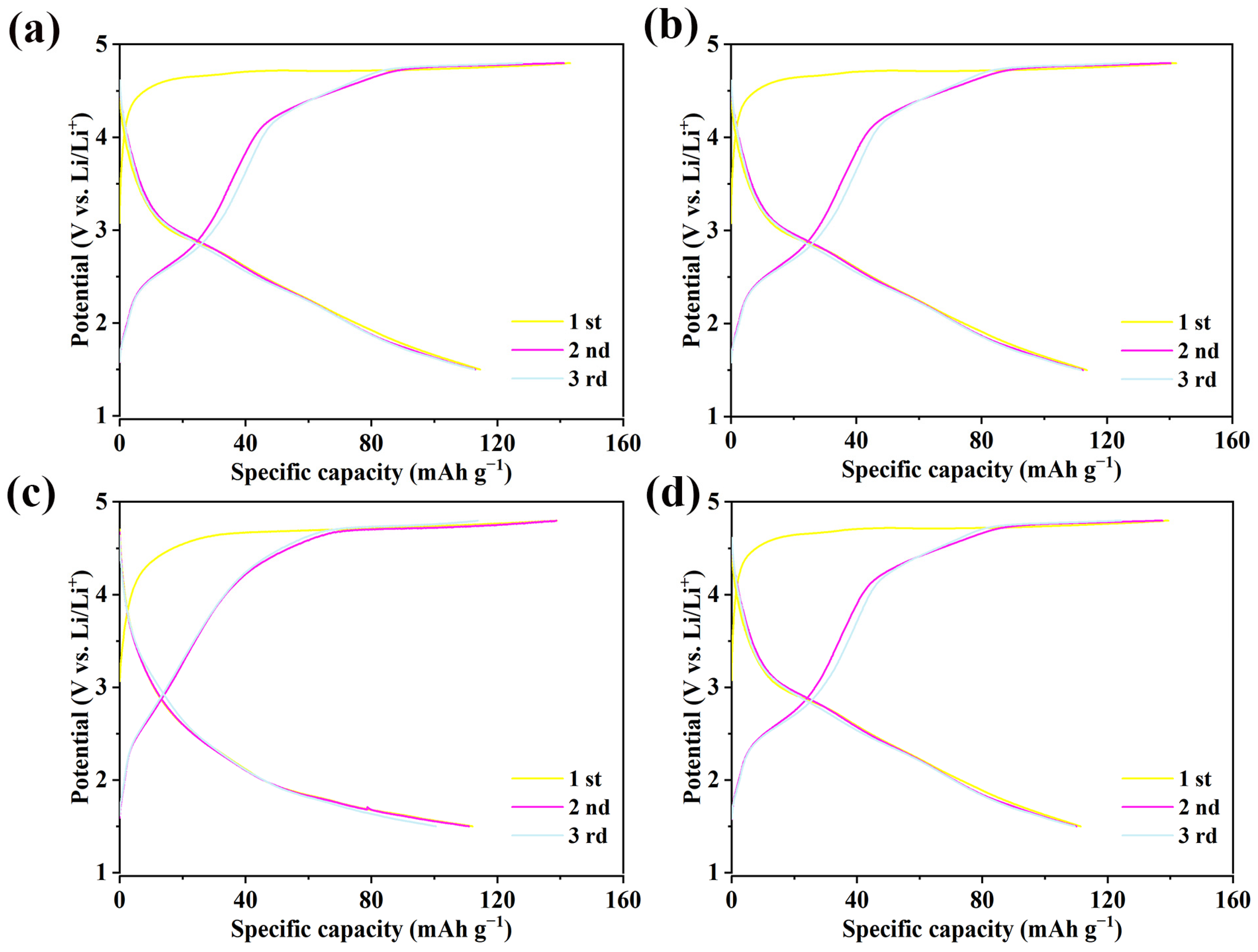
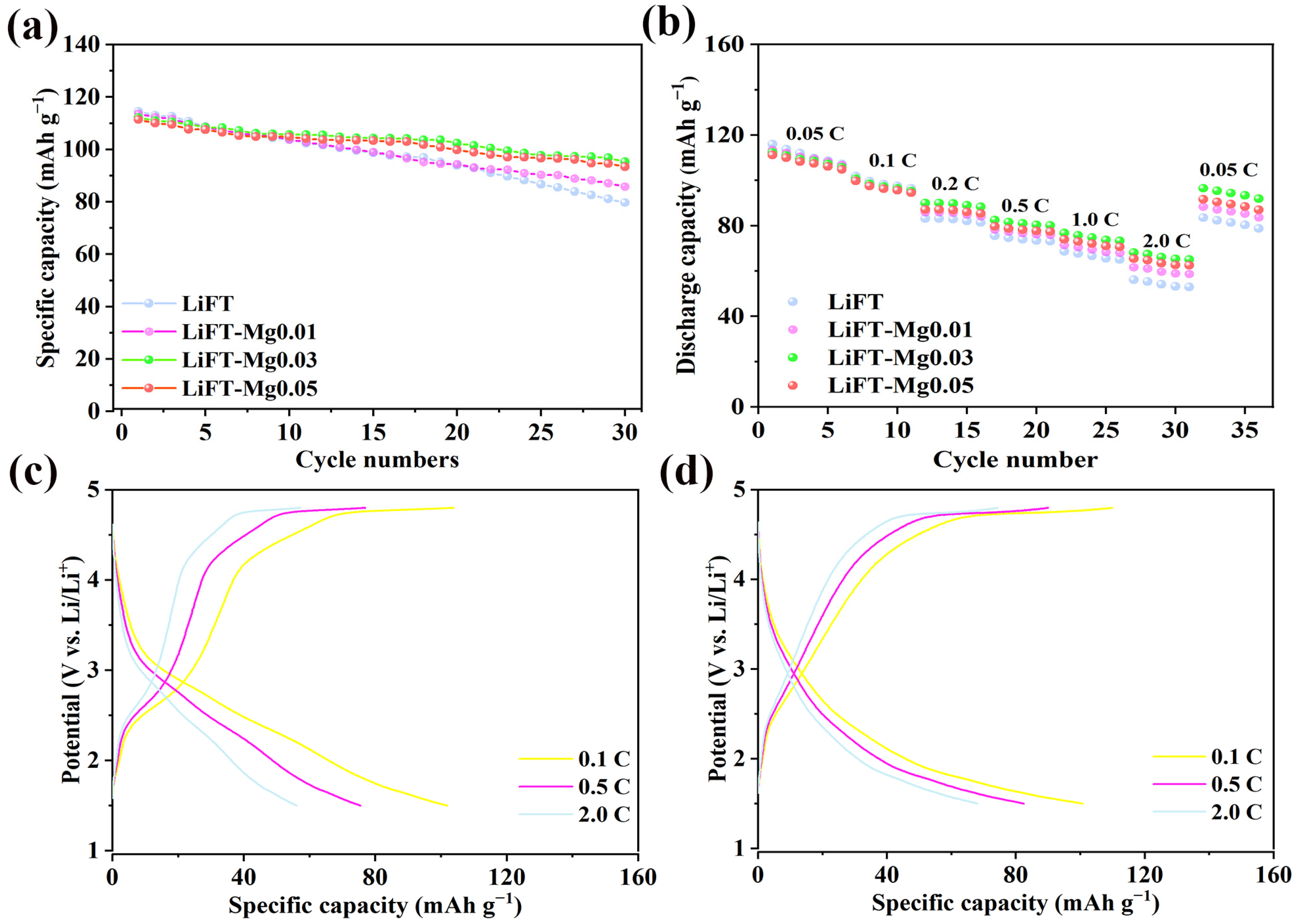
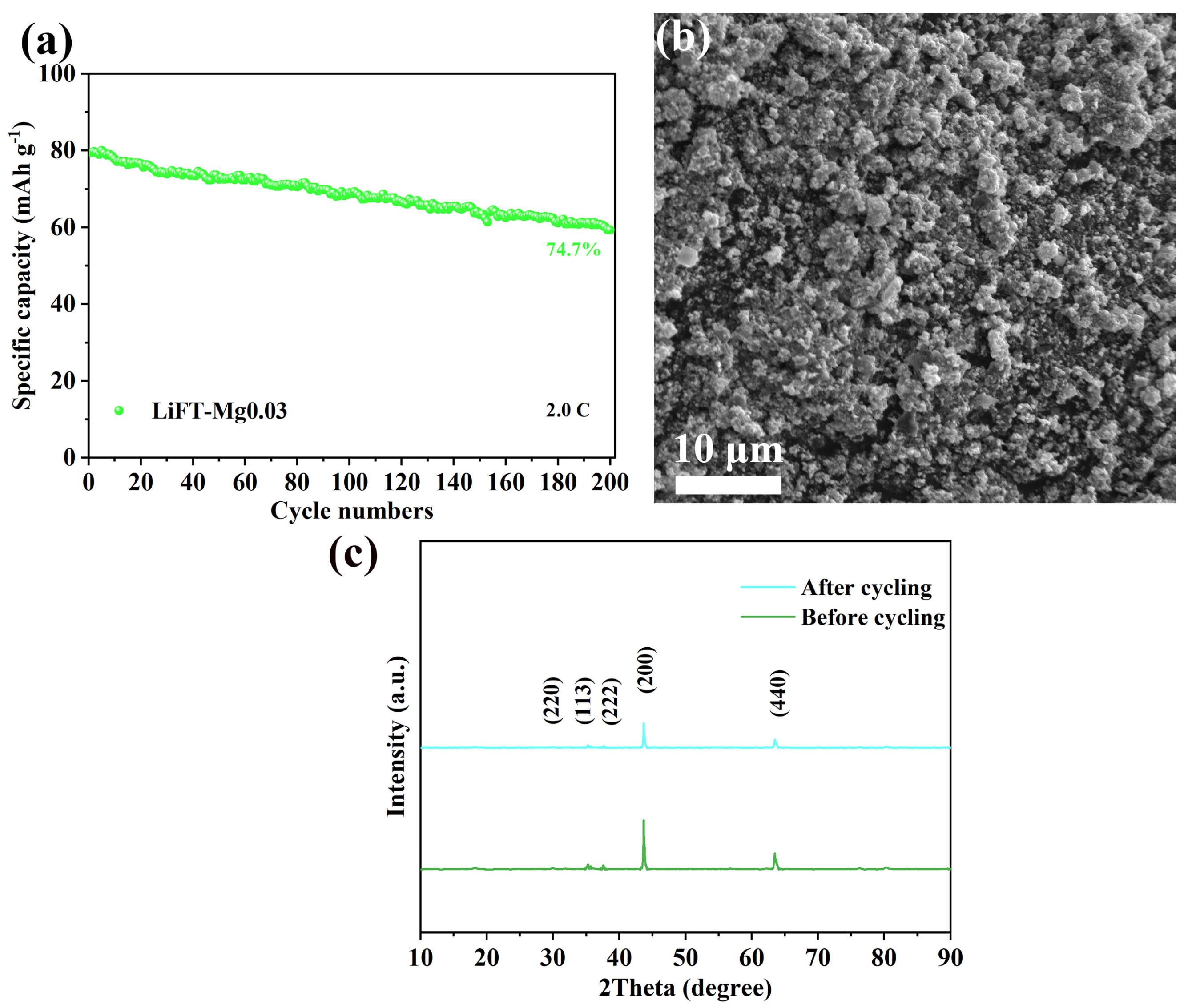
2.6. Electrochemical Properties of Li2MgxFe1−xTiO4 Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material Preparation
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Dai, H.; Wei, X. Multi-level intelligence empowering lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 97, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ghosh, T.; Ju, Z.; Ng, M.F.; Wu, G.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Handoko, A.D.; Kumar, S.; et al. Heterojunction structure of cobalt sulfide cathodes for high-performance magnesium-ion batteries. Matter 2024, 7, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olutogun, M.; Vanderbruggen, A.; Frey, C.; Rudolph, M.; Bresser, D.; Passerini, S. Recycled graphite for more sustainable lithium-ion batteries. Carbon Energy 2024, 6, e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, F.; Shen, M.; Tong, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, H. Advances of LiCoO2 in cathode of aqueous lithium-ion batteries. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2300820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-enabled self-charging lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, G. Toward circular energy: Exploring direct regeneration for lithium-ion battery sustainability. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.R.; Blakely, C.K.; Clapham, J.B.; Davis, J.D.; Bi, W.; Alp, E.E.; Poltavets, V.V. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of novel LiFeTiO4 and Li2FeTiO4 polymorphs with the CaFe2O4-type structures. J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Tang, B.; Jia, D.; Cao, Y. Cation-disordered Li2FeTiO4 nanoparticles with multiple cation and anion redox for symmetric lithium-ion batteries. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 110346, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.B.; Gao, S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Jia, D. Pseudocapacitive behaviors of Li2FeTiO4/C hybrid porous nanotubes for novel lithium-ion battery anodes with superior performances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20225–20230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Yao, C.; Kong, Y.; Ma, L.; Shen, X. Nanostructured cation disordered Li2FeTiO4/graphene composite as high capacity cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Technol. 2016, 31, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, F.; Lyu, M.; Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. Ni-rich cathode materials for stable high-energy lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2024, 126, 109620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Gu, Z.Y.; Heng, Y.L.; Lu, H.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Du, M.; Wang, X.T.; Guo, J.Z.; Dong, F.; et al. P/S-orbital hybridization induced by Mg-doping to active Na sites in Na2FePO4F cathode for long-life and high-rate sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 68, 103319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzma, M.; Dominko, R.; Meden, A.; Makovec, D.; Bele, M.; Jamnik, J.; Gaberšček, M. Electrochemical activity of Li2FeTiO4 and Li2MnTiO4 as potential active materials for Li ion batteries: A comparison with Li2NiTiO4. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Knapp, M.; Yavuz, M.; Ren, S.; Witte, R.; Heinzmann, R.; Hahn, H.; Ehrenberg, H.; Indris, S. Nanoscale spinel LiFeTiO4 for intercalation pseudocapacitive Li+ storage. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y. Synergistic enhancement of ion/electron transport by ultrafine nanoparticles and graphene in Li2FeTiO4/C/G nanofibers for symmetric Li-ion batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 101, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, K.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Reaction mechanisms of layered lithium-rich cathode materials for high-energy lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2208–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Ma, Z.H.; Li, L.; Su, G.; Bao, S.; Lu, J.I. Research on sodium storage performance of Cu and Mg doped P2 type layered oxide cathode materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 030502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Thakur, A.K.; Biswas, K. Raman and FTIR spectroscopy study of LiFeTiO4 and Li2FeTiO4. Ionics 2016, 22, 2045–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Qu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yu, L.; Duan, L.; Lu, W. The effect of elemental doping on nickel-rich NCM cathode materials of lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, M.; He, X. Surface engineering of cathode materials: Enhancing the high performance of lithium-ion batteries. Small 2024, 20, 2402443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Thakur, A.K.; Biswas, K. Density functional theory study of LiFeTiO4. J. Power Sources 2016, 313, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Li, Z.; Cai, L.; Liu, S.; Bu, Z.; Yang, T.; Meng, X.; Xie, R.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Voltage control of multiple electrochemical processes during lithium ion migration in NiFe2O4 ferrite. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 15261–15269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, C.; Zheng, J. Revealing the role of Mg doping in LiFe0.39Mg0.01Mn0.6PO4/C cathode: Enhanced electrochemical performance from improved electrical conductivity and promoted lithium diffusion kinetics. J. Energy Storage 2024, 91, 112108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Lv, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shi, F.N. Review on defects and modification methods of LiFePO4 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Mu, W.; Teng, F. Excess capacity on compound phases of Li2FeTiO4 composite cathode materials synthesized by hydrothermal reaction using optional titanium sources to boost battery performance. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 3200–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupre, N.; Cuisinier, M.; Zheng, Y.; Fernandez, V.; Hamon, J.; Hirayama, M.; Kanno, R.; Guyomard, D. Evolution of LiFePO4 thin films interphase with electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2018, 382, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Luo, S.H. Optimize hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li2FeTiO4 composite cathode materials by using orthogonal experimental design method. Ionics 2020, 26, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, X. Lithium-ion-transfer kinetics of single LiFePO4 particles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 4976–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Xiong, F.; Shadike, Z.; Gao, X.; Chen, J.; Pi, L.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, B.; Adamson, P.; Ma, L.; et al. A layer-structured high entropy oxide with highly reversible Fe3+/Fe4+ redox as advanced cathode material for sodium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2025, 627, 235735. [Google Scholar]


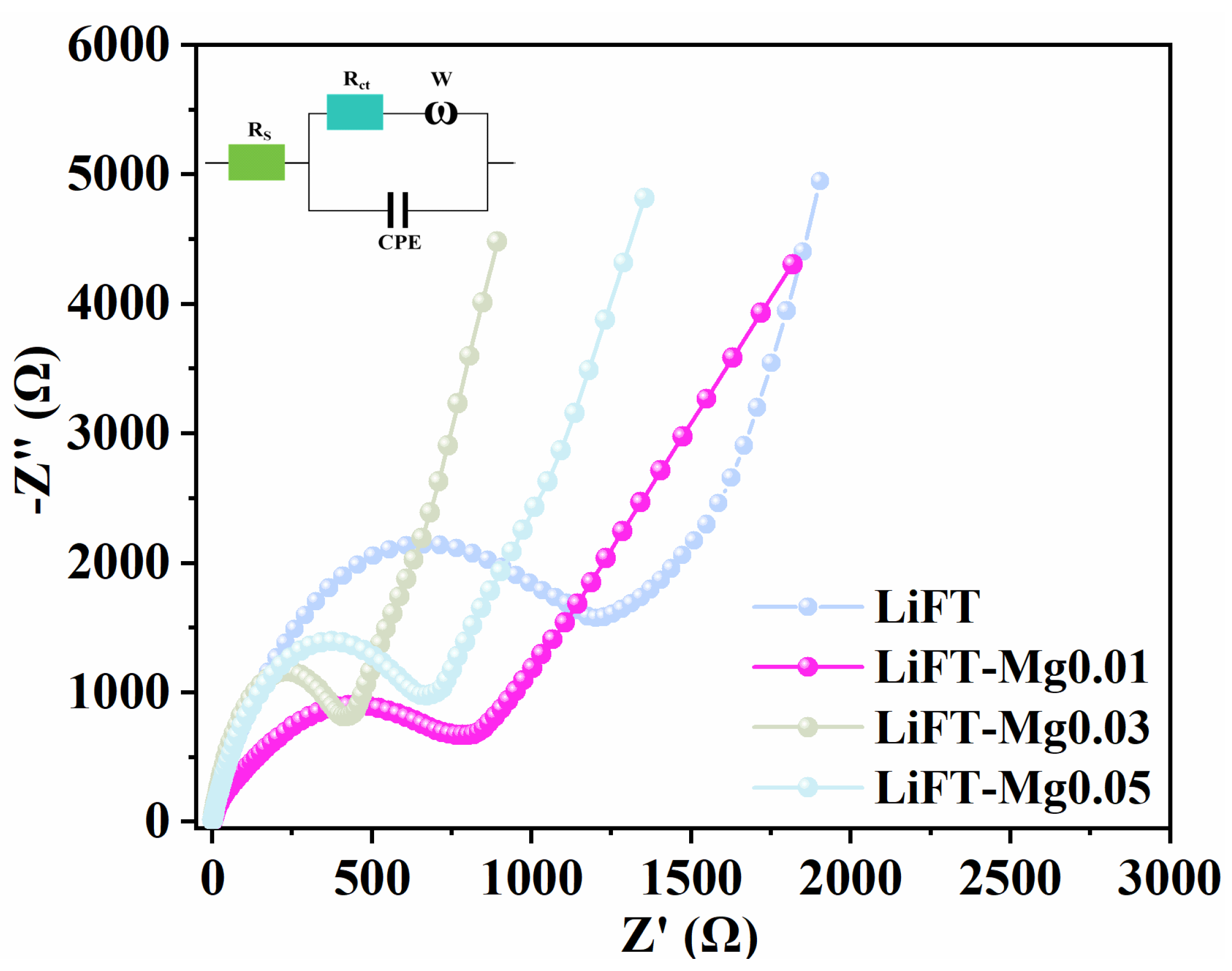

| LiFT | LiFT-Mg0.01 | LiFT-Mg0.03 | LiFT-Mg0.04 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ω) | 8.3 | 7.4 | 5.8 | 6.9 |
| Rct (Ω) | 1200.8 | 802.5 | 408.8 | 671.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, P.; Qu, Y.; Huang, R.; Tian, X.; Li, G.; Luo, S. Mg-Doped Li2FeTiO4 as a High-Performance Cathode Material Enabling Fast and Stable Li-ion Storage. Inorganics 2025, 13, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030076
Hou P, Qu Y, Huang R, Tian X, Li G, Luo S. Mg-Doped Li2FeTiO4 as a High-Performance Cathode Material Enabling Fast and Stable Li-ion Storage. Inorganics. 2025; 13(3):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Pengqing, Yingdong Qu, Rui Huang, Xinru Tian, Guanglong Li, and Shaohua Luo. 2025. "Mg-Doped Li2FeTiO4 as a High-Performance Cathode Material Enabling Fast and Stable Li-ion Storage" Inorganics 13, no. 3: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030076
APA StyleHou, P., Qu, Y., Huang, R., Tian, X., Li, G., & Luo, S. (2025). Mg-Doped Li2FeTiO4 as a High-Performance Cathode Material Enabling Fast and Stable Li-ion Storage. Inorganics, 13(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030076






